Hyperbaric Oxygenation: Can It Be a Novel Supportive Method in Acute Kidney Injury? Data Obtained from Experimental Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Molecular Mechanisms of Hyperbaric Oxygen
2. Materials and Methods
3. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Preconditioning on Acute Kidney Injury
4. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Acute Kidney Injury
4.1. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Post-Ischemic Acute Kidney Injury
4.2. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
4.3. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Glycerol-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
4.4. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Cyclosporine-Induced Nephrotoxicity
4.5. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Gentamicin and Vancomycin-Induced Nephrotoxicity
4.6. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
4.7. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Ischemia-Reperfusion Acute Kidney Injury after Kidney Transplantation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2012, 380, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellum, J.A.; Romagnani, P.; Ashuntantang, G.; Ronco, C.; Zarbock, A.; Anders, J.A. Acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makris, K.; Spanou, L. Acute Kidney Injury: Definition, Pathophysiology and Clinical Phenotypes. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2016, 37, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pesce, F.; Stea, E.D.; Rossini, M.; Fiorentino, M.; Piancone, F.; Infante, B.; Stallone, G.; Castellano, G.; Gesualdo, L. Glomerulonephritis in AKI: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Intervention. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 582272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perazella, M.A.; Rosner, M.H. Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 1220–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaoming, Z. Reducing Oxygen Demand to Alleviate Acute Kidney Injury. Front. Biosci. 2023, 28, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Yang, L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentia, C.; Rizzato, A.; Camporesi, E.; Yang, Z.; Muntean, D.M.; Săndesc, D.; Bosco, G. An overview of protective strategies against ischemia/reperfusion injury: The role of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e00959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; García-Montero, C.; Callejón-Peláez, E.; Sáez, M.A.; Álvarez-Mon, M.A.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Monserrat, J.; Álvarez-Mon, M.; Bujan, L.; et al. A General Overview on the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Applications, Mechanisms and Translational Opportunities. Medicina 2021, 57, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenjancevic, I.; Kibel, A.; Kibel, D.; Seric, V.; Cosic, A. Blood pressure, acid-base and blood gas status and indicators of oxidative stress in healthy male rats exposed to acute hyperbaric oxygenation. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2013, 40, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmann, J.; Smolle, C.; Kamolz, L.P.; Smolle-Juettner, F.M.; Graier, W.F. Survey of Molecular Mechanisms of Hyperbaric Oxygen in Tissue Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannellotto, M.; Garcia, A.Y.; Landa, M.S. Hyperoxia: Effective Mechanism of Hyperbaric Treatment at Mild-Pressure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Duan, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for healthy aging: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Redox Biol. 2022, 53, 102352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schottlender, N.; Gottfried, I.; Ashery, U. Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment: Effects on Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkovitch, M.; Tsadik, R.; Kozer, E.; Abu-Kishk, I. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on kidneys in a rat model. Sci. World J. 2014, 105069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugniaux, J.V.; Coombs, G.B.; Barak, O.F.; Dujic, Z.; Sekhon, M.S.; Ainslie, P.N. Highs and Lows of Hyperoxia: Physiological, Performance, and Clinical Aspects. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 315, R1–R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, H.; Shai, E. The Hyperoxic-hypoxic Paradox. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvagno, M.; Coppalini, G.; Taccone, F.S.; Strapazzon, G.; Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Rocco, M.; Khalife, M.; Balestra, C. The Normobaric Oxygen Paradox-Hyperoxic Hypoxic Paradox: A Novel Expedient Strategy in Hematopoiesis Clinical Issues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratantonio, D.; Virgili, F.; Zucchi, A.; Lambrechts, K.; Latronico, T.; Lafère, P.; Germonpré, P.; Balestra, C. Increasing Oxygen Partial Pressures Induce a Distinct Transcriptional Response in Human PBMC: A Pilot Study on the “Normobaric Oxygen Paradox”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Fang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Dong, H.; Lu, Y.; Lei, C.; Xiong, L. SirT1 mediates hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance in rat brain. J. Cereb. Blood. Flow. Metab. 2013, 33, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.D.; Wang, Z.-B.; Han, G.; Jin, L.; Zhao, P. Hyperbaric oxygen relieves neuropathic pain through AKT/TSC2/mTOR pathway activity to induce autophagy. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.Y.; Cai, R.-X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.-W.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.-D. Analysis the effect of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning on neuronal apoptosis, Ca2+ concentration and caspases expression after spinal cord injury in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3467–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, S.R. Hyperbaric oxygen: Its mechanisms and efficacy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 131S–141S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbach, J.L.; Prieto, J.M.; Wang, A.W.; Hawisher, D.; Cauvi, D.M.; Reyes, T. Early hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves survival in a model of severe sepsis. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2019, 317, R160–R168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerard, S.; Holmdahl, R.; Wing, K. Reactive oxygen species regulate innate but not adaptive inflammation in ZAP70-mutated SKG arthritic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaizu, T.; Enomoto, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Tsuji, K.; Horie, M.; Muneta, T. Hyperbaric oxygen reduces inflammation, oxygenates injured muscle, and regenerates skeletal muscle via macrophage and satellite cell activation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguiano-Hernandez, Y.M.; Contreras-Mendez, L.; de Los Angeles Hernandez-Cueto, M.; Muand Oz-Medina , J.E.; Santillan-Verde, M.A.; Barbosa-Cabrera, R.E.; Delgado-Quintana, C.A.; Trejo-Rosas, S.; Santacruz-Tinoco, C.E.; Ramón-Gallegos, E.; et al. Modification of HIF-1alpha, NF-akappaB, IGFBP-3, VEGF and adiponectin in diabetic foot ulcers treated with hyperbaric oxygen. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2019, 46, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, Z.; Khalatbary, A.R.; Ahmadvand, H.; Zare, Z.; Kian, K. Neuroprotective effects of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy on neuronal death induced by sciatic nerve transection in rat. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, A.C.; Whatmore, J.L.; Harries, L.W.; Winyard, P.G.; Smerdon, G.R.; Eggleton, P. Changes in inflammatory gene expression induced by hyperbaric oxygen treatment in human endothelial cells under chronic wound conditions. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Duan, X.-S.; Xu, L.-J.; Zhao, J.-J.; She, Z.-F.; Chen, W.-W.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Jiang, G.-D. Interleukin-10 mediates the neuroprotection of hyperbaric oxygen therapy against traumatic brain injury in mice. Neuroscience 2014, 266, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyrazoglu, Y.; Topal, T.; Yuksel, R.; Bircan, F.S.; Simsek, K.; Gocgeldi, E.; Ersoz, N.; Korkmaz, A. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen and Preconditioning on Wound Healing in Colonic Anastomoses. J. Investig. Surg. 2015, 28, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, H.-Y.; Lim, S.-W.; Chio, C.-C.; Niu, K.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Kuo, J.-R. Hyperbaric oxygen effects on neuronal apoptosis associations in a traumatic brain injury rat model. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 197, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Handy, R.D.; Moody, A.J.; Bryson, P. Response of blood vessels in vitro to hyperbaric oxygen (HBO): Modulation of VEGF and NO(x) release by external lactate or arginine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1787, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, X. Protective effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment against spinal cord injury in rats via toll-like receptor 2/nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 1911–1919. [Google Scholar]
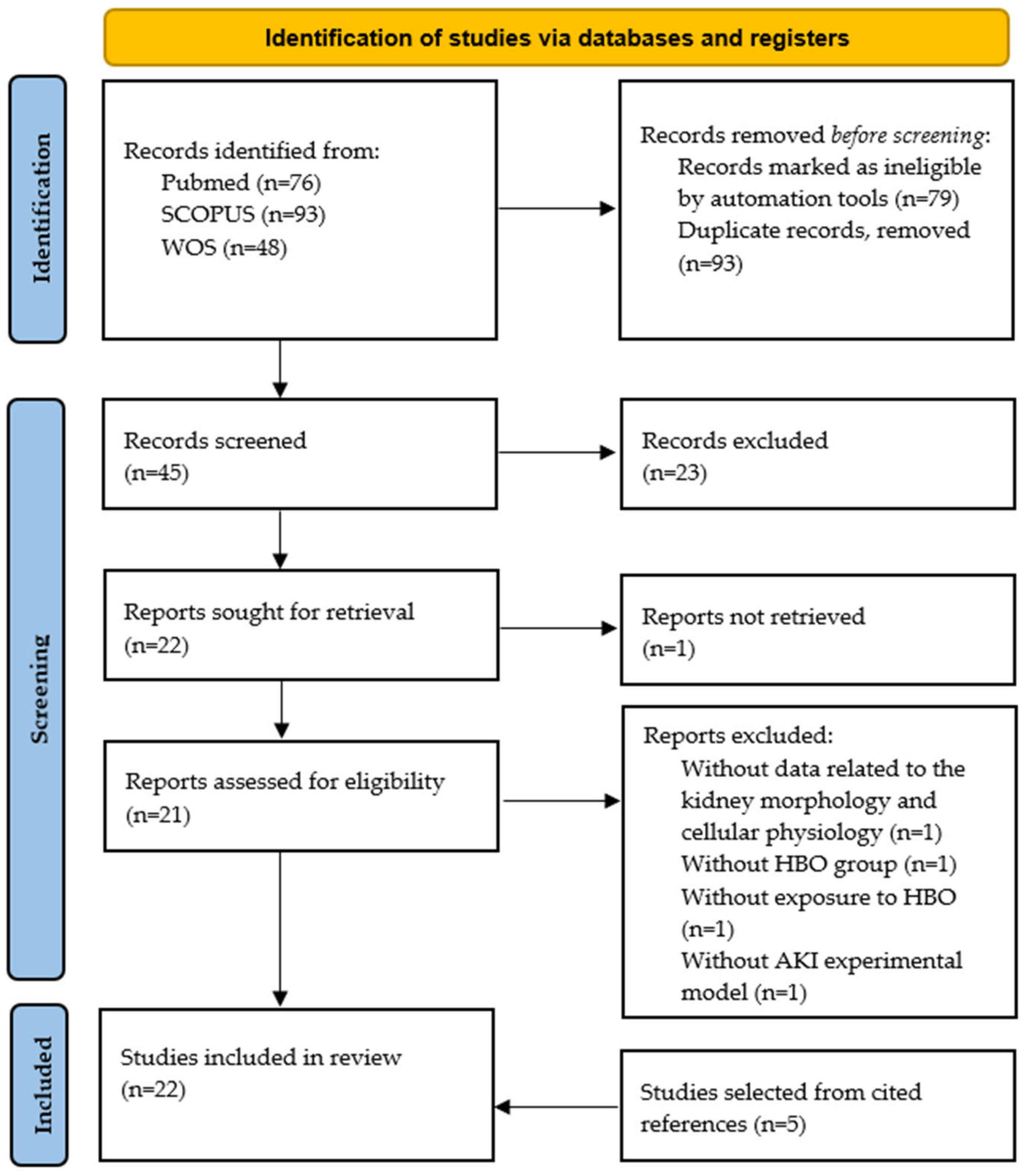
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurer, A.; Ozdogan, M.; Gomceli, I.; Gulbahar, O.; Arikok, T.; Kulacoglu, H.; Dundar, K.; Ozlem, N. Hyperbaric oxygenation attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplant. Proc. 2006, 38, 3337–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Xu, X.; Fan, M.; Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Luo, G.; Chen, L.; Mu, Q.; Feng, Y.; Mao, Q.; et al. Preconditioning with hyperbaric oxygen induces tolerance against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via increased expression of heme oxygenase. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 170, e271–e277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, S.; Ivanov, M.; Miloradovic, Z.; Brkic, P.; Vajic, U.J.; Zivotic, M.; Mihailovic-Stanojevic, N.; Jovovic, D.; Karanovic, D.; Jeremic, R.; et al. Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning and the role of NADPH oxidase inhibition in postischemic acute kidney injury induced in spontaneously hypertensive rats. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesovic Ostojic, J.; Ivanov, M.; Mihailovic-Stanojevic, N.; Karanovic, D.; Kovacevic, S.; Brkic, P.; Zivotic, M.; Vajic, U.J.; Jovovic, D.; Jeremic, R.; et al. Hyperbaric Oxygen Preconditioning Upregulates Heme OxyGenase-1 and Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2 Protein Expression in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats with Induced Postischemic Acute Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, S.; Ivanov, M.; Zivotic, M.; Brkic, P.; Miloradovic, Z.; Jeremic, R.; Mihailovic-Stanojevic, N.; Vajic, U.J.; Karanovic, D.; Jovovic, R.; et al. Immunohistochemical Analysis of 4-HNE, NGAL, and HO-1 Tissue Expression after Apocynin Treatment and HBO Preconditioning in Postischemic Acute Kidney Injury Induced in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlakou, P.; Liakopoulos, V.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Mitis, M.; Dounousi, E. Oxidative Stress and Acute Kidney Injury in Critical Illness: Pathophysiologic Mechanisms-Biomarkers-Interventions, and Future Perspectives. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 6193694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomsa, A.M.; Alexa, A.L.; Junie, M.L.; Rachisan, A.L.; Ciumarnean, L. Oxidative stress as a potential target in acute kidney injury. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, D.P.; Anderson, M.D.; Sutton, T.A. Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1303–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmazgul, E.; Uzun, G.; Cermik, H.; Atasoyu, E.M.; Aydinoz, S.; Yildiz, S. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Urol. Int. 2007, 78, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, I.; Abassi, Z.; Milman, F.; Ovcharenko, E.; Coleman, R.; Winaver, J.; Better, O.S. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment improves GFR in rats with ischaemia/reperfusion renal injury: A possible role for the antioxidant/oxidant balance in the ischaemic kidney. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, R.J.; de Oliveira, P.S.; Cavaglieri, R.C.; Silva, C.; Medeiros, P.R.; Filho, D.M.; Poli-de-Figueiredo, L.F.; Noronha, I.L. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy induces kidney protection in an ischemia/reperfusion model in rats. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 2333–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilhan, H.; Eroglu, M.; Inal, V.; Eyi, Y.E.; Arziman, I.; Yildirim, A.O.; Tansel, A.; Uzun, G.; Yamanel, L. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy alleviates oxidative stress and tissue injury in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Ren. Fail. 2012, 34, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migita, H.; Yoshitake, S.; Tange, Y.; Choijookhuu, N.; Hishikawa, Y. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Suppresses Apoptosis and Promotes Renal Tubular Regeneration after Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Nephrourol. Mon. 2016, 8, e34421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.F.; Chen, K.H.; Wallace, C.G.; Yang, C.C.; Sung, P.H.; Shao, P.L.; Li, Y.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Yip, H.K. Protective effect of combined therapy with hyperbaric oxygen and autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on renal function in rodent after acute ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 3272–3287. [Google Scholar]
- Atasoyu, E.M.; Yildiz, S.; Bilgi, O.; Cermik, H.; Evrenkaya, R.; Aktas, S.; Gültepe, M.; Kandemir, E.G. Investigation of the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2005, 79, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinoz, S.; Uzun, G.; Cermik, H.; Atasoyu, E.M.; Yildiz, S.; Karagoz, B.; Evrenkaya, R. Effects of different doses of hyperbaric oxygen on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Ren. Fail. 2007, 29, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayvaz, S.; Aksu, B.; Kanter, M.; Uzun, H.; Erboga, M.; Colak, A.; Basaran, U.N.; Pul, M. Preventive effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on glycerol-induced myoglobinuric acute renal failure in rats. J. Mol. Histol. 2012, 43, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebi, G.; Yildiz, Ş.; Uzun, G.; Oztas, Y.; Sabuncuoglu, S.; Kutlu, A.; Ilgaz, Y.; Karatop-Cesur, I.; Dogan, E.; Oztas, E. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on rhabdomyolysis-induced myoglobinuric acute renal failure in rats. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasoyu, E.M.; Yildiz, S.; Cimsit, M.; Cermik, H.; Qyrdedi, T.; Evrenkaya, T.R.; Aktas, S.; Uzun, G.; Bilgi, O.; Gultepe, M. Investigation of the effect of hyperbaric oxygen on experimental cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006, 98, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay, H.; Uzun, G.; Onem, Y.; Aydinoz, S.; Yildiz, S.; Bilgi, O.; Topal, T.; Atasoyu, E.M. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Ren. Fail. 2007, 29, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabler, I.M.; Berkovitch, M.; Sandbank, J.; Kozer, E.; Dagan, Z.; Goldman, M.; Bahat, H.; Stav, K.; Zisman, A.; Klin, B.; et al. Exposure to Hyperbaric Oxygen Intensified Vancomycin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkovitch, M.; Shain, Y.; Kozer, E.; Goldman, M.; Abu-Kishk, I. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment and nephrotoxicity induced by gentamicin in rats. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztopuz, Ö.; Türkön, H.; Şehitoğlu, M.H.; Büyük, B.; Uzun, M.; Ovalı, M.A.; Demir, U. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment ameliorates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and expression of kidney injury molecule 1 in the rat model. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2019, 46, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edremitlioğlu, M.; Kiliç, D.; Oter, S.; Kisa, U.; Korkmaz, A.; Coşkun, O.; Bedir, O. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on the renal functions in septic rats: Relation to oxidative damage. Surg. Today 2005, 35, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, X.; Liang, T.; Bao, D.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Du, J.; Chen, A.; Fu, Z.; et al. Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen on Tissue Damage and Expression of Adhesion Molecules and C3 in a Rat Model of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury after Kidney Transplantation. Ann. Transplant. 2020, 25, e919385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumer, M.; Colombel, M.C.; Sawczuk, I.S.; Gobe, G.; Connor, J.; O’Toole, K.M.; Olsson, C.A.; Wise, G.J.; Buttyan, R. Morphologic, biochemical, and molecular evidence of apoptosis during the reperfusion phase after brief periods of renal ischemia. Am. J. Pathol. 1992, 140, 831–838. [Google Scholar]
- Kanagasundaram, N.S.; Arunachalam, C. Assessment and initial management of acute kidney injury. Medicine 2015, 43, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkok, A.; Edelstein, C.L. Pathophysiology of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 967826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, K.R.; Gadanec, L.K.; Qaradakhi, T.; Ali, B.A.; Zulli, A.; Apostolopoulos, V. Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Pathological Mechanisms, Pharmacological Interventions, and Genetic Mitigations. Cancers 2021, 13, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wang, T.; Meng, D. Adverse effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1160774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conconi, M.T.; Baiguera, S.; Guidolin, D.; Furlan, C.; Menti, A.M.; Vigolo, S.; Belloni, A.S.; Parnigotto, P.P.; Nussdorfer, G.G. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on proliferative and apoptotic activities and reactive oxygen species generation in mouse fibroblast 3T3/J2 cell line. J. Investig. Med. 2003, 51, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Fu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yin, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hao, Q.; Bao, D.; Hou, D. Effect of curcumin on glycerol-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Asmari, A.K.; Al Sadoon, K.T.; Obaid, A.A.; Yesunayagam, D.; Tariq, M. Protective effect of quinacrine against glycerol-induced acute kidney injury in rats. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, J.F.; Burfeind, K.G.; Malinoski, D.; Hutchens, M.P. Molecular Mechanisms of Rhabdomyolysis-Induced Kidney Injury: From Bench to Bedside. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 8, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdmann, E.A.; Andoh, T.F.; Yu, L.; Bennett, W.M. Cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Semin. Nephrol. 2003, 23, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobadilla, N.A.; Gamba, G. New insights into the pathophysiology of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity: A role of aldosterone. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2007, 293, F2–F9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Nepovimova, E.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Kuca, K. Mechanism of cyclosporine A nephrotoxicity: Oxidative stress, autophagy, and signalings. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 889–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, W.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Wu, V.C.; Shiao, C.C. Vancomycin-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: A Narrative Review from Pathophysiology to Clinical Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakumar, P.; Rohilla, A.; Thangathirupathi, A. Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: Do we have a promising therapeutic approach to blunt it? Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 2010, 62, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randjelovic, P.; Veljkovic, S.; Stojiljkovic, N.; Sokolovic, D.; Ilic, I. Gentamicin nephrotoxicity in animals: Current knowledge and future perspectives. EXCLI J. 2017, 16, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerapornratana, S.; Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Gómez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, S.; Goggins, E.; Okusa, M.D. The Pathophysiology of Sepsis-Associated AKI. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 1050–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarczak, D.; Kluge, S.; Nierhaus, A. Sepsis-Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Concepts. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 628302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinkel, J.; Arenkiel, B.; Hyldegaard, O. The Mechanisms of Action of Hyperbaric Oxygen in Restoring Host Homeostasis during Sepsis. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, T.J.; Mohr, N.M.; Bailey, O.E. The role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in septic shock: Is it time for human studies? Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2022, 49, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasyan, H. Oxygen therapy for sepsis and prevention of complications. Acute Crit. Care 2022, 37, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Jawdeh, B.G.; Govil, A. Acute Kidney Injury in Transplant Setting: Differential Diagnosis and Impact on Health and Health Care. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyuk, B.; Oztopuz, O. Hyperbaric oxygen mitigates KIM-1 and inflammatory cytokine levels in kidney transplantation. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2023, 50, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
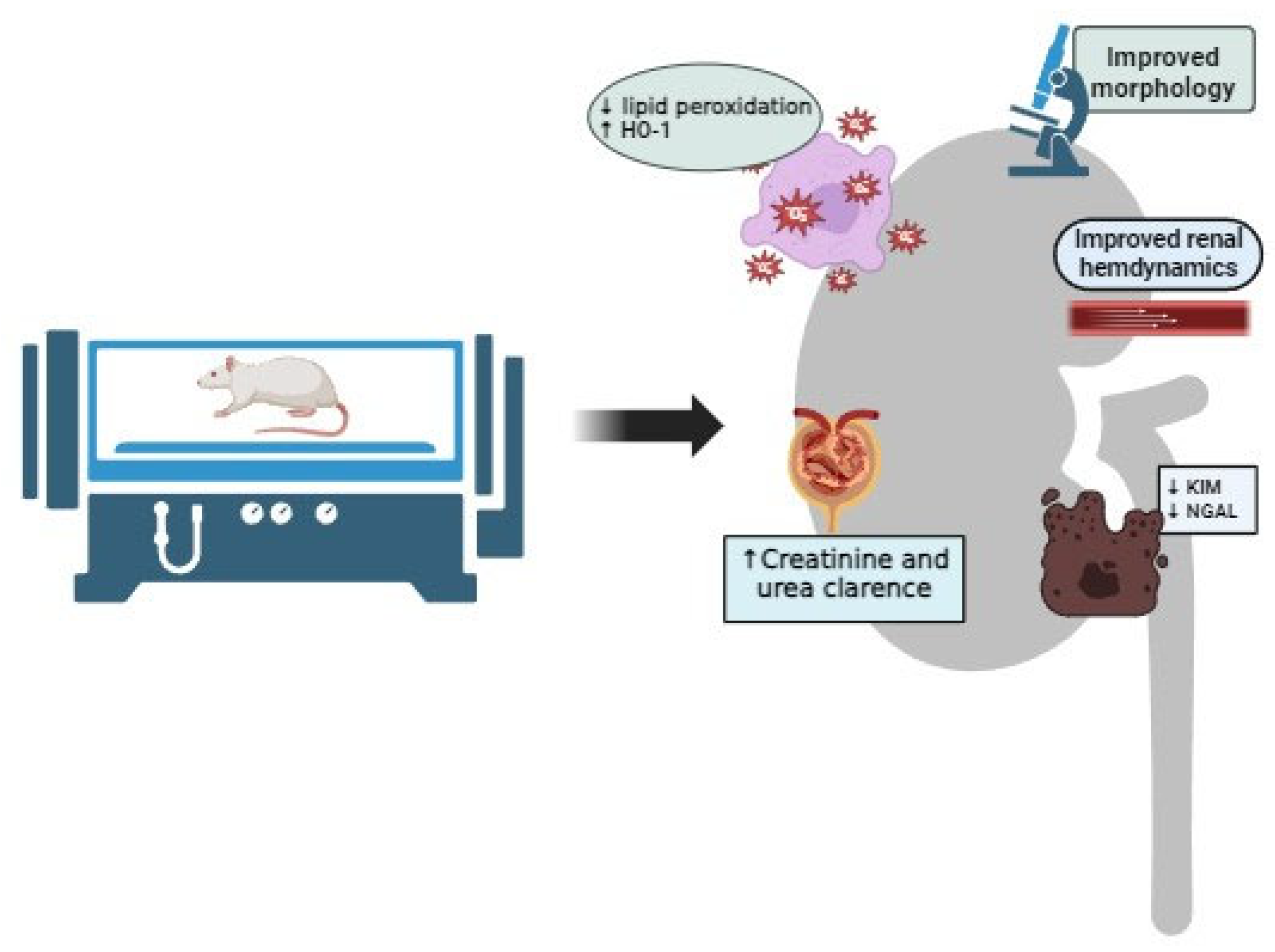
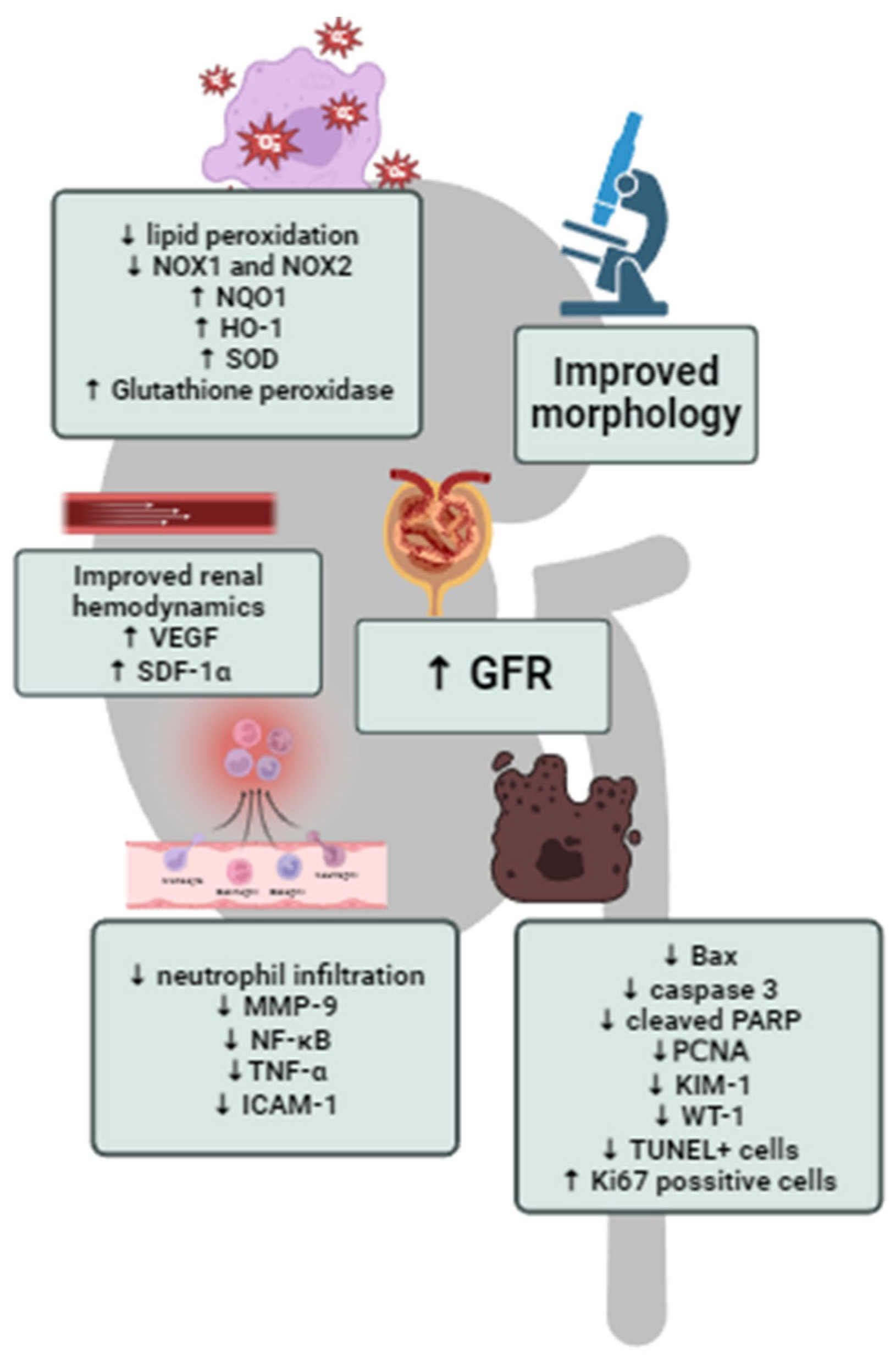
| Author | Experimental Protocol | HBO Exposure | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gurer et al. [36] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.8 ATA, 75 min, 1 single session | HBO significantly decreased lipid peroxidation in kidney tissue and improved renal morphology. |
| He et al. [37] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.5 ATA, 60 min, 2 sessions per day, with total number of 4 sessions | HBO significantly decreased serum urea and creatinine, improved renal morphology, induced expression of HO-1 in kidney tissue. |
| Kovacevic et al. [38] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Spontaneously hypertensive rats | 2.0 ATA, 60 min, 2 sessions per day, with total number of 4 sessions | HBO improved renal hemodynamics, decreased urea, creatinine, phosphate and KIM-1 levels in plasma, improved renal morphology. |
| Nesovic Ostojic et al. [39] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar rats | 2.0 ATA, 60 min, 2 sessions per day, with total number of 4 sessions | HBO in both strains improved clearances of urea, creatinine and phosphate, improved renal morphology and increased Bax expression in kidney tissue. In SHR strain, also decreased plasma KIM-1 levels and increased expression of Bcl-2 and HO-1 in kidney tissue. |
| Kovacevic et. al. [40] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Spontaneously hypertensive rats | 2.0 ATA, 60 min, 2 sessions per day, with total number of 4 sessions | HBO improved clearances of urea, creatinine and phosphate, decreased expression of 4-HNE and NGAL and provoked different HO-1 immunohistochemical expression pattern in kidney tissue. |
| Author | Experimental Protocol | HBO Exposure | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solmazgul et al. [44] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.5 ATA, 60 min, 1 single session | HBO decreased plasma urea and creatinine, improved renal morphology and decreased neutrophil infiltration in kidney tissue. |
| Rubinstein et al. [45] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.5 ATA, 90 min, 2 sessions per day, with total number of 2 sessions | HBO improved renal hemodynamics and GFR, decreased lipid peroxidation and increased SOD activity in kidney tissue. |
| Ramalho et al. [46] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Wistar albino rats | 2.5 ATA, 60 min, 2 sessions per day, with total number of 2 sessions | HBO significantly decreased serum creatinine and urea levels, reduced proteinuria and decreased fractional excretions of sodium and potassium, with also improved renal morphology and decreased PCNA expression in kidney tissue, without any effects on macrophage infiltration or HO-1 expression. |
| Ilhan et al. [47] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.5 ATA, 60 min, 1 session per day, with total number of 5 sessions | HBO decreased lipid peroxidation and improved SOD and glutathione peroxidase activity in kidney tissue, improved renal morphology and decreased neutrophil infiltration in kidney tissue. |
| Migita et al. [48] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.5 ATA, 60 min, 1 single session | HBO improved renal morphology, leading to the lower number of TUNEL+ cells and a higher number of Ki67+ cells in the cortex and outer stripe of the medulla. |
| Ko et al. [49] | Ischemia-reperfusion injury induced in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.4 ATA, 90 min, 1 session per day, with total number of 2 sessions | HBO significantly decreased serum urea and creatinine, improved kidney morphology, decreased oxidative stress (H2DCFDA, Nox-1 and Nox-2 levels), increased antioxidative defense (increased NQO 1 and HO–1), decreased inflammation (decreased MMP-9, TNFα, NF-κB, ICAM-1 and F4/80 and CD14-positive cells in kidney tissue), decreased apoptosis (decreased Bax, caspase 3 and cleaved PARP), increased endothelial cell integrity with increased eNOS and CD31 expression and increased CD31 and fibronection-positive cells, increased podocyte integrity with increased ZO-1, E-cadherin, dystrophin and nephrin expression, increased angiogenesis (SDF-1α and VEGF expression), decreased WT-1 and KIM-1 expression in kidney tissue. |
| Atasoyu et al. [50] | Cisplatin-induced AKI in Wistar albino rats | 2.5 ATA, 60 min, 1 session per day, with total number of 7 sessions | HBO significantly decreased serum urea and creatinine, improved their clearances and improved renal morphology. |
| Aydinoz et al. [51] | Cisplatin-induced AKI in Wistar albino rats | 2.5 ATA, 60 min, 1 session per day, with total number of 6 sessions; 2 session per day, with total number of 12 sessions | HBO decreased lipid peroxidation and improved SOD and glutathione peroxidase activity in kidney tissue, especially after two daily sessions. On the other hand, one daily HBO treatment slightly reduced serum urea and creatinine levels and attenuated histopathological injury, while two daily sessions increased creatinine levels and morphological alterations. |
| Ayvaz et al. [52] | Glycerol-induced AKI in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.5 ATA, 90 min, 1 session per day, with total number of 2 sessions | HBO decreased plasma urea and creatinine levels and increased creatinine clarence, improved renal morphology, decreased lipid peroxidation and increased SOD and catalase activity in kidney tissue, decreased tubular cell apoptosis and decreased PCNA expression. |
| Cebi et al. [53] | Glycerol-induced AKI in Wistar albino rats | 2.4 ATA, 70 min, 2 sessions per day, with total number of 2 sessions | HBO did not have beneficial effects in this experimental setting. |
| Atasoyu et al. [54] | Cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats | 2.5 ATA, 60 min, 1 single session, with total number of 4 sessions | HBO did not have beneficial effects in this experimental setting. |
| Ay et al. [55] | Cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats | 2.5 ATA, 60 min, 1 single session, with total number of 5 sessions | HBO decreased serum urea levels, decreased lipid peroxidation and increased SOD and glutathione peroxidase activity in kidney tissue. |
| Sabler et al. [56] | Vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.0 ATA, 60 min, 1 session per day with total number of 7 sessions | HBO did not have beneficial effects in this experimental setting. |
| Berkovitch et al. [57] | Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.0 ATA, 60 min, 1 session per day with total number of 5 sessions | HBO did not have beneficial effects in this experimental setting. |
| Oztopuz et al. [58] | Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats | 2.5 ATA, 90 min, 1 session per day with total number of 7 sessions | HBO decreased serum urea and creatinine, decreased lipid peroxidation and total oxidant status, improved SOD, glutathione peroxidase activity and total antioxidant status in kidney tissue, improved renal morphology and decreased expression of TNF-α, IL-1β and KIM-1. |
| Edremitlioglu et al. [59] | Sepsis-induced AKI in Wistar albino rats | 2.0 ATA, 90 min, 1 session per 6 h, with total number of 5 sessions | HBO significantly decreased plasma creatinine levels, reduced lipid peroxidation and improved cortical SOD and catalase, and medullar catalase activity in kidney tissue, improved GFR, urine output and renal morphology. |
| Zhao et al. [60] | Ischemia-reperfusion AKI after kidney transplantation in Sprague–Dawley rats | 2.0 ATA, 60 min, 1 session per 2 h, with total number of 3 sessions | HBO significantly decreased serum creatinine levels, decreased immunohistochemical expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and C3 as well as ICAM-1 and C3 mRNA in kidney tissue and improved renal morphology. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovacevic, S.; Mitovic, N.; Brkic, P.; Ivanov, M.; Zivotic, M.; Miloradovic, Z.; Nesovic Ostojic, J. Hyperbaric Oxygenation: Can It Be a Novel Supportive Method in Acute Kidney Injury? Data Obtained from Experimental Studies. Cells 2024, 13, 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131119
Kovacevic S, Mitovic N, Brkic P, Ivanov M, Zivotic M, Miloradovic Z, Nesovic Ostojic J. Hyperbaric Oxygenation: Can It Be a Novel Supportive Method in Acute Kidney Injury? Data Obtained from Experimental Studies. Cells. 2024; 13(13):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131119
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovacevic, Sanjin, Nikola Mitovic, Predrag Brkic, Milan Ivanov, Maja Zivotic, Zoran Miloradovic, and Jelena Nesovic Ostojic. 2024. "Hyperbaric Oxygenation: Can It Be a Novel Supportive Method in Acute Kidney Injury? Data Obtained from Experimental Studies" Cells 13, no. 13: 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131119
APA StyleKovacevic, S., Mitovic, N., Brkic, P., Ivanov, M., Zivotic, M., Miloradovic, Z., & Nesovic Ostojic, J. (2024). Hyperbaric Oxygenation: Can It Be a Novel Supportive Method in Acute Kidney Injury? Data Obtained from Experimental Studies. Cells, 13(13), 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131119








