Abstract
We performed a systematic search of the PubMed database for English-language articles related to the function of adipose-derived stem cells in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. In preclinical models, adipose-derived stem cells protected arteries and the heart from oxidative stress and inflammation and preserved angiogenesis. However, clinical trials did not reiterate successful treatments with these cells in preclinical models. The low success in patients may be due to aging and metabolic reprogramming associated with the loss of proliferation capacity and increased senescence of stem cells, loss of mitochondrial function, increased oxidative stress and inflammation, and adipogenesis with increased lipid deposition associated with the low potential to induce endothelial cell function and angiogenesis, cardiomyocyte survival, and restore heart function. Then, we identify noncoding RNAs that may be mechanistically related to these dysfunctions of human adipose-derived stem cells. In particular, a decrease in let-7, miR-17-92, miR-21, miR-145, and miR-221 led to the loss of their function with obesity, type 2 diabetes, oxidative stress, and inflammation. An increase in miR-34a, miR-486-5p, and mir-24-3p contributed to the loss of function, with a noteworthy increase in miR-34a with age. In contrast, miR-146a and miR-210 may protect stem cells. However, a systematic analysis of other noncoding RNAs in human adipose-derived stem cells is warranted. Overall, this review gives insight into modes to improve the functionality of human adipose-derived stem cells.
1. Introduction
Adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) are easily acquired with high yields and, therefore, are an ideal stem cell source [1]. The International Fat Applied Technology Society, renamed the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science, reached a consensus referring to adipose-derived stem cells for all plastic-adherent, multipotent cell populations isolated from adipose tissue, instead of referring to adipose stromal cells, adipose-derived adult stem cells, or adipose mesenchymal stem cells [2]. ASCs are commonly isolated from the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of adipose tissue. ASCs in white adipose tissue (WAT) have the potential to become preadipocytes, subsequently differentiating into mature adipocytes via adipogenesis involving the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ). Anatomically separated WAT depots, namely subcutaneous WAT (S-WAT) and visceral WAT (V-WAT), are known to be functionally distinct. S-WAT expands to store excess lipids, thus preventing ectopic lipid disposition and organ damage, while the main function of V-WAT is to cushion and protect the visceral organs [3]. However, apart from adipogenesis, ASCs can acquire properties of specialized cells or induce the differentiation of other cell types, among them endothelial cells (ECs) [4], vascular smooth muscle cells [5], and cardiomyocytes [6]. In culture, ASCs retain markers in common with other mesenchymal stromal/stem cells, including CD90, CD73, CD105, and CD44, and remain negative for CD45 and CD31 [7,8,9,10].In addition, the immunological reactivity of ASCs is low because of the low expression of immunogenic surface antigens (CD40, CD40L, CD80, and CD86) and major histocompatibility complex II, allowing allogeneic use [11]. Finally, ASCs exert paracrine function by producing cytokines and growth factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) [12,13].
This review specifically aims at understanding mechanisms by which ASCs may inhibit atherosclerosis and improve heart function and thus protect against cardiovascular diseases. The initial step in atherosclerosis is endothelial dysfunction through mechanical shear stress and chemical stress induced by high glucose, high LDL and low HDL, high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidized LDL, and ANG-II. Injured endothelium attracts inflammatory cells, among them macrophages. Stress induces the polarization of macrophages from an anti-inflammatory M2 to an inflammatory M1 phenotype. M1 macrophages accumulate lipids and differentiate into foam cells. ROS and lipids induce cell death, thereby destabilizing atherosclerotic plaques. High oxidative stress also increases Th1/Th17 and decreases Th2/Treg cell immune response, further enhancing inflammation and cell death [14,15].
We particularly reviewed the role of ASCs exerting therapeutic effects that rely on paracrine secretion. Indeed, ASCs secrete several cytokines, growth factors, and chemokines that modulate oxidative stress, inflammation, immune responses, angiogenesis, and apoptosis in damaged vascular and heart cells [16]. In the heart, the pericardium consists of a thin fibrous layer, nerves, a vascular network, and adipose mass. It also comprises mesenchymal cells, so-called formed cardiac colony-forming unit fibroblasts that give rise to all mesodermal lineages, including smooth muscle, bone, cartilage, adipose, endothelial, and heart muscle cells [17]. Pericardial ASCs constituted intrinsic properties toward myogenesis and vessel formation and thus provided more potent structural repair, translating into functional amelioration after myocardial injury [18].
We discussed first the effect of ASCs in preclinical models, giving insight into underlying mechanisms. Then, we reviewed the clinical data. Because clinical trials did not reproduce successful treatments with ASCs in preclinical models, we tried to identify molecular explanations for the loss of function of ASCs, focusing on aging and metabolic reprogramming. We considered changes in the expression of noncoding RNAs in addition to changes in protein or lipid content because of their association with metabolic and cardiovascular diseases [19].
Currently, one aims to move from cell-based to cell-free therapy with extracellular exosomes of stem cell origin [20], further reducing the immunogenic response and thus improving the safety and increasing the stability upon storage and obtaining a better targeting of the cells and tissues to be treated [21]. Previously, we showed the role of exosome-mediated cell-to-cell communication in affecting pathways involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases [22,23]. Herein, we discussed particularly the role of exosomes secreted by ASCs.
2. Information Resources, Search, and Study Selection
Figure 1 illustrates the strategy and outcome of the literature search.

Figure 1.
Strategy and outcome of the literature search.
We searched the PubMed database for English-language articles related to adipose-derived stem cells in mechanisms related to cardiovascular diseases. The search strategy encompassed a MESH search: (‘Angiogenesis’ [Mesh] OR ‘Atherosclerosis’ [Mesh] OR ‘Myocardial Infarction’ [Mesh] OR ‘Cardiomyopathy’ [Mesh]) OR ‘Heart’ [Mesh]) AND (‘Adipose-derived stem cells’ [Mesh]), identifying 1327 titles. The figure illustrates reasons for the exclusion of papers from this review paper: 552 papers reported only on in vitro experiments on the differentiation of stem cells including incubation with other cells or other components, such as growth factors and their interaction with scaffolds; 82 papers reported on in vivo experiments, for example, comparing fresh, uncultured cells with cells cultured under different conditions but without any mechanistic explanation for diverging results; 388 papers dealing with, in particular, angiogenesis in other diseases like wound healing, bot formation, and oncogenesis and referring to possible value for cardiovascular diseases; 15 papers published by the same authors in several journals but with basically the same content; 129 not reporting original experimental data like review papers, comments, and editorials. In addition, twenty-five papers were excluded because of flawed designs (too small a number of biological replicates or flawed statistics, for example, by not using consistent numbers of biological replicates) and thirty-six because full text was not available in English. The additional thirty-seven references give background information about the properties of ASCs and mechanisms in angiogenesis, atherosclerosis, and ischemia.
3. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Preserve EC Function in Preclinical Models
Endothelial dysfunction links metabolic abnormalities, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia, to cardiovascular diseases [24]. ASCs may protect ECs and their functions by secreting paracrine factors rather than differentiating into mature ECs [25]. Exosomes from ASCs inhibited the expression of miR-342-5p in ECs, thereby reverting their apoptosis [26] (Figure 2).
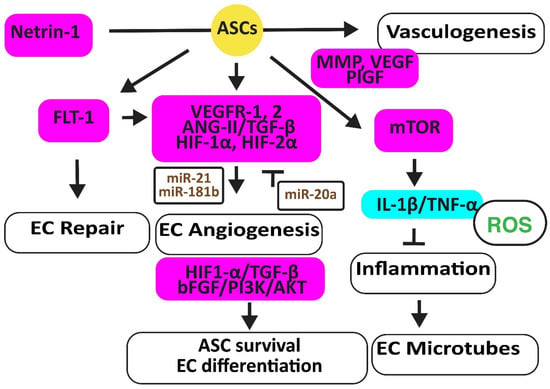
Figure 2.
Adipose-derived stem cells improve EC function. The figure illustrates how adipose-derived stem cells preserve EC repair, angiogenesis, and microtube formation, and how functional ECs preserve the viability and differentiation ability of adipose-derived stem cell differentiation. Increased regulators are in purple boxes and decreased ones are in pale blue boxes. Upregulated noncoding RNAs are in brown. Decreased ROS is in green. Arrowheads reflect activation; hammerheads reflect inhibition.
In a hindlimb ischemic mouse model, ASCs mediated angiogenesis by inducing the FMS-related receptor tyrosine kinase 1 (FLT-1) gene encoding VEGFR1, the kinase insert domain receptor (FLK-1) gene encoding VEGFR2, and the angiopoietin two (ANG-II) gene. ASCs also increased VE-Cadherin, hepatic growth factor (HGF), CD31, myogenic factor (MYF)-5, and TGF-β1 [27]. In addition, hypoxic human ACSs, but not normoxic ASCs, secreted leptin that promoted EC angiogenesis through HIF-2α but not HIF-1α [28]. Furthermore, hypoxia-stimulated ECs secreted TGF-β1, which promoted the viability of ASCs that, in turn, enhanced the angiogenesis ability of human microvascular ECs. However, miR-20a suppressed TGF-β1 [29]. Exosomes secreted by ASCs overexpressing miR-21 promoted vascularization involving HIF-1α, VEGF, stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1), phosphorylated AKT, and phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK1/2) [30]. In addition, exosomal miR-181b induced HIF-1α and VEGF and downregulated the tissue inhibitor of MMP-3, thereby increasing migration ability [31].
Human ASCs overexpressing the high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein increased post-ischemic angiogenesis more than control ASCs through increasing VEGF activity [32]. Engrafted mouse ASCs also induced angiogenesis by activating the mechanistic target of the rapamycin kinase (mTOR) pathway, associated with reduced inflammatory neutrophil/macrophage infiltration, the secretion of pro-inflammatory IL-1β and TNF-α, and apoptosis [33].
Exosomes from ACSs overexpressing glyoxalase-1 (GLO-1) protected ECs from high-glucose stress. They preserved the heart muscle structure and angiogenesis by inducing nitric oxide synthase (NOS), AKT, and MAPK (ERK) and inhibiting the Jun proto-oncogene expression, ROS release, and the activation of the inflammatory nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3). They also inhibited caspase-1 and IL-1β pathways, protecting ECs and cardiomyocytes against cell death [34]. Netrin-1 overexpression increased the vasculogenic capacity of ASCs by inducing metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9, VEGF, and placental growth factor (PlGF) [35] (Figure 2).
4. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Prevent Atherosclerosis in Preclinical Models
Autologous ASCs reduced oxidative stress by increasing the anti-oxidative NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) and heme oxygenase-1 (HMOX1 or HO-1), thereby preventing macrophage polarization from M2 to M1 [36]. In addition, exosomal miR-148a-3p attenuated M1 macrophage polarization and inflammation by activating Notch signaling [37], miR-301a by inhibiting toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 [38], and miR-451 by inhibiting the migration inhibitory factor (MIF) [39]. In addition, blocking miR-130b-3p with H19 in ASCs induced PPARγ and STAT3, promoting macrophage M2 polarization [40]. Hypoxia-induced circular RNA derived from small nucleolar RNA host gene 11 (Circ-SNHG11) in exosomes from ASCs suppressed the high glucose-induced EC damage and retained M2-like macrophage polarization by inhibiting miR-144-3p [41] (Figure 3).
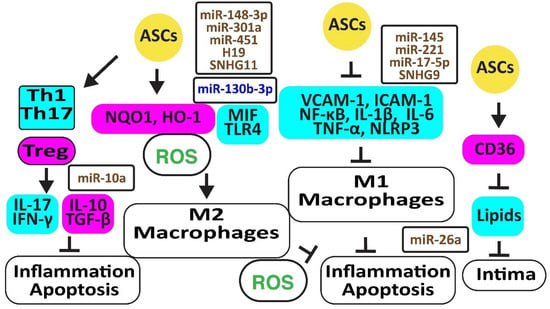
Figure 3.
Adipose-derived stem cells prevent atherosclerosis. The figure illustrates how adipose-derived stem cells preserve protective M2 macrophages and Treg cells associated with decreased oxidative stress and inflammation. Increased regulators are in purple boxes and decreased ones are in pale blue boxes. Upregulated noncoding RNAs are in brown and downregulated ones are in dark blue. Decreased ROS is in green. Arrowheads reflect activation; hammerheads reflect inhibition.
Autologous ASCs reduced inflammation by decreasing the release of vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1, intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB ) in a rat ischemia-reperfusion model [36]. In addition, ASCs inhibited atherosclerosis in a high-fat diet rabbit model by inhibiting the accumulation of oxidized LDL through increased CD36 protein, reverting M1 macrophage polarization, IL-6, and TNF-α release, and apoptosis [42]. Exosomes from ASCs enriched in stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1), a secreted glycoprotein that protects against inflammation, apoptosis, and necrosis, inhibited the production of NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL-1β in ECs, thereby improving angiogenesis [43]. MiR-145 and miR-221 were enriched in ASC exosomes and downregulated pro-inflammatory IL-6, NF-κB, and TNF-α while upregulating anti-inflammatory IL-10 [44]. Exosomal miR-17-5p blocked NLRP3 signaling in ASCs exposed to ANG-II [45]. MiR-26 might also inhibit inflammation by targeting TLR4 [46]. However, inflammatory TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β inhibited the expression of miR-26a in ASCs, reducing their capacity to correct blood lipids [47]. The long noncoding RNA-small nucleolar RNA host gene 9 (lncRNA-SNHG9) in exosomes from ASCs reverted the inflammation and apoptosis of ECs by targeting the TNF receptor type 1-associated death domain protein mRNA [48].
ASCs inhibited the differentiation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells into IL-17-producing Th17 cells by inhibiting RORγt, the key transcription factor for Th17 cells. In contrast, they induced anti-inflammatory CD4+CD25+Foxp3+T regulatory (Treg) cells associated with an increase in IL-10 and TGF-β1 [49]. ASCs also blocked the differentiation of IFN-γ-producing inflammatory Th1 cells [50]. Of interest, rapamycin increased anti-inflammatory TGF-β and IL-10 [51]. MiR-10a-loaded exosomes increased TGF-β1 and decreased IFN-γ [52]. However, miR-10a was downregulated in obesity [53] (Figure 3).
5. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Preserve Heart Function in Preclinical Models
Stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) and its receptor, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), are critical for the recruitment, homing, and engraftment of transplanted ASCs into a myocardial infarction damage site. Activation of the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis by physical training potentiated stem cell therapy reduces vasoconstrictor and inflammatory responses [54]. SDF-1 released by ASCs increased the number of circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and capillary density and reduced hind limb ischemia [55]. Periostin might increase these effects of ACSs, inducing integrin β1, PI3K/AKT, and eNOS [56] (Figure 4).
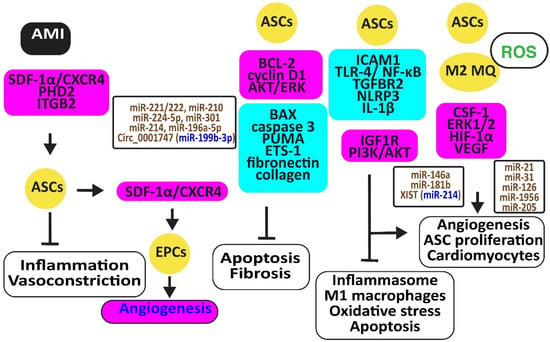
Figure 4.
Adipose-derived stem cells preserve heart function. The figure illustrates how adipose-derived stem cells protect against AMI, injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion and hypoxia-reoxygenation by retaining M2 macrophages, reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, preventing vasoconstriction, and restoring angiogenesis. Increased regulators are in purple boxes and decreased ones are in pale blue boxes. Upregulated noncoding RNAs are in brown and downregulated ones are in dark blue. Decreased ROS is in green. Arrowheads reflect activation; hammerheads reflect inhibition.
Ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) and hypoxia-reoxygenation (H/R) in a rat model triggered myocardial apoptosis through NF-κB, PUMA, and p53, downregulating BCL-2 and upregulating BAX and caspase 3. I/R- and H/R-induced heart damage was associated with fibrosis by inducing ETS-1, fibronectin, and collagen 3 [57]. Intramuscular injection of ASCs or exosomes from ASCs reduced this heart damage and fibrosis by reducing BAX and increasing BCL-2 and cyclin D1. They also inhibited PUMA, ETS-1, fibronectin, and collagen [58]. Of interest, rosuvastatin reinforced the action of ASCs [59]. ASCs in which prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2 (PHD2), a cellular oxygen sensor, was silenced reduced the myocardial infarct size and prevented loss of function in mice by preventing cardiomyocyte cell death [60].
ASC-derived exosomes injected into the myocardium of I/R-treated mice significantly induced miR-221/222 and reduced levels of PUMA and ETS-1, which are associated with lower H2O2-induced apoptosis [61]. MiR-210 in exosomes from hypoxia-exposed ASCs inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis by blocking the expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and death-associated protein kinase 1 [62]. MiR-224-5p increased in exosomes derived from ASCs, downregulated TXNIP, and blocked apoptosis by sustaining the expression of BCL-2 [63], while miR-301 inhibited the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1), decreasing ROS release [64]. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis of miR-214, enriched in the conditioned medium of ASCs, inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis [65]. Circ_0001747, enriched in exosomes from ASCs, elevated the messenger RNA and protein levels of the MCL1 apoptosis regulator, the BCL-2 family member (MCL1), by sequestering miR-199b-3p and attenuating H/R-induced injury [66].
ASCs restored the expression of integrin β2 that specifically blocks ICAM-1 and reduces macrophage accumulation in infarcted myocardium, increasing cell viability, proliferation, and migration [67]. In addition, ASC-derived exosomes mitigated MI-induced cardiac damage by promoting macrophage M2 polarization by restoring the expression of the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1) [68,69]. MiR-146a in ACS-derived exosomes inhibited hypoxia-induced TLR-4 and NF-κB and prevented inflammation-associated myocardial cell apoptosis and fibrosis [70]. MiR-181b also protected cardiomyocytes by suppressing inflammatory TLR4 and NF-κB, cell death signaling, and promoting IGF1R and PI3K/AKT signaling [71]. MiR-671 in ASC-derived exosomes targeted the transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFBR2) and suppressed the phosphorylation of SMAD2, enhancing cardiomyocyte viability and reducing myocardial fibrosis and inflammation [72]. X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) in exosomes from ASCs protected mice against myocardial pyroptosis and arterial fibrillation by reducing the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 in cardiomyocytes by targeting miR-214-3p [73].
ASCs attached to microparticles loaded with neuregulin (NRG) reduced infarct size, stimulated cardiomyocyte proliferation and the formation of arterioles and capillaries, and increased M2 macrophage polarization [74], ultimately promoting angiogenesis through miR-21 and CSF-1 [75]. Hypoxia improved the angiogenic capacity of ASCs by increasing VEGF-A and ANG-II [76]. In addition, exosomes from ASCs promoted angiogenesis by the delivery of miR-31, which targets factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (FIH1) [77]. MiR-126 in ASC-derived exosomes prevented myocardial damage by preventing inflammation, apoptosis, fibrosis, and increasing angiogenesis [78]. Furthermore, miR-205 in exosomes from ASCs increased angiogenesis and improved cardiac function in MI-treated mice by inducing HIF-1α and VEGF [79] (Figure 4).
6. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Are Less Efficient in the Human Clinical Setting Than in Preclinical Models
ASCs delivered to thirteen patients with ischemic heart failure and refractory angina who were not qualified for any form of direct revascularization did not improve LVEF and cardiac output at 12 months of follow-up [80]. In a Danish multi-center double-blinded placebo-controlled phase II study, direct intramyocardial injections of allogeneic ASCs were safe but did not improve myocardial function, structure, or clinical symptoms [81].
The phase II, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled MyStromalCell trial included patients with chronic ischemic heart disease. ASCs did not improve myocardial perfusion, LVEF, myocardial mass, stroke volume, left ventricle end-diastolic volume, end-systolic volume, and the amount of scar tissue [82]. At 3 years follow-up, the bicycle exercise time and the exercise performance in watts were unchanged, but the performance measured in metabolic equivalents (METs) was slightly increased. In the same period, bicycle exercise time and exercise performance declined in the placebo group. Although angina was significantly reduced in the ASC group but not in the placebo group, there was no significant difference between the groups [83]. Furthermore, the intramyocardial delivery of ASCs that were stimulated by VEGF-A165 did not improve exercise ability compared to the placebo [84]. In yet another study including thirty-one patients (seventeen treated with autologous ASCs, fourteen with placebo), ASCs increased the maximal oxygen consumption (MVO2) but not LVEF, left ventricle end-diastolic volume, and end-systolic volume [85]. In the PRECISE Trial, a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial, transendocardial injections of ASCs preserved MRTs and MVO2s while they declined in the control group. The difference in the change in MVO2 from baseline to 6 and 18 months was significantly better in ASC-treated patients compared with the controls. The total left ventricular mass and wall motion score index improved in ASC-treated patients, and inducible ischemia was reduced after 18 months [86]. In the Therapeutic Angiogenesis by Cell Transplantation using ASCs (TACT-ADRC), the ASC cohort improved rest pain and 6 min walking distance. Circulating CD34+ and CD133+ progenitor cell markers increased. The ratio of VEGF-A165b (an anti-angiogenic isoform of VEGF) to total VEGF-A in plasma significantly decreased, as did the TNF-α in macrophages [87]. However, the goal of this study was to assess the effect of autologous ASCs on their ability to promote angiogenesis and suppress tissue inflammation more than their ability to improve heart function.
In conclusion, in contrast to the preclinical models in which ASCs could preserve heart function in patients, they had limited effects. Therefore, we searched for reasons to explain these differences. Comparing the preclinical models and human settings, two main differences emerged. One, most often animals were young and exposed to ischemia for a brief period, whereas heart dysfunction in patients developed over a much longer time. Finally, the age-related metabolic risk factors that contribute to the development of human cardiovascular diseases are not reiterated in animal models. Therefore, in the last part, we looked at the effect of aging and metabolic reprogramming on the functionality of ASCs.
7. Aging and Metabolic Reprogramming Decrease the Number and Function of Human ASCs
Aging is associated with increased oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction-associated cellular damage, contributing to the decline in stemness. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), required for maintaining cellular homeostasis and stemness, decreases not only with age directly but also with age-related metabolic disorders. In addition, NAD+ mitigates the differentiation of ASCs to mature adipocytes, associated with an increase in mitochondrial activity and ROS release [88]. The CD271-positive ASC subpopulation was reduced in the adipose tissues of diabetic patients, associated with decreased angiogenesis and the expression of the adipose stem cell marker SOX2 [89]. Metformin may prevent the differentiation of ASCs to adipocytes and slow down ASC proliferation, preventing these cells from proliferation exhaustion by enhancing the expression of stemness signature genes encoding BMP7, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4 or T-cell activation antigen CD26), SOX2, OCT3/4 (or POU class 5 homeobox 1, POU5F1), WNT2, CD90, and delta-like non-canonical Notch ligand 1 (DLK1) [90]. Older ASCs had an inverse effect on T cell function by augmenting Th1 cells secreting IFN-γ and decreasing the percentage of anti-inflammatory Tregs [91]. Type 2 diabetes may further enhance this age-dependent effect [92]. Furthermore, age impaired the paracrine action of ASCs evidenced by reduced levels of SDF-1α, VEGF, and HGF [93]. In addition, TGF-β1 and proliferative rates of ASCs decreased with donor age [94]. However, another study revealed that a higher number of cell passages has a greater effect on the stemness of ASCs than donor age by itself; for example, by inducing the NF-κB signaling pathway closely related to harmful immune and inflammatory responses [95] (Figure 5).
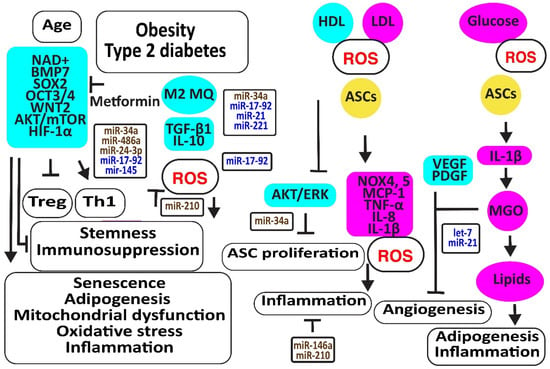
Figure 5.
Aging and metabolic reprogramming decrease the number and function of human adipose-derived stem cells. The figure illustrates how aging, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and hyperlipidemia reduce stemness and induce senescence in ASCs associated with loss of function in association with oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and loss of angiogenesis. Increased regulators are in purple boxes and decreased ones are in pale blue boxes. Upregulated noncoding RNAs are in brown and downregulated ones are in dark blue. Increased ROS is in red. Arrowheads reflect activation; hammerheads reflect inhibition.
MiR-34a is upregulated by high glucose [96]. MiR-34a induced senescence by targeting SIRT1 [97,98,99]. In addition, miR-34a decreased the expression of various cell cycle regulators such as CDKs (-2, -4, -6), cyclins (-E, -D), and stem cell transcription factors KLF-4, OCT-4, SOX-2, and c-Myc. Thereby, it induced adipogenesis and lipid deposition. It increased inflammatory IL-6 and IL-8, further enhancing senescence [100]. In addition, miR-34a, inducing senescence, increased with an increasing number of cell passages [100,101]. MiR-486-5p was increased in obese subjects [102]. The blocking of its overexpression with exosomes from hypoxic ECs activated the AKT/MTOR/HIF-1α pathway, increasing the survival and engraftment of ASCs [103]. MiR-24-3p increased in obese and type 2 diabetes patients [104]. The downregulation of miR-24-3p in ASCs preserved ASC survival by restoring CDK4 expression and phosphorylated Rb protein levels [105]. Its inhibition also improved vascularization and reduced fibrosis after fat grafting [106]. However, ROS- and hypoxia-induced miR-210-3p in diabetic patients reversed the ANG-II-induced mitochondrial ROS accumulation and apoptosis in ASCs, decreased the cell death-inducing p53 target 1 and PKC/Raf-1/MAPK/NF-κB pathways, and increased the proliferation and migration of ASCs through the activation of PDGFR-β, AKT/ERK pathways [107,108,109,110]. MiR-17 was downregulated in diabetic patients [111]. Its downregulation induced oxidative stress and senescence in ASCs by the downregulation of stem cell markers c-Myc, OCT4, and Sca-1, and anti-oxidative HO-1 [112]. MiR-145 was also decreased in obese and diabetic patients, most probably due to a lack of TGF-β1 [113]. Restoring the expression of miR-145-5p in ASCs not only enhanced the expression of migration-associated protein FN1, the proliferation-associated proteins CCNA1 and CCND1, and the stem cell markers NANOG and OCT4 but also improved the functions of ECs and fibroblasts. In addition, miR-145 decreased the expression of senescence-associated protein p21 [114].
Higher LDL and lower HDL levels in patients with metabolic syndrome were associated with more ROS by the induction of oxidative NOX4 and NOX5 and more inflammatory molecules like MCP-1, C-C motif chemokine ligand 3 (CCL3 or MIP1α), and IL-8 [115]. In addition, obese- and particularly type 2 diabetes-derived ASCs released more inflammatory molecules due to the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Remarkably, the immunosuppressive activities of ASCs derived from obese and T2D subjects were reduced and associated with the less effective suppression of lymphocyte proliferation, activation of M2 macrophages, and TGF-β1 secretion than lean-derived ASCs. Treatment of human ASCs from lean subjects with IL-1β mimicked the dysfunctional immune behavior of obese and T2D human ASCs [116]. Exosomes isolated from ASCs enriched in miR-145 and mir-221 downregulated the pro-inflammatory markers IL-6 and NF-κB [44]. However, IFN-γ suppressed miR-221 [117]. In addition, exosomes enriched in miR-21 exerted an anti-inflammatory effect by blocking TLR4 and NF-kB signaling pathways [118]. However, miR-21 was downregulated by high glucose in diabetic patients [119]. In contrast, inflammatory IL-1β produced exosomes that transferred miR-146a to macrophages, protecting them against M1 polarization and reducing TNF-α and Il-6 by repressing NF-κB and AP-1 signaling [120]. Other studies suggested that hypoxia, very small-sized air particles, high glucose, TNF-α, and apolipoprotein E induce miR-146a [121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129].
Hyperglycemia, oxidative stress, altered immune reactions, and inflammation associated with type 2 diabetes limited the promotion of angiogenesis by ASCs [113,130]. Higher glycolysis may be responsible for their reduced angiogenic capacity because methylglyoxal (MGO), a highly reactive dicarbonyl primarily formed as a byproduct of glycolysis in chronic hyperglycemia and diabetes, inhibited VEGF and PDGF release. In addition, MGO induced the differentiation of ASCs to adipocytes, evidenced by the increased expression of PPARγ2 and increased Oil Red-O stainable lipids.
Hypoxia induced let-7 in human ASC-derived extracellular vesicles via the let-7/argonaute 1/VEGF signaling pathway [131]. However, inflammation is associated with an increased expression of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase II (COX2), inducing the methylation of the promoter of let-7 and downregulating let-7 [132]. MiR-21 may increase angiogenesis and enhance its anti-oxidative effects against ROS damage by improving insulin sensitivity by targeting PTEN, inducing PI3K/AKT signaling [133,134]. In addition, miR-21 blocked TLR-4-mediated inflammation [135] (Figure 5).
8. Conclusions
ASCs proved to protect arteries and the heart in preclinical models in which cardiovascular risks associated with obesity, high glucose, low HDL, and high LDL were kept low. When in patients, these risk factors were not controlled; loss of endothelial integrity, oxidative stress, and inflammation may be associated with metabolic reprogramming of ASCs, leading to loss of functionality. Noncoding RNAs were shown to regulate ASC function, and differences in their expression may explain differences in outcomes in preclinical models and patients. Table 1 shows that a decrease in let-7, miR-17-92, miR-21, miR-145, and miR-221 led to the loss of their function with obesity, type 2 diabetes, oxidative stress, and inflammation. An increase in miR-34a, miR-486-5p, and mir-24-3p contributed to the loss of function, with a noteworthy increase in miR-34a with age. In contrast, miR-146a and miR-210 may protect stem cells. However, a systematic analysis of other noncoding RNAs in human adipose-derived stem cells is warranted. Overall, this review gives insight into modes to improve the functionality of human adipose-derived stem cells.

Table 1.
Overview of critical miRs in human adipose-derived stem cells and their regulation by aging and metabolic reprogramming.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhao, L.; Johnson, T.; Liu, D. Therapeutic angiogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells for ischemic diseases. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimble, J.M.; Katz, A.J.; Bunnell, B.A. Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Sugii, S. Adipose Tissue: Understanding the Heterogeneity of Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.J.; McIlhenny, S.; Tulenko, T.; Golesorkhi, N.; Zhang, P.; Larson, R.; Lombardi, J.; Shapiro, I.; DiMuzio, P.J. Endothelial differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells: Effects of endothelial cell growth supplement and shear force. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 152, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, J.; Cai, R.; Kuang, Y. Hypoxia Promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell (VSMC) Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell (ADSC) by Regulating Mettl3 and Paracrine Factors. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 2830565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.K.; Wulur, I.; Alfonso, Z.; Hedrick, M.H. Fat tissue: An underappreciated source of stem cells for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourin, P.; Bunnell, B.A.; Casteilla, L.; Dominici, M.; Katz, A.J.; March, K.L.; Redl, H.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoshimura, K.; Gimble, J.M. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: A joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejaz, A.; Mattesich, M.; Zwerschke, W. Silencing of the small GTPase DIRAS3 induces cellular senescence in human white adipose stromal/progenitor cells. Aging 2017, 9, 860–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Horl, S.; Ejaz, A.; Ernst, S.; Mattesich, M.; Kaiser, A.; Jenewein, B.; Zwierzina, M.E.; Hammerle, S.; Miggitsch, C.; Mitterberger-Vogt, M.C.; et al. CD146 (MCAM) in human cs-DLK1(−)/cs-CD34(+) adipose stromal/progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwierzina, M.E.; Ejaz, A.; Bitsche, M.; Blumer, M.J.; Mitterberger, M.C.; Mattesich, M.; Amann, A.; Kaiser, A.; Pechriggl, E.J.; Horl, S.; et al. Characterization of DLK1(PREF1)+/CD34+ cells in vascular stroma of human white adipose tissue. Stem Cell Res. 2015, 15, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.S.; Lin, G.; Lue, T.F. Allogeneic and xenogeneic transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells in immunocompetent recipients without immunosuppressants. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 2770–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcozzi, C.; Frattini, A.; Borgese, M.; Rossi, F.; Barone, L.; Solari, E.; Valli, R.; Gornati, R. Paracrine effect of human adipose-derived stem cells on lymphatic endothelial cells. Regen. Med. 2020, 15, 2085–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savi, M.; Bocchi, L.; Fiumana, E.; Karam, J.P.; Frati, C.; Bonafe, F.; Cavalli, S.; Morselli, P.G.; Guarnieri, C.; Caldarera, C.M.; et al. Enhanced engraftment and repairing ability of human adipose-derived stem cells, conveyed by pharmacologically active microcarriers continuously releasing HGF and IGF-1, in healing myocardial infarction in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 3012–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginckels, P.; Holvoet, P. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Cardiovascular Diseases and Cancer: Role of Non-coding RNAs. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2022, 95, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakkers, T.R.; Mokry, M.; Civelek, M.; Erdmann, J.; Pasterkamp, G.; Diez Benavente, E.; den Ruijter, H.M. Sex differences in the genetic and molecular mechanisms of coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2023, 384, 117279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghadban, S.; Bunnell, B.A. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Immunomodulatory Effects and Therapeutic Potential. Physiology 2020, 35, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.J.; Chandrakanthan, V.; Xaymardan, M.; Asli, N.S.; Li, J.; Ahmed, I.; Heffernan, C.; Menon, M.K.; Scarlett, C.J.; Rashidianfar, A.; et al. Adult cardiac-resident MSC-like stem cells with a proepicardial origin. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 9, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Nie, L.; Xu, L.; Chen, M.; Ding, Z. Myogenic differentiation and reparative activity of stromal cells derived from pericardial adipose in comparison to subcutaneous origin. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsmans, M.; Holvoet, P. MicroRNA-containing microvesicles regulating inflammation in association with atherosclerotic disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 100, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizoso, F.J.; Eiro, N.; Cid, S.; Schneider, J.; Perez-Fernandez, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, K.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S. A “cell-free treatment” for tendon injuries: Adipose stem cell-derived exosomes. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, H.J.; Holvoet, P. Exosomes: Emerging roles in communication between blood cells and vascular tissues during atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2015, 26, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaverbeke, M.; Gal, D.; Holvoet, P. Functional Role of Cardiovascular Exosomes in Myocardial Injury and Atherosclerosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 998, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietrantonio, N.; Di Tomo, P.; Mandatori, D.; Formoso, G.; Pandolfi, A. Diabetes and Its Cardiovascular Complications: Potential Role of the Acetyltransferase p300. Cells 2023, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Suzuki, E.; Oba, S.; Nishimatsu, H.; Kimura, K.; Nagano, T.; Nagai, R.; Hirata, Y. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells inhibit neointimal formation in a paracrine fashion in rat femoral artery. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 298, H415–H423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Xiao, Y. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome-mediated microRNA-342-5p protects endothelial cells against atherosclerosis. Aging 2020, 12, 3880–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, N.B.; Le, H.T.; Dao, T.T.; Phi, L.T.; Phan, N.K.; Ta, V.T. Allogeneic Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Enhances the Expression of Angiogenic Factors in a Mouse Acute Hindlimb Ischemic Model. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1083, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Monache, S.; Calgani, A.; Sanita, P.; Zazzeroni, F.; Gentile Warschauer, E.; Giuliani, A.; Amicucci, G.; Angelucci, A. Adipose-derived stem cells sustain prolonged angiogenesis through leptin secretion. Growth Factors 2016, 34, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X. HIF1A/miR-20a-5p/TGFbeta1 axis modulates adipose-derived stem cells in a paracrine manner to affect the angiogenesis of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 2091–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Zhao, J.; Nie, F.; Qin, Z.; Xue, H.; Wang, G.; Li, D. Exosomes from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) Overexpressing miR-21 Promote Vascularization of Endothelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z. Exosomes Secreted by Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Contribute to Angiogenesis of Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Following Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation In Vitro Through MicroRNA-181b/TRPM7 Axis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 65, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscetti, F.; Gentileschi, S.; Bertucci, F.; Servillo, M.; Arena, V.; Angelini, F.; Stigliano, E.; Bonanno, G.; Scambia, G.; Sacchetti, B.; et al. The angiogenic properties of human adipose-derived stem cells (HASCs) are modulated by the High mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1). Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 249, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Cheng, K.; Qin, X.; Narsinh, K.H.; Wang, S.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.C.; Xiong, L.; et al. mTORC1 and mTORC2 play different roles in the functional survival of transplanted adipose-derived stromal cells in hind limb ischemic mice via regulating inflammation in vivo. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Pu, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, B.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.; Qin, J.; et al. Exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing glyoxalase-1 protect endothelial cells and enhance angiogenesis in type 2 diabetic mice with limb ischemia. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.L.; Zhu, J.W.; Gao, X.M. Netrin-1 promotes the vasculogenic capacity of human adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2023, 24, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.K.; Yen, C.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Tsai, T.H.; Chang, L.T.; Kao, Y.H.; Chua, S.; Fu, M.; Ko, S.F.; Leu, S.; et al. Autologous transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells markedly reduced acute ischemia-reperfusion lung injury in a rodent model. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Cao, M.; Tao, K.; Xie, S.; Hu, D. Extracellular Vesicles From Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells Affect Notch-miR148a-3p Axis to Regulate Polarization of Macrophages and Alleviate Sepsis in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.W.; Huang, K.T.; Nakano, T.; Chiu, K.W.; Chen, K.D.; Goto, S.; Chen, C.L. MicroRNA-301a inhibition enhances the immunomodulatory functions of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by induction of macrophage M2 polarization. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 2058738420966092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Ji, P. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells regulate M1/M2 macrophage phenotypic polarization to promote bone healing via miR-451a/MIF. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qian, L.; Pi, L.; Meng, X. A therapeutic role of exosomal lncRNA H19 from adipose mesenchymal stem cells in cutaneous wound healing by triggering macrophage M2 polarization. Cytokine 2023, 165, 156175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, H.; Shi, J.; Zhao, H. Hypoxic ADSC-derived exosomes enhance wound healing in diabetic mice via delivery of circ-Snhg11 and induction of M2-like macrophage polarization. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Liang, W.; Shang, H.; Li, H.; Han, Y.; Zhao, W.; Bai, L.; Qin, C. Allogeneic Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Alleviates Atherosclerotic Plaque by Inhibiting Ox-LDL Uptake, Inflammatory Reaction and Endothelial Damage in Rabbits. Cells 2023, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Shi, H.; Peng, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, W.; Lu, X. Exosomes from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing Stanniocalcin-1 Promote Reendothelialization After Carotid Endarterium Mechanical Injury. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, J.Y.; Peng, W.M.; Yuan, B.; Bi, Q.; Xu, Y.J. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells promote chondrogenesis and suppress inflammation by upregulating miR-145 and miR-221. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, Z.; Qin, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Xu, Z.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Exosomal miR-17-5p from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibits abdominal aortic aneurysm by suppressing TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhu, X.; Shi, J. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-26a-5p target TLR4 and protect against diabetic nephropathy. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 12868–12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Yi, C.; Yu, B.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, B.; He, D. The roles and mechanisms of miR-26 derived from exosomes of adipose-derived stem cells in the formation of carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, H.; Ren, X.; Li, H.; Feng, C. SNHG9, delivered by adipocyte-derived exosomes, alleviates inflammation and apoptosis of endothelial cells through suppressing TRADD expression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 872, 172977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, F.; Feng, J. Adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate atopic dermatitis by suppressing the IL-17 expression of Th17 cells in an ovalbumin-induced mouse model. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, A.; Pourfathollah, A.A.; Shahrokhi, S.; Hashemi, S.M.; Moradi, S.L.; Soleimani, M. Immunomodulatory effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the gene expression of major transcription factors of T cell subsets. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 20, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Moon, S.J.; Park, M.J.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, E.J.; Chung, B.H.; Yang, C.W.; Cho, M.L. Optimization of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by rapamycin in a murine model of acute graft-versus-host disease. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolandi, Z.; Mokhberian, N.; Eftekhary, M.; Sharifi, K.; Soudi, S.; Ghanbarian, H.; Hashemi, S.M. Adipose derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes loaded with miR-10a promote the differentiation of Th17 and Treg from naive CD4(+) T cell. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, S.; Mandal, M.; Rakib, A.; Bajwa, A.; Singh, U.P. miR-10a-3p modulates adiposity and suppresses adipose inflammation through TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling pathway. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1213415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaun, M.I.; Kristochek, M.; Dias, L.D.; Peres, T.R.; Lehnen, A.M.; Irigoyen, M.C.; Markoski, M.M. Physical training prior to myocardial infarction potentializes stem cell therapy, SDF-1/CXCR4 axis activation and inhibits the vasoconstrictor response in hypertensive rats. Cytokine 2020, 126, 154912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Shintani, S.; Shibata, R.; Murakami, H.; Murakami, R.; Imaizumi, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Murohara, T. Implantation of adipose-derived regenerative cells enhances ischemia-induced angiogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Yuan, F.; Peng, Z.; Ye, K.; Yang, X.; Huang, L.; Jiang, M.; Lu, X. Periostin enhances adipose-derived stem cell adhesion, migration, and therapeutic efficiency in Apo E deficient mice with hind limb ischemia. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.L.; Lai, T.C.; Lin, S.R.; Lin, S.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Pu, C.M.; Lee, I.T.; Tsai, J.S.; Lee, C.W.; Chen, Y.L. Conditioned medium from adipose-derived stem cells attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury through the microRNA-221/222/PUMA/ETS-1 pathway. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3131–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; He, Z.; Liang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. Exosomes From Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect the Myocardium Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 70, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Cui, M.; Gao, X.; Sun, D.; Qin, X.; Narsinh, K.; Li, C.; Jia, H.; Li, C.; et al. Rosuvastatin enhances the therapeutic efficacy of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for myocardial infarction via PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK pathways. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2013, 108, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.E.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Peng, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, P.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, J.; et al. Prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2 silencing enhances the survival and paracrine function of transplanted adipose-derived stem cells in infarcted myocardium. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.C.; Lee, T.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, S.R.; Lin, S.W.; Pu, C.M.; Tsai, J.S.; Chen, Y.L. MicroRNA-221/222 Mediates ADSC-Exosome-Induced Cardioprotection Against Ischemia/Reperfusion by Targeting PUMA and ETS-1. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 569150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.W.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, R.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Chang, W. Multiplexed targeting of miRNA-210 in stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promotes selective regeneration in ischemic hearts. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Li, D.; Zhou, E.; Gao, E.; Zhang, T.; Sun, S.; Gao, L.; Fan, Y.; Wang, C. Extracellular vesicles from anoxia preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Aging 2021, 13, 6156–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.; Seo, H.H.; Lim, K.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.; Lim, S.; et al. MicroRNA-Mediated Down-Regulation of Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1 (ASK1) Attenuates the Apoptosis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Transplanted into Infarcted Heart. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, S.; Takefuji, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Ishihama, S.; Mori, Y.; Tsuda, T.; Takikawa, T.; Yoshida, T.; Ohashi, K.; Shimizu, Y.; et al. Cardiomyocytes capture stem cell-derived, anti-apoptotic microRNA-214 via clathrin-mediated endocytosis in acute myocardial infarction. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11665–11674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Dai, Z.; Ren, M.; Yang, M. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes with High Amounts of Circ_0001747 Alleviate Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Injury in Myocardial Cells by Targeting MiR-199b-3p/MCL1 Axis. Int. Heart J. 2022, 63, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Yan, K.; Wang, J. Overexpression of integrin beta(2) improves migration and engraftment of adipose-derived stem cells and augments angiogenesis in myocardial infarction. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Zhou, X.; Ge, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 114, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wei, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, T.; Pi, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; et al. Vascular endothelial S1pr1 ameliorates adverse cardiac remodelling via stimulating reparative macrophage proliferation after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Alimujiang, M.; Chen, Q.; Shi, H.; Luo, X. Exosomes derived from miR-146a-modified adipose-derived stem cells attenuate acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage via downregulation of early growth response factor 1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 4433–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.S.; Battsengel, S.; Kuo, C.H.; Pan, L.F.; Lin, Y.M.; Yao, C.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Lin, F.H.; Kuo, W.W.; Huang, C.Y. Stem cells rescue cardiomyopathy induced by P. gingivalis-LPS via miR-181b. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 5869–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, W.; He, Y.; Yang, Q. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Carry MicroRNA-671 to Alleviate Myocardial Infarction Through Inactivating the TGFBR2/Smad2 Axis. Inflammation 2021, 44, 1815–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Liu, T.; Yao, C.; Liu, X.; Du, Q.; Pan, L. LncRNA XIST shuttled by adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles suppresses myocardial pyroptosis in atrial fibrillation by disrupting miR-214-3p-mediated Arl2 inhibition. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Herraez, P.; Saludas, L.; Pascual-Gil, S.; Simon-Yarza, T.; Abizanda, G.; Prosper, F.; Garbayo, E.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J. Transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells combined with neuregulin-microparticles promotes efficient cardiac repair in a rat myocardial infarction model. J. Control. Release 2017, 249, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Johnson, T.K.; Wang, Y.; Thomas, M.; Huynh, K.; Yang, Q.; Bond, V.C.; Chen, Y.E.; Liu, D. Macrophage M2 polarization induced by exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells contributes to the exosomal proangiogenic effect on mouse ischemic hindlimb. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, S.T.; Lokmic, Z.; Peshavariya, H.; Abberton, K.M.; Dusting, G.J.; Lim, S.Y.; Dilley, R.J. Hypoxic conditioning enhances the angiogenic paracrine activity of human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Thomas, M.; McLaughlin, K.; Oguljahan, B.; Henderson, J.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.E.; Liu, D. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells alleviate myocardial infarction via microRNA-31/FIH1/HIF-1alpha pathway. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2022, 162, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Guo, D.; Liu, G.; Chen, G.; Hang, M.; Jin, M. Exosomes from MiR-126-Overexpressing Adscs Are Therapeutic in Relieving Acute Myocardial Ischaemic Injury. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 2105–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, T.; Niu, X.; Hu, L.; Cheng, J.; Guo, D.; Ren, H.; Zhao, R.; Ji, Z.; Liu, P.; et al. ADSC-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial infarction injury by promoting miR-205-mediated cardiac angiogenesis. Biol. Direct 2023, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstanty-Kalandyk, J.; Sadowski, J.; Kedziora, A.; Urbanczyk-Zawadzka, M.; Baran, J.; Banys, P.; Kapelak, B.; Piatek, J. Functional Recovery after Intramyocardial Injection of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells Assessed by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 5556800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A.A.; Mouridsen, M.; Nilsson, B.; Gustafsson, I.; Schou, M.; Nielsen, O.W.; Hove, J.D.; Mathiasen, A.B.; Jorgensen, E.; Helqvist, S.; et al. Danish phase II trial using adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stromal cells for patients with ischaemic heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 1170–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayyum, A.A.; Mathiasen, A.B.; Mygind, N.D.; Vejlstrup, N.G.; Kastrup, J. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging used for Evaluation of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cell Therapy in Patients with Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayyum, A.A.; Mathiasen, A.B.; Helqvist, S.; Jorgensen, E.; Haack-Sorensen, M.; Ekblond, A.; Kastrup, J. Autologous adipose-derived stromal cell treatment for patients with refractory angina (MyStromalCell Trial): 3-years follow-up results. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayyum, A.A.; Mathiasen, A.B.; Mygind, N.D.; Kuhl, J.T.; Jorgensen, E.; Helqvist, S.; Elberg, J.J.; Kofoed, K.F.; Vejlstrup, N.G.; Fischer-Nielsen, A.; et al. Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells for Treatment of Patients with Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease (MyStromalCell Trial): A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 5237063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, T.D.; Pepine, C.J.; Lambert, C.R.; Traverse, J.H.; Schatz, R.; Costa, M.; Povsic, T.J.; David Anderson, R.; Willerson, J.T.; Kesten, S.; et al. The Athena trials: Autologous adipose-derived regenerative cells for refractory chronic myocardial ischemia with left ventricular dysfunction. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 89, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, E.C.; Sanz-Ruiz, R.; Sanchez, P.L.; Lasso, J.; Perez-Cano, R.; Alonso-Farto, J.C.; Perez-David, E.; Fernandez-Santos, M.E.; Serruys, P.W.; Duckers, H.J.; et al. Adipose-derived regenerative cells in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: The PRECISE Trial. Am. Heart J. 2014, 168, 88–95.e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, T.; Kondo, K.; Shibata, R.; Hayashida, R.; Shintani, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Unno, K.; Kikuchi, R.; Kodama, A.; et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis using autologous adipose-derived regenerative cells in patients with critical limb ischaemia in Japan: A clinical pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnapaka, S.; Malekzadeh, H.; Tirmizi, Z.; Arellano, J.A.; Ejaz, A. Nicotinamide Riboside Improves Stemness of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Inhibits Terminal Adipocyte Differentiation. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, O.; Usui, S.; Takashima, S.I.; Nomura, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takeda, Y.; Goten, C.; Hamaoka, T.; Ootsuji, H.; Murai, H.; et al. Diabetes impairs the angiogenic capacity of human adipose-derived stem cells by reducing the CD271(+) subpopulation in adipose tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 517, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnapaka, S.; Yang, K.S.; Flowers, Q.; Faisal, M.; Nerone, W.V.; Rubin, J.P.; Ejaz, A. Metformin Improves Stemness of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by Downmodulation of Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) Signaling. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.; Yao, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of age on biological and functional characterization of adipose-derived stem cells from patients with end-stage liver disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3510–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.H.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhou, H.M.; Song, M.; Li, Y.H.; Tang, M.X.; et al. Adipose-derived stem cells were impaired in restricting CD4(+)T cell proliferation and polarization in type 2 diabetic ApoE(-/-) mouse. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 87, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Park, G.; Hong, H.S. Age affects the paracrine activity and differentiation potential of human adipose-derived stem cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Cao, L.; He, W. The Effect of Age on the Regenerative Potential of Human Eyelid Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 5654917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.M.; Rong, Y.X.; Liang, Z.J.; Hunag, D.L.; Ma, Y.F.; Luo, Z.Z.; Wu, F.X.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Mo, S.; et al. Landscape of transcription and expression regulated by DNA methylation related to age of donor and cell passage in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Aging 2020, 12, 21186–21201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, J.; Roy, S.; Dhas, Y.; Mishra, N. Senescence-associated miR-34a and miR-126 in middle-aged Indians with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liang, W.; Tian, Y.; Ma, F.; Huang, W.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, H. Inhibition of P53/miR-34a improves diabetic endothelial dysfunction via activation of SIRT1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3538–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Muhlinen, N.; Horikawa, I.; Alam, F.; Isogaya, K.; Lissa, D.; Vojtesek, B.; Lane, D.P.; Harris, C.C. p53 isoforms regulate premature aging in human cells. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2379–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Cui, R.; Gu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, X.; Liu, C.; Qu, K.; Lin, T. Identification of Four Oxidative Stress-Responsive MicroRNAs, miR-34a-5p, miR-1915-3p, miR-638, and miR-150-3p, in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 5189138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, H.; Pak, H.J.; Yang, D.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, W.J.; Park, S.J.; Cho, J.A.; Lee, K.W. miR-34a inhibits differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells by regulating cell cycle and senescence induction. Differentiation 2015, 90, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhberian, N.; Bolandi, Z.; Eftekhary, M.; Hashemi, S.M.; Jajarmi, V.; Sharifi, K.; Ghanbarian, H. Inhibition of miR-34a reduces cellular senescence in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells through the activation of SIRT1. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, I.; Sotoda, Y.; Groschner, K.; Rainer, P.P.; Sourij, H. Differences in circulating obesity-related microRNAs in Austrian and Japanese men: A two-country cohort analysis. Metabol. Open 2022, 15, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Tang, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Mei, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Small extracellular vesicles of hypoxic endothelial cells regulate the therapeutic potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via miR-486-5p/PTEN in a limb ischemia model. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ares Blanco, J.; Lambert, C.; Fernandez-Sanjurjo, M.; Morales-Sanchez, P.; Pujante, P.; Pinto-Hernandez, P.; Iglesias-Gutierrez, E.; Menendez Torre, E.; Delgado, E. miR-24-3p and Body Mass Index as Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors in Spanish Women 15 Years after Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, X.; Cai, M.Y.; Shao, T.; Xu, Z.Y.; Liao, Z.; Liu, D.L.; Zhou, M.Y.; Wu, W.P.; Zhou, Y.L.; Mo, M.H.; et al. A circular intronic RNA ciPVT1 delays endothelial cell senescence by regulating the miR-24-3p/CDK4/pRb axis. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Li, Z.; Wei, Q.; Yang, F.; Li, T.; Ke, C.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Ni, B.; Lin, M.; et al. MiR-24-3p regulates the differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells toward pericytes and promotes fat grafting vascularization. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, S.G.; Song, S.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Sung, J.H. Reactive oxygen species-responsive miR-210 regulates proliferation and migration of adipose-derived stem cells via PTPN2. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.H.; Barik, P.; Hsieh, D.J.; Day, C.H.; Ho, T.J.; Chen, R.J.; Kuo, W.W.; Padma, V.V.; Shibu, M.A.; Huang, C.Y. Inhibition of cell death-inducing p53 target 1 through miR-210-3p overexpression attenuates reactive oxygen species and apoptosis in rat adipose-derived stem cells challenged with Angiotensin II. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 532, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.A.; Chang, L.; Cheung, J.; Aouizerat, B.E.; Jelliffe-Pawlowski, L.L.; McLemore, M.R.; Piening, B.; Rand, L.; Ryckman, K.K.; Flowers, E. Systematic review of transcriptome and microRNAome associations with gestational diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 971354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Xing, F.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; He, L.; Ren, C.; Liu, L.; So, K.F.; Xiao, J. Precise Regulation of miR-210 Is Critical for the Cellular Homeostasis Maintenance and Transplantation Efficacy Enhancement of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Acute Liver Failure Therapy. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicka, M.; Major, P.; Wysocki, M.; Marycz, K. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Show Reduced “Stemness” through an Altered Secretome Profile, Impaired Anti-Oxidative Protection, and Mitochondrial Dynamics Deterioration. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Lopez, S.; Albo-Castellanos, C.; Urdinguio, R.G.; Canon, S.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Martinez-Serrano, A.; Fraga, M.F.; Bernad, A. Deregulation of the imprinted DLK1-DIO3 locus ncRNAs is associated with replicative senescence of human adipose-derived stem cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhoyashvili, N.A.; Efimenko, A.Y.; Kochegura, T.N.; Kalinina, N.I.; Koptelova, N.V.; Sukhareva, O.Y.; Shestakova, M.V.; Akchurin, R.S.; Tkachuk, V.A.; Parfyonova, Y.V. Disturbed angiogenic activity of adipose-derived stromal cells obtained from patients with coronary artery disease and diabetes mellitus type 2. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Xiong, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Jiang, T.; Xu, Z.; Yuan, M.; Liu, Y.; et al. The whole profiling and competing endogenous RNA network analyses of noncoding RNAs in adipose-derived stem cells from diabetic, old, and young patients. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva-Olivera, W.; Lhamyani, S.; Coin-Araguez, L.; Castellano-Castillo, D.; Alcaide-Torres, J.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; El Bekay, R.; Tinahones, F.J. Neovascular deterioration, impaired NADPH oxidase and inflammatory cytokine expression in adipose-derived multipotent cells from subjects with metabolic syndrome. Metabolism 2017, 71, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serena, C.; Keiran, N.; Ceperuelo-Mallafre, V.; Ejarque, M.; Fradera, R.; Roche, K.; Nunez-Roa, C.; Vendrell, J.; Fernandez-Veledo, S. Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Alters the Immune Properties of Human Adipose Derived Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 2559–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, M.; Zeremski, M.; Talal, A.H.; Ginwala, R.; Elrod, E.; Grakoui, A.; Li, Q.-G.; Philip, R.; Khan, Z.K.; Jain, P. IFN-alpha-Induced Downregulation of miR-221 in Dendritic Cells: Implications for HCV Pathogenesis and Treatment. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015, 35, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Yu, R. Exosomes From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Suppress the Progression of Chronic Endometritis. Cell Transplant. 2023, 32, 9636897231173736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Yu, M.; Zhao, J.; Mei, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Yu, M.; Liu, F.; Chen, G. miR-21-3p regulates AGE/RAGE signalling and improves diabetic atherosclerosis. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2020, 38, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Hu, R.; Runtsch, M.C.; Kagele, D.A.; Mosbruger, T.L.; Tolmachova, T.; Seabra, M.C.; Round, J.L.; Ward, D.M.; O’Connell, R.M. Exosome-delivered microRNAs modulate the inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.C.; Wu, Y.P.; Li, X.D.; Chen, S.H.; Ye, X.J.; Xue, X.Y.; Xu, N. TNF-alpha-induced exosomal miR-146a mediates mesenchymal stem cell-dependent suppression of urethral stricture. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 23243–23255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Huang, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, L.; Feng, D.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Q. miR-146a-5p Mediates Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Injury in H9c2 Cells by Targeting XIAP. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6581217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Liao, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G. PM2.5 Upregulates MicroRNA-146a-3p and Induces M1 Polarization in RAW264.7 Cells by Targeting Sirtuin1. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, G.; Wang, F.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Hypoxia-Regulated miR-146a Targets Cell Adhesion Molecule 2 to Promote Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, W.Y.; Peng, C.T.; Wang, H.J. MicroRNA-146a-5p Mediates High Glucose-Induced Endothelial Inflammation via Targeting Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 1 Expression. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Feng, B.; Thomas, A.A.; Chakrabarti, S. miR-146a regulates glucose induced upregulation of inflammatory cytokines extracellular matrix proteins in the retina and kidney in diabetes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prattichizzo, F.; Giuliani, A.; Recchioni, R.; Bonafe, M.; Marcheselli, F.; De Carolis, S.; Campanati, A.; Giuliodori, K.; Rippo, M.R.; Brugè, F.; et al. Anti-TNF-alpha treatment modulates SASP and SASP-related microRNAs in endothelial cells and in circulating angiogenic cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11945–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, M.A.; Satoh, M.; Chan, E.K. Interleukin 1beta-Responsive MicroRNA-146a Is Critical for the Cytokine-Induced Tolerance and Cross-Tolerance to Toll-Like Receptor Ligands. J. Innate Immun. 2015, 7, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, J.; Dai, L.; Yu, D.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Dai, K. miR-146a, an IL-1beta responsive miRNA, induces vascular endothelial growth factor and chondrocyte apoptosis by targeting Smad4. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, X. Role of Hyperglycemia in the Senescence of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 665412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S.; Yi, Y. Extracellular vesicles derived from human adipose-derived stem cells promote the exogenous angiogenesis of fat grafts via the let-7/AGO1/VEGF signalling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooki, A.; Del Carmen Rodriguez Pena, M.; Marchionni, L.; Dinalankara, W.; Begum, A.; Hahn, N.M.; VandenBussche, C.J.; Rasheed, Z.A.; Mao, S.; Netto, G.J.; et al. YAP1 and COX2 Coordinately Regulate Urothelial Cancer Stem-like Cells. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, H.; Fu, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. miR-21 modification enhances the performance of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for counteracting urethral stricture formation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5607–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Long, X.; Deng, W.; Wang, Z. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21 protects C-kit+ cardiac stem cells from oxidative injury through the PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, R.; Chen, S. miR-21-5p in extracellular vesicles obtained from adipose tissue-derived stromal cells facilitates tubular epithelial cell repair in acute kidney injury. Cytotherapy 2023, 25, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).