Distinct Effects of Respiratory Viral Infection Models on miR-149-5p, IL-6 and p63 Expression in BEAS-2B and A549 Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.1.1. Poly (I:C) Incubation
2.1.2. Transfection of Cells with S1 or S2
2.2. Transfection of miRNA Mimic/Inhibitor
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.5. Immunoblotting
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.7. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. miR-149-5p Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells after Poly (I:C) Incubation or S1 or S2 Transfection
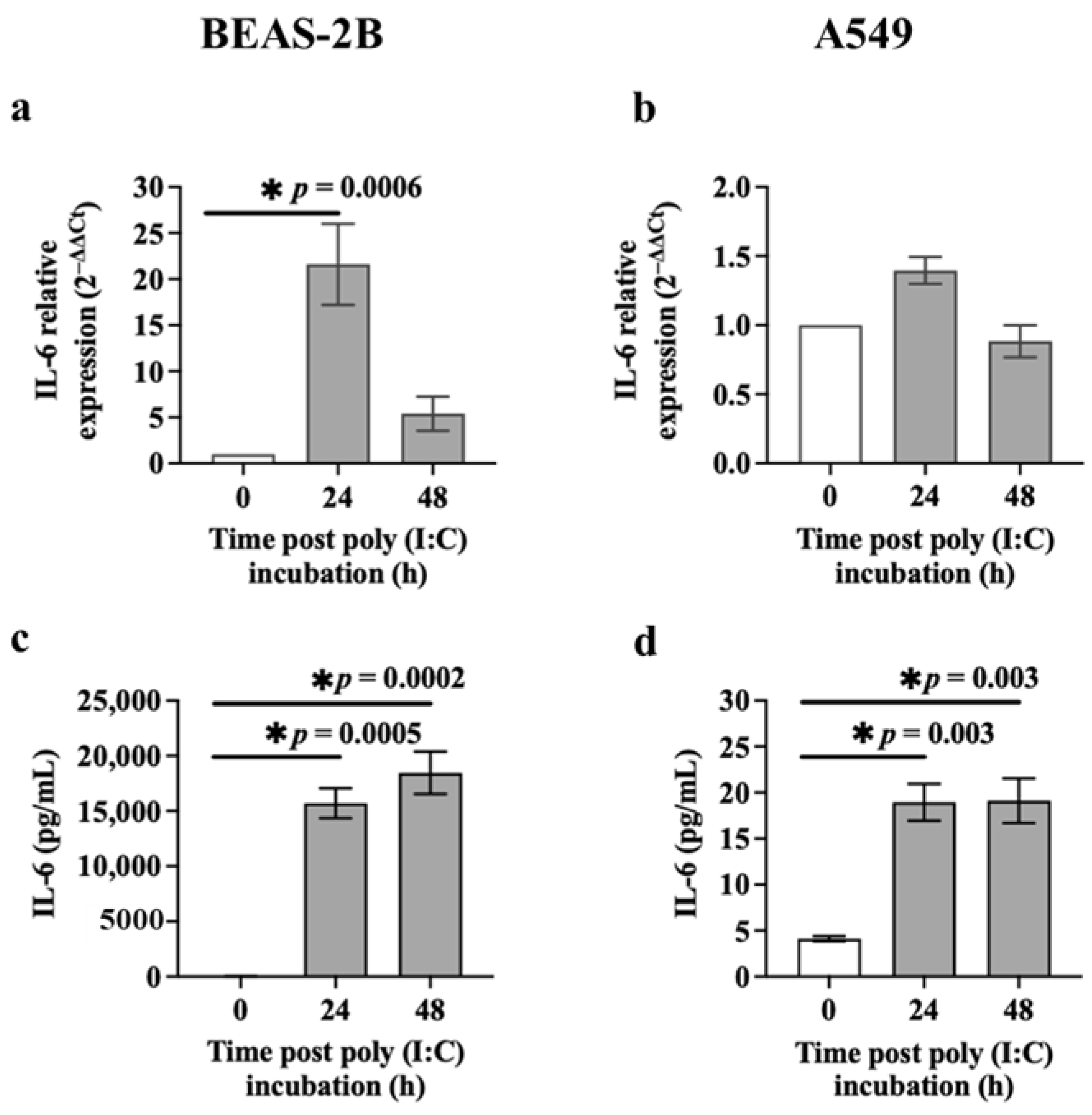
3.2. IL-6 Release from Airway Epithelial Cells after Poly (I:C) Incubation or S1 or S2 Transfection
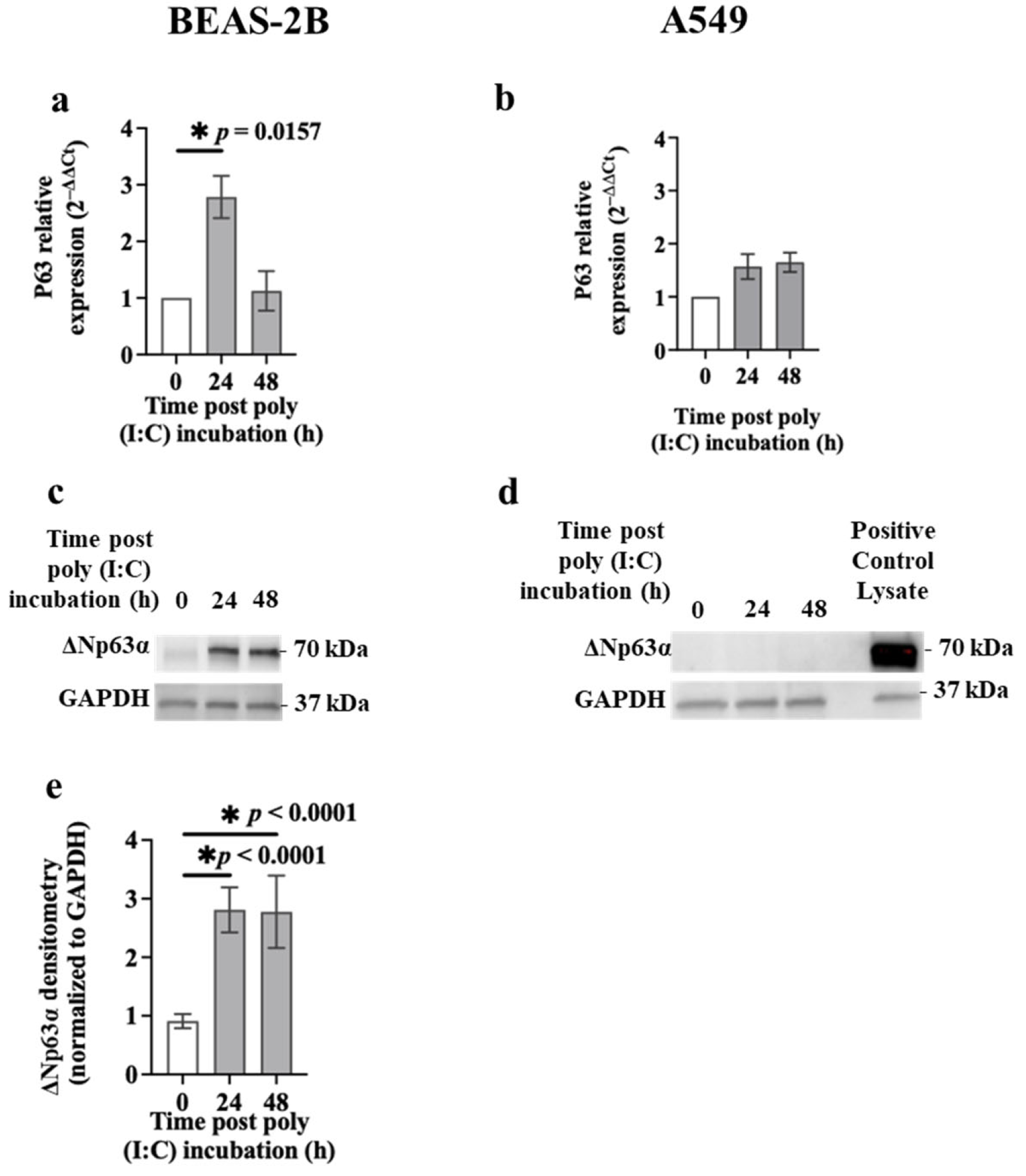
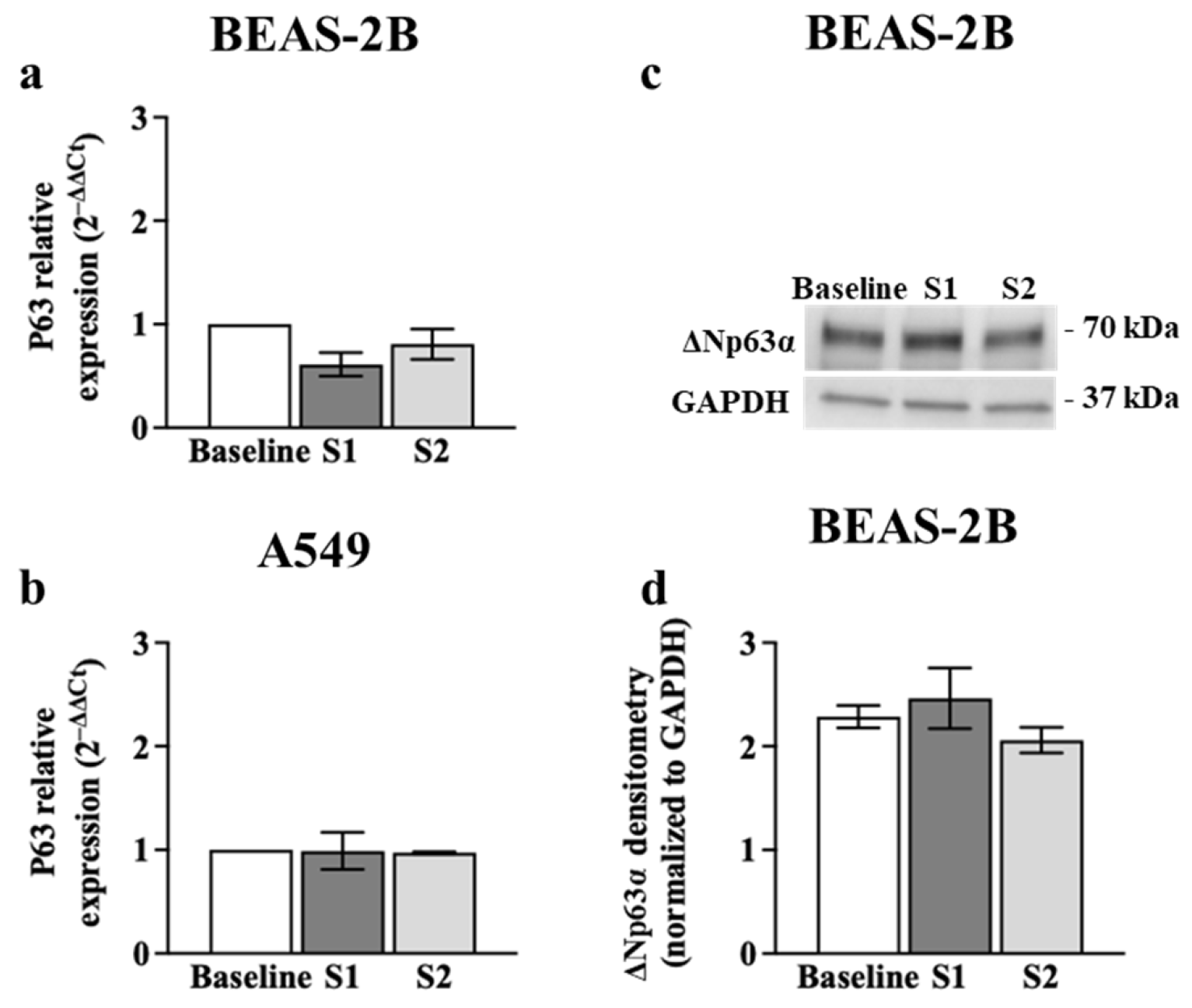
3.3. p63 Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells after Poly (I:C) Incubation or S1 or S2 Transfection
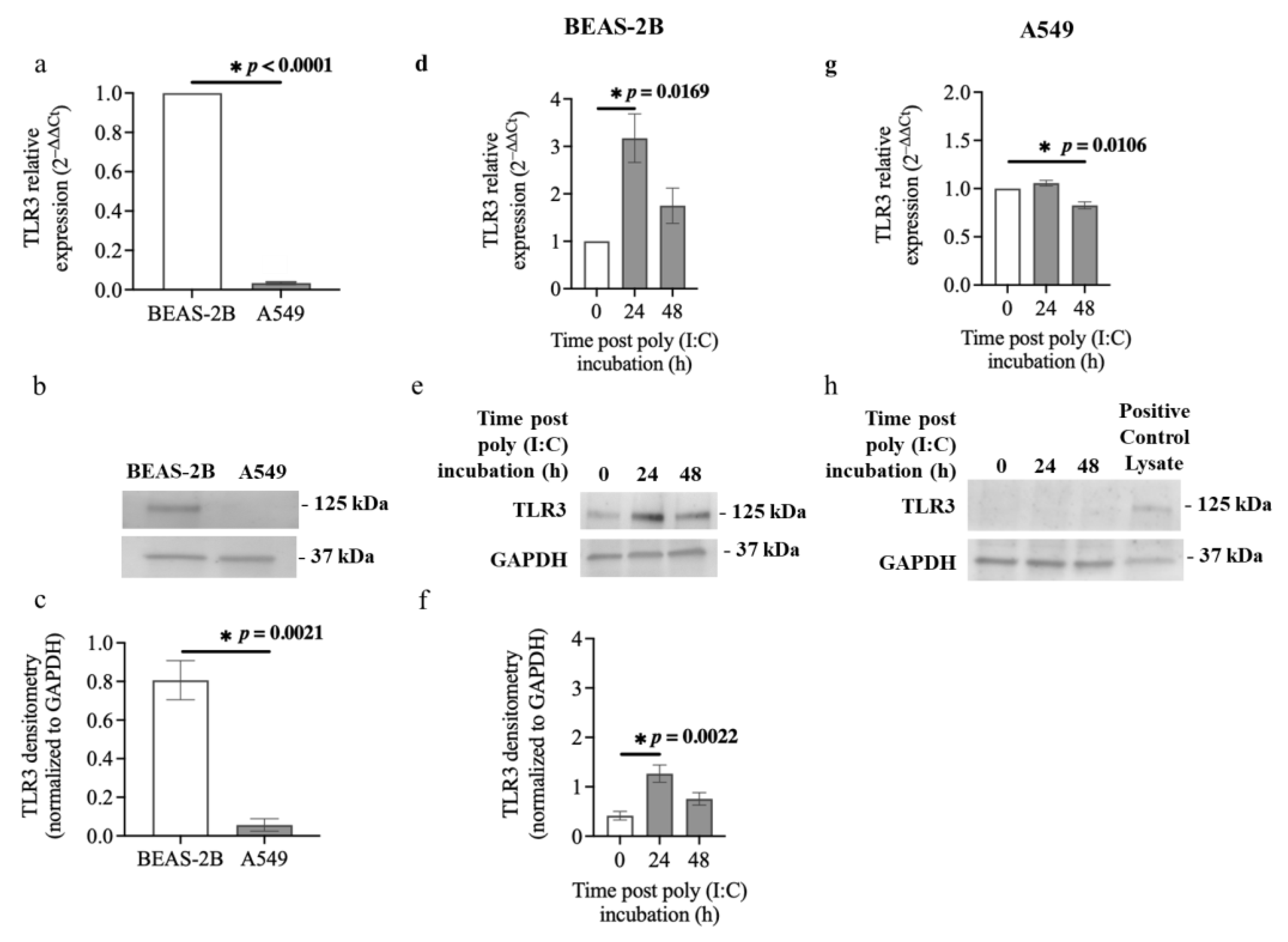
3.4. TLR3 Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells after Poly (I:C) Incubation
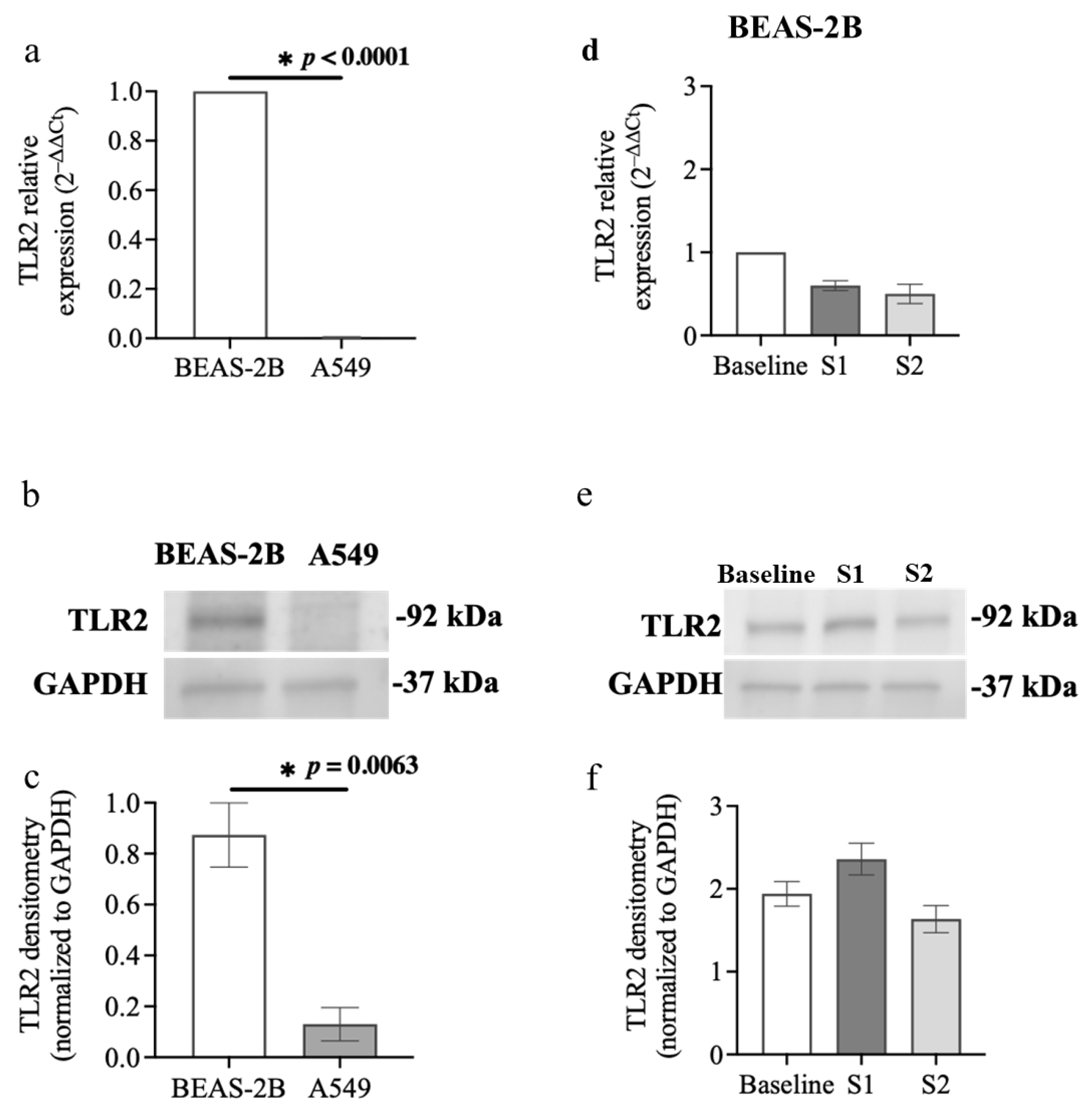
3.5. TLR2 Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells after S1 or S2 Subunit Transfection
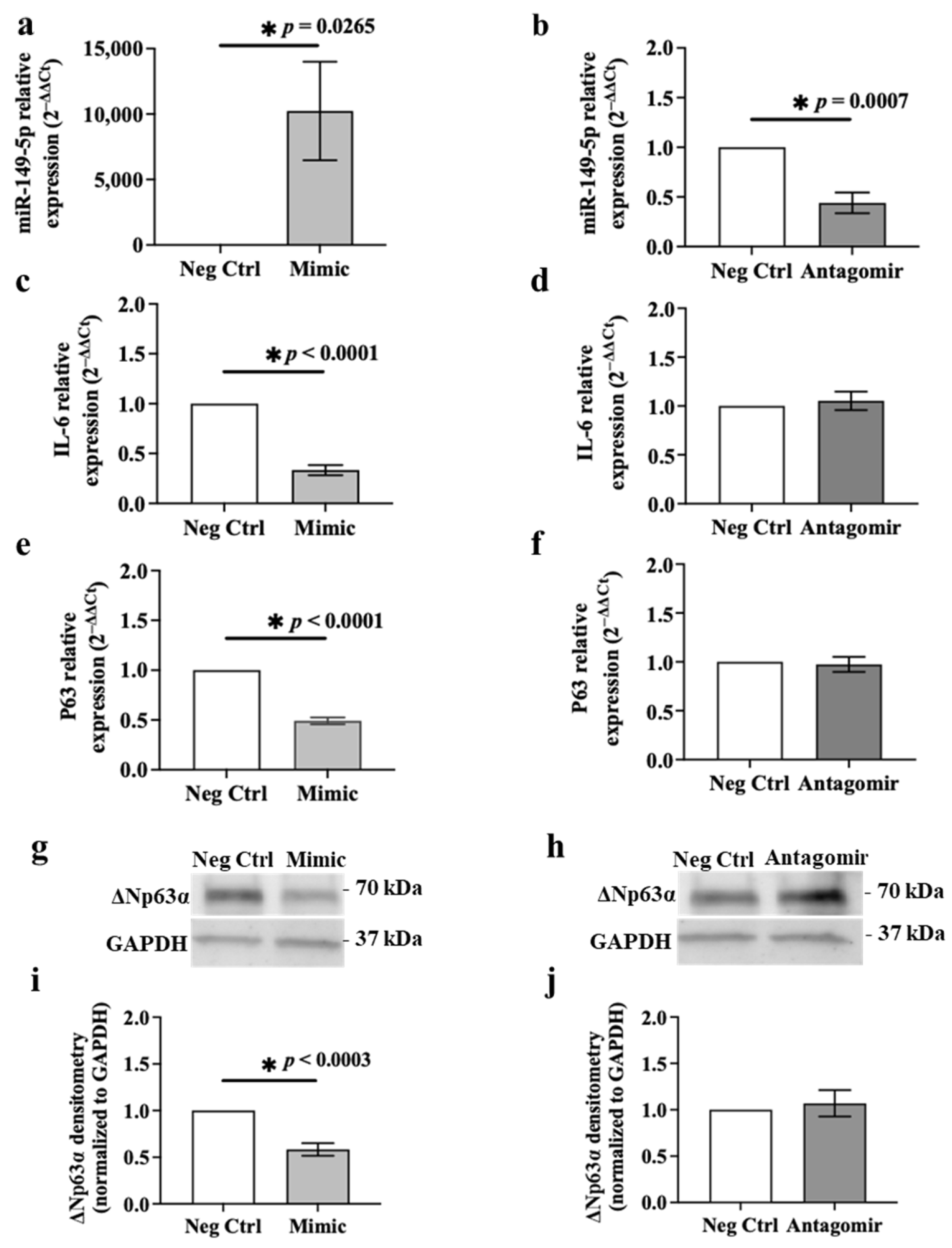
3.6. Ectopic Expression of miR-149-5p Mimic Suppresses IL-6 and p63 Expression in BEAS-2B Cells
3.7. Ectopic Expression of miR-149-5p Mimic Downregulates Poly (I:C)-Induced IL-6 Release in BEAS-2B Cells after 24 h
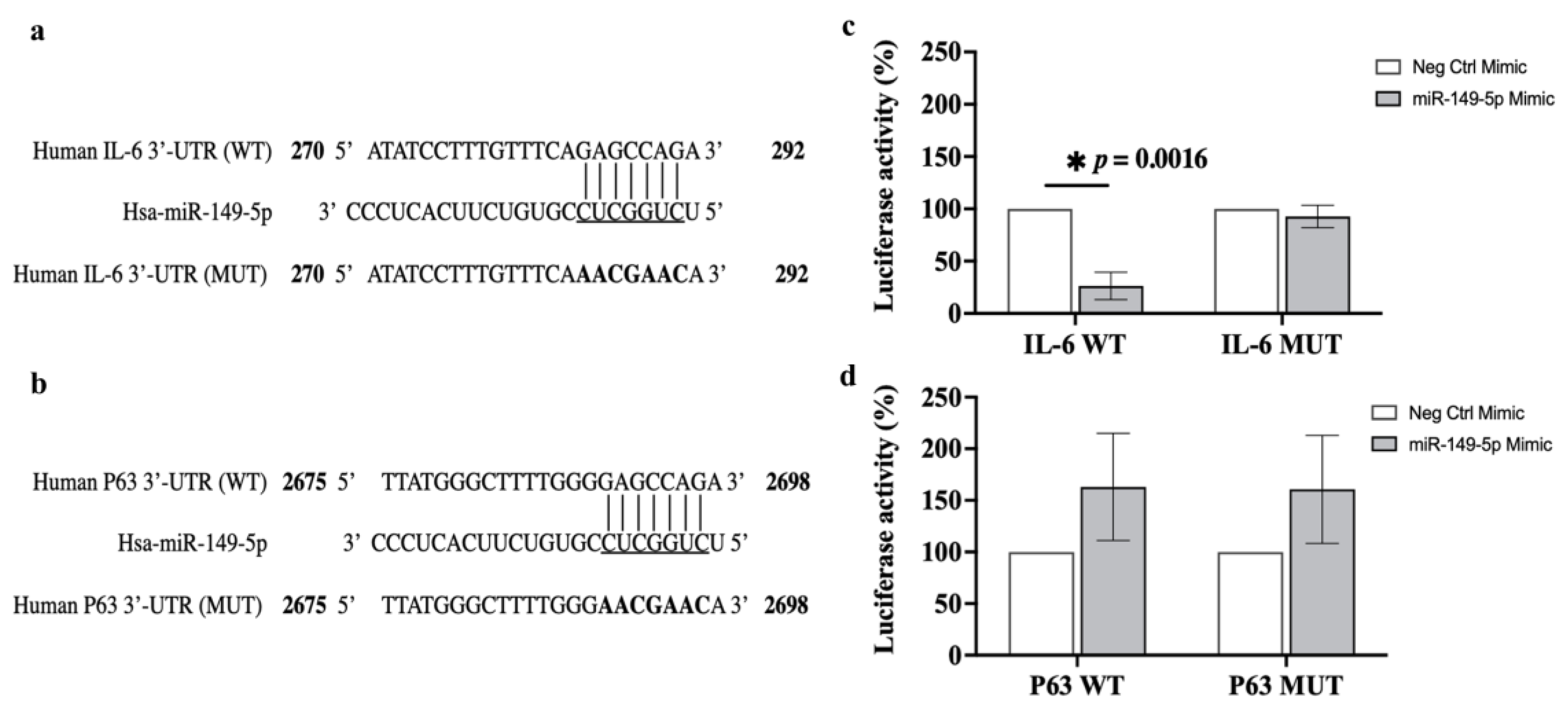
3.8. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, T.; McLean, K.; Campbell, H.; Nair, H. Aetiological role of common respiratory viruses in acute lower respiratory infections in children under five years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health 2015, 5, 010408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Nayak, L.; Das, R.R.; Dwibedi, B.; Singh, A. Viral Agents Causing Acute Respiratory Infections in Children under Five: A Study from Eastern India. Int. J. Pediatr. 2016, 2016, 7235482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, C.A.; Morran, M.P.; Nestor-Kalinoski, A.L. The COVID-19 pandemic: A global health crisis. Physiol. Genom. 2020, 52, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.J.; Jacobson, R.M.; Dowdle, W.R.; Poland, G.A. 2009 H1N1 influenza. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, M.D.; Mahbub, R.M.; Idrees, S.; Nguyen, D.H.; Miemczyk, S.; Pathinayake, P.; Nichol, K.; Hansbro, N.G.; Gearing, L.J.; Hertzog, P.J.; et al. Increased SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Protease, and Inflammatory Responses in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cells Defined with Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 712–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.C.; Starkey, M.R.; Hanish, I.; Parsons, K.; Haw, T.J.; Howland, L.J.; Barr, I.; Mahony, J.B.; Foster, P.S.; Knight, D.A.; et al. Targeting PI3K-p110alpha Suppresses Influenza Virus Infection in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, A.; Wadsworth, S.; Dorscheid, D.; Man, S.F.; Sin, D.D. The airway epithelium: More than just a structural barrier. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2011, 5, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.W.; Yuen, K.M.; Yu, W.C.; Ho, C.C.; Nicholls, J.M.; Peiris, J.S.; Chan, M.C. Influenza H5N1 and H1N1 virus replication and innate immune responses in bronchial epithelial cells are influenced by the state of differentiation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukassen, S.; Chua, R.L.; Trefzer, T.; Kahn, N.C.; Schneider, M.A.; Muley, T.; Winter, H.; Meister, M.; Veith, C.; Boots, A.W.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are primarily expressed in bronchial transient secretory cells. Embo J. 2020, 39, e105114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Hill, T.E.; Yoshikawa, N.; Popov, V.L.; Galindo, C.L.; Garner, H.R.; Peters, C.J.; Tseng, C.T. Dynamic innate immune responses of human bronchial epithelial cells to severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus infection. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillyer, P.; Shepard, R.; Uehling, M.; Krenz, M.; Sheikh, F.; Thayer, K.R.; Huang, L.; Yan, L.; Panda, D.; Luongo, C.; et al. Differential Responses by Human Respiratory Epithelial Cell Lines to Respiratory Syncytial Virus Reflect Distinct Patterns of Infection Control. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareille, M.; Kieninger, E.; Edwards, M.R.; Regamey, N. The airway epithelium: Soldier in the fight against respiratory viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273, Table of Contents. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulou, L.; Holt, A.C.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 2001, 413, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fang, M.; Shi, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2-Induced Innate Immune Responses and the Potential Application Value of Toll-Like Receptor Immunomodulators in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 948770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Zhang, L.; Bhushan, A.; Swanson, B.; Zhang, L.; Mamede, J.I.; Voigt, R.M.; Shaikh, M.; Engen, P.A.; Keshavarzian, A. The SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Promotes MAPK and NF-kB Activation in Human Lung Cells and Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Human Lung and Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Shafiei, M.S.; Longoria, C.; Schoggins, J.; Savani, R.C.; Zaki, H. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-κB pathway. bioRxiv 2021, 10, e68563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredelli, D.; Pariano, M.; Costantini, C.; Graziani, A.; Bozza, S.; Romani, L.; Puccetti, P.; Talesa, V.N.; Antognelli, C. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Spike Protein S1 Induces Methylglyoxal-Derived Hydroimidazolone/Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (MG-H1/RAGE) Activation to Promote Inflammation in Human Bronchial BEAS-2B Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.; Chang, H.; Wei, Z.; Li, J.; Zeng, M. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces inflammation and EMT of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts through the upregulation of GADD45A. Open Med. (Wars) 2023, 18, 20230779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowell, N.C.; Seideman, J.; Raymond, H.A.; Smalley, K.A.; Lamb, R.J.; Egenolf, D.D.; Bugelski, P.J.; Murray, L.A.; Marsters, P.A.; Bunting, R.A.; et al. Long-term activation of TLR3 by Poly(I:C) induces inflammation and impairs lung function in mice. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon, M.; Irvin, C.G. Role of IL-6 in asthma and other inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska-Polak, A.; Brauncajs, M.; Jarzębska, M.; Pawełczyk, M.; Kurowski, M.; Chałubiński, M.; Makowska, J.; Kowalski, M.L. Toll-Like Receptor Agonists Modulate Wound Regeneration in Airway Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, S.M.; Hackett, T.L.; Shaheen, F.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kicic, A.; Stick, S.M.; Knight, D.A. Transcription factor p63 regulates key genes and wound repair in human airway epithelial basal cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, S.; Yu, J. A brief review on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2009, 7, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, P.S.; Plank, M.; Collison, A.; Tay, H.L.; Kaiko, G.E.; Li, J.; Johnston, S.L.; Hansbro, P.M.; Kumar, R.K.; Yang, M.; et al. The emerging role of microRNAs in regulating immune and inflammatory responses in the lung. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 253, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moheimani, F.; Hsu, A.C.; Reid, A.T.; Williams, T.; Kicic, A.; Stick, S.M.; Hansbro, P.M.; Wark, P.A.; Knight, D.A. The genetic and epigenetic landscapes of the epithelium in asthma. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.Y.; Yeung, A.C.; Ngai, K.L.; Li, M.S.; To, K.F.; Tsui, S.K.; Chan, P.K. Effect of avian influenza A H5N1 infection on the expression of microRNA-141 in human respiratory epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moheimani, F.; Koops, J.; Williams, T.; Reid, A.T.; Hansbro, P.M.; Wark, P.A.; Knight, D.A. Influenza A virus infection dysregulates the expression of microRNA-22 and its targets; CD147 and HDAC4, in epithelium of asthmatics. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahamtan, A.; Inchley, C.S.; Marzban, M.; Tavakoli-Yaraki, M.; Teymoori-Rad, M.; Nakstad, B.; Salimi, V. The role of microRNAs in respiratory viral infection: Friend or foe? Rev. Med. Virol. 2016, 26, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Zhou, H.; Mubalake, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, K.; Chu, X.; Wang, R. Regulation and functions of MicroRNA-149 in human cancers. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.-J.; Yao, Y.; Cai, X.-Y.; Cai, Y.-T.; Su, Q.; Fang, G.-Y. MiR-149-5p: An Important miRNA Regulated by Competing Endogenous RNAs in Diverse Human Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 743077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shan, J.-X.; Chen, X.-H.; Zhang, D.; Su, L.-P.; Huang, X.-Y.; Yu, B.-Q.; Zhi, Q.-M.; Li, C.-L.; Wang, Y.-Q.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-149 in cancer-associated fibroblasts mediates prostaglandin E2/interleukin-6 signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targetscan. Available online: https://www.targetscan.org/cgi-bin/targetscan/vert_72/targetscan.cgi?species=Human&gid=&mir_sc=&mir_c=&mir_nc=&mir_vnc=&mirg=miR-149-5p (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- miRDB. Available online: http://www.mirdb.org/ (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Rennie, W.; Liu, C.; Carmack, C.S.; Wolenc, A.; Kanoria, S.; Lu, J.; Long, D.; Ding, Y. STarMir: A web server for prediction of microRNA binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W114–W118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddel, R.R.; Ke, Y.; Gerwin, B.I.; McMenamin, M.G.; Lechner, J.F.; Su, R.T.; Brash, D.E.; Park, J.B.; Rhim, J.S.; Harris, C.C. Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus, or transfection via strontium phosphate coprecipitation with a plasmid containing SV40 early region genes. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 1904–1909. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foster, K.A.; Oster, C.G.; Mayer, M.M.; Avery, M.L.; Audus, K.L. Characterization of the A549 cell line as a type II pulmonary epithelial cell model for drug metabolism. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 243, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, D.; Gentili, V.; Rizzo, S.; Rotola, A.; Rizzo, R. SARS-CoV-2 Spike 1 Protein Controls Natural Killer Cell Activation via the HLA-E/NKG2A Pathway. Cells 2020, 9, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Image Lab Software. Available online: https://www.bio-rad.com/en-uk/product/image-lab-software?ID=KRE6P5E8Z (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Hübner, K.; Karwelat, D.; Pietsch, E.; Beinborn, I.; Winterberg, S.; Bedenbender, K.; Benedikter, B.J.; Schmeck, B.; Vollmeister, E. NF-κB-mediated inhibition of microRNA-149-5p regulates Chitinase-3-like 1 expression in human airway epithelial cells. Cell. Signal. 2020, 67, 109498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotmatics. Available online: https://www.graphpad.com/ (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Koizumi, Y.; Nagase, H.; Nakajima, T.; Kawamura, M.; Ohta, K. Toll-like receptor 3 ligand specifically induced bronchial epithelial cell death in caspase dependent manner and functionally upregulated Fas expression. Allergol. Int. 2016, 65 (Suppl. 1), S30–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sada, M.; Watanabe, M.; Inui, T.; Nakamoto, K.; Hirata, A.; Nakamura, M.; Honda, K.; Saraya, T.; Kurai, D.; Kimura, H.; et al. Ruxolitinib inhibits poly(I:C) and type 2 cytokines-induced CCL5 production in bronchial epithelial cells: A potential therapeutic agent for severe eosinophilic asthma. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, M.C.; Varose, S.Y.; Sawant, U.P.; Fernandes, M.M. Expression of innate immune response genes in upper airway samples of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients: A preliminary study. Indian J. Med. Res. 2021, 153, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Hu, W.L.; Jiang, C.C.; Wang, J.X.; Han, C.C.; Chu, P.; Zhang, L.J.; Thorne, R.F.; Wilmott, J.; Scolyer, R.A.; et al. MicroRNA-149*, a p53-responsive microRNA, functions as an oncogenic regulator in human melanoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15840–15845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Yu, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhong, S.; Zhao, J.; Tang, J. miR-149 in Human Cancer: A Systemic Review. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, M.J.; Irving, A.T.; Forster, S.C.; Marsland, B.J.; Hansbro, P.M.; Hertzog, P.J.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Nold, M.F. Of bats and men: Immunomodulatory treatment options for COVID-19 guided by the immunopathology of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabd0205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, P.; Ronconi, G.; Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.E.; Ross, R.; Frydas, I.; Kritas, S.K. Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): Anti-inflammatory strategies. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost Agents 2020, 34, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B.; Han, Y.; Fu, Z.; Wang, L.; Hu, G.; Ma, Q.; et al. The role of IL-6 in coronavirus, especially in COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1033674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaram, S.; Craig, M.P.; Hill, N.T.; Aljagthmi, A.; Garrido, C.; Paliy, O.; Bottomley, M.; Raymer, M.; Kadakia, M.P. Identification of novel ΔNp63α-regulated miRNAs using an optimized small RNA-Seq analysis pipeline. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, A.F.; Maley, A.M.; Wu, C.; Gilboa, T.; Norman, M.; Lazarovits, R.; Mao, C.-P.; Newton, G.; Chang, M.; Nguyen, K.; et al. Ultra-Sensitive Serial Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 Antigens and Antibodies in Plasma to Understand Disease Progression in COVID-19 Patients with Severe Disease. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1562–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agnillo, F.; Walters, K.A.; Xiao, Y.; Sheng, Z.M.; Scherler, K.; Park, J.; Gygli, S.; Rosas, L.A.; Sadtler, K.; Kalish, H.; et al. Lung epithelial and endothelial damage, loss of tissue repair, inhibition of fibrinolysis, and cellular senescence in fatal COVID-19. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabj7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Karki, R.; Williams, E.P.; Yang, D.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Vogel, P.; Jonsson, C.B.; Kanneganti, T.D. TLR2 senses the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein to produce inflammatory cytokines. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, F.; Gao, Y.; Guo, R.; Ding, L.; Fu, M.; Yi, Y.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Z.J.; Niu, M. E47 upregulates DeltaNp63alpha to promote growth of squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, T.; Meyer, K.; Geerling, L.; Isbell, T.S.; Hoft, D.F.; Brien, J.; Pinto, A.K.; Ray, R.B.; Ray, R. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes IL-6 trans-signaling by activation of angiotensin II receptor signaling in epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.G.; Siripanyaphinyo, U.; Tumkosit, U.; Noranate, N.; A, A.N.; Pan, Y.; Kameoka, M.; Kurosu, T.; Ikuta, K.; Takeda, N.; et al. Poly (I:C), an agonist of toll-like receptor-3, inhibits replication of the Chikungunya virus in BEAS-2B cells. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissari, J.; Sirén, J.; Meri, S.; Julkunen, I.; Matikainen, S. IFN-α Enhances TLR3-Mediated Antiviral Cytokine Expression in Human Endothelial and Epithelial Cells by Up-Regulating TLR3 Expression1. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4289–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, M.; Smith, B.; Szakal, A.; Nelson-Rees, W.; Todaro, G. A continuous tumor-cell line from a human lung carcinoma with properties of type II alveolar epithelial cells. Int. J. Cancer 1976, 17, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahdab, N.; Ward, C.; Hansbro, P.M.; Cummings, S.; Young, J.S.; Moheimani, F. Distinct Effects of Respiratory Viral Infection Models on miR-149-5p, IL-6 and p63 Expression in BEAS-2B and A549 Epithelial Cells. Cells 2024, 13, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110919
Shahdab N, Ward C, Hansbro PM, Cummings S, Young JS, Moheimani F. Distinct Effects of Respiratory Viral Infection Models on miR-149-5p, IL-6 and p63 Expression in BEAS-2B and A549 Epithelial Cells. Cells. 2024; 13(11):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110919
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahdab, Nafeesa, Christopher Ward, Philip M. Hansbro, Stephen Cummings, John S. Young, and Fatemeh Moheimani. 2024. "Distinct Effects of Respiratory Viral Infection Models on miR-149-5p, IL-6 and p63 Expression in BEAS-2B and A549 Epithelial Cells" Cells 13, no. 11: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110919
APA StyleShahdab, N., Ward, C., Hansbro, P. M., Cummings, S., Young, J. S., & Moheimani, F. (2024). Distinct Effects of Respiratory Viral Infection Models on miR-149-5p, IL-6 and p63 Expression in BEAS-2B and A549 Epithelial Cells. Cells, 13(11), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110919





