Generation of Isogenic hiPSCs with Targeted Edits at Multiple Intronic SNPs to Study the Effects of the Type 2 Diabetes Associated KCNQ1 Locus in American Indians
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derivation and Culture
2.2. Differentiating hiPSCs to Beta-like Cells
2.3. RNA Sequencing
2.4. Guide RNA Generation, CRISPR and Single Cell Cloning
2.5. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.6. Copy Number Assay
2.7. Bisulphite Sequencing
2.8. Genomic Stability
2.9. Pluripotency and Differentiation Potential
2.10. Off-Target Effect Analysis
2.11. Flow Cytometry
2.12. Immunocytochemistry
2.13. Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion Assay
3. Results
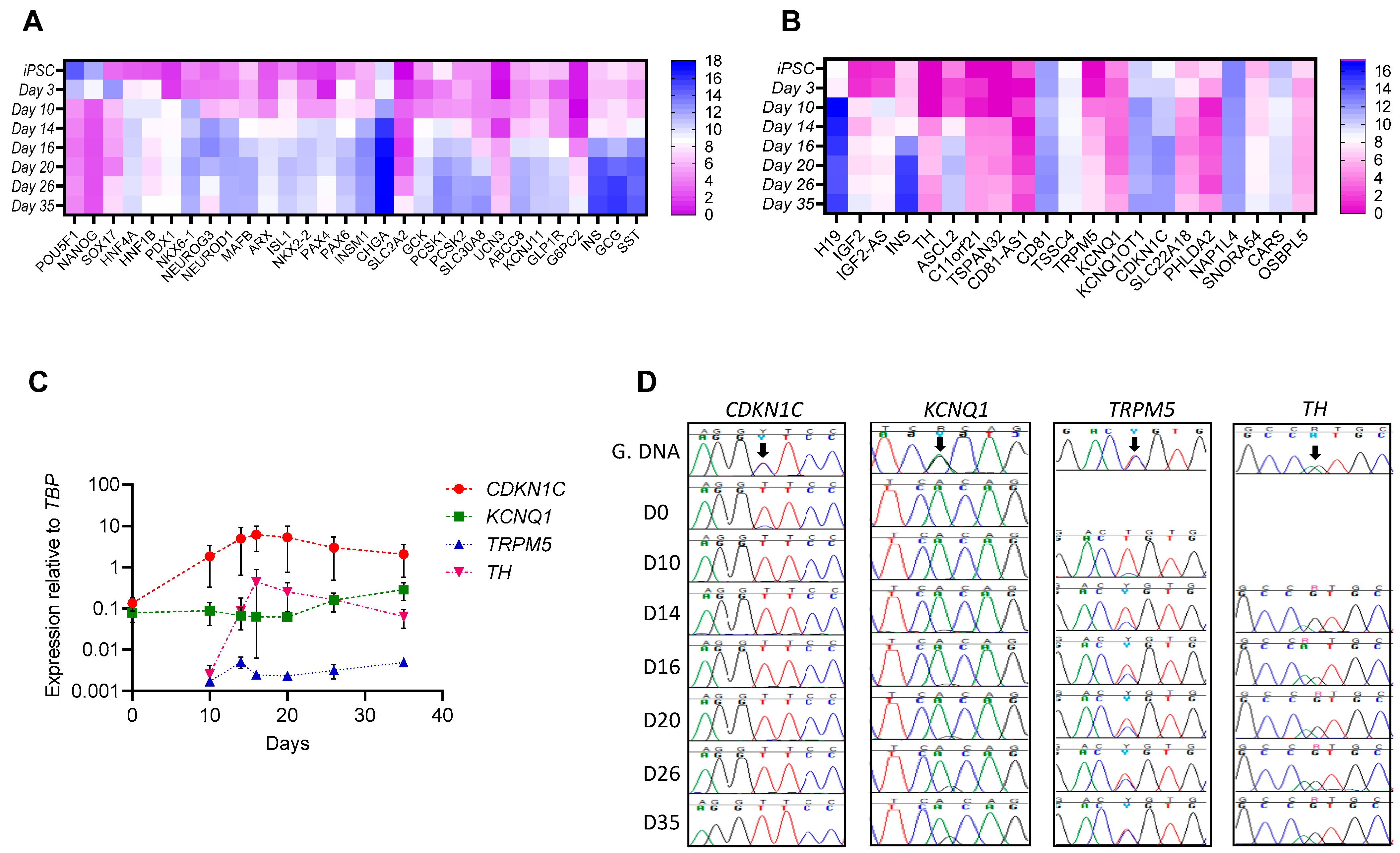
3.1. Differences in Gene Expression and Imprinting Status of KCNQ1, CDKN1C and TRPM5 during Pancreatic Beta-like Cell Differentiation from American Indian hiPSCs
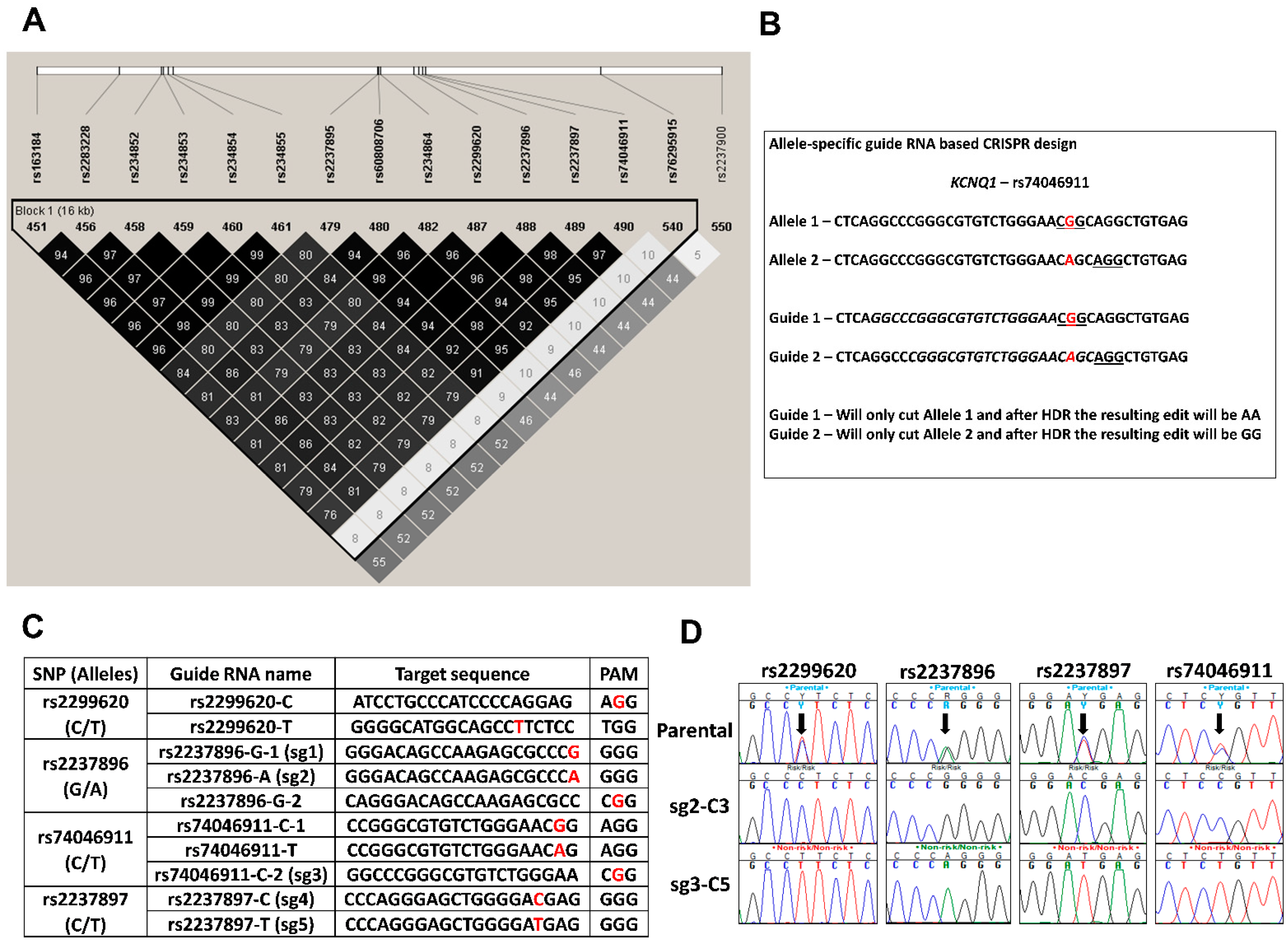
3.2. Generation of Genome-Edited Isogenic hiPSCs
3.2.1. SNP Selection and Allele-Specific Guide RNA Design for CRISPR/CAS9 Editing at the KCNQ1 Locus
3.2.2. Generation of Isogenic Cells Lines Using Allele Specific CRISPR sgRNAs
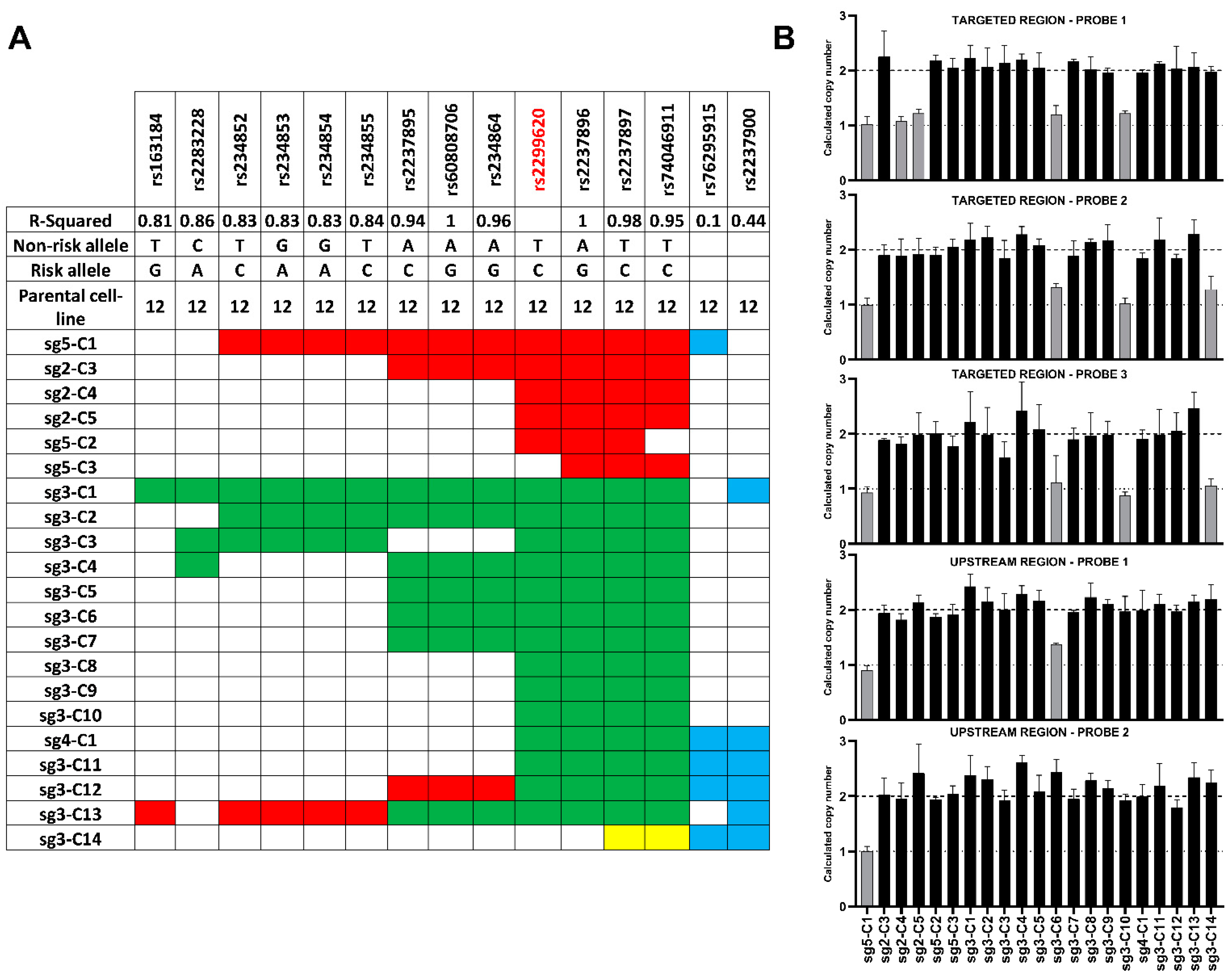
3.3. Characterization of Genome-Edited Isogenic hiPSCs
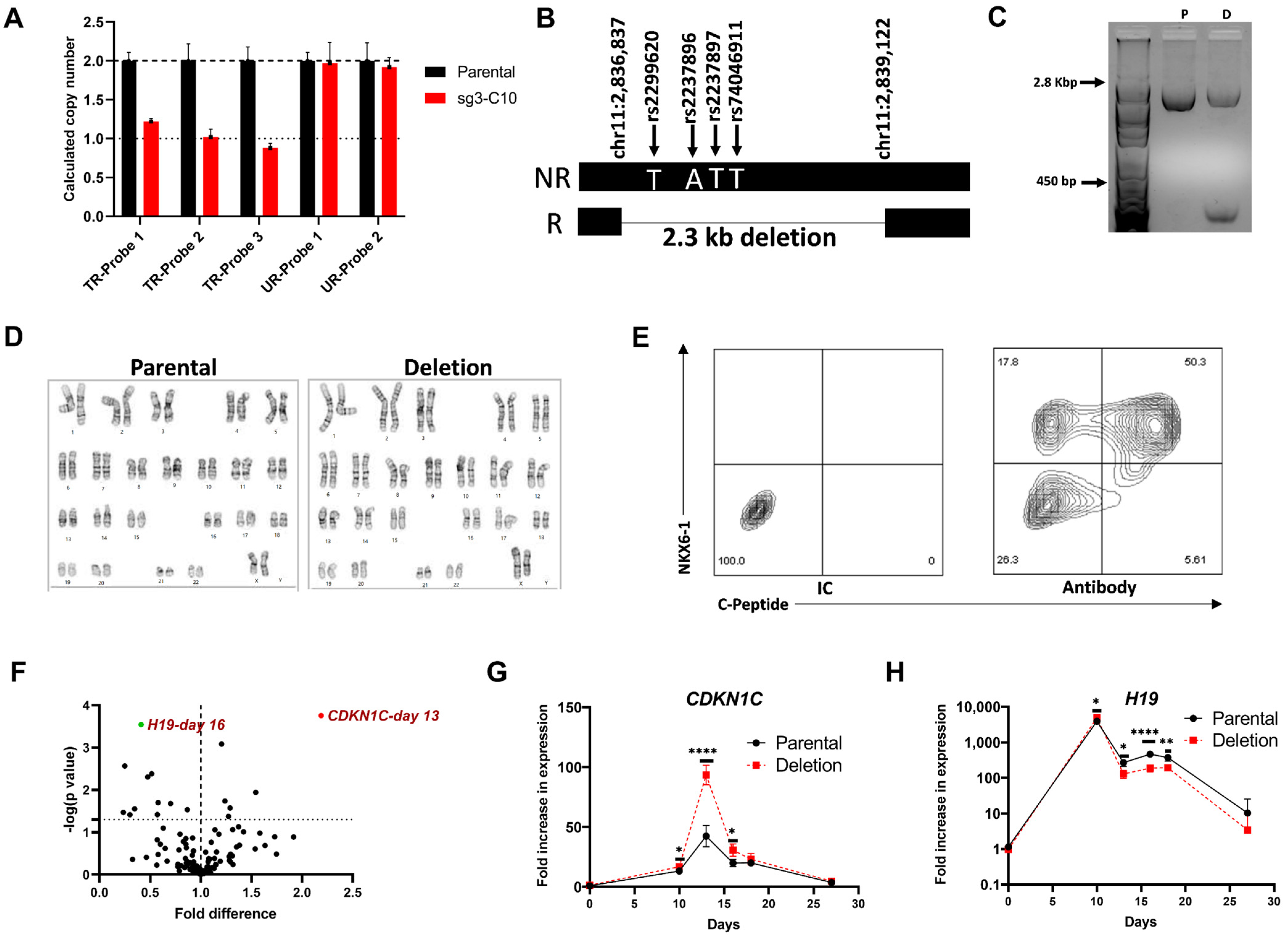
3.3.1. Extended Genotyping and Identification of Large Deletions in the Established Isogenic Cell Lines
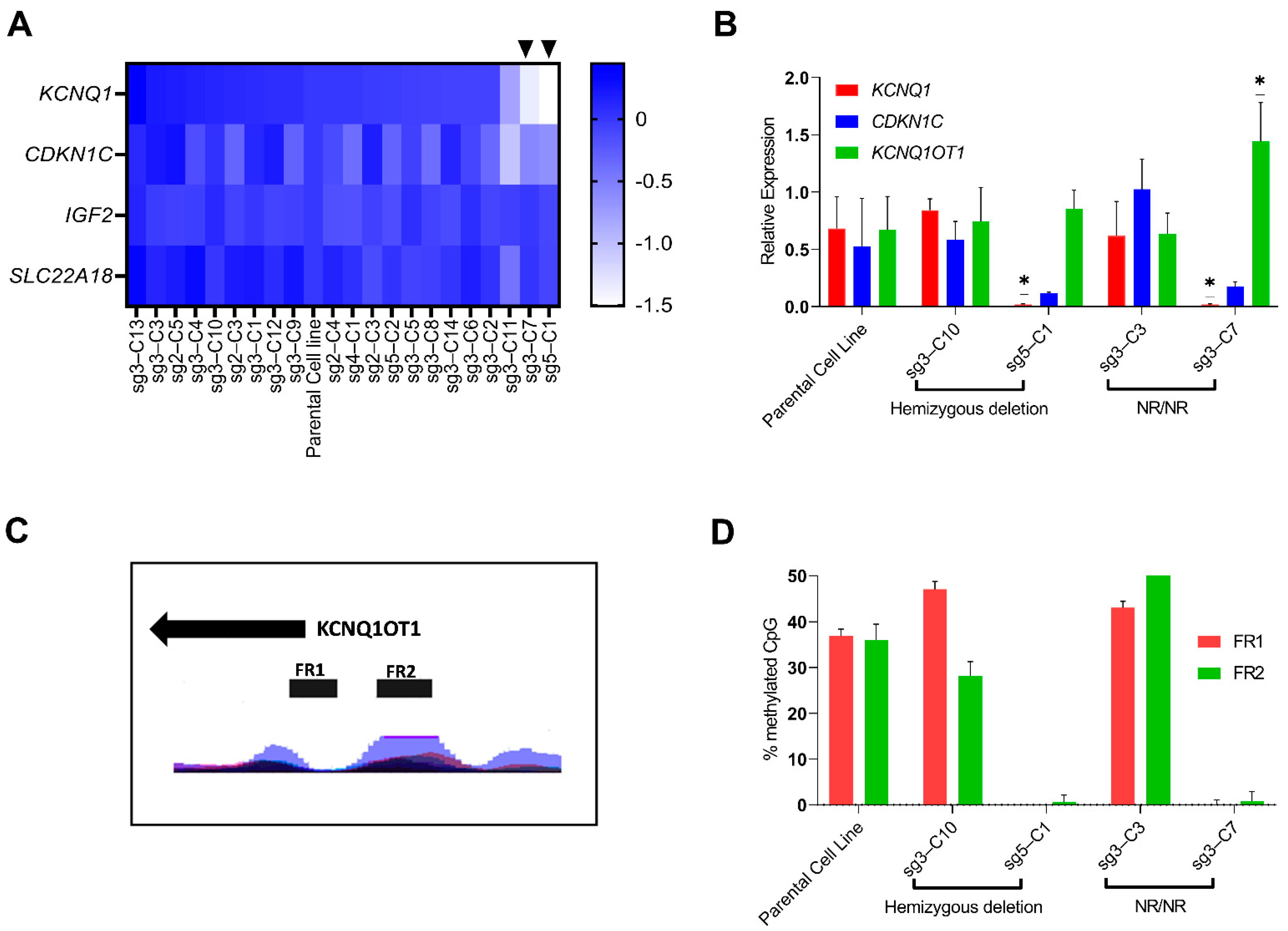
3.3.2. Identification of Clonal Cell Lines with Hypomethylation at the KCNQ1OT1 Promoter Region Resulting in Downregulation of KCNQ1 Expression
3.3.3. Genomic Stability, CRISPR-cas9 Off-Target Effects, and Pluripotency in the Established Isogenic Cell Lines
3.4. Functional Characterization of a Clonal Cell Line with a CRISPR-Induced Hemizygous Deletion in KCNQ1
3.4.1. A 2.3 kb Deletion in KCNQ1 That Spans the 4 Putative Functional SNPs Affects Gene Expression of CDKN1C and H19
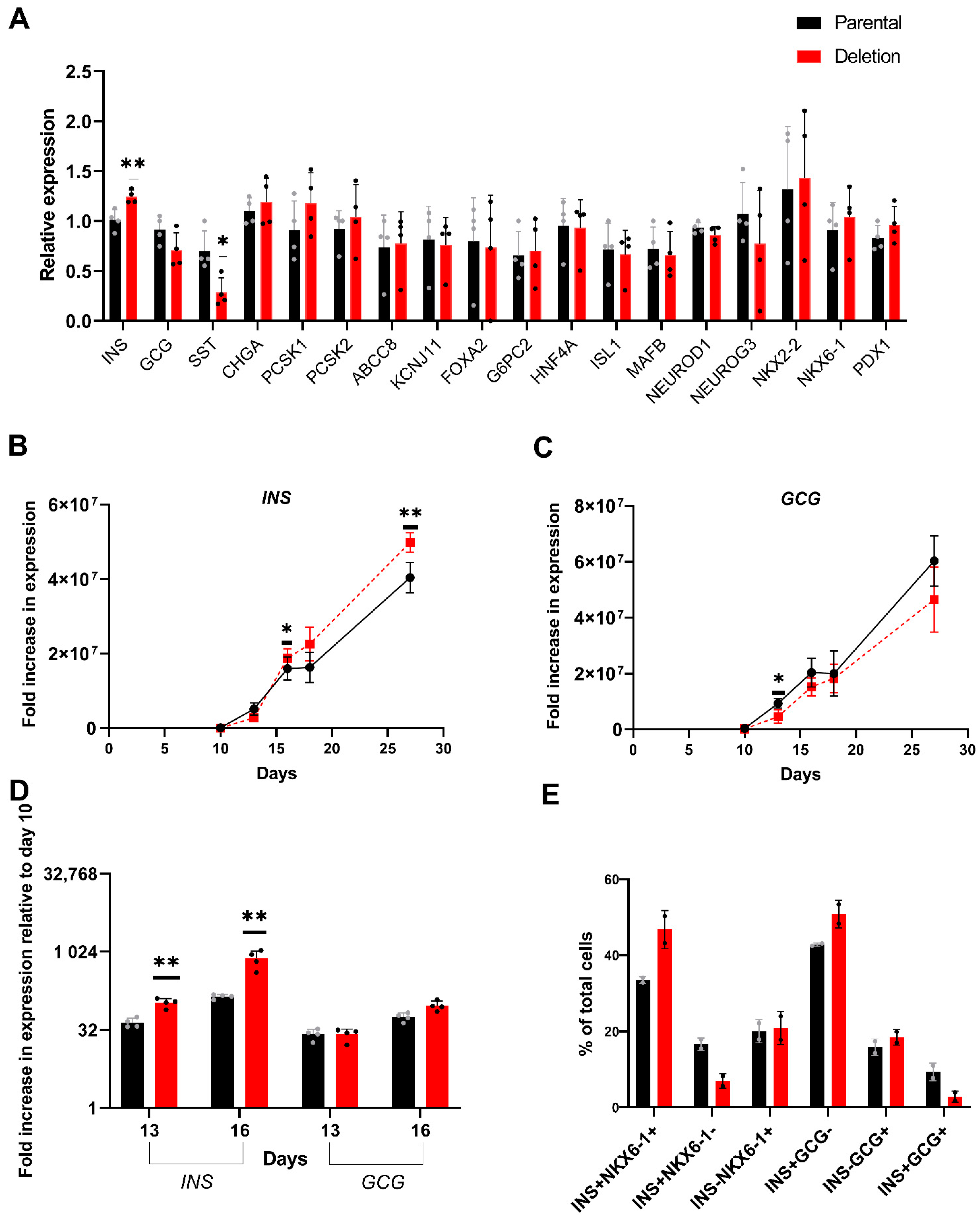
3.4.2. Differential Expression of INS in Day 27 Islet-like Cells Derived from the hiPSC with the 2.3 kb Hemizygous Deletion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, A.P.; Voight, B.F.; Teslovich, T.M.; Ferreira, T.; Segrè, A.V.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Khan, H.; Grallert, H.; Mahajan, A.; et al. Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spracklen, C.N.; Horikoshi, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Lin, K.; Bragg, F.; Moon, S.; Suzuki, K.; Tam, C.H.T.; Tabara, Y.; Kwak, S.-H.; et al. Identification of type 2 diabetes loci in 433,540 East Asian individuals. Nature 2020, 582, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Akiyama, M.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, M.; Hosoe, J.; Shojima, N.; Hozawa, A.; Kadota, A.; Kuriki, K.; Naito, M.; et al. Identification of 28 new susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, A.A.; Zaghloul, N.A.; Chen, G.; Doumatey, A.P.; Leitch, C.C.; Hostelley, T.L.; Nesmith, J.E.; Zhou, J.; Bentley, A.R.; Shriner, D.; et al. ZRANB3 is an African-specific type 2 diabetes locus associated with beta-cell mass and insulin response. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.L.; Muller, Y.L.; Kobes, S.; Guo, T.; Bian, L.; Ossowski, V.; Wiedrich, K.; Sutherland, J.; Wiedrich, C.; Mahkee, D.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study in American Indians Implicates DNER as a Susceptibility Locus for Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Taliun, D.; Thurner, M.; Robertson, N.R.; Torres, J.M.; Rayner, N.W.; Payne, A.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Scott, R.A.; Grarup, N.; et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimas, A.S.; Lagou, V.; Barker, A.; Knowles, J.W.; Mägi, R.; Hivert, M.-F.; Benazzo, A.; Rybin, D.; Jackson, A.U.; Stringham, H.M.; et al. Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Susceptibility Variants on Quantitative Glycemic Traits Reveals Mechanistic Heterogeneity. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2158–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, A.R.; Jonsson, A.; Jackson, A.U.; Wang, N.; van Leewen, N.; Palmer, N.D.; Kobes, S.; Deelen, J.; Boquete-Vilarino, L.; Paananen, J.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study of IVGTT-Based Measures of First-Phase Insulin Secretion Refines the Underlying Physiology of Type 2 Diabetes Variants. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2296–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, L.; Gaulton, K.; Rodriguez-Segui, S.A.; Mularoni, L.; Miguel-Escalada, I.; Akerman, I.; Tena, J.J.; Morán, I.; Gómez-Marín, C.; van de Bunt, M.; et al. Pancreatic islet enhancer clusters enriched in type 2 diabetes risk-associated variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.L.; Guo, T.; Muller, Y.L.; Fleming, J.; Knowler, W.C.; Kobes, S.; Bogardus, C.; Baier, L.J. Strong Parent-of-Origin Effects in the Association of KCNQ1 Variants with Type 2 Diabetes in American Indians. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2984–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, A.; DIAGRAM Consortium; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Masson, G.; Thorleifsson, G.; Sulem, P.; Besenbacher, S.; Jonasdottir, A.; Sigurdsson, A.; Kristinsson, K.T.; et al. Parental origin of sequence variants associated with complex diseases. Nature 2009, 462, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unoki, H.; Takahashi, A.; Kawaguchi, T.; Hara, K.; Horikoshi, M.; Andersen, G.; Ng, D.P.K.; Holmkvist, J.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Jørgensen, T.; et al. SNPs in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in East Asian and European populations. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, K.; Miyake, K.; Horikawa, Y.; Hara, K.; Osawa, H.; Furuta, H.; Hirota, Y.; Mori, H.; Jonsson, A.; Sato, Y.; et al. Variants in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meitinger, T.; Shriner, D.; Chen, B.H.; Lindgren, C.; Chen, W.-M.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Bielinski, S.J.; Yanek, L.R.; Nalls, M.A.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies in African Americans Provides Insights into the Genetic Architecture of Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The SIGMA Type 2 Diabetes Consortium. Sequence variants in SLC16A11 are a common risk factor for type 2 diabetes in Mexico. Nature 2014, 506, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, M.E.; Mackay, D.J.; Nitert, M.D.; Morris, A.P.; Lindgren, C.M.; Berry, A.; Johnson, P.R.; Hanley, N.; Groop, L.C.; McCarthy, M.I.; et al. Insights into the Molecular Mechanism for Type 2 Diabetes Susceptibility at the KCNQ1 Locus from Temporal Changes in Imprinting Status in Human Islets. Diabetes 2013, 62, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzi, S.; Habib, W.A.; Netchine, I. Beckwith-Wiedemann and Russell-Silver Syndromes: From new molecular insights to the comprehension of imprinting regulation. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2014, 21, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezania, A.; Bruin, J.; Arora, P.; Rubin, A.; Batushansky, I.; Asadi, A.; O’Dwyer, S.; Quiskamp, N.; Mojibian, M.; Albrecht, T.; et al. Reversal of diabetes with insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliuca, F.W.; Millman, J.; Gürtler, M.; Segel, M.; Van Dervort, A.; Ryu, J.H.; Peterson, Q.; Greiner, D.; Melton, D.A. Generation of functional human pancreatic β cells in vitro. Cell 2014, 159, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogrebe, N.J.; Augsornworawat, P.; Maxwell, K.G.; Velazco-Cruz, L.; Millman, J.R. Targeting the cytoskeleton to direct pancreatic differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazco-Cruz, L.; Song, J.; Maxwell, K.; Goedegebuure, M.M.; Augsornworawat, P.; Hogrebe, N.; Millman, J.R. Acquisition of Dynamic Function in Human Stem Cell-Derived β Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres, A.; Faust, A.L.; Bushnell, H.; Engquist, E.; Kenty, J.H.-R.; Harb, G.; Poh, Y.-C.; Sintov, E.; Gürtler, M.; Pagliuca, F.W.; et al. Charting cellular identity during human in vitro β-cell differentiation. Nature 2019, 569, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.; Liu, J.S.; Russ, H.A.; Tran, S.; Saxton, M.S.; Chen, R.; Juang, C.; Li, M.-L.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Giacometti, S.; et al. Recapitulating endocrine cell clustering in culture promotes maturation of human stem-cell-derived β cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, R.L.; Rong, R.; Kobes, S.; Muller, Y.L.; Weil, E.J.; Curtis, J.M.; Nelson, R.G.; Baier, L.J. Role of Established Type 2 Diabetes-Susceptibility Genetic Variants in a High Prevalence American Indian Population. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2646–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, Y.L.; Day, S.E.; Kobes, S.; Knowler, W.C.; Hanson, R.L.; Bogardus, C.; Baier, L.J. 1715-P: Identifying Potentially Functional Variants in Regulatory Regions in KCNQ1 that Associate with Type 2 Diabetes in American Indians. Diabetes 2019, 68 (Suppl. 1), 1715-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adikusuma, F.; Piltz, S.; Corbett, M.A.; Turvey, M.; McColl, S.R.; Helbig, K.; Beard, M.R.; Hughes, J.; Pomerantz, R.T.; Thomas, P.Q. Large deletions induced by Cas9 cleavage. Nature 2018, 560, E8–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosicki, M.; Tomberg, K.; Bradley, A. Repair of double-strand breaks induced by CRISPR-Cas9 leads to large deletions and complex rearrangements. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Hanson, R.L.; Traurig, M.; Muller, Y.L.; Ma, L.; Mack, J.; Kobes, S.; Knowler, W.C.; Bogardus, C.; Baier, L.J. TCF7L2 Is Not a Major Susceptibility Gene for Type 2 Diabetes in Pima Indians. Diabetes 2007, 56, 3082–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Tian, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Du, C.; Xie, X.; Kornmann, M.; Yang, Y. The long noncoding RNA H19 promotes cell proliferation via E2F-1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Parra, C.; Jacovetti, C.; Dumortier, O.; Lee, K.; Peyot, M.-L.; Guay, C.; Prentki, M.; Laybutt, D.R.; Van Obberghen, E.; Regazzi, R. Contribution of the Long Noncoding RNA H19 to β-Cell Mass Expansion in Neonatal and Adult Rodents. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2254–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, C.J.; Roberts, J.M. CDK inhibitors: Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgia, S.; Soliz, R.; Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Bhushan, A. p57 and Hes1 coordinate cell cycle exit with self-renewal of pancreatic progenitors. Dev. Biol. 2006, 298, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahara, S.-I.; Etoh, H.; Inoue, H.; Teruyama, K.; Shibutani, Y.; Ihara, Y.; Kawada, Y.; Bartolome, A.; Hashimoto, N.; Matsuda, T.; et al. Paternal allelic mutation at the Kcnq1 locus reduces pancreatic β-cell mass by epigenetic modification of Cdkn1c. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8332–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.-L.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Feng, Y.; Li, L.-C.; Yang, L.; Xu, C.-R. Deciphering Pancreatic Islet β Cell and α Cell Maturation Pathways and Characteristic Features at the Single-Cell Level. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1194–1205.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.; Georgia, S.; Bhushan, A. Formation and regeneration of the endocrine pancreas. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| hPSC Scorecard Scores (X) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line ID | Haplotype | Karyotype | Off-Target Edit | Pluripotency | Ectoderm | Mesoderm | Endoderm |
| Parental Cell line | MRRYRYY | 46, XX | Reference | −0.2 | −0.67 | −0.73 | −1.15 |
| sg2-C3 | CGGCGCC | 46, XX | None detected | −0.5 | −0.38 | −0.6 | −0.83 |
| sg5-C2 | MRRCGCY | 46, XX | Intergenic Indel | −0.37 | −0.62 | −0.99 | −1.22 |
| sg5-C3 | MRRYGCC | 46, XX | None detected | −0.22 | −0.54 | −0.58 | −1.14 |
| sg3-C2 | AAATATT | 46, XX | None detected | 0.08 | −0.62 | −0.72 | −1.28 |
| sg3-C5 | AAATATT | 46, XX | None detected | 0.27 | −0.56 | −0.72 | −1.18 |
| sg3-C8 | MRRTATT | 46, XX | None detected | 0.26 | −0.49 | −0.69 | −1.05 |
| sg3-C9 | MRRTATT | 46, XX | None detected | 0.29 | −0.62 | −0.6 | −1.28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nair, A.K.; Traurig, M.; Sutherland, J.R.; Muller, Y.L.; Grellinger, E.D.; Saporito, L.; Nelson, R.G.; Bogardus, C.; Baier, L.J. Generation of Isogenic hiPSCs with Targeted Edits at Multiple Intronic SNPs to Study the Effects of the Type 2 Diabetes Associated KCNQ1 Locus in American Indians. Cells 2022, 11, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091446
Nair AK, Traurig M, Sutherland JR, Muller YL, Grellinger ED, Saporito L, Nelson RG, Bogardus C, Baier LJ. Generation of Isogenic hiPSCs with Targeted Edits at Multiple Intronic SNPs to Study the Effects of the Type 2 Diabetes Associated KCNQ1 Locus in American Indians. Cells. 2022; 11(9):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091446
Chicago/Turabian StyleNair, Anup K., Michael Traurig, Jeff R. Sutherland, Yunhua L. Muller, Emma D. Grellinger, Lucas Saporito, Robert G. Nelson, Clifton Bogardus, and Leslie J. Baier. 2022. "Generation of Isogenic hiPSCs with Targeted Edits at Multiple Intronic SNPs to Study the Effects of the Type 2 Diabetes Associated KCNQ1 Locus in American Indians" Cells 11, no. 9: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091446
APA StyleNair, A. K., Traurig, M., Sutherland, J. R., Muller, Y. L., Grellinger, E. D., Saporito, L., Nelson, R. G., Bogardus, C., & Baier, L. J. (2022). Generation of Isogenic hiPSCs with Targeted Edits at Multiple Intronic SNPs to Study the Effects of the Type 2 Diabetes Associated KCNQ1 Locus in American Indians. Cells, 11(9), 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091446






