Targeted Demethylation of the TGFβ1 mRNA Promotes Myoblast Proliferation via Activating the SMAD2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The TGFβ1 Expression Level in Myoblast Proliferation and Differentiation Phase
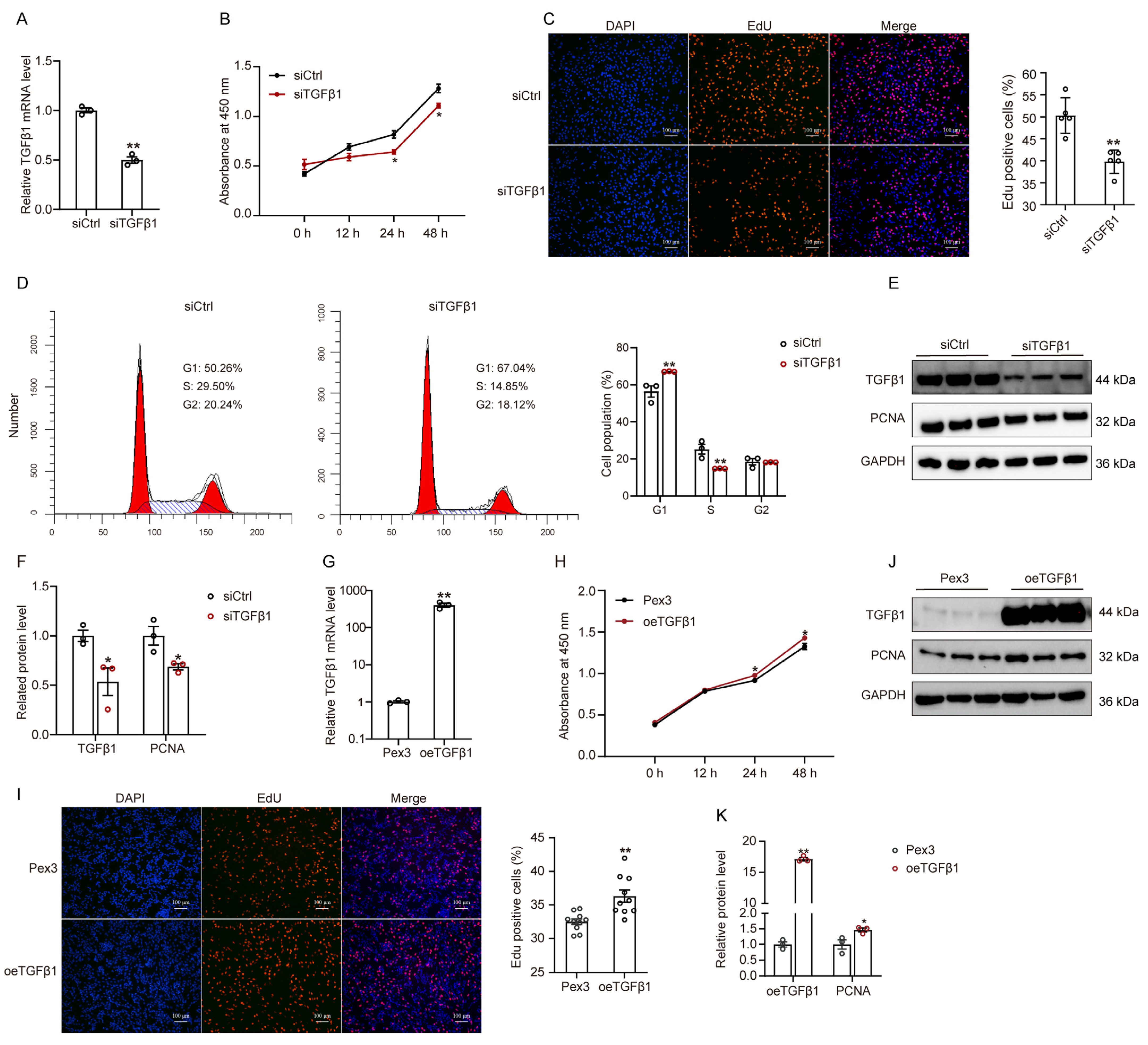
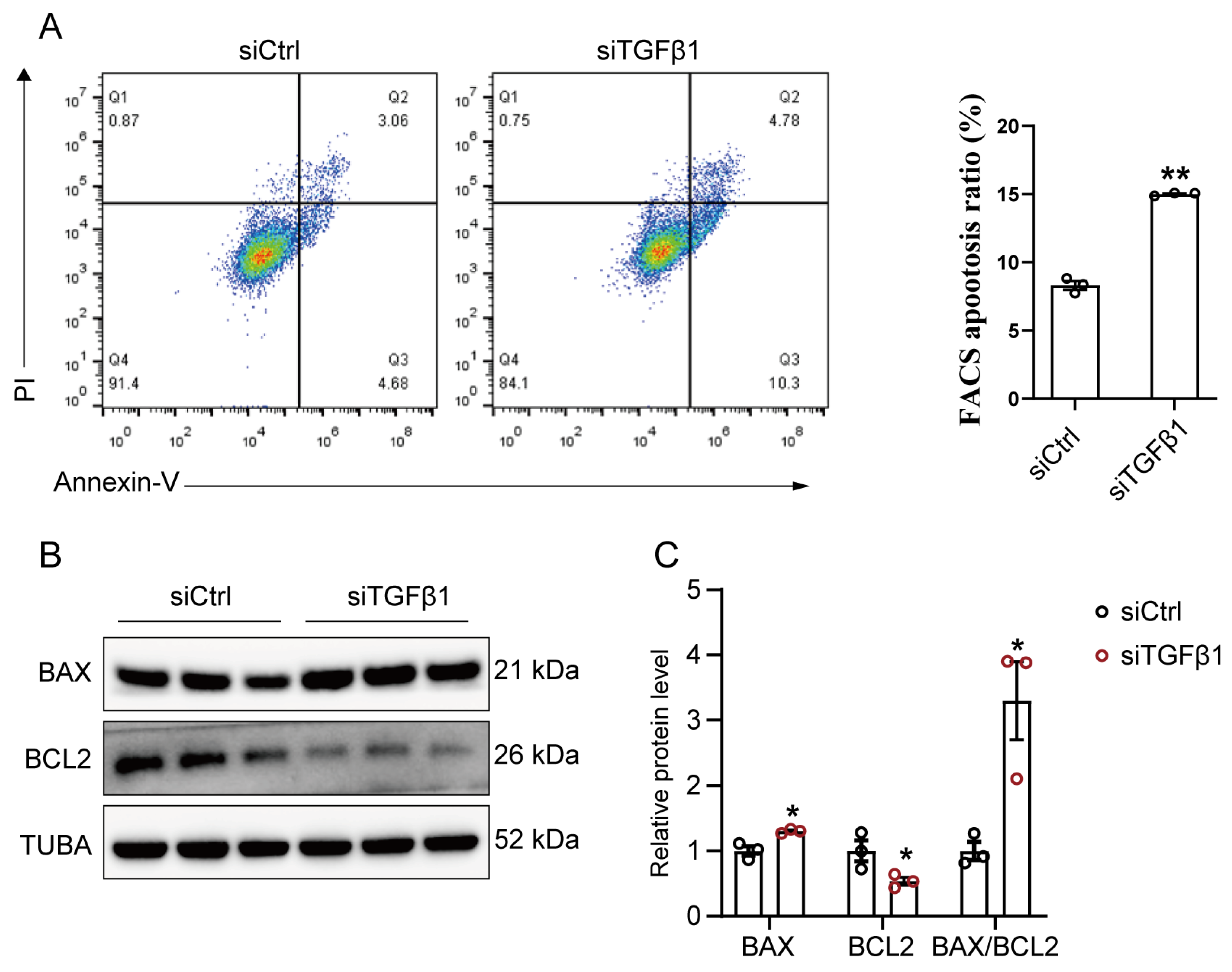
2.2. TGFβ1 Expression Influences the Proliferation and Apoptosis of GPMs
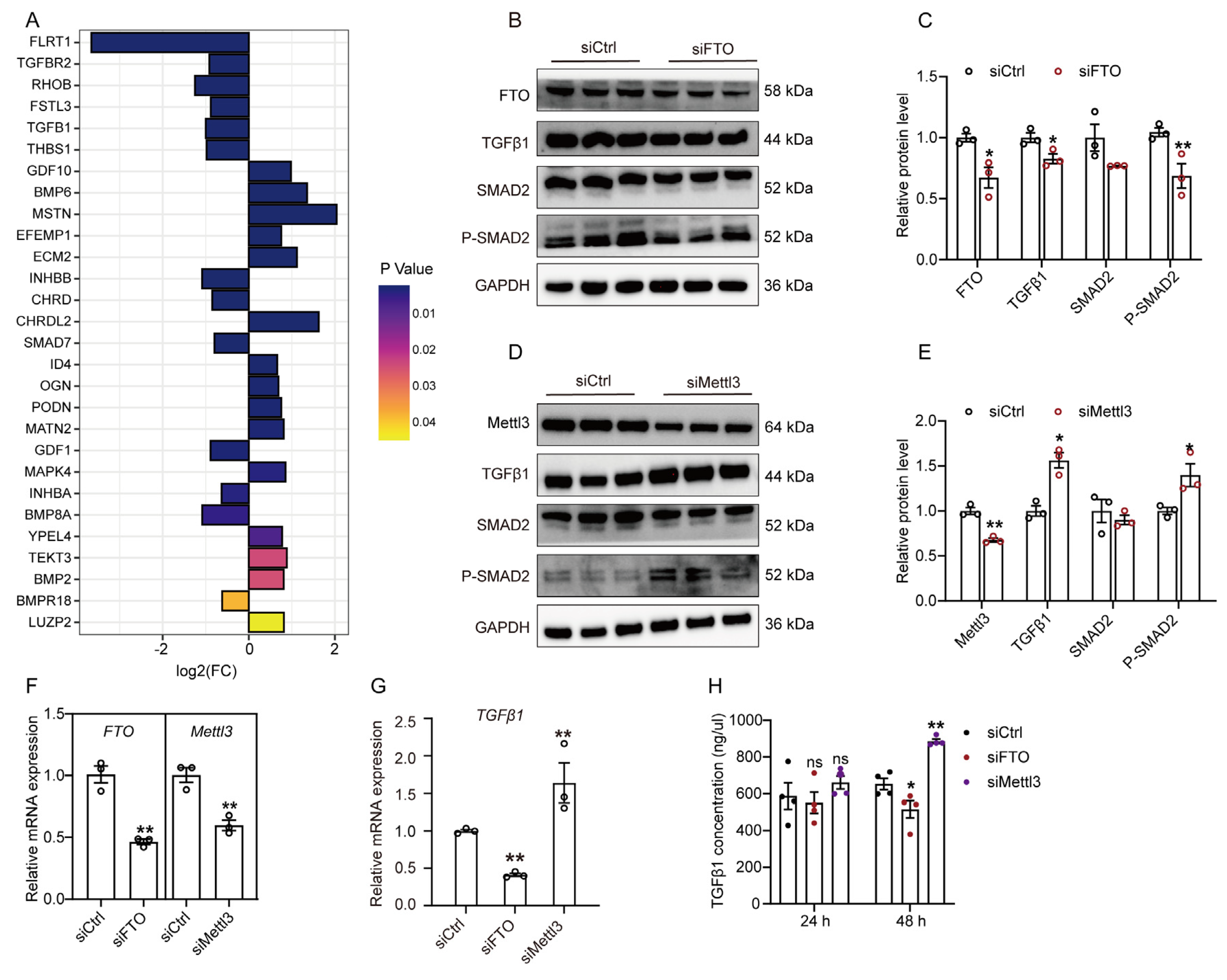
2.3. m6A Regulates the TGFβ1-Mediated SMAD2 Signaling Pathway
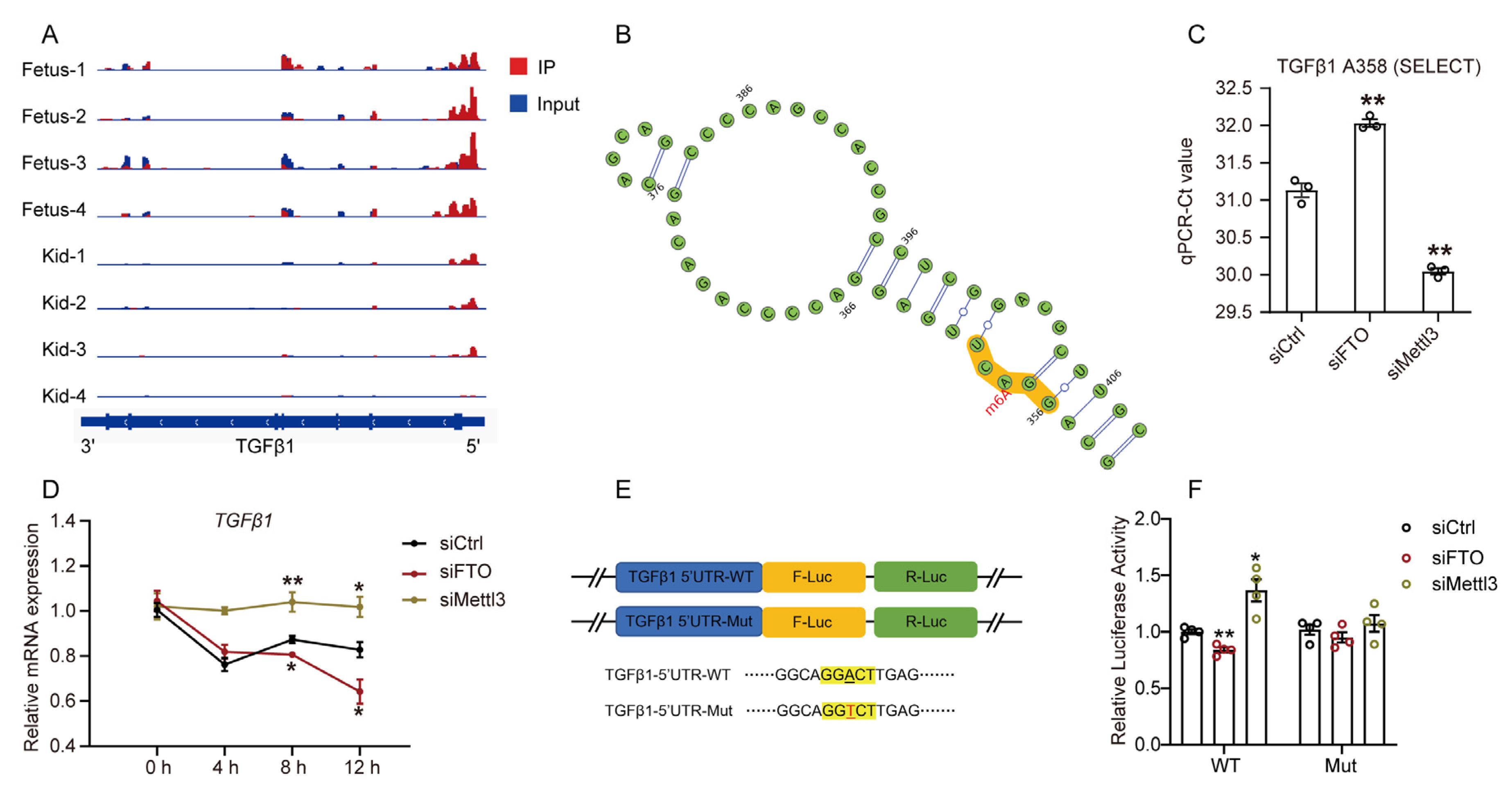
2.4. m6A Regulates TGFβ1 mRNA Stability in GPMs
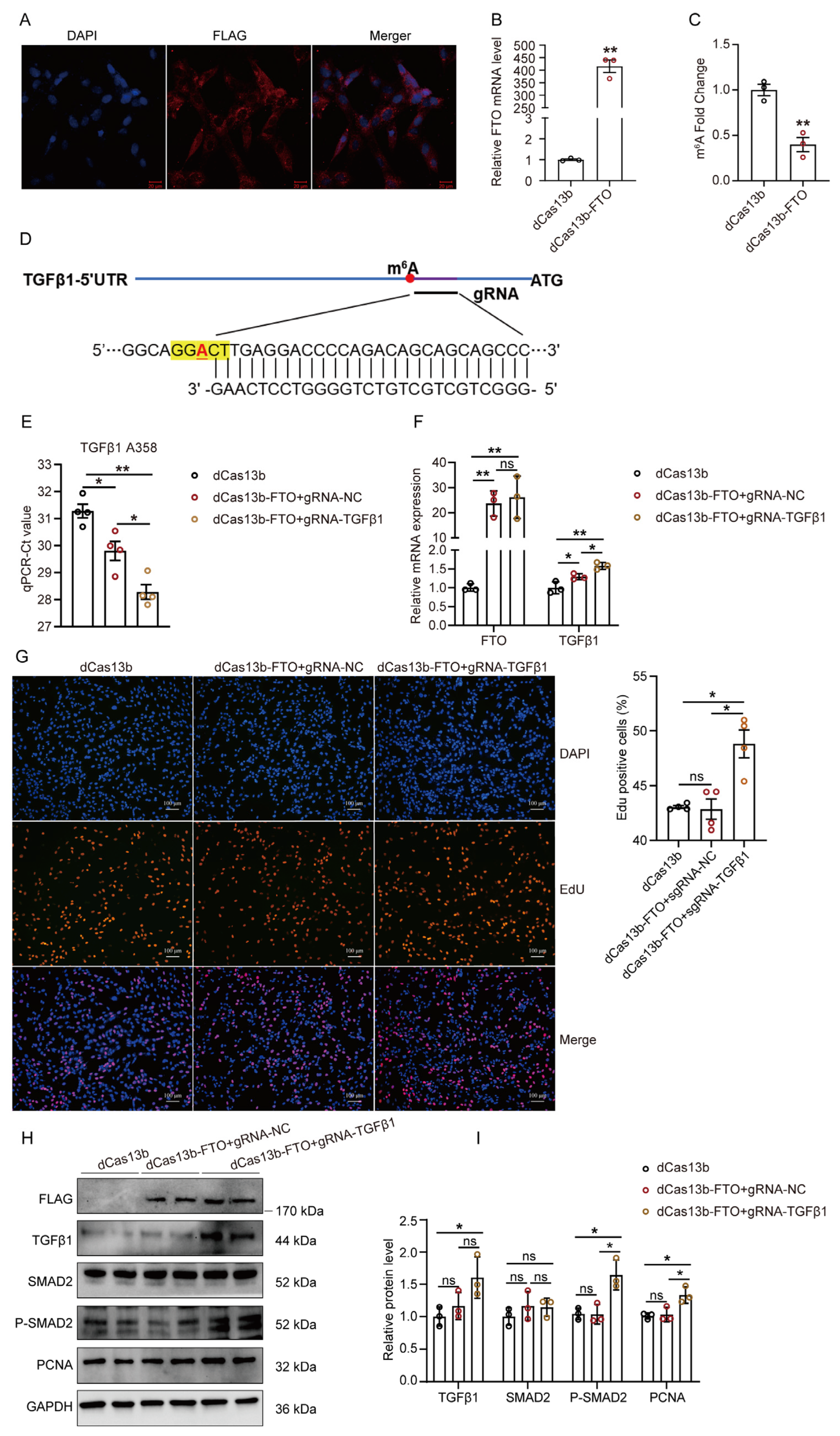
2.5. Targeting Demethylation of TGFβ1 by dCas13b-FTO Regulates the Proliferation of GPMs
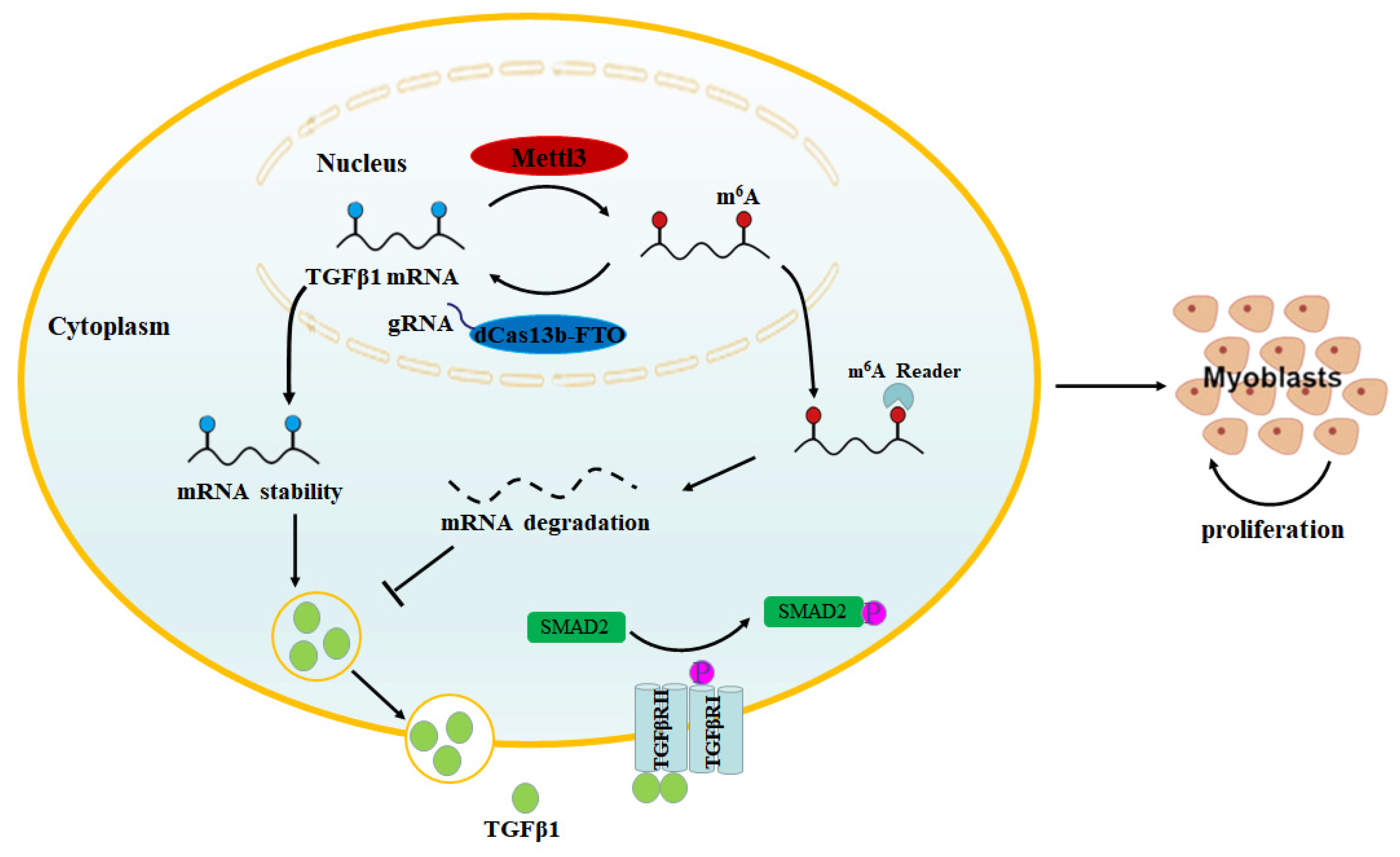
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Cell Culture
5.2. Plasmid Construction, Small Interfering RNA (siRNA), and Cell Transfection
5.3. Immunofluorescence Assay
5.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
5.5. mRNA Stability Analysis
5.6. SELECT qPCR
5.7. RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) Combined with Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RIP-qPCR)
5.8. Cell Proliferation Assay
5.9. Flow Cytometry
5.10. Quantification of m6A Levels
5.11. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
5.12. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assays
5.13. ELISA Assay
5.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- David, C.J.; Massague, J. Contextual determinants of TGFbeta action in development, immunity and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Yang, X.; Zanvit, P.; Cui, K.R.; Ku, W.L.; Jin, W.W.; Zhang, D.F.; Goldberg, N.; Cain, A.; et al. TGF-beta induces ST2 and programs ILC2 development. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; McFarland, D.C.; Velleman, S.G. Effect of Smad3-mediated transforming growth factor-beta 1 signaling on satellite cell proliferation and differentiation in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley, B.; Thomas, M.; Bishop, A.; Sharma, M.; Gilmour, S.; Kambadur, R. Myostatin inhibits myoblast differentiation by down-regulating MyoD expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49831–49840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zentella, A.; Massague, J. Transforming Growth-Factor-Beta Induces Myoblast Differentiation in the Presence of Mitogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5176–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, N.D.; Soroka, A.; Klose, A.; Liu, W.; Chakkalakal, J.V. Smad4 restricts differentiation to promote expansion of satellite cell derived progenitors during skeletal muscle regeneration. eLife 2016, 5, e19484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabort, E.J.; van der Merwe, M.; Loos, B.; Moore, F.P.; Niesler, C.U. TGF-beta’s delay skeletal muscle progenitor cell differentiation in an isoform-independent manner. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, K.; Kasprzycka, P.; Ciemerych, M.A.; Zimowska, M. The role of TGF-beta 1 during skeletal muscle regeneration. Cell Biol. Int. 2017, 41, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Velleman, S.G. Effect of transforming growth factor-beta 1 on embryonic and posthatch muscle growth and development in normal and low score normal chicken. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weist, M.R.; Wellington, M.S.; Bermudez, J.E.; Kostrominova, T.Y.; Mendias, C.L.; Arruda, E.M.; Larkin, L.M. TGF-1 enhances contractility in engineered skeletal muscle. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2013, 7, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, P.C.; He, C. m(6)A RNA methylation: From mechanisms to therapeutic potential. Embo. J. 2021, 40, e105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Shi, Y.F.; Shen, H.F.; Xie, W.Z. m(6)A-binding proteins: The emerging crucial performers in epigenetics. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, W.; Adhikari, S.; Dahal, U.; Chen, Y.S.; Hao, Y.J.; Sun, B.F.; Sun, H.Y.; Li, A.; Ping, X.L.; Lai, W.Y.; et al. Nuclear m(6)A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates mRNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.S.; Roundtree, I.A.; Lu, Z.K.; Han, D.L.; Ma, H.H.; Weng, X.C.; Chen, K.; Shi, H.L.; He, C. N-6-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency. Cell 2015, 161, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.B.; Yu, X.B.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.L.; Gao, B.Y.; Huang, B.X.; Dou, X.Y.; Liu, J.; Zou, Z.Y.; Cui, X.L.; et al. FTO mediates LINE1 m(6)A demethylation and chromatin regulation in mESCs and mouse development. Science 2022, 376, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.J.; Ringeling, F.R.; Vissers, C.; Jacob, F.; Pokrass, M.; Jimenez-Cyrus, D.; Su, Y.J.; Kim, N.S.; Zhu, Y.H.; Zheng, L.L.; et al. Temporal Control of Mammalian Cortical Neurogenesis by m(6)A Methylation. Cell 2017, 171, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.X.; Wu, R.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.L.; Bi, Z.; Yao, Y.X.; Liu, Q.; Shi, H.L.; Wang, F.Q.; Wang, Y.Z. M(6)A mRNA methylation controls autophagy and adipogenesis by targeting Atg5 and Atg7. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosino, J.M.; Hinger, S.A.; Golubeva, V.A.; Barajas, J.M.; Dorn, L.E.; Iyer, C.C.; Sun, H.L.; Arnold, W.D.; He, C.; Accornero, F. The m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 regulates muscle maintenance and growth in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Pei, Y.L.; Zhou, R.; Tang, Z.L.; Yang, Y.L. Regulation of RNA N-6-methyladenosine modification and its emerging roles in skeletal muscle development. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.J.; Liu, J.M.; Zhang, J.; Mu, T.; Feng, X.F.; Ma, R.S.; Gu, Y.L. Regulatory role of RNA N-6-methyladenosine modifications during skeletal muscle development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 929183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, M.; Derynck, R.; Miyazono, K. TGF-beta and the TGF-beta Family: Context-Dependent Roles in Cell and Tissue Physiology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a021873. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, R.; Rahaman, B.; Hurley, C.K.; Posch, P.E. Allelic diversity in the TGFB1 regulatory region: Characterization of novel functional single nucleotide polymorphisms. Hum. Genet. 2006, 119, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.X.; Chen, F.; Peng, Y.X.; Lv, Z.Y.; Lin, X.Y.; Chen, Z.J.; Wang, H.S. N6-Methyladenosine Regulates the Expression and Secretion of TGF beta 1 to Affect the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Cancer Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.D.; Gao, M.W.; Xu, S.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Wu, K.X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.J.; Wang, J.W.; Liu, W.W.; et al. YTHDF2/3 are Required for Somatic Reprogramming through Different RNA Deadenylation Pathways. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, K.P.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, C.F.; Liang, Y.X.; Gao, X.X.; Fan, Y.X.; Wang, F. FTO regulates myoblast proliferation by controlling CCND1 expression in an m(6)A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 401, 112524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencetti, F.; Bernacchioni, C.; Tonelli, F.; Roberts, E.; Donati, C.; Bruni, P. TGF beta 1 evokes myoblast apoptotic response via a novel signaling pathway involving S1P(4) transactivation upstream of Rho-kinase-2 activation. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 4532–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.P.; Fan, Y.X.; Liang, Y.X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, G.M.; Deng, M.T.; Wang, Z.B.; Lu, J.W.; Shi, J.F.; Wang, F.; et al. FTO-mediated demethylation of GADD45B promotes myogenesis through the activation of p38 MAPK pathway. Mol. Ther.-Nucl. Acids 2021, 26, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, Y.; Umemoto, T.; Murakami, M.; Matsui, T.; Funaba, M. Role of Endogenous TGF-beta Family in Myogenic Differentiation of C2C12 Cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2011, 112, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2014, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, J.; Meng, M.; Zheng, Y.; et al. N(6) -Methyladenosine Reader Protein YT521-B Homology Domain-Containing 2 Suppresses Liver Steatosis by Regulation of mRNA Stability of Lipogenic Genes. Hepatology 2021, 73, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.K.; Qiao, H.Y.; Fu, M.H.; Li, G.; Li, W.B.; Chen, Z.; Wei, J.; Liang, B.S. MiR-206 Attenuates Denervation- Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy in Rats Through Regulation of Satellite Cell Differentiation via TGF-beta 1, Smad3, and HDAC4 Signaling. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.B.; Wu, W.J.; Wei, J.L.; Li, P.H.; Huang, R.H. MiR-22 regulates C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation by targeting TGFBR1. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 97, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noirez, P.; Torres, S.; Cebrian, J.; Agbulut, O.; Peltzer, J.; Butler-Browne, G.; Daegelen, D.; Martelly, I.; Keller, A.; Ferry, A. TGF-beta 1 favors the development of fast type identity during soleus muscle regeneration. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2006, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, F.; Taleb, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Datye, A.; Gamage, D.G.; Peccate, C.; Giordani, L.; Millay, D.P.; Gilbert, P.M.; Cadot, B.; et al. TGF beta signaling curbs cell fusion and muscle regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuselladeangelis, M.G.; Molinari, S.; Ledonne, A.; Coletta, M.; Vivarelli, E.; Bouche, M.; Molinaro, M.; Ferrari, S.; Cossu, G. Differential Response of Embryonic and Fetal Myoblasts to Tgf-Beta-a Possible Regulatory Mechanism of Skeletal-Muscle Histogenesis. Development 1994, 120, 925–933. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.J.; Lei, H.; Yang, B.; Diao, L.T.; Liao, J.Y.; He, J.H.; Tao, S.; Hu, Y.X.; Hou, Y.R.; Sun, Y.J.; et al. Dynamic m(6)A mRNA Methylation Reveals the Role of METTL3/14-m(6)A-MNK2-ERK Signaling Axis in Skeletal Muscle Differentiation and Regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 744171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Yao, Y.L.; Han, J.H.; Yang, Y.L.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Z.L.; Gao, F. Longitudinal epitranscriptome profiling reveals the crucial role of N-6-methyladenosine methylation in porcine prenatal skeletal muscle development. J. Genet. Genom. 2020, 47, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudou, K.; Komatsu, T.; Nogami, J.; Maehara, K.; Harada, A.; Saeki, H.; Oki, E.; Maehara, Y.; Ohkawa, Y. The requirement of Mettl3-promoted MyoD mRNA maintenance in proliferative myoblasts for skeletal muscle differentiation. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.N.; Wang, F.; Ke, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, C.H.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.; He, X.Y.; He, Y.; Suo, X.G.; et al. Inhibition of METTL3 attenuates renal injury and inflammation by alleviating TAB3 m6A modifications via IGF2BP2-dependent mechanisms. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabk2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Dong, H.B.; Sun, B.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jia, Y.M.; Jia, L.F.; Zhong, X.; Zhao, R.Q. METTL3/METTL14 Transactivation and m(6)A-Dependent TGF-beta 1 Translation in Activated Kupffer Cells. Cell Mol. Gastroenter 2021, 12, 839–856. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, H.R.; Liu, M.F.; Ma, J.B.; Wu, L.G. YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Han, Y.L.; Wang, Y.R.; Huang, H.; Qian, P.X. Programmable System of Cas13-Mediated RNA Modification and Its Biological and Biomedical Applications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 677587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Tang, M.; Ma, J.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Gimple, R.C.; Prager, B.C.; Tang, H.Z.; Sun, C.R.; Liu, F.Y.; Lin, P.; et al. Epitranscriptomic editing of the RNA N6-methyladenosine modification by dCasRx conjugated methyltransferase and demethylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 7361–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wei, L.H.; Zhang, X.; Jia, G.F. An Elongation- and Ligation-Based qPCR Amplification Method for the Radiolabeling-Free Detection of Locus-Specific N-6-Methyladenosine Modification. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2018, 57, 15995–16000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, K.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F. Targeted Demethylation of the TGFβ1 mRNA Promotes Myoblast Proliferation via Activating the SMAD2 Signaling Pathway. Cells 2023, 12, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071005
Deng K, Liu Z, Li X, Zhang Z, Fan Y, Huang Q, Zhang Y, Wang F. Targeted Demethylation of the TGFβ1 mRNA Promotes Myoblast Proliferation via Activating the SMAD2 Signaling Pathway. Cells. 2023; 12(7):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071005
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Kaiping, Zhipeng Liu, Xiaodan Li, Zhen Zhang, Yixuan Fan, Qunhao Huang, Yanli Zhang, and Feng Wang. 2023. "Targeted Demethylation of the TGFβ1 mRNA Promotes Myoblast Proliferation via Activating the SMAD2 Signaling Pathway" Cells 12, no. 7: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071005
APA StyleDeng, K., Liu, Z., Li, X., Zhang, Z., Fan, Y., Huang, Q., Zhang, Y., & Wang, F. (2023). Targeted Demethylation of the TGFβ1 mRNA Promotes Myoblast Proliferation via Activating the SMAD2 Signaling Pathway. Cells, 12(7), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071005





