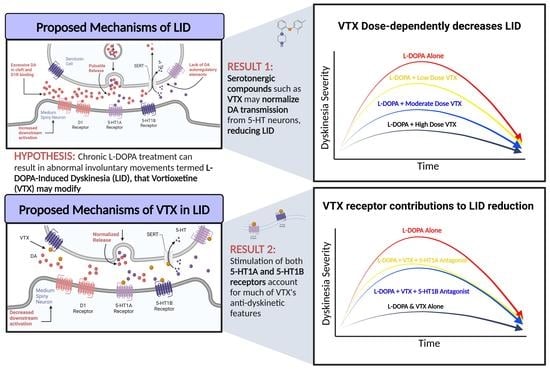
Broad Serotonergic Actions of Vortioxetine as a Promising Avenue for the Treatment of L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Surgeries
2.3. Pharmacological Treatments
2.4. Behavioral Assays and Procedures
2.4.1. Forepaw Adjustment Stepping Test
2.4.2. Abnormal Involuntary Movements Test
2.5. Neurochemical Analyses
2.5.1. Tissue Preparation
2.5.2. HPLC Tissue Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Experimental Design
2.7.1. Experiment 1: Sub-Chronic Vortioxetine Intervention in Dyskinetic Rats
2.7.2. Experiment 3: Role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B Receptors in Vortioxetine’s Behavioral Effects
3. Results
3.1. Development of L-DOPA-Induced AIMs across Experiments
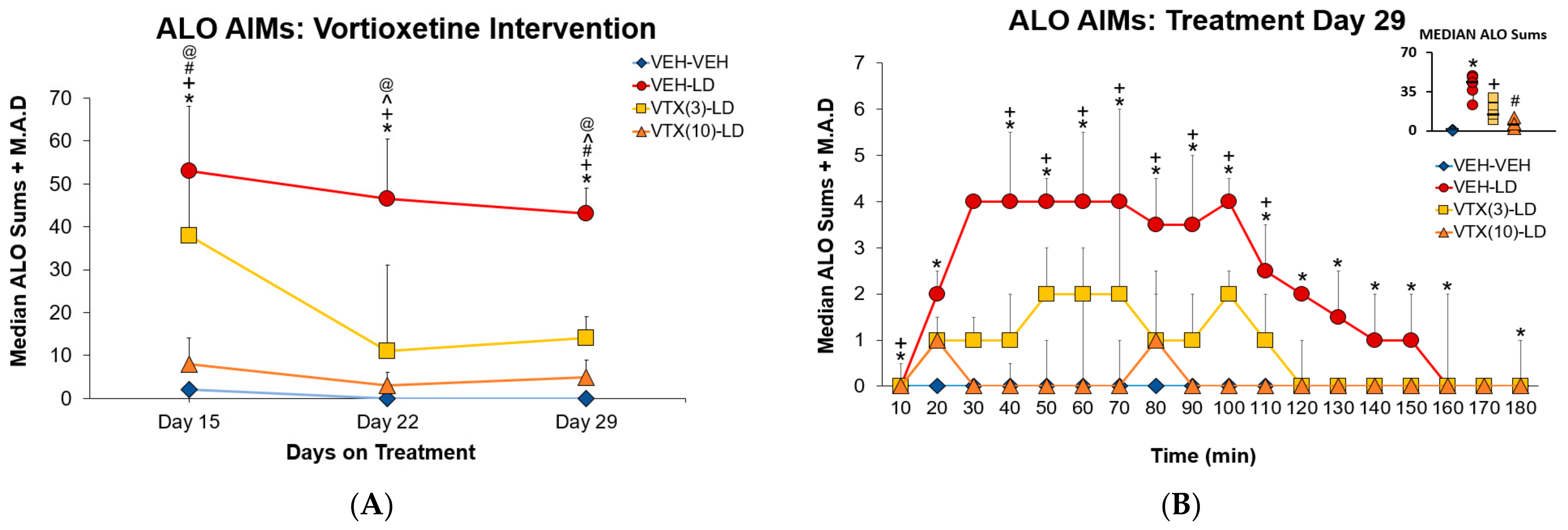
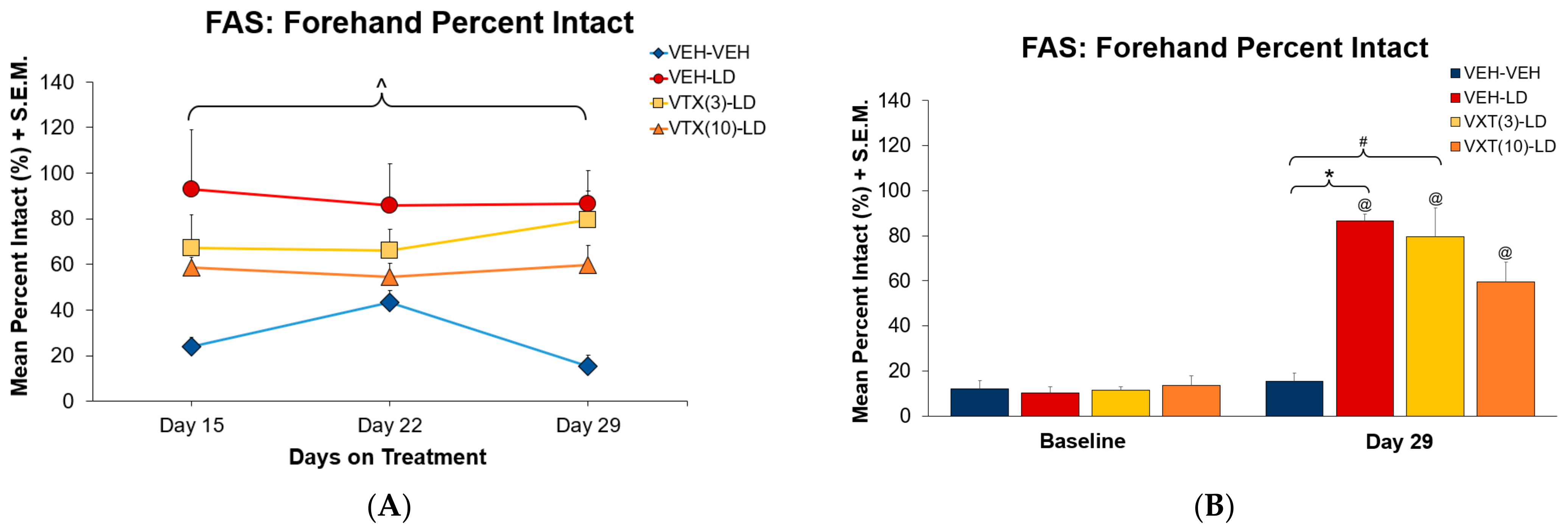
3.2. Experiment 1: Sub-Chronic Vortioxetine Intervention in Dyskinetic Rats
3.3. Experiment 2: Role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B Receptors in Vortioxetine’s Behavioral Effects
3.4. High Performance Liquid Chromatography
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jankovic, J. Parkinson’s disease: Clinical features and diagnosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davie, C.A. A review of Parkinson’s disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2008, 86, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehringer, H.; Hornykiewicz, O. Distribution of noradrenaline and dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) in the human brain and their behavior in diseases of the extrapyramidal system. Park. Relat. Disord. 1998, 4, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Elbaz, A.; Nichols, E.; Abbasi, N.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Adsuar, J.C.; Ansha, M.G.; Choi, J.-Y.J.; Collado-Mateo, D.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, Y.; Wichmann, T.; Factor, S.A.; DeLong, M.R. Parkinson’s disease therapeutics: New developments and challenges since the introduction of levodopa. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 213–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlskog, J.E.; Muenter, M.D. Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov. Disord. 2001, 16, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, B.S.; Lang, A.E. Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1670–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, S.; Ouchchane, L.; Metz, O.; Gerbaud, L.; Durif, F. Impact of the motor complications of Parkinson’s disease on the quality of life. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, D.-C.; Pahwa, R.; Mallya, U. Treatment patterns and associated costs with Parkinson’s disease levodopa induced dyskinesia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 319, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péchevis, M.; Clarke, C.E.; Vieregge, P.; Khoshnood, B.; Deschaseaux-Voinet, C.; Berdeaux, G.; Ziegler, M.; Trial Study Group. Effects of dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease on quality of life and health-related costs: A prospective European study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2005, 12, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, D.; Parent, M.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Dovero, S.; Lees, A.J.; Bezard, E.; Descarries, L.; Cenci, M.A. Maladaptive plasticity of serotonin axon terminals in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, G.; Niccolini, F.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Politis, M. Serotonin transporter in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of positron emission tomography studies. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeda, T.; Nagata, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Kannari, K. Serotonergic hyperinnervation into the dopaminergic denervated striatum compensates for dopamine conversion from exogenously administered l-DOPA. Brain Res. 2005, 1046, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.Y.; Iravani, M.M.; Jackson, M.J.; Rose, S.; Parent, A.; Jenner, P. Morphological changes in serotoninergic neurites in the striatum and globus pallidus in levodopa primed MPTP treated common marmosets with dyskinesia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Seo, S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Jeon, B.S. Putaminal serotonergic innervation: Monitoring dyskinesia risk in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2015, 85, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussakis, A.A.; Politis, M.; Towey, D.; Piccini, P. Serotonin-to-dopamine transporter ratios in Parkinson disease: Relevance for dyskinesias. Neurology 2016, 86, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Politis, M.; Wu, K.; Loane, C.; Brooks, D.J.; Kiferle, L.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Bain, P.; Molloy, S.; Piccini, P. Serotonergic mechanisms responsible for levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, H.; Tomiyama, M. What mechanisms are responsible for the reuptake of levodopa-derived dopamine in Parkinsonian striatum? Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carta, M.; Carlsson, T.; Kirik, D.; Björklund, A. Dopamine released from 5-HT terminals is the cause of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in parkinsonian rats. Brain 2007, 130, 1819–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carta, M.; Carlsson, T.; Muñoz, A.; Kirik, D.; Björklund, A. Serotonin–dopamine interaction in the induction and maintenance of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 172, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellnow, R.C.; Newman, J.H.; Chambers, N.; West, A.R.; Steece-Collier, K.; Sandoval, I.M.; Benskey, M.J.; Bishop, V.; Manfredsson, F. Regulation of dopamine neurotransmission from serotonergic neurons by ectopic expression of the dopamine D2 autoreceptor blocks levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Kannari, K.; Maeda, T.; Tomiyama, M.; Suda, T.; Matsunaga, M. Role of 5-HT neurons in L-DOPA-derived extracellular dopamine in the striatum of 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. NeuroReport 1999, 10, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskow, K.L.; Dupre, K.B.; Barnum, C.J.; Dickinson, S.O.; Park, J.Y.; Bishop, C. The role of the dorsal raphe nucleus in the development, expression, and treatment of L-dopa-induced dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian rats. Synapse 2009, 63, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carta, M.; Tronci, E. Serotonin system implication in l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia: From animal models to clinical investigations. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanza, K.; Bishop, C. Serotonergic targets for the treatment of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajdokht, F.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Majdi, A.; Pashazadeh, F.; Vatandoust, S.M.; Ziaee, M.; Safari, F.; Karimi, P.; Mahmoudi, J. Serotonergic system modulation holds promise for L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias in hemiparkinsonian rats: A systematic review. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 268–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucchi, S.; Frosini, D.; Ripoli, A.; Nicoletti, V.; Linsalata, G.; Bonuccelli, U.; Ceravolo, R. Serotonergic antidepressant drugs and L-dopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 131, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.; George, J.A.; Buchta, W.; Goldenberg, A.A.; Mohamed, M.; Dickinson, S.O.; Eissa, S.; Eskow Jaunarajs, K.L. 5-HT transporter inhibition attenuates l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia without compromising l-DOPA efficacy in hemi-parkinsonian rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 36, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conti, M.M.; Ostock, C.Y.; Lindenbach, D.; Goldenberg, A.A.; Kampton, E.; Dell’isola, R.; Katzman, A.C.; Bishop, C. Effects of prolonged selective serotonin reuptake inhibition on the development and expression of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemi-parkinsonian rats. Neuropharmacology 2014, 77, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munoz, A.; Li, Q.; Gardoni, F.; Marcello, E.; Qin, C.; Carlsson, T.; Kirik, D.; Di Luca, M.; Björklund, A.; Bezard, E.; et al. Combined 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptor agonists for the treatment of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Brain 2008, 131, 3380–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, K.A.; Carlson, N.E.; Nutt, J.G. Short-term paroxetine treatment does not alter the motor response to levodopa in PD. Neurology 2005, 64, 1797–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.G.; Damier, P.; Hicking, C.; Laska, E.; Müller, T.; Olanow, C.W.; Rascol, O.; Russ, H. Sarizotan as a treatment for dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease: A double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidalgo, C.; Ko, W.K.; Tronci, E.; Li, Q.; Stancampiano, R.; Chuan, Q.; Bezard, E.; Carta, M. Effect of serotonin transporter blockade on L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2015, 298, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenbach, D.; Palumbo, N.; Ostock, C.Y.; Vilceus, N.; Conti, M.M.; Bishop, C. Side effect profile of 5-HT treatments for Parkinson’s disease and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.; Sergio, J.; Coyle, M.; Elder, K.; Centner, A.; Cohen, S.; Terry, M.; Lipari, N.; Glinski, J.; Wheelis, E.; et al. The effects of Vilazodone, YL-0919 and Vortioxetine in hemiparkinsonian rats. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239, 2119–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, S.M.; Chambers, N.E.; Conti, M.M.; Bossert, S.C.; Tasber, C.; Sheena, E.; Varney, M.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Bishop, C. Characterizing the differential roles of striatal 5-HT1A auto- and hetero-receptors in the reduction of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 292, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altwal, F.; Moon, C.; West, A.R.; Steiner, H. The multimodal serotonergic agent Vilazodone inhibits L-DOPA-induced gene regulation in striatal projection neurons and associated dyskinesia in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Cells 2020, 9, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Wachtel, S.; Young, D.; Kang, U. Biochemical and anatomical characterization of forepaw adjusting steps in rat models of Parkinson’s disease: Studies on medial forebrain bundle and striatal lesions. Neuroscience 1999, 88, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, M.; Andersson, M.; Winkler, C.; Kirik, D.; Wierup, N.; Cenci, M.A. Pharmacological validation of behavioural measures of akinesia and dyskinesia in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.L.; Bishop, C.; Walker, P.D. Dopamine D1 and D2 receptor contributions to L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the dopamine-depleted rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 81, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.R.; Terry, M.L.; Coyle, M.; Wheelis, E.; Centner, A.; Smith, S.; Glinski, J.; Lipari, N.; Budrow, C.; Manfredsson, F.P.; et al. The multimodal serotonin compound Vilazodone alone, but not combined with the glutamate antagonist Amantadine, reduces L-dopa induced dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2022, 217, 173393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, S.; Stancampiano, R.; Carta, M. Serotonin/dopamine interaction in the induction and maintenance of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia: An update. Prog. Brain Res. 2021, 261, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannari, K.; Kurahashi, K.; Tomiyama, M.; Maeda, T.; Arai, A.; Baba, M.; Suda, T.; Matsunaga, M. Tandospirone citrate, a selective 5-HT1A agonist, alleviates L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. No Shinkei 2002, 54, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chambers, N.E.; Meadows, S.M.; Taylor, A.; Sheena, E.; Lanza, K.; Conti, M.M.; Bishop, C. Effects of muscarinic acetylcholine m1 and m4 receptor blockade on dyskinesia in the hemi-parkinsonian rat. Neuroscience 2019, 409, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depoortere, R.; Johnston, T.H.; Fox, S.H.; Brotchie, J.M.; Newman-Tancredi, A. The selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist, NLX-112, exerts anti-dyskinetic effects in MPTP-treated macaques. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 78, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, A.; Ko, W.K.D.; Costa, G.; Tronci, E.; Fidalgo, C.; Simola, N.; Li, Q.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Bezard, E.; Carta, M.; et al. Antidyskinetic effect of A2A and 5HT1A/1B receptor ligands in two animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronci, E.; Fidalgo, C.; Stancampiano, R.; Carta, M. Effect of selective and non-selective serotonin receptor activation on l-DOPA-induced therapeutic efficacy and dyskinesia in parkinsonian rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 292, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanvi, B.; Lo, N.; Robinson, T. Levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease: Clinical features, pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, C.; Asin, K.E.; Artigas, F. Vortioxetine, a novel antidepressant with multimodal activity: Review of preclinical and clinical data. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 145, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Højer, A.M.; Areberg, J.; Nomikos, G. Vortioxetine: Clinical pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blier, P.; Ward, N.M. Is there a role for 5-HT1A agonists in the treatment of depression? Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 53, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.; Krolewski, D.M.; Eskow, K.L.; Barnum, C.J.; Dupre, K.B.; Deak, T.; Walker, P.D. Contribution of the striatum to the effects of 5-HT1A receptor stimulation in L-DOPA-treated hemiparkinsonian rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaunarajs, K.L.E.; Dupre, K.B.; Steiniger, A.; Klioueva, A.; Moore, A.; Kelly, C.; Bishop, C. Serotonin 1B receptor stimulation reduces D1 receptor agonist-induced dyskinesia. Neuroreport 2009, 20, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezard, E.; Tronci, E.; Pioli, E.Y.; Li, Q.; Porras, G.; Björklund, A.; Carta, M. Study of the antidyskinetic effect of eltoprazine in animal models of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, S.M. Modes and nodes explain the mechanism of action of vortioxetine, a multimodal agent (MMA): Enhancing serotonin release by combining serotonin (5HT) transporter inhibition with actions at 5HT receptors (5HT1A, 5HT1B, 5HT1D, 5HT7 receptors). CNS Spectr. 2015, 20, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Agostino, A.; English, C.D.; Rey, J.A. Vortioxetine (Brintellix): A new serotonergic antidepressant. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, F.J. Parkinson’s disease, antiparkinson medicines, and driving. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboulghasemi, N.; Jahromy, M.H.; Ghasemi, A. Anti-dyskinetic efficacy of 5-HT3 receptor antagonist in the hemi-parkinsonian rat model. IBRO Rep. 2019, 6, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoldan, J.; Friedberg, G.; Livneh, M.; Melamed, E. Psychosis in advanced Parkinson’s disease: Treatment with ondansetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. Neurology 1995, 45, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenkrona, P.; Halldin, C.; Lundberg, J. 5-HTT and 5-HT(1A) receptor occupancy of the novel substance vortioxetine (Lu AA21004). A PET study in control subjects. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, M.; Wu, K.; Loane, C.; Quinn, N.P.; Brooks, D.J.; Rehncrona, S.; Bjorklund, A.; Lindval, O.; Piccini, P. Serotonergic neurons mediate dyskinesia side effects in Parkinson’s patients with neural transplants. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignon, L.J.; Wolf, W.A. 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin reduces striatal glutamate in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupre, K.B.; Eskow, K.L.; Barnum, C.J.; Bishop, C. Striatal 5-HT1A receptor stimulation reduces D1 receptor-induced dyskinesia and improves movement in the hemiparkinsonian rat. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, A.; Carlsson, T.; Tronci, E.; Kirik, D.; Björklund, A.; Carta, M. Serotonin neuron-dependent and-independent reduction of dyskinesia by 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptor agonists in the rat Parkinson model. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 219, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, M.; Kimura, T.; Maeda, T.; Kannari, K.; Matsunaga, M.; Baba, M. A serotonin 5-HT1A receptor agonist prevents behavioral sensitization to L-DOPA in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 52, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Side | DOPAC (ng/mg) | DA (ng/mg) | DOPAC/DA | 5-HIAA (ng/mg) | 5-HT (ng/mg) | 5-HIAA/5-HT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact (right) | 2.06 ± 0.15 | 9.74 ± 1.07 | 0.28 ± 0.03 | 0.69 ± 0.06 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 7.49 ± 0.69 |
| Lesion (left) | 0.12 ± 0.01 * | 0.09 ± 0.01 * | 2.31 ± 0.27 * | 0.05 ± 0.01 * | 0.08 ± 0.01 * | 1.02 ± 0.23 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budrow, C.; Elder, K.; Coyle, M.; Centner, A.; Lipari, N.; Cohen, S.; Glinski, J.; Kinzonzi, N.; Wheelis, E.; McManus, G.; et al. Broad Serotonergic Actions of Vortioxetine as a Promising Avenue for the Treatment of L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia. Cells 2023, 12, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12060837
Budrow C, Elder K, Coyle M, Centner A, Lipari N, Cohen S, Glinski J, Kinzonzi N, Wheelis E, McManus G, et al. Broad Serotonergic Actions of Vortioxetine as a Promising Avenue for the Treatment of L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia. Cells. 2023; 12(6):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12060837
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudrow, Carla, Kayla Elder, Michael Coyle, Ashley Centner, Natalie Lipari, Sophie Cohen, John Glinski, N’Senga Kinzonzi, Emily Wheelis, Grace McManus, and et al. 2023. "Broad Serotonergic Actions of Vortioxetine as a Promising Avenue for the Treatment of L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia" Cells 12, no. 6: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12060837
APA StyleBudrow, C., Elder, K., Coyle, M., Centner, A., Lipari, N., Cohen, S., Glinski, J., Kinzonzi, N., Wheelis, E., McManus, G., Manfredsson, F., & Bishop, C. (2023). Broad Serotonergic Actions of Vortioxetine as a Promising Avenue for the Treatment of L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia. Cells, 12(6), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12060837