Delay of EGF-Stimulated EGFR Degradation in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
2.5. EGFR Degradation
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.7. Binding, Endocytosis, and Trafficking of Alexa Fluor 555 EGF
2.8. Acidic Compartment Staining with LysoTracker Red
2.9. CTSB and CTSD Activities
2.10. β-Hexosamidase Activity
2.11. N-Acetylglucosaminidase Activity
2.12. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.13. Cell Viability
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
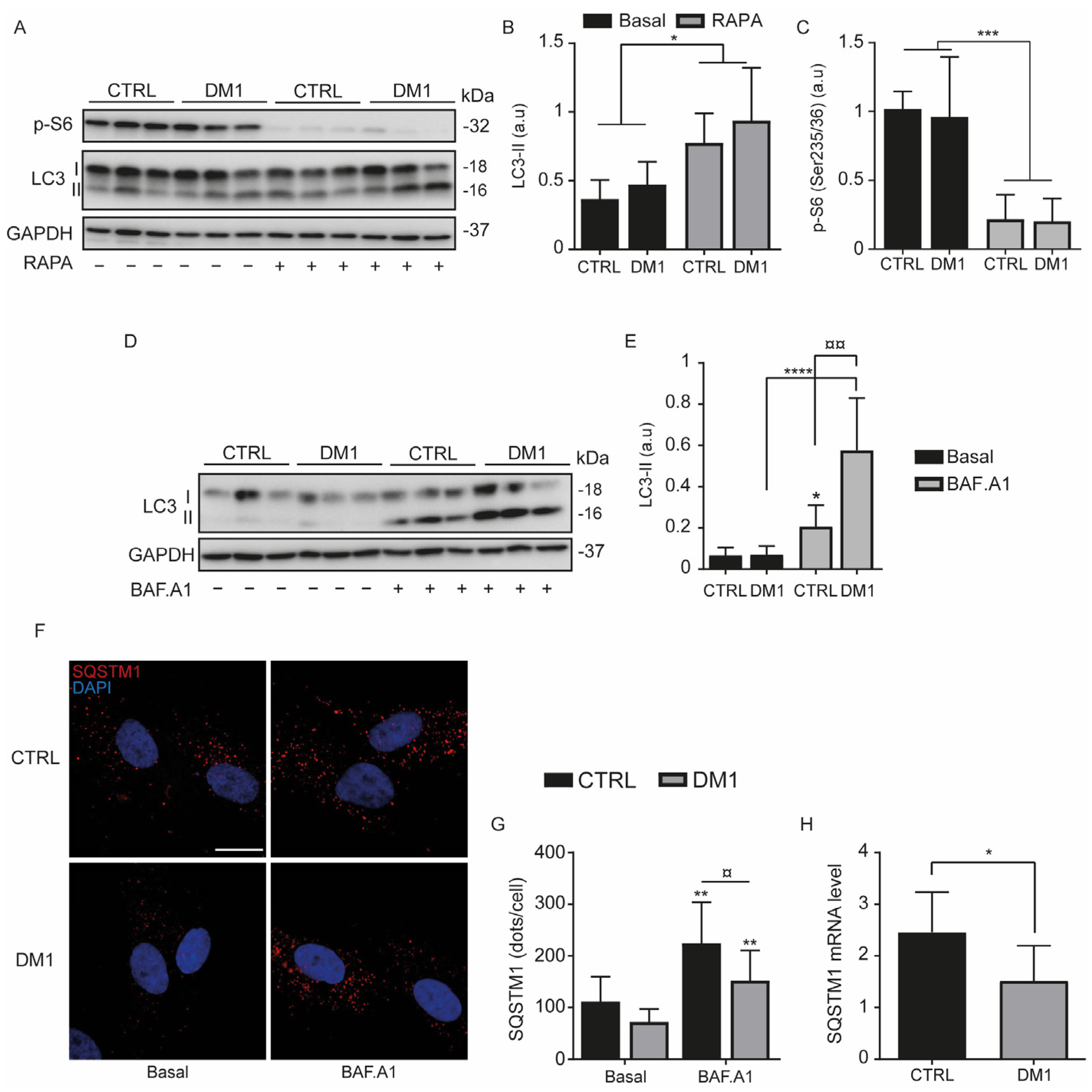
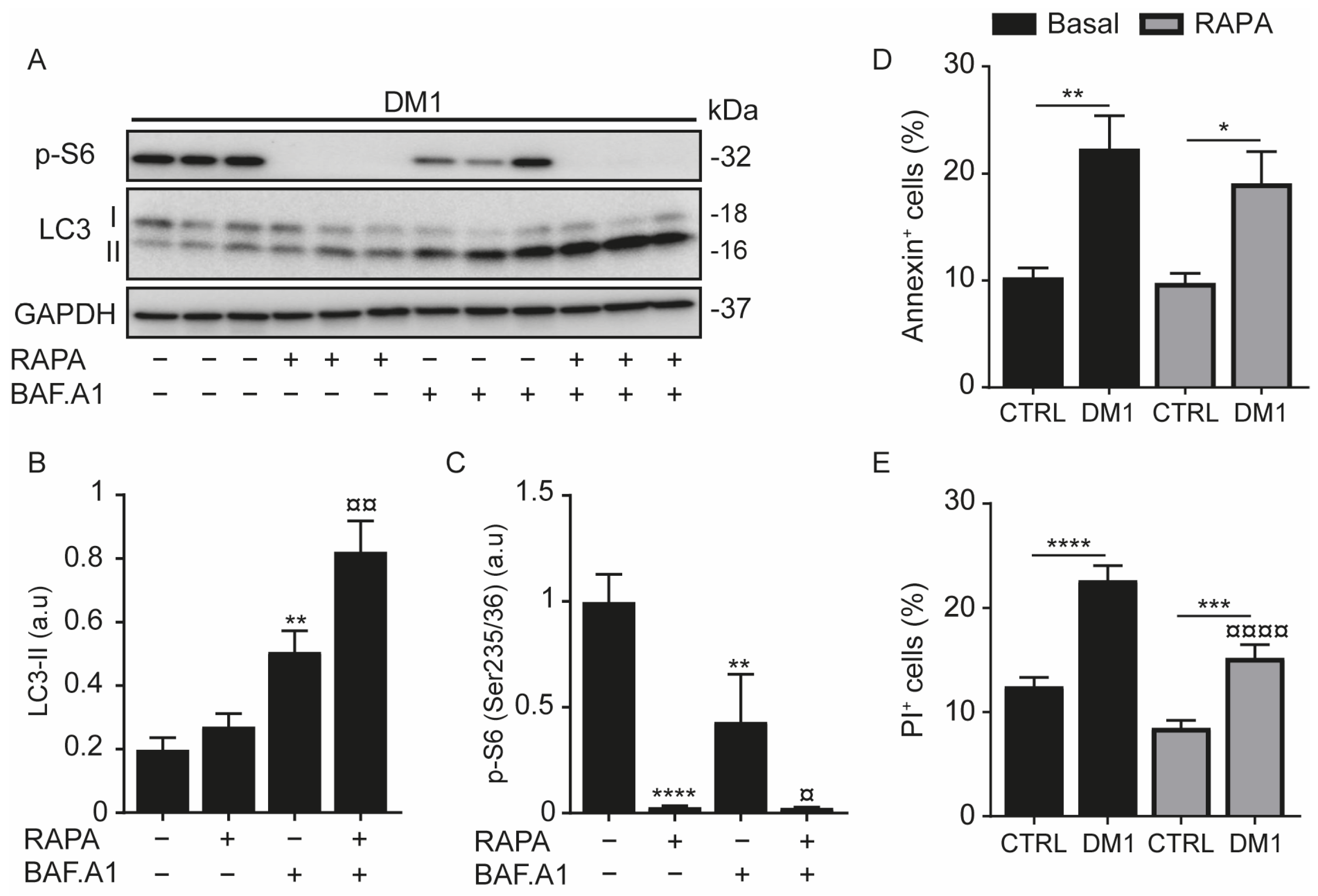
3.1. Increase in Autophagy Flux and Cell Death in DM1 Cells
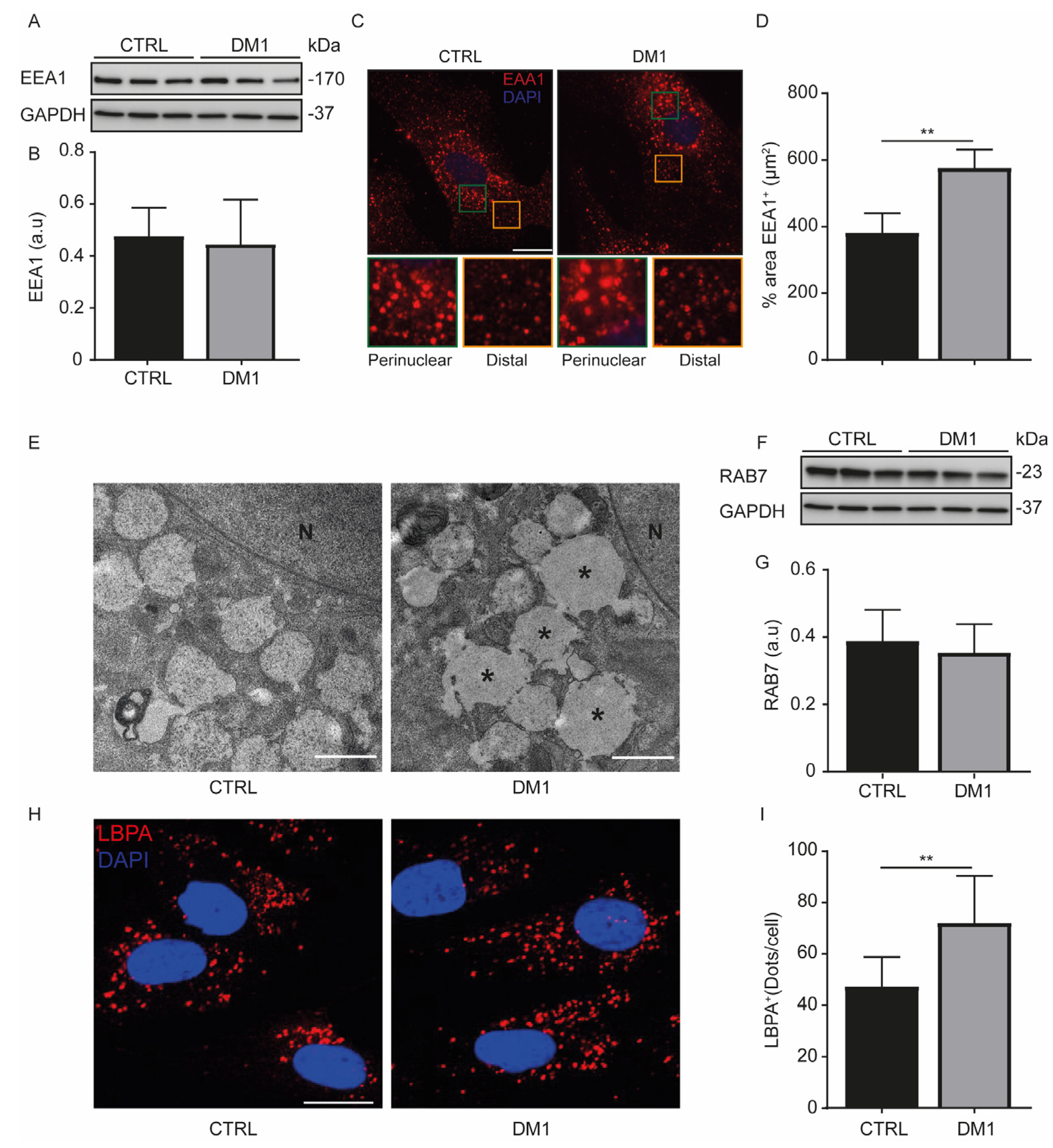
3.2. Enlarged Endosomes in DM1 Cells
3.3. Enhanced Acidic Vesicles and Enzymatic Activities in DM1 Cells
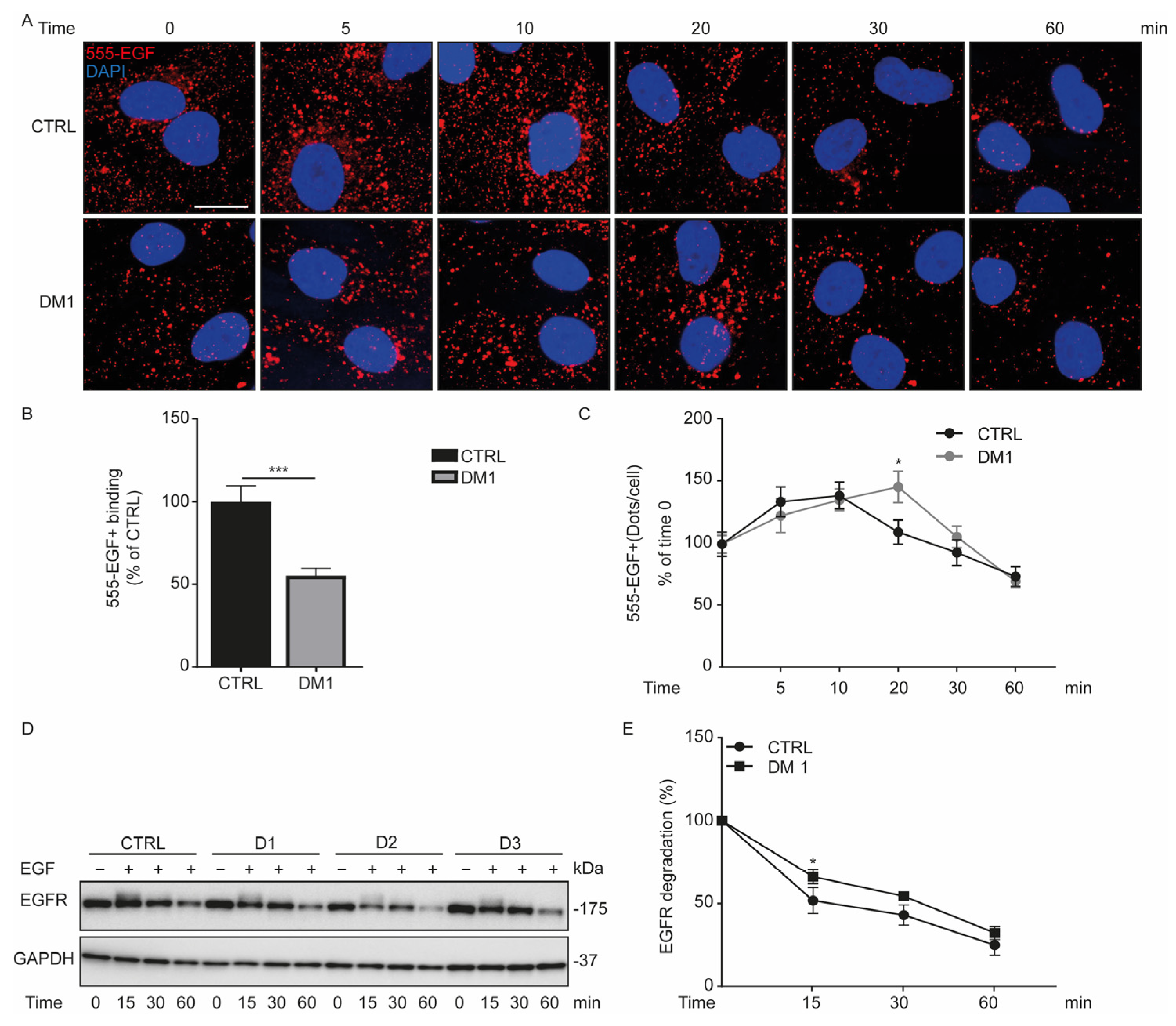
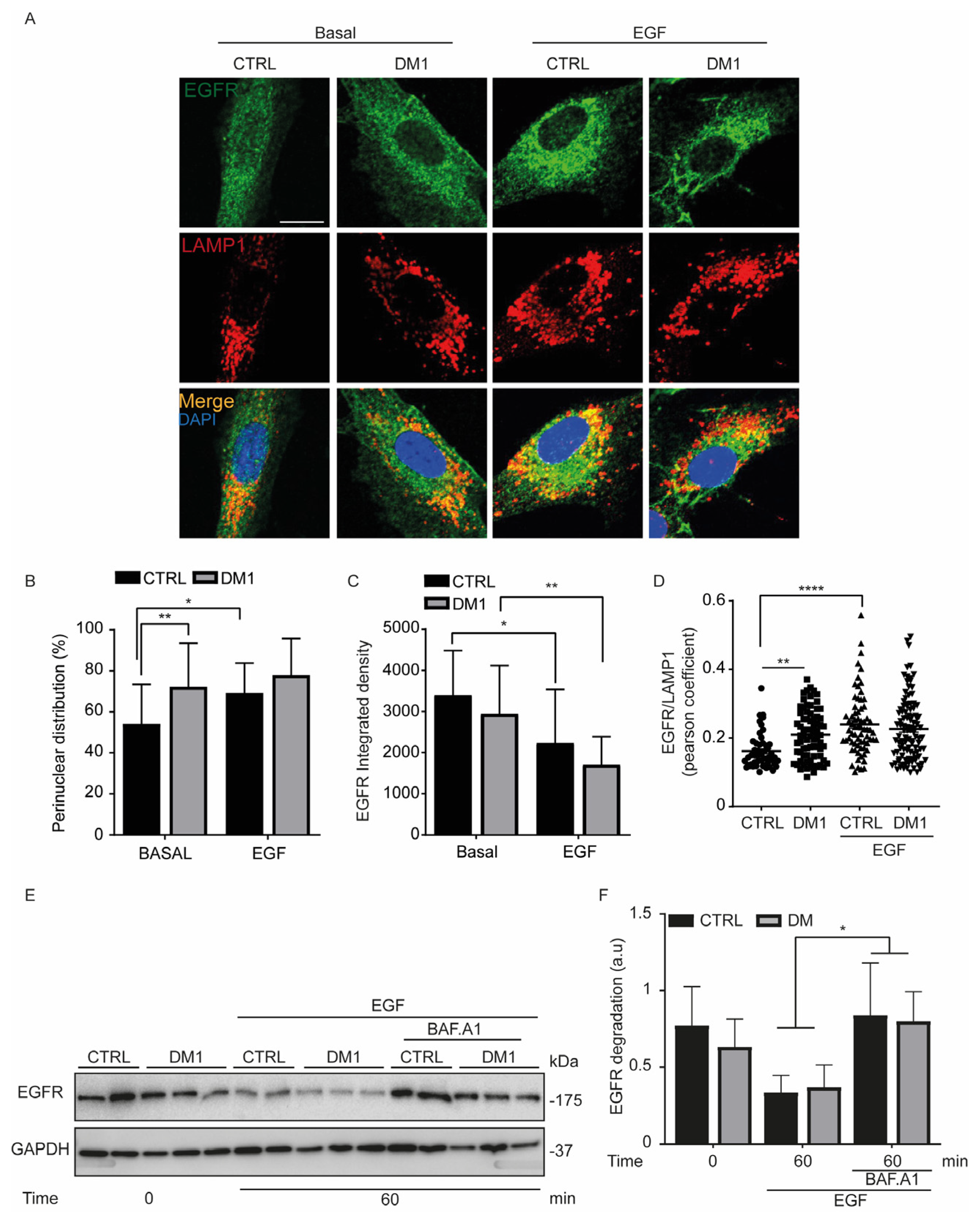
3.4. Defect in Fluorescent EGF Binding and Delay of EGFR Degradation in DM1 Cells
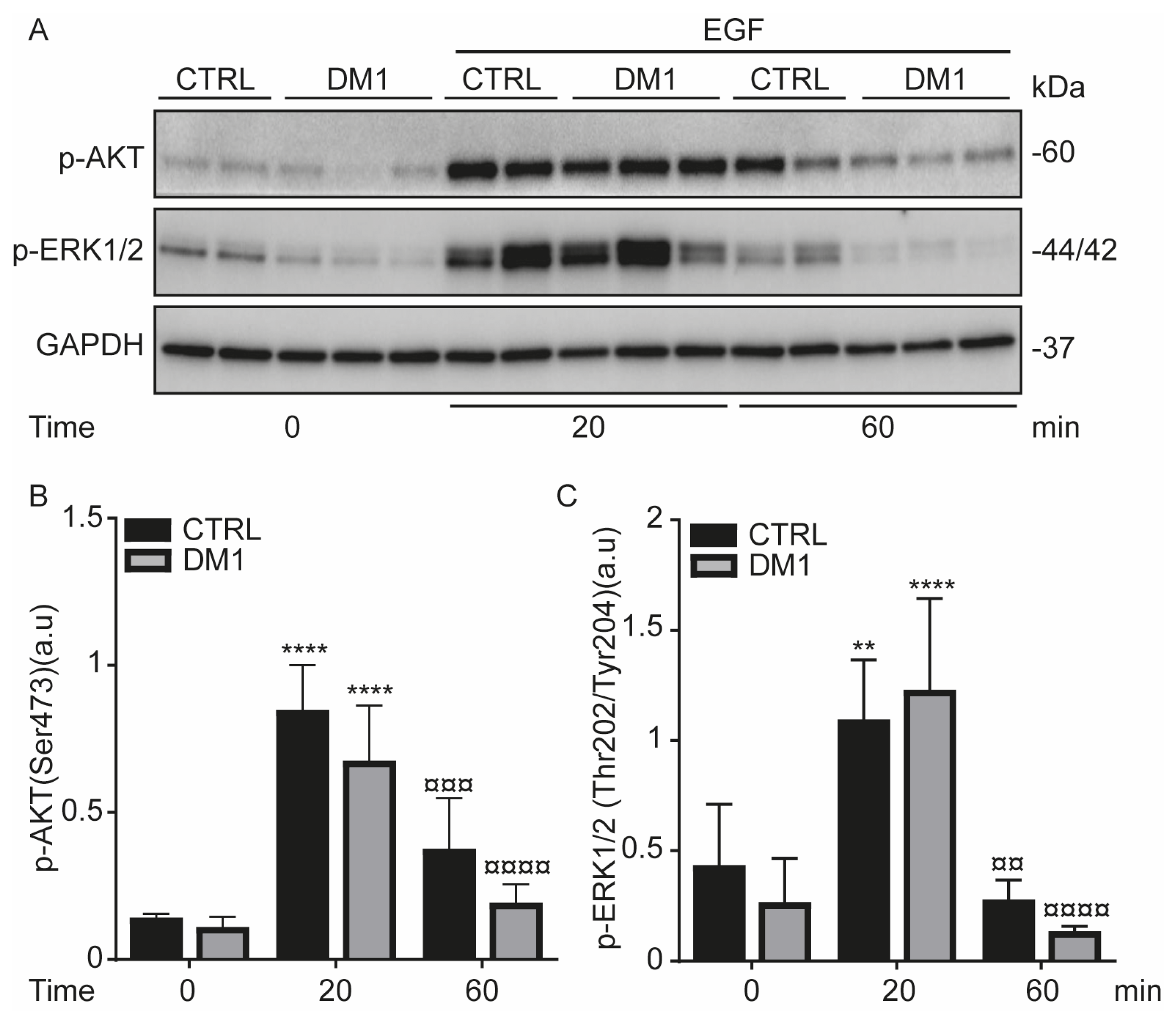
3.5. Activation of EGFR Signaling Pathway upon EGF Stimulation in DM1 Cells
3.6. Endocytosed EGFR Is Sorted and Degraded into Lysosomes in DM1 Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikolic-Kokic, A.; Marinkovic, D.; Peric, S.; Stevic, Z.; Spasic, M.B.; Blagojevic, D.; Rakoc evic-Stojanovic, V. Redox imbalance in peripheral blood of type 1 myotonic dystrophy patients. Redox Rep. 2016, 21, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theadom, A.; Rodrigues, M.; Roxburgh, R.; Balalla, S.; Higgins, C.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Jones, K.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Feigin, V. Prevalence of muscular dystrophies: A systematic literature review. Neuroepidemiology 2014, 43, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, C.; De Antonio, M.; Hamroun, D.; Varet, H.; Fabbro, M.; Rougier, F.; Amarof, K.; Arne Bes, M.C.; Bedat-Millet, A.L.; Behin, A.; et al. Gender as a Modifying Factor Influencing Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 Phenotype Severity and Mortality: A Nationwide Multiple Databases Cross-Sectional Observational Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, A.F.; Hilbert, J.E.; Wood, L.; Martens, W.B.; Nikolenko, N.; Marini-Bettolo, C.; Lochmuller, H.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Moxley, R.T., 3rd; Greene, M.H.; et al. Survival patterns and cancer determinants in families with myotonic dystrophy type 1. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargiela, A.; Cerro-Herreros, E.; Fernandez-Costa, J.M.; Vilchez, J.J.; Llamusi, B.; Artero, R. Increased autophagy and apoptosis contribute to muscle atrophy in a myotonic dystrophy type 1 Drosophila model. Dis. Models Mech. 2015, 8, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, J.A.; Gauthier, M.; Rachdi, L.; Aubert, S.; Giraud-Triboult, K.; Poydenot, P.; Benchoua, A.; Champon, B.; Maury, Y.; Baldeschi, C.; et al. mTOR-dependent proliferation defect in human ES-derived neural stem cells affected by myotonic dystrophy type 1. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loro, E.; Rinaldi, F.; Malena, A.; Masiero, E.; Novelli, G.; Angelini, C.; Romeo, V.; Sandri, M.; Botta, A.; Vergani, L. Normal myogenesis and increased apoptosis in myotonic dystrophy type-1 muscle cells. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morriss, G.R.; Rajapakshe, K.; Huang, S.; Coarfa, C.; Cooper, T.A. Mechanisms of skeletal muscle wasting in a mouse model for myotonic dystrophy type 1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 2789–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockhoff, M.; Rion, N.; Chojnowska, K.; Wiktorowicz, T.; Eickhorst, C.; Erne, B.; Frank, S.; Angelini, C.; Furling, D.; Ruegg, M.A.; et al. Targeting deregulated AMPK/mTORC1 pathways improves muscle function in myotonic dystrophy type I. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodine, S.C.; Stitt, T.N.; Gonzalez, M.; Kline, W.O.; Stover, G.L.; Bauerlein, R.; Zlotchenko, E.; Scrimgeour, A.; Lawrence, J.C.; Glass, D.J.; et al. Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle atrophy in vivo. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Takiguchi, S.; Ito, S.; Itoh, K. EGFstimulated AKT activation is mediated by EGFR recycling via an early endocytic pathway in a gefitinibresistant human lung cancer cell line. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, E.E.; Mendoza, M.C.; Mackey, A.M.; Rameh, L.E.; Blenis, J. AKT facilitates EGFR trafficking and degradation by phosphorylating and activating PIKfyve. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigismund, S.; Argenzio, E.; Tosoni, D.; Cavallaro, E.; Polo, S.; Di Fiore, P.P. Clathrin-mediated internalization is essential for sustained EGFR signaling but dispensable for degradation. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Sun, Y.; Thapa, N.; Liao, Y.; Hedman, A.C.; Anderson, R.A. LAPTM4B is a PtdIns(4,5)P2 effector that regulates EGFR signaling, lysosomal sorting, and degradation. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, A.; Kobayashi, A.; Motoyama, H.; Kitazawa, M.; Takeoka, M.; Miyagawa, S. Impaired degradation followed by enhanced recycling of epidermal growth factor receptor caused by hypo-phosphorylation of tyrosine 1045 in RBE cells. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Puga, M.; Saenz-Antonanzas, A.; Fernandez-Torron, R.; Munain, A.L.; Matheu, A. Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 cells display impaired metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction that are reversed by metformin. Aging 2020, 12, 6260–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhine-Diop, S.M.S.; Rodriguez-Arribas, M.; Martinez-Chacon, G.; Uribe-Carretero, E.; Gomez-Sanchez, R.; Aiastui, A.; Lopez de Munain, A.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Niso-Santano, M.; Gonzalez-Polo, R.A.; et al. Acetylome in Human Fibroblasts from Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhine-Diop, S.M.S.; Rodriguez-Arribas, M.; Canales-Cortes, S.; Martinez-Chacon, G.; Uribe-Carretero, E.; Blanco-Benitez, M.; Duque-Gonzalez, G.; Paredes-Barquero, M.; Alegre-Cortes, E.; Climent, V.; et al. The parkinsonian LRRK2 R1441G mutation shows macroautophagy-mitophagy dysregulation concomitant with endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2021, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Chacon, G.; Paredes-Barquero, M.; Yakhine-Diop, S.M.S.; Uribe-Carretero, E.; Bargiela, A.; Sabater-Arcis, M.; Morales-Garcia, J.; Alarcon-Gil, J.; Alegre-Cortes, E.; Canales-Cortes, S.; et al. Neuroprotective properties of queen bee acid by autophagy induction. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2021, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre-Cortes, E.; Muriel-Gonzalez, A.; Canales-Cortes, S.; Uribe-Carretero, E.; Martinez-Chacon, G.; Aiastui, A.; Lopez de Munain, A.; Niso-Santano, M.; Gonzalez-Polo, R.A.; Fuentes, J.M.; et al. Toxicity of Necrostatin-1 in Parkinson’s Disease Models. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, J.M.; Lompre, A.M.; Moller, J.V.; Falson, P.; le Maire, M. Clean Western blots of membrane proteins after yeast heterologous expression following a shortened version of the method of Perini et al. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 285, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinilla-Macua, I.; Sorkin, A. Methods to study endocytic trafficking of the EGF receptor. Methods Cell Biol. 2015, 130, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Sanchez, R.; Pizarro-Estrella, E.; Yakhine-Diop, S.M.; Rodriguez-Arribas, M.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Fuentes, J.M.; Gonzalez-Polo, R.A. Routine Western blot to check autophagic flux: Cautions and recommendations. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 477, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakhine-Diop, S.M.S.; Niso-Santano, M.; Rodriguez-Arribas, M.; Gomez-Sanchez, R.; Martinez-Chacon, G.; Uribe-Carretero, E.; Navarro-Garcia, J.A.; Ruiz-Hurtado, G.; Aiastui, A.; Cooper, J.M.; et al. Impaired Mitophagy and Protein Acetylation Levels in Fibroblasts from Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2466–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.R.A.; Di Spiezio, A.; Thiessen, N.; Schmidt, L.; Grotzinger, J.; Lullmann-Rauch, R.; Damme, M.; Storck, S.E.; Pietrzik, C.U.; Fogh, J.; et al. Enzyme replacement therapy with recombinant pro-CTSD (cathepsin D) corrects defective proteolysis and autophagy in neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Autophagy 2020, 16, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.S.; Marques, A.R.A.; Padrao, N.; Carvalho, F.A.; Ramalho, J.; Lopes, C.S.; Soares, M.I.L.; Futter, C.E.; Pinho, E.M.T.; Santos, N.C.; et al. Cholesteryl hemiazelate causes lysosome dysfunction impacting vascular smooth muscle cell homeostasis. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs254631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes da Silva, M.; Cutler, D.F. von Willebrand factor multimerization and the polarity of secretory pathways in endothelial cells. Blood 2016, 128, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, S.R.; Mizushima, N. Monitoring and Measuring Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Polo, R.A.; Pizarro-Estrella, E.; Yakhine-Diop, S.M.S.; Rodríguez-Arribas, M.; Gómez-Sánchez, R.; Casado-Naranjo, I.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Fuentes, J.M. The Basics of Autophagy. In Autophagy Networks in Inflammation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, J.; Ghigo, E.; Kalaidzidis, Y.; Zerial, M. Rab conversion as a mechanism of progression from early to late endosomes. Cell 2005, 122, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor endocytosis by wortmannin through activation of Rab5 rather than inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyttinen, J.M.; Niittykoski, M.; Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. Maturation of autophagosomes and endosomes: A key role for Rab7. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, I.J.; Bailey, L.M.; Aghakhani, M.R.; Moss, S.E.; Futter, C.E. EGF stimulates annexin 1-dependent inward vesiculation in a multivesicular endosome subpopulation. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhitomirsky, B.; Farber, H.; Assaraf, Y.G. LysoTracker and MitoTracker Red are transport substrates of P-glycoprotein: Implications for anticancer drug design evading multidrug resistance. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libelius, R.; Jirmanova, I.; Lundquist, I.; Thesleff, S. Increased endocytosis with lysosomal activation in skeletal muscle of dystrophic mouse. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1978, 37, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Li, L.; Puliyappadamba, V.T.; Guo, G.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Mickey, B.; Souza, R.F.; Vo, P.; Herz, J.; Chen, M.R.; et al. Constitutive and ligand-induced EGFR signalling triggers distinct and mutually exclusive downstream signalling networks. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.A.; Slastnikova, T.A. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: Key to Selective Intracellular Delivery. Biochemistry 2020, 85, 967–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.W.; Cheng, C.; Hackett, C.; Feldman, M.; Houseman, B.T.; Nicolaides, T.; Haas-Kogan, D.; James, C.D.; Oakes, S.A.; Debnath, J.; et al. Akt and autophagy cooperate to promote survival of drug-resistant glioma. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.Y.; Guo, X.M.; Wang, H.Q.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.Y.; Huo, Y.C.; Zhang, G.; Feng, J.Z.; Zhang, R.R.; Ma, Y.; et al. MBNL1 reverses the proliferation defect of skeletal muscle satellite cells in myotonic dystrophy type 1 by inhibiting autophagy via the mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libelius, R.; Jirmanova, I.; Lundquist, I.; Thesleff, S.; Barnard, E.A. T-tubule endocytosis in dystrophic chicken muscle and its relation to muscle fiber degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 1979, 48, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.E.; Martel, N.; Ariotti, N.; Xiong, Z.; Lo, H.P.; Ferguson, C.; Rae, J.; Lim, Y.W.; Parton, R.G. In vivo cell biological screening identifies an endocytic capture mechanism for T-tubule formation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugier, C.; Klein, A.F.; Hammer, C.; Vassilopoulos, S.; Ivarsson, Y.; Toussaint, A.; Tosch, V.; Vignaud, A.; Ferry, A.; Messaddeq, N.; et al. Misregulated alternative splicing of BIN1 is associated with T tubule alterations and muscle weakness in myotonic dystrophy. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussini, I.; Di Mauro, S.; Angelini, C. Early ultrastructural and biochemical changes in muscle in dystrophia myotonica. J. Neurol. Sci. 1970, 10, 585–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.; Simpson, J.; Fontana, R.; Kishi-Itakura, C.; Ktistakis, N.T.; Gammoh, N. Targeting of early endosomes by autophagy facilitates EGFR recycling and signalling. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinilla-Macua, I.; Watkins, S.C.; Sorkin, A. Endocytosis separates EGF receptors from endogenous fluorescently labeled HRas and diminishes receptor signaling to MAP kinases in endosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2122–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.; Yu, H.; Choi, E. Insulin receptor endocytosis in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savkur, R.S.; Philips, A.V.; Cooper, T.A. Aberrant regulation of insulin receptor alternative splicing is associated with insulin resistance in myotonic dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.M.; Raja, S.M.; Clubb, R.J.; Tu, C.; George, M.; Band, V.; Band, H. Aberrant trafficking of NSCLC-associated EGFR mutants through the endocytic recycling pathway promotes interaction with Src. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaggaf, R.; St George, D.M.M.; Zhan, M.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Wang, Y.; Wagner, K.R.; Greene, M.H.; Amr, S.; Gadalla, S.M. Cancer Risk in Myotonic Dystrophy Type I: Evidence of a Role for Disease Severity. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018, 2, pky052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Alsaggaf, R.; Meeraus, W.; Gage, J.C.; Anderson, L.A.; Bremer, R.C.; Nikolenko, N.; Lochmuller, H.; Greene, M.H.; et al. Risk of skin cancer among patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1 based on primary care physician data from the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; LaChance, A.; Sinclair, D.A.; Asgari, M.M. Multiple basal cell carcinomas in a patient with myotonic dystrophy type 1. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e227233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renna, L.V.; Bose, F.; Iachettini, S.; Fossati, B.; Saraceno, L.; Milani, V.; Colombo, R.; Meola, G.; Cardani, R. Receptor and post-receptor abnormalities contribute to insulin resistance in myotonic dystrophy type 1 and type 2 skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alegre-Cortés, E.; Giménez-Bejarano, A.; Uribe-Carretero, E.; Paredes-Barquero, M.; Marques, A.R.A.; Lopes-da-Silva, M.; Vieira, O.V.; Canales-Cortés, S.; Camello, P.J.; Martínez-Chacón, G.; et al. Delay of EGF-Stimulated EGFR Degradation in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1). Cells 2022, 11, 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193018
Alegre-Cortés E, Giménez-Bejarano A, Uribe-Carretero E, Paredes-Barquero M, Marques ARA, Lopes-da-Silva M, Vieira OV, Canales-Cortés S, Camello PJ, Martínez-Chacón G, et al. Delay of EGF-Stimulated EGFR Degradation in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1). Cells. 2022; 11(19):3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193018
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlegre-Cortés, Eva, Alberto Giménez-Bejarano, Elisabet Uribe-Carretero, Marta Paredes-Barquero, André R. A. Marques, Mafalda Lopes-da-Silva, Otília V. Vieira, Saray Canales-Cortés, Pedro J. Camello, Guadalupe Martínez-Chacón, and et al. 2022. "Delay of EGF-Stimulated EGFR Degradation in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1)" Cells 11, no. 19: 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193018
APA StyleAlegre-Cortés, E., Giménez-Bejarano, A., Uribe-Carretero, E., Paredes-Barquero, M., Marques, A. R. A., Lopes-da-Silva, M., Vieira, O. V., Canales-Cortés, S., Camello, P. J., Martínez-Chacón, G., Aiastui, A., Fernández-Torrón, R., López de Munain, A., Gomez-Suaga, P., Niso-Santano, M., González-Polo, R. A., Fuentes, J. M., & Yakhine-Diop, S. M. S. (2022). Delay of EGF-Stimulated EGFR Degradation in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1). Cells, 11(19), 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193018









