The Novel Cytokine Interleukin-41/Meteorin-like Is Reduced in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, C.; Simpson, N.; Duffy, L.; O’Reilly, S. Innate Immunity in Systemic Sclerosis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2017, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullard, N.; O’Reilly, S. Role of innate immune system in systemic sclerosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, S.; Ciechomska, M.; Cant, R.; Hügle, T.; van Laar, J.M. Interleukin-6, its role in fibrosing conditions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012, 23, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Abraham, D. Systemic sclerosis: A prototypic multisystem fibrotic disorder. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinckmann, J.; Kim, S.; Wu, J.; Reinhardt, D.P.; Batmunkh, C.; Metzen, E.; Notbohm, H.; Bank, R.A.; Krieg, T.; Hunzelmann, N. Interleukin 4 and prolonged hypoxia induce a higher gene expression of lysyl hydroxylase 2 and an altered cross-link pattern: Important pathogenetic steps in early and late stage of systemic scleroderma? Matrix Biol. 2005, 24, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allanore, Y.; Simms, R.; Distler, O.; Trojanowska, M.; Pope, J.; Denton, C.P.; Varga, J. Systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushach, I.; Burkhardt, A.M.; Martinez, C.; Hevezi, P.A.; Gerber, P.A.; Buhren, B.A.; Schrumpf, H.; Valle-Rios, R.; Vazquez, M.I.; Homey, B.; et al. METEORIN-LIKE is a cytokine associated with barrier tissues and alternatively activated macrophages. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 156, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Fan, M.-B.; Zhang, S.-L.; Qu, Y.; Zheng, S.-L.; Song, J.; Miao, C.-Y. Intestinal Metrnl released into the gut lumen acts as a local regulator for gut antimicrobial peptides. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.R.; Long, J.Z.; White, J.P.; Svensson, K.J.; Lou, J.; Lokurkar, I.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Ruas, J.L.; Wrann, C.D.; Lo, J.C.; et al. Meteorin-like Is a Hormone that Regulates Immune-Adipose Interactions to Increase Beige Fat Thermogenesis. Cell 2014, 157, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushach, I.; Arrevillaga-Boni, G.; Heller, G.N.; Pone, E.; Hernandez-Ruiz, M.; Catalan-Dibene, J.; Hevezi, P.; Zlotnik, A. Meteorin-like/Meteorin-β Is a Novel Immunoregulatory Cytokine Associated with Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3669–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgewood, C.; Russell, T.; Weedon, H.; Baboolal, T.; Watad, A.; Sharif, K.; Cuthbert, R.; Wittmann, M.; Wechalekar, M.; McGonagle, D. The novel cytokine Metrnl/IL-41 is elevated in Psoriatic Arthritis synovium and inducible from both entheseal and synovial fibroblasts. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 208, 108253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupérez, C.; Ferrer-Curriu, G.; Cervera-Barea, A.; Florit, L.; Guitart-Mampel, M.; Garrabou, G.; Zamora, M.; Crispi, F.; Fernandez-Solà, J.; Lupón, J.; et al. Meteorin-like/Meteorin-β protects heart against cardiac dysfunction. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.W.; Pyun, D.H.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, H.J.; Park, E.S.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Hwang, E.J.; Shin, Y.K.; Jeong, J.H. Meteorin-like protein (METRNL)/IL-41 improves LPS-induced inflammatory responses via AMPK or PPARδ–mediated signaling pathways. Adv. Med. Sci. 2021, 66, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wullschleger, S.; Loewith, R.; Hall, M.N. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 2006, 124, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Diao, L.; Xia, W.; Zeng, X.; Li, W.; Zou, J.; Liu, T.; Pang, X.; Wang, Y. Meteorin-like protein elevation post-exercise improved vascular inflammation among coronary artery disease patients by downregulating NLRP3 inflammasome activity. Aging 2023, 15, 14720–14732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, A.R.; Dantas, A.T.; de Oliveira Gonçalves, M.E.; Chêne, C.; Jeljeli, M.; Chouzenoux, S.; Thomas, M.; Cunha, E.G.; de Azevedo Valadares, L.D.; de Melo Gomes, J.V.; et al. PPARγ partial agonist LPSF/GQ-16 prevents dermal and pulmonary fibrosis in HOCl-induced systemic sclerosis (SSc) and modulates cytokine production in PBMC of SSc patients. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Wei, J.; Kim, S.; Barak, Y.; Mori, Y.; Varga, J. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ abrogates Smad-dependent collagen stimulation by targeting the p300 transcriptional coactivator. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2968–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Dong, H.; Lan, Y.; Bi, Y.; Gu, X.; Han, Y.; Yang, C.; Cheng, M.; Gao, J. Metformin attenuates fibroblast activation during pulmonary fibrosis by targeting S100A4 via AMPK-STAT3 axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1089812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirollahi, V.; Wasnick, R.M.; Biasin, V.; Vazquez-Armendariz, A.I.; Chu, X.; Moiseenko, A.; Weiss, A.; Wilhelm, J.; Zhang, J.-S.; Kwapiszewska, G.; et al. Metformin induces lipogenic differentiation in myofibroblasts to reverse lung fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Dai, S.; Sun, J.; Zhu, C. Metformin Inhibits Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Keloid Fibroblasts via the HIF-1α/PKM2 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Yoo, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Oh, S.H.; Kang, J.W.; Yoo, B.R.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, C.S.; Choi, W.H.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Metformin Alleviates Radiation-Induced Skin Fibrosis via the Downregulation of FOXO3. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, F.; Grembiale, R.D.; D’antona, L.; Gallo, E.; D’angelo, S.; Citraro, R.; Visca, P.; Olivieri, I.; De Sarro, G.; Perrotti, N.; et al. Oral Metformin Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Skin Fibrosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1892–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, A.R.; Yoo, J.H.; Moon, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Cho, M.L. Metformin ameliorates scleroderma via inhibiting Th17 cells and reducing mTOR-STAT3 signaling in skin fibroblasts. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, F.; Sherris, D.; Paus, R.; Varmeh, S.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Bayat, A. Keloid disease can be inhibited by antagonizing excessive mTOR signaling with a novel dual TORC1/2 inhibitor. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1642–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, M. 2-Methoxyestradiol inhibits hypoxia-induced scleroderma fibroblast collagen synthesis by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signalling. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, A.; Yanaba, K.; Yoshizaki, A.; Iwata, Y.; Komura, K.; Ogawa, F.; Takenaka, M.; Shimizu, K.; Asano, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Treatment with rapamycin prevents fibrosis in tight-skin and bleomycin-induced mouse models of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2476–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Ji, H.; Yao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; He, H.; Wang, L.; et al. Serum Metrnl is associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Leung, T.-F.; Wong, G.W.-K.; Ko, W.-H.; Cai, M.; He, E.J.; Chu, I.M.-T.; Tsang, M.S.-M.; Chan, B.C.-L.; Ling, J.; et al. Meteorin-β/Meteorin like/IL-41 attenuates airway inflammation in house dust mite-induced allergic asthma. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hügle, T.; O’Reilly, S.; Simpson, R.; Kraaij, M.D.; Bigley, V.; Collin, M.; Krippner-Heidenreich, A.; van Laar, J.M. Tumor necrosis factor–costimulated T lymphocytes from patients with systemic sclerosis trigger collagen production in fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, S.; Hügle, T.; van Laar, J.M. T cells in systemic sclerosis: A reappraisal. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
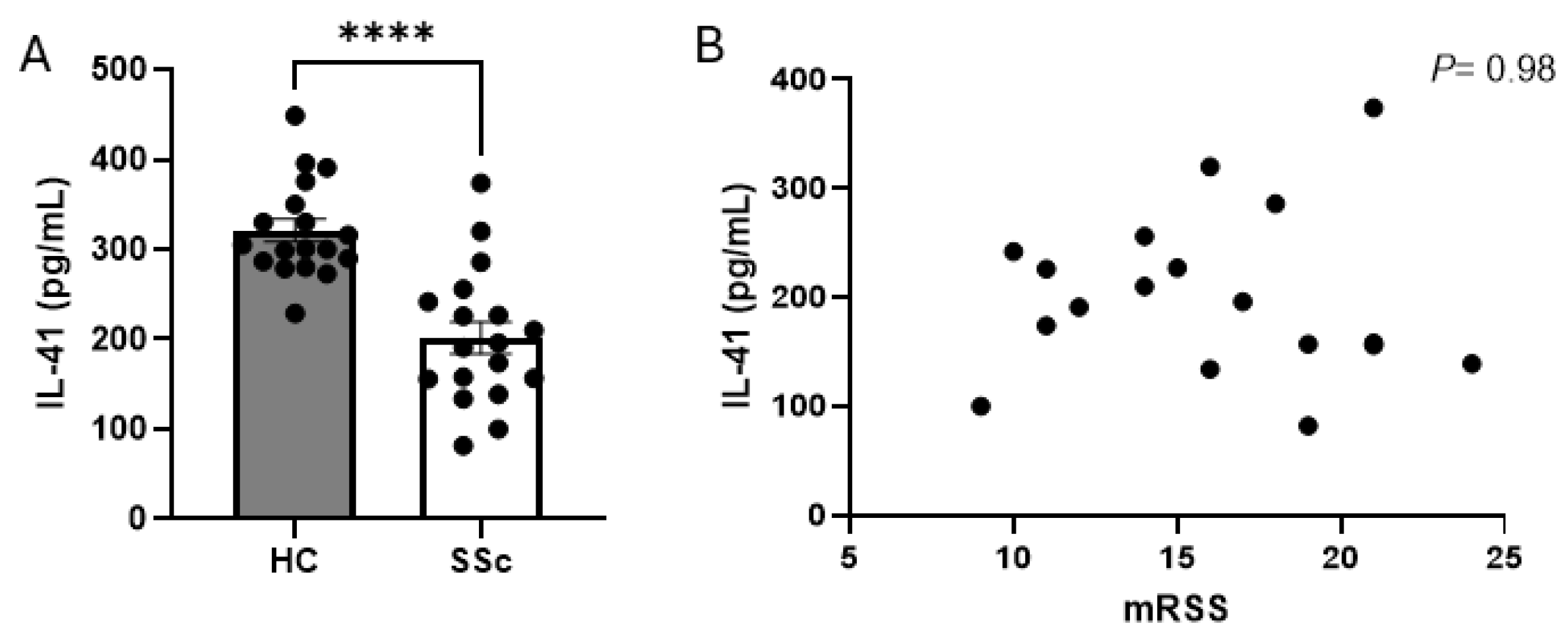
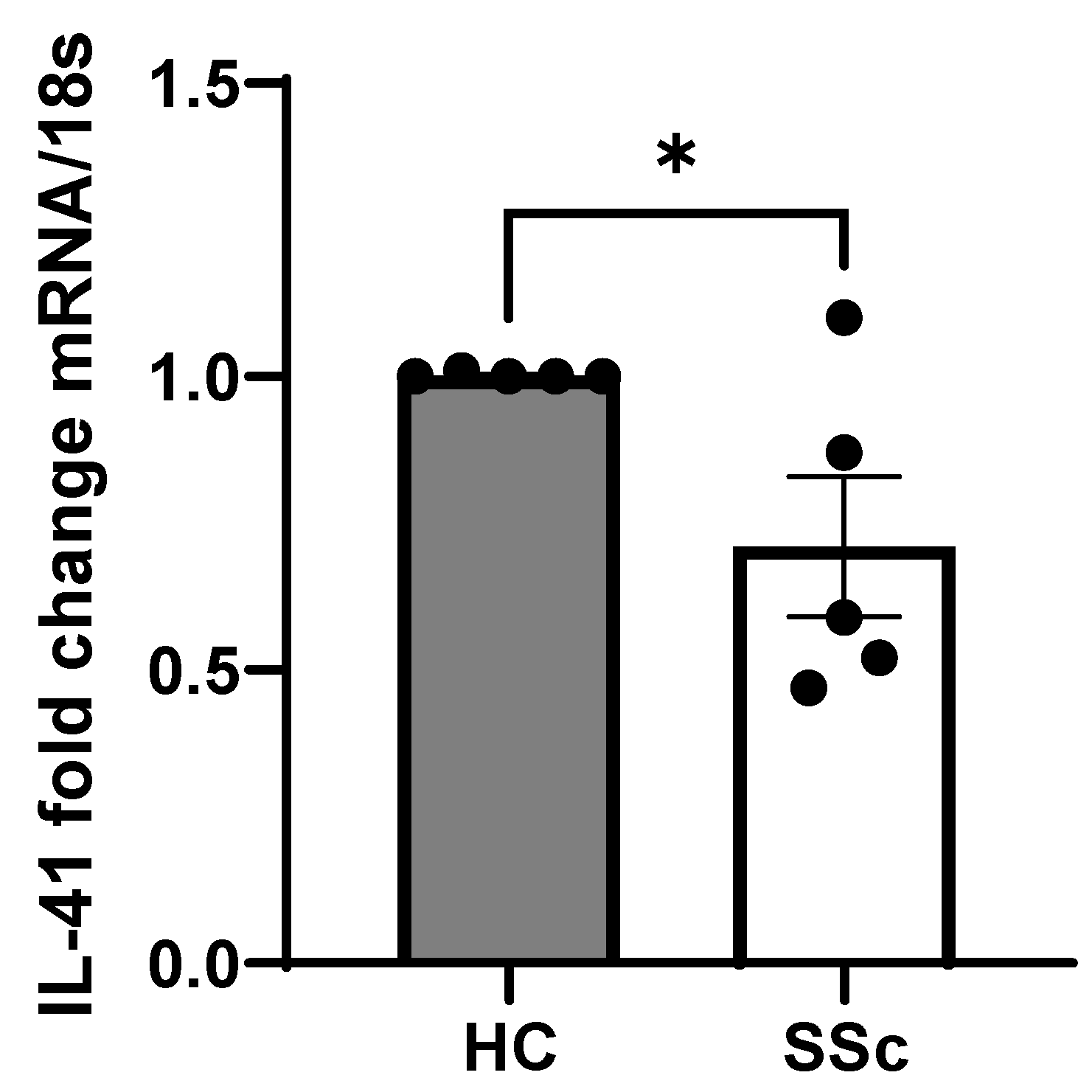

| Patient Number | Age (Years) | Sex | Autoantibodies | mRSS | Treatment | ILD | DLCO% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient_1 | 48 | F | Scl-70 | 9 | None | N | 85 |
| Patient_2 | 54 | F | Scl-70 | 16 | None | N | 82 |
| Patient_3 | 51 | F | RNA-polIII | 10 | None | N | 89 |
| Patient_4 | 66 | F | Scl-70 | 16 | None | Y | 60 |
| Patient_5 | 39 | F | Scl-70 | 11 | None | N | 73 |
| Patient_6 | 52 | F | Scl-70 | 12 | None | N | 79 |
| Patient_7 | 41 | M | Scl-70 | 19 | None | N | 87 |
| Patient_8 | 49 | F | Scl-70 | 14 | None | Y | 57 |
| Patient_9 | 55 | F | RNA-polIII | 17 | None | Y | 52 |
| Patient_10 | 42 | F | Scl-70 | 21 | None | N | 91 |
| Patient_11 | 57 | M | Scl-70 | 14 | None | N | 75 |
| Patient_12 | 35 | F | Scl-70 | 19 | None | N | 82 |
| Patient_13 | 47 | F | Scl-70 | 11 | None | N | 76 |
| Patient_14 | 61 | F | Scl-70 | 15 | None | N | 74 |
| Patient_15 | 55 | F | Scl-70 | 21 | None | Y | 50 |
| Patient_16 | 37 | F | Scl-70 | 18 | None | N | 78 |
| Patient_17 | 47 | F | Scl-70 | 21 | None | N | 83 |
| Patient_18 | 51 | F | Scl-70 | 24 | None | N | 87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freedman, P.; Schock, B.; O’Reilly, S. The Novel Cytokine Interleukin-41/Meteorin-like Is Reduced in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis. Cells 2024, 13, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141205
Freedman P, Schock B, O’Reilly S. The Novel Cytokine Interleukin-41/Meteorin-like Is Reduced in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis. Cells. 2024; 13(14):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141205
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreedman, Paul, Bettina Schock, and Steven O’Reilly. 2024. "The Novel Cytokine Interleukin-41/Meteorin-like Is Reduced in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis" Cells 13, no. 14: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141205
APA StyleFreedman, P., Schock, B., & O’Reilly, S. (2024). The Novel Cytokine Interleukin-41/Meteorin-like Is Reduced in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis. Cells, 13(14), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141205










