Influence of SARS-CoV-2 on Adult Human Neurogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Quantitative Analysis
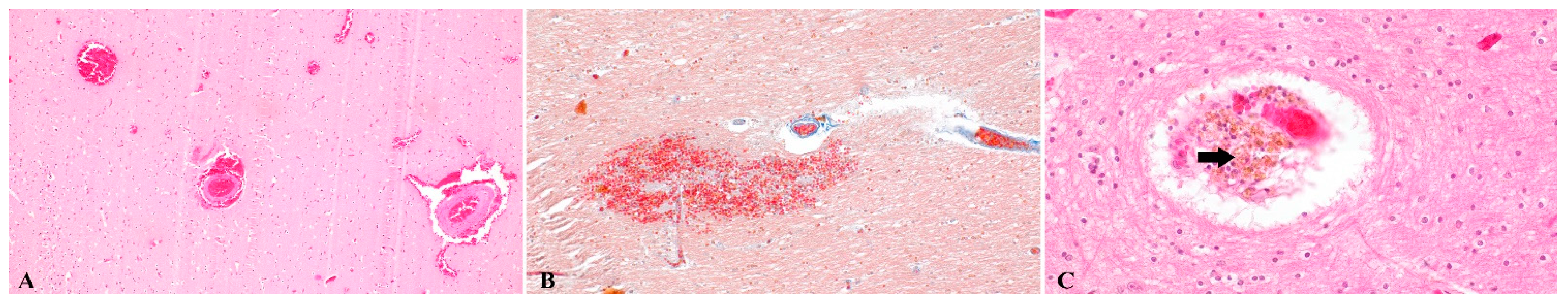
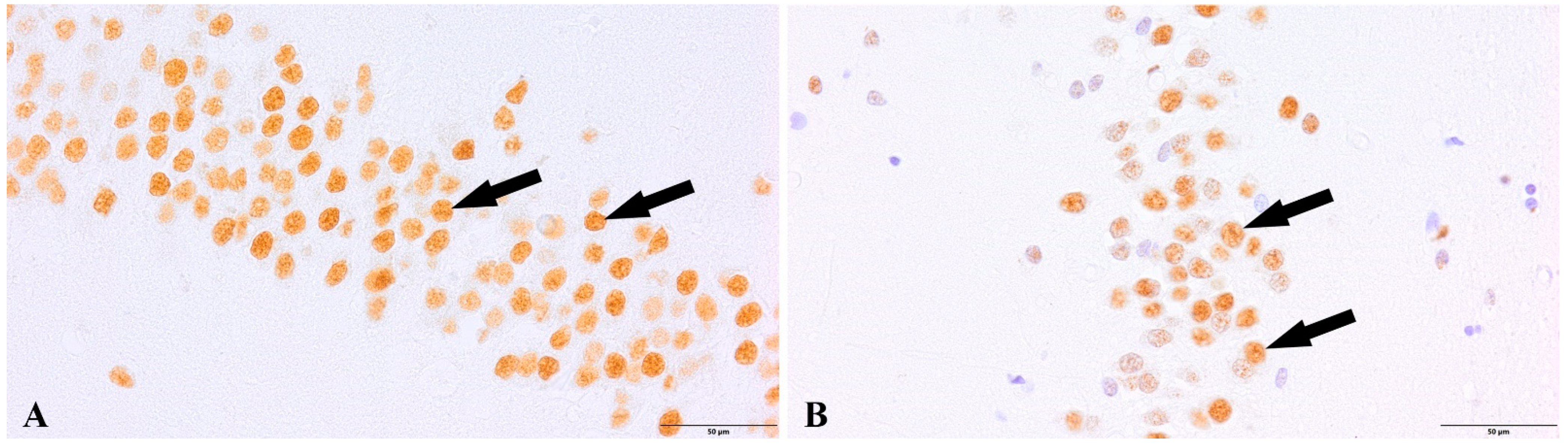
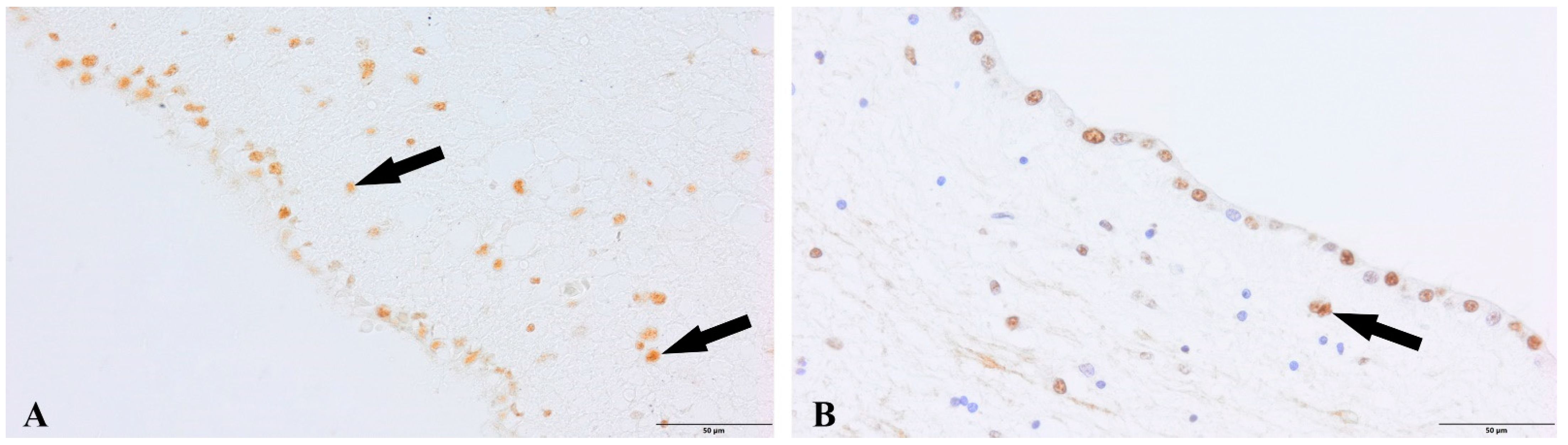
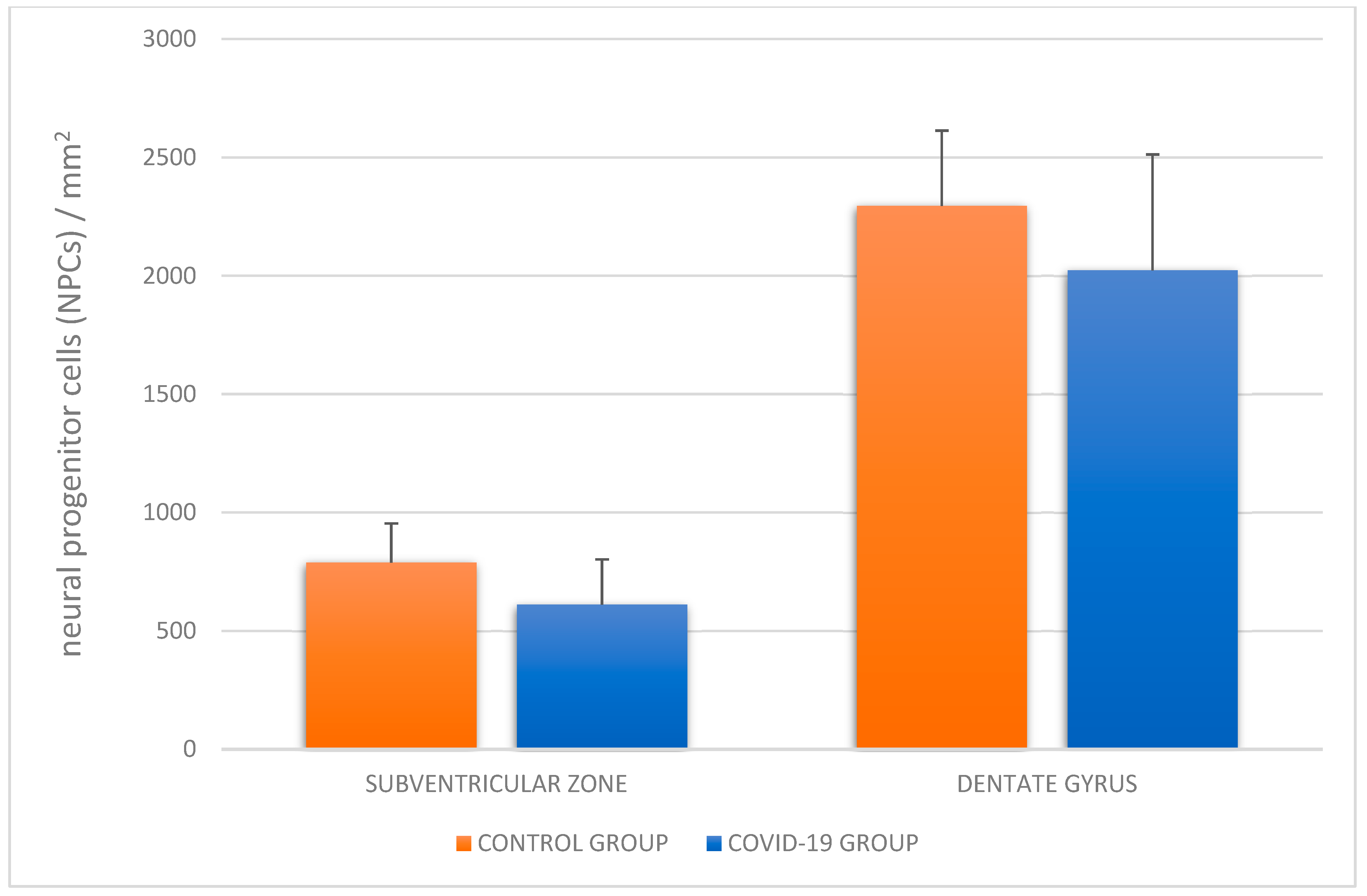
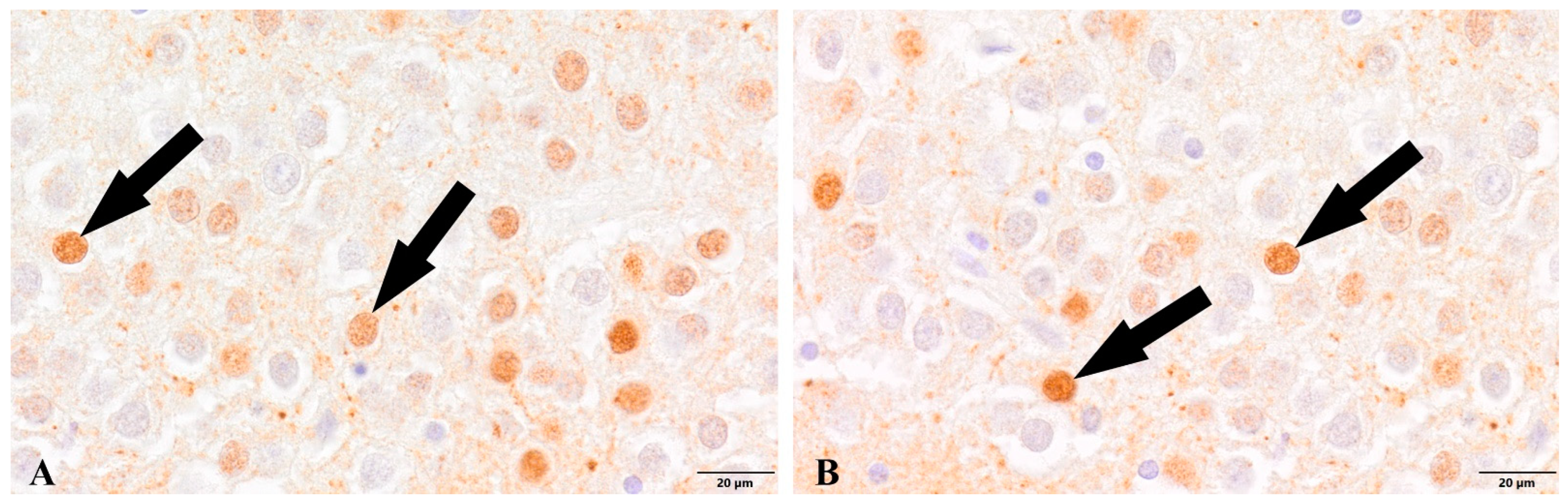
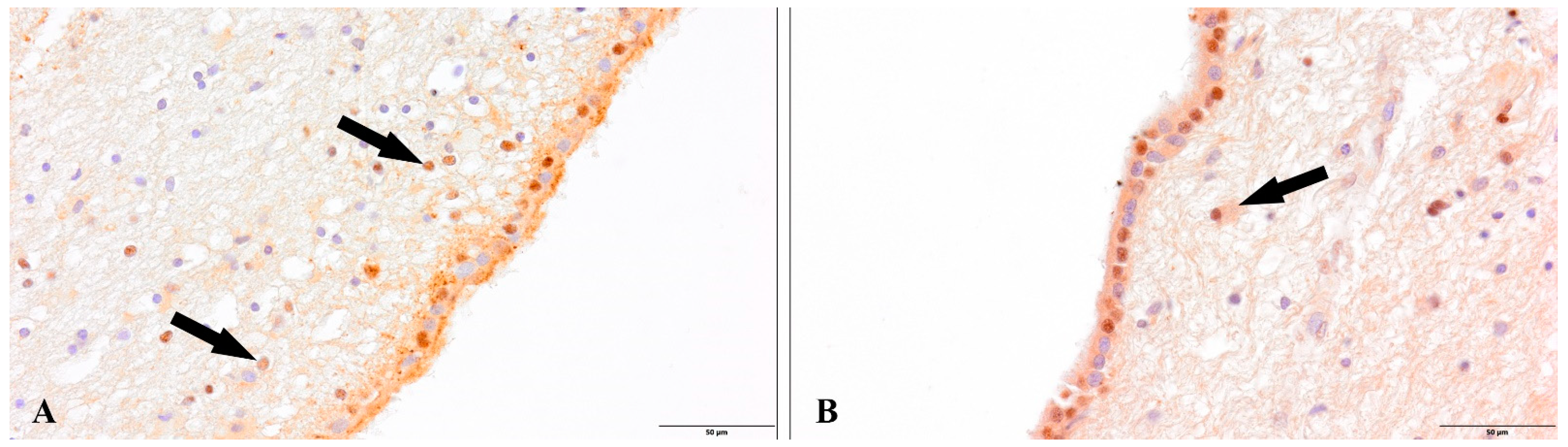
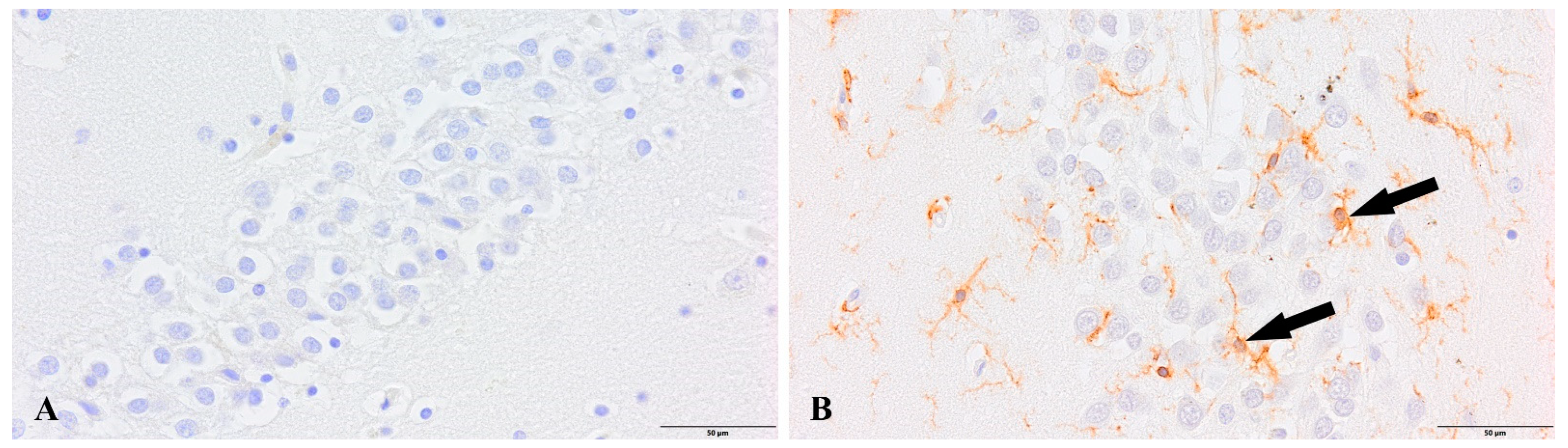
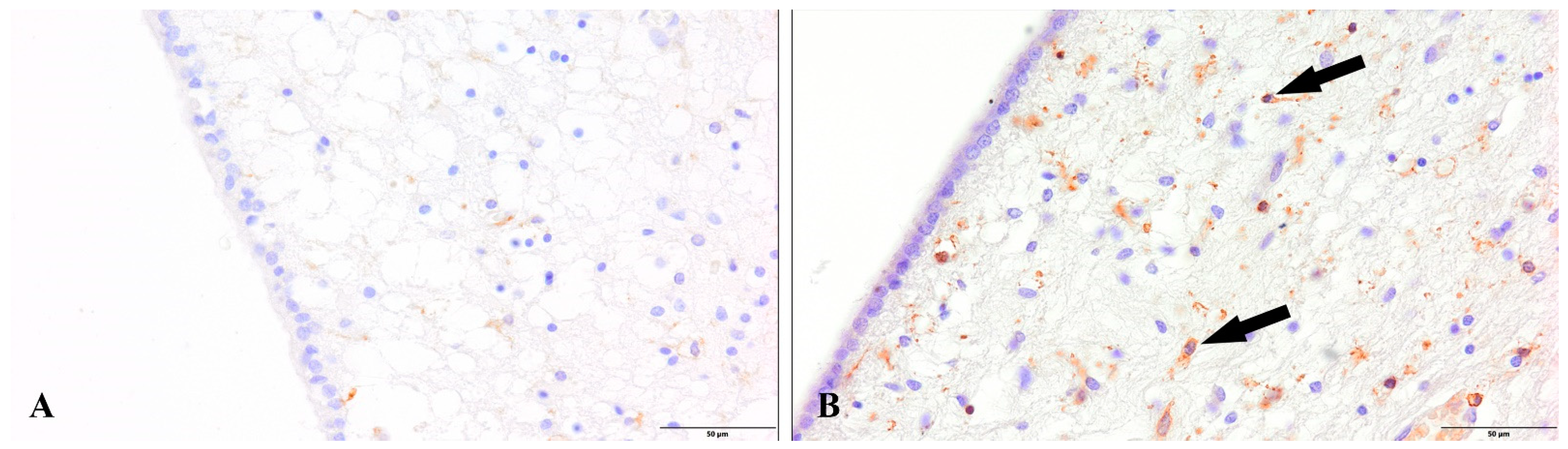
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, W.; Zong, W.; Wang, F.; Ju, S. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A review. Mol. Cancer 2020, 1, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbani, A.V.; Pulakuntla, S.; Pannuru, P.; Aramgam, S.; Badri, K.R.; Reddy, V.D. COVID-19: Comprehensive review on mutations and current vaccines. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 204, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleem, A.; Akbar Samad, A.B.; Slenker, A.K. Emerging Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Novel Therapeutics Against Coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publsihing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bucuvalas, J.; Lai, J.C. Unforeseen consequences of the COVID pandemic. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 2973–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayan, I.; Roth, H.R.; Zhong, A.; Harouni, A.; Gentili, A.; Abidin, A.Z.; Liu, A.; Costa, A.B.; Wood, B.J.; Tsai, C.-S.; et al. Federated learning for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Alharbi, O.M. COVID-19: Disease, management, treatment, and social impact. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaghaslah, D.; Kandasamy, G.; Almanasef, M.; Vasudevan, R.; Chandramohan, S. Review on the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: Its outbreak and current status. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 74, e13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Chang, J.; Hong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varatharaj, A.; Thomas, N.; Ellul, M.A.; Davies, N.W.S.; Pollak, T.A.; Tenorio, E.L.; Sultan, M.; Easton, A.; Breen, G.; Zandi, M.; et al. Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Complications of COVID-19 in 153 Patients: A UK-Wide Surveillance Study. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, D.W.; Hooper, J.E.; Stewart, C.M.; Solomon, I.H. Assessing Brain Capillaries in Coronavirus Disease 2019. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 760–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, P.; Beretta, S.; Piatti, M.; Karantzoulis, A.; Piatti, M.L.; Santoro, P.; Viganò, M.; Giovannelli, G.; Pirro, F.; Montisano, D.A.; et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome related to COVID-19 infection. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, T.; Harii, N.; Goto, J.; Harada, D.; Sugawara, H.; Takamino, J.; Ueno, M.; Sakata, H.; Kondo, K.; Myose, N.; et al. A first case of meningitis/encephalitis associated with SARS-Coronavirus-2. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kananeh, M.F.; Thomas, T.; Sharma, K.; Herpich, F.; Urtecho, J.; Athar, M.K.; Jabbour, P.; Shah, S.O. Arterial and venous strokes in the setting of COVID-19. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 79, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, T.; Shamsi, A.; Anwar, S.; Umair, M.; Hussain, A.; Rehman, M.T.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I. Identification of high-affinity inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: Towards the development of effective COVID-19 therapy. Virus Res. 2020, 288, 198102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsi, A.; Mohammad, T.; Anwar, S.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Rehman, M.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M. Glecaprevir and Maraviroc are high-affinity inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: Possible implication in COVID-19 therapy. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20201256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, A.; Mohammad, T.; Anwar, S.; Amani, S.; Khan, M.S.; Husain, F.M.; Rehman, M.T.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I. Potential drug targets of SARS-CoV-2: From genomics to therapeutics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.C.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Zhong, W.; Hao, P. Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogberg, H.T.; Lam, A.; Ohayon, E.; Shahbaz, M.A.; Clerbaux, L.-A.; Bal-Price, A.; Coecke, S.; Concha, R.; De Bernardi, F.; Edrosa, E.; et al. The Adverse Outcome Pathway Framework Applied to Neurological Symptoms of COVID-19. Cells 2022, 11, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus—Infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, S.S.; Sinha, K.; Majumder, R.; Biswas, A.; Mukhopadhyay, C.D. COVID-19 and central nervous system interplay: A big picturebeyond clinical manifestation. J. Biosci. 2021, 46, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaywant, A.; Vanderlind, W.M.; Alexopoulos, G.S.; Fridman, C.B.; Perlis, R.H.; Gunning, F.M. Frequency and profile of objective cognitive deficits in hospitalized patients recovering from COVID-19. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, R.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Luperdi, S.C.; Estrada, I.; Latorre, A.; González-Jiménez, P.; Feced, L.; Bouzas, L.; Yépez, K.; Ferrando, A.; et al. Short-term neuropsychiatric outcomes and quality of life in COVID-19 survivors. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.; Kremer, S.; Merdji, H.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Schenck, M.; Kummerlen, C.; Collange, O.; Boulay, C.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Ohana, M.; et al. Neurologic Features in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2268–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, R.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Luperdi, S.C.; Estrada, I.; Latorre, A.; González-Jiménez, P.; Bouzas, L.; Yépez, K.; Ferrando, A.; Reyes, S.; et al. Long-term neuropsychiatric outcomes in COVID-19 survivors: A 1-year longitudinal study. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, K.T.; Miller, E.H.; Glendinning, M.D.; Al-Dalahmah, O.; Banu, M.A.; Boehme, A.K.; Boubour, A.L.; Bruce, S.S.; Chong, A.M.; Claassen, J.; et al. COVID-19 neuropathology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center/New York Presbyterian Hospital. Brain 2021, 144, 2696–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, G.; Todisco, M.; Hota, N.; Della Porta, G.; Morbini, P.; Tassorelli, C.; Pisani, A. Neuropathological findings from COVID-19 patients with neurological symptoms argue against a direct brain invasion of SARS-CoV-2: A critical systematic review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3856–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Geng, D.; Mei, N.; Wu, P.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Jia, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xiao, A.; et al. Cerebral Micro-Structural Changes in COVID-19 Patients—An MRI-based 3-month Follow-up Study. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 25, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaunmuktane, Z.; Mahadeva, U.; Green, A.; Sekhawat, V.; Barrett, N.A.; Childs, L.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Thom, M.; Jäger, H.R.; Brandner, S. Microvascular injury and hypoxic damage: Emerging neuropathological signatures in COVID-19. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasemann, S.; Haferkamp, U.; Pfefferle, S.; Woo, M.S.; Heinrich, F.; Schweizer, M.; Appelt-Menzel, A.; Cubukova, A.; Barenberg, J.; Leu, J.; et al. The blood-brain barrier is dysregulated in COVID-19 and serves as a CNS entry route for SARS-CoV-2. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmwald, K.; Gálvez, N.M.; Ríos, M.; Kalergis, A.M. Neurologic Alterations Due to Respiratory Virus Infections. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzba-Bobrowicz, T.; Krajewski, P.; Tarka, S.; Acewicz, A.; Felczak, P.; Stępień, T.; Golan, M.P.; Grzegorczyk, M. Neuropathological analysis of the brains of fifty-two patients with COVID-19. Folia Neuropathol. 2021, 59, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Davis, P.B.; Volkow, N.D.; Berger, N.A.; Kaelber, D.C.; Xu, R. Association of COVID-19 with New-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 89, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, P.S.; Perfilieva, E.; Bjork-Eriksson, T.; Alborn, A.-M.; Nordborg, C.; Peterson, D.A.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.P.; Couillard-Després, S.; Cooper-Kuhn, C.M.; Winkler, J.; Aigner, L.; Kuhn, H.G. Transient expression of doublecortin during adult neurogenesis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 467, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attardo, A.; Fabel, K.; Krebs, J.; Haubensak, W.; Huttner, W.B.; Kempermann, G. Tis21 expression marks not only populations of neurogenic precursor cells but also new postmitotic neurons in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 20, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, H.; Sawamoto, K. Neural stem cells: Involvement in adult neurogenesis and CNS repair. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 2111–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, J.G.; Lin, P.T.; Flanagan, L.A.; Walsh, C.A. Doublecortin is a microtubule-associated protein and is expressed widely by migrating neurons. Neuron 1999, 23, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, R.; Yamashiro, K.; Mochizuki, H.; Cho, N.; Onodera, M.; Mizuno, Y.; Urabe, T. Neurogenesis after transient global ischemia in the adult hippocampus visualized by improved retroviral vector. Stroke 2004, 35, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.J.; Jones, V.; Tabuchi, M.; Allan, S.; Knight, E.; LaFerla, F.M.; Oddo, S.; Verkhratsky, A. Impaired adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of a triple transgenic mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, E.; Hazzalin, C.A.; Kardalinou, E.; Buckle, R.S.; Mahadevan, L.C. Neither ERK nor JNK/SAPK MAP kinase subtypes are essential for histone H3/HMG-14 phosphorylation or c-fos and c-jun induction. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108 Pt 11, 3599–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadee, D.N.; Hendzel, M.; Tylipski, C.P.; Allis, C.D.; Bazett-Jones, D.P.; Wright, J.A.; Davie, J. Increased ser-10 phosphorylation of histone h3 in mitogen-stimulated and oncogene-transformed mouse fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 24914–24920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarelli, L.; Saxe, M.; Gross, C.; Surget, A.; Battaglia, F.; Dulawa, S.; Weisstaub, N.; Lee, J.; Duman, R.; Arancio, O.; et al. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 2003, 301, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erta, M.; Quintana, A.; Hidalgo, J. Interleukin-6, a major cytokine in the central nervous system. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucassen, P.J.; Meerlo, P.; Naylor, A.S.; Van Dam, A.M.; Dayer, A.G.; Fuchs, E.; Oomen, C.A.; Czéh, B. Regulation of adult neurogenesis by stress, sleep disruption, exercise and inflammation: Implications for depression and antidepressant action. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschke, J.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Hagel, C.; Sperhake, J.P.; Schröder, A.S.; Edler, C.; Mushumba, H.; Fitzek, A.; Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M.; et al. Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in Germany: A post-mortem case series. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunc-Ozcan, E.; Peng, C.-Y.; Zhu, Y.; Dunlop, S.R.; Contractor, A.; Kessler, J.A. Activating newborn neurons suppresses depression and anxiety-like behaviors. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxreiter, F.; Regensburger, M.; Winkler, J. Adult neurogenesis in Parkinson’s disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransome, M.I.; Renoir, T.; Hannan, A.J. Hippocampal neurogenesis, cognitive deficits and affective disorder in Huntington’s disease. Neural Plast. 2012, 2012, 874387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Tanzi, R.E. Is Alzheimer’s disease a neurogenesis disorder? Cell Stem Cell 2019, 25, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.A.; Nam, K.H.; Yun, J.; Gim, D.; Joe, D.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.J.; Han, J.W.; Lee, J. Infection of Brain Organoids and 2D Cortical Neurons with SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus. Viruses 2020, 12, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, F.; Pather, S.R.; Huang, W.K.; Zhang, F.; Wong, S.Z.; Zhou, H.; Cubitt, B.; Fan, W.; Chen, C.Z.; Xu, M.; et al. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived neural cells and brain Organoids reveal SARSCoV-2 Neurotropism Predominates in Choroid Plexus Epithelium. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 937–950.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.L.; Staples, H.; Gazi, M.; Carrion, R.; Hsieh, J. SARS-CoV-2 targets glial cells in human cortical organoids. Stem Cell Rep. 2021, 16, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, M.; Anusuyadevi, M.; Aigner, K.M.; Unger, M.S.; Kniewallner, K.M.; de Sousa, D.M.; Altendorfer, B.; Mrowetz, H.; Bogdahn, U.; Aigner, L. TGF-β Signaling: A therapeutic target to reinstate regenerative plasticity in vascular dementia? Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 828–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarlagadda, A.; Alfson, E.; Clayton, A.H. The Blood Brain Barrier and the Role of Cytokines in Neuropsychiatry. Psychiatry 2009, 6, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.; Soung, A.; Sissoko, C.; Nordvig, A.; Canoll, P.; Mariani, M.; Jiang, X.; Bricker, T.; Goldman, J.; Rosoklija, G.; et al. COVID-19 induces neuroinflammation and loss of hippocampal neurogenesis. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Hammack, C.; Ogden, S.C.; Wen, Z.; Qian, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, B.; Shin, J.; Zhang, F.; Lee, E.M.; et al. Zika Virus Infects Human Cortical Neural Progenitors and Attenuates Their Growth. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, C.; Vasek, M.; Vollmer, L.; Sun, T.; Jiang, X.; Klein, R.S. Astrocytes decrease adult neurogenesis during virus-induced memory dysfunction via IL-1. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soung, A.L.; Davé, V.A.; Garber, C.; Tycksen, E.D.; Vollmer, L.L.; Klein, R.S. IL-1 reprogramming of adult neural stem cells limits neurocognitive recovery after viral encephalitis by maintaining a proinflammatory state. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 99, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stępień, T.; Tarka, S.; Chmura, N.; Grzegorczyk, M.; Acewicz, A.; Felczak, P.; Wierzba-Bobrowicz, T. Influence of SARS-CoV-2 on Adult Human Neurogenesis. Cells 2023, 12, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12020244
Stępień T, Tarka S, Chmura N, Grzegorczyk M, Acewicz A, Felczak P, Wierzba-Bobrowicz T. Influence of SARS-CoV-2 on Adult Human Neurogenesis. Cells. 2023; 12(2):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12020244
Chicago/Turabian StyleStępień, Tomasz, Sylwia Tarka, Natalia Chmura, Michał Grzegorczyk, Albert Acewicz, Paulina Felczak, and Teresa Wierzba-Bobrowicz. 2023. "Influence of SARS-CoV-2 on Adult Human Neurogenesis" Cells 12, no. 2: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12020244
APA StyleStępień, T., Tarka, S., Chmura, N., Grzegorczyk, M., Acewicz, A., Felczak, P., & Wierzba-Bobrowicz, T. (2023). Influence of SARS-CoV-2 on Adult Human Neurogenesis. Cells, 12(2), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12020244






