Three Binding Conformations of BIO124 in the Pocket of the PICK1 PDZ Domain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
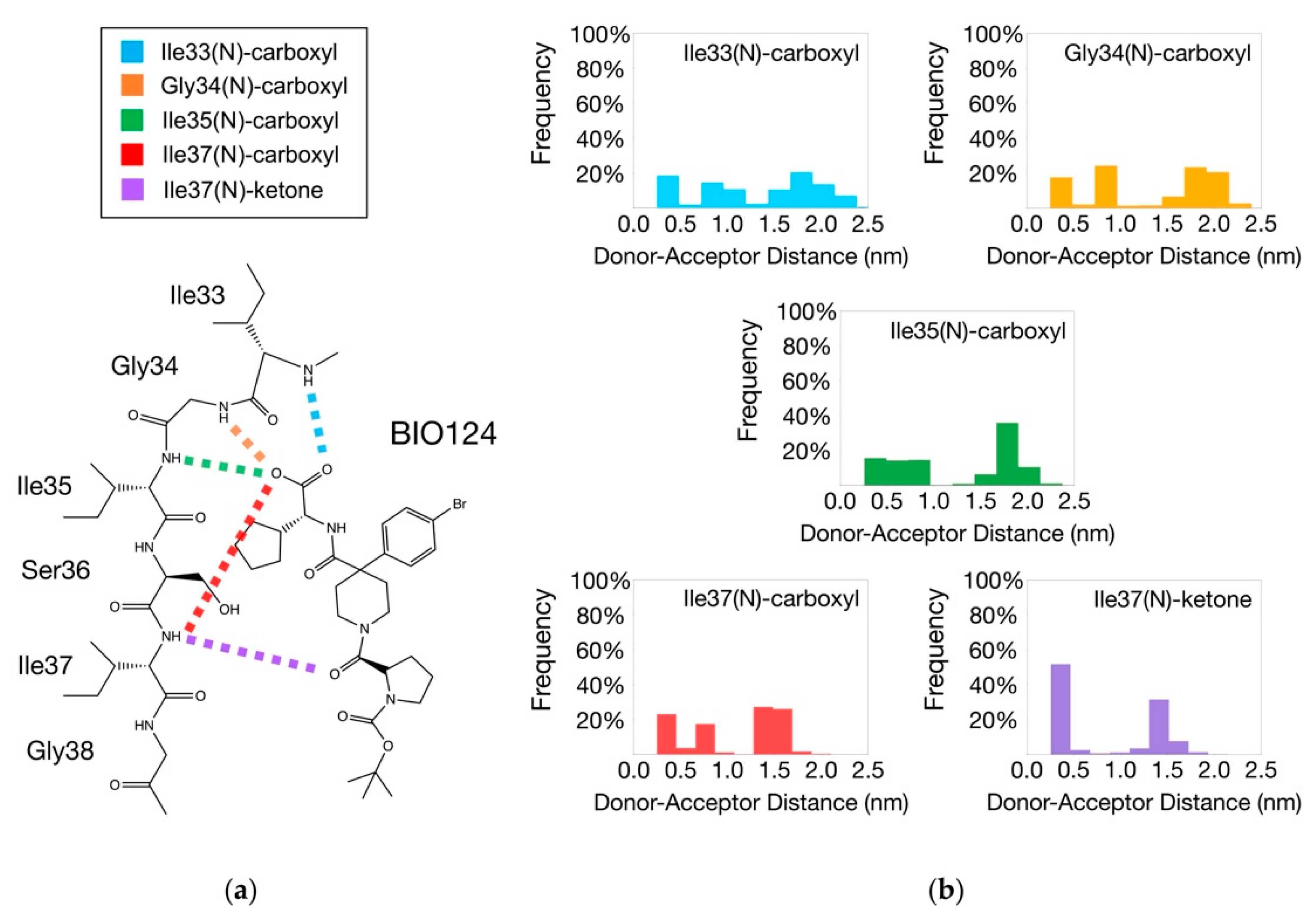
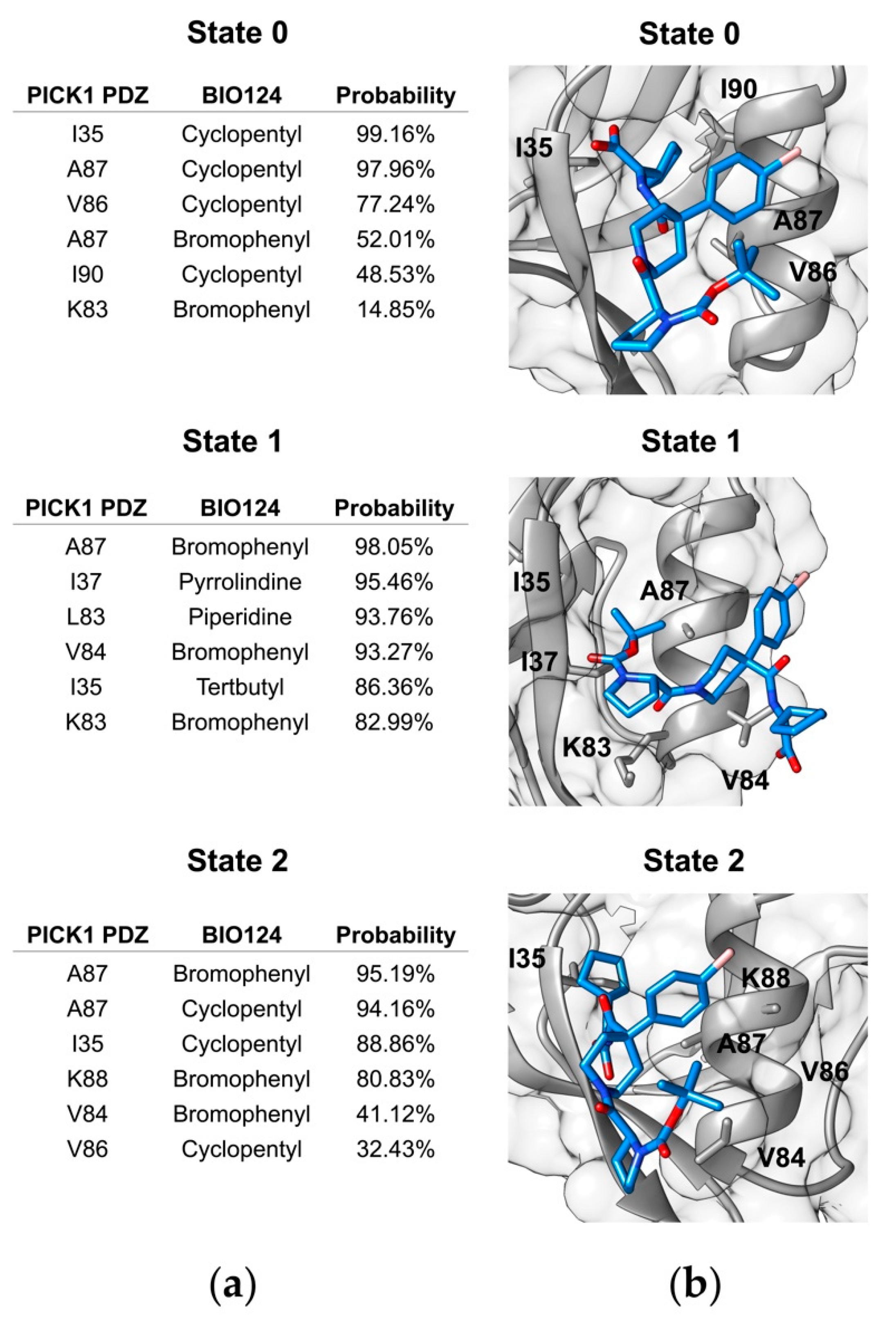
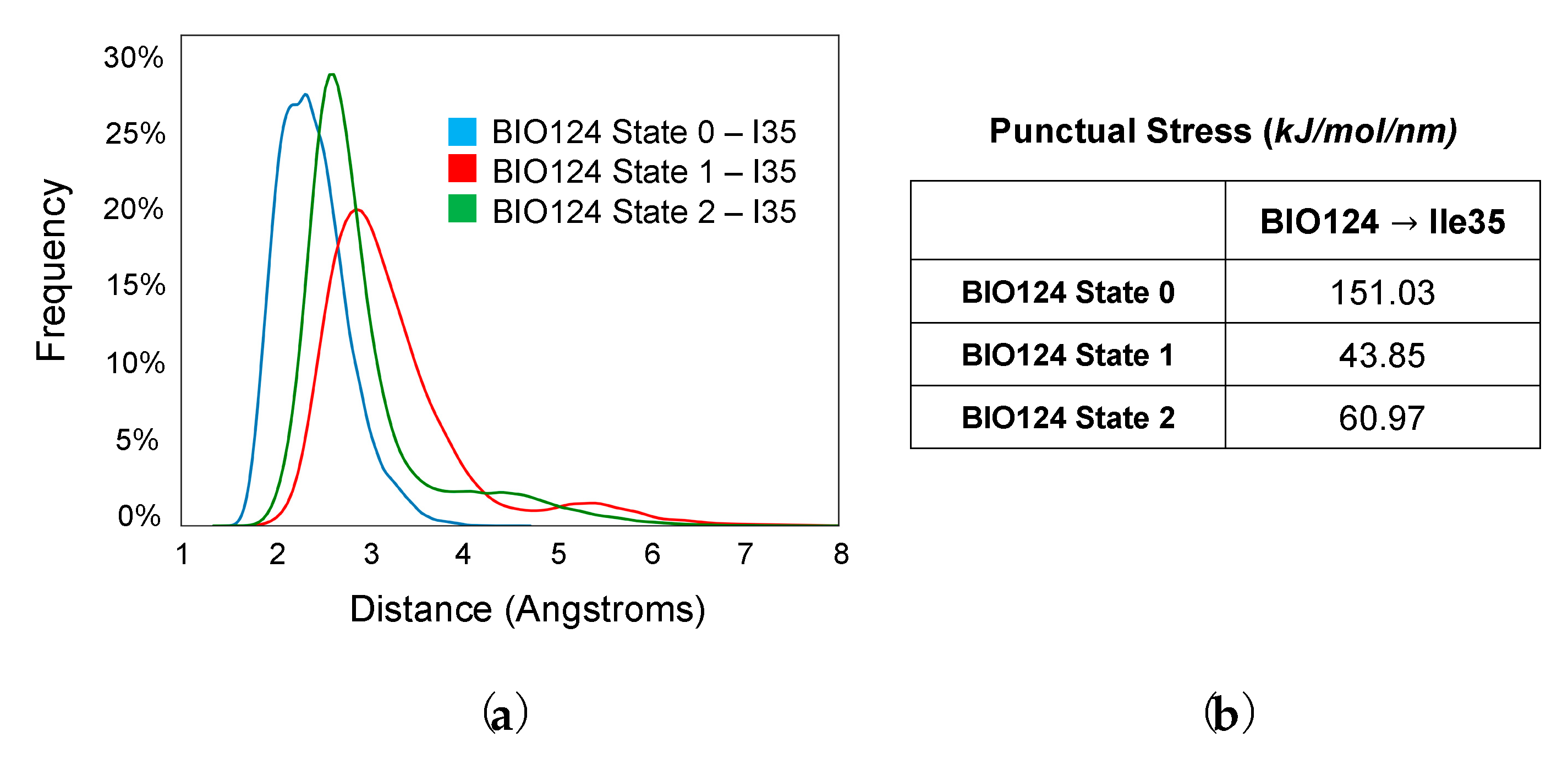
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kennedy, M.B. Origin of PDZ (DHR, GLGF) domains. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponting, C.P. Evidence for PDZ domains in bacteria, yeast, and plants. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabral, J.H.M.; Petosa, C.; Sutcliffe, M.J.; Raza, S.; Byron, O.; Poy, F.; Marfatia, S.M.; Chishti, A.H.; Liddington, R.C. Crystal structure of a PDZ domain. Nature 1996, 382, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ham, M.; Hendriks, W. PDZ domains—Glue and guide. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2003, 30, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Sheng, M. PDZ domain proteins of synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhang, M. Structures and target recognition modes of PDZ domains: Recurring themes and emerging pictures. Biochem. J. 2013, 455, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, K.; Charbonnier, S.; Travé, G. The emerging contribution of sequence context to the specificity of protein interactions mediated by PDZ domains. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2648–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, B.Z.; Lim, W.A. Mechanisma and role of PDZ domains in signaling complex assembly. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3219–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakeman, P.R.; Lanahan, A.A.; O’Brien, R.; Roche, K.; Barnes, C.A.; Huganir, R.L.; Worley, P.F. Homer: A protein that selectively binds metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature 1997, 386, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, G.; Von Zastrow, M.; Friedman, P.A. Role of PDZ Proteins in Regulating Trafficking, Signaling, and Function of GPCRs. Means, Motif, and Opportunity. Adv. Pharmacol. 2011, 62, 279–314. [Google Scholar]
- Tonikian, R.; Zhang, Y.; Sazinsky, S.L.; Currell, B.; Yeh, J.H.; Reva, B.; Held, H.A.; Appleton, B.A.; Evangelista, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. A Specificity Map for the PDZ Domain Family. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doyle, D.A.; Lee, A.; Lewis, J.; Kim, E.; Sheng, M.; MacKinnon, R. Crystal structures of a complexed and peptide-free membrane protein- binding domain: Molecular basis of peptide recognition by PDZ. Cell 1996, 85, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dev, K.K. Making protein interactions druggable: Targeting PDZ domains. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.X.; Lee, H.J.; Zheng, J.J. Therapeutic use of PDZ protein-protein interaction antagonism. Drug News Perspect. 2008, 21, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.N.; Bach, A.; Strømgaard, K.; Gianni, S.; Jemth, P. Ligand binding by PDZ domains. BioFactors 2012, 38, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saupe, J.; Roske, Y.; Schillinger, C.; Kamdem, N.; Radetzki, S.; Diehl, A.; Oschkinat, H.; Krause, G.; Heinemann, U.; Rademann, J. Discovery, structure–activity relationship studies, and crystal structure of nonpeptide inhibitors bound to the Shank3 PDZ domain. ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisurek, M.; Rupp, B.; Wichard, J.; Neuenschwander, M.; Von Kries, J.P.; Frank, R.; Rademann, J.; Kühne, R. Design of chemical libraries with potentially bioactive molecules applying a maximum common substructure concept. Mol. Divers. 2010, 14, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, J.; Shi, D.L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J. Identification of a specific inhibitor of the Dishevelled PDZ domain. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 15495–15503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Zhang, X.; Bao, J.; Cassell, R.; Zheng, J.J. Synthesis of Potent Dishevelled PDZ Domain Inhibitors Guided by Virtual Screening and NMR Studies. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 79, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; You, L.; Xu, Z.; Uematsu, K.; Shan, J.; He, B.; Mikami, I.; Edmondson, L.R.; Neale, G.; Zheng, J.; et al. An antagonist of dishevelled protein-protein interaction suppresses β-catenin–dependent tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahindroo, N.; Punchihewa, C.; Bail, A.M.; Fujii, N. Indole-2-amide based biochemical antagonist of Dishevelled PDZ domain interaction down-regulates Dishevelled-driven Tcf transcriptional activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandy, D.; Shan, J.; Zhang, X.; Rao, S.; Akunuru, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Alpatov, I.; Zhang, X.A.; Lang, R.A.; et al. Discovery and characterization of a small molecule inhibitor of the PDZ domain of dishevelled. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 16256–16263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.; Ma, S.L.; Kim, H.Y.; Yun, J.H.; Heo, J.N.; Lee, W.; Choi, K.Y.; No, K.T. Identification of small-molecule compounds targeting the dishevelled PDZ domain by virtual screening and binding studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 3259–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Choi, J.; Jin, X.; Kim, H.Y.; Yun, J.H.; Lee, W.; Choi, K.Y.; No, K.T. Discovery of a small-molecule inhibitor of Dvl–CXXC5 interaction by computational approaches. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2018, 32, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yeh, S.; Appleton, B.A.; Held, H.A.; Kausalya, P.J.; Phua, D.C.Y.; Wong, W.L.; Lasky, L.A.; Wiesmann, C.; Hunziker, W.; et al. Convergent and Divergent Ligand Specificity among PDZ Domains of the LAP and Zonula Occludens (ZO) Families. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22299–22311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kegelman, T.P.; Wu, B.; Das, S.K.; Talukdar, S.; Beckta, J.M.; Hu, B.; Emdad, L.; Valerie, K.; Sarkar, D.; Furnari, F.B.; et al. Inhibition of radiation-induced glioblastoma invasion by genetic and pharmacological targeting of MDA-9/Syntenin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrido-Urbani, S.; Garg, P.; Ghossoub, R.; Arnold, R.; Lembo, F.; Sundell, G.N.; Kim, P.M.; Lopez, M.; Zimmermann, P.; Sidhu, S.S.; et al. Proteomic peptide phage display uncovers novel interactions of the PDZ1-2 supramodule of syntenin. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grillo-Bosch, D.; Choquet, D.; Sainlos, M. Inhibition of PDZ domain-mediated interactions. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2013, 10, e531–e540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapchak, P.A.; Zhang, H.J. (Eds.) Neuroprotective Therapy for Stroke and Ischemic Disease; Springer: Cham, The Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballarin, B.; Tymianski, M. Discovery and development of NA-1 for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bach, A.; Clausen, B.H.; Møller, M.; Vestergaard, B.; Chi, C.N.; Round, A.; Sørensen, P.L.; Nissen, K.B.; Kastrup, J.S.; Gajhede, M.; et al. A high-affinity, dimeric inhibitor of PSD-95 bivalently interacts with PDZ1-2 and protects against ischemic brain damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcotte, D.J.; Hus, J.-C.C.; Banos, C.C.; Wildes, C.; Arduini, R.; Bergeron, C.; Hession, C.A.; Baker, D.P.; Lin, E.; Guckian, K.M.; et al. Lock and chop: A novel method for the generation of a PICK1 PDZ domain and piperidine-based inhibitor co-crystal structure. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, E.Y.S.; Silvian, L.F.; Marcotte, D.J.; Banos, C.C.; Jow, F.; Chan, T.R.; Arduini, R.M.; Qian, F.; Baker, D.P.; Bergeron, C.; et al. Potent PDZ-Domain PICK1 Inhibitors that Modulate Amyloid Beta-Mediated Synaptic Dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsen, T.S.; Madsen, K.L.; Dyhring, T.; Bach, A.; Peters, D.; Stromgaard, K.; Gether, U. A Fluorescence Polarization Based Screening Assay for Identification of Small Molecule Inhibitors of the PICK1 PDZ Domain. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2011, 14, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daw, M.I.; Chittajallu, R.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Dev, K.K.; Duprat, F.; Henley, J.M.; Collingridge, G.L.; Isaac, J.T. PDZ proteins interacting with C-terminal GluR2/3 are involved in a PKC-dependent regulation of AMPA receptors at hippocampal synapses. Neuron 2000, 28, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsen, M.L.; Thorsen, T.S.; Johner, N.; Ammendrup-Johnsen, I.; Erlendsson, S.; Tian, X.; Simonsen, J.B.; Høiberg-Nielsen, R.; Christensen, N.M.; Khelashvili, G.; et al. Structure of Dimeric and Tetrameric Complexes of the BAR Domain Protein PICK1 Determined by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. Structure 2015, 23, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanley, J.G. PICK1: A multi-talented modulator of AMPA receptor trafficking. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 118, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, K.L.; Thorsen, T.S.; Rahbek-Clemmensen, T.; Eriksen, J.; Gether, U. Protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) reduces reinsertion rates of interaction partners sorted to Rab11-dependent slow recycling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12293–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dev, K.K.; Nishimune, A.; Henley, J.M.; Nakanishi, S. The protein kinase Cα binding protein PICK1 interacts with short but not long form alternative splice variants of AMPA receptor subunits. Neuropharmacology 1999, 38, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ziff, E.B. PICK1 interacts with ABP/GRIP to regulate AMPA receptor trafficking. Neuron 2005, 47, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocca, D.L.; Martin, S.; Jenkins, E.L.; Hanley, J.G. Inhibition of Arp2/3-mediated actin polymerization by PICK1 regulates neuronal morphology and AMPA receptor endocytosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bjerggaard, C.; Fog, J.U.; Hastrup, H.; Madsen, K.; Loland, C.J.; Javitch, J.A.; Gether, U. Surface targeting of the dopamine transporter involves discrete epitopes in the distal C terminus but does not require canonical PDZ domain interactions. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7024–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.N.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y. Multiple faces of protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1): Structure, function, and diseases. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 98, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsen, T.S.; Madsen, K.L.; Rebola, N.; Rathje, M.; Anggono, V.; Bach, A.; Moreira, I.S.; Stuhr-Hansen, N.; Dyhring, T.; Peters, D.; et al. Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor of the PICK1 PDZ domain that inhibits hippocampal LTP and LTD. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Famous, K.R.; Kumaresan, V.; Sadri-Vakili, G.; Schmidt, H.D.; Mierke, D.F.; Cha, J.-H.J.; Pierce, R.C. Phosphorylation-dependent trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors in the nucleus accumbens plays a critical role in the reinstatement of cocaine seeking. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11061–11070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.; De Luca, M.; Wolfheimer, J.; Hernandez, N.; Madsen, K.L.; Schmidt, H.D. Administration of a novel high affinity PICK1 PDZ domain inhibitor attenuates cocaine seeking in rats. Neuropharmacology 2020, 164, 107901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, N.R.; De Luca, M.; Lever, M.B.; Richner, M.; Hansen, A.B.; Noes-Holt, G.; Jensen, K.L.; Rathje, M.; Jensen, D.B.; Erlendsson, S.; et al. A high-affinity, bivalent PDZ domain inhibitor complexes PICK 1 to alleviate neuropathic pain. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e11248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, X.; Staudinger, J.; Huganir, R.L. Clustering of AMPA receptors by the synaptic PD domain-containing protein PICK1. Neuron 1999, 22, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanley, J.G.; Henley, J.M. PICK1 is a calcium-sensor for NMDA-induced AMPA receptor trafficking. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3266–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dev, K.K. PDZ domain protein-protein interactions: A case study with PICK1. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sogaard, R.; Borre, L.; Braunstein, T.H.; Madsen, K.L.; MacAulay, N. Functional Modulation of the Glutamate Transporter Variant GLT1b by the PDZ Domain Protein PICK1. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20195–20207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfonso, S.; Kessels, H.W.; Banos, C.C.; Chan, T.R.; Lin, E.T.; Kumaravel, G.; Scannevin, R.H.; Rhodes, K.J.; Huganir, R.; Guckian, K.M.; et al. Synapto-depressive effects of amyloid beta require PICK1. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 39, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumawat, A.; Chakrabarty, S. Hidden electrostatic basis of dynamic allostery in a PDZ domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5825–E5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhulesia, A.; Gsponer, J.; Vendruscolo, M. Mapping of two networks of residues that exhibit structural and dynamical changes upon binding in a PDZ domain protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8931–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morra, G.; Genoni, A.; Colombo, G. Mechanisms of differential allosteric modulation in homologous proteins: Insights from the analysis of internal dynamics and energetics of PDZ domains. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 5677–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Karplus, M. Signaling pathways of PDZ2 domain: A molecular dynamics interaction correlation analysis. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2009, 74, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalescky, R.; Liu, J.; Tao, P. Identifying key residues for protein allostery through rigid residue scan. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Rauscher, S.; Nawrocki, G.; Ran, T.; Feig, M.; de Groot, B.L.; Grubmüller, H.; MacKerell, A.D. CHARMM36m: An improved force field for folded and intrinsically disordered proteins. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.C.; van der Spoel, D.; van Drunen, R. GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páll, S.; Abraham, M.J.; Kutzner, C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E.; Pall, S.; Abraham, M.J.; Kutzner, C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. Tackling Exascale Software Challenges in Molecular Dynamics Simulations with GROMACS. In Solving Software Challenges for Exascale: International Conference on Exascale Applications and Software, EASC 2014, Stockholm, Sweden, 2–3 April 2014, Revised Selected Papers; Markidis, S., Laure, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 8759, pp. 3–27. ISBN 978-3-319-15976-8. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindah, E.; Páall, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; et al. Gromacs: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nose, S. A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoover, W.G. Canonical dynamics: Equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 1695–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCammon, J.A.; Harvey, S.C. Dynamics of Proteins and Nucleic Acids; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987; ISBN 9781139167864. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, M.E.J.; Girvan, M. Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2004, 69, 026113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, B.J.; Rodrigues, A.P.C.; ElSawy, K.M.; McCammon, J.A.; Caves, L.S.D. Bio3d: An R package for the comparative analysis of protein structures. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2695–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skjaerven, L.; Yao, X.Q.; Scarabelli, G.; Grant, B.J. Integrating protein structural dynamics and evolutionary analysis with Bio3D. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, B.J.; Skjærven, L.; Yao, X.Q. The Bio3D packages for structural bioinformatics. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costescu, B.I.; Gräter, F. Time-resolved force distribution analysis. BMC Biophys. 2013, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.; Wu, H.; Shen, C.; Shi, Y.; Jin, W.; Xia, J.; Zhang, M. Clustering and synaptic targeting of PICK1 requires direct interaction between the PDZ domain and lipid membranes. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4576–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.O.; He, Y. Allosterism in the PDZ Family. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin Jr, R.N.; Poelwijk, F.J.; Raman, A.; Gosal, W.S.; Ranganathan, R. The spatial architecture of protein function and adaptation. Nature 2012, 491, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walma, T.; Spronk, C.A.E.M.; Tessari, M.; Aelen, J.; Schepens, J.; Hendriks, W.; Vuister, G.W. Structure, dynamics and binding characteristics of the second PDZ domain of PTP-BL. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 316, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, N.; Agard, D.A. Intramolecular signaling pathways revealed by modeling anisotropic thermal diffusion. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 351, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, E.J.; Gilmore, S.A.; Mauldin, R.V.; Lee, A.L. Evaluation of Energetic and Dynamic Coupling Networks in a PDZ Domain Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 351, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, B.K.; Agard, D.A. Conserved tertiary couplings stabilize elements in the PDZ fold, leading to characteristic patterns of domain conformational flexibility. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Q.-S.; Wang, C.-H.; Liao, S.-M.; Huang, R.-B. Correlation Analysis for Protein Evolutionary Family Based on Amino Acid Position Mutations and Application in PDZ Domain. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerek, Z.N.; Ozkan, S.B. Change in allosteric network affects binding affinities of PDZ domains: Analysis through perturbation response scanning. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, 1002154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilia, E.; Vuister, G.W.; Lenaerts, T. Accurate Prediction of the Dynamical Changes within the Second PDZ Domain of PTP1e. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, 1002794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lockless, S.W.; Ranganathan, R. Evolutionarily conserved pathways of energetic connectivity in protein families. Science 1999, 286, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gianni, S.; Walma, T.; Arcovito, A.; Calosci, N.; Bellelli, A.; Engström, Å.; Travaglini-Allocatelli, C.; Brunori, M.; Jemth, P.; Vuister, G.W. Demonstration of Long-Range Interactions in a PDZ Domain by NMR, Kinetics, and Protein Engineering. Structure 2006, 14, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erlendsson, S.; Rathje, M.; Heidarsson, P.O.; Poulsen, F.M.; Madsen, K.L.; Teilum, K.; Gether, U. Protein interacting with C-kinase 1 (PICK1) binding promiscuity relies on unconventional PSD-95/discs-large/ZO-1 homology (PDZ) binding modes for nonclass II PDZ ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25327–25340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuentes, E.J.; Der, C.J.; Lee, A.L. Ligand-dependent Dynamics and Intramolecular Signaling in a PDZ Domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 335, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondi, F.; Felline, A.; Seeber, M.; Mariani, S.; Fanelli, F. A mixed protein structure network and elastic network model approach to predict the structural communication in biomolecular systems: The PDZ2 domain from tyrosine phosphatase 1E as a case study. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 2504–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stevens, A.O.; Luo, S.; He, Y. Three Binding Conformations of BIO124 in the Pocket of the PICK1 PDZ Domain. Cells 2022, 11, 2451. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11152451
Stevens AO, Luo S, He Y. Three Binding Conformations of BIO124 in the Pocket of the PICK1 PDZ Domain. Cells. 2022; 11(15):2451. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11152451
Chicago/Turabian StyleStevens, Amy O., Samuel Luo, and Yi He. 2022. "Three Binding Conformations of BIO124 in the Pocket of the PICK1 PDZ Domain" Cells 11, no. 15: 2451. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11152451
APA StyleStevens, A. O., Luo, S., & He, Y. (2022). Three Binding Conformations of BIO124 in the Pocket of the PICK1 PDZ Domain. Cells, 11(15), 2451. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11152451






