Estrogen Mediates the Sexual Dimorphism of GT1b-Induced Central Pain Sensitization
Abstract
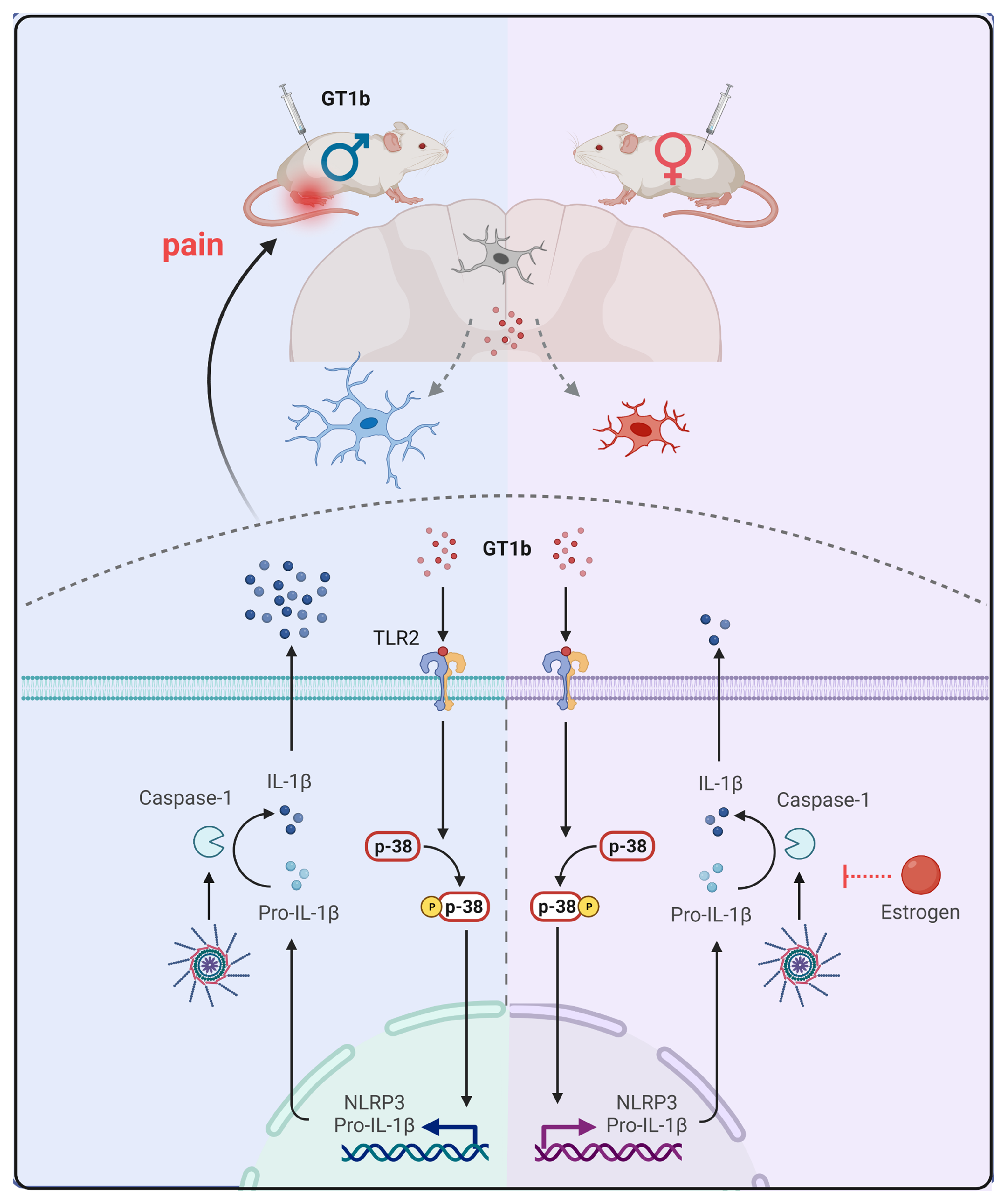
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Intrathecal Injection
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Confocal Microscopy and 3D IMARIS Analysis
2.5. Behavioral Tests
2.6. RNA Extraction and Transcriptome Analysis
2.7. Ovariectomy
2.8. Orchiectomy
2.9. ELISA Assay
2.10. In Vitro Primary Mixed Glia Culture
2.11. Real-Time RT-PCR
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
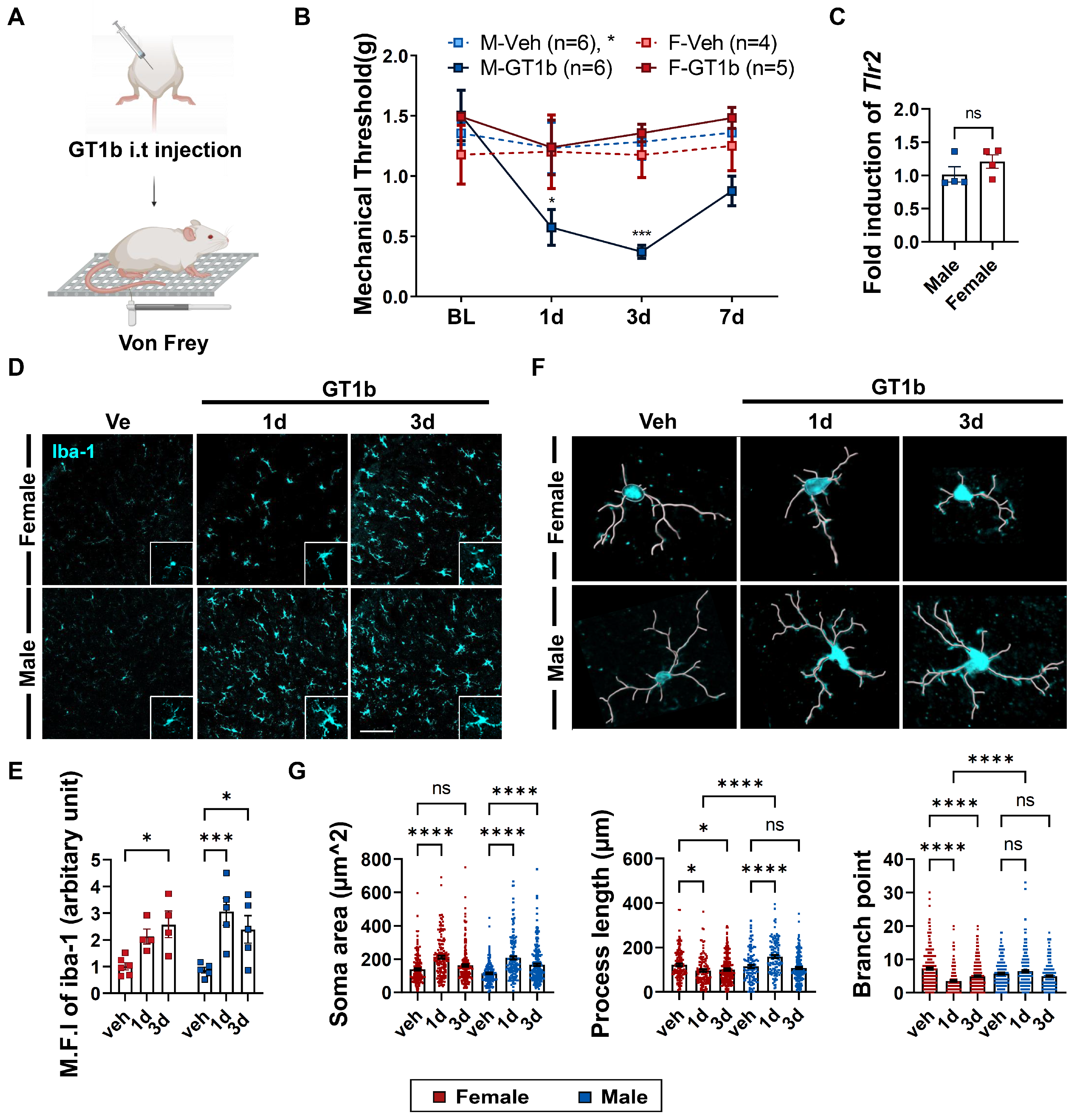
3.1. GT1b-Induced Central Pain Sensitization and Spinal Cord Microglia Activation Are Sexually Dimorphic
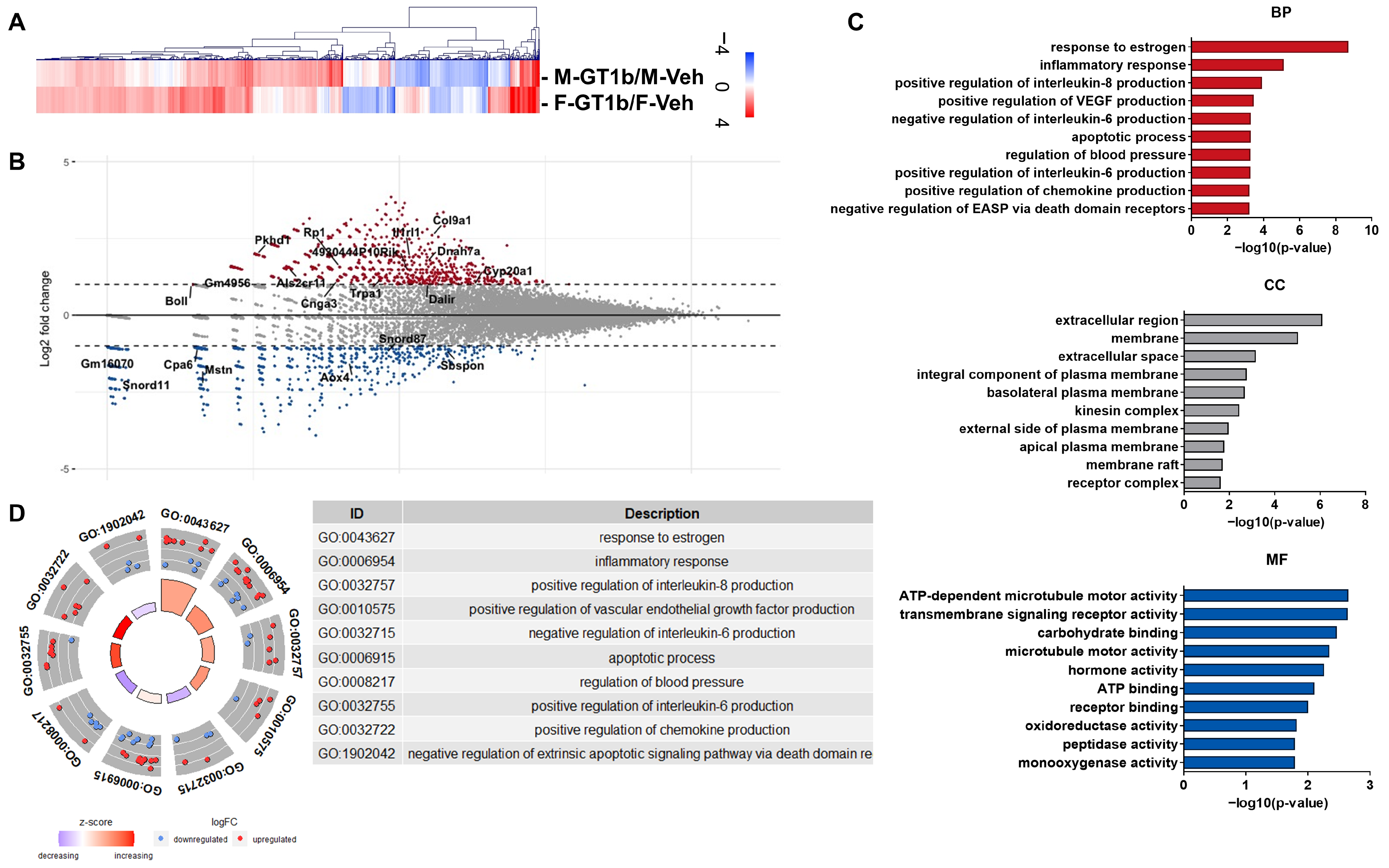
3.2. Sexually Dimorphic Transcriptome Profiles of GT1b-Stimulated Mouse Spinal Cords
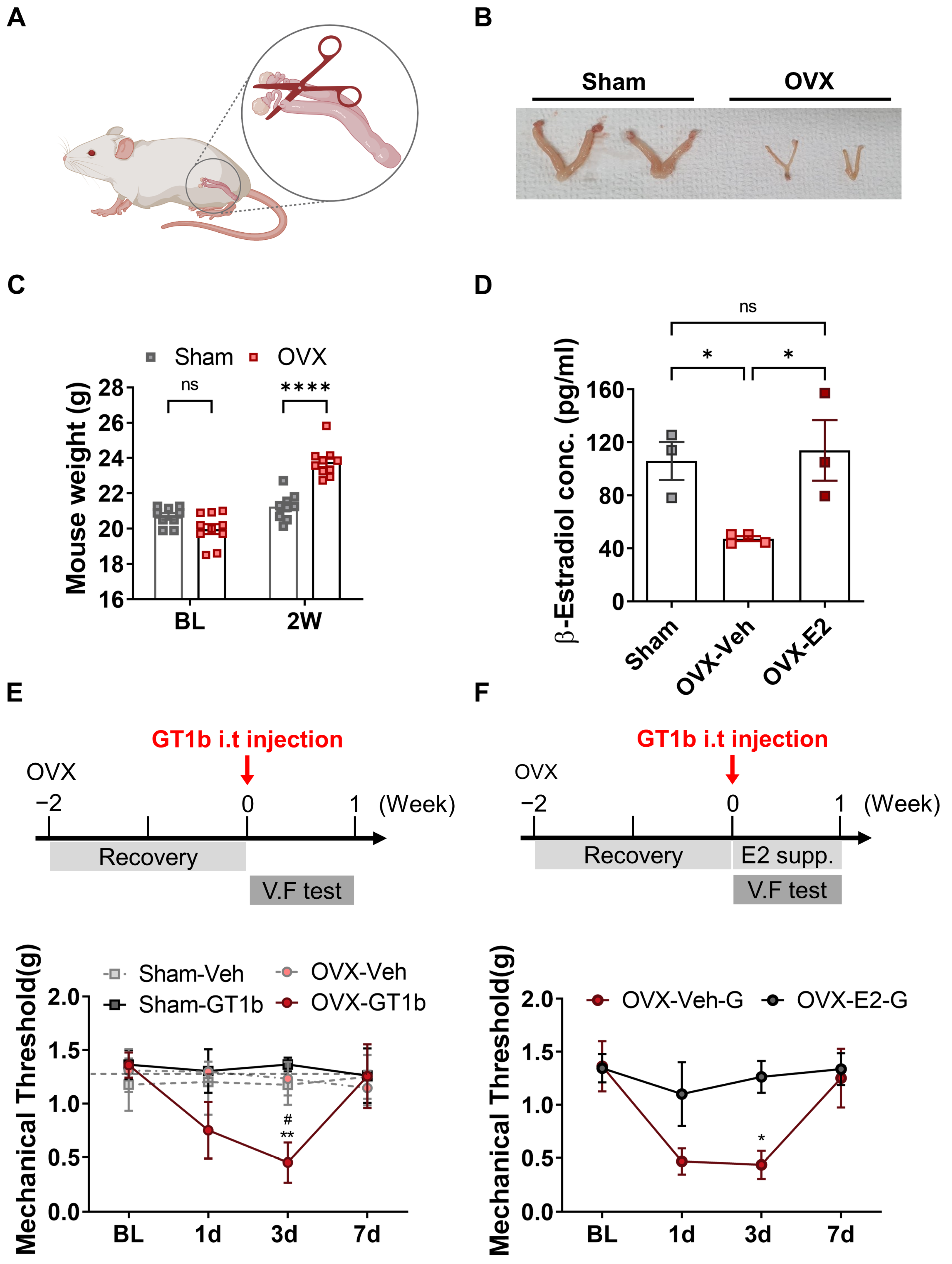
3.3. GT1b-Induced Central Pain Sensitization Is Dependent on Estrogen
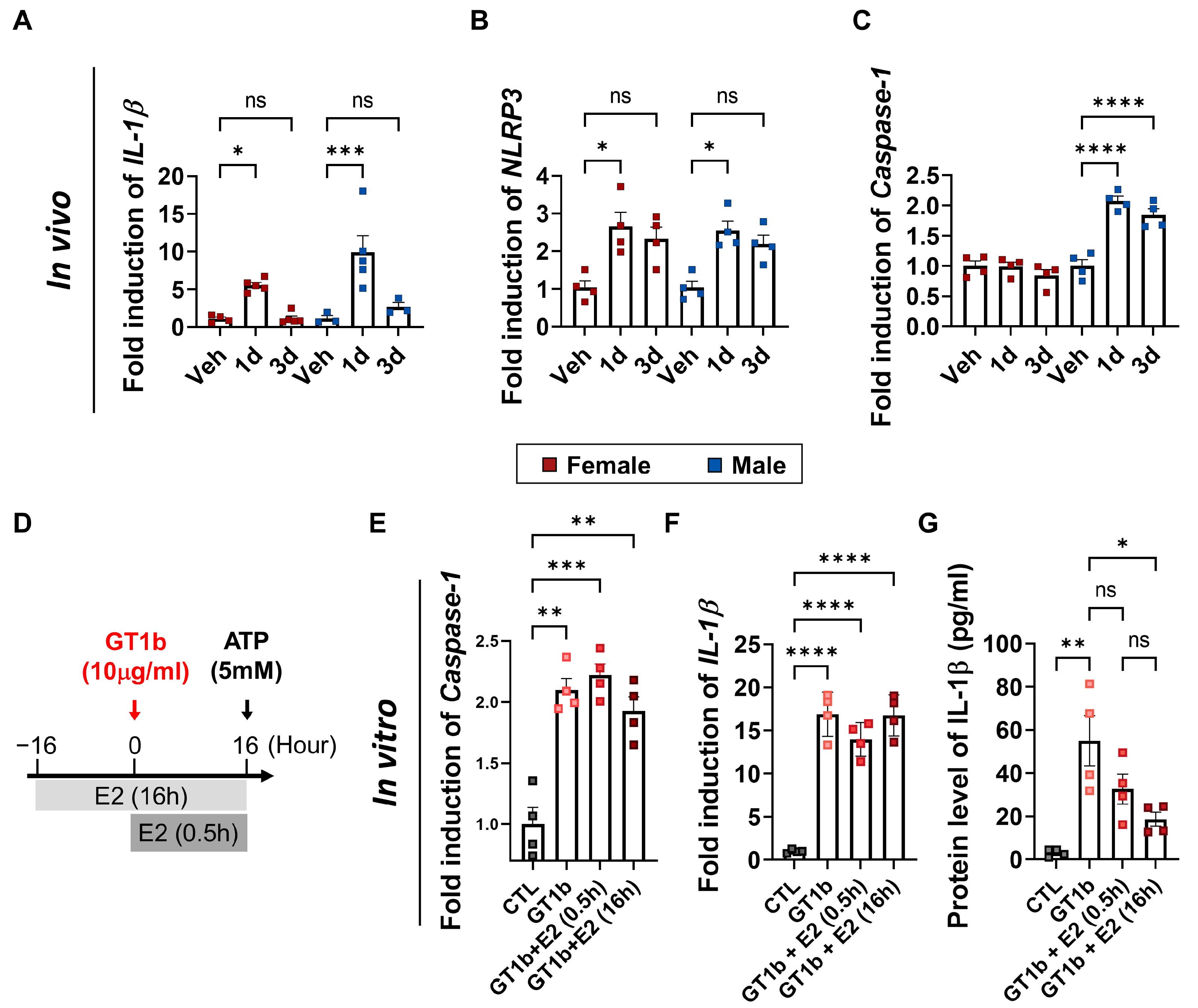
3.4. 17β-Estradiol Inhibits GT1b-Induced Inflammasome Activation and IL-1β Release
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colloca, L.; Ludman, T.; Bouhassira, D.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H.; Yarnitsky, D.; Freeman, R.; Truini, A.; Attal, N.; Finnerup, N.B.; et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.S.; Finnerup, N.B. Allodynia and hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain: Clinical manifestations and mechanisms. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkley, K.J. Sex differences in pain. Behav. Brain Sci. 1997, 20, 371–380, discussion 435–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogil, J.S.; Chanda, M.L. The case for the inclusion of female subjects in basic science studies of pain. Pain 2005, 117, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, V.; Tanga, F.; DeLeo, J.A. Inhibition of microglial activation attenuates the development but not existing hypersensitivity in a rat model of neuropathy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 306, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorge, R.E.; Mapplebeck, J.C.; Rosen, S.; Beggs, S.; Taves, S.; Alexander, J.K.; Martin, L.J.; Austin, J.S.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Chen, D.; et al. Different immune cells mediate mechanical pain hypersensitivity in male and female mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorge, R.E.; LaCroix-Fralish, M.L.; Tuttle, A.H.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Austin, J.S.; Ritchie, J.; Chanda, M.L.; Graham, A.C.; Topham, L.; Beggs, S.; et al. Spinal cord Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory and neuropathic hypersensitivity in male but not female mice. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 15450–15454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.A.; Vainchtein, I.D.; Braz, J.; Hamel, K.; Bernstein, M.; Craik, V.; Dahlgren, M.W.; Ortiz-Carpena, J.; Molofsky, A.B.; Molofsky, A.V.; et al. Regulatory T-cells inhibit microglia-induced pain hypersensitivity in female mice. Elife 2021, 10, e69056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hwang, H.; Lee, S.J. Distinct roles of GT1b and CSF-1 in microglia activation in nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2021, 17, 17448069211020918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, N.T.; Yin, Z.; Guneykaya, D.; Gauthier, C.D.; Hayes, J.P.; D’Hary, A.; Butovsky, O.; Moalem-Taylor, G. Sex-specific transcriptome of spinal microglia in neuropathic pain due to peripheral nerve injury. Glia 2022, 70, 675–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Lee, J.; You, B.; Oh, J.H.; Mok, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yoon, B.E.; Kim, B.G.; Back, S.K.; Park, J.S.; et al. GT1b functions as a novel endogenous agonist of toll-like receptor 2 inducing neuropathic pain. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e102214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.J. Toll-like receptor 2 mediates peripheral nerve injury-induced NADPH oxidase 2 expression in spinal cord microglia. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 7572–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, M.A.; Cho, I.-H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.; Jo, E.-K.; Choi, S.-Y.; Park, K.; Kim, J.S.; Akira, S. A critical role of toll-like receptor 2 in nerve injury-induced spinal cord glial cell activation and pain hypersensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14975–14983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylden, J.L.; Wilcox, G.L. Intrathecal morphine in mice: A new technique. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1980, 67, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.; Pogrel, J.; Chung, J.; Yaksh, T. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, K.; Dubner, R.; Brown, F.; Flores, C.; Joris, J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 1988, 32, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.I.; Bhagabati, N.K.; Braisted, J.C.; Liang, W.; Sharov, V.; Howe, E.A.; Li, J.; Thiagarajan, M.; White, J.A.; Quackenbush, J. TM4 microarray software suite. Methods Enzymol. 2006, 411, 134–193. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Zhou, T.; Choi, C.; Wang, Z.; Benveniste, E.N. Differential regulation and function of Fas expression on glial cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Kouadir, M.; Song, H.; Shi, F. Recent advances in the mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its inhibitors. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyh, J.; Paeschke, S.; Mages, B.; Michalski, D.; Nowicki, M.; Bechmann, I.; Winter, K. Classification of Microglial Morphological Phenotypes Using Machine Learning. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 701673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.; Sherman, B.T.; Huang, D.W.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID-WS: A stateful web service to facilitate gene/protein list analysis. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1805–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.T.; Lee, Y.J.; Dai, X.; Ojeda, N.B.; Lee, H.J.; Tien, L.T.; Fan, L.W. Systemic Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Pain Sensitivity and Spinal Inflammation Were Reduced by Minocycline in Neonatal Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Karmakar, S.; Babu, S.P.S. TLR2 and TLR4 mediated host immune responses in major infectious diseases: A review. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 20, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapplebeck, J.C.S.; Beggs, S.; Salter, M.W. Sex differences in pain: A tale of two immune cells. Pain 2016, 157 (Suppl. S1), S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Luo, X.; Qadri, M.Y.; Berta, T.; Ji, R.R. Sex-Dependent Glial Signaling in Pathological Pain: Distinct Roles of Spinal Microglia and Astrocytes. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelros, P.; Stegmayr, B.; Terént, A. Sex differences in stroke epidemiology: A systematic review. Stroke 2009, 40, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koellhoffer, E.C.; McCullough, L.D. The effects of estrogen in ischemic stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2013, 4, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendedel, A.; Mönnink, F.; Hassanzadeh, G.; Zaminy, A.; Ansar, M.M.; Habib, P.; Slowik, A.; Kipp, M.; Beyer, C. Estrogen Attenuates Local Inflammasome Expression and Activation after Spinal Cord Injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, R.; Wang, R.; Sareddy, G.; Wang, J.; Thiruvaiyaru, D.; Vadlamudi, R.; Zhang, Q.; Brann, D. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Brain after Global Cerebral Ischemia and Regulation by 17β-Estradiol. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 8309031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Ju, B.G.; Yune, T.Y. Estrogen alleviates neuropathic pain induced after spinal cord injury by inhibiting microglia and astrocyte activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis. Dis. 2018, 1864, 2472–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.K.; Ji, R.R. Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: Distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 5189–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.R.; Andriessen, A.S.; Chen, G.; Wang, K.; Jiang, C.; Maixner, W.; Ji, R.-R. Central Nervous System Targets: Glial Cell Mechanisms in Chronic Pain. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Blacklock, A.; Svojanovsky, S.; Smith, P.G. Estrogen elicits dorsal root ganglion axon sprouting via a renin-angiotensin system. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3452–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Feng, J.; Cai, T.; McCarthy, R.; Eschbach, M.D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yi, Z.; Zang, K.; Yuan, Y. Estrogen metabolites increase nociceptor hyperactivity in a mouse model of uterine pain. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e149107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodburn, S.C.; Bollinger, J.L.; Wohleb, E.S. The semantics of microglia activation: Neuroinflammation, homeostasis, and stress. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Chung, S.; Hwang, M.; Kwon, Y.; Han, S.H.; Lee, S.J. Estrogen Mediates the Sexual Dimorphism of GT1b-Induced Central Pain Sensitization. Cells 2023, 12, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050808
Lee J, Chung S, Hwang M, Kwon Y, Han SH, Lee SJ. Estrogen Mediates the Sexual Dimorphism of GT1b-Induced Central Pain Sensitization. Cells. 2023; 12(5):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050808
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jaesung, Seohyun Chung, Minkyu Hwang, Yeongkag Kwon, Seung Hyun Han, and Sung Joong Lee. 2023. "Estrogen Mediates the Sexual Dimorphism of GT1b-Induced Central Pain Sensitization" Cells 12, no. 5: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050808
APA StyleLee, J., Chung, S., Hwang, M., Kwon, Y., Han, S. H., & Lee, S. J. (2023). Estrogen Mediates the Sexual Dimorphism of GT1b-Induced Central Pain Sensitization. Cells, 12(5), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050808





