The Expression of Cellular Prion Protein, PrPC, Favors pTau Propagation and Blocks NMDAR Signaling in Primary Cortical Neurons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Expression Vectors
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Cell Transfection
2.5. Preparation of Human Alpha-Synuclein Fibrils
2.6. AppSw,Ind Transgenic Mice
2.7. ERK1/2 Phosphorylation Assays
2.8. Dynamic Mass Redistribution Label-Free Assays
2.9. Immunocytochemistry
2.10. Cell Viability
2.11. Microfluidics assays of Tau Trafficking
2.12. Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer Assay
2.13. Proximity Ligation Assay
2.14. Data Analysis
3. Results
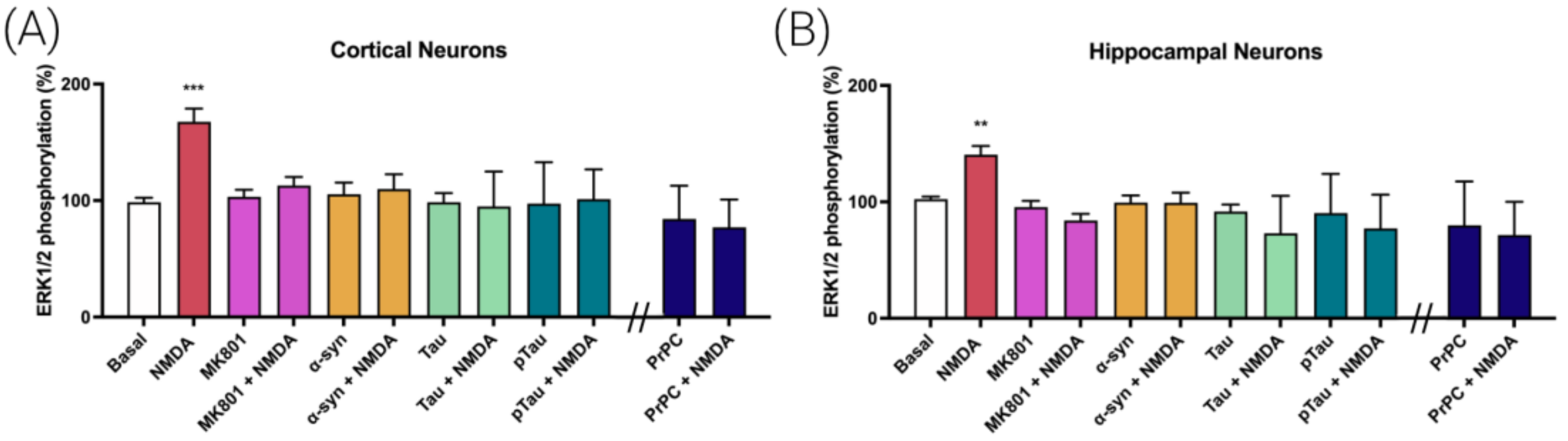
3.1. Prion Protein Blocks NMDA Receptor (NMDAR)-Induced MAPK Signaling in Cortical and Hippocampal Primary Neurons
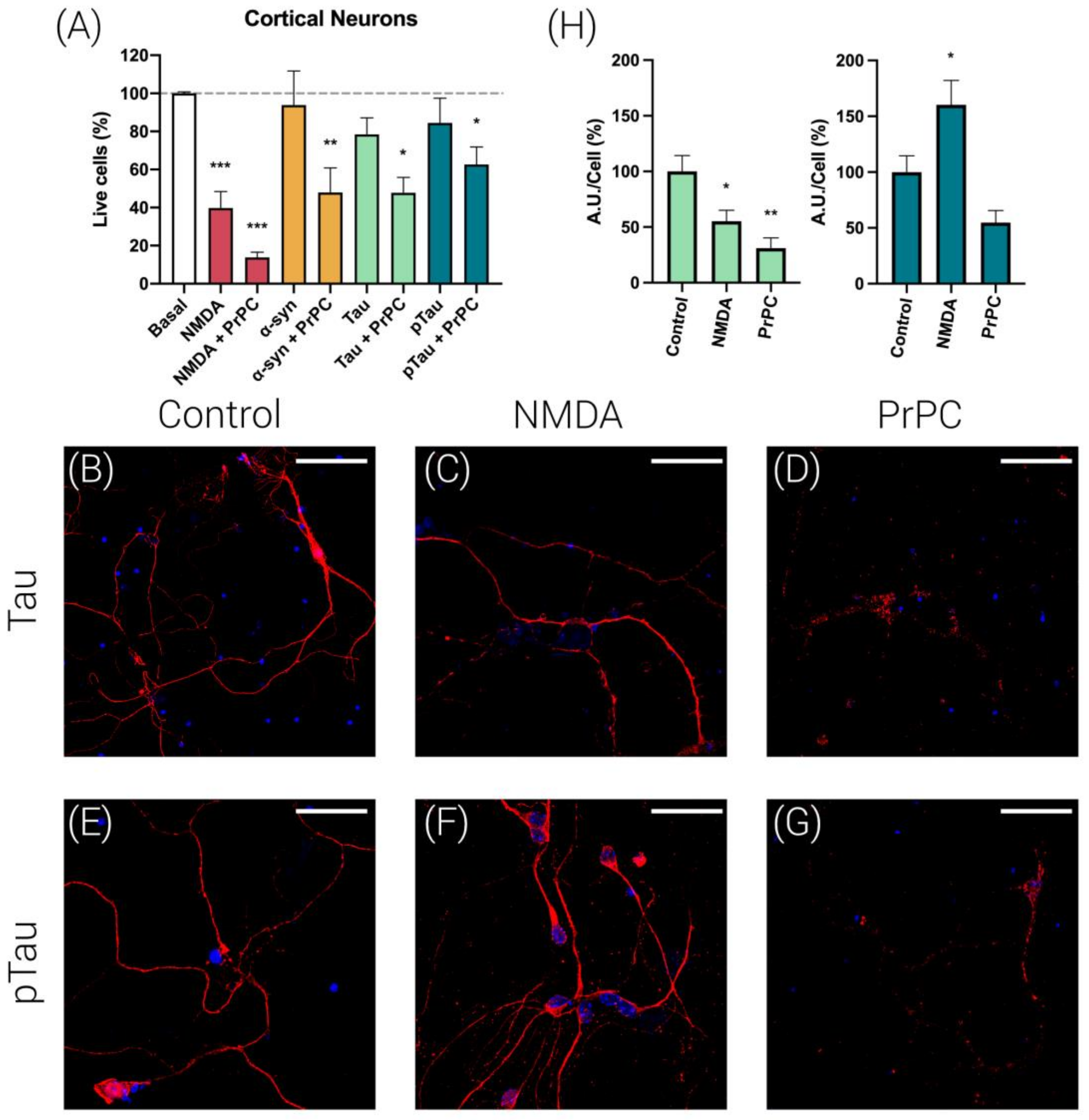
3.2. Prion Protein Potentiates NMDA-Induced Neuronal Excitotoxicity
3.3. PrPC Expression Potentiates Tau and pTau Propagation in Mice Cortical Neurons
3.4. Prion Protein Blocks NMDA Receptor-Induced Signaling in Mice Microglial Cultures
3.5. Prion Protein Polarizes Microglia to an M1 Phenotype
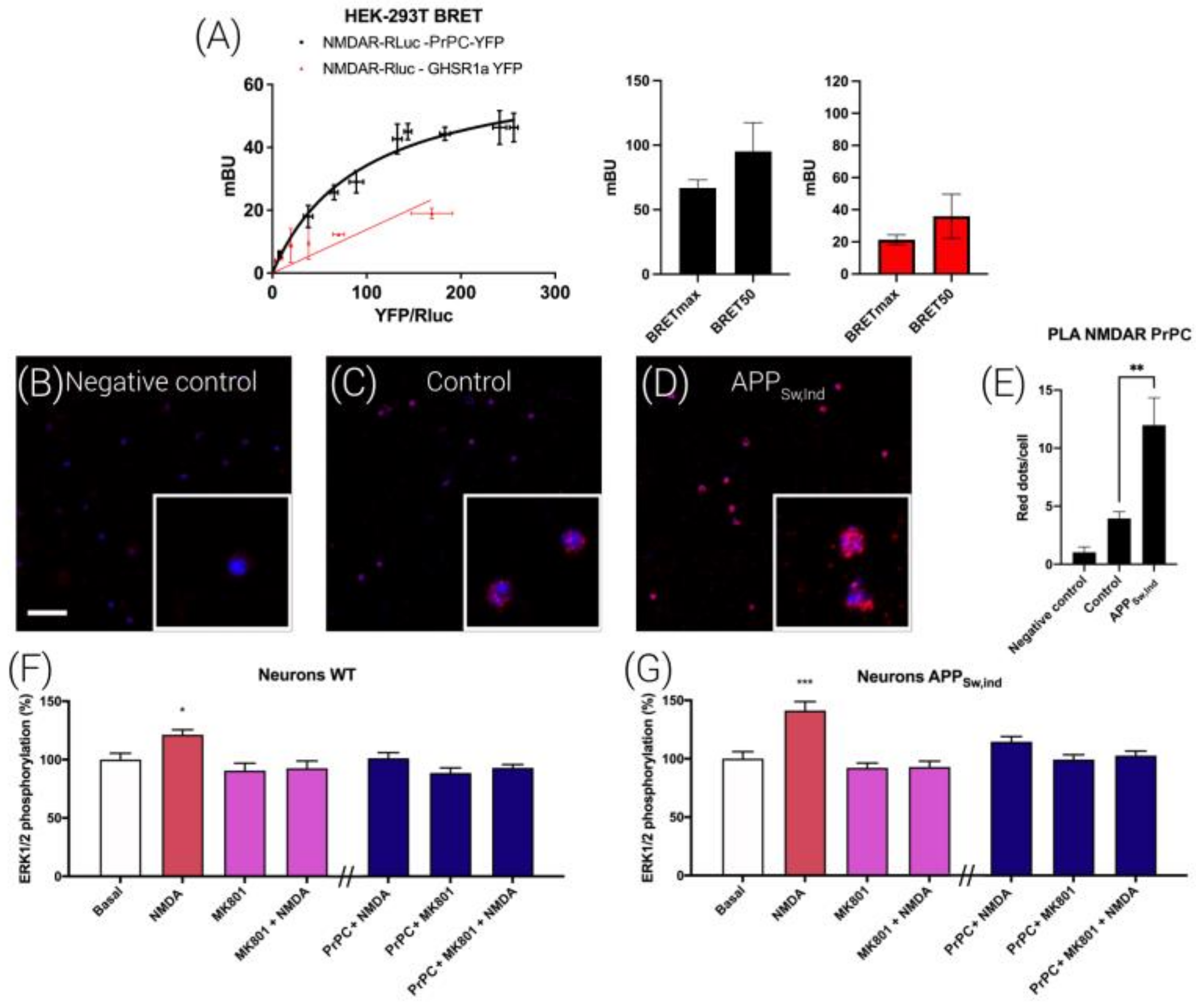
3.6. NMDA-Induced Function Is Regulated by Prion Protein in Transfected HEK-293T Cells
3.7. NMDAR and PrPC Form Macromolecular Complexes in HEK-293T Cells
3.8. Interrelationships between NMDAR and the PrPC in a Mice Model of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, S.A. Paradigm shift in neuroprotection by NMDA receptor blockade: Memantine and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chang, L.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, Y. The role of NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarlus, H.; Heneka, M.T.; Sarlus, H.; Heneka, M.T. Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127, 3240–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.L.; Westbrook, G.L.; Guthrie, P.B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature 1984, 309, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, K.; Liu, F.; Gong, C.-X.; Grundke-Iqbal, I. Tau in Alzheimer Disease and Related Tauopathies. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2010, 7, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Gu, B.J.; Masters, C.L.; Wang, Y.J. A systemic view of Alzheimer disease—Insights from amyloid-β metabolism beyond the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanker, E.E.; Ast, A.; Schindler, F.; Trepte, P.; Schnoegl, S. The pathobiology of perturbed mutant huntingtin protein–protein interactions in Huntington’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2019, 151, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.A.; Poirier, M.A. Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, R.; Tinaz, S. Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, B. Alzheimer’s Disease and Prion Protein. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2013, 2, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salazar, S.V.; Strittmatter, S.M. Cellular prion protein as a receptor for amyloid-β oligomers in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cox, T.O.; Gunther, E.C.; Brody, A.H.; Chiasseu, M.T.; Stoner, A.; Smith, L.M.; Haas, L.T.; Hammersley, J.; Rees, G.; Dosanjh, B.; et al. Anti-PrP C antibody rescues cognition and synapses in transgenic alzheimer mice. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 554–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willbold, D.; Strodel, B.; Schröder, G.F.; Hoyer, W.; Heise, H. Amyloid-type Protein Aggregation and Prion-like Properties of Amyloids. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 8285–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Xiong, S.; Du, X.; Yuan, T.-F.; Peng, B.; Rao, Y. Primary Microglia Isolation from Postnatal Mouse Brains. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 168, e62237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meberg, P.J.; Miller, M.W. Culturing Hippocampal and Cortical Neurons. Methods Cell Biol. 2003, 71, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, P.A.; Kavran, J.M.; Kim, M.-S.; Leahy, D.J. Transient Mammalian Cell Transfection with Polyethylenimine (PEI). In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Nonaka, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Kubo, M.; Shimozawa, A.; Akiyama, H.; Hasegawa, M. Pathological alpha-synuclein propagates through neural networks. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarutani, A.; Hisanaga, S.-I.; Hasegawa, M. The Prion-like Mechanism in Neurodegenerative Diseases-Current Studies and Future Prospects. Brain Nerve 2016, 68, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Aguinaga, D.; Reyes, I.; Canela, E.I.; Lillo, J.; Tarutani, A.; Hasegawa, M.; Del Ser-Badia, A.; Del Rio, J.A.; Kreutz, M.R.; et al. N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Link to the MAP Kinase Pathway in Cortical and Hippocampal Neurons and Microglia Is Dependent on Calcium Sensors and Is Blocked by α-Synuclein, Tau, and Phospho-Tau in Non-transgenic and Transgenic APPSw, Ind Mice. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, R.; Fernández-Suárez, D. Alternatively activated microglia and macrophages in the central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 131, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Romero-Fernandez, W.; Garriga, P.; Ciruela, F.; Narvaez, M.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Palkovits, M.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K. G protein-coupled receptor heterodimerization in the Brain. Methods Enzymol. 2013, 521, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Hagman, B.; Woolfenden, M.; Pinton, L.; Jiménez-beristain, A.; Oflijan, J.; Narvaez, M.; Di Palma, M.; Feltmann, K.; Sartini, S.; et al. Receptor and Ion Channel Detection in the Brain. Neuromethods 2016, 110, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thellung, S.; Gatta, E.; Pellistri, F.; Corsaro, A.; Villa, V.; Vassalli, M.; Robello, M.; Florio, T. Excitotoxicity through NMDA receptors mediates cerebellar granule neuron apoptosis induced by prion protein 90-231 fragment. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 23, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirardini, E.; Restelli, E.; Morini, R.; Bertani, I.; Ortolan, D.; Perrucci, F.; Pozzi, D.; Matteoli, M.; Chiesa, R. Mutant prion proteins increase calcium permeability of AMPA receptors, exacerbating excitotoxicity. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, S.A.G.; Stys, P.K.; Zamponi, G.W.; Tsutsui, S. Cellular prion protein and NMDA receptor modulation: Protecting against excitotoxicity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 2, 25364752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meneghetti, E.; Gasperini, L.; Virgilio, T.; Moda, F.; Tagliavini, F.; Benetti, F.; Legname, G. Prions Strongly Reduce NMDA Receptor S-Nitrosylation Levels at Pre-symptomatic and Terminal Stages of Prion Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 6035–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperini, L.; Meneghetti, E.; Pastore, B.; Benetti, F.; Legname, G. Prion protein and copper cooperatively protect neurons by modulating NMDA receptor through S-nitrosylation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, M.; Yong, X.L.H.; Roche, K.W.; Anggono, V. Regulation of NMDA glutamate receptor functions by the GluN2 subunits. J. Neurochem. 2020, 154, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: Impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercato, M.C.; Vázquez, C.A.; Kornisiuk, E.; Aguirre, A.I.; Colettis, N.; Snitcofsky, M.; Jerusalinsky, D.A.; Baez, M.V. GluN1 and GluN2A NMDA Receptor Subunits Increase in the Hippocampus during Memory Consolidation in the Rat. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stys, P.K.; You, H.; Zamponi, G.W. Copper-dependent regulation of NMDA receptors by cellular prion protein: Implications for neurodegenerative disorders. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, W.; Petersen, R.B.; Lee, H. Cellular prion protein and Alzheimer disease. Prion 2013, 7, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lidón, L.; Vergara, C.; Ferrer, I.; Hernández, F.; Ávila, J.; del Rio, J.A.; Gavín, R. Tau Protein as a New Regulator of Cellular Prion Protein Transcription. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4170–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lv, S.; Stroebel, D.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Paoletti, P.; Zhu, S. Gating mechanism and a modulatory niche of human GluN1-GluN2A NMDA receptors. Neuron 2021, 109, 2443–2456.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, S.; Izzy, S.; Sen, P.; Morsett, L.; El Khoury, J. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peggion, C.; Stella, R.; Lorenzon, P.; Spisni, E.; Bertoli, A.; Massimino, M.L. Microglia in Prion Diseases: Angels or Demons? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Lillo, A.; Lillo, J.; Rebassa, J.-B.; Contestí, J.S.; Saura, C.A.; Franco, R.; Navarro, G. N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and cannabinoid CB 2 receptors form functional complexes in cells of the central nervous system: Insights into the therapeutic potential of neuronal and microglial NMDA receptors. Alzheimers. Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Casanovas, M.; Lillo, A.; Saura, C.A.; Navarro, G. Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists Affects NMDA Glutamate Receptor Function. Potential to Address Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurén, J.; Gimbel, D.A.; Nygaard, H.B.; Gilbert, J.W.; Strittmatter, S.M. Cellular prion protein mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity by amyloid-β oligomers. Nature 2009, 457, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Um, J.W.; Kaufman, A.C.; Kostylev, M.; Heiss, J.K.; Stagi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kerrisk, M.E.; Vortmeyer, A.; Wisniewski, T.; Koleske, A.J.; et al. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Is a Coreceptor for Alzheimer Aβ Oligomer Bound to Cellular Prion Protein. Neuron 2013, 79, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grochowska, K.M.; Yuanxiang, P.; Bär, J.; Raman, R.; Brugal, G.; Sahu, G.; Schweizer, M.; Bikbaev, A.; Schilling, S.; Demuth, H.; et al. Posttranslational modification impact on the mechanism by which amyloid-β induces synaptic dysfunction. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 962–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Raïch, I.; Aguinaga, D.; Saura, C.A.; Franco, R.; Navarro, G. The Expression of Cellular Prion Protein, PrPC, Favors pTau Propagation and Blocks NMDAR Signaling in Primary Cortical Neurons. Cells 2023, 12, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12020283
Rivas-Santisteban R, Raïch I, Aguinaga D, Saura CA, Franco R, Navarro G. The Expression of Cellular Prion Protein, PrPC, Favors pTau Propagation and Blocks NMDAR Signaling in Primary Cortical Neurons. Cells. 2023; 12(2):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12020283
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivas-Santisteban, Rafael, Iu Raïch, David Aguinaga, Carlos A. Saura, Rafael Franco, and Gemma Navarro. 2023. "The Expression of Cellular Prion Protein, PrPC, Favors pTau Propagation and Blocks NMDAR Signaling in Primary Cortical Neurons" Cells 12, no. 2: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12020283
APA StyleRivas-Santisteban, R., Raïch, I., Aguinaga, D., Saura, C. A., Franco, R., & Navarro, G. (2023). The Expression of Cellular Prion Protein, PrPC, Favors pTau Propagation and Blocks NMDAR Signaling in Primary Cortical Neurons. Cells, 12(2), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12020283





