Host HSPD1 Translocation from Mitochondria to the Cytoplasm Induced by Streptococcus suis Serovar 2 Enolase Mediates Apoptosis and Loss of Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Bacterial Strains, Culture Conditions, and Plasmids
2.3. Recombinant Proteins HSPD1 and Eno
2.4. Cell Cultures and Infection Experiments In Vitro
2.5. Annexin V-FITC/PI Staining for Apoptosis Detection
2.6. Analysis of Expression and Distribution of HSPD1 Treated with Eno
2.7. Detection of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Marker JC-1
2.8. Expression of Genes Encoding Permeability Transformation Channel Proteins
2.9. Cell Transfection
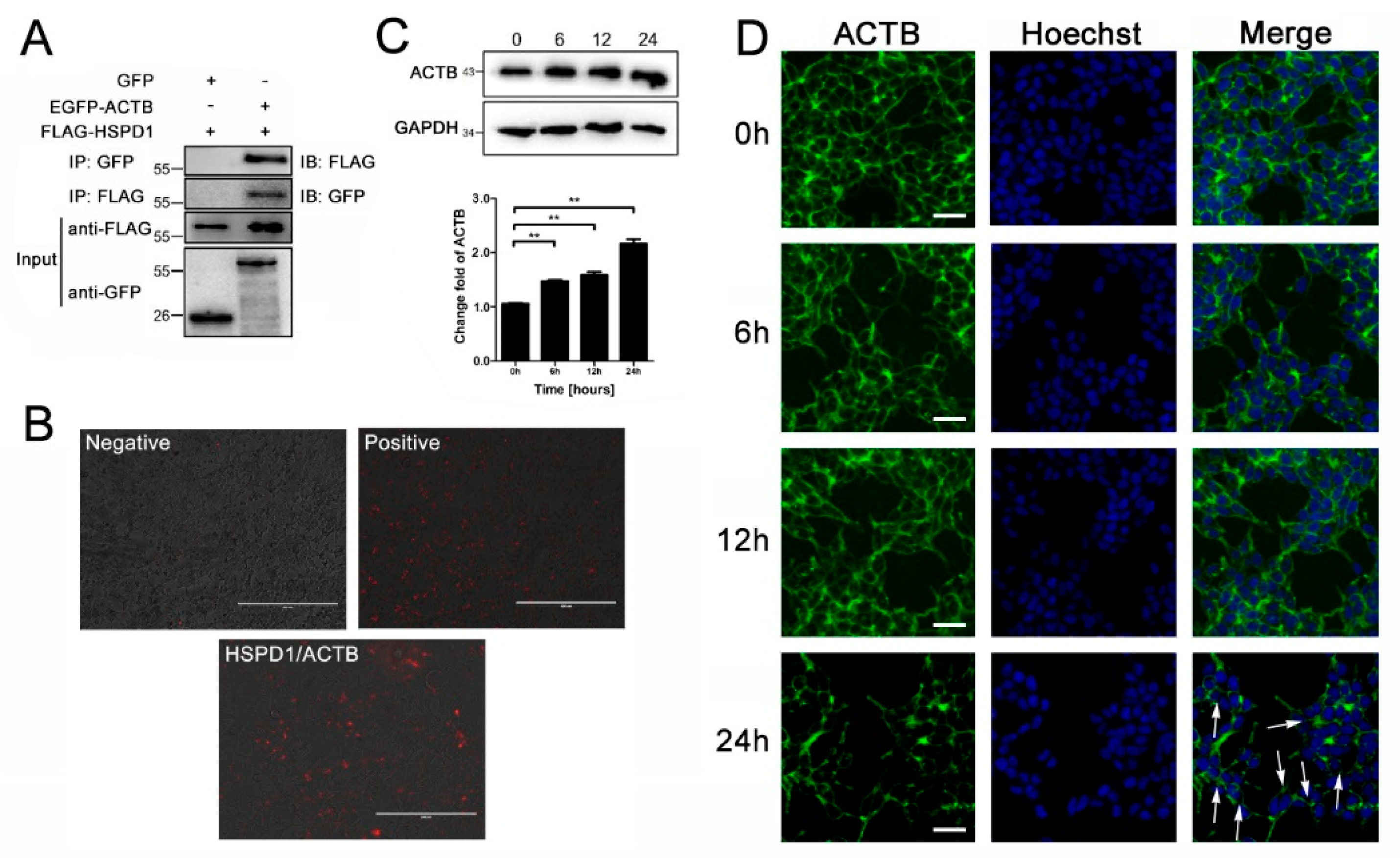
2.10. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of HSPD1 and ACTB
2.11. HSPD1 Knockdown Using siRNA
2.12. Western Blotting
2.13. Establishment and Assessment of the In Vitro BBB Model
2.14. Assessment of the Permeability of BBB Using Evans Blue (EB) Dye
2.15. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Brain Tissues
2.16. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
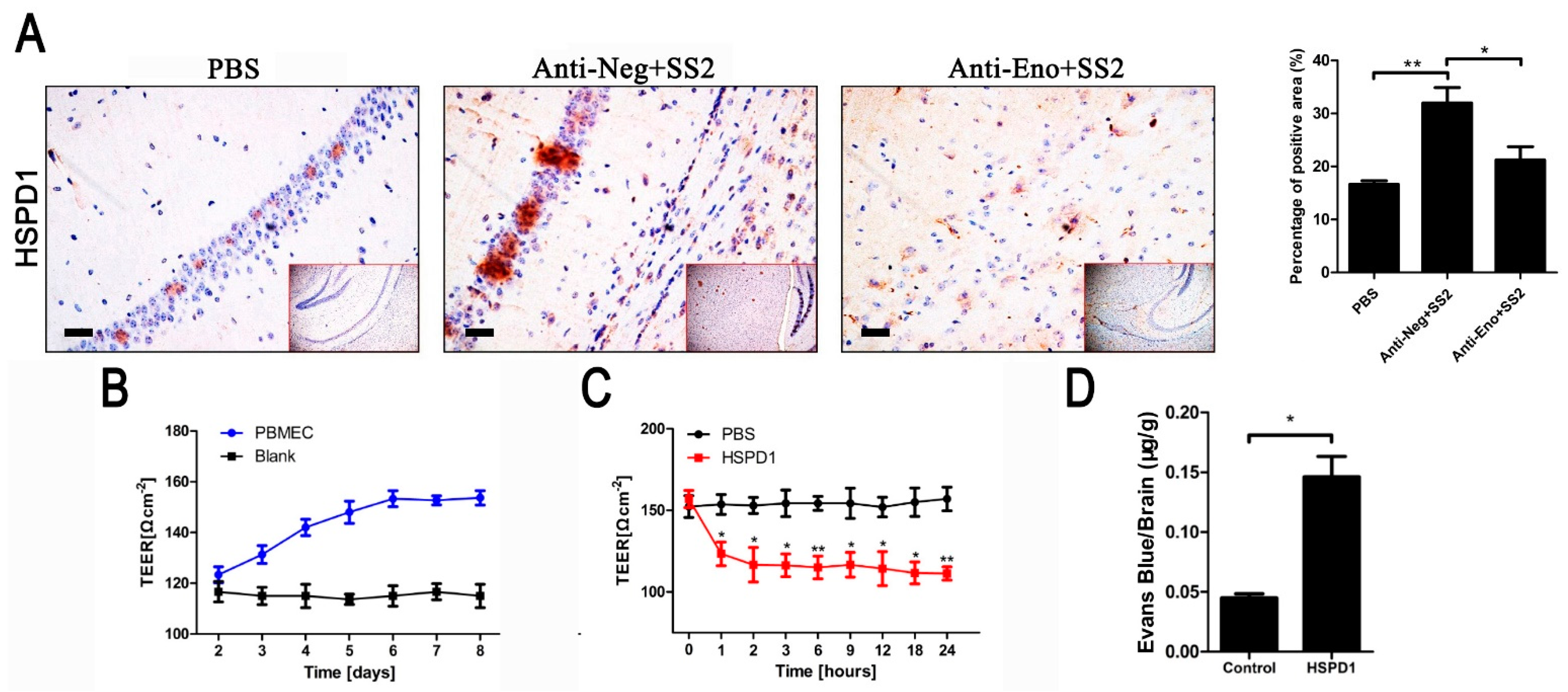
3.1. HSPD1 Enhances BBB Permeability
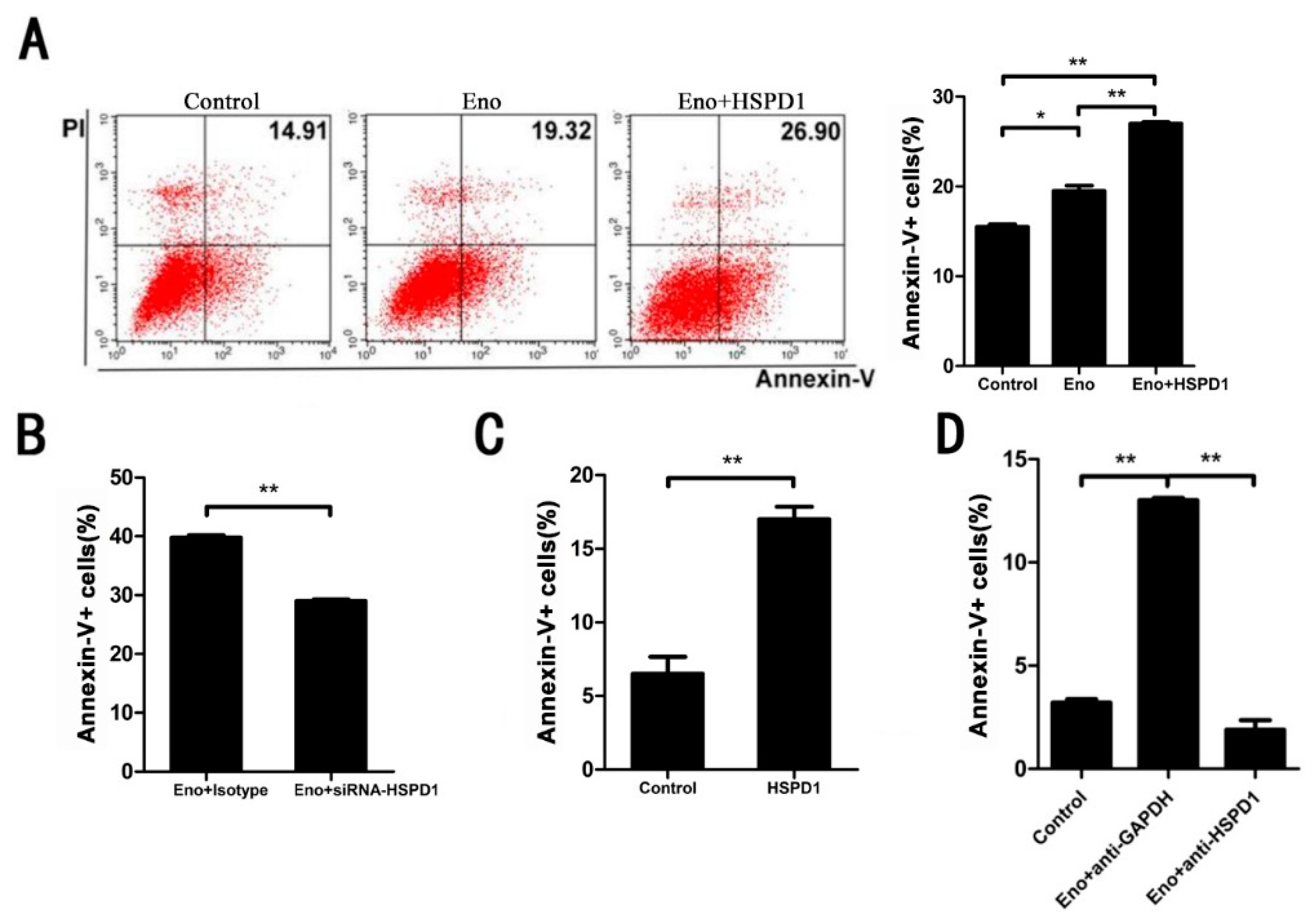
3.2. Increased HSPD1 Promotes PBMECs and 293T Cells Apoptosis
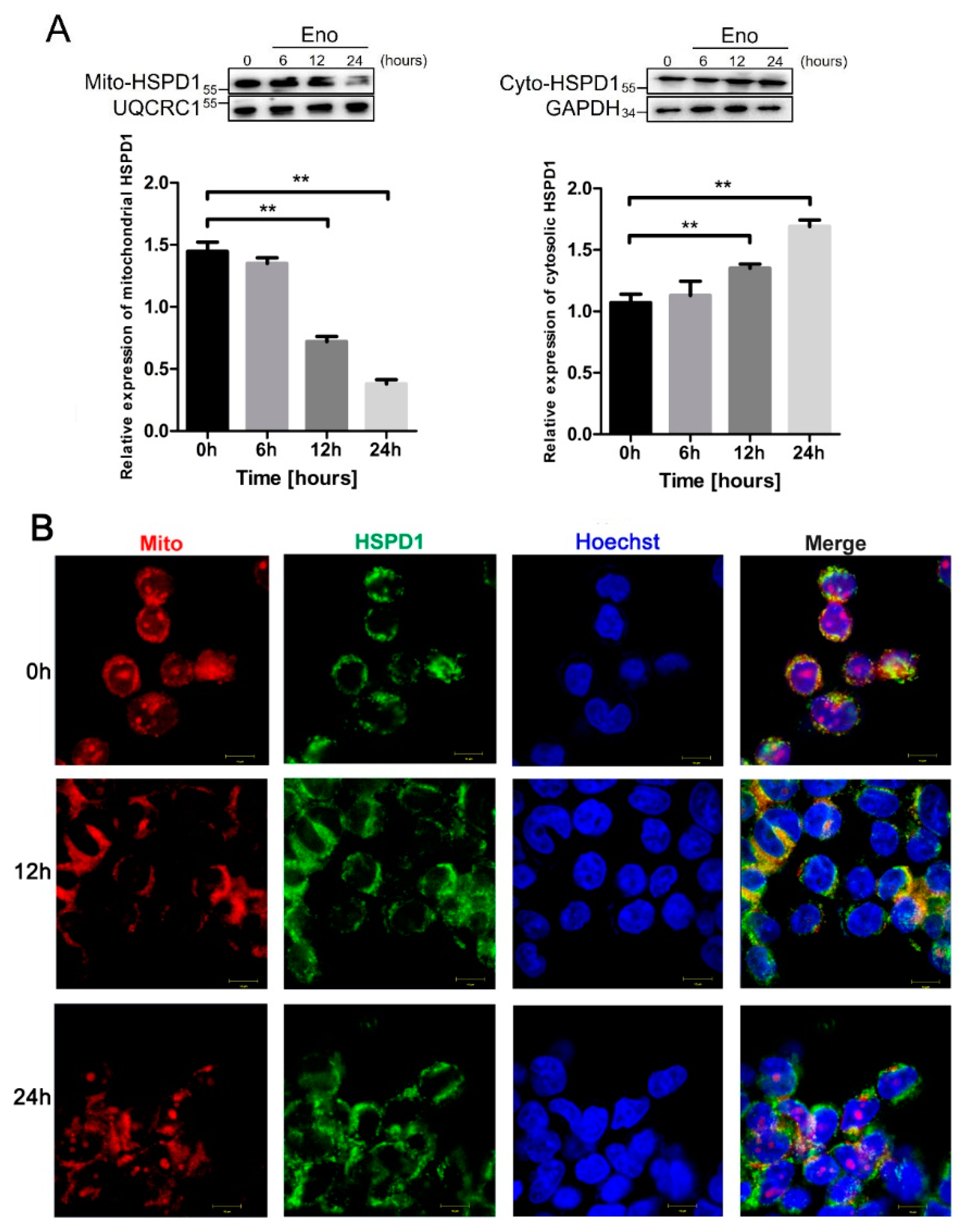
3.3. HSPD1 Translocates from Mitochondria into the Cytoplasm after Eno Treatment
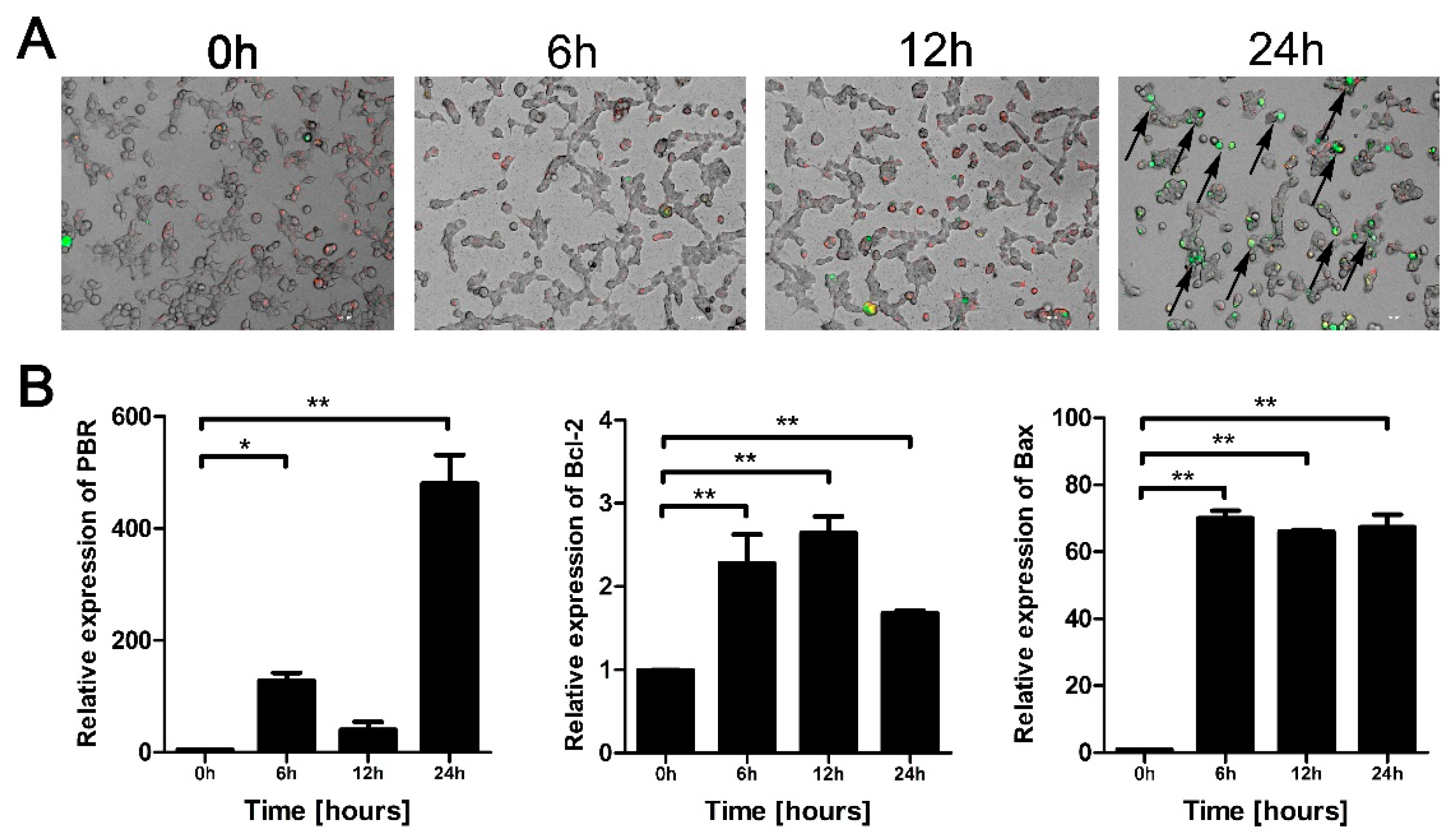
3.4. Eno Increases the Permeability of the Mitochondrial Membrane
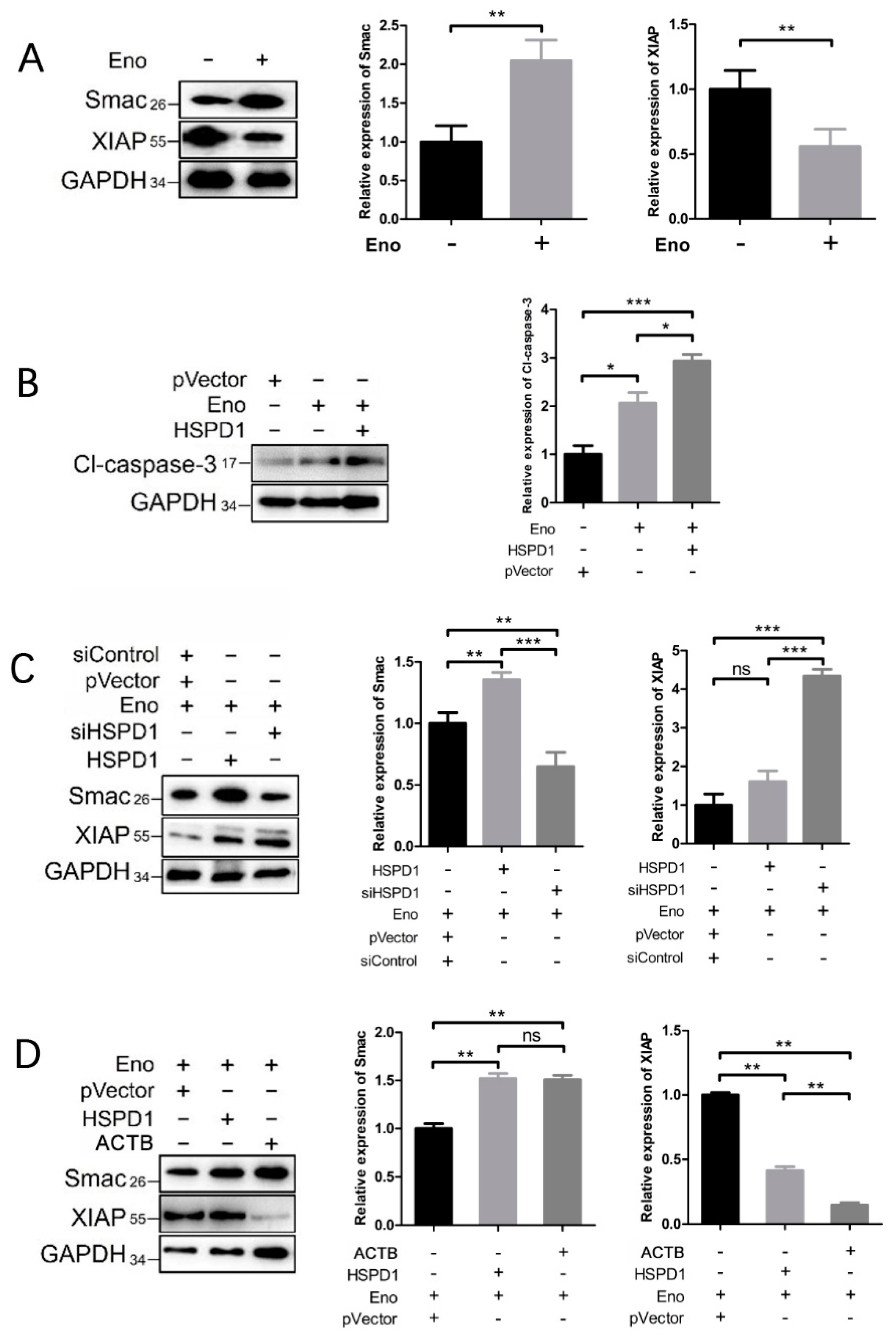
3.5. ACTB Is Increased after Eno Treatment and Interacts with Translocated HSPD1 in the Cytoplasm
3.6. HSPD1 Induces Apoptosis via the Smac-XIAP-Caspase-3 Pathway by Binding to ACTB
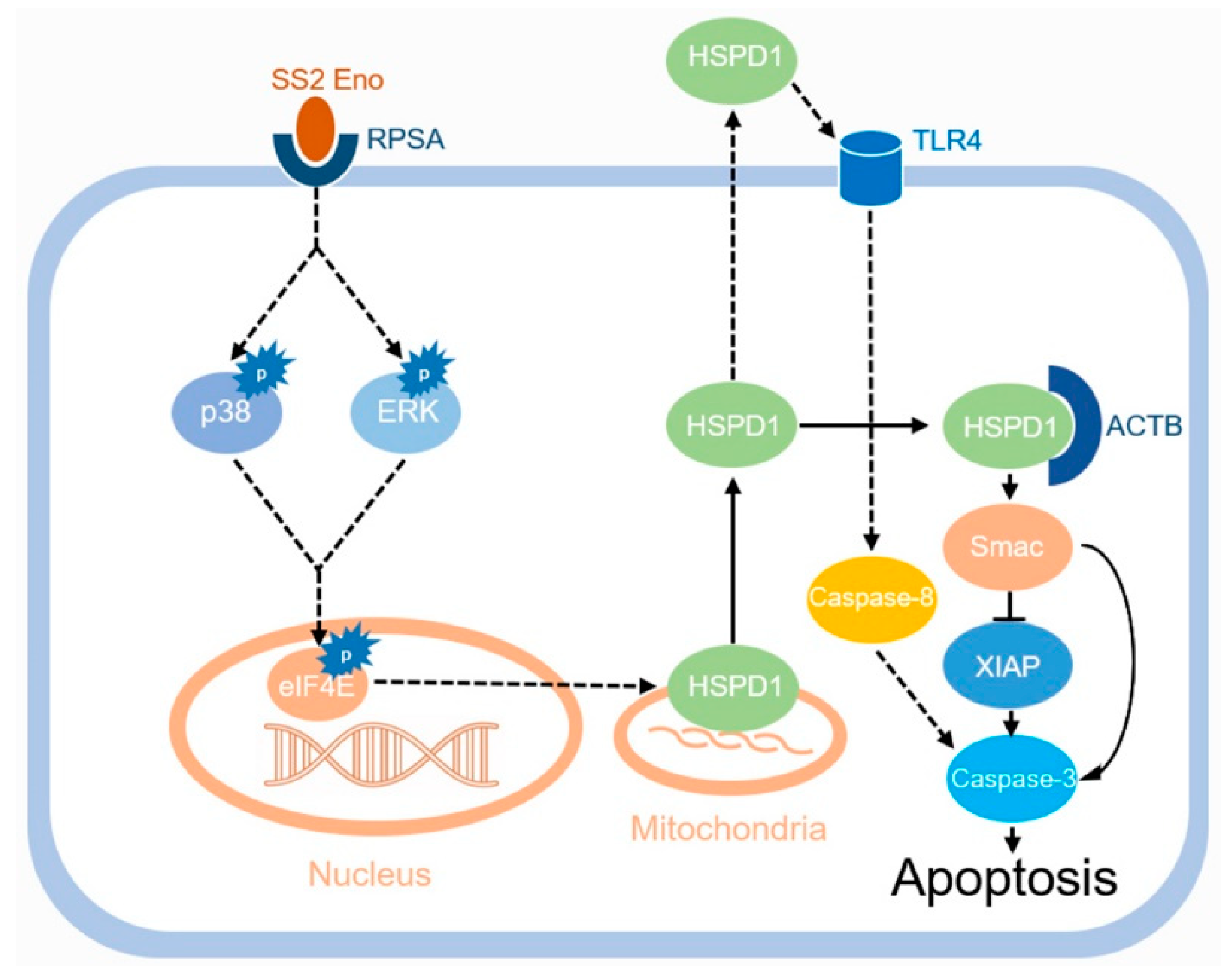
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SS2 | Streptococcus suis serotype 2 |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| Eno | Enolase |
| HSPD1 | Heat shock protein family D member 1 |
| PBMEC | Porcine brain microvascular endothelial cell |
| ACTB | β-actin |
| BCSFB | Blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier |
| PCPECs | Porcine choroid plexus epithelial cell |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| qPCR | Fluorescence quantitative PCR |
| Co-IP | Co-immunoprecipitation |
| TEER | Transendothelial cell electric resistance |
| EB | Evans blue |
| CFU | Colony-forming unit |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| PTP | Permeability transition pore protein |
| BiFC | Bimolecular fluorescence complementary |
| Smac | Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases |
| XIAP | X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein |
References
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M.; Xu, J. Streptococcus suis infections in humans: The Chinese experience and the situation in North America. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2007, 8, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.; Grenier, D. Understanding the virulence of Streptococcus suis: A veterinary, medical, and economic challenge. Med. Mal. Infect. 2018, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejace, J.; Bagley, P.; Wood, E. Streptococcus suis meningitis can require a prolonged treatment course. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mai, N.T.H.; Hoa, N.T.; Nga, T.V.T.; Linh, L.D.; Chau, T.T.H.; Sinh, D.X.; Phu, N.H.; Van Chuong, L.; Diep, T.S.; Campbell, J.; et al. Streptococcus suis Meningitis in Adults in Vietnam. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, S.S.; De Almeida, J.C.; Abrunhosa, J.; Sousa, C.A.E.; Arshad, Q. Pig’s ear: Streptococcus suis Meningitis and its associated inner ear implications. IDCases 2017, 10, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Samkar, A.; Brouwer, M.C.; Schultsz, C.; Van Der Ende, A.; van de Beek, D. Streptococcus suis Meningitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, S.R.; Macedo-Ramos, H.; Santos, F.; Quadros-De-Souza, L.; Paiva, M.; Pinto, T.; Teixeira, L.; Baetas-Da-Cruz, W. Streptococcus pneumoniae infection regulates expression of neurotrophic factors in the olfactory bulb and cultured olfactory ensheathing cells. Neuroscience 2016, 317, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenbaum, T.; Papandreou, T.; Gellrich, D.; Friedrichs, U.; Seibt, A.; Adam, R.; Wewer, C.; Galla, H.-J.; Schwerk, C.; Schroten, H. Polar bacterial invasion and translocation ofStreptococcus suisacross the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrierin vitro. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The Blood–Brain Barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, M.M.J.; Desa, M.N.M. Mechanisms of Blood Brain Barrier Disruption by Different Types of Bacteria, and Bacterial–Host Interactions Facilitate the Bacterial Pathogen Invading the Brain. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 1349–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canback, B.; Andersson, S.G.E.; Kurland, C.G. The global phylogeny of glycolytic enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6097–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Pan, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Shao, Z.; Ge, J.; Zheng, F.; et al. Streptococcus suisEnolase Functions as a Protective Antigen Displayed on the Bacterial Cell Surface. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Xia, X.; Sun, C.; Feng, X.; Gu, J.; Du, C.; et al. Enolase of Streptococcus Suis Serotype 2 Enhances Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability by Inducing IL-8 Release. Inflammation 2016, 39, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lei, S.; Jia, L.; Xia, X.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, R.; Li, S.; Qu, G.; Gu, J.; et al. Streptococcus suis serotype 2 enolase interaction with host brain microvascular endothelial cells and RPSA-induced apoptosis lead to loss of BBB integrity. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyżewski, Z.; Gregorczyk, K.P.; Szczepanowska, J.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L. Functional role of Hsp60 as a positive regulator of human viral infection progression. Acta Virol. 2018, 62, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füst, G.; Beck, Z.; Bánhegyi, D.; Kocsis, J.; Bíró, A.; Prohászka, Z. Antibodies against heat shock proteins and cholesterol in HIV infection. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kanai, F.; Kawakami, T.; Tateishi, K.; Ijichi, H.; Kawabe, T.; Arakawa, Y.; Kawakami, T.; Nishimura, T.; Shirakata, Y.; et al. Interaction of the hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) with heat shock protein 60 enhances HBx-mediated apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Ahmad, I.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Z. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of tylosin against Streptococcus suis in pigs. BMC Veter. Res. 2018, 14, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, N.; Gu, J.; Sun, C.; Feng, X.; Han, W.; Jiang, J.X.; Lei, L. Selection of Potential Virulence Factors Contributing to Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Penetration into the Blood-Brain Barrier in an In Vitro Co-Culture Model. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wu, T.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Bao, C.; Liu, M.; Ji, Y.; Feng, X.; Gu, J.; et al. Caveolae/rafts protect human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells from Streptococcus suis serotype 2 α-enolase-mediated injury. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 254, 108981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.S.W.; Ye, Y.; Johnson, K.; Poe, J.; Johnson, S.; Bobrowski, W.; Garrido, R.; Madhu, C. Porcine Brain Microvessel Endothelial Cells as an in Vitro Model to Predict in Vivo Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petito, C.K.; Schaefer, J.A.; Plum, F. Ultrastructural characteristics of the brain and blood-brain barrier in experimental seizures. Brain Res. 1977, 127, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiserman, J.P.; Chen, L.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, S.C.; Tran, A.L.; Siebenborn, N.; Knowlton, A.A. TLR4 mutation and HSP60-induced cell death in adult mouse cardiac myocytes. Cell Stress Chaperon. 2015, 20, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-C.; Stice, J.P.; Chen, L.; Jung, J.S.; Gupta, S.; Wang, Y.; Baumgarten, G.; Trial, J.; Knowlton, A.A. Extracellular Heat Shock Protein 60, Cardiac Myocytes, and Apoptosis. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siemen, D.; Ziemer, M. What is the nature of the mitochondrial permeability transition poreand What is it Not? IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Fang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Smac, a Mitochondrial Protein that Promotes Cytochrome c–Dependent Caspase Activation by Eliminating IAP Inhibition. Cell 2000, 102, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, A.M.; Ekert, P.G.; Pakusch, M.; Silke, J.; Connolly, L.M.; Reid, G.E.; Moritz, R.L.; Simpson, R.J.; Vaux, D.L. Identification of DIABLO, a Mammalian Protein that Promotes Apoptosis by Binding to and Antagonizing IAP Proteins. Cell 2000, 102, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Guo, J.; Cheng, C.; Gu, B. Human infection caused by Streptococcus suis serotype 2 in China: Report of two cases and epidemic distribution based on sequence type. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.C.; Simpson, N.; Join-Lambert, O.; Federici, C.; Laran-Chich, M.-P.; Maïssa, N.; Bouzinba-Ségard, H.; Morand, P.C.; Chretien, F.; Taouji, S.; et al. Pathogenic Neisseria meningitidis utilizes CD147 for vascular colonization. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, S.; Carlin, A.F.; Khosravi, A.; Weiman, S.; Banerjee, A.; Quach, D.; Hightower, G.; Mitchell, T.; Doran, K.S.; Nizet, V. The surface-anchored NanA protein promotes pneumococcal brain endothelial cell invasion. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charland, N.; Nizet, V.; Rubens, C.E.; Kim, K.S.; Lacouture, S.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Interactions with Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanier, G.; Segura, M.; Friedl, P.; Lacouture, S.; Gottschalk, M. Invasion of Porcine Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells by Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Weiyi, L.; Yu, M.; Hong, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Zhe, M.; Hongjie, F. The serine/threonine protein kinase of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 affects the ability of the pathogen to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samali, A.; Cai, J.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Jones, D.P.; Orrenius, S. Presence of a pre-apoptotic complex of pro-caspase-3, Hsp60 and Hsp10 in the mitochondrial fraction of Jurkat cells. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, D.; Choy, G.; Tang, D.G. Cytosolic Accumulation of HSP60 during Apoptosis with or without Apparent Mitochondrial Release: Evidence that its pro-apoptotic or pro-survival functions involve differential interactions with caspase-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 31289–31301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcik, M.; Gibson, H.; Korneluk, R.G. XIAP: Apoptotic brake and promising therapeutic target. Apoptosis 2001, 6, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, C.; Rappa, F.; Sciumè, C.; Gammazza, A.M.; Barone, R.; Bucchieri, F.; David, S.; Curcurù, G.; Msc, C.C.B.; Pitruzzella, A.; et al. Heat shock protein 60 levels in tissue and circulating exosomes in human large bowel cancer before and after ablative surgery. Cancer 2015, 121, 3230–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, C.; Bucchieri, F.; Merendino, A.M.; Fucarino, A.; Burgio, G.; Corona, D.F.V.; Barbieri, G.; David, S.; Farina, F.; Zummo, G.; et al. The Odyssey of Hsp60 from Tumor Cells to Other Destinations Includes Plasma Membrane-Associated Stages and Golgi and Exosomal Protein-Trafficking Modalities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, F.; Gammazza, A.M.; Piccionello, A.P.; Campanella, C.; Pace, A.; De Macario, E.C.; Macario, A.J. Hsp60 chaperonopathies and chaperonotherapy: Targets and agents. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 18, 185–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, T.; Jia, L.; Lei, S.; Jiang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Langford, P.R.; Liu, H.; Lei, L. Host HSPD1 Translocation from Mitochondria to the Cytoplasm Induced by Streptococcus suis Serovar 2 Enolase Mediates Apoptosis and Loss of Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity. Cells 2022, 11, 2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132071
Wu T, Jia L, Lei S, Jiang H, Liu J, Li N, Langford PR, Liu H, Lei L. Host HSPD1 Translocation from Mitochondria to the Cytoplasm Induced by Streptococcus suis Serovar 2 Enolase Mediates Apoptosis and Loss of Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity. Cells. 2022; 11(13):2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132071
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Tong, Li Jia, Siyu Lei, Hexiang Jiang, Jianan Liu, Na Li, Paul R. Langford, Hongtao Liu, and Liancheng Lei. 2022. "Host HSPD1 Translocation from Mitochondria to the Cytoplasm Induced by Streptococcus suis Serovar 2 Enolase Mediates Apoptosis and Loss of Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity" Cells 11, no. 13: 2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132071
APA StyleWu, T., Jia, L., Lei, S., Jiang, H., Liu, J., Li, N., Langford, P. R., Liu, H., & Lei, L. (2022). Host HSPD1 Translocation from Mitochondria to the Cytoplasm Induced by Streptococcus suis Serovar 2 Enolase Mediates Apoptosis and Loss of Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity. Cells, 11(13), 2071. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132071






