Monochromatic Light Pollution Exacerbates High-Fat Diet-Induced Adipocytic Hypertrophy in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Treatment and Light Exposure
2.2. Glucose and Insulin Tolerance Test
2.3. Commercial Kits Detection
2.4. Histology Staining
2.5. Quantitative Real Time (RT)-PCR Analysis
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
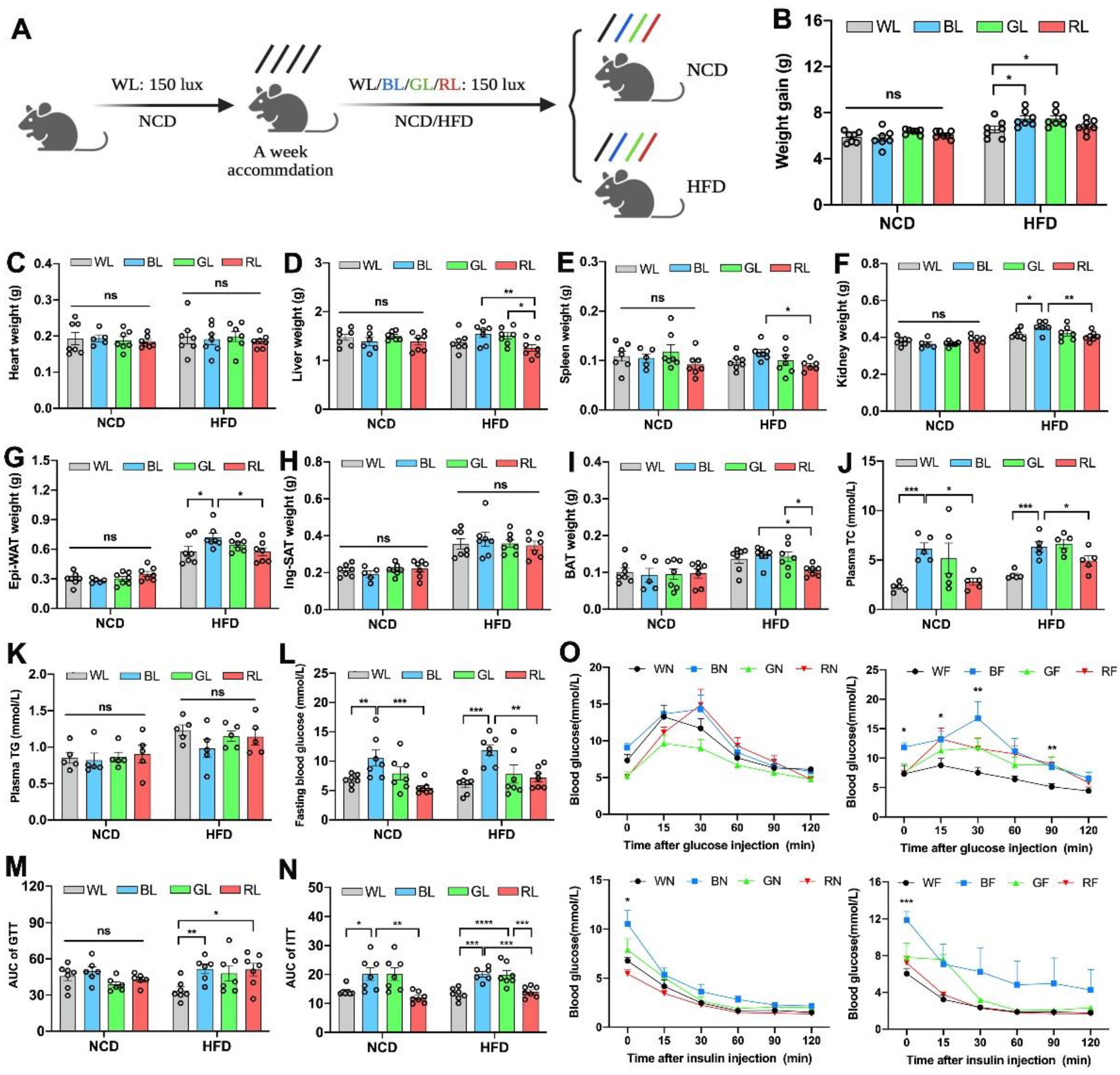
3.1. Effects of Monochromatic Light Exposure on Metabolic Disorders in Mice
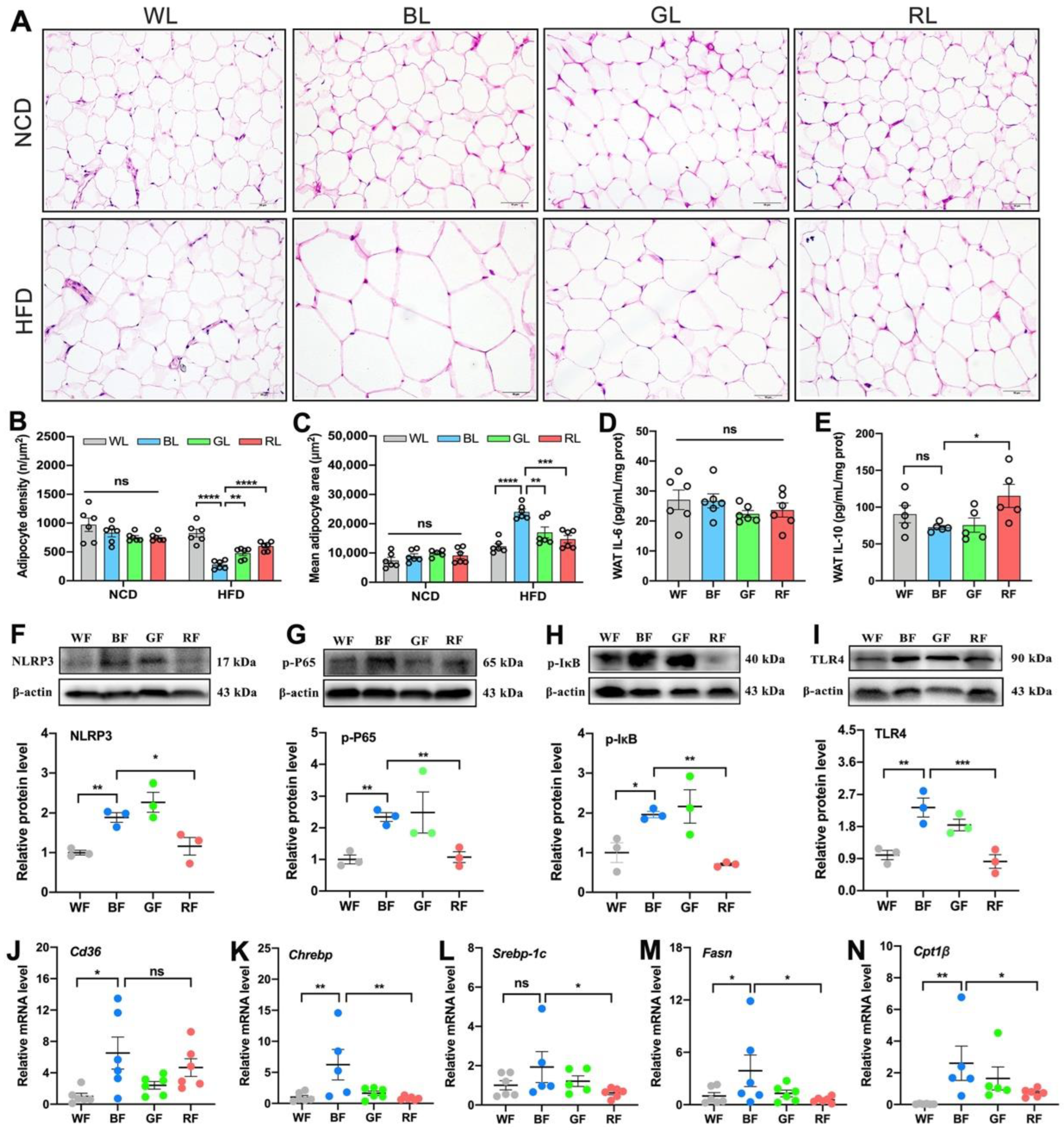
3.2. Effects of Monochromatic Light Exposure on WAT Hypertrophy and Inflammation in Mice
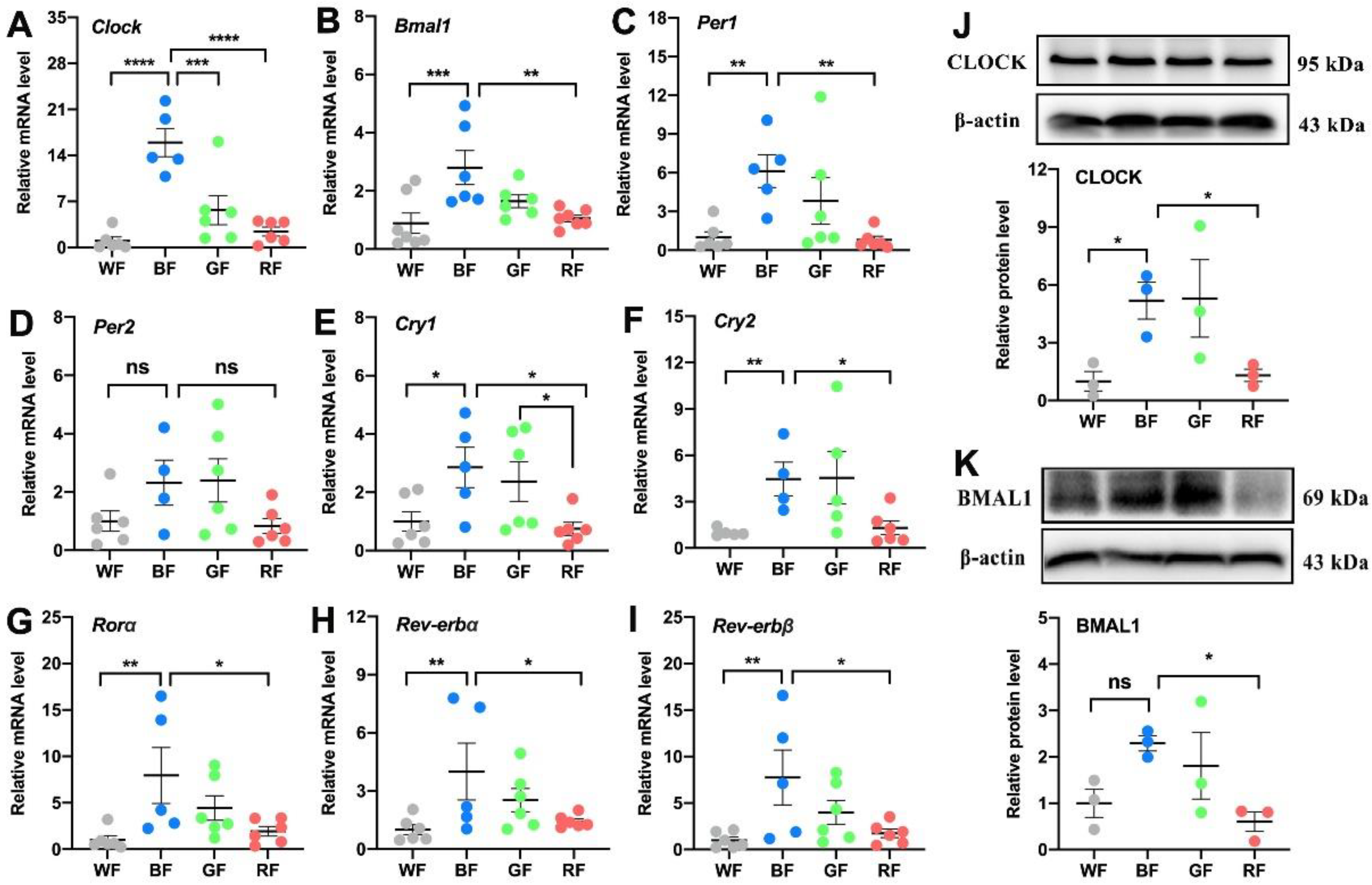
3.3. Effects of Monochromatic Light Exposure on the Expression of Circadian Clock in the WAT
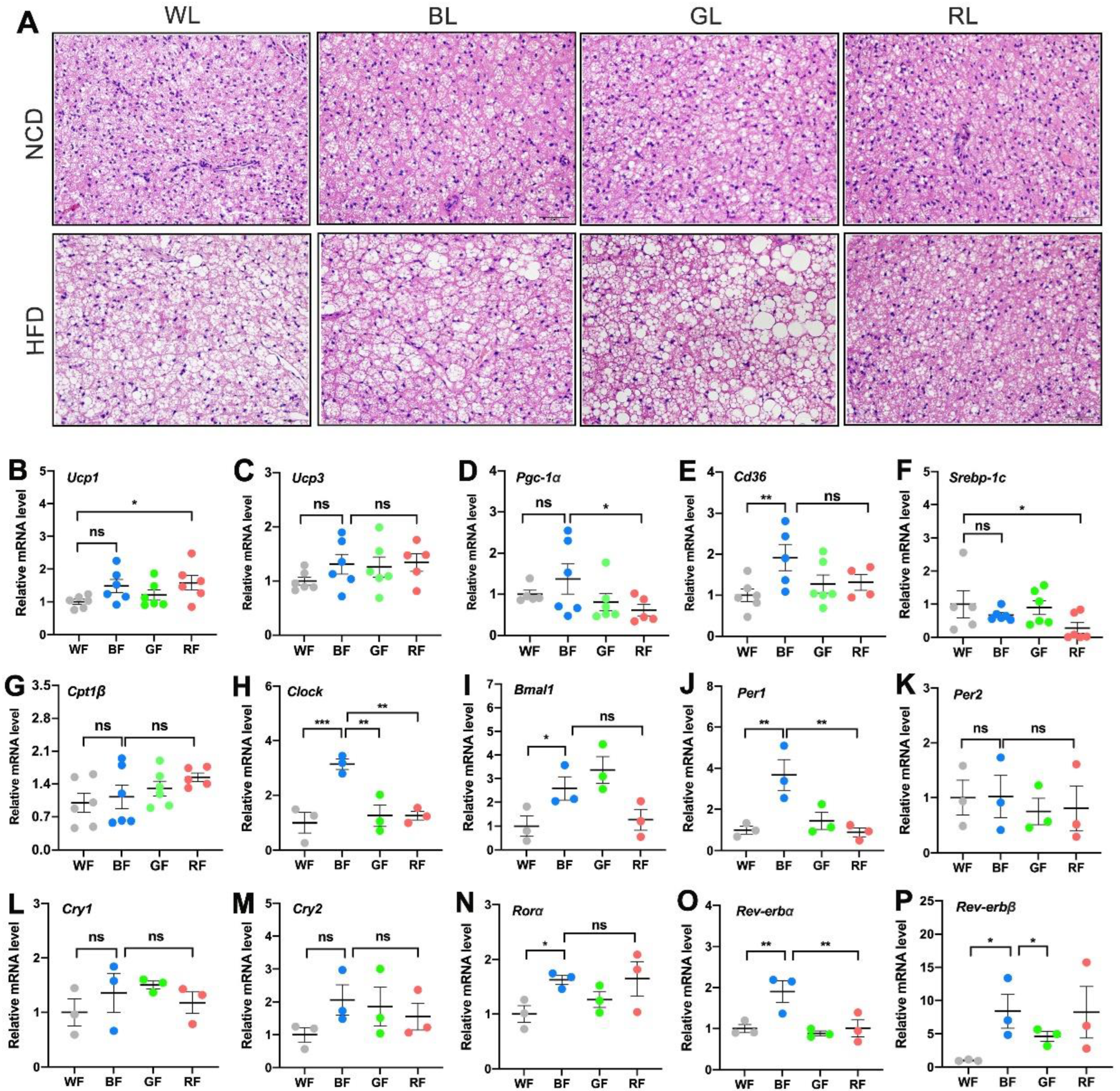
3.4. Effects of Monochromatic Light Exposure on BAT Whitening and Expression Levels of Circadian Genes in the BAT
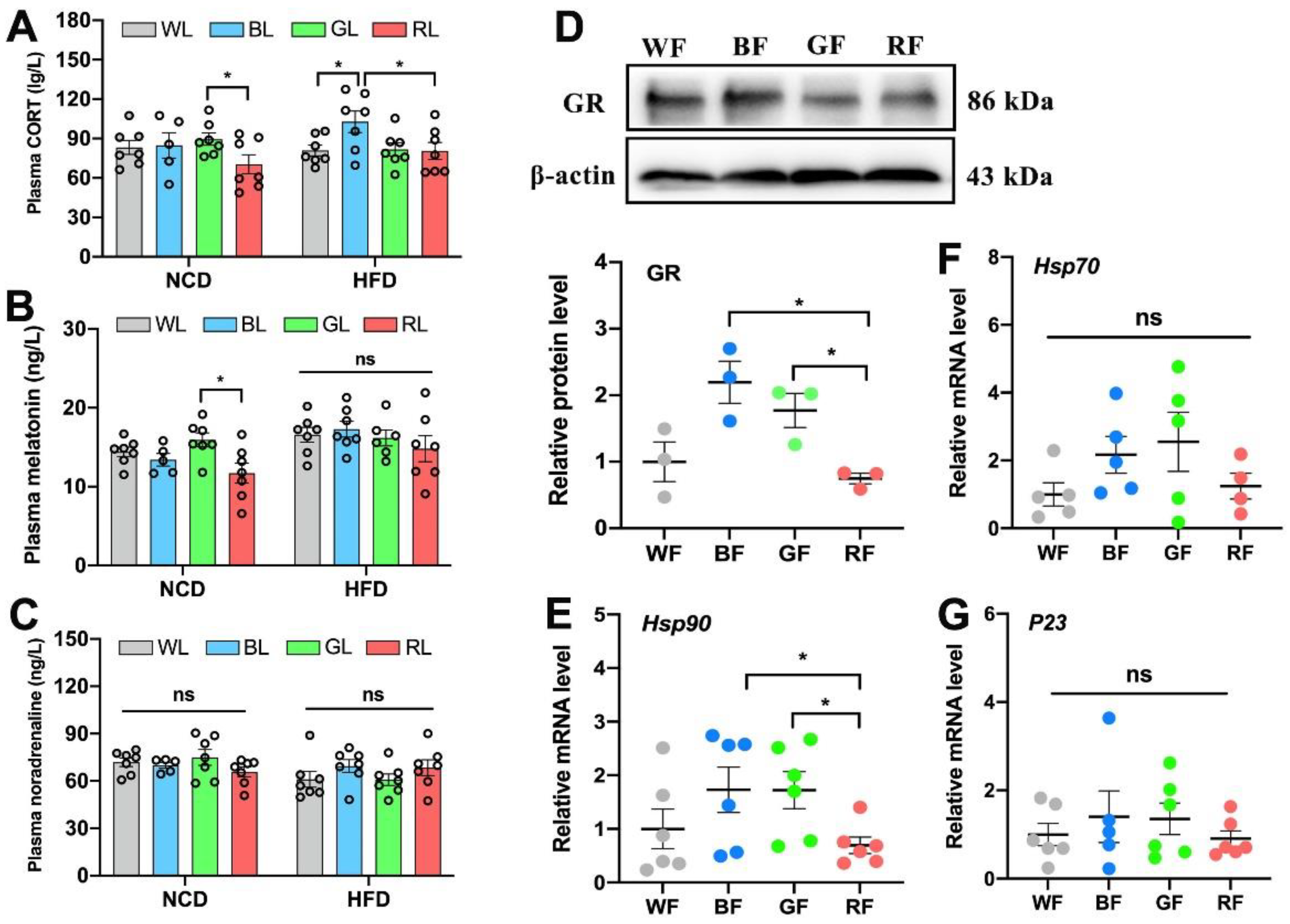
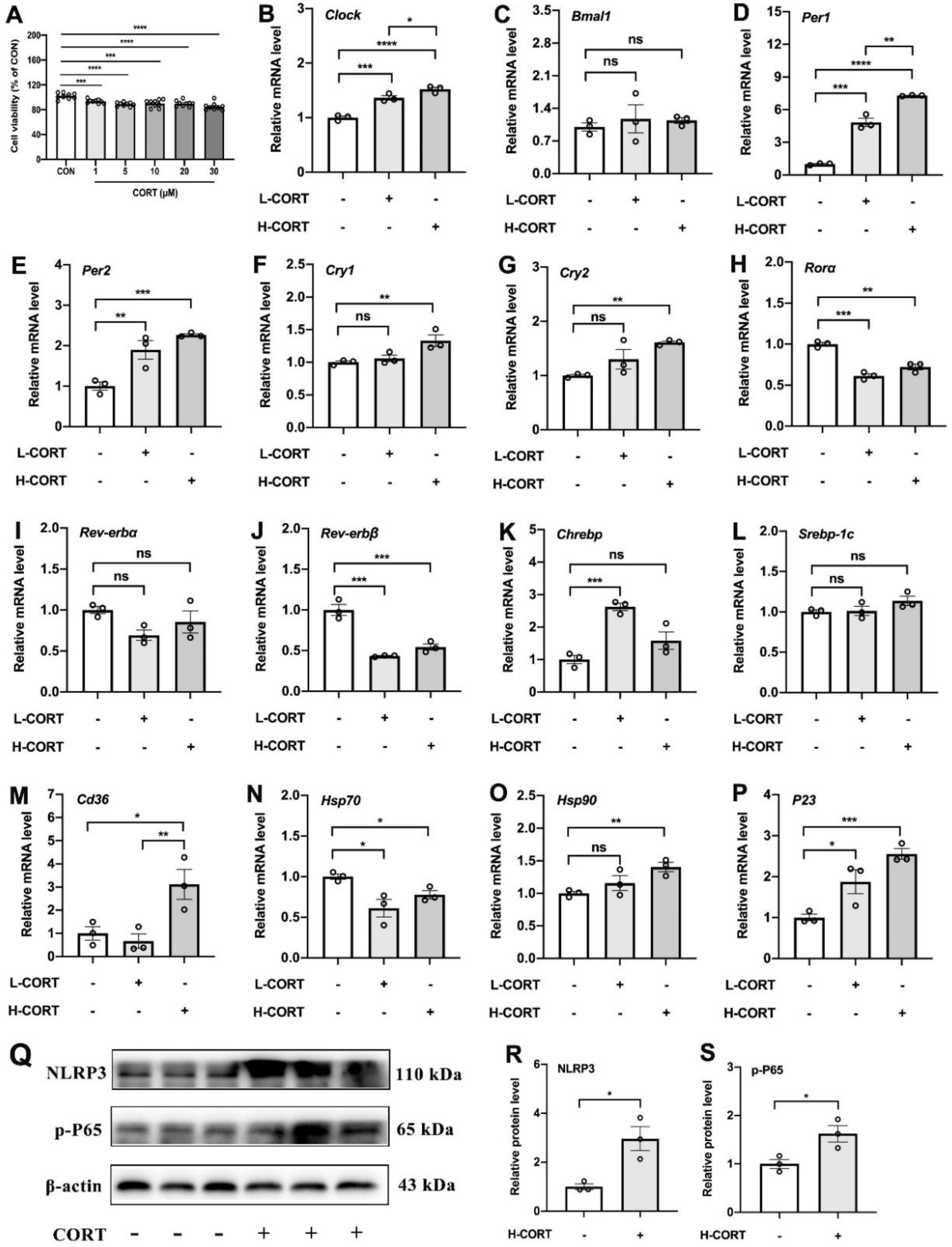
3.5. The Role of CORT in Interference with the Adipose Circadian Clock
4. Discussion
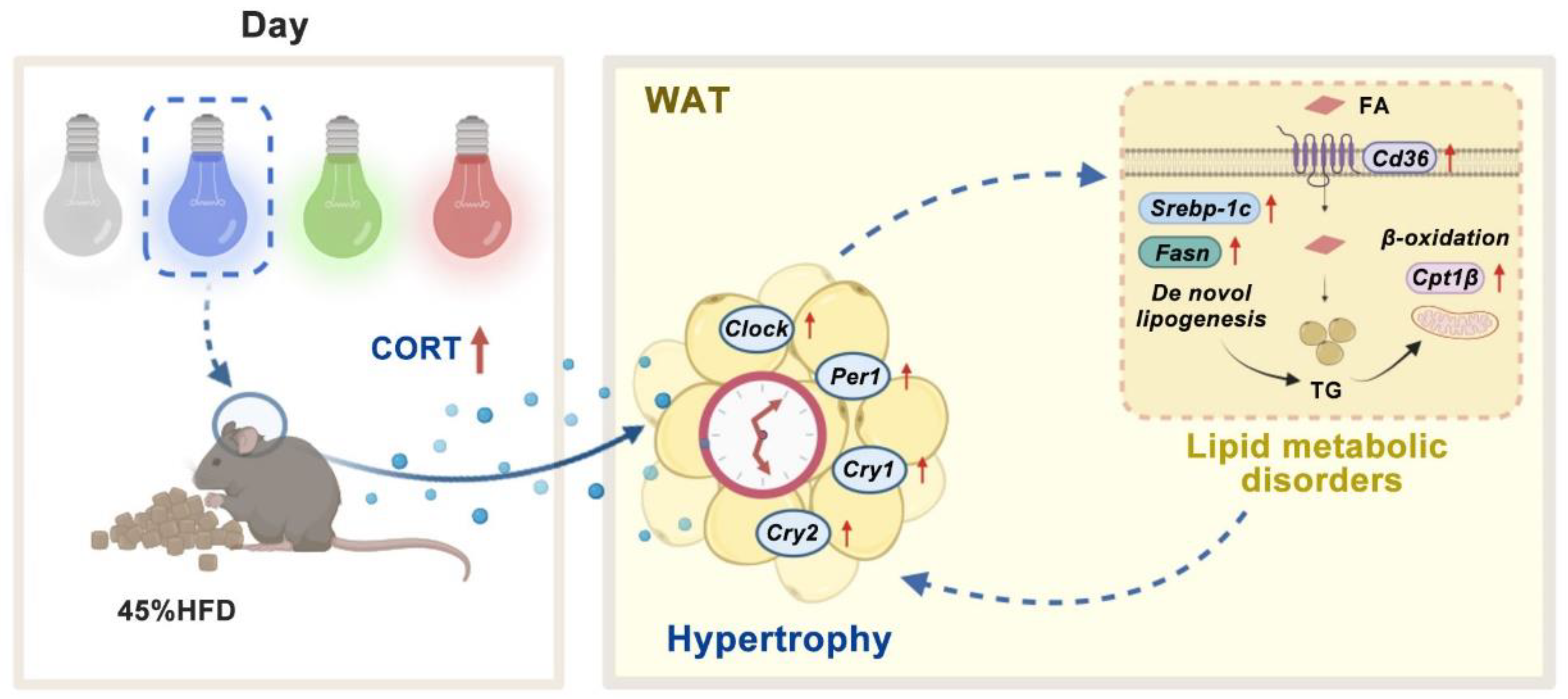
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaston, K.J.; Visser, M.E.; Hölker, F. The biological impacts of artificial light at night: The research challenge. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, T.; Malik, I.; Kumar, V. Illuminated night alters behaviour and negatively affects physiology and metabolism in diurnal zebra finches. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. The role of light pollution in mammalian metabolic homeostasis and its potential interventions: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jones, R.R.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Jia, P.; James, P.; Xiao, Q. A large prospective investigation of outdoor light at night and obesity in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaki, Y.; Obayashi, K.; Saeki, K.; Fujita, K.; Iwata, N.; Kitajima, T. Bedroom light exposure at night and obesity in individuals with bipolar disorder: A cross-sectional analysis of the APPLE cohort. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 230, 113281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Z.; Zeng, X.W.; Deb, B.; Tabet, M.; Xu, S.L.; Wu, Q.Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, H.M.; Chen, D.H.; Chen, G.B.; et al. Outdoor light at night, overweight, and obesity in school-aged children and adolescents. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borck, P.; Batista, T.; Vettorazzi, J.; Soares, G.; Lubaczeuski, C.; Guan, D.; Boschero, A.; Vieira, E.; Lazar, M.; Carneiro, E. Nighttime light exposure enhances Rev-erbα-targeting microRNAs and contributes to hepatic steatosis. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2018, 85, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, F.; Xia, K.; Wei, L.; Xing, L.; Wu, S.; Shi, Y.; Lam, S.M.; Shui, G.; Xiang, X.; Russell, R.; et al. Effects of constant light exposure on sphingolipidomics and progression of NASH in high-fat-fed rats. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 1978–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borck, P.C.; Rickli, S.; Vettorazzi, J.F.; Batista, T.M.; Boschero, A.C.; Vieira, E.; Carneiro, E.M. Effect of nighttime light exposure on glucose metabolism in protein-restricted mice. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 252, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Qiu, H.; Gu, Y. Light intensity alters the effects of light-induced circadian disruption on glucose and lipid metabolism in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 322, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgin, P.; Hubbard, J. Alerting or somnogenic light: Pick your color. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e2000111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumanova, V.S.; Okuliarova, M.; Zeman, M. Differential effects of constant light and dim light at night on the circadian control of metabolism and hehavior. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opperhuizen, A.L.; Stenvers, D.J.; Jansen, R.D.; Foppen, E.; Fliers, E.; Kalsbeek, A. Light at night acutely impairs glucose tolerance in a time-, intensity- and wavelength-dependent manner in rats. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaifa, I.K.; Bahari, H.; Yong, Y.K.; Noor, S.M. Endothelial dysfunction in obesity-induced inflammation: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, I.; Walsh, K. The Whitening of brown fat and its implications for weight management in obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, J.; Hong, F.; Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Xue, T.; Jia, L.; Zhai, Y. Melatonin prevents obesity through modulation of gut microbiota in mice. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62, e12399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonken, L.; Nelson, R. The effects of light at night on circadian clocks and metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 648–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, G.D.; Skene, D.J.; Arendt, J.; Cade, J.E.; Grant, P.J.; Hardie, L.J. Circadian rhythm and sleep disruption: Causes, metabolic consequences, and countermeasures. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 584–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiehn, J.T.; Tsang, A.H.; Heyde, I.; Leinweber, B.; Kolbe, I.; Leliavski, A.; Oster, H. Circadian rhythms in adipose tissue physiology. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 7, 383–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froy, O.; Garaulet, M. The Circadian clock in white and brown adipose tissue: Mechanistic, endocrine, and clinical aspects. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. Monochromatic blue light not green light exposure is associated with continuous light-induced hepatic steatosis in high fat diet fed-mice via oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, Y.S.; Song, J.Y.; Joo, E.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, E.; Lee, S.K.; Jung, K.Y. Outdoor artificial light at night, obesity, and sleep health: Cross-sectional analysis in the KoGES study. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masís-Vargas, A.; Hicks, D.; Kalsbeek, A.; Mendoza, J. Blue light at night acutely impairs glucose tolerance and increases sugar intake in the diurnal rodent Arvicanthis ansorgei in a sex-dependent manner. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, F.; Pan, S.; Xu, P.; Xue, T.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Jia, L.; Qiao, X.; Li, L.; Zhai, Y. Melatonin orchestrates lipid homeostasis through the hepatointestinal circadian clock and microbiota during constant light exposure. Cells 2020, 9, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, N.; Ayaki, M.; Yanagawa, T.; Hattori, A.; Negishi, K.; Mori, T.; Nakamura, T.J.; Tsubota, K. Suppression of Blue Light at Night Ameliorates Metabolic Abnormalities by Controlling Circadian Rhythms. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 3786–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, M.; Shen, Z.; Shang, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, C. Green light exposure aggravates high-fat diet feeding-induced hepatic steatosis and pancreatic dysfunction in male mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canbay, A.; Bechmann, L.; Gerken, G. Lipid metabolism in the liver. Z. Für Gastroenterol. 2007, 45, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooley, J.J. Circadian regulation of lipid metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turek, F.W.; Joshu, C.; Kohsaka, A.; Lin, E.; Ivanova, G.; McDearmon, E.; Laposky, A.; Losee-Olson, S.; Easton, A.; Jensen, D.R.; et al. Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian Clock mutant mice. Science 2005, 308, 1043–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimba, S.; Ogawa, T.; Hitosugi, S.; Ichihashi, Y.; Nakadaira, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Tezuka, M.; Kosuge, Y.; Ishige, K.; Ito, Y.; et al. Deficient of a clock gene, brain and muscle Arnt-like protein-1 (BMAL1), induces dyslipidemia and ectopic fat formation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennaway, D.J.; Varcoe, T.J.; Voultsios, A.; Boden, M.J. Global loss of bmal1 expression alters adipose tissue hormones, gene expression and glucose metabolism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Latre, A.; Eckel-Mahan, K. Nutrients and the circadian clock: A partnership controlling adipose tissue function and health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, S.; Engelhardt, M.; Schaupp, P.; Lappe, C.; Ivanov, I.V. The inner clock-Blue light sets the human rhythm. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201900102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.S.; Laberge, L.; Sasseville, A.; Bérubé, M.; Alain, S.; Lavoie, J.; Houle, J.; Hébert, M. Timely use of in-car dim blue light and blue blockers in the morning does not improve circadian adaptation of fast rotating shift workers. Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, D.; Ganem, J.; Guillaumond, F.; Laforge-Anglade, G.; François-Bellan, A.M.; Bosler, O.; Becquet, D. Influence of the corticosterone rhythm on photic entrainment of locomotor activity in rats. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2004, 19, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Items | Light Exposure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WL | BL | GL | RL | |
| Light wavelength (nm) | 400–700 | Peak at 444 | Peak at 528 | Peak at 624 |
| Light intensity (lux) | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Light: dark cycle (h) | 14:10 | 14:10 | 14:10 | 14:10 |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Product Size | Accession | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd36 | F: GTGCAAAACCCAGATGACGT | R: TCCAACAGACAGTGAAGGCT | 180 | NM_001159558.1 |
| Chrebp | F: GTGTGTGGTTTCGTGACCC | R: CACTTGTGGTATTCGCGCATC | 128 | NM_001359237.1 |
| Srebp-1c | F: ATCGCAAACAAGCTGACCTG | R: AGATCCAGGTTTGAGGTGGG | 115 | NM_001388389.1 |
| Fasn | F: TCCTGGAACGAGAACACGATCT | R: GAGACGTGTCACTCCTGGACTTG | 138 | NM_007988.3 |
| Cpt1β | F: GGCACCTCTTCTGCCTTTAC | R: TTTGGGTCAAACATGCAGAT | 136 | NM_009948.2 |
| Clock | F: ATGGTGTTTACCGTAAGCTGTAG | R: CTCGCGTTACCAGGAAGCAT | 197 | XM_011249402.3 |
| Bmal1 | F: CAGAGCCGGAGCAGGAAAAATAGGT | R: CAGGGGGAGGCGTACTTGTGATGT | 128 | NM_001374642.1 |
| Per1 | F: CGGATTGTCTATATTTCGGAGCA | R: TGGGCAGTCGAGATGGTGTA | 142 | NM_001159367.2 |
| Per2 | F: GAAAGCTGTCACCACCATAGAA | R: AACTCGCACTTCCTTTTCAGG | 186 | NM_011066.3 |
| Cry1 | F: CACTGGTTCCGAAAGGGACTC | R: CTGAAGCAAAAATCGCCACCT | 153 | NM_007771.3 |
| Cry2 | F: CACTGGTTCCGCAAAGGACTA | R: CCACGGGTCGAGGATGTAGA | 102 | NM_009963.4 |
| Rorα | F: TCCAAATCCCACCTGGAAAC | R: GGAAGGTCTGCCACGTTATCTG | 70 | NM_001289916.1 |
| Rve-erbα | F: TACATTGGCTCTAGTGGCTCC | R: CAGTAGGTGATGGTGGGAAGTA | 127 | NM_145434.4 |
| Rve-erbβ | F: GGAAACACTCATCCGTGCACTA | R: ATCGAAGATCTGGCAACTTTAGAA | 101 | NM_001145425.2 |
| Ucp1 | F: TAAGCCGGCTGAGATCTTGT | R: GGCCTCTACGACTCAGTCCA | 84 | NM_009463.3 |
| Ucp3 | F: CTGCACCGCCAGATGAGTTT | R: ATCATGGCTTGAAATCGGACC | 191 | NM_009464.3 |
| Pgc-1α | F: TATGGAGTGACATAGAGTGTGCT | R: CCACTTCAATCCACCCAGAAAG | 134 | NM_008904.3 |
| Hsp70 | F: CGGTGCCCGCCTACTTC | R: TCCTTCTTGTGCTTCCTCTTGA | 322 | NM_005346.6 |
| Hsp90 | F: ACGAGGAAGAGAAGAAGAAAATGG | R: GCAGGGTGAAGACACAAGCC | 131 | NM_001271971.2 |
| P23 | F: ATGCGTTTGGAGAAGGACAGA | R: CAGGGATGAAGTGATGGTGAG | 210 | NM_001289785.1 |
| Gapdh | F: CCGAGAATGGGAAGCTTGTC | R: TTCTCGTGGTTCACACCCATC | 232 | NM_001289726.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Ren, F.; Chen, Y. Monochromatic Light Pollution Exacerbates High-Fat Diet-Induced Adipocytic Hypertrophy in Mice. Cells 2022, 11, 3808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233808
Guan Q, Li Y, Wang Z, Cao J, Dong Y, Ren F, Chen Y. Monochromatic Light Pollution Exacerbates High-Fat Diet-Induced Adipocytic Hypertrophy in Mice. Cells. 2022; 11(23):3808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233808
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Qingyun, Yixuan Li, Zixu Wang, Jing Cao, Yulan Dong, Fazheng Ren, and Yaoxing Chen. 2022. "Monochromatic Light Pollution Exacerbates High-Fat Diet-Induced Adipocytic Hypertrophy in Mice" Cells 11, no. 23: 3808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233808
APA StyleGuan, Q., Li, Y., Wang, Z., Cao, J., Dong, Y., Ren, F., & Chen, Y. (2022). Monochromatic Light Pollution Exacerbates High-Fat Diet-Induced Adipocytic Hypertrophy in Mice. Cells, 11(23), 3808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233808







