Familial Adult Myoclonus Epilepsy: A Non-Coding Repeat Expansion Disorder of Cerebellar–Thalamic–Cortical Loop
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. History of the Disease across Different Acronyms
1.2. Japanese Families
1.3. Non-Japanese Families
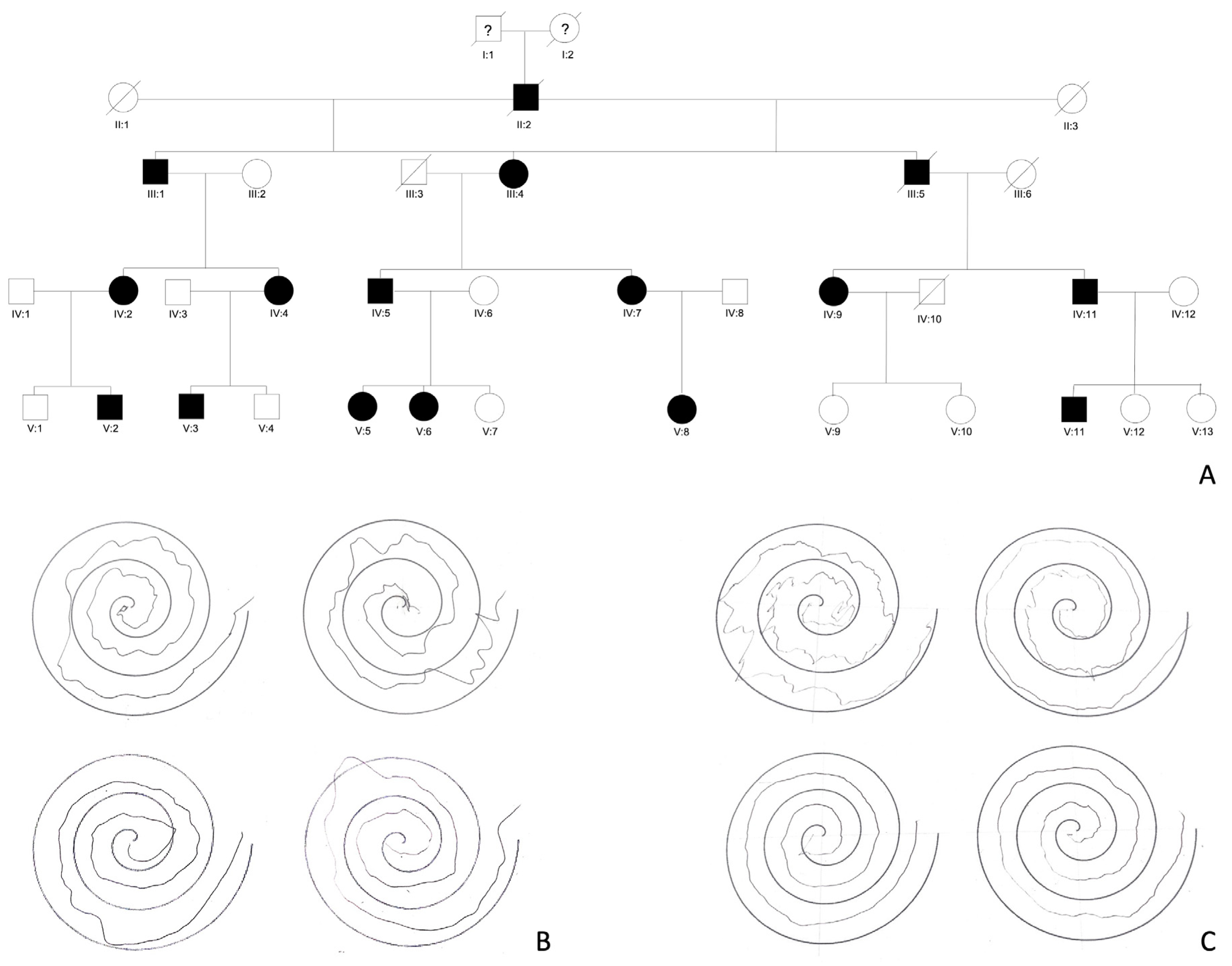
2. Clinical Features
2.1. Cortical Tremor and Myoclonus
2.2. Seizures
2.3. Additional Clinical Features
3. Disease Course
4. Neurophysiological Investigations
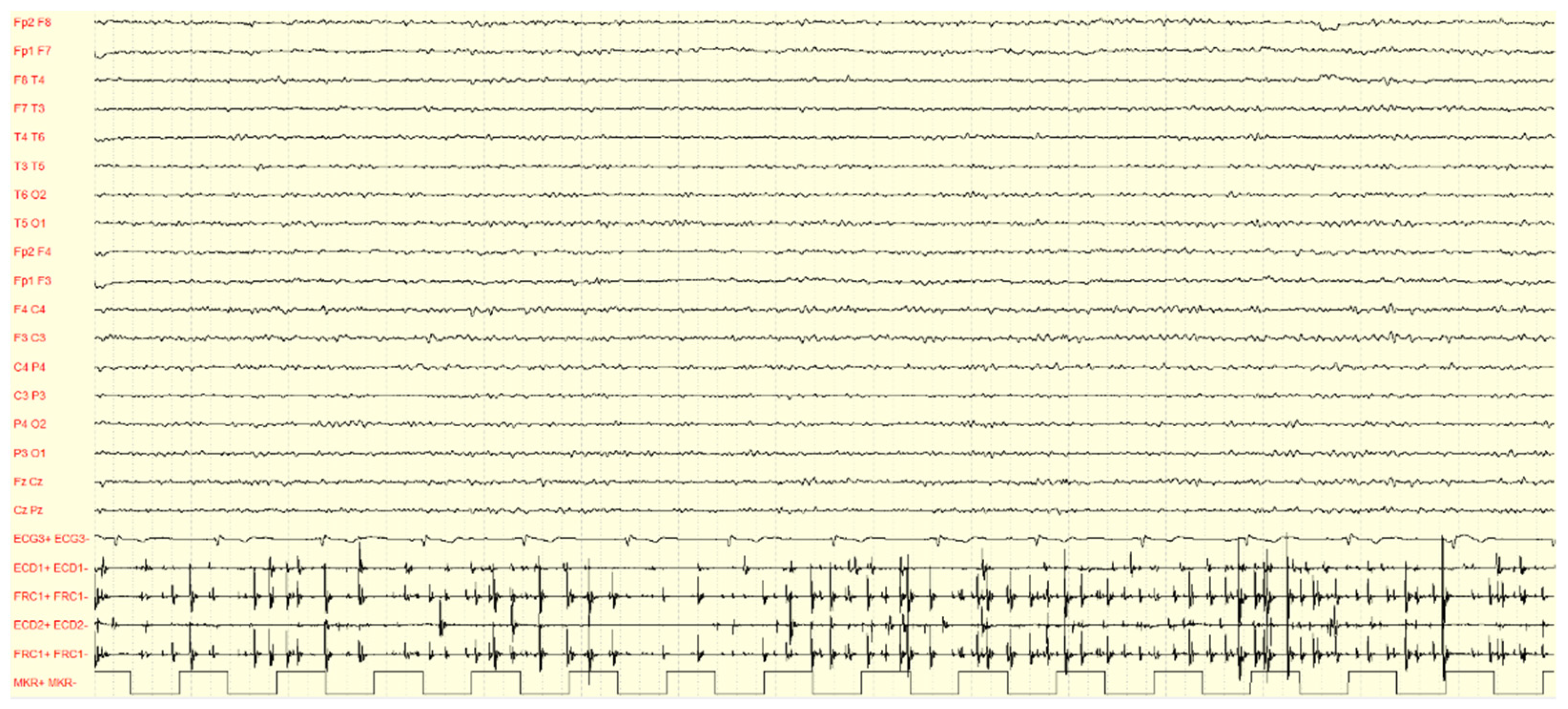
4.1. EEG-EMG Polygraphy
4.2. Jerk-Locked Back Averaging (J-LBA) Analysis
4.3. Cortico-Muscular Coherence Analysis
4.4. Giant Somatosensory-Evoked Potential (SEP) and High-Frequency Oscillations (HFOs)
4.5. Long-Latency Reflexes (LLRs)
4.6. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
5. Neuroradiology
6. Genetics
6.1. Identification of FAME Loci
6.2. Non-Coding TTTTA and TTTCA Repeat Expansions
6.3. Genotype-Phenotype Correlation
7. Pathophysiology
8. Treatment Strategies and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ikeda, A.; Kakigi, R.; Funai, N.; Neshige, R.; Kuroda, Y.; Shibasaki, H. Cortical Tremor: A Variant of Cortical Reflex Myoclonus. Neurology 1990, 40, 1561. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2215948 (accessed on 17 October 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibasaki, H. AAEE minimonograph #30: Electrophysiologic studies of myoclonus. Muscle Nerve 1988, 11, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakigi, R.; Shibasaki, H. Generator mechanisms of giant somatosensory evoked potentials in cortical reflex myoclonus. Brain 1987, 110 Pt 5, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyama, E.; Kumamoto, T.; Ikeda, T.; Iwakiri, T.; Uchino, M.; Araki, S. A family of familial myoclonic epilepsy characterized by middle-adult onset presenting with finger tremorous involuntary movements and benign course. Clin. Neurol. 1985, 25, 1491–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Uyama, E.; Fu, Y.H.; Ptácek, L.J. Familial adult myoclonic epilepsy (FAME). Adv. Neurol. 2005, 95, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Inazuki, G.; Naito, H.; Ohama, E.; Kawase, Y.; Honma, Y.; Tokiguchi, S.; Hasegawa, S.; Tamura, K.; Kawai, K.; Nagai, H. A clinical study and neuropathological findings of a familial disease with myoclonus and epilepsy. The nosological place of a familial essential myoclonus and epilepsy (FEME). Seishin-Shinkeigaku 1990, 92, 1–21. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, T. Benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy (BAFME). Kawasaki Med. J. 1991, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Okuma, Y.; Shimo, Y.; Hatori, K.; Hattori, T.; Tanaka, S.; Mizuno, Y. Familial cortical tremor with epilepsy. Park. Relat. Disord. 1997, 3, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, Y.; Shimo, Y.; Shimura, H.; Hatori, K.; Hattori, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kondo, T.; Mizuno, Y. Familial cortical tremor with epilepsy: An underrecognized familial tremor. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 1998, 100, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, K.; Ikeda, A.; Mima, T.; Kimura, K.; Nagahama, Y.; Kamioka, Y.; Murone, L.; Kimura, J.; Shibasaki, H. Familial cortical myoclonic tremor as unique form of cortical reflex myoclonus. Mov. Disord. 1997, 12, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, M.; Yasuda, T.; Terao, A.; Nakamura, M.; Ueno, S.; Tanabe, H.; Tanaka, T.; Onuma, T.; Goto, Y.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Localization of a gene for benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy to chromosome 8q23.3-q24.1. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 65, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plaster, N.M.; Uyama, E.; Uchino, M.; Ikeda, T.; Flanigan, K.M.; Kondo, I.; Ptácek, L.J. Genetic localization of the familial adult myoclonic epilepsy (FAME) gene to chromosome 8q24. Neurology 1999, 53, 1180–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurizio, E.; Sebastiano, A.M.; Raffaele, F.; Carmela, S.; Stefano, D.G.; Maria, B.; Roberto, M.; Carlo, A.T. Familial cortical tremor, epilepsy and mental retardation. Arch. Neurol. 1998, 55, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrini, R.; Bonanni, P.; Patrignani, A.; Brown, P.; Parmeggiani, L.; Grosse, P.; Brovedani, P.; Moro, F.; Aridon, P.; Carrozzo, R.; et al. Autosomal dominant cortical myoclonus and epilepsy (ADCME) with complex partial seizures and generalized seizures. A newly recognized epilepsy syndrome with linkage to chromosome 2p11.1-q12.2. Brain 2001, 124, 2459–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Falco, F.A.; Striano, P.; de Falco, A.; Striano, S.; Santangelo, R.; Perretti, A.; Balbi, P.; Cecconi, M.; Zara, F. Benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy. Genetic heterogeneity and allelelism with ADCME. Neurology 2003, 60, 1381–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striano, P.; Chifari, R.; Striano, S.; De Fusco, M.; Elia, M.; Guerrini, R.; Casari, G.; Canevini, M.P. A new benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy (BAFME) pedigree suggesting linkage to chromosome 2p11.1-q12.2. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laubage, P.; Amer, L.O.; Simonetta-Moreau, M.; Attane, F.; Tannier, C.; Clanet, M.; Castelnovo, G.; An-Gourfinkel, I.; Agid, Y.; Brice, A. Absence of linkage to 8q24 in a European family with familial adult myoclonic epilepsy (FAME). Neurology 2002, 58, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rootselaar, F.; Callenbach, P.M.C.; Hottenga, J.J.; Speelman, H.D.; Brouwer, O.F.; Tijssen, M.A. A Dutch family with familial cortical tremor with epilepsy. Clinical characteristics and exclusion of linkage to chromosome 8q23.3-q24.1. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, O.F.; Callenbach, P.M.C.; van Rootselaar, F.; Hottenga, J.J.; Van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Frants, R.R. A Dutch family with ‘Familial Cortical Tremor with Epilepsy’: Exclusion of linkage to chromosomes 8q and 2p [abstract]. Epilepsia 2002, 43 (Suppl. S8), 128. [Google Scholar]
- Striano, P.; Zara, F.; Striano, S. Autosomal dominant cortical tremor, myoclonus and epilepsy: Many syndromes, one phenotype. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2005, 111, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rootselaar, A.F.; van Schaik, I.N.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Koelman, J.H.; Callenbach, P.M.; Tijssen, M.A. Familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy: A single syndromic classification for a group of pedigrees bearing common features. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnin, E.; Vidailhet, M.; Depienne, C.; Saint-Martin, C.; Bouteiller, D.; LeGuern, E.; Apartis, E.; Rumbach, L.; Labauge, P. Familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy (FCMTE): Clinical characteristics and exclusion of linkages to 8q and 2p in a large French family. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 165, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depienne, C.; Magnin, E.; Bouteiller, D.; Stevanin, G.; Saint-Martin, C.; Vidailhet, M.; Apartis, E.; Hirsch, E.; LeGuern, E.; Labauge, P.; et al. Familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy: The third locus (FCMTE3) maps to 5p. Neurology 2010, 74, 2000–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.Y.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wang, K.; Xiao, S.M.; Li, Y.N.; Lei, S.F.; Chen, X.D.; Xiao, B.; Deng, H.W. Absence of linkage to 8q23.3-q24.1 and 2p11.1-q12.2 in a new BAFME pedigree in China: Indication of a third locus for BAFME. Epilepsy Res. 2005, 65, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hu, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, G. A Chinese benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy pedigree suggesting linkage to chromosome 5p15.31-p15.1. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 69, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Sun, W.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Hu, G. Genetic analysis of a Chinese family provides further evidence for linkage of familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy to 5p15.31-p15. Neurol. India 2015, 63, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeetong, P.; Ausavarat, S.; Bhidayasiri, R.; Piravej, K.; Pasutharnchat, N.; Desudchit, T.; Chunharas, C.; Loplumlert, J.; Limotai, C.; Suphapeetiporn, K.; et al. A newly identified locus for benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy on chromosome 3q26.32-3q28. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 21, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crompton, D.E.; Sadleir, L.G.; Bromhead, C.J.; Bahlo, M.; Bellows, S.T.; Arsov, T.; Harty, R.; Lawrence, K.M.; Dunne, J.W.; Berkovic, S.F.; et al. Familial adult myoclonic epilepsy: Recognition of mild phenotypes and refinement of the 2q locus. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydin Özemir, Z.; Oğuz Akarsu, E.; Matur, Z.; Öge, A.E.; Baykan, B. Autosomal Dominant Cortical Tremor, Myoclonus, and Epilepsy Syndrome mimicking Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2016, 53, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.M.; Nath, K.; Kumawat, B.L.; Khandelwal, D. Autosomal dominant cortical tremor, myoclonus, and epilepsy (ADCME): Probable first family from India. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2014, 17, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, R.; Viswanathan, N.; Shanmugam, G.; Sankaralingam, S.; Essaki, B.; Chelladurai, R.P. Autosomal dominant cortical tremor, myoclonus, and epilepsy (ADCME) in a unique south Indian community. Epilepsia 2016, 57, e56–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bennett, M.F.; Oliver, K.L.; Regan, B.M.; Bellows, S.T.; Schneider, A.L.; Rafehi, H.; Sikta, N.; Crompton, D.E.; Coleman, M.; Hildebrand, M.S.; et al. Familial adult myoclonic epilepsy type 1 SAMD12 TTTCA repeat expansion arose 17,000 years ago and is present in Sri Lankan and Indian families. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 33van Coller, R.; van Rootselaar, A.F.; Schutte, C.; van der Meyden, C.H. Familial cortical myoclonic tremor and epilepsy: Description of a new South African pedigree with 30 year follow up. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 38, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitomi, T.; Kondo, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Takahashi, R.; Ikeda, A. Clinical anticipation in Japanese families of benign adult familial myoclonus epilepsy. Epilepsia 2012, 53, e33–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagorio, I.; Zara, F.; Striano, S.; Striano, P. Familial adult myoclonic epilepsy: A new expansion repeats disorder. Seizure 2019, 67, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Striano, P.; Zara, F. Autosomal dominant cortical tremor, myoclonus and epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2016, 18, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Ende, T.; Sharifi, S.; van der Salm, S.M.A.; van Rootselaar, A.F. Familial Cortical Myoclonic Tremor and Epilepsy, an Enigmatic Disorder: From Phenotypes to Pathophysiology and Genetics. A Systematic Review. Tremor Other Hyperkinet. Mov. 2018, 8, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardella, E.; Tinuper, P.; Marini, C.; Guerrini, R.; Parrini, E.; Bisulli, F.; Liguori, R.; Montagna, P.; Lugaresi, E. Autosomal dominant early-onset cortical myoclonus, photic-induced myoclonus, and epilepsy in a large pedigree. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdain, F.; Apartis, E.; Trocello, J.M.; Vidal, J.S.; Masnou, P.; Vercueil, L.; Vidailhet, M. Clinical analysis in familial cortical myoclonic tremor allows differential diagnosis with essential tremor. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, M.A.; Kroes, T.; Veneziano, L.; Bennett, M.F.; Florian, R.; Schneider, A.L.; Coppola, A.; Licchetta, L.; Franceschetti, S.; Suppa, A.; et al. Intronic ATTTC repeat expansions in STARD7 in familial adult myoclonic epilepsy linked to chromosome 2. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suppa, A.; Berardelli, A.; Brancati, F.; Marianetti, M.; Barrano, G.; Mina, C.; Pizzuti, A.; Sideri, G. Clinical, neuropsychological, neurophysiologic, and genetic features of a new Italian pedigree with familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1284–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, A.; Rocchi, L.; Magrinelli, F.; Mulroy, E.; Berardelli, A.; Rothwell, J.C.; Bhatia, K.P. Unravelling the enigma of cortical tremor and other forms of cortical myoclonus. Brain 2020, 143, 2653–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licchetta, L.; Pippucci, T.; Bisulli, F.; Cantalupo, G.; Magini, P.; Alvisi, L.; Baldassari, S.; Martinelli, P.; Naldi, I.; Vanni, N.; et al. A novel pedigree with familial cortical myoclonic tremor and epilepsy (FCMTE): Clinical characterization, refinement of the FCMTE2 locus, and confirmation of a founder haplotype. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1298–1306, Erratum in Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saka, E.; Saygi, S. Familial adult onset myoclonic epilepsy associated with migraine. Seizure 2000, 9, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manabe, Y.; Narai, H.; Warita, H.; Hayashi, T.; Shiro, Y.; Sakai, K.; Kashihara, K.; Shoji, M.; Abe, K. Benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy (BAFME) with night blindness. Seizure 2002, 11, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coppola, A.; Santulli, L.; Del Gaudio, L.; Minetti, C.; Striano, S.; Zara, F.; Striano, P. Natural history and long-term evolution in families with autosomal dominant cortical tremor, myoclonus, and epilepsy. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rootselaar, A.F.; van der Salm, S.M.; Bour, L.J.; Edwards, M.J.; Brown, P.; Aronica, E.; Rozemuller-Kwakkel, J.M.; Koehler, P.J.; Koelman, J.H.; Rothwell, J.C.; et al. Decreased cortical inhibition and yet cerebellar pathology in ‘familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy’. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 2378–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Aronica, E.; Koelman, J.H.; Tijssen, M.A.; Van Rootselaar, A.F. Familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy and cerebellar changes: Description of a new pathology case and review of the literature. Tremor Other Hyperkinet. Mov. 2012, 2, tre-02-82-472-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, A.; Caccavale, C.; Santulli, L.; Balestrini, S.; Cagnetti, C.; Licchetta, L.; Esposito, M.; Bisulli, F.; Tinuper, P.; Provinciali, L.; et al. Psychiatric comorbidities in patients from seven families with autosomal dominant cortical tremor, myoclonus, and epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 56, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, T.; Takahashi, R.; Ikeda, A. Recent advance in research of benign adult familial myoclonus epilepsy (BAFME): Is BAFME a progressive disorder? Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2014, 54, 1142–1145. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hitomi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Sakurai, T.; Ueda, S.; Jingami, N.; Kanazawa, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Takahashi, R.; Ikeda, A. Benign adult familial myoclonus epilepsy is a progressive disorder: No longer idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2016, 18, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, J.C.; Obeso, J.A.; Marsden, C.D. On the significance of giant somatosensory evoked potentials in cortical myoclonus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1984, 47, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, J.C.; Obeso, J.A.; Marsden, C.D. Electrophysiology of somatosensory reflex myoclonus. Adv. Neurol. 1986, 43, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shibasaki, H.; Kuroiwa, Y. Electroencephalographic correlates of myoclonus. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1975, 39, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Kuroiwa, Y. Electroencephalographic studies myoclonus. Brain 1978, 101, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassim, F.; Houdayer, E. Neurophysiology of myoclonus. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2006, 36, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, T.; Akamatsu, N.; Tanaka, A.; Tsuji, S.; Uozumi, T. Electroencephalographic features of benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, T.; Inouchi, M.; Takeyama, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Sultana, S.; Inoue, T.; Nakayama, Y.; Shimotake, A.; Matsuhashi, M.; Matsumoto, R.; et al. Sleep is associated with reduction of epileptiform discharges in benign adult familial myoclonus epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. Case Rep. 2018, 11, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licchetta, L.; Bisulli, F.; Ferri, L.; Cantalupo, G.; Alvisi, L.; Vignatelli, L.; Loddo, G.; Provini, F.; Tinuper, P. Cortical myoclonic tremor induced by fixation-off sensitivity: An unusual cause of insomnia. Neurology 2018, 91, 1061–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Farmer, S.F.; Halliday, D.M.; Marsden, J.; Rosenberg, J.R. Coherent cortical and muscle discharge in cortical myoclonus. Brain 1999, 122 Pt 3, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosse, P.; Guerrini, R.; Parmeggiani, L.; Bonanni, P.; Pogosyan, A.; Brown, P. Abnormal corticomuscular and intermuscular coupling in high-frequency rhythmic myoclonus. Brain 2003, 126 Pt 2, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Rootselaar, A.F.; Maurits, N.M.; Koelman, J.H.; van der Hoeven, J.H.; Bour, L.J.; Leenders, K.L.; Brown, P.; Tijssen, M.A. Coherence analysis differentiates between cortical myoclonic tremor and essential tremor. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibasaki, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Neshige, R.; Tobimatsu, S.; Fukui, R. Pathogenesis of giant somatosensory evoked potentials in progressive myoclonic epilepsy. Brain 1985, 108 Pt 1, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striano, P.; Manganelli, F.; Boccella, P.; Perretti, A.; Striano, S. Levetiracetam in patients with cortical myoclonus: A clinical and electrophysiological study. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi, K.; Neshige, S.; Hitomi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Tojima, M.; Matsuhashi, M.; Shimotake, A.; Fujii, D.; Matsumoto, R.; Kasama, S.; et al. Low-dose perampanel improves refractory cortical myoclonus by the dispersed and suppressed paroxysmal depolarization shifts in the sensorimotor cortex. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbioso, R.; Striano, P.; Tomasevic, L.; Bilo, L.; Esposito, M.; Manganelli, F.; Coppola, A. Abnormal sensorimotor cortex and thalamo-cortical networks in familial adult myoclonic epilepsy type 2: Pathophysiology and diagnostic implications. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojima, M.; Hitomi, T.; Matsuhashi, M.; Neshige, S.; Usami, K.; Oi, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Takeyama, H.; Shimotake, A.; Takahashi, R.; et al. A Biomarker for Benign Adult Familial Myoclonus Epilepsy: High-Frequency Activities in Giant Somatosensory Evoked Potentials. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striano, P.; Caranci, F.; Di Benedetto, R.; Tortora, F.; Zara, F.; Striano, S. (1)H-MR spectroscopy indicates prominent cerebellar dysfunction in benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Gong, J.; Xu, L.; Long, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A case-control proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study confirms cerebellar dysfunction in benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buijink, A.W.; Caan, M.W.; Tijssen, M.A.; Hoogduin, J.M.; Maurits, N.M.; van Rootselaar, A.F. Decreased cerebellar fiber density in cortical myoclonic tremor but not in essential tremor. Cerebellum 2013, 12, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijink, A.W.; Broersma, M.; van der Stouwe, A.M.; Sharifi, S.; Tijssen, M.A.; Speelman, J.D.; Maurits, N.M.; van Rootselaar, A.F. Cerebellar Atrophy in Cortical Myoclonic Tremor and Not in Hereditary Essential Tremor-a Voxel-Based Morphometry Study. Cerebellum 2016, 15, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Cen, Z.; Yuan, J.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Xie, F.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Ouyang, Z.; et al. White matter alterations in familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy type 1. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Zeng, L.L.; Song, Y.; Shen, H.; Fang, P.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Altered cerebellar-cerebral functional connectivity in benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Cen, Z.; Wei, W.; Xie, F.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H.; Hu, Y.; Yang, D.; Lou, Y.; et al. Altered Cerebello-Motor Network in Familial Cortical Myoclonic Tremor With Epilepsy Type 1. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madia, F.; Striano, P.; Di Bonaventura, C.; de Falco, A.; de Falco, F.A.; Manfredi, M.; Casari, G.; Striano, S.; Minetti, C.; Zara, F. Benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy (BAFME): Evidence of an extended founder haplotype on chromosome 2p11.1-q12.2 in five Italian families. Neurogenetics 2008, 9, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Nakamura, M.; Yasuda, T.; Ueno, S.; Kaneko, S.; Sano, A. Remapping and mutation analysis of benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy in a Japanese pedigree. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 56, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, Z.D.; Xie, F.; Lou, D.N.; Lu, X.J.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; Li, D.; Yin, H.M.; Wang, Z.J.; et al. Fine mapping and whole-exome sequencing of a familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy family. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2015, 168, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henden, L.; Freytag, S.; Afawi, Z.; Baldassari, S.; Berkovic, S.F.; Bisulli, F.; Canafoglia, L.; Casari, G.; Crompton, D.E.; Depienne, C.; et al. Identity by descent fine mapping of familial adult myoclonus epilepsy (FAME) to 2p11.2-2q11.2. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fusco, M.; Vago, R.; Striano, P.; Di Bonaventura, C.; Zara, F.; Mei, D.; Kim, M.S.; Muallem, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. The α2B-adrenergic receptor is mutant in cortical myoclonus and epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Rootselaar, A.F.; Groffen, A.J.; de Vries, B.; Callenbach, P.M.C.; Santen, G.W.E.; Koelewijn, S.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Buijink, A.; Tijssen, M.A.J.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M. δ-Catenin (CTNND2) missense mutation in familial cortical myoclonic tremor and epilepsy. Neurology 2017, 89, 2341–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, Z.D.; Xie, F.; Xiao, J.F.; Luo, W. Rational search for genes in familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy, clues from recent advances. Seizure 2016, 34, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishiura, H.; Doi, K.; Mitsui, J.; Yoshimura, J.; Matsukawa, M.K.; Fujiyama, A.; Toyoshima, Y.; Kakita, A.; Takahashi, H.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Expansions of intronic TTTCA and TTTTA repeats in benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Lu, L.; Zhou, D. Familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy: TTTCA/TTTTA repeat expansions and expanding phenotype in two Chinese families. Brain Res. 2020, 1737, 146796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Hu, Z.M.; Li, J.C.; Li, N.; Wang, J.L.; Liang, F.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Q.; et al. Long-read sequencing identified intronic repeat expansions in SAMD12 from Chinese pedigrees affected with familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 56, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasaki, A.; Nakamura, M.; Urata, Y.; Hiwatashi, H.; Yokoyama, I.; Yasuda, T.; Onuma, T.; Wada, K.; Kaneko, S.; Kan, R.; et al. DNA analysis of benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy reveals associations between the pathogenic TTTCA repeat insertion in SAMD12 and the nonpathogenic TTTTA repeat expansion in TNRC6A. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 66, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, R.; Bhoyar, R.C.; Viswanathan, N.; Rajagopal, R.E.; Essaki, B.; Suroliya, V.; Chelladurai, R.; Sankaralingam, S.; Shanmugam, G.; Vayanakkan, S.; et al. Genomic analysis of patients in a South Indian Community with autosomal dominant cortical tremor, myoclonus and epilepsy suggests a founder repeat expansion mutation in the SAMD12 gene. Brain Commun. 2020, 3, fcaa214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, R.T.; Kraft, F.; Leitão, E.; Kaya, S.; Klebe, S.; Magnin, E.; van Rootselaar, A.F.; Buratti, J.; Kühnel, T.; Schröder, C.; et al. Unstable TTTTA/TTTCA expansions in MARCH6 are associated with Familial Adult Myoclonic Epilepsy type 3. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeetong, P.; Pongpanich, M.; Srichomthong, C.; Assawapitaksakul, A.; Shotelersuk, V.; Tantirukdham, N.; Chunharas, C.; Suphapeetiporn, K.; Shotelersuk, V. TTTCA repeat insertions in an intron of YEATS2 in benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy type 4. Brain 2019, 142, 3360–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, A.I.; Loureiro, J.R.; Costa, C.; Ordóñez-Ugalde, A.; Marcelino, H.; Oliveira, C.L.; Loureiro, J.L.; Dhingra, A.; Brandão, E.; Cruz, V.T.; et al. A Pentanucleotide ATTTC Repeat Insertion in the Non-coding Region of DAB1, Mapping to SCA37, Causes Spinocerebellar Ataxia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loureiro, J.R.; Oliveira, C.L.; Mota, C.; Castro, A.F.; Costa, C.; Loureiro, J.L.; Coutinho, P.; Martins, S.; Sequeiros, J.; Silveira, I. Mutational mechanism for DAB1 (ATTTC)n insertion in SCA37: ATTTT repeat lengthening and nucleotide substitution. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Kurihara, S.; Shibasaki, H. Possible anticipation in BAFME: Three generations examined in a Japanese family. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 1076–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.X.; Liu, Q.; Lu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, X.Q.; Sun, H.Y.; Wu, L.W.; Cui, L.Y.; Zhang, X. TTTCA repeat expansion causes familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cen, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xie, F.; Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Wu, H.; Chen, S.; et al. Intronic pentanucleotide TTTCA repeat insertion in the SAMD12 gene causes familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy type 1. Brain 2018, 141, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, J.A.; van der Walt, P.E.; Nakayama, J.; Fu, Y.H.; Corfield, V.; Brink, P.; Ptacek, L. FAME 3: A novel form of progressive myoclonus and epilepsy. Neurology 2007, 68, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striano, P.; Louis, E.D.; Manto, M. Autosomal dominant cortical tremor, myoclonus, and epilepsy: Is the origin in the cerebellum? Editorial. Cerebellum 2013, 12, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Striano, P.; Coppola, A.; Dubbioso, R.; Minetti, C. Cortical tremor: A tantalizing conundrum between cortex and cerebellum. Brain 2020, 143, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, P.K.; Paulson, H.L. RNA-mediated neurodegeneration in repeat expansion disorders. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Ashizawa, T. RNA toxicity and foci formation in microsatellite expansion diseases. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2017, 44, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.L.; Jones, K.L.; Yeo, G.W. Repeat RNA expansion disorders of the nervous system: Post-transcriptional mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 56, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, B.; Robberecht, W.; Van Den Bosch, L. RNA toxicity in non-coding repeat expansion disorders. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Hitomi, T.; Matsumoto, R.; Watanabe, M.; Takahashi, R.; Ikeda, A. Nationwide survey in Japan endorsed diagnostic criteria of benign adult familial myoclonus epilepsy. Seizure 2018, 61, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, A.; Shibasaki, H.; Tashiro, K.; Mizuno, Y.; Kimura, J. Clinical trial of piracetam in patients with myoclonus: Nationwide multiinstitution study in Japan. The Myoclonus/Piracetam Study Group. Mov. Disord. 1996, 11, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striano, P.; Coppola, A.; Madia, F.; Pezzella, M.; Ciampa, C.; Zara, F.; Striano, S. Life-threatening status epilepticus following gabapentin administration in a patient with benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 1995–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Katagai, A.; Okudera, R.; Fujita, M.; Tomiyama, M. Carbamazepine-induced convulsive status epilepticus in benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy: A case report. Neurol. Sci. 2022; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, R.; Versace, V.; Höller, Y.; Sebastianelli, L.; Brigo, F.; Lochner, P.; Golaszewski, S.; Saltuari, L.; Trinka, E. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in myoclonus of different aetiologies. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 140, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdayer, E.; Devanne, H.; Tyvaert, L.; Defebvre, L.; Derambure, P.; Cassim, F. Low frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over premotor cortex can improve cortical tremor. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, R.; Nelles, D.A.; Pirie, E.; Blue, S.M.; Marina, R.J.; Wang, H.; Chaim, I.A.; Thomas, J.D.; Zhang, N.; Nguyen, V.; et al. Elimination of Toxic Microsatellite Repeat Expansion RNA by RNA-Targeting Cas9. Cell 2017, 170, 899–912.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemener, A.M.; Bachelot, L.; Forestier, A.; Donnou-Fournet, E.; Gilot, D.; Galibert, M.D. The powerful world of antisense oligonucleotides: From bench to bedside. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2020, 11, e1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, D.R. Nusinersen, an antisense oligonucleotide drug for spinal muscular atrophy. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuccurullo, C.; Striano, P.; Coppola, A. Familial Adult Myoclonus Epilepsy: A Non-Coding Repeat Expansion Disorder of Cerebellar–Thalamic–Cortical Loop. Cells 2023, 12, 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121617
Cuccurullo C, Striano P, Coppola A. Familial Adult Myoclonus Epilepsy: A Non-Coding Repeat Expansion Disorder of Cerebellar–Thalamic–Cortical Loop. Cells. 2023; 12(12):1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121617
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuccurullo, Claudia, Pasquale Striano, and Antonietta Coppola. 2023. "Familial Adult Myoclonus Epilepsy: A Non-Coding Repeat Expansion Disorder of Cerebellar–Thalamic–Cortical Loop" Cells 12, no. 12: 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121617
APA StyleCuccurullo, C., Striano, P., & Coppola, A. (2023). Familial Adult Myoclonus Epilepsy: A Non-Coding Repeat Expansion Disorder of Cerebellar–Thalamic–Cortical Loop. Cells, 12(12), 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121617






