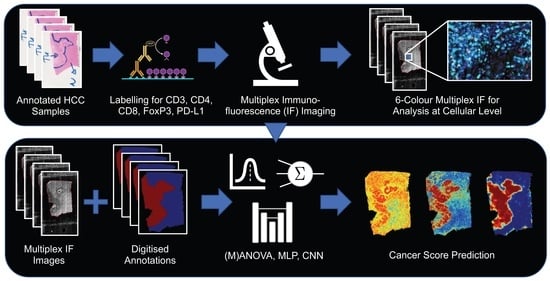
A Deep-Learning-Computed Cancer Score for the Identification of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Area Based on a Six-Colour Multiplex Immunofluorescence Panel
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- First, we tested a correlation-based selection of individual cell features (ICFs) by calculating the absolute correlation value of each feature with the pathologists’ assignment and then combining the five features with the highest correlations into a cancer score.
- (2)
- We then tested a multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA)-based selection of features, combining only the features with the highest correlations with the pathologist’s assignment and those with the lowest correlations with the previously selected features to calculate the cancer score.
- (3)
- Next, we tested an MLP, a feedforward artificial neural network trained with all the features as input and formulated the computation of the cancer score as a regression task. As the MLP is trained on individual cells, the context is only taken into account indirectly.
- (4)
- Finally, we trained a U-net, a CNN architecture specifically designed for semantic biomedical image segmentation, which also takes into account the spatial context [10].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.1.1. General
2.1.2. Protocol
2.2. Immunofluorescence Staining
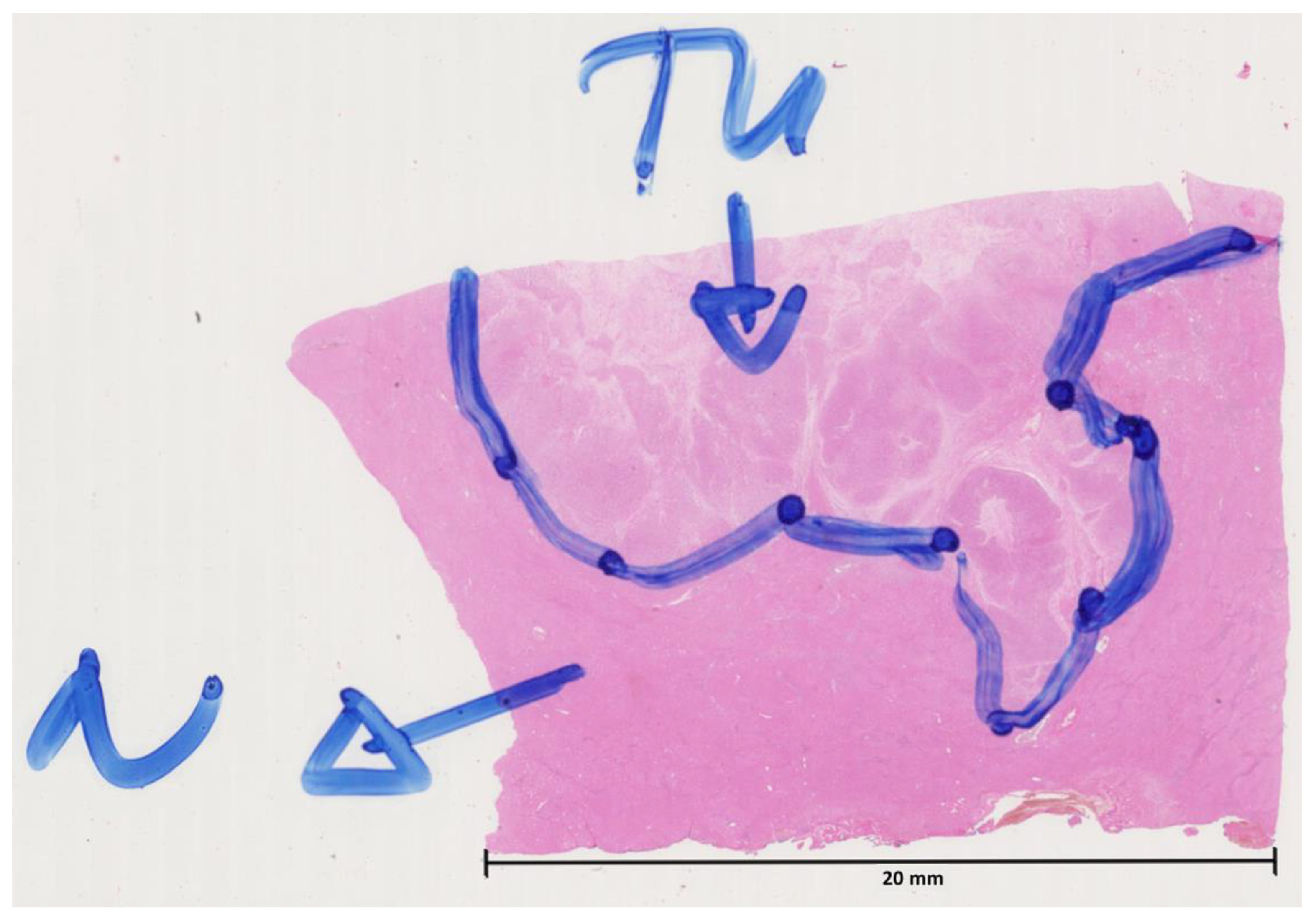
2.3. Creation of Models for the Identification of the Cancer Area
2.3.1. Model Using Correlation-Based Selection of Individual Cell Features
2.3.2. Model Using MANOVA-Based Selection of Individual Cell Features
2.3.3. Model Using a Multilayer Perceptron
2.3.4. Model Using a U-Net
2.3.5. Training Details
2.4. Creation of Models for the Identification of the Cancer Area
3. Results
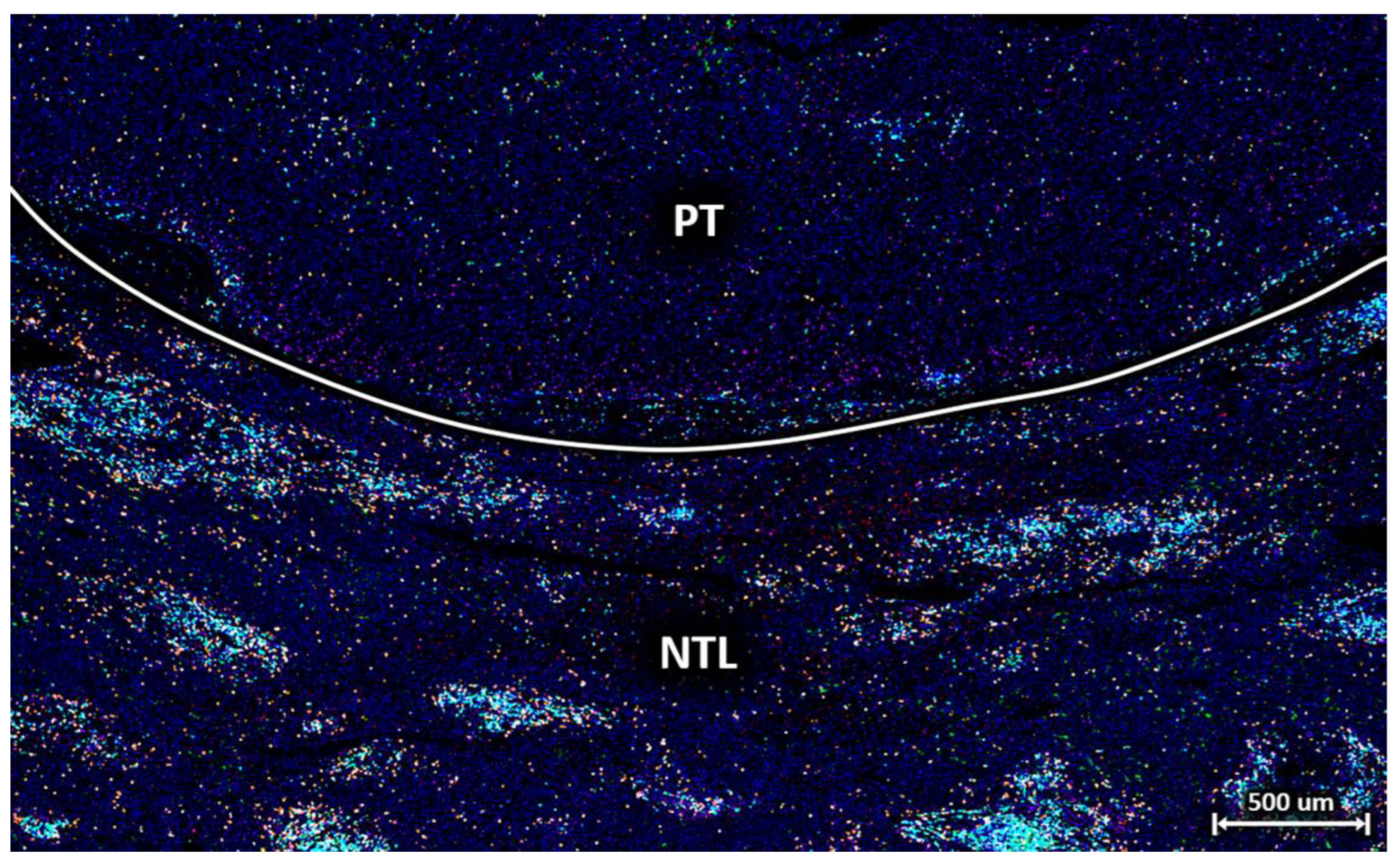
3.1. T Cell Characterisation in Primary Tumour and Non-Tumour Tissues of HCC Patients
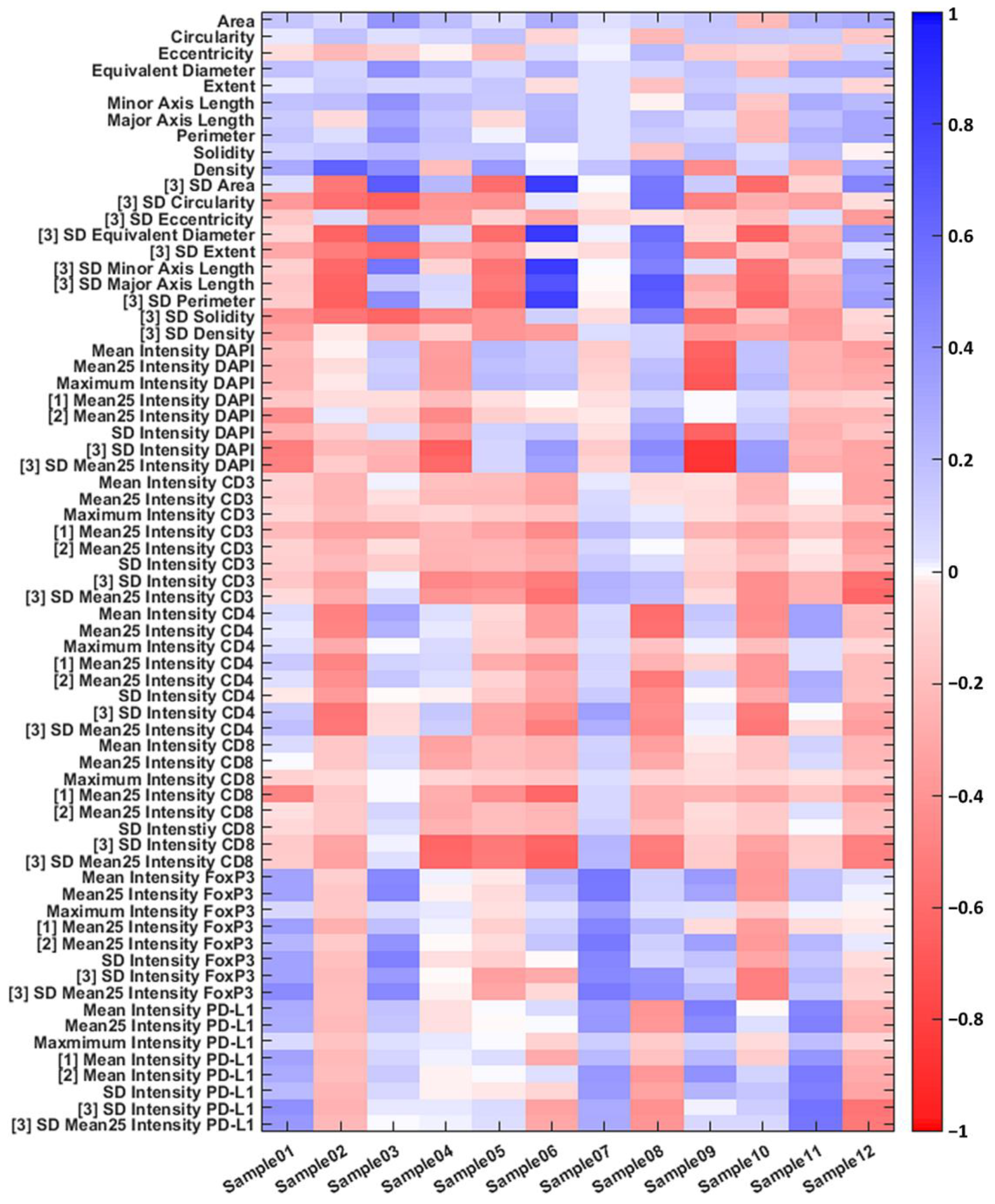
3.2. Individual Cell Features Show Strong Heterogeneity between Patients
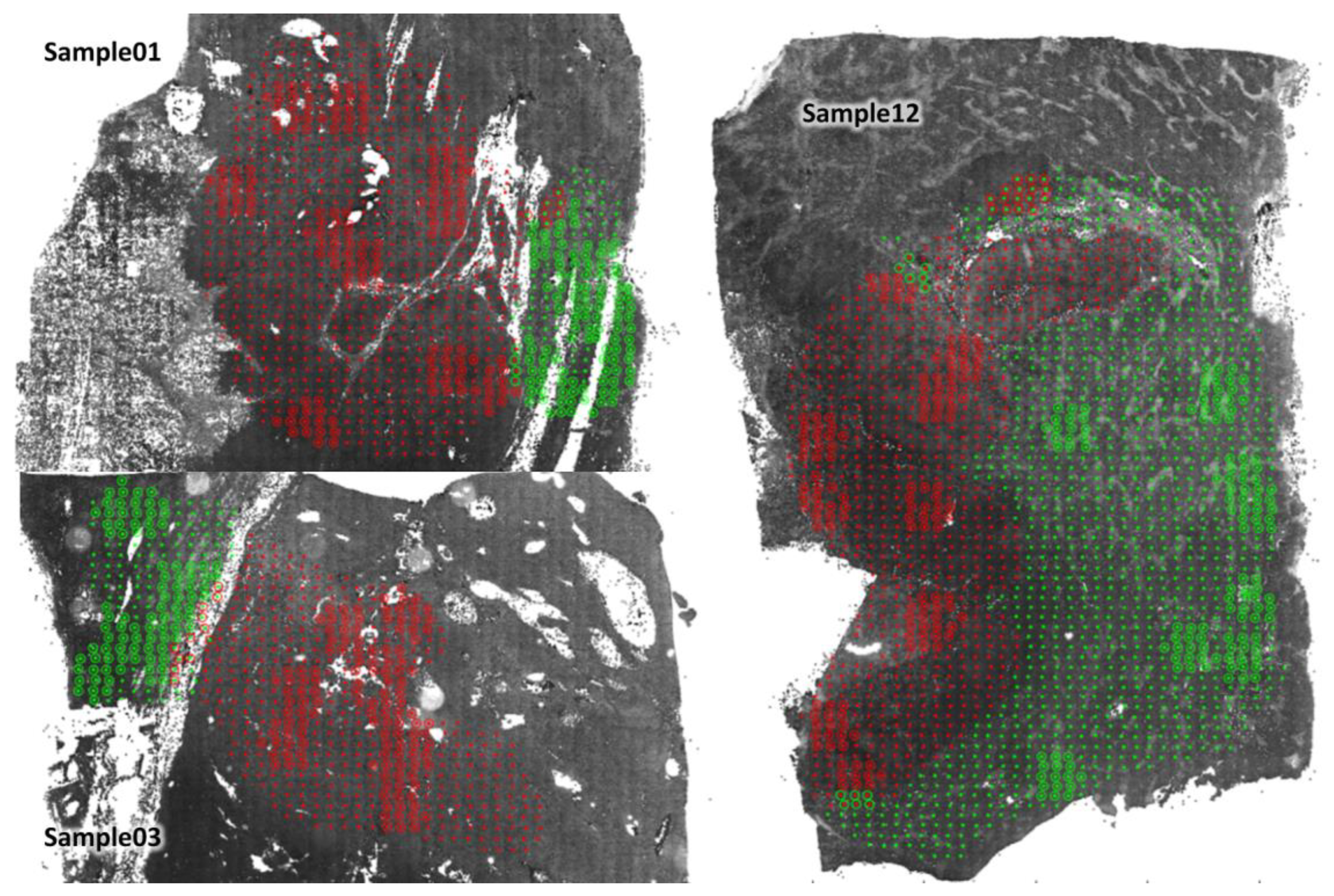
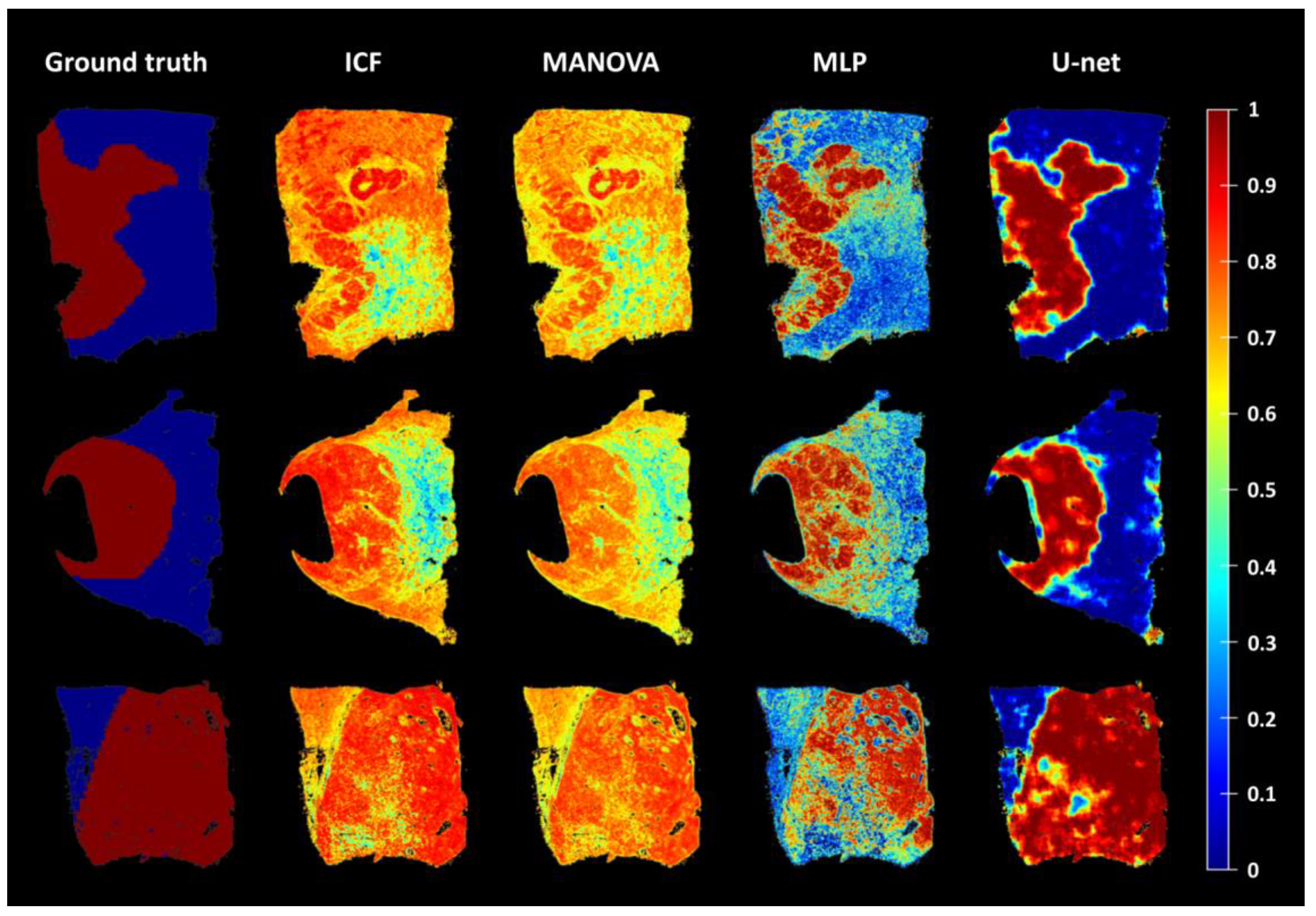
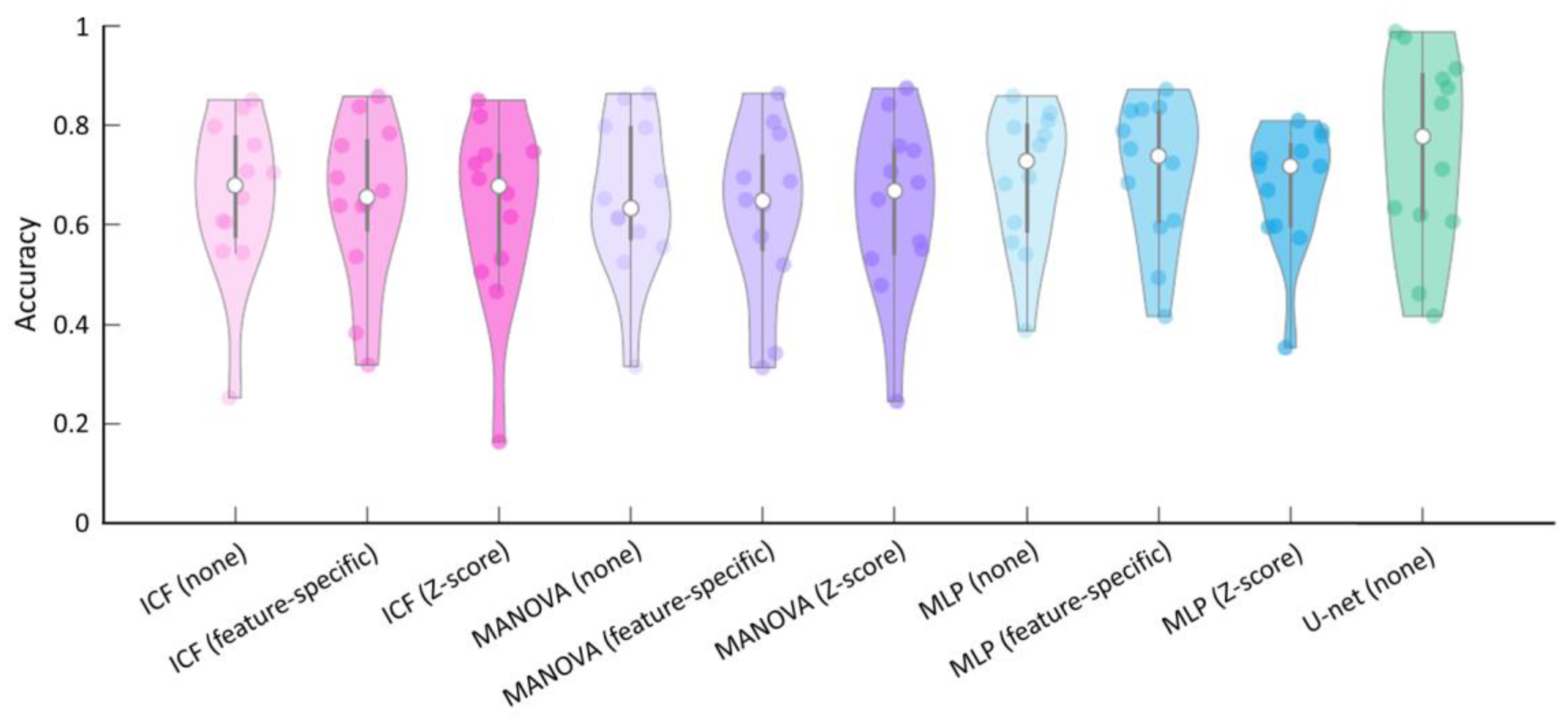
3.3. Comparison and Evaluation of the Average Accuracy of the ICF, MANOVA, MLP, and U-Net Models
3.4. Influence of Individual Cell Features on the Accuracy of the U-Net
3.5. Assessment of the Robustness of the U-Net
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.-L.; Ji, Q.-H.; An, J.-J.; Masuda, S.; Tsuneyama, K. Clinicopathological analysis of CD8-positive lymphocytes in the tumor parenchyma and stroma of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 2284–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakolwiboon, S. Heterogeneity of The CD90+ Population in Different Stages of Hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Proteom. Bioinform. 2014, 7, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruni, D.; Angell, H.K.; Galon, J. The immune contexture and Immunoscore in cancer prognosis and therapeutic efficacy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A. Fundamentals of Cytological Diagnosis and Its Biological Basis. In Pathobiology of Human Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 3311–3344. ISBN 978-0-12-386457-4. [Google Scholar]
- Tarnowski, B.I.; Spinale, F.G.; Nicholson, J.H. DAPI as a Useful Stain for Nuclear Quantitation. Biotech. Histochem. 1991, 66, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Ke, Z.; Liu, K.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Yin, H.; Chen, Z. Identification of DAPI-stained normal, inflammatory, and carcinoma hepatic cells based on hyperspectral microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lin, S.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z. Hyperspectral microscopy combined with DAPI staining for the identification of hepatic carcinoma cells. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinge, U.; Dievernich, A.; Stegmaier, J. Quantitative Characterization of Macrophage, Lymphocyte, and Neutrophil Subtypes Within the Foreign Body Granuloma of Human Mesh Explants by 5-Marker Multiplex Fluorescence Microscopy. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 777439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikut, R.; Bartschat, A.; Doneit, W.; Ordiano, J.Á.G.; Schott, B.; Stegmaier, J.; Waczowicz, S.; Reischl, M. The MATLAB Toolbox SciXMiner: User’s Manual and Programmer’s Guide. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.03298. [Google Scholar]
- Stringer, C.; Wang, T.; Michaelos, M.; Pachitariu, M. Cellpose: A generalist algorithm for cellular segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. ISBN 978-3-319-24573-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; He, Y.; Yao, C.; Wang, S.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Classification and Segmentation of Hyperspectral Data of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Samples Using 1-D Convolutional Neural Network. Cytometry 2020, 97, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Fu, S.; Li, Z.; Huang, F.; Yin, H.; Chen, Z. Classification of hyperspectral images for detection of hepatic carcinoma cells based on spectral–spatial features of nucleus. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2020, 13, 2050002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wei, C.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Lin, L.; Ni, M.; Chen, J.; Zhuo, S. Automated classification of hepatocellular carcinoma differentiation using multiphoton microscopy and deep learning. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Klein, C.; Caruso, S.; Maille, P.; Laleh, N.G.; Sommacale, D.; Laurent, A.; Amaddeo, G.; Gentien, D.; Rapinat, A.; et al. Artificial intelligence predicts immune and inflammatory gene signatures directly from hepatocellular carcinoma histology. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foersch, S.; Glasner, C.; Woerl, A.-C.; Eckstein, M.; Wagner, D.-C.; Schulz, S.; Kellers, F.; Fernandez, A.; Tserea, K.; Kloth, M.; et al. Multistain deep learning for prediction of prognosis and therapy response in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kather, J.N.; Heij, L.R.; Grabsch, H.I.; Loeffler, C.; Echle, A.; Muti, H.S.; Krause, J.; Niehues, J.M.; Sommer, K.A.J.; Bankhead, P.; et al. Pan-cancer image-based detection of clinically actionable genetic alterations. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kather, J.N.; Pearson, A.T.; Halama, N.; Jäger, D.; Krause, J.; Loosen, S.H.; Marx, A.; Boor, P.; Tacke, F.; Neumann, U.P.; et al. Deep learning can predict microsatellite instability directly from histology in gastrointestinal cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, M.; Cai, S.; Coskun, A.F. Multiplex bioimaging of single-cell spatial profiles for precision cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.M.; Asselin-Labat, M.-L.; Nguyen, Q.; Berthelet, J.; Tan, X.; Wimmer, V.C.; Merino, D.; Rogers, K.L.; Naik, S.H. Spatial omics and multiplexed imaging to explore cancer biology. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 997–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, S.; Baars, M.J.D.; Vercoulen, Y. Multiplex Tissue Imaging: Spatial Revelations in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2022, 14, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, A.; Quan, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Cao, P.; et al. A single-cell atlas of the multicellular ecosystem of primary and metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zheng, L.; Yoo, J.-K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Kang, B.; Hu, R.; Huang, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Landscape of Infiltrating T Cells in Liver Cancer Revealed by Single-Cell Sequencing. Cell 2017, 169, 1342–1356.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Seow, J.J.W.; Dutertre, C.-A.; Pai, R.; Blériot, C.; Mishra, A.; Wong, R.M.M.; Singh, G.S.N.; Sudhagar, S.; Khalilnezhad, S.; et al. Onco-fetal Reprogramming of Endothelial Cells Drives Immunosuppressive Macrophages in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell 2020, 183, 377–394.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Yuan, F.; Qi, F.; Sun, J.; Rao, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, P.; Fang, T.; Yang, B.; Xia, J. Expression and clinical significance of LAG-3, FGL1, PD-L1 and CD8+T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma using multiplex quantitative analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartrand, G.; Cheng, P.M.; Vorontsov, E.; Drozdzal, M.; Turcotte, S.; Pal, C.J.; Kadoury, S.; Tang, A. Deep Learning: A Primer for Radiologists. RadioGraphics 2017, 37, 2113–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-J.; Wang, C.-K.; Fang, Y.-H.D.; Wang, J.-Y.; Su, F.-C.; Tsai, H.-M.; Lin, Y.-J.; Tsai, H.-W.; Yeh, L.-R. Clinical application of mask region-based convolutional neural network for the automatic detection and segmentation of abnormal liver density based on hepatocellular carcinoma computed tomography datasets. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Category | |
|---|---|---|
| Age at surgery (years) | Median: 69.0 (range 53.5–82.6) | |
| Gender | Male | 8 (66.7%) |
| Female | 4 (33.3%) | |
| Tumour status (UICC7) * | pT1 | 3 (25.0%) |
| pT2 | 4 (33.3%) | |
| pT3a | 3 (25.0%) | |
| pT3b | 1 (8.3%) | |
| pT4 | 0 | |
| Not classified | 1 (8.3%) | |
| Regional lymph nodes (UICC7) * | pNX | 12 (100.0) |
| Distant metastasis (UICC7) * | pM1 | 1 (8.3%) |
| Recurrence | No | 8 (66.7%) |
| Yes | 4 (33.3%) | |
| Vital status | Dead | 9 (75.0%) |
| Alive | 3 (25.0%) |
| Antibody | Clone | Dilution | Incubation Time | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD3 | F7.2.38 | 1:1000 | 30 min | Dako |
| CD4 | 4B12 | 1:500 | 30 min | Dako |
| PD-L1 | 22C3 | 1:200 | 30 min | Dako |
| CD8 | CD8/144B | 1:500 | 30 min | Dako |
| FoxP3 | PCH101 | 1:250 | 30 min | eBioscience |
| Lymphocyte Panel | PT | NTL | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD3 | CD4 | CD8 | FoxP3 | PD-L1 | Mean (SD) (%) | Mean (SD) (%) | |
| All “positive” cells for a given marker irrespective of the other markers (n. d. = not defined; pos. = positive). | |||||||
| pos. | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | 3.85 (4.23) | 8.08 (6.48) | <0.001 * |
| n. d. | pos. | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | 2.83 (3.77) | 6.14 (7.57) | 0.023 * |
| n. d. | n. d. | pos. | n. d. | n. d. | 0.90 (1.31) | 3.21 (3.01) | <0.001 * |
| n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | pos. | n. d. | 5.23 (9.05) | 3.05 (5.22) | 0.006 * |
| n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | pos. | 4.00 (6.89) | 3.81 (6.30) | 0.693 |
| All possible marker combinations (pos. = positive; neg. = negative) | |||||||
| neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. | 86.26 (14.16) | 82.19 (15.00) | 0.022 * |
| pos. | neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. | 2.46 (3.70) | 4.30 (3.63) | <0.001 * |
| neg. | pos. | neg. | neg. | neg. | 1.41 (1.98) | 2.83 (3.58) | 0.026 * |
| neg. | neg. | pos. | neg. | neg. | 0.31 (0.44) | 1.54 (1.58) | <0.001 * |
| neg. | neg. | neg. | pos. | neg. | 4.14 (8.37) | 1.81 (3.28) | 0.002 * |
| neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. | pos. | 2.78 (5.36) | 2.07 (3.54) | 0.598 |
| pos. | pos. | neg. | neg. | neg. | 0.61 (0.99) | 1.66 (2.24) | 0.006 * |
| pos. | neg. | pos. | neg. | neg. | 0.22 (0.30) | 0.82 (0.99) | <0.001 * |
| pos. | neg. | neg. | pos. | neg. | 0.14 (0.19) | 0.15 (0.22) | 0.880 |
| pos. | neg. | neg. | neg. | pos. | 0.13 (0.33) | 0.25 (0.44) | 0.174 |
| neg. | pos. | pos. | neg. | neg. | 0.15 (0.42) | 0.20 (0.30) | 0.077 |
| neg. | pos. | neg. | pos. | neg. | 0.12 (0.31) | 0.20 (0.38) | 0.454 |
| neg. | pos. | neg. | neg. | pos. | 0.20 (0.56) | 0.37 (0.77) | 0.448 |
| neg. | neg. | pos. | pos. | neg. | 0.01 (0.05) | 0.04 (0.08) | 0.018 * |
| neg. | neg. | pos. | neg. | pos. | 0.04 (0.10) | 0.08 (0.17) | 0.245 |
| neg. | neg. | neg. | pos. | pos. | 0.62 (1.13) | 0.45 (1.16) | 0.026 * |
| pos. | pos. | pos. | neg. | neg. | 0.06 (0.12) | 0.28 (0.44) | 0.012 * |
| pos. | pos. | neg. | pos. | neg. | 0.07 (0.13) | 0.12 (0.21) | 0.071 |
| pos. | pos. | neg. | neg. | pos. | 0.07 (0.17) | 0.22 (0.44) | 0.271 |
| pos. | neg. | pos. | pos. | neg. | 0.02 (0.10) | 0.02 (0.05) | 0.006 * |
| pos. | neg. | pos. | neg. | pos. | 0.02 (0.06) | 0.06 (0.11) | 0.013 * |
| pos. | neg. | neg. | pos. | pos. | 0.02 (0.08) | 0.06 (0.21) | 0.109 |
| neg. | pos. | pos. | pos. | neg. | 0.01 (0.08) | 0.02 (0.04) | 0.369 |
| neg. | pos. | pos. | neg. | pos. | 0.03 (0.12) | 0.04 (0.10) | 0.408 |
| neg. | pos. | neg. | pos. | pos. | 0.04 (0.10) | 0.07 (0.19) | 0.515 |
| neg. | neg. | pos. | pos. | pos. | 0.00 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.06) | 0.250 |
| pos. | pos. | pos. | pos. | neg. | 0.00 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.05) | <0.001 * |
| pos. | pos. | pos. | neg. | pos. | 0.01 (0.04) | 0.05 (0.12) | 0.011 * |
| pos. | pos. | neg. | pos. | pos. | 0.03 (0.10) | 0.05 (0.14) | 0.032 * |
| pos. | neg. | pos. | pos. | pos. | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.01 (0.03) | 0.017 * |
| neg. | pos. | pos. | pos. | pos. | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.01 (0.03) | 0.030 * |
| pos. | pos. | pos. | pos. | pos. | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.01 (0.03) | 0.016 * |
| Method | Normalisation | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF | None | 0.65 (0.16) | 0.82 (0.10) | 0.49 (0.17) | 0.65 (0.23) |
| Feature-specific | 0.65 (0.16) | 0.78 (0.17) | 0.51 (0.16) | 0.64 (0.24) | |
| Z-score | 0.63 (0.18) | 0.90 (0.10) | 0.27 (0.16) | 0.61 (0.22) | |
| MANOVA | None | 0.65 (0.15) | 0.81 (0.07) | 0.52 (0.19) | 0.65 (0.24) |
| Feature-specific | 0.63 (0.16) | 0.75 (0.15) | 0.51 (0.18) | 0.63 (0.25) | |
| Z-score | 0.64 (0.17) | 0.91 (0.07) | 0.32 (0.14) | 0.61 (0.22) | |
| MLP | None | 0.69 (0.14) | 0.66 (0.24) | 0.67 (0.12) | 0.66 (0.24) |
| Feature-specific | 0.70 (0.14) | 0.66 (0.25) | 0.67 (0.11) | 0.66 (0.24) | |
| Z-score | 0.67 (0.12) | 0.77 (0.12) | 0.60 (0.15) | 0.69 (0.23) | |
| U-net | None | 0.75 (0.19) | 0.62 (0.31) | 0.87 (0.14) | 0.75 (0.23) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dievernich, A.; Stegmaier, J.; Achenbach, P.; Warkentin, S.; Braunschweig, T.; Neumann, U.P.; Klinge, U. A Deep-Learning-Computed Cancer Score for the Identification of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Area Based on a Six-Colour Multiplex Immunofluorescence Panel. Cells 2023, 12, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071074
Dievernich A, Stegmaier J, Achenbach P, Warkentin S, Braunschweig T, Neumann UP, Klinge U. A Deep-Learning-Computed Cancer Score for the Identification of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Area Based on a Six-Colour Multiplex Immunofluorescence Panel. Cells. 2023; 12(7):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071074
Chicago/Turabian StyleDievernich, Axel, Johannes Stegmaier, Pascal Achenbach, Svetlana Warkentin, Till Braunschweig, Ulf Peter Neumann, and Uwe Klinge. 2023. "A Deep-Learning-Computed Cancer Score for the Identification of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Area Based on a Six-Colour Multiplex Immunofluorescence Panel" Cells 12, no. 7: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071074
APA StyleDievernich, A., Stegmaier, J., Achenbach, P., Warkentin, S., Braunschweig, T., Neumann, U. P., & Klinge, U. (2023). A Deep-Learning-Computed Cancer Score for the Identification of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Area Based on a Six-Colour Multiplex Immunofluorescence Panel. Cells, 12(7), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071074