IL-33 via PKCμ/PRKD1 Mediated α-Catenin Phosphorylation Regulates Endothelial Cell-Barrier Integrity and Ischemia-Induced Vascular Leakage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Experimental Animals
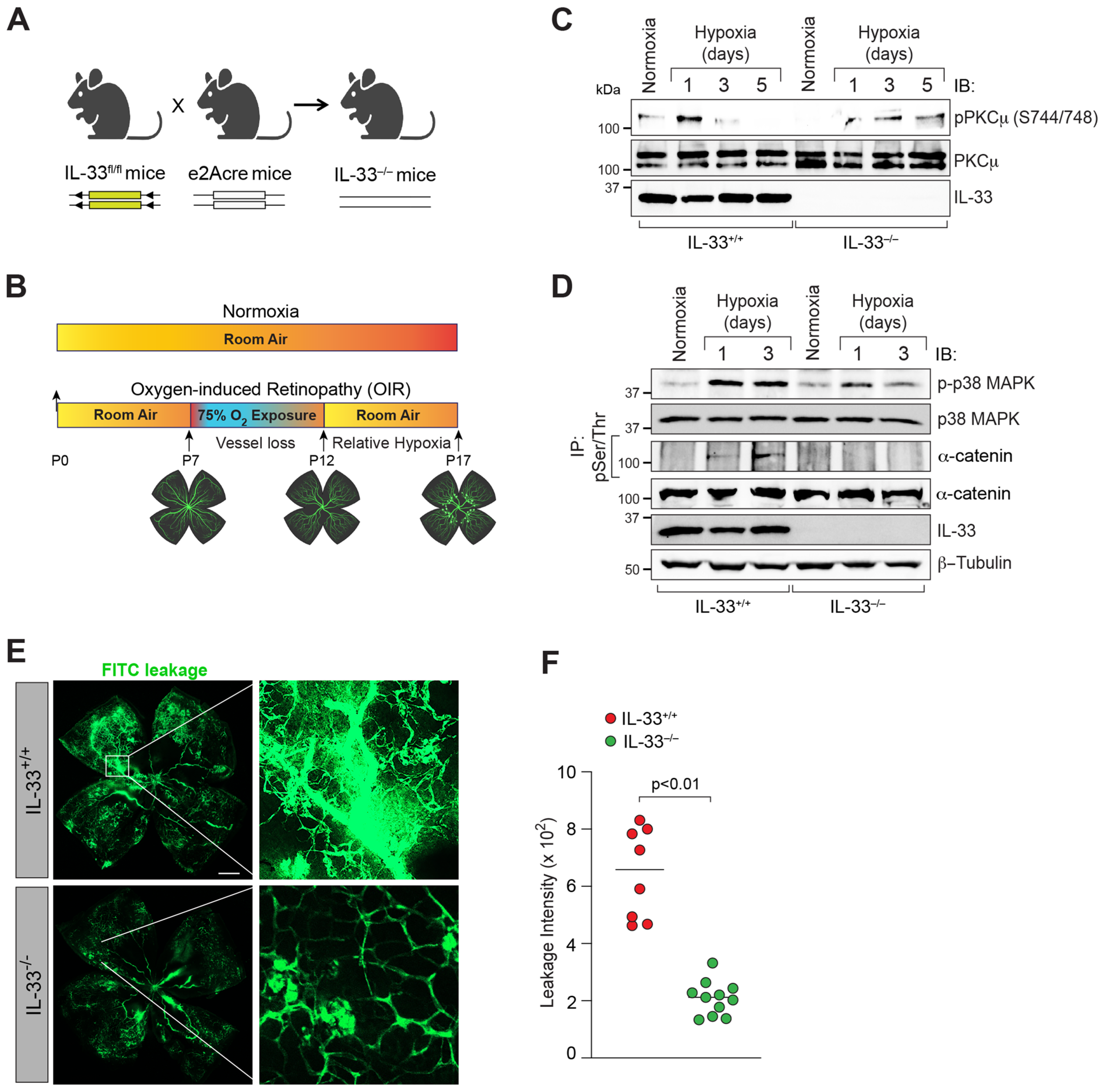
2.3. IL-33 Knockout Mice Generation
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy (OIR)
2.6. Measurement of OIR-Induced Vascular Leakage in Mice Retina
2.7. FITC-Dextran Flux Assay
2.8. Electric Cell-Substrate Impedance Sensing (ESIC)
2.9. Cell-Surface Receptor Internalization
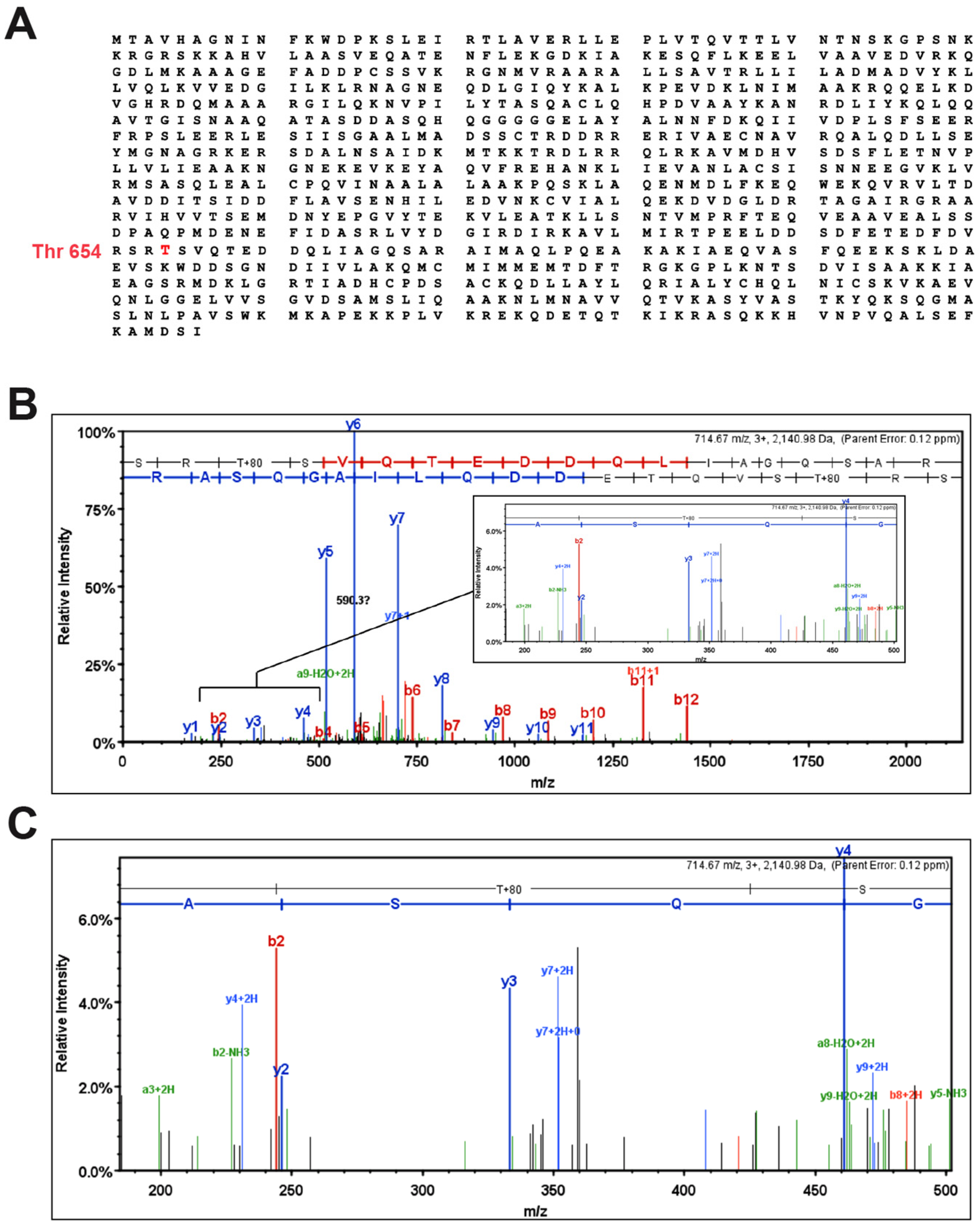
2.10. Immunoprecipitation and Mass Spectroscopy
2.11. Immunofluorescence
2.12. Western Blotting
2.13. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. IL-33 Disrupts Human Retinal Endothelial Cell-Barrier Integrity
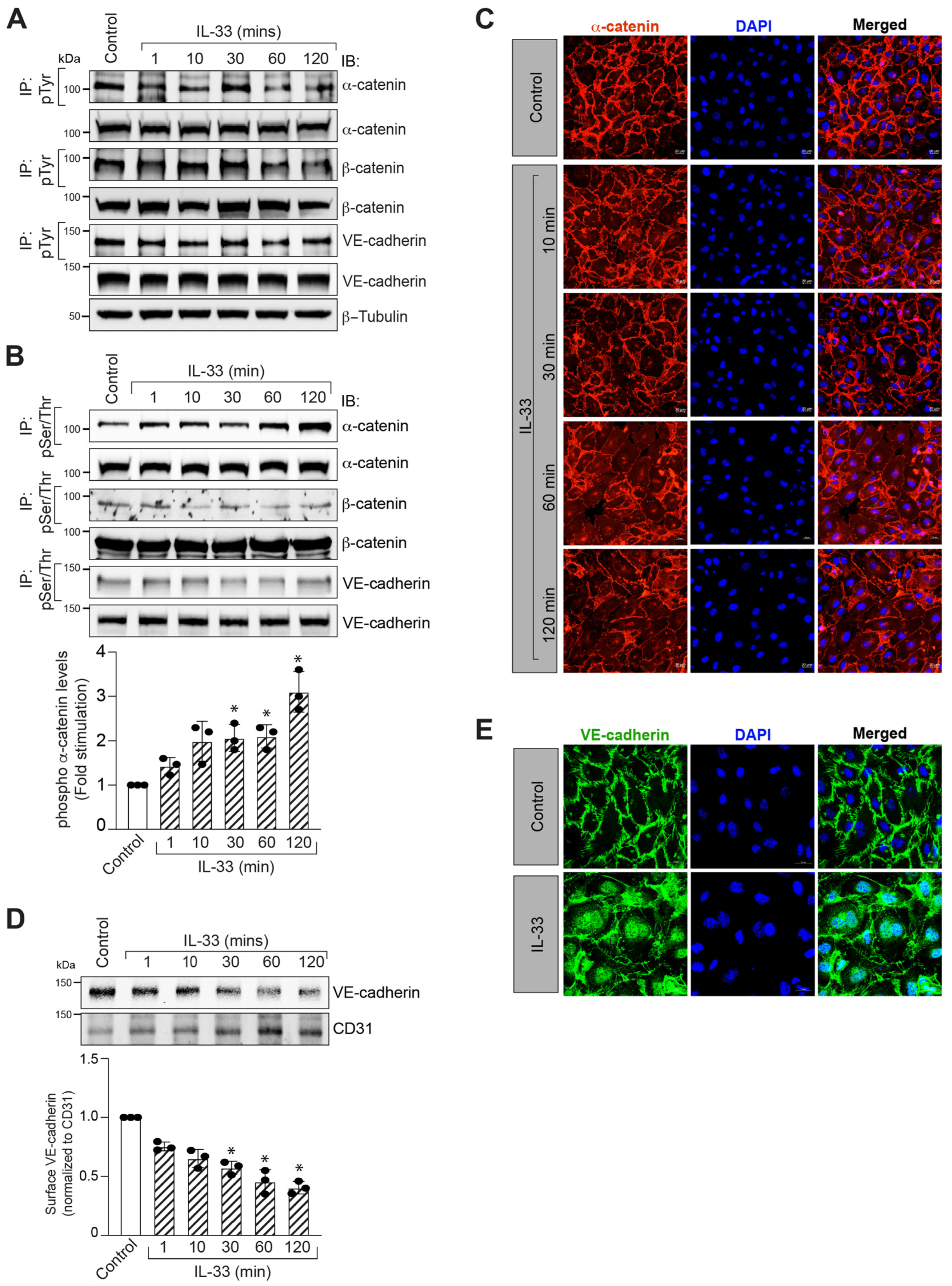
3.2. IL-33 Promotes α-Catenin Phosphorylation and Adherens Junction Disruption
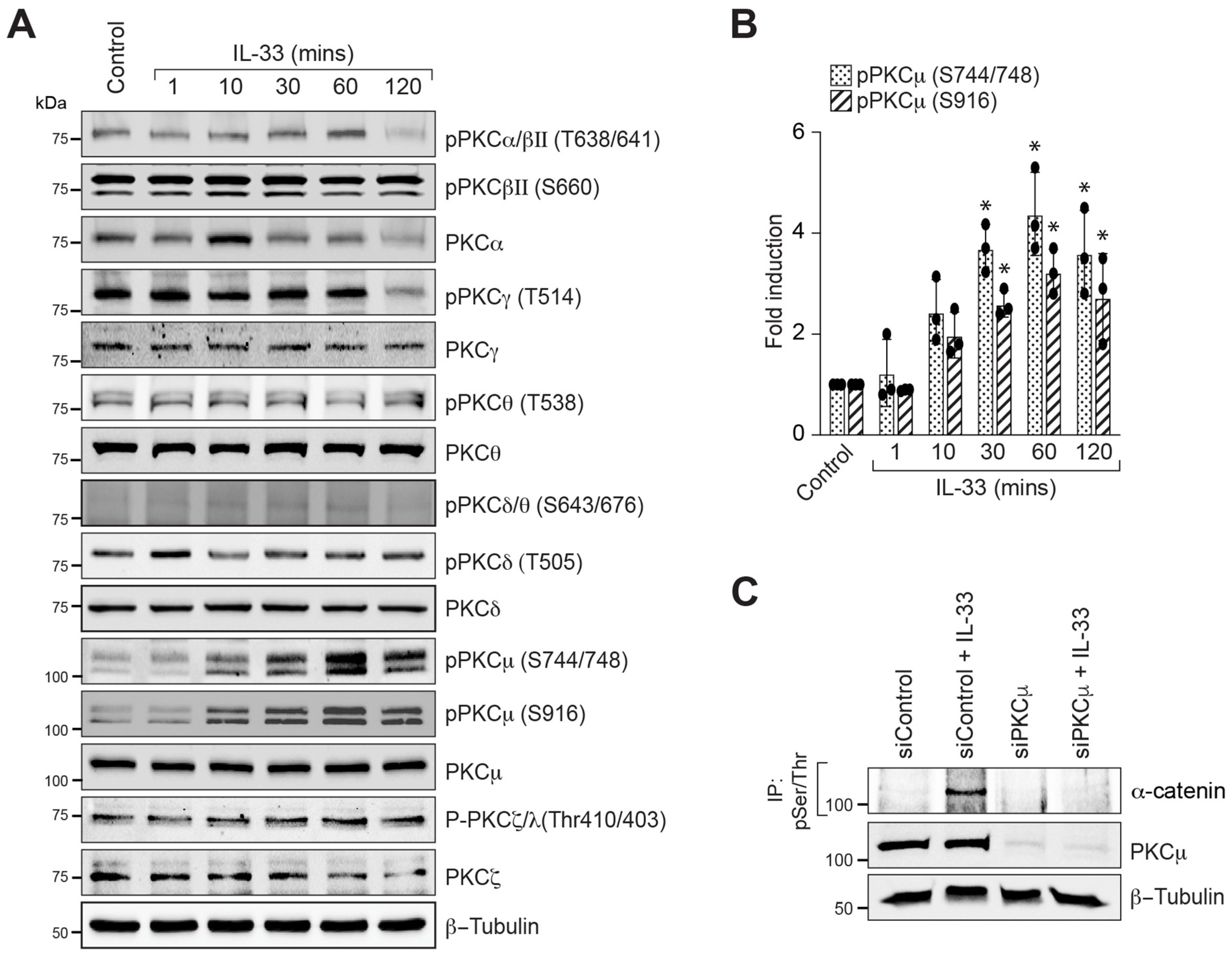
3.3. PKCμ Regulates α-Catenin Phosphorylation and Endothelial Barrier Disruption
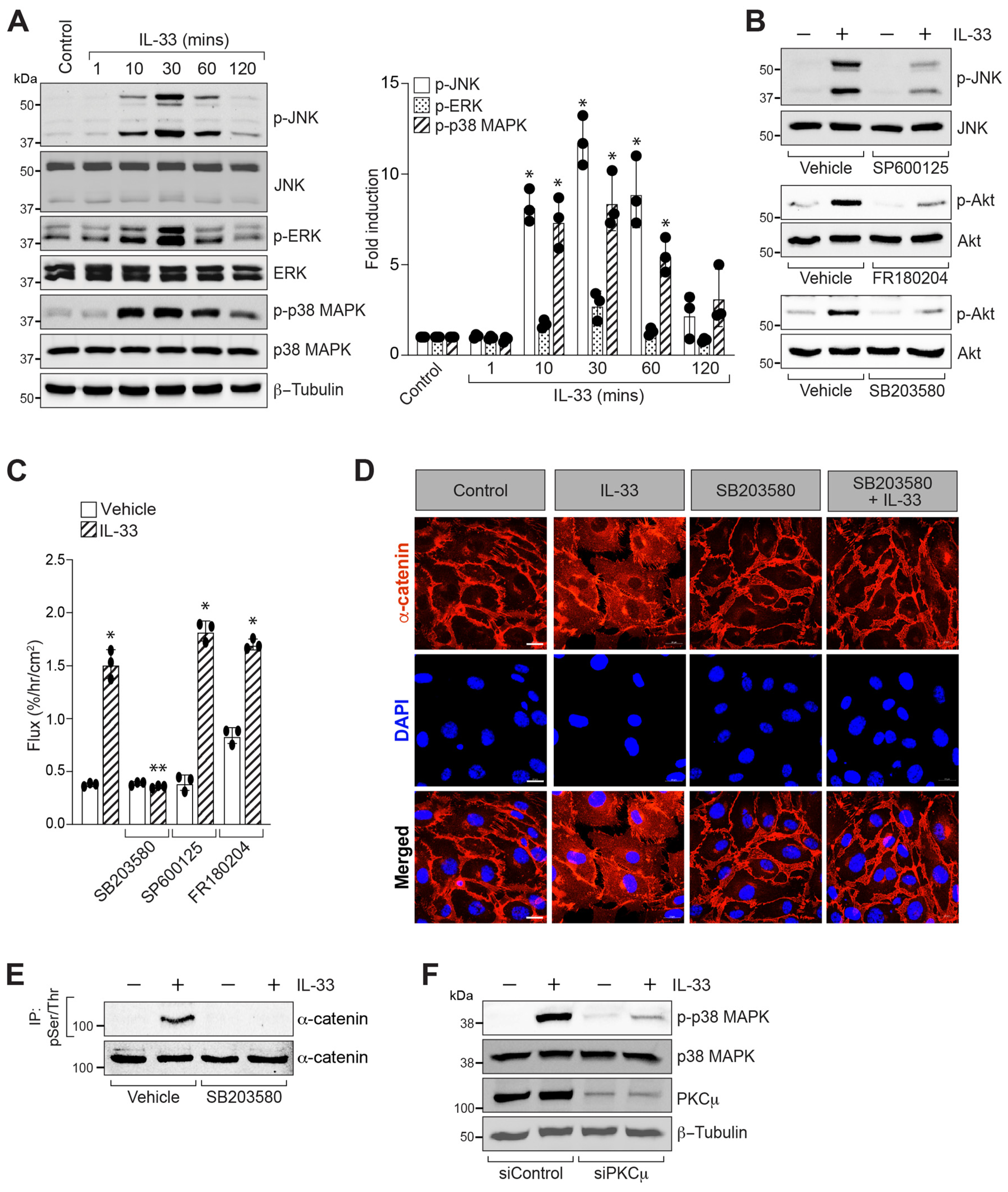
3.4. p38 MAPK Mediates IL-33-Induced Retinal Endothelial Cell-Barrier Disruption
3.5. IL-33 Regulates iBRB Integrity in Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy (OIR)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campochiaro, P.A. Molecular pathogenesis of retinal and choroidal vascular diseases. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 49, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Physiology and Medicine. Cell 2012, 148, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruttiger, M. Development of the retinal vasculature. Angiogenesis 2007, 10, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.L.; Skuli, N.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia-Induced Angiogenesis: Good and Evil. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 1117–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, R.S.; Chen, D.S.; Ferrara, N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell 2019, 176, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, K.L.; Hurwitz, H.I. Anti-VEGF Therapies in the Clinic. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, Y.M.; Sodhi, A. Anti-angiogenic therapy for retinal disease. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 242, 271–307. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.M.; Regillo, C.D. Anti-VEGF Agents in the Treatment of Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration: Applying Clinical Trial Results to the Treatment of Everyday Patients. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 144, 627–637.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghøj, M.S.; Sørensen, T.L. Tachyphylaxis during treatment of exudative age-related macular degeneration with ranibizumab. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, A.K.; Sanfilippo, P.G.; Hewitt, A.W.; Liang, H.; Lamoureux, E.; Wang, J.J.; Connell, P.P. Vitreous biomarkers in diabetic retinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2014, 28, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabrawey, M.; Elsherbiny, M.; Nussbaum, J.; Othman, A.; Megyerdi, S.; Tawfik, A. Targeting neovascularization in ischemic retinopathy: Recent advances. Expert Rev. Ophthalmol. 2013, 8, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Park, J.K.; Duh, E.J. Novel Targets Against Retinal Angiogenesis in Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2012, 12, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shechter, R.; London, A.; Schwartz, M. Orchestrated leukocyte recruitment to immune-privileged sites: Absolute barriers versus educational gates. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, X.; Mao, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Tang, S.; Rizzolo, L.J. Differential Expression of Claudins in Retinas during Normal Development and the Angiogenesis of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 7556–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Stahl, A.; Krah, N.M.; Seaward, M.R.; Dennison, R.J.; Sapieha, P.; Hua, J.; Hatton, C.J.; Juan, A.M.; Aderman, C.M.; et al. Wnt Signaling Mediates Pathological Vascular Growth in Proliferative Retinopathy. Circulation 2011, 124, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, S.; Liew, G.; Michaelides, M. Retinitis pigmentosa-associated cystoid macular oedema: Pathogenesis and avenues of intervention. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 101, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, W.I.; Nelson, W.J. Re-solving the Cadherin-Catenin-Actin Conundrum. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35593–35597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shasby, D.M.; Ries, D.R.; Shasby, S.S.; Winter, M.C. Histamine stimulates phosphorylation of adherens junction proteins and alters their link to vimentin. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2002, 282, L1330–L1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, D.J.; Hyun, S.-W.; Grigoryev, D.N.; Garg, P.; Gong, P.; Singh, I.S.; Passaniti, A.; Hasday, J.D.; Goldblum, S.E. TNF-α increases tyrosine phosphorylation of vascular endothelial cadherin and opens the paracellular pathway through fyn activation in human lung endothelia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L1232–L1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudry-Clergeon, H.; Stengel, D.; Ninio, E.; Vilgrain, I. Platelet-activating factor increases VE-cadherin tyrosine phosphoryla-tion in mouse endothelial cells and its association with the PtdIns3 kinase. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, S.; Lampugnani, M.G.; Corada, M.; Dejana, E.; Risau, W. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces VE-cadherin ty-rosine phosphorylation in endothelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111, 1853–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, S.M.; Cheresh, D.A. Pathophysiological consequences of VEGF-induced vascular permeability. Nature 2005, 437, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, U.; Funke, R.; Ebnet, K.; Vorschmitt, H.; Koch, S.; Vestweber, D. Association of Csk to VE-cadherin and inhibition of cell proliferation. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allingham, M.J.; van Buul, J.D.; Burridge, K. ICAM-1-mediated, Src- and Pyk2-dependent vascular endothelial cadherin ty-rosine phosphorylation is required for leukocyte transendothelial migration. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4053–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallez, Y.; Cand, F.; Cruzalegui, F.; Wernstedt, C.; Souchelnytskyi, S.; Vilgrain, I.; Huber, P. Src kinase phosphorylates vascular endothelial-cadherin in response to vascular endothelial growth factor: Identification of tyrosine 685 as the unique target site. Oncogene 2006, 26, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampugnani, M.G.; Corada, M.; Andriopoulou, P.; Esser, S.; Risau, W.; Dejana, E. Cell confluence regulates tyrosine phos-phorylation of adherens junction components in endothelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavard, J.; Gutkind, J.S. VEGF controls endothelial-cell permeability by promoting the beta-arrestin-dependent endocytosis of VE-cadherin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, K.; Tan, X.; Wu, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, L. Tetramethylpyrazine protects retinal capillary en-dothelial cells (TR-iBRB2) against IL-1β-induced nitrative/oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21775–21790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvette, W.; Ming, M.S.; Riemke, A.B.; Riccardo, N.; Nilisha, F. IL-1 Family Members Mediate Cell Death, Inflammation and Angiogenesis in Retinal Degenerative Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, H.J.; Min, J.K.; Pyun, B.J.; Maeng, Y.S.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kwon, Y.G. Interleukin-33 induces an-giogenesis and vascular permeability through ST2/TRAF6-mediated endothelial nitric oxide production. Blood 2009, 114, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küchler, A.M.; Pollheimer, J.; Balogh, J.; Sponheim, J.; Manley, L.; Sorensen, D.R.; Angelis, P.M.D.; Scott, H.; Haraldsen, G. Nuclear interleukin-33 is generally expressed in resting endothelium but rapidly lost upon angiogenic or proinflammatory ac-tivation. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Bisen, S.; Kaur, G.; Van Buren, E.C.; Rao, G.N.; Singh, N.K. IL-33 enhances Jagged1 mediated NOTCH1 intra-cellular domain (NICD) deubiquitination and pathological angiogenesis in proliferative retinopathy. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, E.J.; Fukuhara, D.; Weström, S.; Padhan, N.; Sjöström, E.O.; van Meeteren, L.; He, L.; Orsenigo, F.; Dejana, E.; Bentley, K.; et al. The endothelial adaptor molecule TSAd is required for VEGF-induced angiogenic sprouting through junctional c-Src activation. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-L.; Chhiba, K.D.; Krier-Burris, R.; Hosakoppal, S.; Berdnikovs, S.; Miller, M.L.; Bryce, P.J. Allergic inflammation is initiated by IL-33–dependent crosstalk between mast cells and basophils. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakso, M.; Pichel, J.G.; Gorman, J.R.; Sauer, B.; Okamoto, Y.; Lee, E.; Alt, F.W.; Westphal, H. Efficient in vivo manipulation of mouse genomic sequences at the zygote stage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5860–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Kundumani-Sridharan, V.; Gadiparthi, L.; Johnson, D.A.; Tigyi, G.J.; Rao, G.N. PLD1-dependent PKCgamma activation downstream to Src is essential for the development of pathologic retinal neovascularization. Blood 2010, 116, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.E.; Wesolowski, E.; McLellan, A.; Kostyk, S.K.; D’Amato, R.; Sullivan, R.; D’Amore, P.A. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- El-Tanani, S.; Yumnamcha, T.; Singh, L.P.; Ibrahim, A.S. Differential Effects of Cytopathic Hypoxia on Human Retinal En-dothelial Cellular Behavior: Implication for Ischemic Retinopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbiner, B.M. Regulation of cadherin-mediated adhesion in morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbleib, J.M.; Nelson, W.J. Cadherins in development: Cell adhesion, sorting, and tissue morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Takeichi, M. Remodeling of the Adherens Junctions during Morphogenesis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2009, 89, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimm, D.L.; Koslov, E.R.; Kebriaei, P.; Cianci, C.D.; Morrow, J.S. Alpha 1(E)-catenin is an actin-binding and -bundling protein mediating the attachment of F-actin to the membrane adhesion complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8813–8817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, R.; Malik, A.B.; Minshall, R.D.; Kouklis, P.; Ellis, C.A.; Tiruppathi, C. Ca2+ signalling and PKCa activate increased endothelial permeability by disassembly of VE-cadherin junctions. J. Physiol. 2001, 533, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pampou, S.; Fujikawa, K.; Varticovski, L. Opposing effect of angiopoietin-1 on VEGF-mediated disruption of en-dothelial cell-cell interactions requires activation of PKC beta. J. Cell Physiol. 2004, 198, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbiev, T.; Birukova, A.; Liu, F.; Nurmukhambetova, S.; Gerthoffer, W.T.; Garcia, J.G.N.; Verin, A.D. p38 MAP kinase-dependent regulation of endothelial cell permeability. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, L911–L918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Dai, Y.; Pan, K.; Deng, Y.; Meng, Y.; Xu, T. PPAR-γ promotes p38 MAP kinase-mediated endothelial cell permeability through activating Sirt3. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.L.; Sasaki, D.T.; Murray, B.W.; O’Leary, E.C.; Sakata, S.T.; Xu, W.; Leisten, J.C.; Motiwala, A.; Pierce, S.; Satoh, Y.; et al. SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13681–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Medina, B.E.; Ross, J.A.; Kirken, R.A. Interleukin-2 Receptor Œ≤ Thr-450 Phosphorylation Is a Positive Regulator for Receptor Complex Stability and Activation of Signaling Molecules. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20972–20983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Jiang, M.S.; Adams, J.L.; Lee, J.C. Pyridinylimidazole Compound SB 203580 Inhibits the Activity but Not the Activation of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 263, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lali, F.V.; Hunt, A.E.; Turner, S.J.; Foxwell, B.M. The pyridinyl imidazole inhibitor SB203580 blocks phosphoinosi-tide-dependent protein kinase activity, protein kinase B phosphorylation, and retinoblastoma hyperphosphorylation in inter-leukin-2-stimulated T cells independently of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 7395–7402. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Ye, J.; Wu, X.; Bian, Z.; Chen, X. The p38 MAPK Inhibitor SB203580 Abrogates Tumor Necrosis Factor-Induced Proliferative Expansion of Mouse CD4+Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daruich, A.; Matet, A.; Moulin, A.; Kowalczuk, L.; Nicolas, M.; Sellam, A.; Rothschild, P.-R.; Omri, S.; Gélizé, E.; Jonet, L.; et al. Mechanisms of macular edema: Beyond the surface. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 63, 20–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, P.; Voronov, E.; Dinarello, C.A.; Apte, R.N.; Cohen, I. Alarmins: Feel the Stress. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Lv, Z.; Yi, D.; Huang, Q.; Corrigan, C.J.; Wang, W.; Quangeng, Z.; Ying, S. Nasal administration of interleukin-33 induces airways angiogenesis and expression of multiple angiogenic factors in a murine asthma surrogate. Immunology 2016, 148, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon, T.; Hemo, I.; Itin, A.; Pe’er, J.; Stone, J.; Keshet, E. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, K.; Franco, C.A.; Philippides, A.; Blanco, R.; Dierkes, M.; Gebala, V.; Stanchi, F.; Jones, M.; Aspalter, I.M.; Cagna, G.; et al. The role of differential VE-cadherin dynamics in cell rear-rangement during angiogenesis. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2014, 16, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, W.H.; Klezovitch, O.; Fernandez, T.E.; Delrow, J.; Vasioukhin, V. alphaE-catenin controls cerebral cortical size by reg-ulating the hedgehog signaling pathway. Science 2006, 311, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpal, R.; Pellikka, M.; Patel, R.R.; Hui, F.Y.; Godt, D.; Tepass, U. Mutational analysis supports a core role for Drosophila Œ±-catenin in adherens junction function. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, C.; Kelleher, D. Protein Kinase C and the Cytoskeleton. Cell. Signal. 1998, 10, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.C. Regulation of protein kinase C. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 1997, 9, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, P.K.; Eker, P.; Sandvig, K.; van Deurs, B. Phorbol Myristate Acetate Selectively Stimulates Apical Endocytosis via Protein Kinase C in Polarized MDCK Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1995, 217, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennartz, M.R. Phospholipases and phagocytosis: The role of phospholipid-derived second messengers in phagocytosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.J.; Tang, H. Identification of Protein Kinase D2 as a Pivotal Regulator of Endothelial Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwendt, M.; Dieterich, S.; Rennecke, J.; Kittstein, W.; Mueller, H.J.; Johannes, F.J. Inhibition of protein kinase C mu by various inhibitors. Differentiation from protein kinase c isoenzymes. FEBS Lett. 1996, 392, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, D. Requirement of protein kinase D tyrosine phosphorylation for VEGF-A165-induced angiogenesis through its interaction and regulation of phospholipase C gamma phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 32550–32558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers Gibson, T.; Xu, B.E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinase Pathways: Regulation and Physiological Functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Elimban, V.; Nijjar, M.S.; Gupta, S.K.; Dhalla, N.S. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2003, 8, 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, M.; de la Blanca, E.P.; Jiménez, E. P2Y Receptors Activate MAPK/ERK through a Pathway Involving PI3K/PDK1/PKC-Zeta in Human Vein Endothelial Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 18, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, L.G.; He, J.-S.; Ostergaard, H.L. A Novel PKC Regulates ERK Activation and Degranulation of Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes: Plasticity in PKC Regulation of ERK. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Song, J.-T.; Ji, X.-F.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Cong, M.-L.; Liu, D.-X. Sodium Ferulate Protects against Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in Mice by Regulating the MAPK/ERK and JNK Pathways. BioMed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 3754942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.-H.; Park, B.-S.; Kim, I.-R.; Sung, I.-Y.; Cho, Y.-C.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, Y.-D. A novel combination treatment to stimulate bone healing and regeneration under hypoxic conditions: Photobiomodulation and melatonin. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cui, B.; Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Du, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, P. Protein kinase D1 regulates hypoxic metabolism through HIF-1Œ± and glycolytic enzymes incancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2018, 40, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vestweber, D.; Wessel, F.; Nottebaum, A.F. Similarities and differences in the regulation of leukocyte extravasation and vas-cular permeability. Semin. Immunopathol. 2014, 36, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, D.; Kaur, G.; Bisen, S.; Sharma, A.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Singh, N.K. IL-33 via PKCμ/PRKD1 Mediated α-Catenin Phosphorylation Regulates Endothelial Cell-Barrier Integrity and Ischemia-Induced Vascular Leakage. Cells 2023, 12, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050703
Sharma D, Kaur G, Bisen S, Sharma A, Ibrahim AS, Singh NK. IL-33 via PKCμ/PRKD1 Mediated α-Catenin Phosphorylation Regulates Endothelial Cell-Barrier Integrity and Ischemia-Induced Vascular Leakage. Cells. 2023; 12(5):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050703
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Deepti, Geetika Kaur, Shivantika Bisen, Anamika Sharma, Ahmed S. Ibrahim, and Nikhlesh K. Singh. 2023. "IL-33 via PKCμ/PRKD1 Mediated α-Catenin Phosphorylation Regulates Endothelial Cell-Barrier Integrity and Ischemia-Induced Vascular Leakage" Cells 12, no. 5: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050703
APA StyleSharma, D., Kaur, G., Bisen, S., Sharma, A., Ibrahim, A. S., & Singh, N. K. (2023). IL-33 via PKCμ/PRKD1 Mediated α-Catenin Phosphorylation Regulates Endothelial Cell-Barrier Integrity and Ischemia-Induced Vascular Leakage. Cells, 12(5), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050703







