Pyrotinib Targeted EGFR-STAT3/CD24 Loop-Mediated Cell Viability in TSC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Wound-Healing Assays
2.4. Immunoblotting Analysis
2.5. Real-Time qPCR and Primers
2.6. Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and Co-IP Assay
2.8. Cytosolic and Nuclear Extractions
2.9. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.10. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.11. Animal Experiments
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
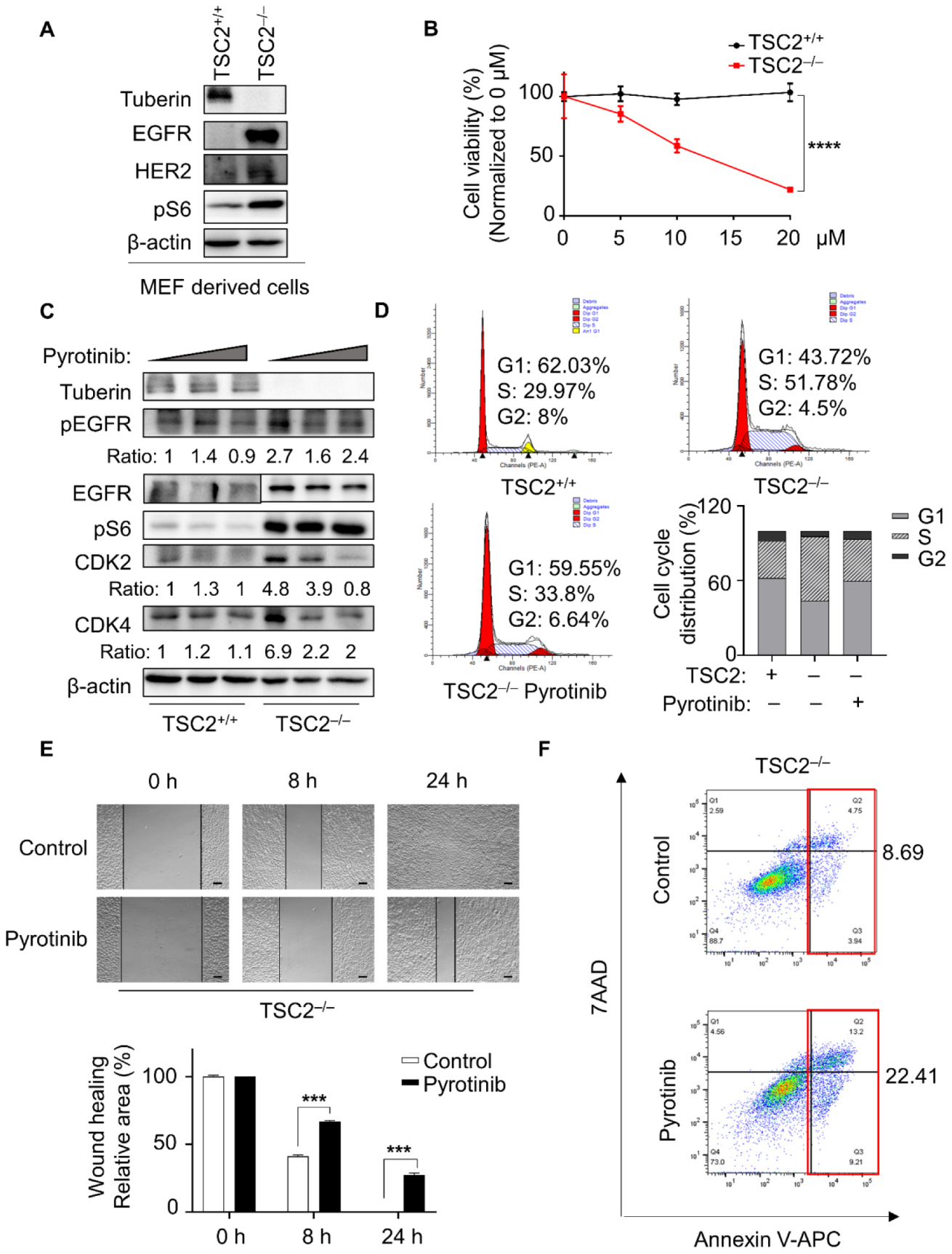
3.1. Pyrotinib Specifically Reduced Cellular Viability of TSC2-Deficient Cells
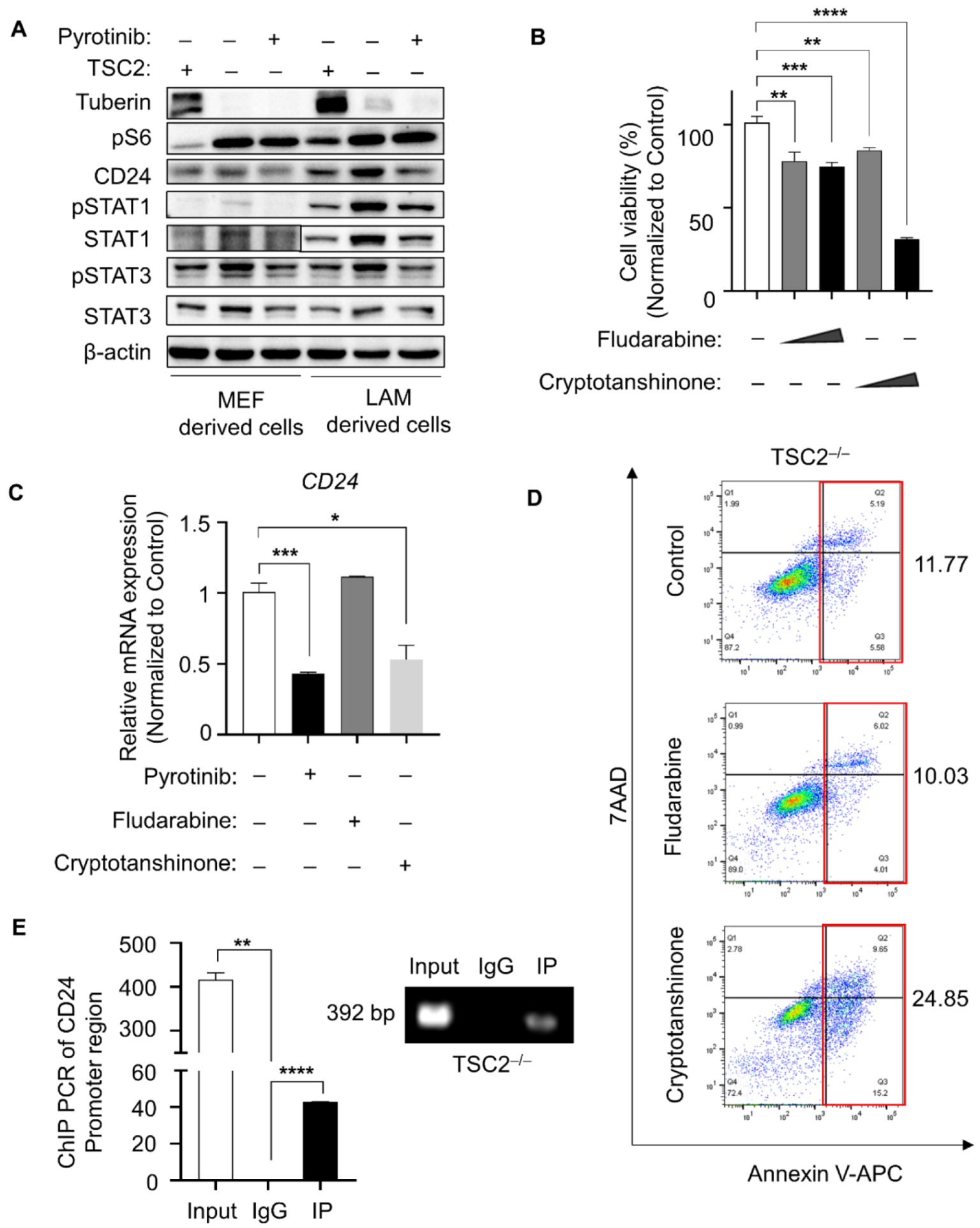
3.2. Elevated CD24 Level Promoted Cell Vitality of TSC2-Deficient Cells
3.3. CD24 Transcriptional Level Upregulated by Phosphor-STAT3
3.4. Binding with CD24 Enhanced Phosphor-EGFR Function
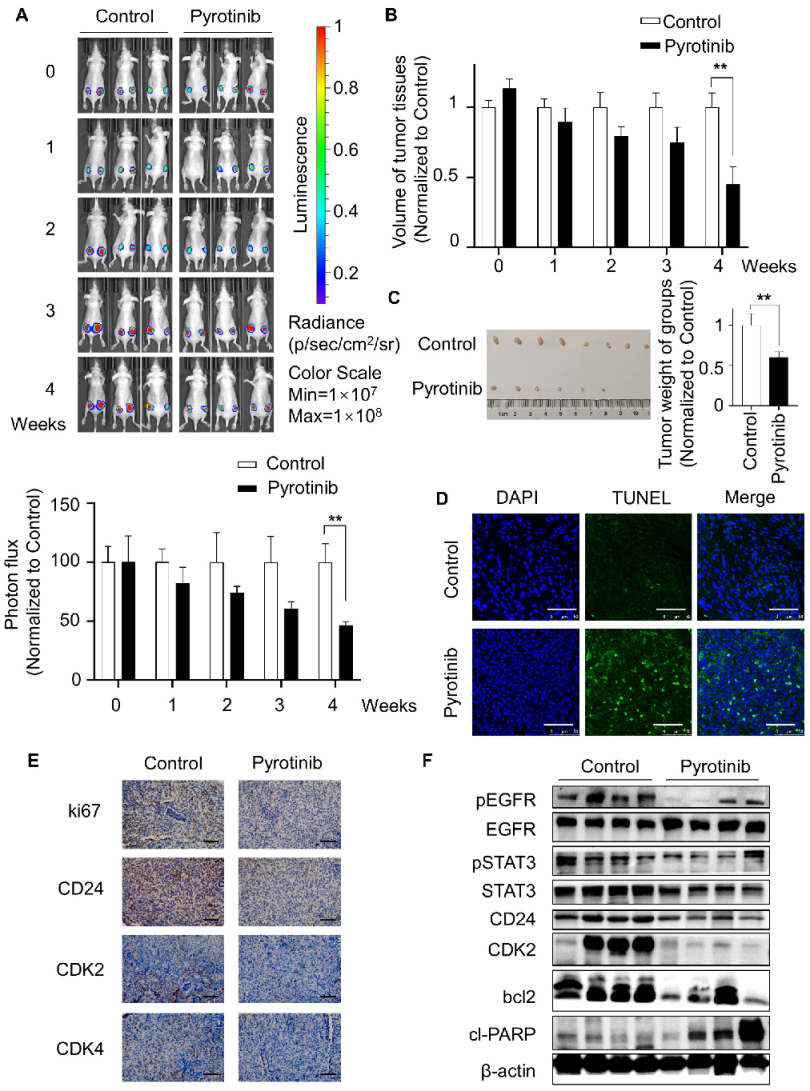
3.5. Pyrotinib Impeded the Viability of TSC2 Deficient Cells In Vivo
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klover, P.J.; Thangapazham, R.L.; Kato, J.; Wang, J.-A.; Anderson, S.A.; Hoffmann, V.; Steagall, W.K.; Li, S.; McCart, E.; Nathan, N.; et al. Tsc2 disruption in mesenchymal progenitors results in tumors with vascular anomalies overexpressing Lgals3. eLife 2017, 6, e23202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoki, K.; Zhu, T.; Guan, K.-L. TSC2 Mediates Cellular Energy Response to Control Cell Growth and Survival. Cell 2003, 115, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorek, B.; Lam, H.C.; Khabibullin, D.; Liu, H.J.; Nijmeh, J.; Triboulet, R.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Gregory, R.I.; Henske, E.P. TSC2 regulates microRNA biogenesis via mTORC1 and GSK3beta. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Cohen, E.E.W. Did Everolimus Break the Rules? Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3807–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.H.; Zupanc, M.L. Long-Term Everolimus Treatment in Individuals With Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: A Review of the Current Literature. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 53, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabora, S.L.; Jozwiak, S.; Franz, D.N.; Roberts, P.S.; Nieto, A.; Chung, J.; Choy, Y.S.; Reeve, M.P.; Thiele, E.; Egelhoff, J.C.; et al. Mutational analysis in a cohort of 224 tuberous sclerosis patients indicates increased severity of TSC2, compared with TSC1, disease in multiple organs. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 68, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; Wentink, M.; van den Heuvel, D.; Mozaffari, M.; Ekong, R.; Povey, S.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Metcalfe, K.; Vallee, S.; Krueger, S.; et al. Functional assessment of variants in the TSC1 and TSC2 genes identified in individuals with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.H.; Tsai, K.W.; Chiu, S.Y.; Kuo, W.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Jiang, S.S.; Chang, K.J.; Hung, W.C.; Wang, L.H. Identification of the Novel Role of CD24 as an Oncogenesis Regulator and Therapeutic Target for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkal, A.A.; Brewer, R.E.; Markovic, M.; Kowarsky, M.; Barkal, S.A.; Zaro, B.W.; Krishnan, V.; Hatakeyama, J.; Dorigo, O.; Barkal, L.J.; et al. CD24 signalling through macrophage Siglec-10 is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2019, 572, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Gu, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, B.; Cui, J.; Dong, J.; Du, J. CD24 associates with EGFR and supports EGF/EGFR signaling via RhoA in gastric cancer cells. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbutt, N.; Pedersen, M.W.; Johns, T.G. Targeting the ERBB family in cancer: Couples therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Du, F.; Dieras, V.; Curigliano, G. The role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of HER2+ metastatic breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 154, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Wan, X.; Sun, A.; Zhou, M.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; et al. RUNX1/EGFR pathway contributes to STAT3 activation and tumor growth caused by hyperactivated mTORC1. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 23, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.A. Pyrotinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1751–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Lv, D.; Chen, S.Q.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Ying, S.; Wu, X.; Hua, F.; Wang, W.; Xu, C.; et al. Pyrotinib in Patients with HER2-Amplified Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Prospective, Multicenter, Single-Arm Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z.; Tong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Pyrotinib or Lapatinib Combined With Capecitabine in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer With Prior Taxanes, Anthracyclines, and/or Trastuzumab: A Randomized, Phase II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2610–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, O.; Wieland, E.; Marquet, P.; Brunet, M. Pharmacodynamic Monitoring of mTOR Inhibitors. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xu, H. Integrins as attractive targets for cancer therapeutics. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2726–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.A.; Mahajan, S.; Ritz, J. Fludarabine-induced immunosuppression is associated with inhibition of STAT1 signaling. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xia, X.; Li, H.; Qiu, C.; Liao, Y.; Chen, H.; He, Z.; Song, Z.; et al. Activated STAT3 signaling pathway by ligature-induced periodontitis could contribute to neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in rats. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.M.; Wang, C.G.; Zhu, M.; Xing, R.; Cui, J.T.; Li, W.M.; Yu, D.D.; Wang, S.B.; Zhu, W.; Ye, Y.J.; et al. STAT3 signaling drives EZH2 transcriptional activation and mediates poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Hung, M.C. EGFR signaling pathway in breast cancers: From traditional signal transduction to direct nuclear translocalization. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 95, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, H.; Munshi, A. HER2 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Sensitization to Cancers Resistant to HER2 Antibodies. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2020, 25, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, K.A.; Crino, P.B. The tuberous sclerosis complex. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1184, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salussolia, C.L.; Klonowska, K.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Sahin, M. Genetic Etiologies, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2019, 20, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKeigan, J.P.; Krueger, D.A. Differentiating the mTOR inhibitors everolimus and sirolimus in the treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moir, L.M. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Current understanding and potential treatments. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 158, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesma, E.; Grande, V.; Ancona, S.; Carelli, S.; Di Giulio, A.M.; Gorio, A. Anti-EGFR antibody efficiently and specifically inhibits human TSC2−/− smooth muscle cell proliferation. Possible treatment options for TSC and LAM. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesma, E.; Chiaramonte, E.; Ancona, S.; Orpianesi, E.; Di Giulio, A.M.; Gorio, A. Anti-EGFR antibody reduces lung nodules by inhibition of EGFR-pathway in a model of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 315240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesma, E.; Eloisa, C.; Isaia, E.; Grande, V.; Ancona, S.; Orpianesi, E.; Di Giulio, A.M.; Gorio, A. Development of a lymphangioleiomyomatosis model by endonasal administration of human TSC2−/− smooth muscle cells in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Su, W.C.; Hsia, T.C.; Tsai, C.M.; Ou, S.H.; Yu, C.J.; Chang, G.C.; Ho, C.L.; Sequist, L.V.; et al. Afatinib for patients with lung adenocarcinoma and epidermal growth factor receptor mutations (LUX-Lung 2): A phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.W.; Forbes, J.T.; Shah, C.; Wyatt, S.K.; Manning, H.C.; Olivares, M.G.; Sanchez, V.; Dugger, T.C.; de Matos Granja, N.; Narasanna, A.; et al. Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin is required for optimal antitumor effect of HER2 inhibitors against HER2-overexpressing cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 7266–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Liu, G.X.; Fang, Y.; Cao, Z.Y.; Du, H.H.; Fu, J.; Qian, K. Clinicopathological and prognostic value of CD24 expression in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2017, 32, e182–e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyvazi, S.; Kazemi, B.; Dastmalchi, S.; Bandehpour, M. Involvement of CD24 in Multiple Cancer Related Pathways Makes It an Interesting New Target for Cancer Therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 18, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Tu, X.; Xie, W.; He, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J. Antibody-based targeting of CD24 enhances antitumor effect of cetuximab via attenuating phosphorylation of Src/STAT3. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Granberg, K.J.; Hu, L.; Haapasalo, H.; Annala, M.J.; Cogdell, D.E.; Verploegen, M.; Moore, L.M.; Fuller, G.N.; et al. IGFBP2 potentiates nuclear EGFR-STAT3 signaling. Oncogene 2016, 35, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzmann, F.M.; Ejaz, A.; Wiegers, G.J.; Mandl, M.; Brucker, C.; Lechner, S.; Rauchenwald, T.; Zwierzina, M.; Baumgarten, S.; Wagner, S.; et al. Quiescence, Stemness and Adipogenic Differentiation Capacity in Human DLK1−/CD34+/CD24+ Adipose Stem/Progenitor Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Luo, J.; He, Z.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Li, H.G.; Xie, D.; Cai, M.Y. STEAP3 promotes cancer cell proliferation by facilitating nuclear trafficking of EGFR to enhance RAC1-ERK-STAT3 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Luo, X.; Wu, B.; Peng, P.; Dai, Y.; Hu, G.; Qiu, H.; Yuan, X. Pyrotinib enhances the radiosensitivity of HER2overexpressing gastric and breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 2634–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosonaga, M.; Arima, Y.; Sugihara, E.; Kohno, N.; Saya, H. Expression of CD24 is associated with HER2 expression and supports HER2-Akt signaling in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Pei, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, F.; Li, T.; Fu, Z.; et al. Pyrotinib Targeted EGFR-STAT3/CD24 Loop-Mediated Cell Viability in TSC. Cells 2022, 11, 3064. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193064
Han X, Zhang Y, Li Y, Lin Z, Pei X, Feng Y, Yang J, Li F, Li T, Fu Z, et al. Pyrotinib Targeted EGFR-STAT3/CD24 Loop-Mediated Cell Viability in TSC. Cells. 2022; 11(19):3064. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193064
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Xiao, Yupeng Zhang, Yin Li, Zhoujun Lin, Xiaolin Pei, Ya Feng, Juan Yang, Fei Li, Tianjiao Li, Zhenkun Fu, and et al. 2022. "Pyrotinib Targeted EGFR-STAT3/CD24 Loop-Mediated Cell Viability in TSC" Cells 11, no. 19: 3064. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193064
APA StyleHan, X., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Lin, Z., Pei, X., Feng, Y., Yang, J., Li, F., Li, T., Fu, Z., Wang, C., & Li, C. (2022). Pyrotinib Targeted EGFR-STAT3/CD24 Loop-Mediated Cell Viability in TSC. Cells, 11(19), 3064. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193064





