Protein Kinase A Regulates Platelet Phosphodiesterase 3A through an A-Kinase Anchoring Protein Dependent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Platelet and Megakaryocyte Isolation
2.3. Platelet Aggregation
2.4. Measurement of cAMP
2.5. PKA Activity Assay
2.6. Measurement of PDE Activity
2.7. Subcellular Fractionation
2.8. Immunoprecipitation, cAMP Pull Down, and Immunoblotting
2.9. Mass Spectrometry
2.10. Immunofluorescence and DuolinkTM Proximity Ligation Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
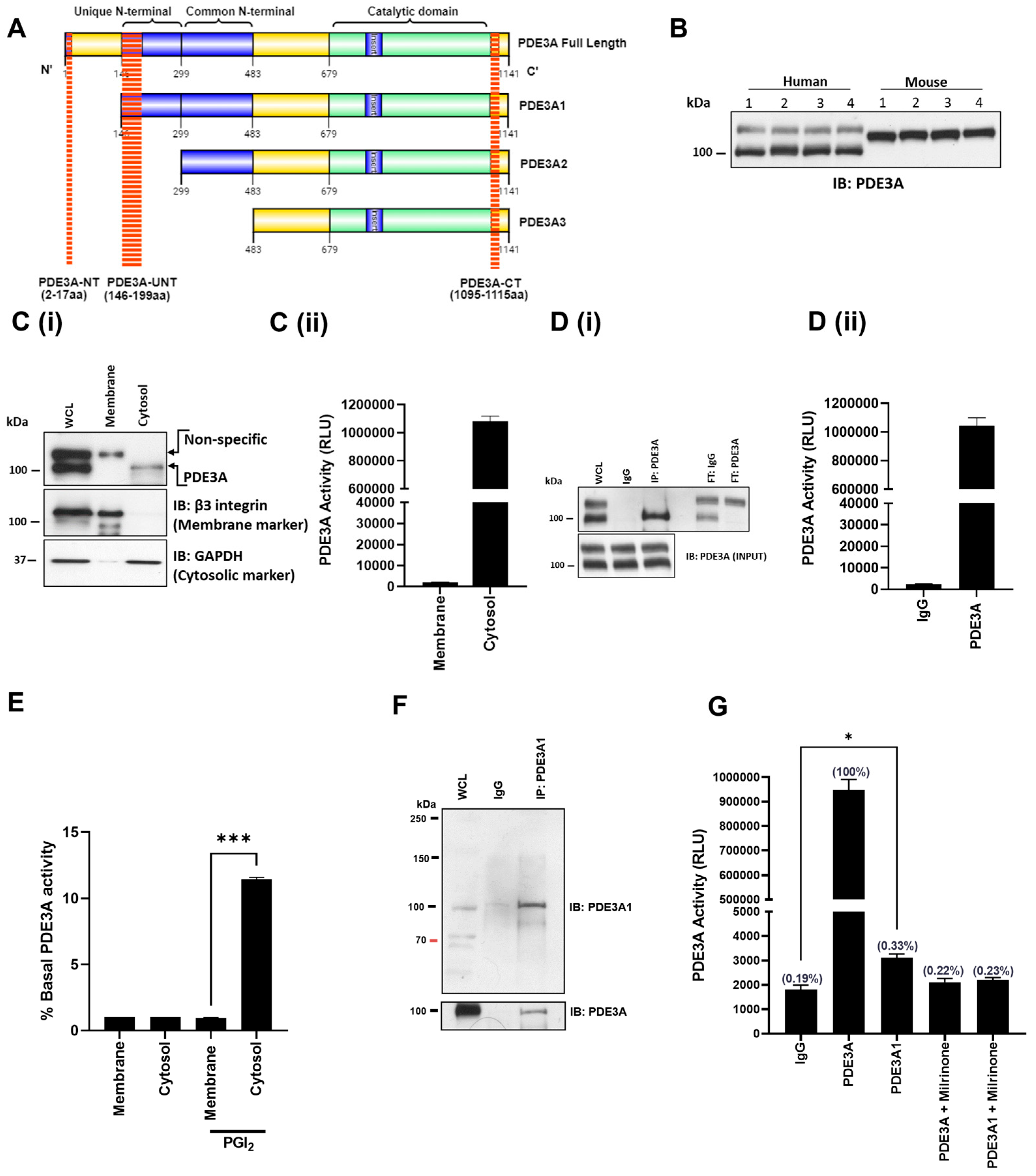
3.1. Identification of PDE3A Isoforms in Platelets
3.2. PDE3A Is Transiently Phosphorylated and Activated by PKA in Response to PGI2
3.3. AKAP Disruption Reduces cAMP-Signalling-Mediated Activation of PDE3A
3.4. AKAP7δ Is Expressed and Acts as an AKAP in Human Platelets
3.5. PDE3A Exists in a Complex with PKA Type II and AKAP7δ in Platelets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radomski, M.W.; Palmer, R.M.; Moncada, S. The Anti-Aggregating Properties of Vascular Endothelium: Interactions between Prostacyclin and Nitric Oxide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1987, 92, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.Y.; Jones, S.; Ntrakwah, A.; Naseem, K.M.; Farndale, R.W.; Mahaut-Smith, M.P. Platelet Ca(2+) Responses Coupled to Glycoprotein Vi and Toll-Like Receptors Persist in the Presence of Endothelial-Derived Inhibitors: Roles for Secondary Activation of P2 × 1 Receptors and Release from Intracellular Ca(2+) Stores. Blood 2012, 119, 3613–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburima, A.; Wraith, K.S.; Raslan, Z.; Law, R.; Magwenzi, S.; Naseem, K.M. Camp Signaling Regulates Platelet Myosin Light Chain (Mlc) Phosphorylation and Shape Change through Targeting the Rhoa-Rho Kinase-Mlc Phosphatase Signaling Pathway. Blood 2013, 122, 3533–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raslan, Z.; Magwenzi, S.; Aburima, A.; Taskén, K.; Naseem, K.M. Targeting of Type I Protein Kinase a to Lipid Rafts Is Required for Platelet Inhibition by the 3’,5’-Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate-Signaling Pathway. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 1721–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Raslan, Z.; Aburima, A.; Magwenzi, S.; Wraith, K.S.; Spurgeon, B.E.J.; Hindle, M.S.; Law, R.; Febbraio, M.; and Naseem, K.M. Atherogenic Lipid Stress Induces Platelet Hyperactivity through Cd36-Mediated Hyposensitivity to Prostacyclin: The Role of Phosphodiesterase 3a. Haematologica 2020, 105, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburima, A.; Berger, M.; Spurgeon, B.E.J.; Webb, B.A.; Wraith, K.S.; Febbraio, M.; Poole, A.W.; Naseem, K.M. Thrombospondin-1 Promotes Hemostasis through Modulation of Camp Signaling in Blood Platelets. Blood 2021, 137, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.; Geiger, J.; Gambaryan, S.; Veit, J.; Vaudel, M.; Nollau, P.; Kohlbacher, O.; Martens, L.; Walter, U.; Sickmann, A.; et al. Time-Resolved Characterization of Camp/Pka-Dependent Signaling Reveals That Platelet Inhibition Is a Concerted Process Involving Multiple Signaling Pathways. Blood 2014, 123, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, U.R.; Walter, U.; Eigenthaler, M. Taming Platelets with Cyclic Nucleotides. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 62, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, J.W.; Oler, A.J.; Tolley, N.D.; Hunter, B.N.; Low, E.N.; Nix, D.A.; Yost, C.C.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Weyrich, A.S. Genome-Wide Rna-Seq Analysis of Human Mouse Platelet Transcriptomes. Blood 2011, 118, e101–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijge, M.A.; Ansink, K.; Vanschoonbeek, K.; Heemskerk, J.W. Control of Platelet Activation by Cyclic Amp Turnover and Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase Type-3. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, J.M.; Brenna, K.J.; Colman, R.W.; Sheth, S.B. Differential Regulation of Human Platelet Responses by Cgmp Inhibited and Stimulated Camp Phosphodiesterases. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 87, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyazono, H.; Nakamura, K.; Shinkawa, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sakata, R.; Yamada, K. Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation and the Release of P-Selectin from Platelets by Cilostazol. Thromb. Res. 2001, 101, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, H.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Shirakawa, R.; Higashi, T.; Kawato, M.; Ikeda, T.; Tabuchi, A.; Morimoto, T.; et al. Evaluation of the Antiplatelet Effects of Cilostazol, a Phosphodiesterase 3 Inhibitor, by Vasp Phosphorylation and Platelet Aggregation. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 1844–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Yoo, S.Y.; Suh, J.; Park, K.H.; Park, Y.; Tantry, U.S.; Park, K.S.; Han, S.H.; Kang, W.C.; Shin, D.H.; et al. Efficacy of Cilostazol on Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation, Inflammation and Myonecrosis in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: The Accel-Loading-Acs (Accelerated Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation, Inflammation and Myonecrosis by Adjunctive Cilostazol Loading in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome) Study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 190, 370–375. [Google Scholar]
- Gresele, P.; Momi, S.; Falcinelli, E. Anti-Platelet Therapy: Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 72, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, A.; Monterisi, S.; Stangherlin, A.; Zoccarato, A.; Koschinski, A.; Surdo, N.C.; Mongillo, M.; Sawa, A.; Jordanides, N.E.; Mountford, J.C.; et al. Pka and Pde4d3 Anchoring to Akap9 Provides Distinct Regulation of Camp Signals at the Centrosome. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongillo, M.; McSorley, T.; Evellin, S.; Sood, A.; Lissandron, V.; Terrin, A.; Huston, E.; Hannawacker, A.; Lohse, M.J.; Pozzan, T.; et al. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Analysis of Camp Dynamics in Live Neonatal Rat Cardiac Myocytes Reveals Distinct Functions of Compartmentalized Phosphodiesterases. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongillo, M.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Terrin, A.; Lissandron, V.; Cheung, Y.F.; Dostmann, W.R.; Pozzan, T.; Kass, D.A.; Paolocci, N.; Houslay, M.D.; et al. Compartmentalized Phosphodiesterase-2 Activity Blunts Beta-Adrenergic Cardiac Inotropy Via an No/Cgmp-Dependent Pathway. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, K.; Zaccolo, M. Axelrod Symposium 2019: Phosphoproteomic Analysis of G-Protein-Coupled Pathways. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, J.M.; Vaudel, M.; Gambaryan, S.; Radau, S.; Walter, U.; Martens, L.; Geiger, J.; Sickmann, A.; Zahedi, R.P. The First Comprehensive and Quantitative Analysis of Human Platelet Protein Composition Allows the Comparative Analysis of Structural and Functional Pathways. Blood 2012, 120, e73–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Shen, W.; Vandeput, F.; Szabo-Fresnais, N.; Krall, J.; Degerman, E.; Goetz, F.; Klussmann, E.; Movsesian, M.; Manganiello, V. Regulation of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Atpase 2 (Serca2) Activity by Phosphodiesterase 3a (Pde3a) in Human Myocardium: Phosphorylation-Dependent Interaction of Pde3a1 with Serca2. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 6763–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Colman, R.W. Thrombin Regulates Intracellular Cyclic Amp Concentration in Human Platelets through Phosphorylation/Activation of Phosphodiesterase 3a. Blood 2007, 110, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.W.; Mackintosh, C.; Hers, I. Protein Kinase C-Mediated Phosphorylation and Activation of Pde3a Regulate Camp Levels in Human Platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12339–12348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtner, H.; Calaminus, S.D.; Sinclair, A.; Monypenny, J.; Blundell, M.P.; Leon, C.; Holyoake, T.L.; Thrasher, A.J.; Michie, A.M.; Vukovic, M.; et al. Megakaryocytes Assemble Podosomes That Degrade Matrix and Protrude through Basement Membrane. Blood 2013, 121, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidoux, G.; Gerbaud, P.; Dompierre, J.; Lygren, B.; Solstad, T.; Evain-Brion, D.; Taskén, K. A Pka-Ezrin-Cx43 Signaling Complex Controls Gap Junction Communication and Thereby Trophoblast Cell Fusion. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 4172–4185. [Google Scholar]
- Vandeput, F.; Szabo-Fresnais, N.; Ahmad, F.; Kho, C.; Lee, A.; Krall, J.; Dunlop, A.; Hazel, M.W.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Hajjar, R.J.; et al. Selective Regulation of Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase Pde3a Isoforms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19778–19783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns-Hamuro, L.L.; Ma, Y.; Kammerer, S.; Reineke, U.; Self, C.; Cook, C.; Olson, G.L.; Cantor, C.R.; Braun, A.; Taylor, S.S. Designing Isoform-Specific Peptide Disruptors of Protein Kinase a Localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4072–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, E.; Klaasse, G.; Leurs, U.; Heck, A.J.; Martin, N.I.; Scholten, A. Charting the Interactome of Pde3a in Human Cells Using an Ibmx Based Chemical Proteomics Approach. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.R.; Lygren, B.; Berge, T.; Hoshi, N.; Wong, W.; Taskén, K.; Scott, J.D. Delineation of Type I Protein Kinase a-Selective Signaling Events Using an Ri Anchoring Disruptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21535–21545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lygren, B.; Carlson, C.R.; Santamaria, K.; Lissandron, V.; McSorley, T.; Litzenberg, J.; Lorenz, D.; Wiesner, B.; Rosenthal, W.; Zaccolo, M.; et al. Akap Complex Regulates Ca2+ Re-Uptake into Heart Sarcoplasmic Reticulum. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aye, T.T.; Mohammed, S.; van den Toorn, H.W.; van Veen, T.A.; van der Heyden, M.A.; Scholten, A.; Heck, A.J. Selectivity in Enrichment of Camp-Dependent Protein Kinase Regulatory Subunits Type I and Type Ii and Their Interactors Using Modified Camp Affinity Resins. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2009, 8, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henn, V.; Edemir, B.; Stefan, E.; Wiesner, B.; Lorenz, D.; Theilig, F.; Schmitt, R.; Vossebein, L.; Tamma, G.; Beyermann, M.; et al. Identification of a Novel a-Kinase Anchoring Protein 18 Isoform and Evidence for Its Role in the Vasopressin-Induced Aquaporin-2 Shuttle in Renal Principal Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26654–26665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacAla, L.J.; Hayslett, J.P.; Smallwood, J.I. Technical Note: Measurement of Camp-Dependent Protein Kinase Activity Using a Fluorescent-Labeled Kemptide. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 1746–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dodge, K.L.; Khouangsathiene, S.; Kapiloff, M.S.; Mouton, R.; Hill, E.V.; Houslay, M.D.; Langeberg, L.K.; Scott, J.D. Makap Assembles a Protein Kinase a/Pde4 Phosphodiesterase Camp Signaling Module. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskén, K.A.; Collas, P.; Kemmner, W.A.; Witczak, O.; Conti, M.; Taskén, K. Phosphodiesterase 4d and Protein Kinase a Type Ii Constitute a Signaling Unit in the Centrosomal Area. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 21999–22002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- el-Daher, S.S.; Eigenthaler, M.; Walter, U.; Furuichi, T.; Miyawaki, A.; Mikoshiba, K.; Kakkar, V.V.; Authi, K.S. Distribution and Activation of Camp- and Cgmp-Dependent Protein Kinases in Highly Purified Human Platelet Plasma and Intracellular Membranes. Thromb. Haemost. 1996, 76, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Daher, S.S.; Patel, Y.; Siddiqua, A.; Hassock, S.; Edmunds, S.; Maddison, B.; Patel, G.; Goulding, D.; Lupu, F.; Wojcikiewicz, R.J.; et al. Distinct Localization and Function of (1,4,5)Ip(3) Receptor Subtypes and the (1,3,4,5)Ip(4) Receptor Gap1(Ip4bp) in Highly Purified Human Platelet Membranes. Blood 2000, 95, 3412–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechsler, J.; Choi, Y.H.; Krall, J.; Ahmad, F.; Manganiello, V.C.; Movsesian, M.A. Isoforms of Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase Pde3a in Cardiac Myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 38072–38078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalil, J.S.; Law, R.; Raslan, Z.; Cheah, L.T.; Hindle, M.S.; Aburima, A.A.; Kearney, M.T.; Naseem, K.M. Protein Kinase A Regulates Platelet Phosphodiesterase 3A through an A-Kinase Anchoring Protein Dependent Manner. Cells 2024, 13, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131104
Khalil JS, Law R, Raslan Z, Cheah LT, Hindle MS, Aburima AA, Kearney MT, Naseem KM. Protein Kinase A Regulates Platelet Phosphodiesterase 3A through an A-Kinase Anchoring Protein Dependent Manner. Cells. 2024; 13(13):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131104
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalil, Jawad S., Robert Law, Zaher Raslan, Lih T. Cheah, Matthew S. Hindle, Ahmed A. Aburima, Mark T. Kearney, and Khalid M. Naseem. 2024. "Protein Kinase A Regulates Platelet Phosphodiesterase 3A through an A-Kinase Anchoring Protein Dependent Manner" Cells 13, no. 13: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131104
APA StyleKhalil, J. S., Law, R., Raslan, Z., Cheah, L. T., Hindle, M. S., Aburima, A. A., Kearney, M. T., & Naseem, K. M. (2024). Protein Kinase A Regulates Platelet Phosphodiesterase 3A through an A-Kinase Anchoring Protein Dependent Manner. Cells, 13(13), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131104




