Cell Tracking by Magnetic Particle Imaging: Methodology for Labeling THP-1 Monocytes with Magnetic Nanoparticles for Cellular Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs)
2.2. Cell Line: THP-1 Monocytes
2.3. Biological Media
2.4. Field-Flow Fractionation (F3)
2.5. Ultraviolet/Visible Spectrophotometer (UV/Vis)
2.6. Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy (MPS)
2.7. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.8. Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron
2.9. Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
2.10. Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI)
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Basic Characterization of the MNP
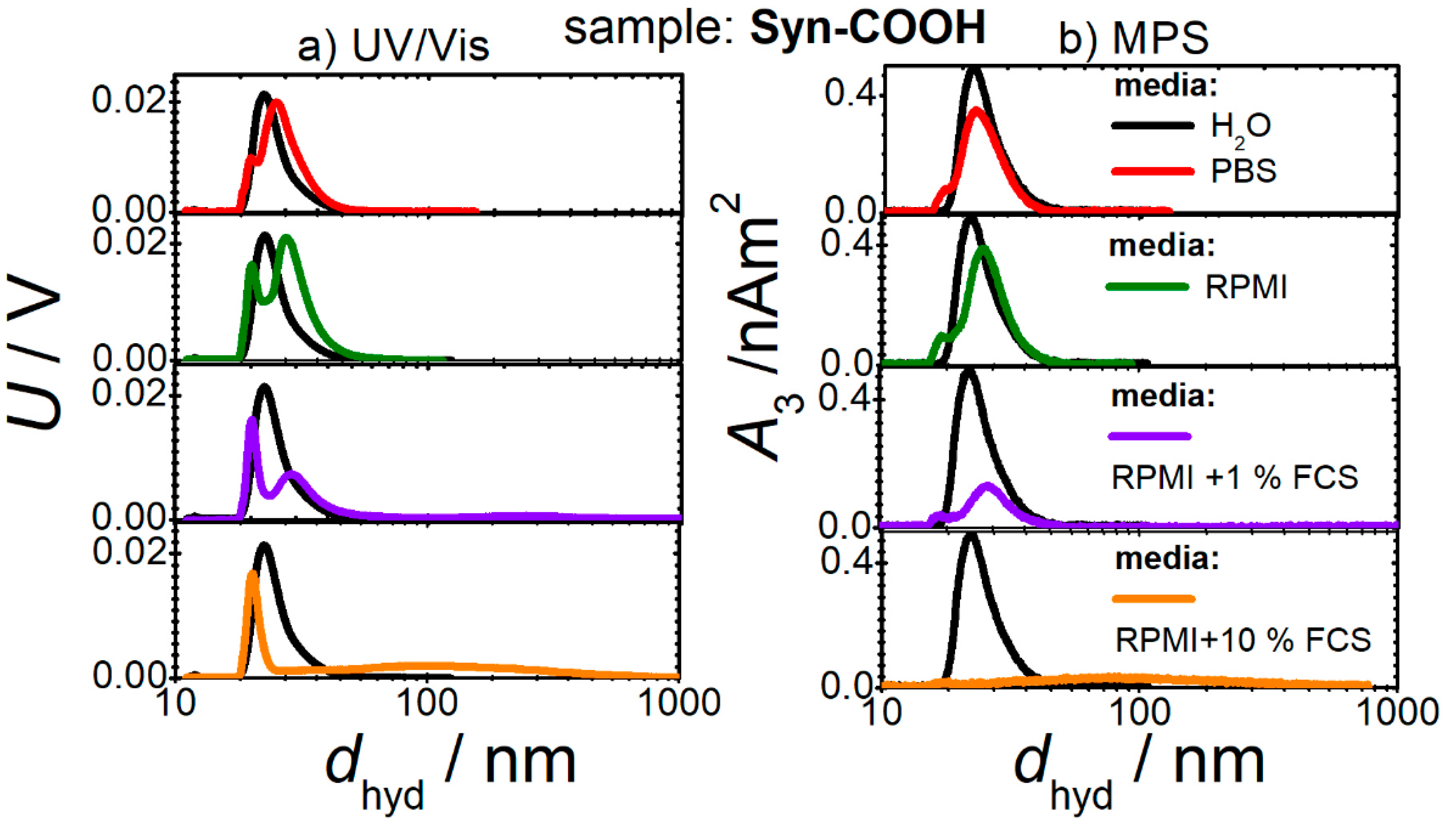
3.2. MNP–Media Interactions before Cell Contact
3.3. MNP–Media Interactions during Cell Contact
3.3.1. Media Check
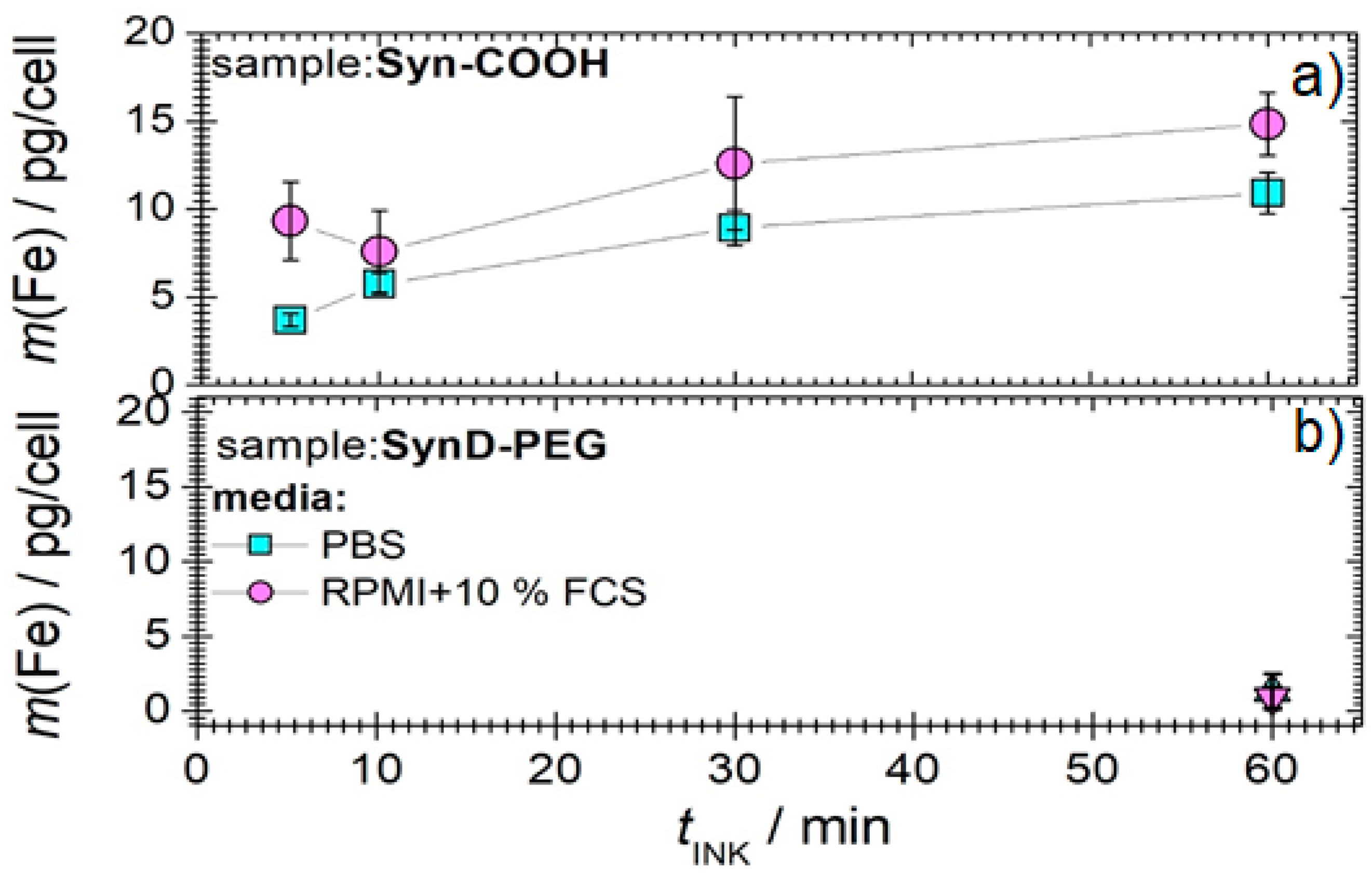
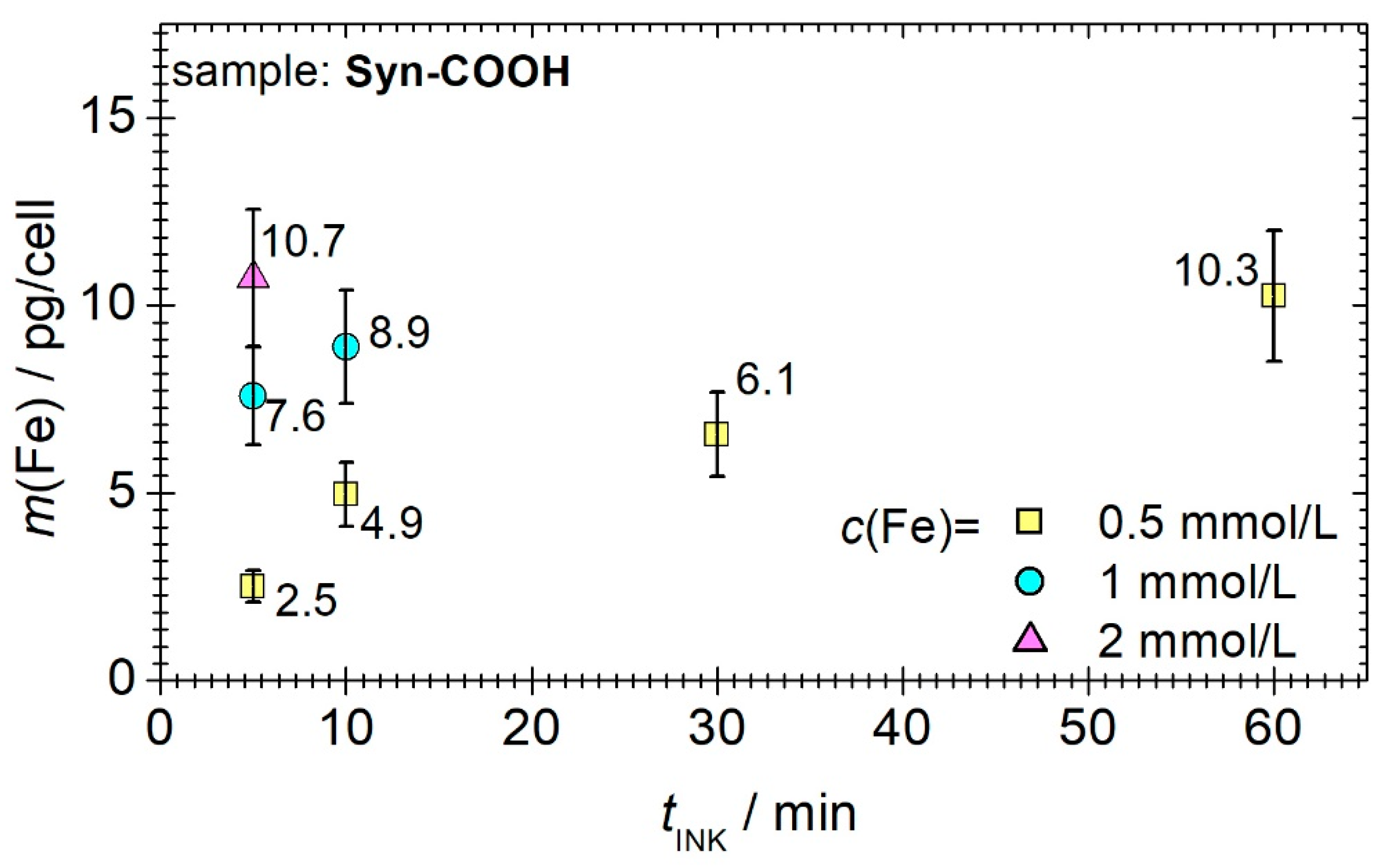
3.3.2. Incubation Time and Iron Concentration
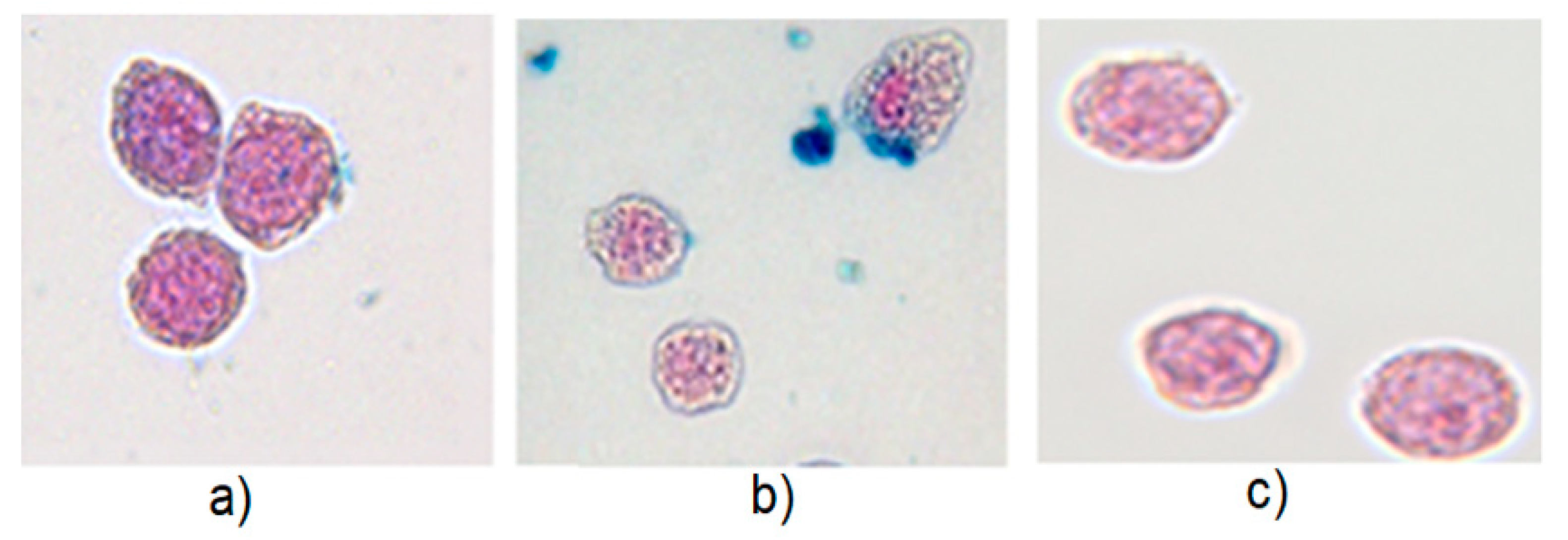
3.3.3. Washing of MNP-Loaded Cells
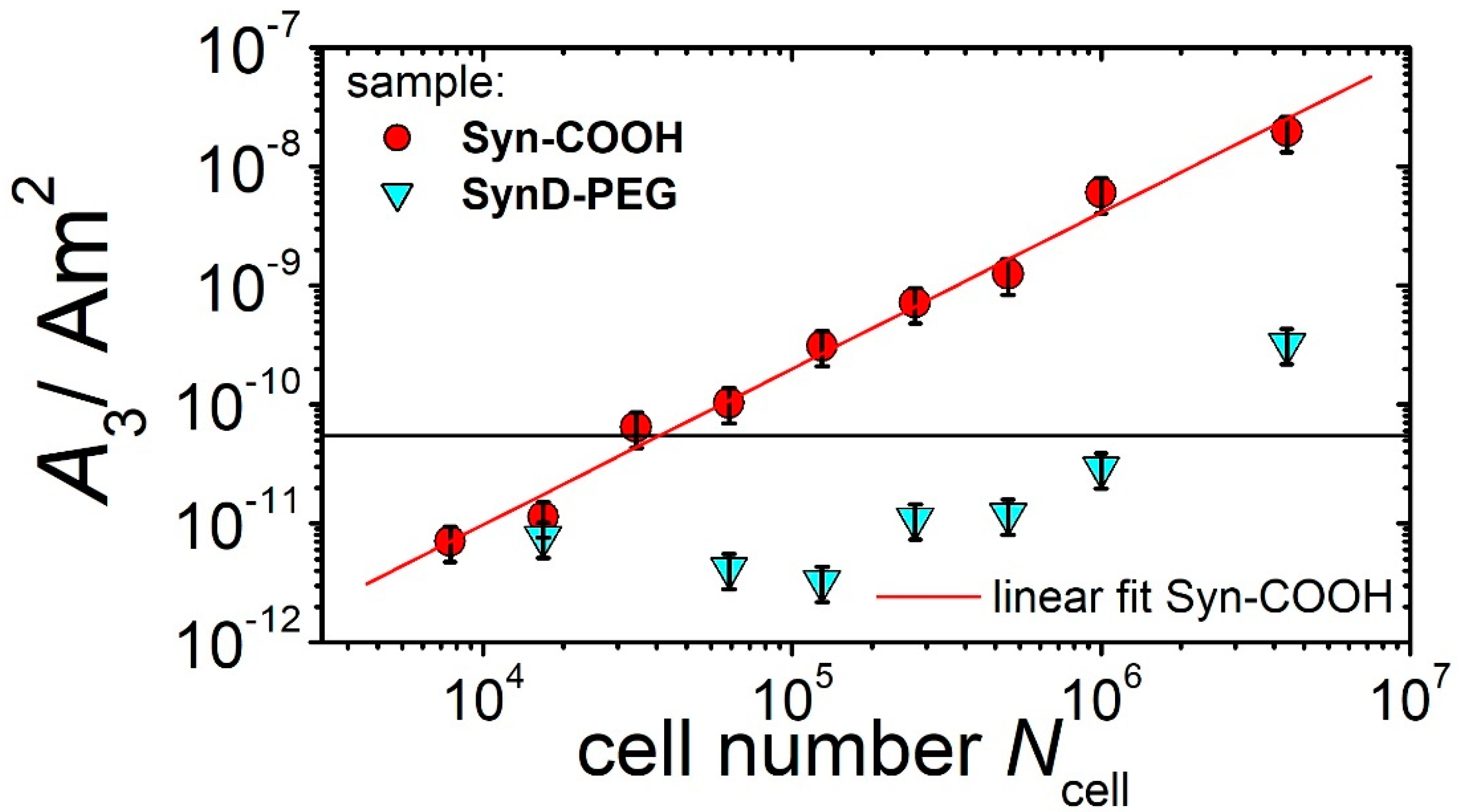
3.3.4. Sensitivity, Linearity, and Limit of Detection
3.4. MPI Visualization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paysen, H.; Loewa, N.; Stach, A.; Wells, J.; Kosch, O.; Twamley, S.; Makowski, M.R.; Schaeffter, T.; Ludwig, A.; Wiekhorst, F. Cellular uptake of magnetic nanoparticles imaged and quantified by magnetic particle imaging. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulte, J.W.M.; Kraitchman, D.L. Iron oxide MR contrast agents for molecular and cellular imaging. NMR Biomed. 2004, 17, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschbaum, K.; Sonner, J.K.; Zeller, M.W.; Deumelandt, K.; Bode, J.; Sharma, R.; Krüwel, T.; Fischer, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Costa da Silva, M.; et al. In vivo nanoparticle imaging of innate immune cells can serve as a marker of disease severity in a model of multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13227–13232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissleder, R.; Nahrendorf, M.; Pittet, M.J. Imaging macrophages with nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Nair, M.G. Macrophages in wound healing: Activation and plasticity. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwien, H.; Hermann, S.; Zhang, X.; Korpos, E.; Song, J.; Kopka, K.; Faust, A.; Wenning, C.; Gross, C.C.; Honold, L.; et al. Imaging matrix metalloproteinase activity in multiple sclerosis as a specific marker of leukocyte penetration of the blood-brain barrier. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 364ra152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coillard, A.; Segura, E. In vivo Differentiation of Human Monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernsen, M.R.; Guenoun, J.; van Tiel, S.T.; Krestin, G.P. Nanoparticles and clinically applicable cell tracking. BJR 2015, 88, 20150375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchinski, D.J.; Taha, M.; Yang, R.; Nathoo, N.; Dunn, J.F. Iron Oxide as an Mri Contrast Agent for Cell Tracking: Supplementary Issue. Magn. Reson. Insights 2015, 8s1, MRI.S23557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza de Schellenberger, A.; Kratz, H.; Farr, T.; Loewa, N.; Hauptmann, R.; Wagner, S.; Taupitz, M.; Schnorr, J.; Schellenberger, E. Labeling of mesenchymal stem cells for MRI with single-cell sensitivity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, O.M.; Ramirez, R.; McCarty, S.; Mattrey, R.F. Toward absolute quantification of iron oxide nanoparticles as well as cell internalized fraction using multiparametric MRI: Ionp Quantification Using Multiparametric MRI. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2012, 7, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlpeter, R.; Dahnke, H.; Matuszewski, L.; Persigehl, T.; von Wallbrunn, A.; Allkemper, T.; Heindel, W.L.; Schaeffter, T.; Bremer, C. R2 and R2* Mapping for Sensing Cell-bound Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles: In Vitro and Murine in Vivo Testing. Radiology 2007, 245, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makar, A.B.; McMartin, K.E.; Palese, M.; Tephly, T.R. Formate assay in body fluids: Application in methanol poisoning. Biochem. Med. 1975, 13, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joos, A.; Löwa, N.; Wiekhorst, F.; Gleich, B.; Haase, A. Size-dependent MR relaxivities of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 427, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Wilhelm, C.; Clément, O.; Gazeau, F. Cell labeling with magnetic nanoparticles: Opportunity for magnetic cell imaging and cell manipulation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 11, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayol, D.; Luciani, N.; Lartigue, L.; Gazeau, F.; Wilhelm, C. Managing Magnetic Nanoparticle Aggregation and Cellular Uptake: A Precondition for Efficient Stem-Cell Differentiation and MRI Tracking. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulte, J.W.M.; Daldrup-Link, H.E. Clinical Tracking of Cell Transfer and Cell Transplantation: Trials and Tribulations. Radiology 2018, 289, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chiu-Lam, A.; Rivera-Rodriguez, A.; DeGroff, R.; Savliwala, S.; Sarna, N.; Rinaldi-Ramos, C.M. Long circulating tracer tailored for magnetic particle imaging. Nanotheranostics 2021, 5, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmo, A.; Löwa, N.; Peter, J.; Wiekhorst, F. Physical characterization of biomedical magnetic nanoparticles using multi-detector centrifugal field-flow fractionation. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 7, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwa, N.; Radon, P.; Gutkelch, D.; August, R.; Wiekhorst, F. Hyphenation of Field-Flow Fractionation and Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy. Chromatography 2015, 2, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kegel, J. Formulierung und Charakterisierung Steroidaler, NanoCompounds’ mit Hilfe eines Aufbauenden Verfahrens; Cuvillier Verlag: Göttingen, Germany, 2006; ISBN 978-3-7369-2012-5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Che, P.; Ma, Y. More sensitive way to determine iron using an iron(II)−1, 10-phenanthroline complex and capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 749, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberbeck, D.; Lange, A.; Hentschel, M. Identification of aggregates of magnetic nanoparticles in ferrofluids at low concentrations. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, P.; Fock, J.; Frandsen, C.; Hansen, M.F.; Balceris, C.; Ludwig, F.; Posth, O.; Wetterskog, E.; Bogart, L.K.; Southern, P.; et al. Relating Magnetic Properties and High Hyperthermia Performance of Iron Oxide Nanoflowers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 3068–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paysen, H.; Wells, J.; Kosch, O.; Steinhoff, U.; Franke, J.; Trahms, L.; Schaeffter, T.; Wiekhorst, F. Improved sensitivity and limit-of-detection using a receive-only coil in magnetic particle imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 13NT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löwa, N.; Seidel, M.; Radon, P.; Wiekhorst, F. Magnetic nanoparticles in different biological environments analyzed by magnetic particle spectroscopy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 427, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paysen, H.; Wells, J.; Kosch, O.; Steinhoff, U.; Trahms, L.; Schaeffter, T.; Wiekhorst, F. Towards quantitative magnetic particle imaging: A comparison with magnetic particle spectroscopy. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 56712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| ID | Supplier | Coating | MPS | DLS | SAXS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A3* (Am2/kg(Fe)) | A5/A3 (%) | dhyd (nm) | PDI | ζ at pH = 7 (mV) | dc,SAXS(nm) | σ (nm) | |||
| Syn-COOH | Micromod | Citrate | 3.4 ± 0.05 | 12.6 ± 0.07 | 23.4 ± 6.2 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | −13.8 ± 2.1 | 13.5 ± 0.2 | 0.27 ± 0.01 |
| SynD-PEG | Micromod | PEG–dextran | 6.1 ± 0.03 | 22.1 ± 0.05 | 47.7 ± 17.2 | 0.1 ± 0.03 | −4.6 ± 1.2 | 15.0 ± 0.3 | 0.31 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Remmo, A.; Löwa, N.; Kosch, O.; Eberbeck, D.; Ludwig, A.; Kampen, L.; Grüttner, C.; Wiekhorst, F. Cell Tracking by Magnetic Particle Imaging: Methodology for Labeling THP-1 Monocytes with Magnetic Nanoparticles for Cellular Imaging. Cells 2022, 11, 2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182892
Remmo A, Löwa N, Kosch O, Eberbeck D, Ludwig A, Kampen L, Grüttner C, Wiekhorst F. Cell Tracking by Magnetic Particle Imaging: Methodology for Labeling THP-1 Monocytes with Magnetic Nanoparticles for Cellular Imaging. Cells. 2022; 11(18):2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182892
Chicago/Turabian StyleRemmo, Amani, Norbert Löwa, Olaf Kosch, Dietmar Eberbeck, Antje Ludwig, Lena Kampen, Cordula Grüttner, and Frank Wiekhorst. 2022. "Cell Tracking by Magnetic Particle Imaging: Methodology for Labeling THP-1 Monocytes with Magnetic Nanoparticles for Cellular Imaging" Cells 11, no. 18: 2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182892
APA StyleRemmo, A., Löwa, N., Kosch, O., Eberbeck, D., Ludwig, A., Kampen, L., Grüttner, C., & Wiekhorst, F. (2022). Cell Tracking by Magnetic Particle Imaging: Methodology for Labeling THP-1 Monocytes with Magnetic Nanoparticles for Cellular Imaging. Cells, 11(18), 2892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182892






