Brain Region Differences in α1- and α5-Subunit-Containing GABAA Receptor Proteomes Revealed with Affinity Purification and Blue Native PAGE Proteomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Brain Material
2.2. Immunoprecipitation and SDS-PAGE
2.3. Blue Native-PAGE (BN-PAGE)
2.4. HPLC-ESI MS/MS
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Immunocytochemistry
3. Results
3.1. Composition of α5-Containing GABAA Receptor from Hippocampus and Olfactory Bulb
3.2. Composition of α1-Containing GABAA Receptor from Hippocampus and Olfactory Bulb

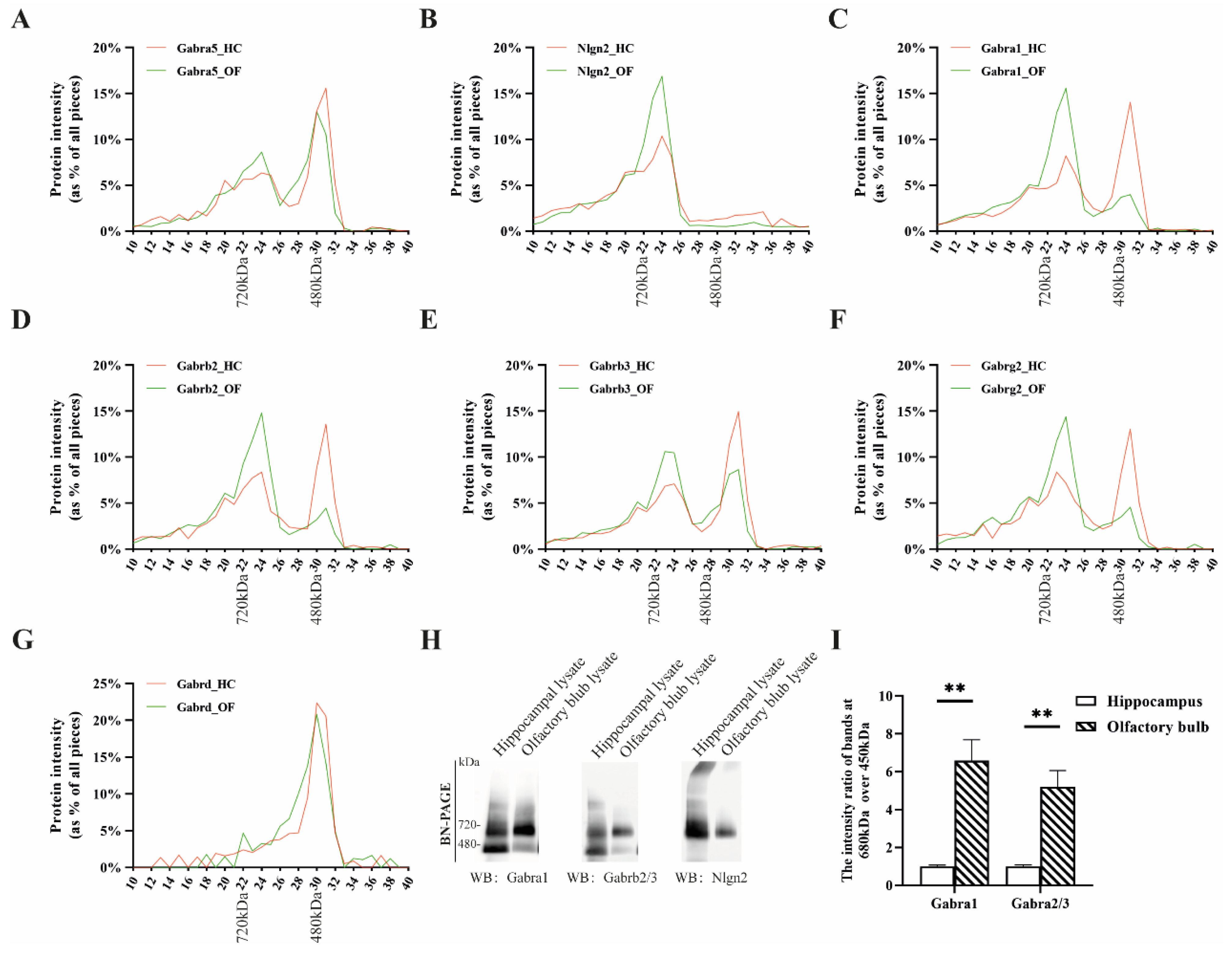
3.3. Analysis of Hippocampal and Olfactory Bulb GABAAR Subcomplexes with Blue Native Gel Electrophoresis–Mass Spectrometry
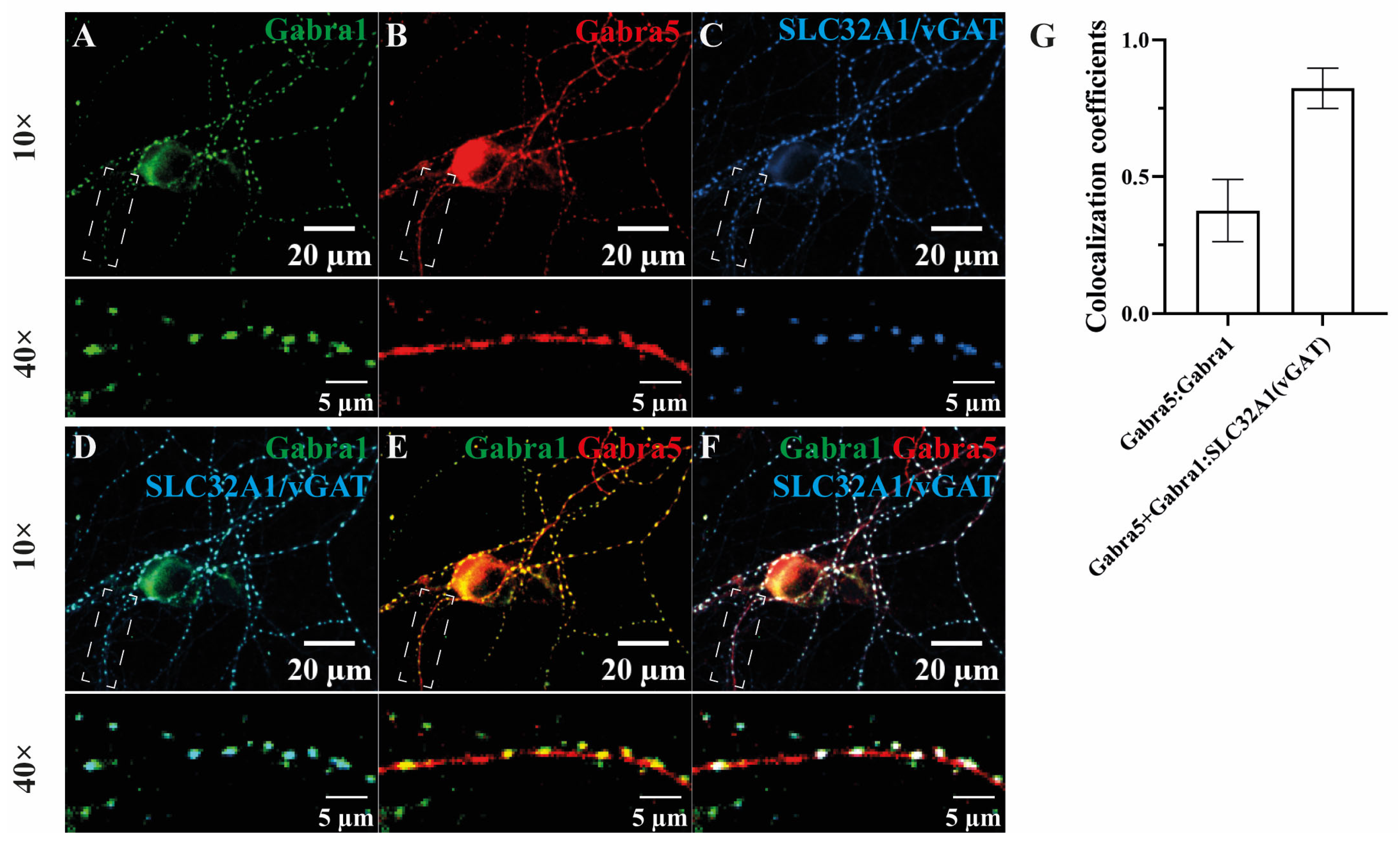
3.4. The Subcellular Localization of the α1- and α5-Subunit-Containing Receptors in Cultured Hippocampus Neurons
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sigel, E.; Steinmann, M.E. Structure, function, and modulation of GABAA receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40224–40231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritschy, J.-M.; Johnson, D.K.; Mohler, H.; Rudolph, U. Independent assembly and subcellular targeting of GABAA-receptor subtypes demonstrated in mouse hippocampal and olfactory neurons in vivo. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 249, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieghart, W.; Fuchs, K.; Tretter, V.; Ebert, V.; Jechlinger, M.; Höger, H.; Adamiker, D. Structure and subunit composition of GABAA receptors. Neurochem. Int. 1999, 34, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.W.; Sieghart, W. GABAA receptors: Subtypes provide diversity of function and pharmacology. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusser, Z.; Sieghart, W.; Somogyi, P. Segregation of different GABAAReceptors to synaptic and extrasynaptic membranes of cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leil, T.A.; Chen, Z.-W.; Chang, C.-S.S.; Olsen, R.W. GABAAReceptor-associated protein traffics GABAAReceptors to the plasma membrane in neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 11429–11438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretter, V.; Mukherjee, J.; Maric, H.-M.; Schindelin, H.; Sieghart, W.; Moss, S.J. Gephyrin, the enigmatic organizer at GABAergic synapses. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danglot, L.; Triller, A.; Bessis, A. Association of gephyrin with synaptic and extrasynaptic GABAa receptors varies during development in cultured hippocampal neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagarajan, S.K.; Ghosh, H.; Yévenes, G.E.; Nikonenko, I.; Ebeling, C.; Schwerdel, C.; Sidler, C.; Zeilhofer, H.U.; Gerrits, B.; Muller, D.; et al. Regulation of GABAergic synapse formation and plasticity by GSK3β-dependent phosphorylation of gephyrin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulopoulos, A.; Aramuni, G.; Meyer, G.; Soykan, T.; Hoon, M.; Papadopoulos, T.; Zhang, M.; Paarmann, I.; Fuchs, C.; Harvey, K.; et al. Neuroligin 2 Drives Postsynaptic Assembly at Perisomatic Inhibitory Synapses through Gephyrin and Collybistin. Neuron 2009, 63, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, D.D.; Tuffy, L.P.; Papadopoulos, T.; Brose, N. The role of neurexins and neuroligins in the formation, maturation, and function of vertebrate synapses. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2012, 22, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, E.C.; Pendolino, V.; Kontou, G.; McGee, T.P.; Sheehan, D.F.; López-Doménech, G.; Farrant, M.; Kittler, J.T. An Essential Role for the Tetraspanin LHFPL4 in the Cell-Type-Specific Targeting and Clustering of Synaptic GABA A Receptors. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martenson, J.S.; Yamasaki, T.; Chaudhury, N.H.; Albrecht, D.; Tomita, S. Assembly rules for GABAA receptor complexes in the brain. eLife 2017, 6, e30826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, T.; Hoyos-Ramirez, E.; Martenson, J.S.; Morimoto-Tomita, M.; Tomita, S. GARLH Family Proteins Stabilize GABAA Receptors at Synapses. Neuron 2017, 93, 1138–1152.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraiscos, V.B.; Elliott, E.M.; You-Ten, K.E.; Cheng, V.Y.; Belelli, D.; Newell, J.G.; Jackson, M.F.; Lambert, J.J.; Rosahl, T.W.; Wafford, K.A.; et al. Tonic inhibition in mouse hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons is mediated by α5 subunit-containing γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3662–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarnowska, E.D.; Keist, R.; Rudolph, U.; Pearce, R.A.; Pelkey, K.A.; Chittajallu, R.; Craig, M.T.; Tricoire, L.; Wester, J.C.; McBain, C.J.; et al. GABAA Receptor α5 Subunits Contribute to GABAA,slow Synaptic Inhibition in Mouse Hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 101, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, C.; Fresu, L.; Howell, O.; McKernan, R.M.; Atack, J.R. Autoradiographic localization of α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1999, 822, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinson, N.; Kuenzi, F.M.; Jarolimek, W.; Maubach, K.A.; Cothliff, R.; Sur, C.; Smith, A.; Otu, F.M.; Howell, O.; Atack, J.R.; et al. Enhanced Learning and Memory and Altered GABAergic Synaptic Transmission in Mice Lacking the α5 Subunit of the GABAAReceptor. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 5572–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, C.; Quirk, K.; Dewar, D.; Atack, J.; McKernan, R. Rat and Human Hippocampal α5 Subunit-Containing γ-Aminobutyric AcidAReceptors Have α5β3γ2 Pharmacological Characteristics. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Oh, G.H.T.; Orser, B.A. Etomidate Targets α5γ-Aminobutyric Acid Subtype A Receptors to Regulate Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Blockade. Anesthesiology 2009, 111, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellot, G.; Cherubini, E. GABAergic signaling as therapeutic target for autism spectrum disorders. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.Z.; Ernst, M.; Treven, M.; Cerne, R.; Wakulchik, M.; Li, X.; Jones, T.M.; Gleason, S.D.; Morrow, D.; Schkeryantz, J.M.; et al. Negative allosteric modulation of alpha 5-containing GABAA receptors engenders antidepressant-like effects and selectively prevents age-associated hyperactivity in tau-depositing mice. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, M.A.; Horder, J.; Myers, J.; Coghlan, S.; Stokes, P.; Erritzoe, D.; Howes, O.; Lingford-Hughes, A.; Murphy, D.; Nutt, D. The brain GABA-benzodiazepine receptor alpha-5 subtype in autism spectrum disorder: A pilot [11C]Ro15-4513 positron emission tomography study. Neuropharmacology 2013, 68, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissman, R.; Mishizen-Eberz, A.; Carter, T.; Wolfe, B.; De Blas, A.; Miralles, C.; Ikonomovic, M.; Armstrong, D. Biochemical analysis of GABAA receptor subunits α1, α5, β1, β2 in the hippocampus of patients with Alzheimer’s disease neuropathology. Neuroscience 2003, 120, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, F.H.; Has, A.T.C. The α5-Containing GABAA Receptors—A Brief Summary. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loebrich, S.; Bähring, R.; Katsuno, T.; Tsukita, S.; Kneussel, M. Activated radixin is essential for GABAA receptor α5 subunit anchoring at the actin cytoskeleton. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brünig, I.; Scotti, E.; Sidler, C.; Fritschy, J. Intact sorting, targeting, and clustering of γ-aminobutyric acid A receptor subtypes in hippocampal neurons in vitro. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 443, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crestani, F.; Keist, R.; Fritschy, J.-M.; Benke, D.; Vogt, K.; Prut, L.; Blüthmann, H.; Möhler, H.; Rudolph, U. Trace fear conditioning involves hippocampal α5 GABAA receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8980–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glykys, J.; Mody, I. Hippocampal Network Hyperactivity After Selective Reduction of Tonic Inhibition in GABAA Receptor α5 Subunit–Deficient Mice. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 95, 2796–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, S.B.; de Blas, A.L. α5 Subunit-containing GABAA receptors form clusters at GABAergic synapses in hippocampal cultures. NeuroReport 2002, 13, 2355–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenosil, G.A.; Gasser, E.M.S.; Rudolph, U.; Keist, R.; Fritschy, J.-M.; Vogt, K.E. Specific Subtypes of GABAAReceptors Mediate Phasic and Tonic Forms of Inhibition in Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, M.L.; Jacob, T.C. Synaptic localization of α5 GABA (A) receptors via gephyrin interaction regulates dendritic outgrowth and spine maturation. Dev. Neurobiol. 2015, 75, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Koopmans, F.; Paliukhovich, I.; van der Spek, S.J.F.; Dong, J.; Smit, A.B.; Li, K.W. Blue Native PAGE–Antibody Shift in Conjunction with Mass Spectrometry to Reveal Protein Subcomplexes: Detection of a Cerebellar α1/α6-Subunits Containing γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor Subtype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Spek, S.J.F.; Pandya, N.J.; Koopmans, F.; Paliukhovich, I.; van der Schors, R.C.; Otten, M.; Smit, A.B.; Li, K.W. Expression and Interaction Proteomics of GluA1- and GluA3-Subunit-Containing AMPARs Reveal Distinct Protein Composition. Cells 2022, 11, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schagger, H.; Cramer, W.A.; Vonjagow, G. Analysis of molecular masses and oligomeric states of protein complexes by blue native electrophoresis and isolation of membrane protein complexes by two-dimensional native electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 217, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Spek, S.J.F.; Koopmans, F.; Paliukhovich, I.; Ramsden, S.L.; Harvey, K.; Harvey, R.J.; Smit, A.B.; Li, K.W. Glycine Receptor Complex Analysis Using Immunoprecipitation-Blue Native Gel Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry. Proteomics 2020, 20, e1900403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Pandya, N.J.; Koopmans, F.; Castelo-Székelv, V.; van der Schors, R.C.; Smit, A.B.; Li, K.W. Interaction proteomics reveals brain region-specific AMPA receptor complexes. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 5695–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanou, E.; Koopmans, F.; Pita-Illobre, D.; Klaassen, R.V.; Özer, B.; Charalampopoulos, I.; Smit, A.B.; Li, K.W. Suspension TRAPping Filter (sTRAP) Sample Preparation for Quantitative Proteomics in the Low µg Input Range Using a Plasmid DNA Micro-Spin Column: Analysis of the Hippocampus from the 5xFAD Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Cells 2023, 12, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, F.; Brunner, A.D.; Frank, M.; Ha, A.; Bludau, I.; Voytik, E.; Kaspar-Schoenefeld, S.; Lubeck, M.; Raether, O.; Bache, N.; et al. diaPASEF: Parallel accumulation–serial fragmentation combined with data-independent acquisition. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demichev, V.; Messner, C.B.; Vernardis, S.I.; Lilley, K.S.; Ralser, M. DIA-NN: Neural networks and interference correction enable deep proteome coverage in high throughput. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, F.; Li, K.W.; Klaassen, R.V.; Smit, A.B. MS-DAP Platform for Downstream Data Analysis of Label-Free Proteomics Uncovers Optimal Workflows in Benchmark Data Sets and Increased Sensitivity in Analysis of Alzheimer’s Biomarker Data. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolte, S.; Cordelières, F.P. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 224, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirker, S.; Schwarzer, C.; Wieselthaler, A.; Sieghart, W.; Sperk, G. GABAA receptors: Immunocytochemical distribution of 13 subunits in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience 2000, 101, 815–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, S.; Li, R.-W.; Miralles, C.; Yang, B.-Y.; De Blas, A. Clustered and non-clustered GABAA receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2006, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serwanski, D.R.; Miralles, C.P.; Christie, S.B.; Mehta, A.K.; Li, X.; De Blas, A.L. Synaptic and nonsynaptic localization of GABAA receptors containing the α5 subunit in the rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 499, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherubini, E. Phasic GABA(A)-Mediated Inhibition. In Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies [Internet], 4th ed.; Noebels, J.L., Avoli, M., Rogawski, M.A., Olsen, R.W., Delgado-Escueta, A.V., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, F.; Ruano, D.; Vitorica, J. Native gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors from rat hippocampus, containing both alpha 1 and alpha 5 subunits, exhibit a single benzodiazepine binding site with alpha 5 pharmacological properties. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 290, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lüscher, B.; A Keller, C. Regulation of GABAA receptor trafficking, channel activity, and functional plasticity of inhibitory synapses. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 102, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Olsen, R.W. GABAA receptor associated proteins: A key factor regulating GABAA receptor function. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, K.H.; Arigoni, M.; Drescher, U.; Scheurer, L.; Malherbe, P.; Möhler, H.; Benson, J.A. Stoichiometry of a recombinant GABAA receptor deduced from mutation-induced rectification. NeuroReport 1993, 5, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Kang, Y.; Cassidy, R.M.; Moon, K.-M.; Lewis, R.; Wong, R.O.; Foster, L.J.; Craig, A.M. Clptm1 Limits Forward Trafficking of GABAA Receptors to Scale Inhibitory Synaptic Strength. Neuron 2018, 97, 596–610.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trobiani, L.; Meringolo, M.; Diamanti, T.; Bourne, Y.; Marchot, P.; Martella, G.; Dini, L.; Pisani, A.; De Jaco, A.; Bonsi, P. The neuroligins and the synaptic pathway in autism spectrum disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 119, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.I.; Laurent, G. Role of GABAergic inhibition in shaping odor-evoked spatiotemporal patterns in the Drosophila antennal lobe. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 9069–9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Bai, J.; Bandla, C.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kamatchinathan, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Prakash, A.; Frericks-Zipper, A.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database resources in 2022: A hub for mass spectrometry-based proteomics evidences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D543–D552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Koopmans, F.; Gonzalez-Lozano, M.A.; Smit, A.B.; Li, K.W. Brain Region Differences in α1- and α5-Subunit-Containing GABAA Receptor Proteomes Revealed with Affinity Purification and Blue Native PAGE Proteomics. Cells 2024, 13, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010014
Chen M, Koopmans F, Gonzalez-Lozano MA, Smit AB, Li KW. Brain Region Differences in α1- and α5-Subunit-Containing GABAA Receptor Proteomes Revealed with Affinity Purification and Blue Native PAGE Proteomics. Cells. 2024; 13(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Miao, Frank Koopmans, Miguel A. Gonzalez-Lozano, August B. Smit, and Ka Wan Li. 2024. "Brain Region Differences in α1- and α5-Subunit-Containing GABAA Receptor Proteomes Revealed with Affinity Purification and Blue Native PAGE Proteomics" Cells 13, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010014
APA StyleChen, M., Koopmans, F., Gonzalez-Lozano, M. A., Smit, A. B., & Li, K. W. (2024). Brain Region Differences in α1- and α5-Subunit-Containing GABAA Receptor Proteomes Revealed with Affinity Purification and Blue Native PAGE Proteomics. Cells, 13(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13010014






