From Youthful Vigor to Aging Decline: Unravelling the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Determinants of Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Aging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Intrinsic Mechanisms
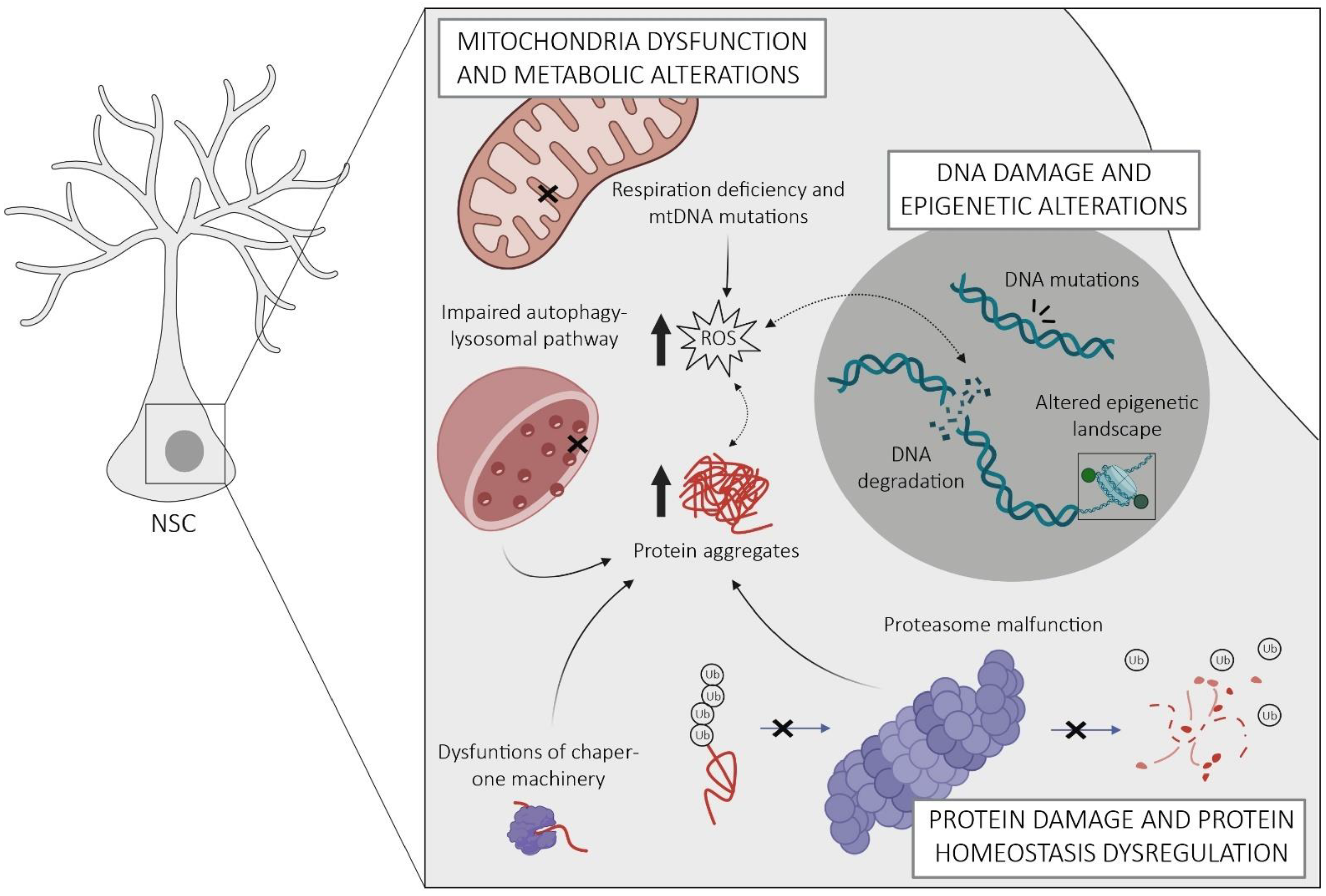
2.1. Protein Homeostasis Dysregulation
2.2. Mitochondria Dysfunction and Metabolic Alterations
2.3. DNA Damage and Epigenetic Alterations
2.4. Cellular Senescence
3. Neurogenic Niche
3.1. Astrocytes
3.2. Microglia
3.3. Microvasculature, Endothelial Cells, and Pericytes
4. Systemic Milieu
4.1. Blood-Derived Factors and Extracellular Vesicles (ECVs)
4.2. Gut Microbiome
4.3. Peripheral Immune Cells
4.4. Glymphatic System and Meningeal Lymphatic System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altman, J.; Das, G.D. Autoradiographic and Histological Evidence of Postnatal Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1965, 124, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doetsch, F.; Caille, I.; Lim, D.A.; Garcı, J.M.; Alvarez-buylla, A. Subventricular Zone Astrocytes Are Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Mammalian Brain. Cell 1999, 97, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.D.; Takahashi, J.; Gage, F.H. The Adult Rat Hippocampus Contains Primordial Neural Stem Cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1997, 8, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaguidi, M.A.; Wheeler, M.A.; Shapiro, J.S.; Stadel, R.P.; Sun, G.J.; Ming, G.L.; Song, H. In Vivo Clonal Analysis Reveals Self-Renewing and Multipotent Adult Neural Stem Cell Characteristics. Cell 2011, 145, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encinas, J.M.; Michurina, T.V.; Peunova, N.; Park, J.H.; Tordo, J.; Peterson, D.A.; Fishell, G.; Koulakov, A.; Enikolopov, G. Division-Coupled Astrocytic Differentiation and Age-Related Depletion of Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, G.A.; Bottes, S.; Betizeau, M.; Jörg, D.J.; Carta, S.; Simons, B.D.; Helmchen, F.; Jessberger, S. Live Imaging of Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Hippocampus. Science 2018, 359, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.T.; Schafer, S.T.; Gage, F.H. Adult Neurogenesis in the Hippocampus: From Stem Cells to Behavior. Cell 2016, 167, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrayeva, A.; Bay, M.; Pu, E.; Jörg, D.J.; Peng, L.; Jun, H.; Zhang, N.; Aaron, D.; Lin, C.; Resler, G.; et al. Early Stem Cell Aging in the Mature Brain. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 955–966.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazutkin, A.; Podgorny, O.; Enikolopov, G. Modes of Division and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 374, 112118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbán, N.; Van Den Berg, D.L.C.; Forget, A.; Andersen, J.; Demmers, J.A.A.; Hunt, C.; Ayrault, O.; Guillemot, F. Return to Quiescence of Mouse Neural Stem Cells by Degradation of a Proactivation Protein. Science 2016, 353, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.; Rigo, P.; Stiehl, T.; Gaber, Z.B.; Austin, S.H.L.; Masdeu, M.d.M.; Edwards, A.; Urbán, N.; Marciniak-Czochra, A.; Guillemot, F. Coordinated Changes in Cellular Behavior Ensure the Lifelong Maintenance of the Hippocampal Stem Cell Population. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 863–876.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bast, L.; Calzolari, F.; Strasser, M.K.; Hasenauer, J.; Theis, F.J.; Ninkovic, J.; Marr, C. Increasing Neural Stem Cell Division Asymmetry and Quiescence Are Predicted to Contribute to the Age-Related Decline in Neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3231–3240.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottes, S.; Jaeger, B.N.; Pilz, G.A.; Jörg, D.J.; Cole, J.D.; Kruse, M.; Harris, L.; Korobeynyk, V.I.; Mallona, I.; Helmchen, F.; et al. Long-Term Self-Renewing Stem Cells in the Adult Mouse Hippocampus Identified by Intravital Imaging. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbán, N.; Blomfield, I.M.; Guillemot, F. Quiescence of Adult Mammalian Neural Stem Cells: A Highly Regulated Rest. Neuron 2019, 104, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, S.; Matsuda, T.; Nakashima, K. Regulation of Adult Mammalian Neural Stem Cells and Neurogenesis by Cell Extrinsic and Intrinsic Factors. Cells 2021, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.G.; Dickinson-Anson, H.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus of the Adult Rat: Age-Related Decrease of Neuronal Progenitor Proliferation. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizon, J.L.; Gallagher, M. Production of New Cells in the Rat Dentate Gyrus over the Lifespan: Relation to Cognitive Decline. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempin, F.; Kempermann, G. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Aging. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 257, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessberger, S.; Toni, N.; Clemenson, G.D.; Ray, J.; Gage, F.H. Directed Differentiation of Hippocampal Stem/Progenitor Cells in the Adult Brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Jiménez, E.P.; Flor-García, M.; Terreros-Roncal, J.; Rábano, A.; Cafini, F.; Pallas-Bazarra, N.; Ávila, J.; Llorens-Martín, M. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Is Abundant in Neurologically Healthy Subjects and Drops Sharply in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattiangady, B.; Shetty, A.K. Aging Does Not Alter the Number or Phenotype of Putative Stem/Progenitor Cells in the Neurogenic Region of the Hippocampus. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugert, S.; Basak, O.; Knuckles, P.; Haussler, U.; Fabel, K.; Götz, M.; Haas, C.A.; Kempermann, G.; Taylor, V.; Giachino, C. Quiescent and Active Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells with Distinct Morphologies Respond Selectively to Physiological and Pathological Stimuli and Aging. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bottes, S.; Fisch, R.; Zehnder, C.; Cole, J.D.; Pilz, G.A.; Helmchen, F.; Simons, B.D.; Jessberger, S. Chronic in Vivo Imaging Defines Age-Dependent Alterations of Neurogenesis in the Mouse Hippocampus. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimone, J.B.; Li, Y.; Lee, S.W.; Clemenson, G.D.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Regulation and Function of Adult Neurogenesis: From Genes to Cognition. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 991–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeda, S.A.; Luo, J.; Mosher, K.I.; Zou, B.; Britschgi, M.; Bieri, G.; Stan, T.M.; Fainberg, N.; Ding, Z.; Eggel, A.; et al. The Ageing Systemic Milieu Negatively Regulates Neurogenesis and Cognitive Function. Nature 2011, 477, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagne, A.; Barnes, S.R.; Sweeney, M.D.; Halliday, M.R.; Sagare, A.P.; Zhao, Z.; Toga, A.W.; Jacobs, R.E.; Liu, C.Y.; Amezcua, L.; et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in the Aging Human Hippocampus. Neuron 2015, 85, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Negredo, P.; Yeo, R.W.; Brunet, A. Aging and Rejuvenation of Neural Stem Cells and Their Niches. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 202–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, I.; Vilchez, D. The Mechanistic Links Between Proteasome Activity, Aging and Agerelated Diseases. Curr. Genom. 2014, 15, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, F.U.; Bracher, A.; Hayer-Hartl, M. Molecular Chaperones in Protein Folding and Proteostasis. Nature 2011, 475, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, D. Recognition and Processing of Ubiquitin-Protein Conjugates by the Proteasome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 477–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, Y.; Schmauck-Medina, T.; Hansen, M.; Morimoto, R.I.; Simon, A.K.; Bjedov, I.; Palikaras, K.; Simonsen, A.; Johansen, T.; Tavernarakis, N.; et al. Autophagy in Healthy Aging and Disease. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeman, D.S.; Hebestreit, K.; Ruetz, T.; Webb, A.E.; McKay, A.; Pollina, E.A.; Dulken, B.W.; Zhao, X.; Yeo, R.W.; Ho, T.T.; et al. Lysosome Activation Clears Aggregates and Enhances Quiescent Neural Stem Cell Activation during Aging. Science 2018, 359, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Piao, W.; Takamura, T.; Kori, H.; Miyachi, H.; Kitano, S.; Iwamoto, Y.; Yamada, M.; Imayoshi, I.; Shioda, S.; et al. Enhanced Lysosomal Degradation Maintains the Quiescent State of Neural Stem Cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk, W.I.M.; Rainbolt, T.K.; Dolan, P.T.; Webb, A.E.; Brunet, A.; Frydman, J.; Vonk, W.I.M.; Rainbolt, T.K.; Dolan, P.T.; Webb, A.E.; et al. Differentiation Drives Widespread Rewiring of the Neural Stem Cell Chaperone Network Differentiation Drives Widespread Rewiring of the Neural Stem Cell Chaperone Network. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 329–345.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audesse, A.J.; Webb, A.E. Mechanisms of Enhanced Quiescence in Neural Stem Cell Aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 191, 111323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, A.E.; Brunet, A. FOXO Transcription Factors: Key Regulators of Cellular Quality Control. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäffner, I.; Minakaki, G.; Khan, M.A.; Balta, E.A.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; Schwarz, T.J.; Beckervordersandforth, R.; Winner, B.; Webb, A.E.; DePinho, R.A.; et al. FoxO Function Is Essential for Maintenance of Autophagic Flux and Neuronal Morphogenesis in Adult Neurogenesis. Neuron 2018, 99, 1188–1203.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.L.; Pilz, G.A.; Araúzo-Bravo, M.J.; Barral, Y.; Jessberger, S. A Mechanism for the Segregation of Age in Mammalian Neural Stem Cells. Science 2015, 349, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrosian, T.A.; Houtman, J.; Eguiguren, J.S.; Ghassemzadeh, S.; Rund, N.; Novaresi, N.M.; Hu, L.; Parylak, S.L.; Denli, A.M.; Randolph-Moore, L.; et al. Lamin B1 Decline Underlies Age-related Loss of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e105819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatt, M.P.; Tran, L.M.; Vetere, G.; Storer, M.A.; Simonetta, J.V.; Miller, F.D.; Frankland, P.W.; Kaplan, D.R. Restoration of Hippocampal Neural Precursor Function by Ablation of Senescent Cells in the Aging Stem Cell Niche. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajani, S.; Giacomini, C.; Marinaro, F.; De Pietri Tonelli, D.; Contestabile, A.; Gasparini, L. Lamin B1 Levels Modulate Differentiation into Neurons during Embryonic Corticogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- bin Imtiaz, M.K.; Jaeger, B.N.; Bottes, S.; Machado, R.A.C.; Vidmar, M.; Moore, D.L.; Jessberger, S. Declining Lamin B1 Expression Mediates Age-Dependent Decreases of Hippocampal Stem Cell Activity. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 967–977.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahabikashi, A.; Adam, S.A.; Medalia, O.; Goldman, R.D. Nuclear Lamins: Structure and Function in Mechanobiology. APL Bioeng. 2022, 6, 011503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckervordersandforth, R.; Ebert, B.; Schäffner, I.; Moss, J.; Fiebig, C.; Shin, J.; Moore, D.L.; Ghosh, L.; Trinchero, M.F.; Stockburger, C.; et al. Role of Mitochondrial Metabolism in the Control of Early Lineage Progression and Aging Phenotypes in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Neuron 2017, 93, 560–573.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Berg, D.A.; Zhu, Y.; Shin, J.Y.; Song, J.; Bonaguidi, M.A.; Enikolopov, G.; Nauen, D.W.; Christian, K.M.; Ming, G.L.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq with Waterfall Reveals Molecular Cascades Underlying Adult Neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Scandella, V.; Montessuit, S.; Zamboni, N.; Martinou, J.C.; Knobloch, M. Mitochondrial Pyruvate Metabolism Regulates the Activation of Quiescent Adult Neural Stem Cells. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadd5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, G.A.; Sprenger, H.G.; Ndoci, K.; Chandragiri, S.; Acton, R.J.; Schatton, D.; Kochan, S.M.V.; Sakthivelu, V.; Jevtic, M.; Seeger, J.M.; et al. Metabolic Control of Adult Neural Stem Cell Self-Renewal by the Mitochondrial Protease YME1L. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khacho, M.; Clark, A.; Svoboda, D.S.; Azzi, J.; MacLaurin, J.G.; Meghaizel, C.; Sesaki, H.; Lagace, D.C.; Germain, M.; Harper, M.E.; et al. Mitochondrial Dynamics Impacts Stem Cell Identity and Fate Decisions by Regulating a Nuclear Transcriptional Program. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchegaray, J.P.; Mostoslavsky, R. Interplay between Metabolism and Epigenetics: A Nuclear Adaptation to Environmental Changes. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Esbensen, Y.; Kunke, D.; Suganthan, R.; Rachek, L.; Bjørås, M.; Eide, L. Mitochondrial DNA Damage Level Determines Neural Stem Cell Differentiation Fate. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9746–9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Yao, M.J.; Zhai, Q.W.; Jiao, J.W.; Yuan, X.B.; Poo, M.M. SIRT1 Suppresses Self-Renewal of Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells. Development 2014, 141, 4697–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-González, X.R. Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Common Denominator in Neurodevelopmental Disorders? Dev. Neurosci. 2021, 43, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinat, D.; Coppes, R.P.; Barazzuol, L. DNA Damage-Induced Inflammatory Microenvironment and Adult Stem Cell Response. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khacho, M.; Harris, R.; Slack, R.S. Mitochondria as Central Regulators of Neural Stem Cell Fate and Cognitive Function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Menzies, K.J.; Auwerx, J. The Role of Mitochondria in Stem Cell Fate and Aging. Dev. 2018, 145, dev143420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Youle, R.J.; Finkel, T. The Mitochondrial Basis of Aging. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, I.R.; Fochesatto, C.; De Andrade, A.; Santos, M.; Hagen, M.; Bello-Klein, A.; Netto, C.A. Total Antioxidant Capacity Is Impaired in Different Structures from Aged Rat Brain. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2005, 23, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raber, J.; Villasana, L.; Rosenberg, J.; Zou, Y.; Huang, T.T.; Fike, J.R. Irradiation Enhances Hippocampus-Dependent Cognition in Mice Deficient in Extracellular Superoxide Dismutase. Hippocampus 2011, 21, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, M.; Braun, S.M.G.; Zurkirchen, L.; Von Schoultz, C.; Zamboni, N.; Araúzo-Bravo, M.J.; Kovacs, W.J.; Karalay, Ö.; Suter, U.; MacHado, R.A.C.; et al. Metabolic Control of Adult Neural Stem Cell Activity by Fasn-Dependent Lipogenesis. Nature 2013, 493, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, M.; Pilz, G.A.; Ghesquière, B.; Kovacs, W.J.; Wegleiter, T.; Moore, D.L.; Hruzova, M.; Zamboni, N.; Carmeliet, P.; Jessberger, S. A Fatty Acid Oxidation-Dependent Metabolic Shift Regulates Adult Neural Stem Cell Activity. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, E.A.; Makin, R.; Sweet, I.R.; Trevelyan, A.J.; Miwa, S.; Horner, P.J.; Turnbull, D.M. Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Subventricular Zone Oxidize Fatty Acids to Produce Energy and Support Neurogenic Activity. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2306–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sênos Demarco, R.; Clémot, M.; Jones, D.L. The Impact of Ageing on Lipid-Mediated Regulation of Adult Stem Cell Behavior and Tissue Homeostasis. Mech. Aging Dev. 2020, 189, 111278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.; Lithgow, G.J.; Link, W. Long Live FOXO: Unraveling the Role of FOXO Proteins in Aging and Longevity. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaker, Z.; Aïd, S.; Berry, H.; Holzenberger, M. Suppression of IGF-I Signals in Neural Stem Cells Enhances Neurogenesis and Olfactory Function during Aging. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandhorst, S.; Choi, I.Y.; Wei, M.; Cheng, C.W.; Sedrakyan, S.; Navarrete, G.; Dubeau, L.; Yap, L.P.; Park, R.; Vinciguerra, M.; et al. A Periodic Diet That Mimics Fasting Promotes Multi-System Regeneration, Enhanced Cognitive Performance, and Healthspan. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, D.M.; Mahesula, S.; Fonseca, R.S.; Zhu, C.; Kokovay, E. Calorie Restriction Protects Neural Stem Cells from Age-Related Deficits in the Subventricular Zone. Aging 2019, 11, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, S.; Leone, L.; Barbati, S.A.; Samengo, D.; Piacentini, R.; Maulucci, G.; Toietta, G.; Spinelli, M.; McBurney, M.; Pani, G.; et al. A CREB-Sirt1-Hes1 Circuitry Mediates Neural Stem Cell Response to Glucose Availability. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Cho, W.; Zhou, J.; Birnbaum, S.G.; Sinton, C.M.; McKay, R.M.; Parada, L.F. Pten Deletion in Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells Causes Cellular Abnormalities and Alters Neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 5880–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahara, S.; Yanagawa, Y.; O’Leary, D.D.M.; Stevens, C.F. The Fraction of Cortical GABAergic Neurons Is Constant from near the Start of Cortical Neurogenesis to Adulthood. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 4755–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.-I.; Guarente, L. NAD+ and Sirtuins in Aging and Disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, C.; Reddy, P.H.; Palle, K. DNA Repair Fidelity in Stem Cell Maintenance, Health, and Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Shiue, K.; Schomberg, D.; Zhou, F.C. Cellular Epigenetic Modifications of Neural Stem Cell Differentiation. Cell Transplant. 2009, 18, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maybury-Lewis, S.Y.; Brown, A.K.; Yeary, M.; Sloutskin, A.; Dhakal, S.; Juven-Gershon, T.; Webb, A.E. Changing and Stable Chromatin Accessibility Supports Transcriptional Overhaul during Neural Stem Cell Activation and Is Altered with Age. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, B.; Pothof, J.; Vijg, J.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.J. The Central Role of DNA Damage in the Ageing Process. Nature 2021, 592, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zocher, S.; Toda, T. Epigenetic Aging in Adult Neurogenesis. Hippocampus 2023, 33, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezone, A.; Olivieri, F.; Napoli, M.V.; Procopio, A.; Avvedimento, E.V.; Gabrielli, A. Inflammation and DNA Damage: Cause, Effect or Both. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, A.; Van Deursen, J.M.; Rudolph, K.L.; Schumacher, B. Impact of Genomic Damage and Ageing on Stem Cell Function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Simon, M.; Seluanov, A.; Gorbunova, V. DNA Damage and Repair in Age-Related Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, K.J.; Maslov, A.Y.; Pruitt, S.C. Accumulation of Mutations and Somatic Selection in Aging Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. Aging Cell 2004, 3, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Pellegatta, S.; Favaro, R.; Pisati, F.; Roncaglia, P.; Testa, G.; Nicolis, S.K.; Finocchiaro, G.; D’Adda Di Fagagna, F. DNA Damage in Mammalian Neural Stem Cells Leads to Astrocytic Differentiation Mediated by BMP2 Signaling through JAK-STAT. Stem Cell Rep. 2013, 1, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzuol, L.; Ju, L.; Jeggo, P.A. A Coordinated DNA Damage Response Promotes Adult Quiescent Neural Stem Cell Activation. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daynac, M.; Chicheportiche, A.; Pineda, J.R.; Gauthier, L.R.; Boussin, F.D.; Mouthon, M.A. Quiescent Neural Stem Cells Exit Dormancy upon Alteration of GABAAR Signaling Following Radiation Damage. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 11, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Abdallah, N.M.B.; Slomianka, L.; Vyssotski, A.L.; Lipp, H.P. Early Age-Related Changes in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in C57 Mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, D.; Lier, A.; Geiselhart, A.; Thalheimer, F.B.; Huntscha, S.; Sobotta, M.C.; Moehrle, B.; Brocks, D.; Bayindir, I.; Kaschutnig, P.; et al. Exit from Dormancy Provokes DNA-Damage-Induced Attrition in Haematopoietic Stem Cells. Nature 2015, 520, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellström, N.A.K.; Björk-Eriksson, T.; Blomgren, K.; Kuhn, H.G. Differential Recovery of Neural Stem Cells in the Subventricular Zone and Dentate Gyrus After Ionizing Radiation. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamakis, G.; Brüne, D.; Ravichandran, S.; Bolz, J.; Fan, W.; Ziebell, F.; Stiehl, T.; Catalá-Martinez, F.; Kupke, J.; Zhao, S.; et al. Quiescence Modulates Stem Cell Maintenance and Regenerative Capacity in the Aging Brain. Cell 2019, 176, 1407–1419.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeyev, M.; Shokolenko, I.; Wilson, G.; LeDoux, S. The Maintenance of Mitochondrial DNA Integrity—Critical Analysis and Update. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelnour, E.; Bonev, B. Decoding the Organization, Dynamics, and Function of the 4D Genome. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocher, S.; Overall, R.W.; Lesche, M.; Dahl, A.; Kempermann, G. Environmental Enrichment Preserves a Young DNA Methylation Landscape in the Aged Mouse Hippocampus. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontier, G.; Iyer, M.; Shea, J.M.; Bieri, G.; Wheatley, E.G.; Ramalho-Santos, M.; Villeda, S.A. Tet2 Rescues Age-Related Regenerative Decline and Enhances Cognitive Function in the Adult Mouse Brain. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 1974–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobe, E.M.; Gao, Y.; Eisinger, B.E.; Mladucky, J.K.; Giuliani, C.C.; Kelnhofer, L.E.; Zhao, X. Methyl-Cpg-Binding Protein MBD1 Regulates Neuronal Lineage Commitment through Maintaining Adult Neural Stem Cell Identity. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Barkho, B.Z.; Luo, Y.; Smrt, R.D.; Santistevan, N.J.; Liu, C.; Kuwabara, T.; Gage, F.H.; Zhao, X. Epigenetic Regulation of the Stem Cell Mitogen Fgf-2 by Mbd1 in Adult Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27644–27652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwafuchi-Doi, M.; Zaret, K.S. Pioneer Transcription Factors in Cell Reprogramming. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2679–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaret, K.S. Pioneer Transcription Factors Initiating Gene Network Changes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2020, 54, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, A.A.S.F.; Vasconcelos, F.F.; Drechsel, D.; Marie, C.; Johnston, C.; Dolle, D.; Bithell, A.; Gillotin, S.; van den Berg, D.L.C.; Ettwiller, L.; et al. Ascl1 Coordinately Regulates Gene Expression and the Chromatin Landscape during Neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1544–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomfield, I.M.; Rocamonde, B.; del Mar Masdeu, M.; Mulugeta, E.; Vaga, S.; van den Berg, D.L.C.; Huillard, E.; Guillemot, F.; Urbán, N. Id4 Promotes the Elimination of the Pro-Activation Factor Ascl1 to Maintain Quiescence of Adult Hippocampal Stem Cells. Elife 2019, 8, e48561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.; Urbán, N.; Achimastou, A.; Ito, A.; Simic, M.; Ullom, K.; Martynoga, B.; Lebel, M.; Göritz, C.; Frisén, J.; et al. A Transcriptional Mechanism Integrating Inputs from Extracellular Signals to Activate Hippocampal Stem Cells. Neuron 2014, 83, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, A.L.M.; Cavallaro, M.; Braida, D.; Di Cristofano, A.; Canta, A.; Vezzani, A.; Ottolenghi, S.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Sala, M.; DeBiasi, S.; et al. Sox2 Deficiency Causes Neurodegeneration and Impaired Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Brain. Development 2004, 131, 3805–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, J.A.; Favaro, R.; Zhu, Y.; Pagin, M.; Ngan, C.Y.; Wong, C.H.; Tjong, H.; Vermunt, M.W.; Martynoga, B.; Barone, C.; et al. Mapping the Global Chromatin Connectivity Network for Sox2 Function in Neural Stem Cell Maintenance. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 462–476.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimadamore, F.; Amador-Arjona, A.; Chen, C.; Huang, C.T.; Terskikh, A.V. SOX2-LIN28/Let-7 Pathway Regulates Proliferation and Neurogenesis in Neural Precursors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador-Arjona, A.; Cimadamore, F.; Huang, C.T.; Wright, R.; Lewis, S.; Gage, F.H.; Terskikh, A.V. SOX2 Primes the Epigenetic Landscape in Neural Precursors Enabling Proper Gene Activation during Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1936–E1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, T.; Hsu, J.Y.; Linker, S.B.; Hu, L.; Schafer, S.T.; Mertens, J.; Jacinto, F.V.; Hetzer, M.W.; Gage, F.H. Nup153 Interacts with Sox2 to Enable Bimodal Gene Regulation and Maintenance of Neural Progenitor Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 618–634.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Garcia, E.; Moreno-Cugnon, L.; Garcia, I.; Borras, C.; Revuelta, M.; Izeta, A.; Lopez-Lluch, G.; de Pancorbo, M.M.; Vergara, I.; Vina, J.; et al. SOX2 Expression Diminishes with Ageing in Several Tissues in Mice and Humans. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 177, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestres, I.; Houtman, J.; Calegari, F.; Toda, T. A Nuclear Belt Fastens on Neural Cell Fate. Cells 2022, 11, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peric-Hupkes, D.; Meuleman, W.; Pagie, L.; Bruggeman, S.W.M.; Solovei, I.; Brugman, W.; Gräf, S.; Flicek, P.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; van Lohuizen, M.; et al. Molecular Maps of the Reorganization of Genome-Nuclear Lamina Interactions during Differentiation. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Li, M.; Shao, S.; Li, C.; Ai, S.; Xue, B.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Fan, X.; et al. Nuclear Peripheral Chromatin-Lamin B1 Interaction Is Required for Global Integrity of Chromatin Architecture and Dynamics in Human Cells. Protein Cell 2022, 13, 258–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, I.; Diniz, L.P.; Damico, I.V.; Araujo, A.P.B.; Neves, L.d.S.; Vargas, G.; Leite, R.E.P.; Suemoto, C.K.; Nitrini, R.; Jacob-Filho, W.; et al. Loss of Lamin-B1 and Defective Nuclear Morphology Are Hallmarks of Astrocyte Senescence in Vitro and in the Aging Human Hippocampus. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Hayano, M.; Griffin, P.T.; Amorim, J.A.; Bonkowski, M.S.; Apostolides, J.K.; Salfati, E.L.; Blanchette, M.; Munding, E.M.; Bhakta, M.; et al. Loss of Epigenetic Information as a Cause of Mammalian Aging. Cell 2023, 186, 305–326.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Segura, A.; Nehme, J.; Demaria, M. Hallmarks of Cellular Senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, X. Evidence and Perspectives of Cell Senescence in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, G.P.; Lee, X.; Basile, G.; Acosta, M.; Scott, G.; Roskelley, C.; Medrano, E.E.; Linskens, M.; Rubelj, I.; Pereira-Smith, O.; et al. A Biomarker That Identifies Senescent Human Cells in Culture and in Aging Skin in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9363–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.; Lin, A.W.; McCurrach, M.E.; Beach, D.; Lowe, S.W. Oncogenic Ras Provokes Premature Cell Senescence Associated with Accumulation of P53 and P16(INK4a). Cell 1997, 88, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherr, C.J.; Roberts, J.M. CDK Inhibitors: Positive and Negative Regulators of G1-Phase Progression. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlenius, H.; Visan, V.; Kokaia, M.; Lindvall, O.; Kokaia, Z. Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells Retain Their Potential for Proliferation and Differentiation into Functional Neurons despite Lower Number in Aged Brain. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4408–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbach, A.; Witte, O.W. Divide or Commit—Revisiting the Role of Cell Cycle Regulators in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molofsky, A.V.; Slutsky, S.G.; Joseph, N.M.; He, S.; Pardal, R.; Krishnamurthy, J.; Sharpless, N.E.; Morrison, S.J. Increasing P16INK4a Expression Decreases Forebrain Progenitors and Neurogenesis during Ageing. Nature 2006, 443, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, L.; D’Andrea, G.; Ceccarelli, M.; Ferri, A.; Scardigli, R.; Tirone, F. P16Ink4a Prevents the Activation of Aged Quiescent Dentate Gyrus Stem Cells by Physical Exercise. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Cantón, R.; Perez-Villalba, A.; Morante-Redolat, J.M.; Marqués-Torrejón, M.Á.; Pallás, M.; Pérez-Sánchez, F.; Fariñas, I. Regulation of the P19Arf/P53 Pathway by Histone Acetylation Underlies Neural Stem Cell Behavior in Senescence-Prone SAMP8 Mice. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deursen, J.M. The Role of Senescent Cells in Ageing. Nature 2014, 509, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, A.; Laberge, R.M.; Demaria, M.; Campisi, J. Lamin B1 Loss Is a Senescence-Associated Biomarker. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, C.; Tuntevski, K.; Beatini, S.; Pelizzoli, R.; Lo Van, A.; Mangoni, D.; Cossu, R.M.; Pascarella, G.; Bianchini, P.; Bielefeld, P.; et al. Piwil2 (Mili) Sustains Neurogenesis and Prevents Cellular Senescence in the Postnatal Hippocampus. EMBO Rep. 2023, 24, e53801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaise, T.; Fukui, M.; Sueda, R.; Piao, W.; Yamada, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Imayoshi, I.; Kageyama, R. Functional Rejuvenation of Aged Neural Stem Cells by Plagl2 and Anti-Dyrk1a Activity. Genes Dev. 2022, 36, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-D.; Zhu, Y.-T.; Shi, Y.-H.; Liu, X.-X.; Su, W.-R.; Zhuo, Y.-H. Deciphering Adult Neural Stem Cells with Single-Cell Sequencing. Stem Cells Dev. 2023, 32, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhong, C.; Bonaguidi, M.A.; Sun, G.J.; Hsu, D.; Gu, Y.; Meletis, K.; Huang, Z.J.; Ge, S.; Enikolopov, G.; et al. Neuronal Circuitry Mechanism Regulating Adult Quiescent Neural Stem-Cell Fate Decision. Nature 2012, 489, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, J.; Gebara, E.; Bushong, E.A.; Sánchez-Pascual, I.; O’Laoi, R.; El M’Gharia, I.; Kocher-Braissant, J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Toni, N. Fine Processes of Nestin-GFP-Positive Radial Glia-like Stem Cells in the Adult Dentate Gyrus Ensheathe Local Synapses and Vasculature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2536–E2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassé, F.; Richetin, K.; Toni, N. Astrocytes’ Contribution to Adult Neurogenesis in Physiology and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, B.A.; Weiss, S. Generation of Neurons and Astrocytes from Isolated Cells of the Adult Mammalian Central Nervous System. Science 1992, 255, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, F.H.; Coates, P.W.; Palmer, T.D.; Kuhn, H.G.; Fisher, L.J.; Suhonen, J.O.; Peterson, D.A.; Suhr, S.T.; Ray, J. Survival and Differentiation of Adult Neuronal Progenitor Cells Transplanted to the Adult Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11879–11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.D.; Ray, J.; Gage, F.H. FGF-2-Responsive Neuronal Progenitors Reside in Proliferative and Quiescent Regions of the Adult Rodent Brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1995, 6, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, L.P.; Qin, X.H.; Li, S.J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Hu, H.H.; Fang, Y.Y.; Gao, Y.B.; Li, X.W.; et al. Astrocytic Adenosine 5′-Triphosphate Release Regulates the Proliferation of Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Hippocampus. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Gebara, E.G.; Moullec, K.; Toni, N. D-Serine Increases Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Haydon, P.G.; Oliet, S.H.R.; Robitaille, R.; Volterra, A. Gliotransmitters Travel in Time and Space. Neuron 2014, 81, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizen, N.; Inoue, T.; Shimizu, T.; Tabu, K.; Kagawa, T.; Taga, T. A Growth-Promoting Signaling Component Cyclin D1 in Neural Stem Cells Has Antiastrogliogenic Function to Execute Self-Renewal. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 1602–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunç, B.S.; Toprak, F.; Toprak, S.F.; Sozer, S. In Vitro Investigation of Growth Factors Including MGF and IGF-1 in Neural Stem Cell Activation, Proliferation, and Migration. Brain Res. 2021, 1759, 147366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, T.; Piriz, J.; Duflot, S.; Fernandez, A.M.; Gaitan, G.; Gomez-Pinedo, U.; Verdugo, J.M.G.; Leroy, F.; Soya, H.; Nuñez, A.; et al. Neuronal Activity Drives Localized Blood-Brain-Barrier Transport of Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-I into the CNS. Neuron 2010, 67, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.M.; Torres-Alemán, I. The Many Faces of Insulin-like Peptide Signalling in the Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auletta, M.; Nielsen, F.C.; Gammeltoft, S. Receptor-mediated Endocytosis and Degradation of Insulin-like Growth Factor I and II in Neonatal Rat Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 1992, 31, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, J.L.; Carro, E.; Torres-Alemán, I. Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factor I Mediates Exercise-Induced Increases in the Number of New Neurons in the Adult Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 1628–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.; Cai, W.; Carlson, S.W.; Saatman, K.E.; Andres, D.A. IGF-1 Mediated Neurogenesis Involves a Novel RIT1/Akt/Sox2 Cascade. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, D.C.; Colamarino, S.A.; Song, H.J.; Désiré, L.; Mira, H.; Consiglio, A.; Lein, E.S.; Jessberger, S.; Lansford, H.; Dearie, A.R.; et al. Wnt Signalling Regulates Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Nature 2005, 437, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Inoue, K.; Iwamura, H.; Terashima, K.; Soya, H.; Asashima, M.; Kuwabara, T. Reduction in Paracrine Wnt3 Factors during Aging Causes Impaired Adult Neurogenesis. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3570–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, S.H.L.; Gabarró-Solanas, R.; Rigo, P.; Paun, O.; Harris, L.; Guillemot, F.; Urbán, N. Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling Is Dispensable for Adult Neural Stem Cell Homeostasis and Activation. Development 2021, 148, dev199629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehrs, C. The Complex World of WNT Receptor Signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, R.; Manzoor, M.; Hussain, A. Wnt Signaling Pathway: A Comprehensive Review. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, E.M.; Paucer, A.; Kornblum, H.I.; Plamer, T.D.; Geschwind, D.H. Endogenous Wnt Signaling Maintains Neural Progenitor Cell Potency. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, T.; Hsieh, J.; Muotri, A.; Yeo, G.; Warashina, M.; Lie, D.C.; Moore, L.; Nakashima, K.; Asashima, M.; Gage, F.H. Wnt-Mediated Activation of NeuroD1 and Retro-Elements during Adult Neurogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Sun, G.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Ye, P.; Zhao, C.; Yu, R.T.; Gage, F.H.; Evans, R.M.; Shi, Y. Orphan Nuclear Receptor TLX Activates Wnt/Β-Catenin Signalling to Stimulate Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Self-Renewal. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seib, D.R.M.; Corsini, N.S.; Ellwanger, K.; Plaas, C.; Mateos, A.; Pitzer, C.; Niehrs, C.; Celikel, T.; Martin-Villalba, A. Loss of Dickkopf-1 Restores Neurogenesis in Old Age and Counteracts Cognitive Decline. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppt, J.; Wittmann, M.; Schäffner, I.; Billmann, C.; Zhang, J.; Vogt-Weisenhorn, D.; Prakash, N.; Wurst, W.; Taketo, M.M.; Lie, D.C. Β-Catenin Signaling Modulates the Tempo of Dendritic Growth of Adult-Born Hippocampal Neurons. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e104472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Corzo, L.; Calatayud-Baselga, I.; Casares-Crespo, L.; Mora-Martínez, C.; Julián Escribano-Saiz, J.; Hortigüela, R.; Asenjo-Martínez, A.; Jordán-Pla, A.; Ercoli, S.; Flames, N.; et al. The Transcription Factor LEF1 Interacts with NFIX and Switches Isoforms during Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Quiescence. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 912319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.H.; Bonaguidi, M.A.; Kitabatake, Y.; Sun, J.; Song, J.; Kang, E.; Jun, H.; Zhong, C.; Su, Y.; Guo, J.U.; et al. Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 3 Regulates Activity-Dependent Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, R.S.; Conway, A.; Pangarkar, C.; Bergen, J.; Lim, K.-I.; Shah, P.; Bissell, M.; Schaffer, D.V. Astrocytes Regulate Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis through Ephrin-B Signaling. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmsson, U.; Faiz, M.; De Pablo, Y.; Sjöqvist, M.; Andersson, D.; Widestrand, Å.; Potokar, M.; Stenovec, M.; Smith, P.L.P.; Shinjyo, N.; et al. Astrocytes Negatively Regulate Neurogenesis through the Jagged1-Mediated Notch Pathway. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehm, O.; Göritz, C.; Covic, M.; Schäffner, I.; Schwarz, T.J.; Karaca, E.; Kempkes, B.; Kremmer, E.; Pfrieger, F.W.; Espinosa, L.; et al. RBPJκ-Dependent Signaling Is Essential for Long-Term Maintenance of Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 13794–13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ables, J.L.; DeCarolis, N.A.; Johnson, M.A.; Rivera, P.D.; Gao, Z.; Cooper, D.C.; Radtke, F.; Hsieh, J.; Eisch, A.J. Notch1 Is Required for Maintenance of the Reservoir of Adult Hippocampal Stem Cells. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 10484–10492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imayoshi, I.; Sakamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Mori, K.; Kageyama, R. Essential Roles of Notch Signaling in Maintenance of Neural Stem Cells in Developing and Adult Brains. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 3489–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavado, A.; Oliver, G. Jagged1 Is Necessary for Postnatal and Adult Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus. Dev. Biol. 2014, 388, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Spelke, D.P.; Lee, Y.K.; Chung, J.K.; Yu, C.H.; Schaffer, D.V.; Groves, J.T. Spatiomechanical Modulation of EphB4-Ephrin-B2 Signaling in Neural Stem Cell Differentiation. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisvert, M.M.; Erikson, G.A.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Allen, N.J. The Aging Astrocyte Transcriptome from Multiple Regions of the Mouse Brain. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.L.; Ousman, S.S. Astrocytes and Aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Hattiangady, B.; Shetty, G.A. Stem/Progenitor Cell Proliferation Factors FGF-2, IGF-1, and VEGF Exhibit Early Decline during the Course of Aging in the Hippocampus: Role of Astrocytes. Glia 2005, 51, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, G.M.; Peterson, D.A. Phenotypic and Gene Expression Modification with Normal Brain Aging in GFAP-Positive Astrocytes and Neural Stem Cells. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalo, U.; Palygin, O.; Rasooli-Nejad, S.; Andrew, J.; Haydon, P.G.; Pankratov, Y. Exocytosis of ATP From Astrocytes Modulates Phasic and Tonic Inhibition in the Neocortex. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, C.J.; Braun, L.; Jiang, Y.; Hester, M.E.; Zhang, L.; Riolo, M.; Wang, H.; Rao, M.; Altura, R.A.; Kaspar, B.K. Aging Brain Microenvironment Decreases Hippocampal Neurogenesis through Wnt-Mediated Survivin Signaling. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.E.; Liddelow, S.A.; Chakraborty, C.; Münch, A.E.; Heiman, M.; Barres, B.A. Normal Aging Induces A1-like Astrocyte Reactivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1896–E1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Schardien, K.; Wigdahl, B.; Nonnemacher, M.R. Roles of Neuropathology-Associated Reactive Astrocytes: A Systematic Review. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulken, B.W.; Buckley, M.T.; Navarro Negredo, P.; Saligrama, N.; Cayrol, R.; Leeman, D.S.; George, B.M.; Boutet, S.C.; Hebestreit, K.; Pluvinage, J.V.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis Reveals T Cell Infiltration in Old Neurogenic Niches. Nature 2019, 571, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.K.; Dolman, D.E.M.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.K.; He, Y.; Park, J.S.; Bieri, G.; Snethlage, C.E.; Lin, K.; Gontier, G.; Wabl, R.; Plambeck, K.E.; Udeochu, J.; et al. Β2-Microglobulin Is a Systemic Pro-Aging Factor That Impairs Cognitive Function and Neurogenesis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdö, F.; Denes, L.; De Lange, E. Age-Associated Physiological and Pathological Changes at the Blood-Brain Barrier: A Review. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A.; Reed, M.J.; Logsdon, A.F.; Rhea, E.M.; Erickson, M.A. Healthy Aging and the Blood–Brain Barrier. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.B.; Yang, A.C.; Yousef, H.; Lee, D.; Chen, W.; Schaum, N.; Lehallier, B.; Quake, S.R.; Wyss-Coray, T. Brain Endothelial Cells Are Exquisite Sensors of Age-Related Circulatory Cues. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 4418–4432.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.N.; Shi, K.; He, W.; Sun, J.H.; Van Kaer, L.; Shi, F.D.; Liu, Q. Neuroblast Senescence in the Aged Brain Augments Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity Leading to Impaired Neurogenesis and Cognition. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérit, S.; Fidan, E.; Macas, J.; Czupalla, C.J.; Figueiredo, R.; Vijikumar, A.; Yalcin, B.H.; Thom, S.; Winter, P.; Gerhardt, H.; et al. Astrocyte-Derived Wnt Growth Factors Are Required for Endothelial Blood-Brain Barrier Maintenance. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 199, 101937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, E.W.; Lian, J.; Ozga, A.J.; Miyabe, Y.; Ji, S.W.; Bromley, S.K.; Mempel, T.R.; Luster, A.D. CXCL10 Stabilizes T Cell-Brain Endothelial Cell Adhesion Leading to the Induction of Cerebral Malaria. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, H.; Conboy, M.J.; Morgenthaler, A.; Schlesinger, C.; Bugaj, L.; Paliwal, P.; Greer, C.; Conboy, I.M.; Schaffer, D. Systemic Attenuation of the TGF-β Pathway by a Single Drug Simultaneously Rejuvenates Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Myogenesis in the Same Old Mammal. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11959–11978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.C.; Stevens, M.Y.; Chen, M.B.; Lee, D.P.; Stähli, D.; Gate, D.; Contrepois, K.; Chen, W.; Iram, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Physiological Blood–Brain Transport Is Impaired with Age by a Shift in Transcytosis. Nature 2020, 583, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavali, M.; Klingener, M.; Kokkosis, A.G.; Garkun, Y.; Felong, S.; Maffei, A.; Aguirre, A. Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling Regulates Neural Stem Cell Quiescence during Homeostasis and after Demyelination. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpf, J.; Unichenko, P.; Chalmers, N.; Beyer, F.; Wittmann, M.T.; Schneider, J.; Fidan, E.; Reis, A.; Beckervordersandforth, J.; Brandner, S.; et al. Dentate Gyrus Astrocytes Exhibit Layer-Specific Molecular, Morphological and Physiological Features. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1626–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.; Encinas, J.M.; Deudero, J.J.; Chancey, J.H.; Enikolopov, G.; Overstreet-Wadiche, L.S.; Tsirka, S.E.; Maletic-Savatic, M. Microglia Shape Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis through Apoptosis-Coupled Phagocytosis. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Aparicio, I.; Paris, I.; Sierra-Torre, V.; Plaza-Zabala, A.; Rodríguez-Iglesias, N.; Márquez-Ropero, M.; Beccari, S.; Huguet, P.; Abiega, O.; Alberdi, E.; et al. Microglia Actively Remodel Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis through the Phagocytosis Secretome. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 1453–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Iglesias, N.; Sierra, A.; Valero, J. Rewiring of Memory Circuits: Connecting Adult Newborn Neurons with the Help of Microglia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Onaizi, M.; Al-Khalifah, A.; Qasem, D.; Elali, A. Role of Microglia in Modulating Adult Neurogenesis in Health and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurga, A.M.; Paleczna, M.; Kuter, K.Z. Overview of General and Discriminating Markers of Differential Microglia Phenotypes. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.C.; Taylor, D.L.; Pocock, J.M. Microglia Release Activators of Neuronal Proliferation Mediated by Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase, Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase/Akt and Delta-Notch Signalling Cascades. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochgerner, H.; Zeisel, A.; Lönnerberg, P.; Linnarsson, S. Conserved Properties of Dentate Gyrus Neurogenesis across Postnatal Development Revealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Sierra, A.; Stevens, B.; Tremblay, M.E.; Aguzzi, A.; Ajami, B.; Amit, I.; Audinat, E.; Bechmann, I.; Bennett, M.; et al. Microglia States and Nomenclature: A Field at Its Crossroads. Neuron 2022, 110, 3458–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butovsky, O.; Talpalar, A.E.; Ben-Yaakov, K.; Schwartz, M. Activation of Microglia by Aggregated β-Amyloid or Lipopolysaccharide Impairs MHC-II Expression and Renders Them Cytotoxic Whereas IFN-γ and IL-4 Render Them Protective. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 29, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butovsky, O.; Ziv, Y.; Schwartz, A.; Landa, G.; Talpalar, A.E.; Pluchino, S.; Martino, G.; Schwartz, M. Microglia Activated by IL-4 or IFN-γ Differentially Induce Neurogenesis and Oligodendrogenesis from Adult Stem/Progenitor Cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2006, 31, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, Y.; Ron, N.; Butovsky, O.; Landa, G.; Sudai, E.; Greenberg, N.; Cohen, H.; Kipnis, J.; Schwartz, M. Immune Cells Contribute to the Maintenance of Neurogenesis and Spatial Learning Abilities in Adulthood. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunan, R.; Sivasathiaseelan, H.; Khan, D.; Zaben, M.; Gray, W. Microglial VPAC1R Mediates a Novel Mechanism of Neuroimmune-Modulation of Hippocampal Precursor Cells via IL-4 Release. Glia 2014, 62, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadagno, J.; Xu, X.; Karajgikar, M.; Brown, A.; Cregan, S.P. Microglia-Derived TNFα Induces Apoptosis in Neural Precursor Cells via Transcriptional Activation of the Bcl-2 Family Member Puma. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenguer, G.; Duart-Abadia, P.; Jordán-Pla, A.; Domingo-Muelas, A.; Blasco-Chamarro, L.; Ferrón, S.R.; Morante-Redolat, J.M.; Fariñas, I. Adult Neural Stem Cells Are Alerted by Systemic Inflammation through TNF-α Receptor Signaling. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 285–299.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, A.; Gottfried-Blackmore, A.C.; McEwen, B.S.; Bulloch, K. Microglia Derived from Aging Mice Exhibit an Altered Inflammatory Profile. Glia 2007, 55, 341–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjabi, S.; Zenewicz, L.A.; Kamanaka, M.; Flavell, R.A. Anti-Inflammatory and pro-Inflammatory Roles of TGF-β, IL-10, and IL-22 in Immunity and Autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudvarski Stankovic, N.; Teodorczyk, M.; Ploen, R.; Zipp, F.; Schmidt, M.H.H. Microglia–Blood Vessel Interactions: A Double-Edged Sword in Brain Pathologies. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, C.T.; Claasen, J.H.; Bonde, S.; Kokaia, Z.; Lindvall, O. Inflammation Is Detrimental for Neurogenesis in Adult Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13632–13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes Are Induced by Activated Microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefendehl, J.K.; Neher, J.J.; Sühs, R.B.; Kohsaka, S.; Skodras, A.; Jucker, M. Homeostatic and Injury-Induced Microglia Behavior in the Aging Brain. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluvinage, J.V.; Wyss-Coray, T. Systemic Factors as Mediators of Brain Homeostasis, Ageing and Neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschallinger, J.; Iram, T.; Zardeneta, M.; Lee, S.E.; Lehallier, B.; Haney, M.S.; Pluvinage, J.V.; Mathur, V.; Hahn, O.; Morgens, D.W.; et al. Lipid-Droplet-Accumulating Microglia Represent a Dysfunctional and Proinflammatory State in the Aging Brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaiyan, S.; Kannaiyan, N.; Snaidero, N.; Brioschi, S.; Biber, K.; Yona, S.; Edinger, A.L.; Jung, S.; Rossner, M.J.; Simons, M. Age-Related Myelin Degradation Burdens the Clearance Function of Microglia during Aging. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruwaka, K.; Ikegami, A.; Tachibana, Y.; Ohno, N.; Konishi, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Kato, D.; Ono, R.; Kiyama, H.; et al. Dual Microglia Effects on Blood Brain Barrier Permeability Induced by Systemic Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermeier, B.; Daneman, R.; Ransohoff, R.M. Development, Maintenance and Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooradian, A.D. Effect of Aging on the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neurobiol. Aging 1988, 9, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, C.M.; Piselli, J.; Temple, S.; Dai, G.; Thompson, D.M. Endothelial Cells Exposed to Fluid Shear Stress Support Diffusion Based Maturation of Adult Neural Progenitor Cells. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2018, 11, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavazoie, M.; Van der Veken, L.; Silva-Vargas, V.; Louissaint, M.; Colonna, L.; Zaidi, B.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Doetsch, F. A Specialized Vascular Niche for Adult Neural Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Bennett, S.; Kuek, V.; Xiang, C.; Xu, H.; Rosen, V.; Xu, J. Endothelial Cells Produce Angiocrine Factors to Regulate Bone and Cartilage via Versatile Mechanisms. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5957–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, R.; Zhou, L.; Agalliu, D.; Cahoy, J.D.; Kaushal, A.; Barres, B.A. The Mouse Blood-Brain Barrier Transcriptome: A New Resource for Understanding the Development and Function of Brain Endothelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottone, C.; Krusche, B.; Whitby, A.; Clements, M.; Quadrato, G.; Pitulescu, M.E.; Adams, R.H.; Parrinello, S. Direct Cell-Cell Contact with the Vascular Niche Maintains Quiescent Neural Stem Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.C.; Ferrón, S.R.; Vicente, D.; Porlan, E.; Perez-Villalba, A.; Trujillo, C.M.; D’Ocón, P.; Fariñas, I. Endothelial NT-3 Delivered by Vasculature and CSF Promotes Quiescence of Subependymal Neural Stem Cells through Nitric Oxide Induction. Neuron 2014, 83, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licht, T.; Keshet, E. The Vascular Niche in Adult Neurogenesis. Mech. Dev. 2015, 138, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, E.D.; Kuwahara, A.A.; Messer, R.L.; Wyss-Coray, T. Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells Regulate the Neurogenic Niche by Secreting VEGF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4128–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licht, T.; Rothe, G.; Kreisel, T.; Wolf, B.; Benny, O.; Rooney, A.G.; Ffrench-Constant, C.; Enikolopov, G.; Keshet, E. VEGF Preconditioning Leads to Stem Cell Remodeling and Attenuates Age-Related Decay of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7828–E7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Jiao, X.; Zuzga, D.S.; Liu, Y.; Fong, D.M.; Young, D.; During, M.J. VEGF Links Hippocampal Activity with Neurogenesis, Learning and Memory. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ford, M.C.; Lavik, E.B.; Madri, J.A. Modeling the Neurovascular Niche: VEGF- and BDNF-Mediated Cross-Talk between Neural Stem Cells and Endothelial Cells: An in Vitro Study. J. Neurosci. 2006, 84, 1621–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, M.H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Eisch, A.J. Dynamic Expression of TrkB Receptor Protein on Proliferating and Maturing Cells in the Adult Mouse Dentate Gyrus. Hippocampus 2008, 18, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, W.; Cheng, X.; Ji, W.; Guo, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, N.; Chen, Y.; et al. Brain Endothelial Cells Maintain Lactate Homeostasis and Control Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 25, 754–767.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, J.R.; Daynac, M.; Chicheportiche, A.; Cebrian-Silla, A.; Sii Felice, K.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Boussin, F.D.; Mouthon, M.A. Vascular-Derived TGF-β Increases in the Stem Cell Niche and Perturbs Neurogenesis during Aging and Following Irradiation in the Adult Mouse Brain. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, B.; Yadav, A.; Agarwal, S.; Tiwari, S.K.; Chaturvedi, R.K. Inhibition of the Transforming Growth Factor-/SMAD Cascade Mitigates the Anti-Neurogenic Effects of the Carbamate Pesticide Carbofuran. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 19423–19440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, H.; Czupalla, C.; Lee, D.; Burke, A.; Chen, M.; Zandstra, J.; Berber, E.; Lehallier, B.; Mathur, V.; Nair, R.; et al. Aged Blood Inhibits Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Activates Microglia through VCAM1 at the Blood-Brain Barrier. bioRxiv 2018, bioRxiv:242198. [Google Scholar]
- Armulik, A.; Genové, G.; Mäe, M.; Nisancioglu, M.H.; Wallgard, E.; Niaudet, C.; He, L.; Norlin, J.; Lindblom, P.; Strittmatter, K.; et al. Pericytes Regulate the Blood-Brain Barrier. Nature 2010, 468, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.D.; Winkler, E.A.; Sagare, A.P.; Singh, I.; LaRue, B.; Deane, R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Pericytes Control Key Neurovascular Functions and Neuronal Phenotype in the Adult Brain and during Brain Aging. Neuron 2010, 68, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, E.E.; Liu, C.; Silva-Vargas, V.; Doetsch, F. Regional and Stage-Specific Effects of Prospectively Purified Vascular Cells on the Adult V-SVZ Neural Stem Cell Lineage. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4528–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Keasey, M.P.; Malone, H.M.; Lovins, C.; Sante, R.R.; Razskazovskiy, V.; Hagg, T. Vitronectin from Brain Pericytes Promotes Adult Forebrain Neurogenesis by Stimulating CNTF. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 312, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, M.; Shimizu, F.; Sano, Y.; Takeshita, Y.; Maeda, T.; Fujikawa, S.; Honda, M.; Sato, R.; Kanda, T. Difference in Cytokines, Chemokines and Growth Factors Produced by Blood–Brain Barrier- and Blood–Nerve Barrier-Composing Cells. Clin. Exp. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 10, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenhoven, J.; Jansson, D.; Smyth, L.C.; Dragunow, M. Brain Pericytes As Mediators of Neuroinflammation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, T.; Sasson, E.; Bell, B.; Grunewald, M.; Kumar, S.; Kreisel, T.; Ben-Zvi, A.; Keshet, E. Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells Facilitate Access from Circulation via Apical Cytoplasmic Processes. Elife 2020, 9, e52134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacar, B.; Herman, P.; Platel, J.C.; Kubera, C.; Hyder, F.; Bordey, A. Neural Progenitor Cells Regulate Capillary Blood Flow in the Postnatal Subventricular Zone. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 16435–16448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeda, S.A.; Plambeck, K.E.; Middeldorp, J.; Castellano, J.M.; Mosher, K.I.; Luo, J.; Smith, L.K.; Bieri, G.; Lin, K.; Berdnik, D.; et al. Young Blood Reverses Age-Related Impairments in Cognitive Function and Synaptic Plasticity in Mice. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucia, C.; Murphy, T.; Maruszak, A.; Wright, P.; Powell, T.R.; Hartopp, N.; De Jong, S.; O’Sullivan, M.J.; Breen, G.; Price, J.; et al. Serum from Older Adults Increases Apoptosis and Molecular Aging Markers in Human Hippocampal Progenitor Cells. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 2151–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.K.; Verovskaya, E.; Bieri, G.; Horowitz, A.M.; von Ungern-Sternberg, S.N.I.; Lin, K.; Seizer, P.; Passegué, E.; Villeda, S.A. The Aged Hematopoietic System Promotes Hippocampal-Dependent Cognitive Decline. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Inflammaging: Disturbed Interplay between Autophagy and Inflammasomes. Aging 2012, 4, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The Hallmarks of Aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M.; Lehner, B.; Kraus, S.; Sander, P.R.; Marschallinger, J.; Rivera, F.J.; Trümbach, D.; Ueberham, U.; Reitsamer, H.A.; Strauss, O.; et al. TGF-Beta Signalling in the Adult Neurogenic Niche Promotes Stem Cell Quiescence as Well as Generation of New Neurons. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 1444–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonntag, W.E.; Ramsey, M.; Carter, C.S. Growth Hormone and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) and Their Influence on Cognitive Aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2005, 4, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, N.R.; Zieba, M.; Bye, N. Do Glucocorticoids Contribute to Brain Aging? Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 37, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouten, M.; Bielefeld, P.; Garcia-Corzo, L.; Passchier, E.M.J.; Gradari, S.; Jungenitz, T.; Pons-Espinal, M.; Gebara, E.; Martín-Suárez, S.; Lucassen, P.J.; et al. Circadian Glucocorticoid Oscillations Preserve a Population of Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells in the Aging Brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1382–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, T. Stress, Glucocorticoid Hormones, and Hippocampal Neural Progenitor Cells: Implications to Mood Disorders. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdanipour, A.; Sagha, M.; Noori-Zadeh, A.; Pakzad, I.; Tiraihi, T. In Vitro Study of the Long-Term Cortisol Treatment Effects on the Growth Rate and Proliferation of the Neural Stem/Precursor Cells. Neurol. Res. 2015, 37, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, A.M.; Dillon, E.L.; Urban, R.J.; Sheffield-Moore, M. The Role of Androgens and Estrogens on Healthy Aging and Longevity. J. Gerontol.-Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransome, M.I.; Boon, W.C. Testosterone-Induced Adult Neurosphere Growth Is Mediated by Sexually-Dimorphic Aromatase Expression. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggioli, T.; Vujic, A.; Yang, P.; MacIas-Trevino, C.; Uygur, A.; Loffredo, F.S.; Pancoast, J.R.; Cho, M.; Goldstein, J.; Tandias, R.M.; et al. Circulating Growth Differentiation Factor 11/8 Levels Decline with Age. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, E.; Luiten, P.G.M. Cerebral Microvascular Pathology in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 64, 575–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsimpardi, L.; Litterman, N.K.; Schein, P.A.; Miller, C.M.; Loffredo, F.S.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Chen, J.W.; Lee, R.T.; Wagers, A.J.; Rubin, L.L. Vascular and Neurogenic Rejuvenation of the Aging Mouse Brain by Young Systemic Factors. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 2014, 344, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozek, C.; Krolewski, R.C.; Buchanan, S.M.; Rubin, L.L. Growth Differentiation Factor 11 Treatment Leads to Neuronal and Vascular Improvements in the Hippocampus of Aged Mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Jadavji, N.M.; Yoo, H.S.; Smith, P.D. Recombinant Growth Differentiation Factor 11 Influences Short-Term Memory and Enhances Sox2 Expression in Middle-Aged Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 341, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding Light on the Cell Biology of Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepko, T.; Pusch, M.; Müller, T.; Schulte, D.; Ehses, J.; Kiebler, M.; Hasler, J.; Huttner, H.B.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Vandendriessche, C.; et al. Choroid Plexus-derived MiR-204 Regulates the Number of Quiescent Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Brain. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Uchiyama, J.; Imami, K.; Ishihama, Y.; Kageyama, R.; Kobayashi, T. Novel Roles of Small Extracellular Vesicles in Regulating the Quiescence and Proliferation of Neural Stem Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 762293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Mesci, P.; Carromeu, C.; McClatchy, D.R.; Schiapparelli, L.; Yates, J.R.; Muotri, A.R.; Cline, H.T. Exosomes Regulate Neurogenesis and Circuit Assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16086–16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallis, R.; Mizen, H.; Bishop, C.L. The Bright and Dark Side of Extracellular Vesicles in the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 189, 111263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Aging Microenvironment and Age-Related Diseases. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A.; Clemens, Z.J.; Shinde, S.N.; Sivakumar, S.; Pius, A.; Bhatia, A.; Picciolini, S.; Carlomagno, C.; Gualerzi, A.; Bedoni, M.; et al. Regulation of Aged Skeletal Muscle Regeneration by Circulating Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszczyk, A.M.; Fox-Quick, S.; Vo, H.T.; Nettles, D.; Pugh, P.C.; Overstreet-Wadiche, L.; King, G.D. Klotho Regulates Postnatal Neurogenesis and Protects against Age-Related Spatial Memory Loss. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 59, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.; Koh, D.; Jeon, H.B.; Kim, K.M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Senescence. Mol. Cells 2022, 45, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensà, E.; Guescini, M.; Giuliani, A.; Bacalini, M.G.; Ramini, D.; Corleone, G.; Ferracin, M.; Fulgenzi, G.; Graciotti, L.; Prattichizzo, F.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles Deliver MiR-21 and MiR-217 as pro-Senescence Effectors to Endothelial Cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1725285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, G.B.; Pilonis, N.; Ptacek, R.; Raboch, J.; Vnukova, M.; Kream, R.M. Gut, Microbiome, and Brain Regulatory Axis: Relevance to Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Disorders. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossad, O.; Batut, B.; Yilmaz, B.; Dokalis, N.; Mezö, C.; Nent, E.; Nabavi, L.S.; Mayer, M.; Maron, F.J.M.; Buescher, J.M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Drives Age-Related Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Damage in Microglia via the Metabolite N 6-Carboxymethyllysine. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandilya, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar Jha, N.; Kumar Kesari, K.; Ruokolainen, J. Interplay of Gut Microbiota and Oxidative Stress: Perspective on Neurodegeneration and Neuroprotection. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 38, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derecki, N.C.; Cardani, A.N.; Yang, C.H.; Quinnies, K.M.; Crihfield, A.; Lynch, K.R.; Kipnis, J. Regulation of Learning and Memory by Meningeal Immunity: A Key Role for IL-4. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niebling, J.; Rünker, A.E.; Schallenberg, S.; Kretschmer, K.; Kempermann, G. Myelin-Specific T Helper 17 Cells Promote Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis through Indirect Mechanisms. F1000Research 2014, 3, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.A.; Steiner, B.; Akpinarli, A.; Kammertoens, T.; Nassenstein, C.; Braun, A.; Blankenstein, T.; Kempermann, G. CD4-Positive T Lymphocytes Provide a Neuroimmunological Link in the Control of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3979–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plog, B.A.; Nedergaard, M. The Glymphatic System in Central Nervous System Health and Disease: Past, Present, and Future. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2018, 13, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, T.; Hjorth, P.G.; Holst, S.C.; Hrabětová, S.; Kiviniemi, V.; Lilius, T.; Lundgaard, I.; Mardal, K.A.; Martens, E.A.; Mori, Y.; et al. The Glymphatic System: Current Understanding and Modeling. iScience 2022, 25, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Mesquita, S.; Louveau, A.; Vaccari, A.; Smirnov, I.; Cornelison, R.C.; Kingsmore, K.M.; Contarino, C.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Farber, E.; Raper, D.; et al. Functional Aspects of Meningeal Lymphatics in Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2018, 560, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, G.; Limanaqi, F.; Busceti, C.L.; Mastroiacovo, F.; Nicoletti, F.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Fornai, F. Glymphatic System as a Gateway to Connect Neurodegeneration From Periphery to CNS. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 639140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, B.T.; Iliff, J.J.; Xia, M.; Wang, M.; Wei Bs, H.S.; Zeppenfeld, D.; Xie, L.; Hongyi Kang, B.S.; Xu, Q.; Liew, J.A.; et al. Impairment of Paravascular Clearance Pathways in the Aging Brain. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondolfi, L.; Ermini, F.; Long, J.M.; Ingram, D.K.; Jucker, M. Impact of Age and Caloric Restriction on Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus of C57BL/6 Mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2004, 25, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Clemenson, G.D.; Gage, F.H. New Neurons in an Aged Brain. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 227, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Puma, D.D.; Piacentini, R.; Leone, L.; Gironi, K.; Marcocci, M.E.; De Chiara, G.; Palamara, A.T.; Grassi, C. Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 Infection Impairs Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis via Amyloid-β Protein Accumulation. Stem Cells 2019, 37, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furutachi, S.; Matsumoto, A.; Nakayama, K.I.; Gotoh, Y. P57 Controls Adult Neural Stem Cell Quiescence and Modulates the Pace of Lifelong Neurogenesis. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, A.; Martín-Suárez, S.; Valcárcel-Martín, R.; Pascual-Brazo, J.; Aelvoet, S.A.; Abiega, O.; Deudero, J.J.; Brewster, A.L.; Bernales, I.; Anderson, A.E.; et al. Neuronal Hyperactivity Accelerates Depletion of Neural Stem Cells and Impairs Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 488–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kippin, T.E.; Martens, D.J.; Van Der Kooy, D. P21 Loss Compromises the Relative Quiescence of Forebrain Stem Cell Proliferation Leading To Exhaustion of Their Proliferation Capacity. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez Peinado, P.; Urbach, A. From Youthful Vigor to Aging Decline: Unravelling the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Determinants of Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Aging. Cells 2023, 12, 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12162086
Jiménez Peinado P, Urbach A. From Youthful Vigor to Aging Decline: Unravelling the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Determinants of Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Aging. Cells. 2023; 12(16):2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12162086
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez Peinado, Patricia, and Anja Urbach. 2023. "From Youthful Vigor to Aging Decline: Unravelling the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Determinants of Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Aging" Cells 12, no. 16: 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12162086
APA StyleJiménez Peinado, P., & Urbach, A. (2023). From Youthful Vigor to Aging Decline: Unravelling the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Determinants of Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Aging. Cells, 12(16), 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12162086





