Age-Related NAFLD: The Use of Probiotics as a Supportive Therapeutic Intervention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
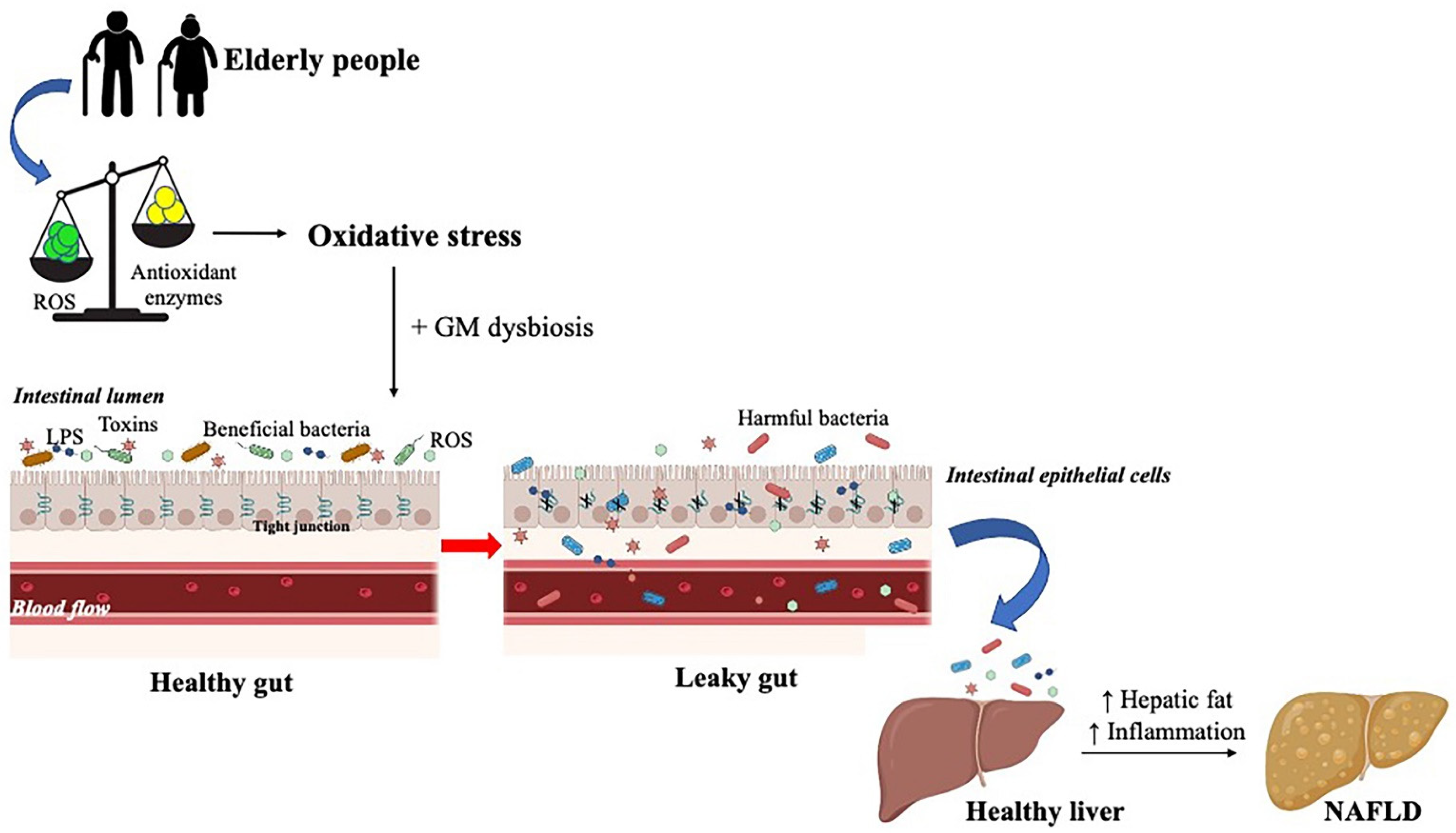
3. Gut Microbiota and Oxidative Stress
4. Gut Microbiota and NAFLD Development in Animal Models
5. Changes in Gut Microbiota in Animal Models of NAFLD
6. Association between Gut Microbiota and NAFLD Development in Humans
7. Probiotics
7.1. Preclinical Studies of Probiotic Supplementation in NAFLD
7.2. Clinical Trials of Probiotic Supplementation in NAFLD
8. Other Therapeutic Options
9. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut Microbiome and Health: Mechanistic Insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-J.; Wu, E. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Immune Homeostasis and Autoimmunity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. Role and Mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNee, W.; Rabinovich, R.A.; Choudhury, G. Ageing and the Border between Health and Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1332–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, E.C.; Haschak, M.J.; Popovic, B.; Brown, B.N. Macrophages in the Aging Liver and Age-Related Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridi, A.; Chrysavgis, L.; Koutsilieris, M.; Chatzigeorgiou, A. The Role of Senescence in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Progression to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2020, 71, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Huerta-Salgado, C.; Orozco-Aguilar, J.; Aguirre, F.; Tacchi, F.; Simon, F.; Cabello-Verrugio, C. Role of Oxidative Stress in Hepatic and Extrahepatic Dysfunctions during Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Wu, C.; Guo, X. Advances in the Involvement of Gut Microbiota in Pathophysiology of NAFLD. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrncir, T.; Hrncirova, L.; Kverka, M.; Hromadka, R.; Machova, V.; Trckova, E.; Kostovcikova, K.; Kralickova, P.; Krejsek, J.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H. Gut Microbiota and NAFLD: Pathogenetic Mechanisms, Microbiota Signatures, and Therapeutic Interventions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Arrese, M.; Trauner, M. Recent Insights into the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2018, 13, 321–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The Multiple-Hit Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.-Y.; Lin, J.-H.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Chiang, P.-F.R.; Ho, H.-H. Probiotics and Their Metabolites Reduce Oxidative Stress in Middle-Aged Mice. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pasqua, L.G.; Cagna, M.; Berardo, C.; Vairetti, M.; Ferrigno, A. Detailed Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Drug-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Update. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardo, C.; Di Pasqua, L.G.; Cagna, M.; Richelmi, P.; Vairetti, M.; Ferrigno, A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: Current Issues and Future Perspectives in Preclinical and Clinical Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Rinella, M.E.; Sanyal, A.J.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Goodman, Z.; Cohen, D.E.; Loomba, R. From NAFLD to MAFLD: Implications of a Premature Change in Terminology. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Meta-Analytic Assessment of Prevalence, Incidence, and Outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinjuvadia, R.; Antaki, F.; Lohia, P.; Liangpunsakul, S. The Association between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Metabolic Abnormalities in the United States Population. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The Global Epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, A.; Berardo, C.; Di Pasqua, L.G.; Cagna, M.; Siciliano, V.; Richelmi, P.; Vairetti, M. The Selective Blockade of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-5 Attenuates Fat Accumulation in an In Vitro Model of Benign Steatosis. Eur. J. Histochem. 2020, 64, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peverill, W.; Powell, L.W.; Skoien, R. Evolving Concepts in the Pathogenesis of NASH: Beyond Steatosis and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8591–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P.; Saksena, S. Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: Definitions and Pathogenesis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 17, S377–S384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbard, L.; George, J. Animal Models of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilherme, A.; Virbasius, J.V.; Puri, V.; Czech, M.P. Adipocyte Dysfunctions Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Tas, E.; Yakar, S.; Muzumdar, R. Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Aging. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 455, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzilai, N.; Huffman, D.M.; Muzumdar, R.H.; Bartke, A. The Critical Role of Metabolic Pathways in Aging. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postic, C.; Girard, J. Contribution of de Novo Fatty Acid Synthesis to Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance: Lessons from Genetically Engineered Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; So, J.-S.; Park, J.-G.; Lee, A.-H. Transcriptional Control of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism by SREBP and ChREBP. Semin. Liver Dis. 2013, 33, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdeva, O.; Borodkina, D.; Uchasova, E.; Dyleva, Y.; Barbarash, O. Leptin Resistance: Underlying Mechanisms and Diagnosis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Herrera, K.; Florio, A.A.; Moore, M.; Marrero, A.; Tamez, M.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Mattei, J. The Leptin System and Diet: A Mini Review of the Current Evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 749050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margetic, S.; Gazzola, C.; Pegg, G.; Hill, R. Leptin: A Review of Its Peripheral Actions and Interactions. Int. J. Obes. 2002, 26, 1407–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoio, D.M.; Lynis Dohm, G. Peripheral Metabolic Actions of Leptin. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 16, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K. Role of Insulin Resistance and Lipotoxicity in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2009, 13, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Y. Review Article: Is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease a Spectrum, or Are Steatosis and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Distinct Conditions? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 36, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Peng, Z.-G. Targeting Lipophagy as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 197, 114933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carotti, S.; Aquilano, K.; Zalfa, F.; Ruggiero, S.; Valentini, F.; Zingariello, M.; Francesconi, M.; Perrone, G.; Alletto, F.; Antonelli-Incalzi, R.; et al. Lipophagy Impairment Is Associated with Disease Progression in NAFLD. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grefhorst, A.; van de Peppel, I.P.; Larsen, L.E.; Jonker, J.W.; Holleboom, A.G. The Role of Lipophagy in the Development and Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 601627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
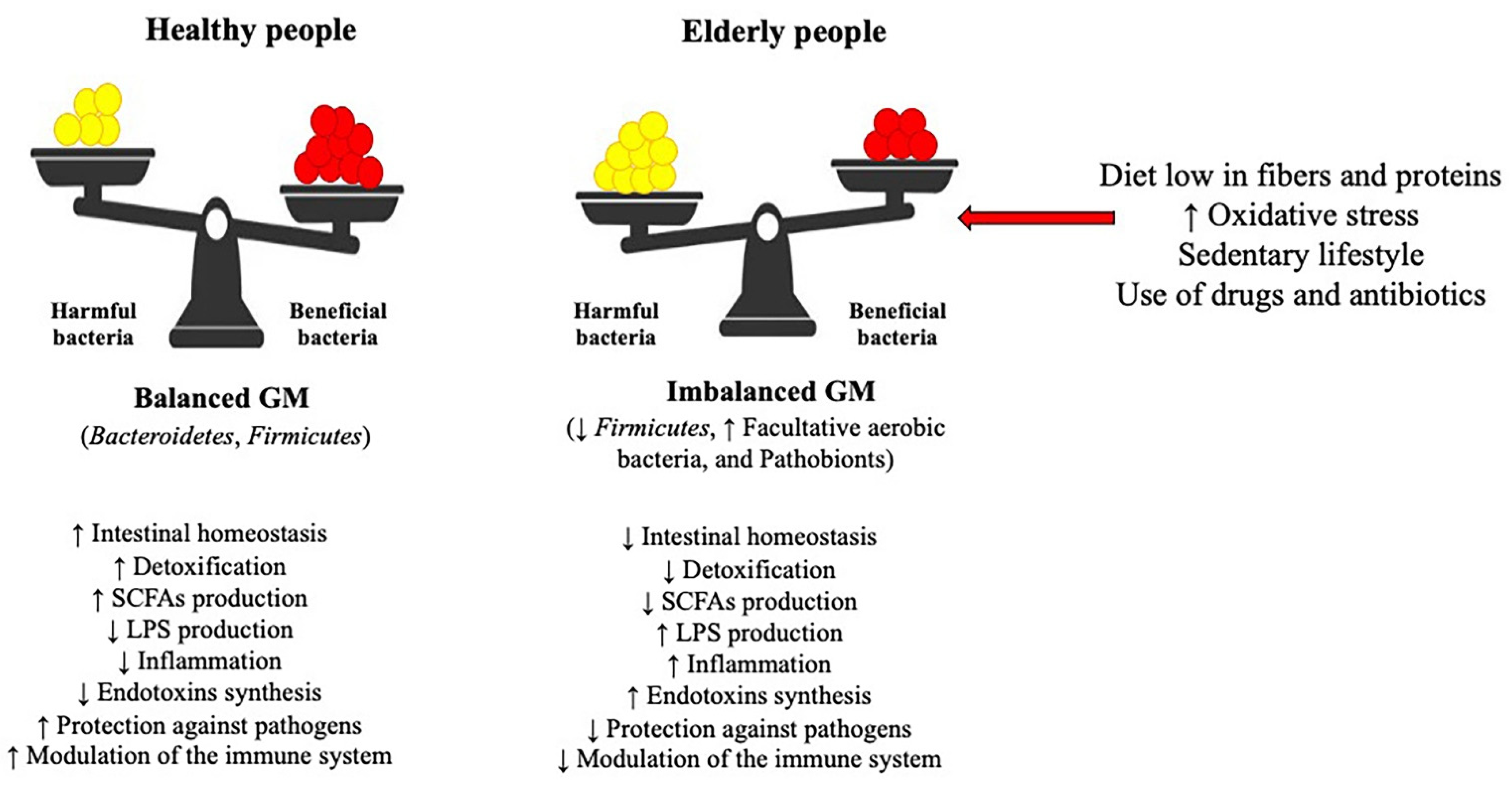
- Cӑtoi, A.F.; Corina, A.; Katsiki, N.; Vodnar, D.C.; Andreicuț, A.D.; Stoian, A.P.; Rizzo, M.; Pérez-Martínez, P. Gut Microbiota and Aging-A Focus on Centenarians. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Abu-Ali, G.; Huttenhower, C. The Healthy Human Microbiome. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Fernández, M.; Porras, D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Román-Sagüillo, S.; González-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Aging, Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Diseases: Management through Physical Exercise and Nutritional Interventions. Nutrients 2020, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciano, F.; Vajro, P. Oxidative Stress and Gut Microbiota. In Gastrointestinal Tissue; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 113–123. ISBN 978-0-12-805377-5. [Google Scholar]
- Collado, M.C.; Rautava, S.; Aakko, J.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S. Human Gut Colonisation May Be Initiated in Utero by Distinct Microbial Communities in the Placenta and Amniotic Fluid. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, M.H.; Brummer, R.J.M.; Rastall, R.A.; Weersma, R.K.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faas, M.; Eggersdorfer, M. The Role of the Microbiome for Human Health: From Basic Science to Clinical Applications. Eur J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, M.J.; Cusack, S.; O’Sullivan, O.; Greene-Diniz, R.; de Weerd, H.; Flannery, E.; Marchesi, J.R.; Falush, D.; Dinan, T.; Fitzgerald, G.; et al. Composition, Variability, and Temporal Stability of the Intestinal Microbiota of the Elderly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, Stability and Resilience of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Ostan, R.; Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Brigidi, P.; Capri, M.; Franceschi, C. Gut Microbiota Changes in the Extreme Decades of Human Life: A Focus on Centenarians. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, B.; Misra, A.; Banerjee, S. Role of Gut Microbiota in Combating Oxidative Stress. In Oxidative Stress in Microbial Diseases; Chakraborti, S., Chakraborti, T., Chattopadhyay, D., Shaha, C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 43–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jasirwan, C.O.M.; Lesmana, C.R.A.; Hasan, I.; Sulaiman, A.S.; Gani, R.A. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathways of Mechanisms. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2019, 38, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.M.; Mercante, J.W.; Neish, A.S. Reactive Oxygen Production Induced by the Gut Microbiota: Pharmacotherapeutic Implications. CMC 2012, 19, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, D.; Parfrey, L.W.; Zaneveld, J.; Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. Human-Associated Microbial Signatures: Examining Their Predictive Value. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, A.; Hernández-Arriaga, A.; Brandt, A.; Sánchez, V.; Nier, A.; Jung, F.; Kehm, R.; Höhn, A.; Grune, T.; Frahm, C.; et al. Microbiota Profiling in Aging-Associated Inflammation and Liver Degeneration. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 311, 151500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R. Emerging Interrelationship Between the Gut Microbiome and Cellular Senescence in the Context of Aging and Disease: Perspectives and Therapeutic Opportunities. Probiotics Antimicro. Prot. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Peña, C.; Álvarez-Cisneros, T.; Quiroz-Baez, R.; Friedland, R.P. Microbiota and Aging. A Review and Commentary. Arch. Med. Res. 2017, 48, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jazwinski, S.M. The Gut Microbiota and Healthy Aging: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2018, 64, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Ding, Z.; Ishaq, M.; Bacha, A.S.; Khan, I.; Hanif, A.; Li, W.; Guo, X. Understanding the Effects of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Possible Probiotics Role: Recent Updates. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Fern, L.A.; Rashidah Pg Hj Ismail, D.S.N.; Chaiyasut, C. The Influence of Probiotics on Bile Acids in Diseases and Aging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, N.; Arboleya, S.; Valdés, L.; Stanton, C.; Ross, P.; Ruiz, L.; Gueimonde, M.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G. The Human Intestinal Microbiome at Extreme Ages of Life. Dietary Intervention as a Way to Counteract Alterations. Front. Genet. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, C.; Bajaj, J.S. Chronic Liver Diseases and the Microbiome—Translating Our Knowledge of Gut Microbiota to Management of Chronic Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.A.; Schattenberg, J.M. NAFLD in the Elderly. CIA 2021, 16, 1633–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudshoorn, C.; van der Cammen, T.J.M.; McMurdo, M.E.T.; van Leeuwen, J.P.T.M.; Colin, E.M. Ageing and Vitamin D Deficiency: Effects on Calcium Homeostasis and Considerations for Vitamin D Supplementation. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz Rajoka, M.S.; Thirumdas, R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Umair, M.; Khurshid, M.; Hayat, H.F.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Pallarés, N.; Martí-Quijal, F.J.; Barba, F.J. Role of Food Antioxidants in Modulating Gut Microbial Communities: Novel Understandings in Intestinal Oxidative Stress Damage and Their Impact on Host Health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Extensive Impact of Non-Antibiotic Drugs on Human Gut Bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, A.; Marchesi, N.; Govoni, S.; Barbieri, A. Targeting the Microbiota in Pharmacology of Psychiatric Disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.L.; Sinha, S.; Lindner, A.B. The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly of ROS: New Insights on Aging and Aging-Related Diseases from Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Model Organisms. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Liew, W.-P.-P.; Sulaiman Rahman, H. Antioxidant and Oxidative Stress: A Mutual Interplay in Age-Related Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, V.; Izzo, V.; Corbi, G.; Russomanno, G.; Manzo, V.; De Lise, F.; Di Donato, A.; Filippelli, A. Antioxidant Supplementation in the Treatment of Aging-Associated Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delli Bovi, A.P.; Marciano, F.; Mandato, C.; Siano, M.A.; Savoia, M.; Vajro, P. Oxidative Stress in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. An Updated Mini Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 595371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houser, M.C.; Tansey, M.G. The Gut-Brain Axis: Is Intestinal Inflammation a Silent Driver of Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis? npj Parkinson’s Dis. 2017, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardeni, T.; Tanes, C.E.; Bittinger, K.; Mattei, L.M.; Schaefer, P.M.; Singh, L.N.; Wu, G.D.; Murdock, D.G.; Wallace, D.C. Host Mitochondria Influence Gut Microbiome Diversity: A Role for ROS. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaaw3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Veiga, P. Rethinking Diet to Aid Human–Microbe Symbiosis. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Stewart, A.G.; Woodman, O.L.; Ritchie, R.H.; Qin, C.X. Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Review of Its Mechanism, Models and Medical Treatments. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 603926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Min, B.-H.; Ganesan, R.; Gebru, Y.A.; Sharma, S.P.; Park, E.; Won, S.-M.; Jeong, J.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Cha, M.-G.; et al. Gut Microbiome in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Role. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Gut Microbiota and Human NAFLD: Disentangling Microbial Signatures from Metabolic Disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Gou, Y.K.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The Gut Microbiota as an Environmental Factor That Regulates Fat Storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckhed, F.; Manchester, J.K.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. From the Cover: Mechanisms Underlying the Resistance to Diet-Induced Obesity in Germ-Free Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaden-Volynets, V.; Basic, M.; Neumann, U.; Pretz, D.; Rings, A.; Bleich, A.; Bischoff, S.C. Lack of Liver Steatosis in Germ-Free Mice Following Hypercaloric Diets. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpton, S.R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R.; Loomba, R. Current Concepts, Opportunities, and Challenges of Gut Microbiome-Based Personalized Medicine in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, T.; Llopis, M.; Lepage, P.; Bruneau, A.; Rabot, S.; Bevilacqua, C.; Martin, P.; Philippe, C.; Walker, F.; Bado, A.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Determines Development of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. Gut 2013, 62, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Ching, Y.H.; Li, Y.P.; Liu, J.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, Y.W.; Yang, S.S.; Huang, W.C.; Chuang, H.L. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Exacerbated in High-Fat Diet-Fed Gnotobiotic Mice by Colonization with the Gut Microbiota from Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; Jorquera, F.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Functional Interactions between Gut Microbiota Transplantation, Quercetin, and High-Fat Diet Determine Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Development in Germ-Free Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.M.; Bieghs, V.; Heymann, F.; Hu, W.; Dreymueller, D.; Liao, L.; Frissen, M.; Ludwig, A.; Gassler, N.; Pabst, O.; et al. CX3CR1 Is a Gatekeeper for Intestinal Barrier Integrity in Mice: Limiting Steatohepatitis by Maintaining Intestinal Homeostasis. Hepatology 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Di Pasqua, L.G.; Berardo, C.; Siciliano, V.; Richelmi, P.; Perlini, S.; Ferrigno, A.; Vairetti, M. Animal Models of Steatosis (NAFLD) and Steatohepatitis (NASH) Exhibit Hepatic Lobe-Specific Gelatinases Activity and Oxidative Stress. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.Z.; Li, Y.T.; Wu, W.R.; Shi, D.; Fang, D.Q.; Yang, L.Y.; Bian, X.Y.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.W.; et al. Dynamic Alterations in the Gut Microbiota and Metabolome during the Development of Methionine-Choline-Deficient Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.M.; Mohs, A.; Kilic, K.; Candels, L.S.; Elfers, C.; Bennek, E.; Ben Schneider, L.; Heymann, F.; Gassler, N.; Penders, J.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Protects against MCD Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayudham, A.; Dolganiuc, A.; Ellis, M.; Petrasek, J.; Kodys, K.; Mandrekar, P.; Szabo, G. VSL#3 Probiotic Treatment Attenuates Fibrosis without Changes in Steatohepatitis in a Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Model in Mice. Hepatology 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Moschen, A.R. Multiple Parallel Hits Hypothesis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Revisited After a Decade. Hepatology 2021, 73, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruss, A.; Kanuri, G.; Wagnerberger, S.; Haub, S.; Bischoff, S.C.; Bergheim, I. Toll-like Receptor 4 Is Involved in the Development of Fructose-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Mice. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenkel, O.; Puengel, T.; Govaere, O.; Abdallah, A.T.; Mossanen, J.C.; Kohlhepp, M.; Liepelt, A.; Lefebvre, E.; Luedde, T.; Hellerbrand, C.; et al. Therapeutic Inhibition of Inflammatory Monocyte Recruitment Reduces Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabl, B. Linking Intestinal Homeostasis and Liver Disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 29, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-Mediated Dysbiosis Regulates Progression of NAFLD and Obesity. Nature 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Gómez, A.; Brescia, P.; Rescigno, M.; Romero-Gómez, M. Gut-Liver Axis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Impact of the Metagenome, End Products, and the Epithelial and Vascular Barriers. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, K.T.; Enos, R.T.; Bader, J.E.; Sougiannis, A.T.; Carson, M.S.; Chatzistamou, I.; Carson, J.A.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M.; Murphy, E.A. Prolonged High-Fat-Diet Feeding Promotes Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Alters Gut Microbiota in Mice. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 619–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Zorita, S.; Aguirre, L.; Milton-Laskibar, I.; Fernández-Quintela, A.; Trepiana, J.; Kajarabille, N.; Mosqueda-Solís, A.; González, M.; Portillo, M.P. Relationship between Changes in Microbiota and Liver Steatosis Induced by High-Fat Feeding—A Review of Rodent Models. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An Obesity-Associated Gut Microbiome with Increased Capacity for Energy Harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of Gut Microbiomes in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Patients: A Connection between Endogenous Alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zheng, R.D.; Sun, X.Q.; Ding, W.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Fan, J.G. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. HBPD INT 2017, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alferink, L.J.M.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Erler, N.S.; Vojinovic, D.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; de Knegt, R.J.; Amin, N.; Ikram, M.A.; Janssen, H.L.A.; et al. Microbiomics, Metabolomics, Predicted Metagenomics, and Hepatic Steatosis in a Population-Based Study of 1,355 Adults. Hepatology 2021, 73, 968–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Chierico, F.; Nobili, V.; Vernocchi, P.; Russo, A.; De Stefanis, C.; Gnani, D.; Furlanello, C.; Zandonà, A.; Paci, P.; Capuani, G.; et al. Gut Microbiota Profiling of Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Obese Patients Unveiled by an Integrated Meta-Omics-Based Approach. Hepatology 2017, 65, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Seguritan, V.; Li, W.; Long, T.; Klitgord, N.; Bhatt, A.; Dulai, P.S.; Caussy, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Highlander, S.K.; et al. Gut Microbiome-Based Metagenomic Signature for Non-Invasive Detection of Advanced Fibrosis in Human Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1054–1062.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jiang, X.; Cao, M.; Ge, J.; Bao, Q.; Tang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, L. Altered Fecal Microbiota Correlates with Liver Biochemistry in Nonobese Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, M.; Ahmed, I.; Gillevet, P.M.; Probert, C.S.; Ratcliffe, N.M.; Smith, S.; Greenwood, R.; Sikaroodi, M.; Lam, V.; Crotty, P.; et al. Fecal Microbiome and Volatile Organic Compound Metabolome in Obese Humans with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 868–875.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A.; et al. The Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Associated with Gut Dysbiosis and Shift in the Metabolic Function of the Gut Microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, L.; Capurso, L. FAO/WHO Guidelines on Probiotics: 10 Years Later. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Garg, R. PROBIOTICS. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 27, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Salminen, S. Probiotics. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 510–515. [Google Scholar]
- Aeron, G.; Morya, S. Probiotics as Therapeutics. JARB 2017, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Versalovic, J. Probiotics-Host Communication: Modulation of Signaling Pathways in the Intestine. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, M.A.K.; Sarker, M.; Li, T.; Yin, J. Probiotic Species in the Modulation of Gut Microbiota: An Overview. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S.H.; Flint, H.J. Probiotics and Prebiotics and Health in Ageing Populations. Maturitas 2013, 75, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G.; Jass, J.; Sebulsky, M.T.; McCormick, J.K. Potential Uses of Probiotics in Clinical Practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanklecha, M.; Verma, L.; Pai, U.; Mishra, S.; Maqsood, S.; Birla, A. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Evaluation in Acute Diarrhea (LEAD): An Observational Study. Cureus 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Nakamura, F.; Kanzato, H.; Sawada, D.; Hirata, H.; Nishimura, A.; Kajimoto, O.; Fujiwara, S. Clinical Effects of Lactobacillus Acidophilus Strain L-92 on Perennial Allergic Rhinitis: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surawicz, C.M.; Elmer, G.W.; Speelman, P.; McFarland, L.V.; Chinn, J.; Van Belle, G. Prevention of Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea by Saccharomyces Boulardii: A Prospective Study. Gastroenterology 1989, 96, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; An, J.; Shimada, T.; Liu, S.; Maeyama, K. Oral Administration of Enterococcus Faecalis FK-23 Suppresses Th17 Cell Development and Attenuates Allergic Airway Responses in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.-J.; Wang, J.-Y. Children with Atopic Dermatitis Show Clinical Improvement after Lactobacillus Exposure. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, J.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, S.I.; Han, Y.S.; Choi, Y.O.; Lee, S.Y.; Ahn, K.M.; Ji, G.E. Effect of Probiotic Mix (Bifidobacterium Bifidum, Bifidobacterium Lactis, Lactobacillus Acidophilus) in the Primary Prevention of Eczema: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Pediatric Allergy Immunol. 2010, 21, e386–e393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaziano, R.; Sabbatini, S.; Roselletti, E.; Perito, S.; Monari, C. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae-Based Probiotics as Novel Antimicrobial Agents to Prevent and Treat Vaginal Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayouni, A.; Bastani, P.; Ziyadi, S.; Mohammad-Alizadeh-Charandabi, S.; Ghalibaf, M.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Mehrabany, E.V. Effects of Probiotics on the Recurrence of Bacterial Vaginosis: A Review. J. Low. Genit. Tract. Dis. 2014, 18, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moludi, J.; Kafil, H.S.; Qaisar, S.A.; Gholizadeh, P.; Alizadeh, M.; Vayghyan, H.J. Effect of Probiotic Supplementation along with Calorie Restriction on Metabolic Endotoxemia, and Inflammation Markers in Coronary Artery Disease Patients: A Double Blind Placebo Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutr. J. 2021, 20, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Yue, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, M.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Zhao, J.; et al. Lactobacillus Plantarum CCFM1143 Alleviates Chronic Diarrhea via Inflammation Regulation and Gut Microbiota Modulation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 746585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamallat, Y.; Meyiah, A.; Kuugbee, E.D.; Hago, A.M.; Chiwala, G.; Awadasseid, A.; Bamba, D.; Zhang, X.; Shang, X.; Luo, F.; et al. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Induced Epithelial Cell Apoptosis, Ameliorates Inflammation and Prevents Colon Cancer Development in an Animal Model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuugbee, E.D.; Shang, X.; Gamallat, Y.; Bamba, D.; Awadasseid, A.; Suliman, M.A.; Zang, S.; Ma, Y.; Chiwala, G.; Xin, Y.; et al. Structural Change in Microbiota by a Probiotic Cocktail Enhances the Gut Barrier and Reduces Cancer via TLR2 Signaling in a Rat Model of Colon Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2908–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudeau, J.; Glasser, A.-L.; Julien, S.; Colombel, J.-F.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A. Inhibitory Effect of Probiotic Escherichia Coli Strain Nissle 1917 on Adhesion to and Invasion of Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Adherent-Invasive, E. Coli Strains Isolated from Patients with Crohn’s Disease: INHIBITORY EFFECT OF PROBIOTIC E. COLI NISSLE 1917 ON AIEC COLONIZATION. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis, T.; Pothoulakis, C. Efficacy and Safety of the Probiotic Saccharomyces Boulardii for the Prevention and Therapy of Gastrointestinal Disorders. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2012, 5, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Li, N.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Yue, Y.; Jiao, W.; Wang, N.; Song, Y.; Huo, G.; Li, B. Lactobacillus Acidophilus Alleviates Type 2 Diabetes by Regulating Hepatic Glucose, Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5804–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Huang, Z.; He, Z.; Yue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W. Protective Effect of Bifidobacterium Bifidum FSDJN7O5 and Bifidobacterium Breve FHNFQ23M3 on Diarrhea Caused by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7271–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, Å.; Bennet, R.; Viitanen, M.; Palmgren, A.-C.; Nord, C.E. Influence of Lactobacillus F19 on Intestinal Microflora in Children and Elderly Persons and Impact on Helicobacter Pylori Infections. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2002, 14, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlivak, P.; Odraska, J.; Ferencik, M.; Ebringer, L.; Jahnova, E.; Mikes, Z. One-Year Application of Probiotic Strain Enterococcus Faecium M-74 Decreases Serum Cholesterol Levels. Bratisl Lek Listy 2005, 106, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pakdaman, M.N.; Udani, J.K.; Molina, J.P.; Shahani, M. The Effects of the DDS-1 Strain of Lactobacillus on Symptomatic Relief for Lactose Intolerance - a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Clinical Trial. Nutr. J. 2015, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lata, J.; Novotný, I.; Příbramská, V.; Juránková, J.; Frič, P.; Kroupa, R.; Stibůrek, O. The Effect of Probiotics on Gut Flora, Level of Endotoxin and Child–Pugh Score in Cirrhotic Patients: Results of a Double-Blind Randomized Study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 19, 1111–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunia, M.K.; Sharma, B.C.; Sharma, P.; Sachdeva, S.; Srivastava, S. Probiotics Prevent Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1003–1008.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Ma, F.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacteria Attenuate the Development of Metabolic Disorders, with Inter- and Intra-Species Differences. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3509–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.; Na, G.Y.; Chu, J.; Joung, H.; Kim, B.-K.; Lim, S. Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus Plantarum K50 on Lipids in Koreans with Obesity: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Clinical Trial. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 790046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukam, K.C.; Hayes, K.; Summers, K.; Reid, G. Probiotic Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GR-1 and Lactobacillus Reuteri RC-14 May Help Downregulate TNF-Alpha, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10 and IL-12 (P70) in the Neurogenic Bladder of Spinal Cord Injured Patient with Urinary Tract Infections: A Two-Case Study. Adv. Urol. 2009, 2009, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Chaiyasut, C. A review on anti-aging properties of probiotics. Int. J. App. Pharm. 2018, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, N.; Valdés-Varela, L.; González, S.; Gueimonde, M.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G. Nutrition and the Gut Microbiome in the Elderly. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahtinen, S.J.; Tammela, L.; Korpela, J.; Parhiala, R.; Ahokoski, H.; Mykkänen, H.; Salminen, S.J. Probiotics Modulate the Bifidobacterium Microbiota of Elderly Nursing Home Residents. AGE 2009, 31, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampelli, S.; Candela, M.; Severgnini, M.; Biagi, E.; Turroni, S.; Roselli, M.; Carnevali, P.; Donini, L.; Brigidi, P. A Probiotics-Containing Biscuit Modulates the Intestinal Microbiota in the Elderly. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, L.; Pinto, A.; Bourdel-Marchasson, I.; Ostan, R.; Brigidi, P.; Turroni, S.; Hrelia, S.; Hrelia, P.; Bereswill, S.; Fischer, A.; et al. Impact of Personalized Diet and Probiotic Supplementation on Inflammation, Nutritional Parameters and Intestinal Microbiota—The “RISTOMED Project”: Randomized Controlled Trial in Healthy Older People. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Prasad, J.; Gill, H.; Stevenson, L.; Gopal, P. Impact of Consumption of Different Levels of Bifidobacterium Lactis HN019 on the Intestinal Microflora of Elderly Human Subjects. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2007, 11, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, M.A.K.; Sarker, M.; Wan, D. Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics on Cytokine Profiles. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8063647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- María Remes-Troche, J.; Coss-Adame, E.; Ángel Valdovinos-Díaz, M.; Gómez-Escudero, O.; Eugenia Icaza-Chávez, M.; Antonio Chávez-Barrera, J.; Zárate-Mondragón, F.; Antonio Velarde-Ruíz Velasco, J.; Rafael Aceves-Tavares, G.; Antonio Lira-Pedrín, M.; et al. Lactobacillus Acidophilus LB: A Useful Pharmabiotic for the Treatment of Digestive Disorders. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 175628482097120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, B.; Delgado, S.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Lourenço, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Margolles, A. Probiotics, Gut Microbiota, and Their Influence on Host Health and Disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemarajata, P.; Versalovic, J. Effects of Probiotics on Gut Microbiota: Mechanisms of Intestinal Immunomodulation and Neuromodulation. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Treatment Improves Intestinal Permeability and Modulates Microbiota Dysbiosis in an Experimental Model of Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Farhadi, A.; Jakate, S.M.; Tang, Y.; Shaikh, M.; Keshavarzian, A. Lactobacillus GG Treatment Ameliorates Alcohol-Induced Intestinal Oxidative Stress, Gut Leakiness, and Liver Injury in a Rat Model of Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Alcohol 2009, 43, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Drabik, K.A.; Waypa, T.S.; Musch, M.W.; Alverdy, J.C.; Schneewind, O.; Chang, E.B.; Petrof, E.O. Soluble Factors from Lactobacillus GG Activate MAPKs and Induce Cytoprotective Heat Shock Proteins in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, C1018–C1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-S.; Choi, J.W.; Jhun, J.; Kwon, J.Y.; Lee, B.-I.; Yang, C.W.; Park, S.-H.; Cho, M.-L. Lactobacillus Acidophilus Improves Intestinal Inflammation in an Acute Colitis Mouse Model by Regulation of Th17 and Treg Cell Balance and Fibrosis Development. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, R.; Shinde, T.; Gundamaraju, R.; Gondalia, S.; Karpe, A.; Beale, D.; Martoni, C.; Eri, R. Lactobacillus Acidophilus DDS-1 Modulates the Gut Microbiota and Improves Metabolic Profiles in Aging Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Song, L.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, S.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Ren, Z. Lactobacillus Plantarum Prevents Obesity via Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in High-Fat Feeding Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, C.; Petito, V.; Del Chierico, F.; Mangiola, F.; Pecere, S.; Schiavoni, E.; Pizzoferrato, M.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Putignani, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. P115 Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 Modulate Gut Microbiota Composition in Ulcerative Colitis Patients. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, S133–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlee, M.; Wehkamp, J.; Altenhoefer, A.; Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Stange, E.F.; Fellermann, K. Induction of Human β-Defensin 2 by the Probiotic Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 Is Mediated through Flagellin. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Matamoros, S.; Geurts, L.; Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D. Saccharomyces Boulardii Administration Changes Gut Microbiota and Reduces Hepatic Steatosis, Low-Grade Inflammation, and Fat Mass in Obese and Type 2 Diabetic Db/Db Mice. mBio 2014, 5, e01011–e01014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grander, C.; Adolph, T.E.; Wieser, V.; Lowe, P.; Wrzosek, L.; Gyongyosi, B.; Ward, D.V.; Grabherr, F.; Gerner, R.R.; Pfister, A.; et al. Recovery of Ethanol-Induced Akkermansia Muciniphila Depletion Ameliorates Alcoholic Liver Disease. Gut 2018, 67, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, P.W.; Marchesi, J.R.; Hill, C. Next-Generation Probiotics: The Spectrum from Probiotics to Live Biotherapeutics. Nat. Microbiol 2017, 2, 17057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Qv, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Berglund, B.; Li, L. An Update on the Efficacy and Functionality of Probiotics for the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Engineering 2021, 7, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, Y.S.; Seki, E. Toll-like Receptors in Alcoholic Liver Disease, Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Carcinogenesis: The Role of TLR in ALD, NASH and HCC. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Shi, L.P.; Shi, L.; Xu, L. Efficacy of probiotics on the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2018, 57, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, A.; Frank, D.N.; Harnke, B.; Bambha, K. Systematic review: Microbial dysbiosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharm. 2015, 42, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Dalbeni, A. Treatments for NAFLD: State of Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, A.; Bonelli, P.; Tuccillo, F.M.; Goldfine, I.D.; Evans, J.L.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Mancini, A. Role of Gut Microbiota and Oxidative Stress in the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease to Hepatocarcinoma: Current and Innovative Therapeutic Approaches. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumpail, B.; Li, A.; John, N.; Sallam, S.; Shah, N.; Kwong, W.; Cholankeril, G.; Kim, D.; Ahmed, A. The Therapeutic Implications of the Gut Microbiome and Probiotics in Patients with NAFLD. Diseases 2019, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, J.; Wu, H.; Yu, D.; Li, W. Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Bacillus Subtilis B10 on Biochemical and Molecular Parameters in the Serum and Liver of High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajro, P.; Mandato, C.; Veropalumbo, C.; De Micco, I. Probiotics: A Possible Role in Treatment of Adult and Pediatric Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Ann. Hepatol 2013, 12, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Nie, S.-P.; Zhu, K.-X.; Ding, Q.; Li, C.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M.-Y. Lactobacillus Plantarum NCU116 Improves Liver Function, Oxidative Stress and Lipid Metabolism in Rats with High Fat Diet Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, C.; Zhang, X.; Gao, L.; Li, S. Lactobacillus Plantarum NA136 Improves the Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating the AMPK/Nrf2 Pathway. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5843–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Zeng, D.; Wang, H.; Ni, X.; Yi, D.; Pan, K.; Jing, B. Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Lactobacillus Johnsonii BS15 by Attenuating Inflammation and Mitochondrial Injury and Improving Gut Environment in Obese Mice. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6817–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritze, Y.; Bárdos, G.; Claus, A.; Ehrmann, V.; Bergheim, I.; Schwiertz, A.; Bischoff, S.C. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Protects against Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e80169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Huang, C.; Cheng, M. Dietary Blueberry and Bifidobacteria Attenuate Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Rats by Affecting SIRT1-Mediated Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wan, Y.; Fang, Q.; Lu, W.; Cai, W. Supplementation with Probiotics Modifies Gut Flora and Attenuates Liver Fat Accumulation in Rat Nonalcoh.holic Fatty Liver Disease Model. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 50, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubnov, R.V.; Babenko, L.P.; Lazarenko, L.M.; Mokrozub, V.V.; Demchenko, O.A.; Nechypurenko, O.V.; Spivak, M.Y. Comparative Study of Probiotic Effects of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria Strains on Cholesterol Levels, Liver Morphology and the Gut Microbiota in Obese Mice. EPMA J. 2017, 8, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; He, J.; Gao, N.; Lu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Probiotics May Delay the Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Restoring the Gut Microbiota Structure and Improving Intestinal Endotoxemia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Inoue, I.; Tanaka, M.; Matsuda, N.; Nakano, T.; Awata, T.; Katayama, S.; Alpers, D.H.; Komoda, T. Clostridium Butyricum MIYAIRI 588 Improves High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 3534–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Hua, J.; Li, Z. Probiotics Improve High Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance by Increasing Hepatic NKT Cells. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Probiotics and Antibodies to TNF Inhibit Inflammatory Activity and Improve Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2003, 37, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munukka, E.; Rintala, A.; Toivonen, R.; Nylund, M.; Yang, B.; Takanen, A.; Hänninen, A.; Vuopio, J.; Huovinen, P.; Jalkanen, S.; et al. Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii Treatment Improves Hepatic Health and Reduces Adipose Tissue Inflammation in High-Fat Fed Mice. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.B.; Jun, D.W.; Kang, B.-K.; Lim, J.H.; Lim, S.; Chung, M.-J. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Multispecies Probiotic Mixture in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, R.; Yang, X.; Dai, J.; Huang, M.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Okekunle, A.P.; Gao, G.; Onwuka, J.U.; et al. Yogurt Improves Insulin Resistance and Liver Fat in Obese Women with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepideh, A.; Karim, P.; Hossein, A.; Leila, R.; Hamdollah, M.; Mohammad, E.G.; Mojtaba, S.; Mohammad, S.; Ghader, G.; Seyed Moayed, A. Effects of Multistrain Probiotic Supplementation on Glycemic and Inflammatory Indices in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.; De Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Conde, R.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Primo, D.; De La Fuente, B.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of a Probiotic on Liver Aminotransferases in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: A Double Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci 2011, 15, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Derosa, G.; Guasti, L.; D’Angelo, A.; Martinotti, C.; Valentino, M.C.; Di Matteo, S.; Bruno, G.M.; Maresca, A.M.; Gaudio, G.V.; Maffioli, P. Probiotic Therapy with VSL#3® in Patients with NAFLD: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 846873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavakhi, A.; Minakari, M.; Firouzian, H.; Assali, R.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Ferns, G. Effect of a Probiotic and Metformin on Liver Aminotransferases in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Double Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Kobyliak, N.; Abenavoli, L.; Mykhalchyshyn, G.; Kononenko, L.; Boccuto, L.; Kyriienko, D.; Dynnyk, O. A Multi-Strain Probiotic Reduces the Fatty Liver Index, Cytokines and Aminotransferase Levels in NAFLD Patients: Evidence from a Randomized Clinical Trial. JGLD 2018, 27, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, P.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Zheng, P. Co-Administration of Cholesterol-Lowering Probiotics and Anthraquinone from Cassia Obtusifolia, L. Ameliorate Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, S.M.; Park, G.-S.; Lee, Y.H.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kang, J.; Lee, H.-J. Beneficial Effects of Lactobacillus Plantarum Strains on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High Fat/High Fructose Diet-Fed Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, G. Probiotic Bifidobacterium Lactis V9 Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis and Inflammation in Rats with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. AMB Expr. 2020, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.; Rafraf, M.; Somi, M.H.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Effects of Probiotic Yogurt Consumption on Metabolic Factors in Individuals with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7386–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duseja, A.; Acharya, S.K.; Mehta, M.; Chhabra, S.; Shalimar, R.S.; Das, A.; Dattagupta, S.; Dhiman, R.K.; Chawla, Y.K. High Potency Multistrain Probiotic Improves Liver Histology in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Proof of Concept Study. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2019, 6, e000315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H. Gut Microbiota and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Insights on Mechanisms and Therapy. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fianchi, F.; Liguori, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Grieco, A.; Miele, L. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) as Model of Gut–Liver Axis Interaction: From Pathophysiology to Potential Target of Treatment for Personalized Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary Modulation of the Human Colonic Microbiota: Introducing the Concept of Prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary Fiber and Prebiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vrese, M.; Schrezenmeir, J. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics. Food Biotechnology 2008, 111, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, E.S.; Byrne, C.S.; Morrison, D.J.; Murphy, K.G.; Preston, T.; Tedford, C.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Fountana, S.; Serrano-Contreras, J.I.; Holmes, E.; et al. Dietary Supplementation with Inulin-Propionate Ester or Inulin Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Adults with Overweight and Obesity with Distinct Effects on the Gut Microbiota, Plasma Metabolome and Systemic Inflammatory Responses: A Randomised Cross-over Trial. Gut 2019, 68, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, D.; Haque, M.M.; Gote, M.; Jain, M.; Bhaduri, A.; Dubey, A.K.; Mande, S.S. A Prospective Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Response Relationship Study to Investigate Efficacy of Fructo-Oligosaccharides (FOS) on Human Gut Microflora. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, P.; Chen, M.; Luo, Y.; Prabhakar, M.; Zheng, H.; He, Y.; Qi, Q.; Long, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Fructooligosaccharide (FOS) and Galactooligosaccharide (GOS) Increase Bifidobacterium but Reduce Butyrate Producing Bacteria with Adverse Glycemic Metabolism in Healthy Young Population. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnell, J.A.; Raman, M.; Rioux, K.P.; Reimer, R.A. The Potential Role of Prebiotic Fibre for Treatment and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Associated Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubioul, C.A.; Horsmans, Y.; Lambert, P.; Danse, E.; Delzenne, N.M. Effects of Oligofructose on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Results of a Pilot Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.-G. Effect of Lactulose on Establishment of a Rat Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Model. WJG 2005, 11, 5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ichimura, M.; Tsuneyama, K.; Moritoki, Y.; Tsunashima, H.; Omagari, K.; Hara, M.; Yasuda, I.; Miyakawa, H.; Kikuchi, K. Fructo-Oligosaccharides and Intestinal Barrier Function in a Methionine–Choline-Deficient Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M.; Aliashrafi, S.; Javadzadeh, Y.; AsghariJafarabadi, M. The Effect of Chlorella Vulgaris Supplementation on Liver Enzymes, Serum Glucose and Lipid Profile in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Health Promot. Perspect. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, L.; Ghavami, M.; Khoshbaten, M.; Safaiyan, A.; Barzegari, A.; Pourghassem Gargari, B. The Effect of Probiotic and/or Prebiotic on Liver Function Tests in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Double Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Iran. Red Crescent. Med. J. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulevic, J.; Juric, A.; Walton, G.E.; Claus, S.P.; Tzortzis, G.; Toward, R.E.; Gibson, G.R. Influence of Galacto-Oligosaccharide Mixture (B-GOS) on Gut Micro.obiota, Immune Parameters and Metabonomics in Elderly Persons. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulevic, J.; Drakoularakou, A.; Yaqoob, P.; Tzortzis, G.; Gibson, G.R. Modulation of the Fecal Microflora Profile and Immune Function by a Novel Trans-Galactooligosaccharide Mixture (B-GOS) in Healthy Elderly Volunteers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, G.E.; van den Heuvel, E.G.H.M.; Kosters, M.H.W.; Rastall, R.A.; Tuohy, K.M.; Gibson, G.R. A Randomised Crossover Study Investigating the Effects of Galacto-Oligosaccharides on the Faecal Microbiota in Men and Women over 50 Years of Age. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Vacante, M.; Antic, T.; Giordano, M.; Chisari, G.; Acquaviva, R.; Mastrojeni, S.; Malaguarnera, G.; Mistretta, A.; Li Volti, G.; et al. Bifidobacterium Longum with Fructo-Oligosaccharides in Patients with Non Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslamparast, T.; Poustchi, H.; Zamani, F.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic Supplementation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofidi, F.; Poustchi, H.; Yari, Z.; Nourinayyer, B.; Merat, S.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic Supplementation in Lean Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Pilot, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorletti, E.; Afolabi, P.R.; Miles, E.A.; Smith, D.E.; Almehmadi, A.; Alshathry, A.; Childs, C.E.; Del Fabbro, S.; Bilson, J.; Moyses, H.E.; et al. Synbiotics Alter Fecal Microbiomes, But Not Liver Fat or Fibrosis, in a Randomized Trial of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1597–1610.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferolla, S.; Couto, C.; Costa-Silva, L.; Armiliato, G.; Pereira, C.; Martins, F.; Ferrari, M.; Vilela, E.; Torres, H.; Cunha, A.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Synbiotic Supplementation on Hepatic Steatosis and Anthropometric Parameters, But Not on Gut Permeability in a Population with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, A.; Mohammadi, V.; Gholi, Z.; Esmaillzade, A.; Feizi, A.; Askari, G. The Effect of Synbiotic Supplementation on Body Composition and Lipid Profile in Patients with NAFLD: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial Study. Iran. Red Crescent. Med. J. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, A.; Askari, G.; Esmailzade, A.; Feizi, A.; Mohammadi, V. The Effect of Symbiotic Supplementation on Liver Enzymes, c-Reactive Protein and Ultrasound Findings in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Clinical Trial. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, M.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Forssten, S.D.; Nikkilä, J.; Tiihonen, K.; Rautonen, N.; Lahtinen, S.J. Gut Microbiota of Healthy Elderly NSAID Users Is Selectively Modified with the Administration of Lactobacillus Acidophilus NCFM and Lactitol. AGE 2012, 34, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, S.; Cleary, S.; Bahrami, B.; Reynolds, N.; Macfarlane, G.T. Synbiotic Consumption Changes the Metabolism and Composition of the Gut Microbiota in Older People and Modifies Inflammatory Processes: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study. Aliment. Pharm. 2013, 38, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosch, S.; Woodmansey, E.J.; Paterson, J.C.M.; McMurdo, M.E.T.; Macfarlane, G.T. Microbiological Effects of Consuming a Synbiotic Containing Bifidobacterium Bifidum, Bifidobacterium Lactis, and Oligofructose in Elderly Persons, Determined by Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction and Counting of Viable Bacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez-Fernández, M.; Porras, D.; Petrov, P.; Román-Sagüillo, S.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Soluyanova, P.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; González-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Jover, R.; et al. The Synbiotic Combination of Akkermansia Muciniphila and Quercetin Ameliorates Early Obesity and NAFLD through Gut Microbiota Reshaping and Bile Acid Metabolism Modulation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.O.; Gluck, M. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: An Update on Clinical Practice. Clin. Endosc. 2019, 52, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Faecal Microbiota Transplantation in Clinical Practice. Gut 2018, 67, 196.2–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Pan, Q.; Shen, F.; Cao, H.; Ding, W.; Chen, Y.; Fan, J. Total Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis in Mice via Beneficial Regulation of Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lezana, T.; Raurell, I.; Bravo, M.; Torres-Arauz, M.; Salcedo, M.T.; Santiago, A.; Schoenenberger, A.; Manichanh, C.; Genescà, J.; Martell, M.; et al. Restoration of a Healthy Intestinal Microbiota Normalizes Portal Hypertension in a Rat Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Liver Failure/Cirrhosis/Portal Hypertension. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witjes, J.J.; Smits, L.P.; Pekmez, C.T.; Prodan, A.; Meijnikman, A.S.; Troelstra, M.A.; Bouter, K.E.C.; Herrema, H.; Levin, E.; Holleboom, A.G.; et al. Donor Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Alters Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Obese Individuals with Steatohepatitis. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1578–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, L.; Rahman, A.; Nair Parvathy, S.; Beaton, M.; Silverman, J.; Qumosani, K.; Hramiak, I.; Hegele, R.; Joy, T.; Meddings, J.; et al. Allogenic Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Improves Abnormal Small Intestinal Permeability: A Randomized Control Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease | Probiotic | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Acute diarrhea | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG | [110] |
| Allergic rhinitis | Lactobacillus acidophilus L-92 | [111] |
| Antibiotic-associated diarrhea | Saccharomyces boulardii | [112] |
| Asthma | Enterococcus faecalis FK-23 | [113] |
| Atopic dermatitis | Lactobacillus paracasei, and Lactobacillus fermentum | [114] |
| Atopic eczema | Mixture (Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium lactis, and Lactobacillus acidophilus) | [115] |
| Bacterial vaginosis | Saccharomyces cerevisiae Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1, and Lactobacillus fermentum RC-14 | [116] [117] |
| Cardiovascular disorder | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG | [118] |
| Chronic diarrhea | Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM1143 | [119] |
| Colon cancer | Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus acidophilus, Mixture (Bifidobacteria bifidum, and Bifidobacteria infantum) | [120] [121] |
| Crohn’s disease | Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 Saccharomyces boulardii | [122] [123] |
| Diabetes | Lactobacillus acidophilus | [124] |
| Diarrhea | Bifidobacterium bifidum FSDJN705, and Bifidobacterium breve FHNFQ23M3 | [125] |
| Gastroenteritis | Lactobacillus F19 | [126] |
| Hypercholesterolemia | Enterococcus faecium M-74 | [127] |
| Lactose intolerance | Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 | [128] |
| Liver disorder | Escherichia coli Nissle VSL#3 | [129] [130] |
| Metabolic disorder | Bifidobacterium adolescentis Z25 | [131] |
| Obesity | Lactobacillus plantarum K50 | [132] |
| Urinary tract infections | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-a and Lactobacillus reuteri RC-14 | [133] |
| Lactobacilli | Bifidobacteria | Saccharomyces | Other species |
|---|---|---|---|
| L. acidophilus | B. adolescentis | S. boulardii | Bacillus subtilis |
| L. casei | B. animalis | S. cerevisiae | Enterococcus faecalis |
| L. crispatus | B. bifidum | Escherichia coli | |
| L. fermentum | B. breve | Lactococcus lactis | |
| L. gallinarum | B. infantis | Streptococcus thermophilus | |
| L. gasseri | B. longum | ||
| L. helveticus | |||
| L. johnsonii | |||
| L. lactis | |||
| L. paracasei | |||
| L. plantarum | |||
| L. reuteri | |||
| L. rhamnosus |
| Probiotic | Model | Diet | Duration | Treatment Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG | Mice | High-fructose diet-induced NAFLD | 8 weeks | 1. Improvement of the accumulation of fat in the liver 2. Reduction of liver inflammation (↓TNFα, ↓IL-8R, ↓IL-1β), as well as steatosis 3. Increase in gut beneficial bacteria 4. Restoration of tight junction proteins, resulting in gut barrier function amelioration | [167] |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GGand Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 | Sprague-Dawley rats | High-fat diet-induced NAFLD | 21 weeks | 1. Reduction of gut endotoxemia level, as well as the expression of inflammatory cytokines 2. Amelioration of GM and intestinal barrier function 3. Increase in CYP7A1 and LDL-R, resulting in improvement of lipid metabolism and insulin resistance | [183] |
| Bifidobacterium infantis, Lactobacillus acidopilus, Bacillus cereus | Rats | High-fat/high-sucrose diet-induced NAFLD | 12 weeks | 1. Downregulation of LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway, resulting in slowing the progression of NAFLD 2. Improvement of GM dysbiosis and the intestinal barrier function 3. Reduction of body weight 4. Decrease in TNFα, and IL-18 expression, as well as ALT, AST, GGT, and ALP activities | [171] |
| Lactobacillus plantarum ATG-K2and ATG-K6 | Wistar rats | High-fat and fructose-diet-induced NAFLD | 8 weeks | 1. Modulation of GM 2. Downregulating of de novo lipogenesis-associated genes 3. Reduction of body weight and hepatic lipid accumulation 4. Increasing of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, GPx, CAT), and decreasing of ALT and AST serum levels | [184] |
| Bifidobacterium animalissubsp. Lactis V9 | Wistar rats | High-fat diet-induced NAFLD | 9 weeks | 1. Decrease in ALT, AST, TLR4, and TLR9 levels, resulting in alleviation of hepatic steatosis and liver damage 2. Reduction of serum glucose level, as well as hepatic triglycerides and free fatty acids accumulation 3. Restoration of hepatic phosphorylated-AMPK and PPAR-α levels, and reduction of SREBP-1c and FAS expression 4. Attenuation of liver inflammation, by inhibiting inflammatory cytokines synthesis (IL-6, IL-1β, TNFα) | [185] |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus La5, Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 | 72 NAFLD patients | 8 weeks | 1. Decreasing of ALT and AST activity 2. Reduction of triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol serum levels, as well as total cholesterol | [186] | |
| Multiprobiotic “Lactocare” (L. casei, L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, L. bulgaricus, B. breve, B. longum, Streptococcus thermophilus) | 42 NAFLD patients | 8 weeks | 1. Decrease in TNFα and IL-6 expression, as well as FBS and insulin | [178] | |
| Probiotics mixture (Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Enterococcus; Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus) | 200 NAFLD patients | 1 month | 1. Improvement of GM composition, by inhibiting TNFα expression and ameliorating adiponectin level 2. Decrease in ALT and AST serum levels 3. Amelioration of lipid metabolism and fatty liver | [157] | |
| Multiprobiotic “Symbiter” (Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Propionibacterium, Acetobacter) | 58 NAFLD patients | 8 weeks | 1. Reduction of liver fat (↓total cholesterol and ↓triglycerides) 2. Decreasing of AST and GGT activity, as well as TNFα and IL-6 expression | [182] | |
| Lactobacillus paracasei DSM 24733, Lactobacillus plantarum DSM 24730, Lactobacillus acidophilus DSM 24735 and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus DSM 24734, Bifidobacterium longum DSM 24736, Bifidobacterium infantis DSM 24737, Bifidobacterium breve DSM 24732, and Streptococcus thermophilus DSM 24731 | 30 NAFLD patients | 12 months | 1. Improvement of liver histology 2. Reduction in steatohepatitis 3. Decrease in ALP, AST, and ALT activity, as well as endotoxins, TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels | [187] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campagnoli, L.I.M.; Marchesi, N.; Vairetti, M.; Pascale, A.; Ferrigno, A.; Barbieri, A. Age-Related NAFLD: The Use of Probiotics as a Supportive Therapeutic Intervention. Cells 2022, 11, 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182827
Campagnoli LIM, Marchesi N, Vairetti M, Pascale A, Ferrigno A, Barbieri A. Age-Related NAFLD: The Use of Probiotics as a Supportive Therapeutic Intervention. Cells. 2022; 11(18):2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182827
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampagnoli, Lucrezia Irene Maria, Nicoletta Marchesi, Mariapia Vairetti, Alessia Pascale, Andrea Ferrigno, and Annalisa Barbieri. 2022. "Age-Related NAFLD: The Use of Probiotics as a Supportive Therapeutic Intervention" Cells 11, no. 18: 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182827
APA StyleCampagnoli, L. I. M., Marchesi, N., Vairetti, M., Pascale, A., Ferrigno, A., & Barbieri, A. (2022). Age-Related NAFLD: The Use of Probiotics as a Supportive Therapeutic Intervention. Cells, 11(18), 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11182827










