Exhaled Nitric Oxide as Biomarker of Type 2 Diseases
Abstract
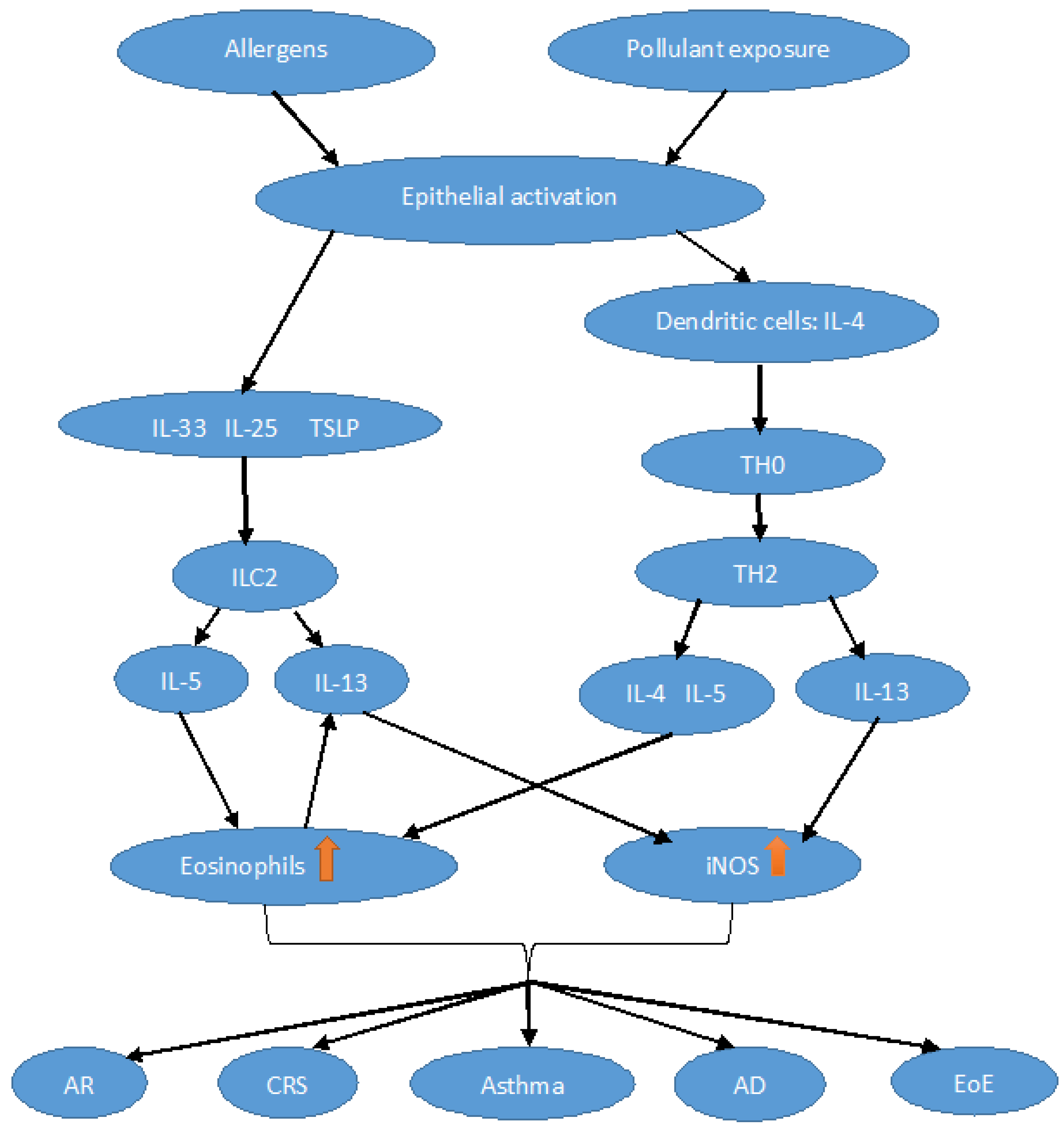
1. Introduction
2. Physiopathological Aspects
3. Exhaled NO in Type 2 Lower Airway Diseases
3.1. FeNO in T2 High Asthma
3.2. FeNO in Cough Variant Asthma
3.3. FeNO in COPD
4. Exhaled NO in Type 2 Upper Airway Diseases
4.1. FeNO in Allergic Rhinitis
4.2. FeNO in Chronic Rhino-Sinusitis
5. FeNO in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
6. Exhaled NO in Other Type 2 Diseases
6.1. Atopic Dermatitis
6.2. Food Allergy
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiss, H.; Orlos, Z.; Gellert, A.; Megyesfalvi, Z.; Mikaczo, A.; Sarkozi, A.; Vasko, A.; Miklos, Z.; Horvath, I. Exhaled Biomarkers for Point-of-Care Diagnosis: Recent Advances and New Challenges in Breathomics. Micromachines 2023, 14, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, S.; Palmer, R.M.; Higgs, E.A. Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991, 43, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Escamilla-Gil, J.M.; Fernandez-Nieto, M.; Acevedo, N. Understanding the Cellular Sources of the Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) and Its Role as a Biomarker of Type 2 Inflammation in Asthma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5753524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medrek, S.K.; Parulekar, A.D.; Hanania, N.A. Predictive Biomarkers for Asthma Therapy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormile, M.; Mormile, I.; Fuschillo, S.; Rossi, F.W.; Lamagna, L.; Ambrosino, P.; de Paulis, A.; Maniscalco, M. Eosinophilic Airway Diseases: From Pathophysiological Mechanisms to Clinical Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alving, K.; Malinovschi, A. Basic aspects of exhaled nitric oxide. Eur. Respir. Monogr. 2010, 49, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadoran, Z.; Carlstrom, M.; Mirmiran, P.; Ghasemi, A. Nitric oxide: To be or not to be an endocrine hormone? Acta. Physiol. 2020, 229, e13443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoiland, R.L.; Caldwell, H.G.; Howe, C.A.; Nowak-Fluck, D.; Stacey, B.S.; Bailey, D.M.; Paton, J.F.R.; Green, D.J.; Sekhon, M.S.; Macleod, D.B.; et al. Nitric oxide is fundamental to neurovascular coupling in humans. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 4927–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, I.; Sandor, N.T.; Ruttner, Z.; McLaughlin, A.C. Role of nitric oxide in regulating cerebrocortical oxygen consumption and blood flow during hypercapnia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1994, 14, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, R.; Lahti, A.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, M.C.; Cisneros Serrano, C. What is the added value of FeNO as T2 biomarker? Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 957106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, B.M.; Shusterman, D.J.; Zhao, K. Nasal nitric oxide flux from the paranasal sinuses. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 23, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veen, R.C. Nitric oxide and T helper cell immunity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2001, 1, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuccio, G.; Ambrosino, P.; Merola, C.; Manzo, F.; Motta, A.; Rea, G.; Cantone, E.; Maniscalco, M. Clinical Applications of Nasal Nitric Oxide in Allergic Rhinitis: A Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindicci, C.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Ito, M.; Elliott, M.W.; Hogg, J.C.; Barnes, P.J.; Ito, K. Nitric oxide synthase isoenzyme expression and activity in peripheral lung tissue of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardolo, F.L.; Caramori, G.; Ito, K.; Capelli, A.; Brun, P.; Abatangelo, G.; Papi, A.; Chung, K.F.; Adcock, I.; Barnes, P.J.; et al. Nitrosative stress in the bronchial mucosa of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarsingh, H.; Leusink, J.; Bos, I.S.; Zaagsma, J.; Meurs, H. Arginase strongly impairs neuronal nitric oxide-mediated airway smooth muscle relaxation in allergic asthma. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.L.; Friedman, A.J. Nitric oxide therapy for dermatologic disease. Future. Sci. OA 2015, 1, FSO37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, S.A.; Steinert, J.R. Nitric Oxide-Mediated Posttranslational Modifications: Impacts at the Synapse. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5681036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Lipton, S.A. Emerging roles of S-nitrosylation in protein misfolding and neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, M.K.; Kartawy, M.; Amal, H. The role of nitric oxide in brain disorders: Autism spectrum disorder and other psychiatric, neurological, and neurodegenerative disorders. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haun, F.; Nakamura, T.; Shiu, A.D.; Cho, D.H.; Tsunemi, T.; Holland, E.A.; La Spada, A.R.; Lipton, S.A. S-nitrosylation of dynamin-related protein 1 mediates mutant huntingtin-induced mitochondrial fragmentation and neuronal injury in Huntington’s disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellos, L.F.; Begovich, A.B.; Reynolds, R.L.; Caillier, S.J.; Brassat, D.; Schmidt, S.; Grams, S.E.; Walker, K.; Steiner, L.L.; Cree, B.A.; et al. Linkage and association with the NOS2A locus on chromosome 17q11 in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, J.R.; Kanwar, R.K.; Krissansen, G.W. Simultaneous neuroprotection and blockade of inflammation reverses autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain 2004, 127, 1313–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Lassmann, H. The role of nitric oxide in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2002, 1, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Gu, Z.; Nakamura, T.; Shi, Z.Q.; Ma, Y.; Gaston, B.; Palmer, L.A.; Rockenstein, E.M.; Zhang, Z.; Masliah, E.; et al. Nitrosative stress linked to sporadic Parkinson’s disease: S-nitrosylation of parkin regulates its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10810–10814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, M.A.; Do, H.T.; Miley, G.P.; Silverman, R.B. Inducible nitric oxide synthase: Regulation, structure, and inhibition. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 158–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosova, M.; Mokra, D.; Pepucha, L.; Plevkova, J.; Buday, T.; Sterusky, M.; Bencova, A. Physiology of nitric oxide in the respiratory system. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatera, K.; Mukae, H. Possible pathogenic roles of nitric oxide in asthma. Respir. Investig. 2019, 57, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akata, K.; Yatera, K.; Wang, K.Y.; Naito, K.; Ogoshi, T.; Noguchi, S.; Kido, T.; Toyohira, Y.; Shimokawa, H.; Yanagihara, N.; et al. Decreased Bronchial Eosinophilic Inflammation and Mucus Hypersecretion in Asthmatic Mice Lacking All Nitric Oxide Synthase Isoforms. Lung 2016, 194, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.; Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Maspero, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Pirozzi, G.; Sutherland, E.R.; Evans, R.R.; Joish, V.N.; et al. Dupilumab efficacy and safety in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma despite use of medium-to-high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a long-acting beta2 agonist: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled pivotal phase 2b dose-ranging trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Lemanske, R.F.; Hanania, N.A.; Korenblat, P.E.; Parsey, M.V.; Arron, J.R.; Harris, J.M.; Scheerens, H.; Wu, L.C.; Su, Z.; et al. Lebrikizumab treatment in adults with asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Korn, S.; Howarth, P.; Bleecker, E.R.; Buhl, R.; Keene, O.N.; Ortega, H.; Chanez, P. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): A multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibana, K.; Trudeau, J.B.; Mustovich, A.T.; Hu, H.; Zhao, J.; Balzar, S.; Chu, H.W.; Wenzel, S.E. IL-13 induced increases in nitrite levels are primarily driven by increases in inducible nitric oxide synthase as compared with effects on arginases in human primary bronchial epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, V.; Mih, J.D.; George, S.C. Measurement of IL-13-induced iNOS-derived gas phase nitric oxide in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormile, I.; Granata, F.; Detoraki, A.; Pacella, D.; Della Casa, F.; De Rosa, F.; Romano, A.; de Paulis, A.; Rossi, F.W. Predictive Response to Immunotherapy Score: A Useful Tool for Identifying Eligible Patients for Allergen Immunotherapy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Spigna, G.; Ladogana, P.; Covelli, B.; Ricciardone, M.; Salzano, S.; Spalletti Cernia, D.; Mormile, I.; Varriale, G.; Catapano, O.; Spadaro, G.; et al. Component resolved diagnosis by recombinant allergens in patients with allergies to inhalants. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.; Falk, G.W. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormile, I.; Petraroli, A.; Loffredo, S.; Rossi, F.W.; Mormile, M.; Del Mastro, A.; Spadaro, G.; de Paulis, A.; Bova, M. Episodic Angioedema with Hypereosinophilia (Gleich’s Syndrome): A Case Report and Extensive Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibille, A.; Corhay, J.L.; Louis, R.; Ninane, V.; Jerusalem, G.; Duysinx, B. Eosinophils and Lung Cancer: From Bench to Bedside. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamant, Z.; Vijverberg, S.; Alving, K.; Bakirtas, A.; Bjermer, L.; Custovic, A.; Dahlen, S.E.; Gaga, M.; Gerth van Wijk, R.; Giacco, S.D.; et al. Toward clinically applicable biomarkers for asthma: An EAACI position paper. Allergy 2019, 74, 1835–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, A.; Giner, J.; Torrejon, M.; Belda, A.; Mateus, E.; Granel, C.; Torrego, A.; Ramos-Barbon, D.; Plaza, V. Clinical and inflammatory features of asthma with dissociation between fractional exhaled nitric oxide and eosinophils in induced sputum. J. Asthma 2016, 53, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.; Ford, L.; Pearlman, D.; Spector, S.; Sher, L.; Skobieranda, F.; Wang, L.; Kirkesseli, S.; Rocklin, R.; Bock, B.; et al. Dupilumab in persistent asthma with elevated eosinophil levels. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Pham, T.H.; Garcia Gil, E.; Salapa, K.; Ren, P.; Parnes, J.R.; Colice, G.; Griffiths, J.M. Baseline type 2 biomarker levels and response to tezepelumab in severe asthma. Allergy 2022, 77, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, J.C.; Comhair, S.A.; Erzurum, S.C.; Klein, D.F.; Lipscomb, M.F.; Kavuru, M.S.; Samoszuk, M.K.; Hazen, S.L. Eosinophils are a major source of nitric oxide-derived oxidants in severe asthma: Characterization of pathways available to eosinophils for generating reactive nitrogen species. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5763–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justiz Vaillant, A.A.; Modi, P.; Jan, A. Atopy. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, J.G.; Marino, M.J.; Luong, A.U. Unified Airway Disease: Future Directions. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 56, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maspero, J.; Adir, Y.; Al-Ahmad, M.; Celis-Preciado, C.A.; Colodenco, F.D.; Giavina-Bianchi, P.; Lababidi, H.; Ledanois, O.; Mahoub, B.; Perng, D.W.; et al. Type 2 inflammation in asthma and other airway diseases. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00576–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic-Grle, S.; Stajduhar, A.; Lampalo, M.; Rnjak, D. Biomarkers in Different Asthma Phenotypes. Genes 2021, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, S.A.; Yates, D.; Robbins, R.A.; Logan-Sinclair, R.; Shinebourne, E.A.; Barnes, P.J. Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Lancet 1994, 343, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, S.A.; Chung, K.F.; Evans, D.; O’Connor, B.J.; Barnes, P.J. Increased exhaled nitric oxide in asthma is mainly derived from the lower respiratory tract. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jatakanon, A.; Lim, S.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Chung, K.F.; Barnes, P.J. Correlation between exhaled nitric oxide, sputum eosinophils, and methacholine responsiveness in patients with mild asthma. Thorax 1998, 53, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, N.; Saxena, D.; Dileep, A.; Adrish, M.; Hanania, N.A. Update on the Role of FeNO in Asthma Management. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanania, N.A.; Wenzel, S.; Rosen, K.; Hsieh, H.J.; Mosesova, S.; Choy, D.F.; Lal, P.; Arron, J.R.; Harris, J.M.; Busse, W. Exploring the effects of omalizumab in allergic asthma: An analysis of biomarkers in the EXTRA study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Pavord, I.D.; Maspero, J.; Wenzel, S.; Rabe, K.F.; Busse, W.W.; Ford, L.; Sher, L.; FitzGerald, J.M.; et al. Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Moderate-to-Severe Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Corren, J.; Bourdin, A.; Chupp, G.; Israel, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Griffiths, J.M.; Hellqvist, A.; Bowen, K.; et al. Tezepelumab in Adults and Adolescents with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrasch, S.; Linde, K.; Rucker, G.; Sommer, H.; Karsch-Volk, M.; Kleijnen, J.; Jorres, R.A.; Schneider, A. Accuracy of FENO for diagnosing asthma: A systematic review. Thorax 2017, 72, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Mansur, A.H.; Brightling, C.E. Clinical utility of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in severe asthma management. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dweik, R.A.; Boggs, P.B.; Erzurum, S.C.; Irvin, C.G.; Leigh, M.W.; Lundberg, J.O.; Olin, A.C.; Plummer, A.L.; Taylor, D.R.; American Thoracic Society Committee on Interpretation of Exhaled Nitric Oxide Levels (FENO) for Clinical Applications. An official ATS clinical practice guideline: Interpretation of exhaled nitric oxide levels (FENO) for clinical applications. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.F. Increasing utility of FeNO as a biomarker of type-2 inflammation in severe asthma. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1083–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, F.; Sprio, A.E.; Baroso, A.; Riccardi, E.; Pizzimenti, S.; Carriero, V.; Arrigo, E.; Di Stefano, A.; Ricciardolo, F.L.M. Predictors of Low and High Exhaled Nitric Oxide Values in Asthma: A Real-World Study. Respiration 2022, 101, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lin, W.; Gu, H.; Ying, K.; Li, T.; Shao, H. Study on the Relationship Between Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Cell Count, Th1/Th2 Cytokines and Pulmonary Function in Patients with Cough Variant Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.; Shen, H.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, Z.; Cai, S.; Huang, K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Lin, J.; Hao, C.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Cough-Chinese Thoracic Society (CTS) Asthma Consortium. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 6314–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Kim, J.T.; Kang, H.; Yoo, Y.; Koh, Y.Y. Sputum eosinophilia in cough-variant asthma as a predictor of the subsequent development of classic asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lougheed, M.D.; Turcotte, S.E.; Fisher, T. Cough variant asthma: Lessons learned from deep inspirations. Lung 2012, 190, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-j.; Huang, X.-y.; Lin, G.-p.; Liu, Y.-l.; Xie, C.-m. Validity of fractional exhaled nitric oxide and small airway function indices in diagnosis of cough-variant asthma. J. Asthma 2018, 55, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredi, P.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Meah, S.; Barnes, P.J.; Usmani, O.S. A novel approach to partition central and peripheral airway nitric oxide. Chest 2014, 145, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Shi, C.; Yu, S.; Wen, S.; Sha, B.; Xu, X.; Yu, L. A comparative study on the value of lower airway exhaled nitric oxide combined with small airway parameters for diagnosing cough-variant asthma. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2023, 17, 17534666231181259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, F.; Guo, Y.; Ma, H.; Han, B.; Yi, J.; Kong, X. Diagnostic Value of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Small Airway Function in Differentiating Cough-Variant Asthma from Typical Asthma. Can. Respir. J. 2021, 2021, 9954411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, F.; Wu, S.; Yang, X. Inflammatory Subtypes in Classic Asthma and Cough Variant Asthma. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, F. Small airway dysfunction in patients with cough variant asthma: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybka-Fraczek, A.; Dabrowska, M.; Grabczak, E.M.; Bialek-Gosk, K.; Klimowicz, K.; Truba, O.; Nejman-Gryz, P.; Paplinska-Goryca, M.; Krenke, R. Inflammatory Phenotypes of Cough Variant Asthma as Response Predictors to Anti-Asthmatic Therapy. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, W.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, W.; Luo, W.; Yi, F.; Dai, Y.; Li, S.; Lin, J.; et al. Identification of cough-variant asthma phenotypes based on clinical and pathophysiologic data. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, R.; Hao, C.; Yu, X.; Tian, Z.; Yuan, Y. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) Combined with Pulmonary Function Parameters Shows Increased Sensitivity and Specificity for the Diagnosis of Cough Variant Asthma in Children. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 3832–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Fang, Z.K.; Fang, S.; Shen, Q.X.; He, X.; Wang, C.L.; Yu, H.P. Comparison of functional parameters of small airways between patients with typical asthma and cough-variant asthma. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2017, 37, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.H.; Wright, C.E.; Hart, S.; Crooks, M.; Morice, A. Phenotyping patients with chronic cough: Evaluating the ability to predict the response to anti-inflammatory therapy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zeng, G.S.; Wu, L.L.; Zi, M.; Fang, Z.K.; Fan, H.Z.; Yu, H.P. Diagnostic value of FeNO and MMEF for predicting cough variant asthma in chronic cough patients with or without allergic rhinitis. J. Asthma 2021, 58, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebl, E.; Abdel-moety, H. Assessment of the role of fractional exhaled nitric oxide as a predictor of airway eosinophilia and corticosteroid responsiveness in patients with chronic cough. Egypt. J. Bronchol. 2020, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.; Rane, S.; Mandrekar, S.; Mesquita, A.M. Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation in Patients with Stable Biomass Smoke-versus Tobacco Smoke-Associated Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Health Pollut. 2019, 9, 191209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Kolsum, U.; Brightling, C.E.; Locantore, N.; Agusti, A.; Tal-Singer, R.; ECLIPSE Investigators. Eosinophilic inflammation in COPD: Prevalence and clinical characteristics. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Inflammatory endotypes in COPD. Allergy 2019, 74, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borish, L.; Teague, W.G.; Patrie, J.T.; Wavell, K.W.; Barros, A.J.; Malpass, H.C.; Lawrence, M.G. Further evidence of a type 2 inflammatory signature in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or emphysema. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 130, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, S.A.; Steiling, K.; van den Berge, M.; Hijazi, K.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Postma, D.S.; Lenburg, M.E.; Spira, A.; Woodruff, P.G. Asthma-COPD overlap. Clinical relevance of genomic signatures of type 2 inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, M.; Majori, M.; Cacciani, G.C.; Consigli, G.F.; de’Munari, E.; Pesci, A. Increased exhaled nitric oxide in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 1999, 54, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutgers, S.R.; van der Mark, T.W.; Coers, W.; Moshage, H.; Timens, W.; Kauffman, H.F.; Koeter, G.H.; Postma, D.S. Markers of nitric oxide metabolism in sputum and exhaled air are not increased in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 1999, 54, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Chowdhury, B.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Magnussen, H.; Page, C.P.; Postma, D.; Saetta, M. Pulmonary biomarkers in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansarin, K.; Chatkin, J.M.; Ferreira, I.M.; Gutierrez, C.A.; Zamel, N.; Chapman, K.R. Exhaled nitric oxide in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Relationship to pulmonary function. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 17, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.J.; Huang, X.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Lin, G.P.; Xie, C.M. Importance of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in the differentiation of asthma-COPD overlap syndrome, asthma, and COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2016, 11, 2385–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerba, M.; Radaeli, A.; Olivini, A.; Damiani, G.; Ragnoli, B.; Montuschi, P.; Ricciardolo, F.L. Exhaled nitric oxide as a biomarker in COPD and related comorbidities. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 271918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietkowski, Z.; Kucharewicz, I.; Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, A. The influence of inhaled corticosteroids on exhaled nitric oxide in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Med. 2005, 99, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agusti, A.G.; Villaverde, J.M.; Togores, B.; Bosch, M. Serial measurements of exhaled nitric oxide during exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 14, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcazar-Navarrete, B.; Ruiz Rodriguez, O.; Conde Baena, P.; Romero Palacios, P.J.; Agusti, A. Persistently elevated exhaled nitric oxide fraction is associated with increased risk of exacerbation in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1701457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maziak, W.; Loukides, S.; Culpitt, S.; Sullivan, P.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Barnes, P.J. Exhaled nitric oxide in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Laurentiis, G.; Maniscalco, M.; Cianciulli, F.; Stanziola, A.; Marsico, S.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Sofia, M. Exhaled nitric oxide monitoring in COPD using a portable analyzer. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 21, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, D.M.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Kostikas, K.; Grize, L.; Tamm, M.; Stolz, D. Variability of fractional exhaled nitric oxide is associated with the risk and aetiology of COPD exacerbations. Respirology 2023, 28, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindisi, G.; De Vittori, V.; De Nola, R.; Di Mauro, A.; De Castro, G.; Baldassarre, M.E.; Cicinelli, E.; Cinicola, B.; Duse, M.; Zicari, A.M. The Role of Nasal Nitric Oxide and Anterior Active Rhinomanometry in the Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma: A Message for Pediatric Clinical Practice. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranz, R.J.; Lozano, N.A.; Lozano, A.; Alegre, G.; Robredo, P.; Visconti, P.; Cruz, A.A. Relationship between exhaled nitric oxide and biomarkers of atopy in children and adolescents with allergic rhinitis. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2022, 73, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Hsu, J.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Wu, J.R.; Dai, Z.K. Nasal Airflow Measured by Rhinomanometry Correlates with FeNO in Children with Asthma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Bot, C.M.; Moed, H.; Bindels, P.J.; van Wijk, R.G.; Berger, M.Y.; de Groot, H.; de Jongste, J.C.; van der Wouden, J.C. Exhaled nitric oxide measures allergy not symptoms in children with allergic rhinitis in primary care: A prospective cross-sectional and longitudinal cohort study. Prim. Care Respir. J. 2013, 22, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosova, M.; Bencova, A.; Mokra, D.; Plevkova, J.; Pepucha, L.; Buday, T. Exhaled and Nasal Nitric Oxide—Impact for Allergic Rhinitis. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, S123–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Kubo, S.; Sakashita, M.; Tokunaga, T.; Susuki, D.; Narita, N.; Ogi, K.; Kanno, M.; Yamashita, S.; et al. Efficacy of mometasone furoate nasal spray for nasal symptoms, quality of life, rhinitis-disturbed sleep, and nasal nitric oxide in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012, 33, e9–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, F.; de Benedictis, F.M.; Muggeo, V.; Giordano, P.; Loffredo, M.S.; Iacoviello, G.; Armenio, L. Exhaled nitric oxide, total serum IgE and allergic sensitization in childhood asthma and allergic rhinitis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 16, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.S.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Baek, J.; Park, H.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Sohn, M.H.; Kim, K.E. Exhaled nitric oxide is associated with allergic inflammation in children. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2011, 26, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.; Raza, A.; Karmaus, W.; Mitchell, F.; Grundy, J.; Kurukulaaratchy, R.J.; Arshad, S.H.; Roberts, G. Influence of atopy and asthma on exhaled nitric oxide in an unselected birth cohort study. Thorax 2010, 65, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Striz, I.; Golebski, K.; Strizova, Z.; Loukides, S.; Bakakos, P.; Hanania, N.A.; Jesenak, M.; Diamant, Z. New insights into the pathophysiology and therapeutic targets of asthma and comorbid chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyposis. Clin. Sci. 2023, 137, 727–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58, 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Desrosiers, M.; Khan, A.H. Burden of Disease in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, T.M.; Mullol, J.; Woessner, K.M.; Amin, N.; Mannent, L.P. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps and Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.W.; Chanez, P.; Menzella, F.; Canonica, G.W.; Louis, R.; Cosio, B.G.; Lugogo, N.L.; Mohan, A.; Burden, A.; McDermott, L.; et al. Onset of effect and impact on health-related quality of life, exacerbation rate, lung function, and nasal polyposis symptoms for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma treated with benralizumab (ANDHI): A randomised, controlled, phase 3b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, G.; Melone, G.; Guida, G.; Pirola, F.; Malvezzi, L.; Pelaia, C.; Mariani, A.; Racca, F.; Malipiero, G.; Ferri, S.; et al. Extended nitric oxide analysis in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, with or without associated asthma. J. Breath Res. 2020, 15, 016007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Lou, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Predictive significance of computed tomography in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 6, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, G.; Casini, M.; Malvezzi, L.; Pirola, F.; Russo, E.; Nappi, E.; Quintina Muci, G.; Montagna, C.; Messina, M.R.; Ferri, S.; et al. Very rapid improvement of extended nitric oxide parameters, associated with clinical and functional betterment, in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) treated with Dupilumab. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 33, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, G.; Rolla, G.; Badiu, I.; Marsico, P.; Pizzimenti, S.; Bommarito, L.; De Stefani, A.; Usai, A.; Bugiani, M.; Malinovschi, A.; et al. Determinants of exhaled nitric oxide in chronic rhinosinusitis. Chest 2010, 137, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambara, R.; Minami, T.; Akazawa, H.; Tsuji, F.; Sasaki, T.; Inohara, H.; Horii, A. Lower Airway Inflammation in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Determined by Exhaled Nitric Oxide. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 173, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Asako, M.; Ooka, H.; Kanda, A.; Tomoda, K.; Yasuba, H. Residual exhaled nitric oxide elevation in asthmatics is associated with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Asthma 2015, 52, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.; Calabrese, C.; D’Amato, M.; Guida, P.; Molino, A.; Aliani, M.; De Tullio, R.; Foschino Barbaro, M.; Ricciardolo, F.L.M.; Carpagnano, G.E. Association between exhaled nitric oxide and nasal polyposis in severe asthma. Respir. Med. 2019, 152, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.A.; Cha, H.; Yang, S.K.; Ryu, H.T.; Kim, D.W.; Hong, S.N.; Yang, M.S.; Kim, D.W. The Role of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Diagnosing Asthmatic Type 2 Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2023, 37, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Katzka, D.A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, E.C.; Hernandez, M.; Dellon, E.S. Eosinophilic Esophagitis and the Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases: Approach to Diagnosis and Management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.; Nguyen-Traxler, A.; Lee, E.M.; Yip, J.S.; Weinstock, J.V.; Chan, W.W.; Ngo, P.; Weinstein, B.J.; Bonis, P.A. Assessment of fractionated exhaled nitric oxide as a biomarker for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012, 33, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, G.T.; Liacouras, C.A.; Collins, M.H.; Gupta, S.K.; Justinich, C.; Putnam, P.E.; Bonis, P.; Hassall, E.; Straumann, A.; Rothenberg, M.E.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: A systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1342–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Becker, N.Q.; Raja, S.; Scarpignato, C.; Lynch, K.L.; Ahuja, N.K.; Horsley-Silva, J.L. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Updates on key unanswered questions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1481, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rhijn, B.D.; Bredenoord, A.J. Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Based on Pathophysiological Evidence. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Chevalier, R.; Friesen, C.; Ryan, J.; Sherman, A.; Page, S. Diagnostic role of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis, relationship with gastric and duodenal eosinophils. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 15, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, M.J.; Guerrero, R.A.; Gonzalez-Vallina, R. Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide in the evaluation for eosinophilic esophagitis in children. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012, 109, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.; Iyer, V.; Katzka, D.; Ravi, K.; Lennon, R.; Pendegraft, R.; Geno, D.; Alexander, J. Poor Relationship Between Fractionated Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Disease Activity in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Dysphagia 2019, 34, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josyabhatla, R.; Abrenica, C.; Mai, T.; Hashmi, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Mosquera, R.; Van Arsdall, M.; Navarro, F.; Tchakarov, A.; Tatevian, N.; et al. Plasma Biomarkers and Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in the Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 76, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salava, A.; Rieppo, R.; Lauerma, A.; Salo, V. Age-dependent Distribution of Atopic Dermatitis in Primary Care: A Nationwide Population-based Study from Finland. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2022, 102, adv00738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakok, T.; Woolf, R.; Smith, C.H.; Weidinger, S.; Flohr, C. Atopic dermatitis: The skin barrier and beyond. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czubaj-Kowal, M.; Nowicki, G.J.; Kurzawa, R.; Polak, M.; Slusarska, B. Factors Influencing the Concentration of Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in School Children Aged 8–9-Years-Old in Krakow, with High FeNO Values ≥ 20 ppb. Medicina 2022, 58, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gupta, N. Exhaled nitric oxide atopy, and spirometry in asthma and rhinitis patients in India. Adv. Respir. Med. 2017, 85, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, C.A.; Arkwright, P.D.; Bruggen, M.C.; Busse, W.; Gadina, M.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Kabashima, K.; Mitamura, Y.; Vian, L.; Wu, J.; et al. Type 2 immunity in the skin and lungs. Allergy 2020, 75, 1582–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiniak, S.; Rachel, M. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Teenagers and Adults with Atopic Dermatitis. Adv. Respir. Med. 2022, 90, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinelli, C.; Caffarelli, C.; Strid, J.; Jaffe, A.; Atherton, D.J. Measurement of nitric oxide and 8-isoprostane in exhaled breath of children with atopic eczema. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2009, 34, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdeniz, N.; Aktaş, A.; Erdem, T.; Akyüz, M.; Özdemir, S. Nitric oxide levels in atopic dermatitis. Pain Clin. 2004, 16, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, L. Potential biomarkers of atopic dermatitis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1028694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniuchi, S.; Kojima, T.; Hara Mt, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Sasai, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kobayashi, Y. Increased serum nitrate levels in infants with atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2001, 56, 693–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadi, N.S.; Shakiba, S.; Afshari, K.; Haj-Mirzaian, A.; Vesaghati, S.; Gharagozlou, S.; Foroumadi, R.; Shafaroodi, H.; Ostadhadi, S.; Dehpour, A.R. Possible Involvement of Nitric Oxide in the Antipruritic Effect of Metformin on Chloroquine-Induced Scratching in Mice. Dermatology 2020, 236, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuppi, J.D.; Downs, S.H.; Downie, S.R.; Marks, G.B.; Salome, C.M. Exhaled nitric oxide levels in atopic children: Relation to specific allergic sensitisation, AHR, and respiratory symptoms. Thorax 2002, 57, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.R.; Pijnenburg, M.W.; Smith, A.D.; De Jongste, J.C. Exhaled nitric oxide measurements: Clinical application and interpretation. Thorax 2006, 61, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanusch, B.; Sinningen, K.; Brinkmann, F.; Dillenhofer, S.; Frank, M.; Jockel, K.H.; Koerner-Rettberg, C.; Holtmann, M.; Legenbauer, T.; Langrock, C.; et al. Characterization of the L-Arginine/Nitric Oxide Pathway and Oxidative Stress in Pediatric Patients with Atopic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food allergy: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, S.A.; Munoz-Furlong, A.; Sampson, H.A. Fatalities due to anaphylactic reactions to foods. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourihane, J.O. Peanut allergy. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2011, 58, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.L.; Brown, T.; Edgar, J.D.; Shields, M.D. Peanut allergy and allergic airways inflammation. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 21, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, K.; Bhatia, R.; Belcher, J.; Patchett, K.; McElduff, P.; Collison, A.; Mattes, J. The fraction of exhaled nitric oxide improves prediction of clinical allergic reaction to peanut challenge in children. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, E.; Bhatia, R.; Preece, K.; McElduff, P.; McEvoy, M.; Collison, A.; Mattes, J. Reproducibility of serum IgE, Ara h2 skin prick testing and fraction of exhaled nitric oxide for predicting clinical peanut allergy in children. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, E.; Bhatia, R.; Preece, K.; McEvoy, M.; Collison, A.; Mattes, J. Change in exhaled nitric oxide during peanut challenge is related to severity of reaction. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patelis, A.; Alving, K.; Middelveld, R.; James, A.; Ono, J.; Ohta, S.; Izuhara, K.; Borres, M.P.; Forsberg, B.; Janson, C.; et al. IgE sensitization to food allergens and airborne allergens in relation to biomarkers of type 2 inflammation in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| FeNO | Major Cell Source | Related Biomarkers | Stimulating Factors | NOS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asthma | ↑ | Epithelial cells Macrophages Eosinophils Macrophages Mononuclear cells | Sputum eosinophils Blood eosinophils Total IgE Serum periostin | IL-4 IL-13 TNF-alfa IFN-gamma TSLP | iNOS |
| COPD | ↑ or → | Epithelial cells Pneumocytes type macrophages Vascular smooth muscle cells | Blood eosinophils Sputum eosinophils at exacerbation | TNF-alfa Reactive oxygen species | iNOS nNOS |
| AR | ↑ | Epithelial cells Macrophages Eosinophils Neutrophils | Blood eosinophils Total IgE | IL-4 IL-13 | iNOS |
| CRSwNP | ↑ | Blood eosinophils Polyp eosinophils | TSLP IL-13 | iNOS | |
| EoE | ↑ or → | Esophageal epithelium | Esophageal eosinophils | iNOS | |
| AD | ↑ | Macrophagis Langerhans cells Keratinocytes | N° of positive skin prick tests | TNF-alfa IL-2 IL-6 IFN-gamma | iNOS |
| Food Allergy | ↑ | ? | ? | S-ECP Periostin | ? |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maniscalco, M.; Fuschillo, S.; Mormile, I.; Detoraki, A.; Sarnelli, G.; Paulis, A.d.; Spadaro, G.; Cantone, E., on behalf of PATH-2 TASK FORCE. Exhaled Nitric Oxide as Biomarker of Type 2 Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12212518
Maniscalco M, Fuschillo S, Mormile I, Detoraki A, Sarnelli G, Paulis Ad, Spadaro G, Cantone E on behalf of PATH-2 TASK FORCE. Exhaled Nitric Oxide as Biomarker of Type 2 Diseases. Cells. 2023; 12(21):2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12212518
Chicago/Turabian StyleManiscalco, Mauro, Salvatore Fuschillo, Ilaria Mormile, Aikaterini Detoraki, Giovanni Sarnelli, Amato de Paulis, Giuseppe Spadaro, and Elena Cantone on behalf of PATH-2 TASK FORCE. 2023. "Exhaled Nitric Oxide as Biomarker of Type 2 Diseases" Cells 12, no. 21: 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12212518
APA StyleManiscalco, M., Fuschillo, S., Mormile, I., Detoraki, A., Sarnelli, G., Paulis, A. d., Spadaro, G., & Cantone, E., on behalf of PATH-2 TASK FORCE. (2023). Exhaled Nitric Oxide as Biomarker of Type 2 Diseases. Cells, 12(21), 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12212518










