Expression of Trace Amine-Associated Receptors in the Murine and Human Hippocampus Based on Public Transcriptomic Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Inclusion Criteria for Datasets
2.2. Raw Data Normalization and Analysis
2.3. Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Data
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
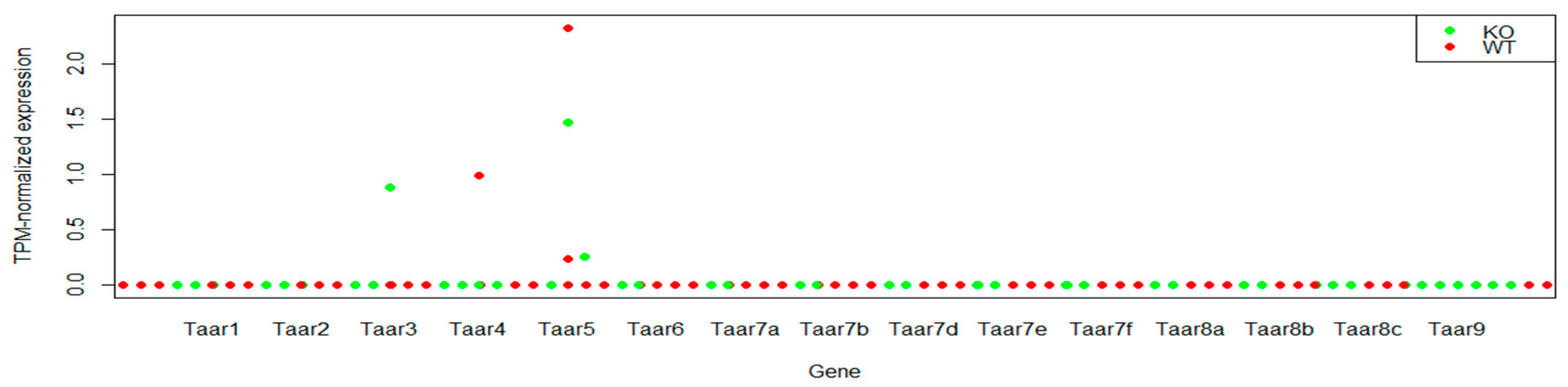
3.1. TAARs mRNA Expression in Whole Hippocampal Specimens
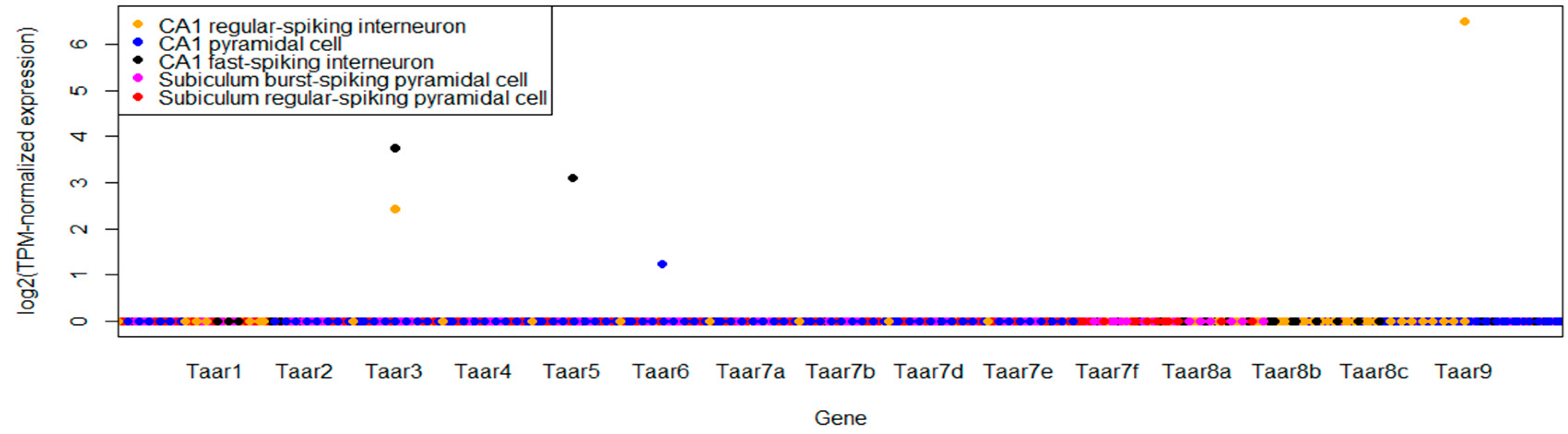
3.2. TAARs mRNA Expression in CA1 Pyramidal Cells
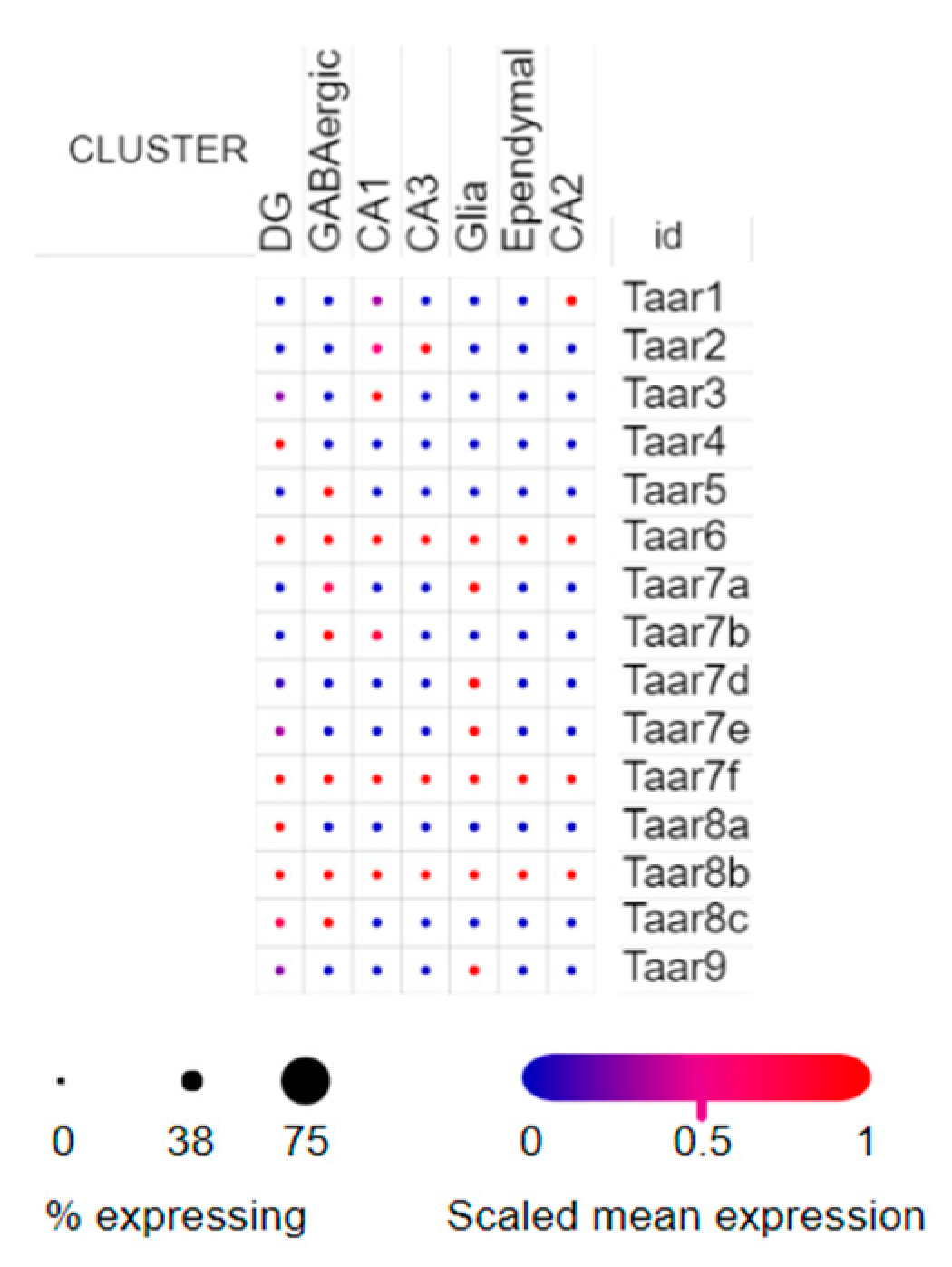
3.3. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data
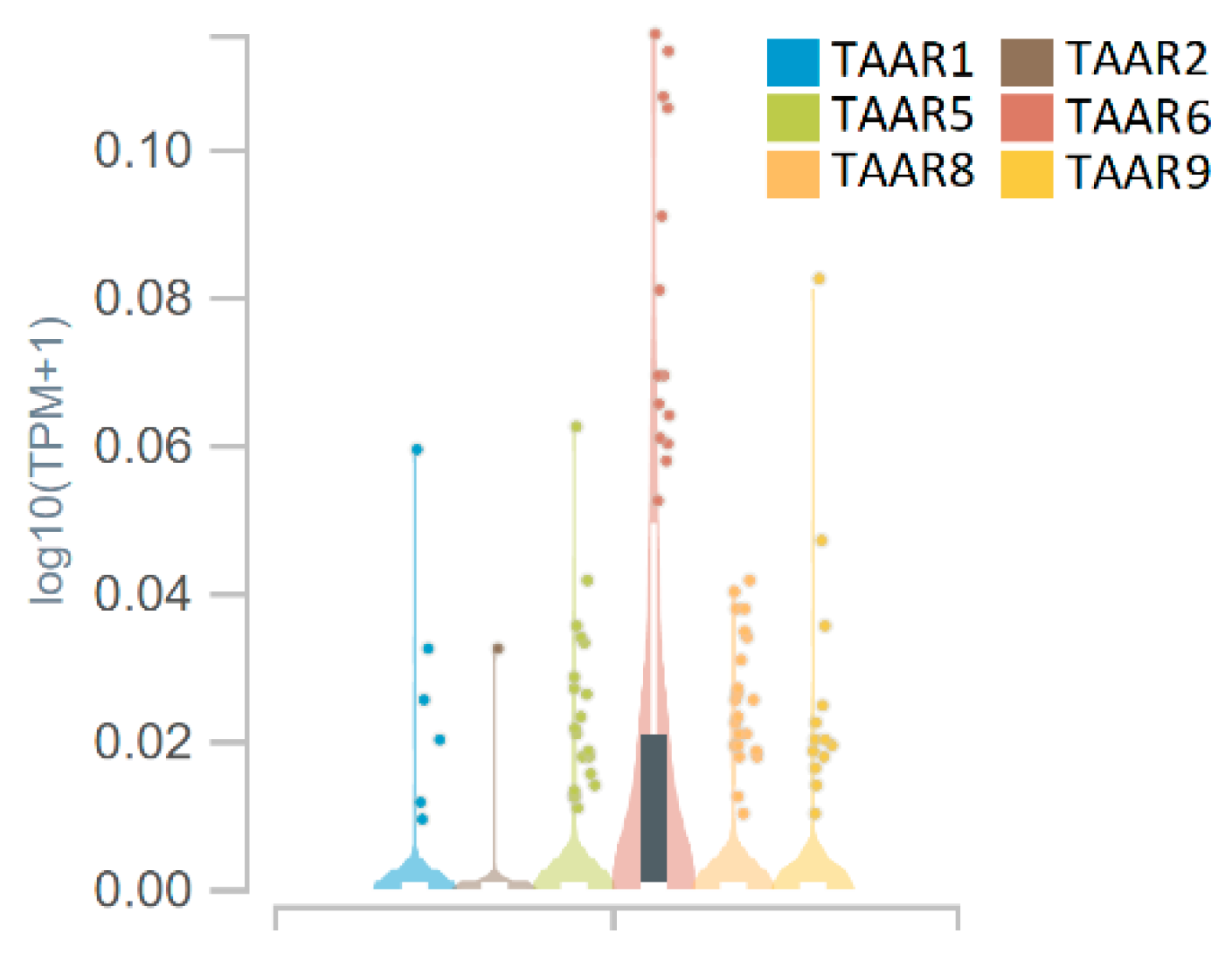
3.4. Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Data for TAARs Expression in the Human Hippocampus
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altman, J.; Das, G.D. Autoradiographic and Histological Evidence of Postnatal Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1965, 124, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.G.; Toda, T.; Gage, F.H. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: A Coming-of-Age Story. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 10401–10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.T.; Schafer, S.T.; Gage, F.H. Adult Neurogenesis in the Hippocampus: From Stem Cells to Behavior. Cell 2016, 167, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lennington, J.B.; Yang, Z.; Conover, J.C. Neural Stem Cells and the Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2003, 1, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempermann, G.; Song, H.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the Adult Hippocampus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a018812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knobloch, M.; Braun, S.M.G.; Zurkirchen, L.; von Schoultz, C.; Zamboni, N.; Araúzo-Bravo, M.J.; Kovacs, W.J.; Karalay, Ö.; Suter, U.; Machado, R.A.C.; et al. Metabolic Control of Adult Neural Stem Cell Activity by Fasn-Dependent Lipogenesis. Nature 2013, 493, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.; Berg, D.A.; Zhu, Y.; Shin, J.Y.; Song, J.; Bonaguidi, M.A.; Enikolopov, G.; Nauen, D.W.; Christian, K.M.; Ming, G.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq with Waterfall Reveals Molecular Cascades Underlying Adult Neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jhaveri, D.J.; Nanavaty, I.; Prosper, B.W.; Marathe, S.; Husain, B.F.A.; Kernie, S.G.; Bartlett, P.F.; Vaidya, V.A. Opposing Effects of A2- and β-Adrenergic Receptor Stimulation on Quiescent Neural Precursor Cell Activity and Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Singh, S.; Shukla, S. Physiological and Functional Basis of Dopamine Receptors and Their Role in Neurogenesis: Possible Implication for Parkinson’s Disease. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1179069518779829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borowsky, B.; Adham, N.; Jones, K.A.; Raddatz, R.; Artymyshyn, R.; Ogozalek, K.L.; Durkin, M.M.; Lakhlani, P.P.; Bonini, J.A.; Pathirana, S.; et al. Trace Amines: Identification of a Family of Mammalian G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8966–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunzow, J.R.; Sonders, M.S.; Arttamangkul, S.; Harrison, L.M.; Zhang, G.; Quigley, D.I.; Darland, T.; Suchland, K.L.; Pasumamula, S.; Kennedy, J.L.; et al. Amphetamine, 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine, Lysergic Acid Diethylamide, and Metabolites of the Catecholamine Neurotransmitters Are Agonists of a Rat Trace Amine Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainetdinov, R.R.; Hoener, M.C.; Berry, M.D. Trace Amines and Their Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 549–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberles, S.D. Trace Amine-Associated Receptors: Ligands, Neural Circuits, and Behaviors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Efimova, E.V.; Kozlova, A.A.; Razenkova, V.; Katolikova, N.V.; Antonova, K.A.; Sotnikova, T.D.; Merkulyeva, N.S.; Veshchitskii, A.S.; Kalinina, D.S.; Korzhevskii, D.E.; et al. Increased Dopamine Transmission and Adult Neurogenesis in Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 5 (TAAR5) Knockout Mice. Neuropharmacology 2021, 182, 108373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimova, E.V.; Katolikova, N.V.; Kanov, E.V.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Trace Amine-Associated Receptors at the Cross-Road between Innate Olfaction of Amines, Emotions, and Adult Neurogenesis. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 17, 1257–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimova, E.V.; Kuvarzin, S.R.; Mor, M.S.; Katolikova, N.V.; Shemiakova, T.S.; Razenkova, V.; Ptukha, M.; Kozlova, A.A.; Murtazina, R.Z.; Smirnova, D.; et al. Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 2 Is Expressed in the Limbic Brain Areas and Is Involved in Dopamine Regulation and Adult Neurogenesis. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 847410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, S.; Sukhanov, I.; Efimova, E.V.; Kozlova, A.; Antonova, K.A.; Illiano, P.; Leo, D.; Merkulyeva, N.; Kalinina, D.; Musienko, P.; et al. Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 5 Provides Olfactory Input Into Limbic Brain Areas and Modulates Emotional Behaviors and Serotonin Transmission. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for Functional Genomics Data Sets–Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinforma. Oxf. Engl. 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma Powers Differential Expression Analyses for RNA-Sequencing and Microarray Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodorou, I.; Moreno, P.; Manning, J.; Fuentes, A.M.-P.; George, N.; Fexova, S.; Fonseca, N.A.; Füllgrabe, A.; Green, M.; Huang, N.; et al. Expression Atlas Update: From Tissues to Single Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D77–D83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceolin, L.; Bouquier, N.; Vitre-Boubaker, J.; Rialle, S.; Severac, D.; Valjent, E.; Perroy, J.; Puighermanal, E. Cell Type-Specific MRNA Dysregulation in Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons of the Fragile X Syndrome Mouse Model. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauterborn, J.C.; Rex, C.S.; Kramár, E.; Chen, L.Y.; Pandyarajan, V.; Lynch, G.; Gall, C.M. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Rescues Synaptic Plasticity in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10685–10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Földy, C.; Darmanis, S.; Aoto, J.; Malenka, R.C.; Quake, S.R.; Südhof, T.C. Single-Cell RNAseq Reveals Cell Adhesion Molecule Profiles in Electrophysiologically Defined Neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5222–E5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Habib, N.; Li, Y.; Heidenreich, M.; Swiech, L.; Avraham-Davidi, I.; Trombetta, J.J.; Hession, C.; Zhang, F.; Regev, A. Div-Seq: Single-Nucleus RNA-Seq Reveals Dynamics of Rare Adult Newborn Neurons. Science 2016, 353, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferragud, A.; Howell, A.D.; Moore, C.F.; Ta, T.L.; Hoener, M.C.; Sabino, V.; Cottone, P. The Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 Agonist RO5256390 Blocks Compulsive, Binge-like Eating in Rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1458–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.F.; Sabino, V.; Cottone, P. Trace Amine Associated Receptor 1 (TAAR1) Modulation of Food Reward. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotnikova, T.D.; Caron, M.G.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Trace Amine-Associated Receptors as Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinina, D.S.; Ptukha, M.A.; Goriainova, A.V.; Merkulyeva, N.S.; Kozlova, A.A.; Murtazina, R.Z.; Shemiakova, T.S.; Kuvarzin, S.R.; Vaganova, A.N.; Volnova, A.B.; et al. Role of the Trace Amine Associated Receptor 5 (TAAR5) in the Sensorimotor Functions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaganova, A.N.; Murtazina, R.Z.; Shemyakova, T.S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; Katolikova, N.V.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Pattern of TAAR5 Expression in the Human Brain Based on Transcriptome Datasets Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudel, F.; Guiraudie-Capraz, G.; Féron, F. Limbic Expression of MRNA Coding for Chemoreceptors in Human Brain—Lessons from Brain Atlases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Q. TAAR Agonists. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Suzuki, S.; Kumamaru, E.; Adachi, N.; Richards, M.; Kunugi, H. BDNF Function and Intracellular Signaling in Neurons. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, C.Y.; Hyun, S.-A.; Ko, M.Y.; Lee, B.-S.; Hwang, D.Y.; Ka, M. 2-Phenylethylamine (PEA) Ameliorates Corticosterone-Induced Depression-Like Phenotype via the BDNF/TrkB/CREB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-S.; Kim, C.-J.; Shin, M.-S.; Lim, B.-V. Treadmill Exercise Ameliorates Memory Impairment through ERK-Akt-CREB-BDNF Signaling Pathway in Cerebral Ischemia Gerbils. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2020, 16, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, C.; Bortolato, M.; Bali, N.; Godar, S.C.; Scott, A.L.; Chen, K.; Thompson, R.F.; Shih, J.C. Cognitive Abnormalities and Hippocampal Alterations in Monoamine Oxidase A and B Knockout Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12816–12821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinter, J.; Mühlhaus, J.; Wienchol, C.L.; Yi, C.-X.; Nürnberg, D.; Morin, S.; Grüters, A.; Köhrle, J.; Schöneberg, T.; Tschöp, M.; et al. Inverse Agonistic Action of 3-Iodothyronamine at the Human Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 5. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertolini, A.; Grittani, N.; Ippolito, C.; Moscato, S.; Mattii, L.; Frascarelli, S.; Zucchi, R.; Rutigliano, G. The Combination of L-Thyroxine and 3-Iodothyronamine Enhances Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Murine Model of Hypothyroidism. Thyroid 2021, 31, 1–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurino, A.; Landucci, E.; Raimondi, L. Central Effects of 3-Iodothyronamine Reveal a Novel Role for Mitochondrial Monoamine Oxidases. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, M.E.; De Siena, G.; Saba, A.; Marchini, M.; Landucci, E.; Gerace, E.; Zazzeri, M.; Musilli, C.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.; Matucci, R.; et al. Pharmacological Effects of 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) in Mice Include Facilitation of Memory Acquisition and Retention and Reduction of Pain Threshold. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gourley, S.L.; Wu, F.J.; Kiraly, D.D.; Ploski, J.E.; Kedves, A.T.; Duman, R.S.; Taylor, J.R. Regionally Specific Regulation of ERK MAP Kinase in a Model of Antidepressant-Sensitive Chronic Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glyakina, A.V.; Pavlov, C.D.; Sopova, J.V.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Leonova, E.I.; Galzitskaya, O.V. Search for Structural Basis of Interactions of Biogenic Amines with Human TAAR1 and TAAR6 Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, C.; Gómez-Tamayo, J.C.; Nebel, J.-C.; Pardo, L.; Gonzalez, A. Identifying Human Diamine Sensors for Death Related Putrescine and Cadaverine Molecules. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1005945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Guo, L.; Qian, X.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Zhu, C.; Ma, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, H.; et al. Two Entry Tunnels in Mouse TAAR9 Suggest the Possibility of Multi-Entry Tunnels in Olfactory Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Li, S.; Dai, W.; Guo, L.; Xu, Z.; Scott, A.M.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Q.; Dexheimer, T.S.; et al. Convergent Olfactory Trace Amine-Associated Receptors Detect Biogenic Polyamines with Distinct Motifs via a Conserved Binding Site. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, L.R.; Kondoh, K.; Ye, X.; Yoon, K.; Hernandez, M.; Buck, L.B. Combinatorial Effects of Odorants on Mouse Behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3300–E3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almeida-Santos, D.; Duarte, A.C.; Gonçalves, I.; Ferreira, C.L.; Ferrer, I.; Ishikawa, H.; Schwerk, C.; Schroten, H.; Santos, C.R.A. Cadaverine and Spermine Elicit Ca2+ Uptake in Human CP Cells via a Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 Dependent Pathway. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad, G.M.; Gilad, V.H.; Casanova, M.F.; Casero, R.A. Polyamines and Their Metabolizing Enzymes in Human Frontal Cortex and Hippocampus: Preliminary Measurements in Affective Disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 1995, 38, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gupta, N.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, H. Age-Related Changes in Polyamines in Memory-Associated Brain Structures in Rats. Neuroscience 2008, 155, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, G.P.; Rubin, M.A.; Mello, C.F. Modulation of Learning and Memory by Natural Polyamines. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 112, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, F.; Iqbal, Z. Regulation of N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor-Mediated Calcium Transport and Norepinephrine Release in Rat Hippocampus Synaptosomes by Polyamines. Neurochem. Res. 1994, 19, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, P. Behavioral and Neurochemical Effects of Acute Putrescine Depletion by Difluoromethylornithine in Rats. Neuroscience 2009, 161, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaterre, J.; Strambi, C.; Aouane, A.; Strambi, A.; Rougon, G.; Cayre, M. A Novel Role for Polyamines in Adult Neurogenesis in Rodent Brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühauf-Perez, P.K.; Temp, F.R.; Pillat, M.M.; Signor, C.; Wendel, A.L.; Ulrich, H.; Mello, C.F.; Rubin, M.A. Spermine Protects from LPS-Induced Memory Deficit via BDNF and TrkB Activation. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2018, 149, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedi, K.; Huttinger, F.; Morrison, R.; Murray-Stewart, T.; Casero, R.A.; Strauss, K.I. Polyamine Catabolism Is Enhanced after Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, K.; Kashiwagi, K. Functional Roles of Polyamines and Their Metabolite Acrolein in Eukaryotic Cells. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 1473–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindvall, O.; Kokaia, Z. Neurogenesis Following Stroke Affecting the Adult Brain. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a019034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallach, J.V. Endogenous Hallucinogens as Ligands of the Trace Amine Receptors: A Possible Role in Sensory Perception. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 72, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Garcia, J.A.; Calleja-Conde, J.; Lopez-Moreno, J.A.; Alonso-Gil, S.; Sanz-SanCristobal, M.; Riba, J.; Perez-Castillo, A. N,N-Dimethyltryptamine Compound Found in the Hallucinogenic Tea Ayahuasca, Regulates Adult Neurogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmeier, A.; Obermueller, S.; Meyer, C.A.; Revel, F.G.; Buchy, D.; Chaboz, S.; Dernick, G.; Wettstein, J.G.; Iglesias, A.; Rolink, A.; et al. Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 Activation Silences GSK3β Signaling of TAAR1 and D2R Heteromers. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, M.; Ahmad, M.H.; Srivastav, S.; Rizvi, M.A.; Mondal, A.C. A Selective D2 Dopamine Receptor Agonist Alleviates Depression through Up-Regulation of Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Increased Neurogenesis in Hippocampus of the Prenatally Stressed Rats. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 136, 104730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bräunig, J.; Dinter, J.; Höfig, C.S.; Paisdzior, S.; Szczepek, M.; Scheerer, P.; Rosowski, M.; Mittag, J.; Kleinau, G.; Biebermann, H. The Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 Agonist 3-Iodothyronamine Induces Biased Signaling at the Serotonin 1b Receptor. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, L.; Deloménie, C.; David, I.; Rainer, Q.; Marouard, M.; Delacroix, H.; David, D.J.; Gardier, A.M.; Guilloux, J.-P. Ventral Hippocampal Molecular Pathways and Impaired Neurogenesis Associated with 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B Receptors Disruption in Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 521, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.-N.; Huang, Y.; Yu, X.; Lang, B.; Ding, Y.-Q.; Zhang, L. Divergent Roles of Central Serotonin in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yanpallewar, S.U.; Fernandes, K.; Marathe, S.V.; Vadodaria, K.C.; Jhaveri, D.; Rommelfanger, K.; Ladiwala, U.; Jha, S.; Muthig, V.; Hein, L.; et al. A2-Adrenoceptor Blockade Accelerates the Neurogenic, Neurotrophic, and Behavioral Effects of Chronic Antidepressant Treatment. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
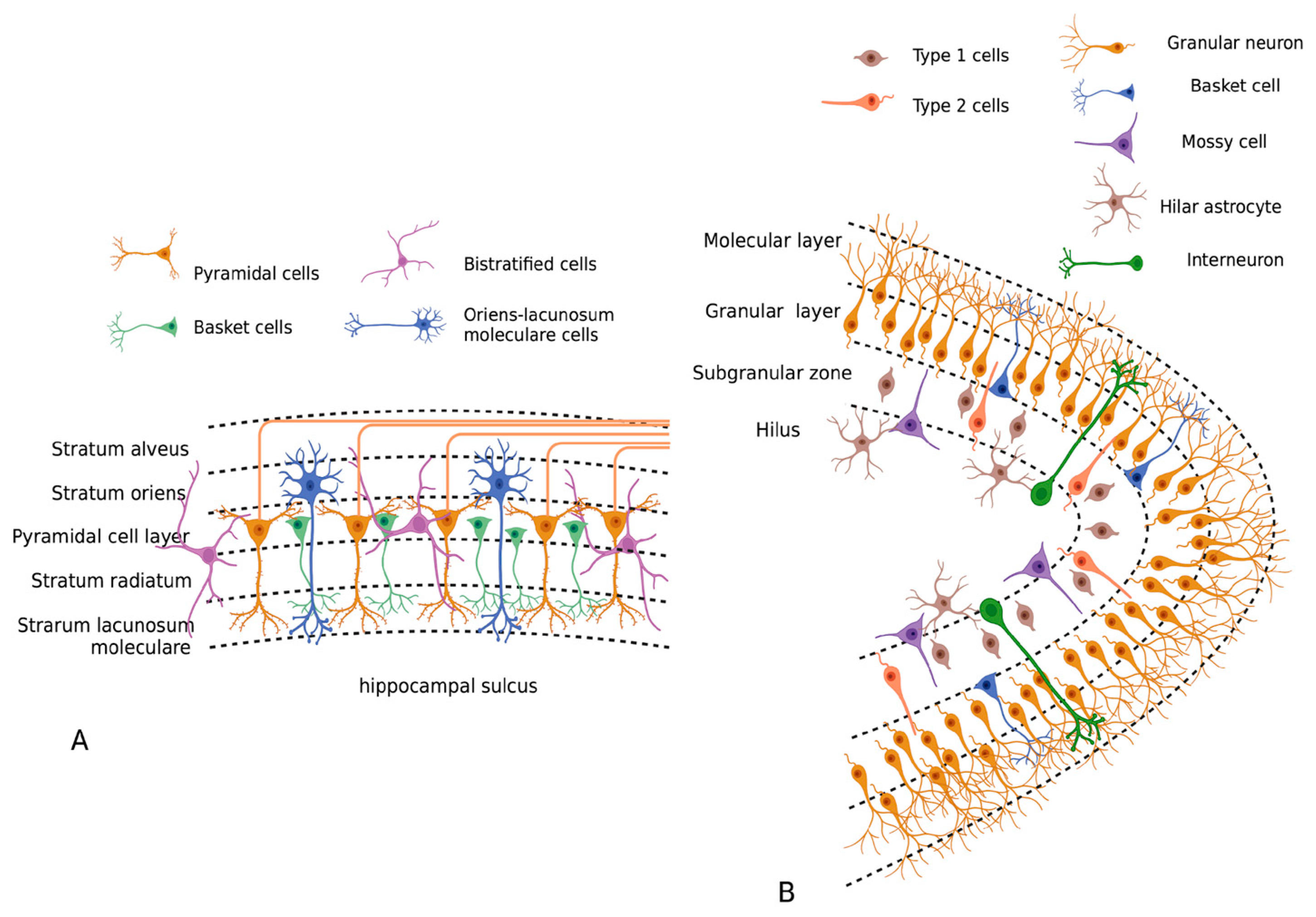

| Accession Number | Title | Number of Samples | Experiment Design |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole-tissue data | |||
| GSE84503 | Activity-dependent regulation of alternative cleavage and polyadenylation (APA) during hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) [RNA-Seq] | 6 control samples/6 experimental samples | Acute hippocampal slices after chemically induced long-term potentiation induction, potentiated slices and time-matched control slices were studied 1 hr and 3 hr after the intervention |
| GSE147842 | Adult mouse hippocampal transcriptome changes associated with long-term behavioral and metabolic effects of gestational air pollution toxicity | 10 control samples/10 experimental samples | Pregnant dams were exposed to urban derived nanosized particulate matter during the gestational period. The effects were studied in adults |
| GSE148075 | Wild mice with different social network sizes vary in brain gene expression | 14 in the “high gregariousness” group and 15 in “low gregariousness” group | Dataset from three brain regions (hypothalamus, prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, only hippocampal samples were included in the review) from wild mice presenting large or small social network sizes |
| GSE166831 | Altered hippocampal transcriptome dynamics following sleep deprivation | 9 control samples/9 experimental samples | Whole hippocampus RNA profiles of mice who were either sleep-deprived for 5 h or left undisturbed |
| Cell fractions data | |||
| GSE94559 | Hippocampus CA1 pyramidal cells Transcriptomic profile in WT and Fmr1 KO mice, using Wfs1-CreERT2:RiboTag:Frm1 knockout and wild-type mice | 6 control samples/6 experimental samples | Pairwise comparison of CA1 pyramidal cells in wild-type and Fmr1 KO mice |
| Single-cell data | |||
| GSE75386 | Single-cell RNAseq of electrophysiologically characterized neurons of the hippocampus | 93 single-cell samples | CA1 cholecystokinin, parvalbumin and pyramidal neurons, as well as subiculum burst and regular firing pyramidal neurons, were studied |
| SCP1 | Single nucleus RNA-seq of cell diversity in the adult mouse hippocampus | 1367 single nuclei | Nuclei from hippocampal anatomical sub-regions DG, CA1, CA2, CA3 and lowly abundant GABAergic neurons were analyzed |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katolikova, N.V.; Vaganova, A.N.; Efimova, E.V.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Expression of Trace Amine-Associated Receptors in the Murine and Human Hippocampus Based on Public Transcriptomic Data. Cells 2022, 11, 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111813
Katolikova NV, Vaganova AN, Efimova EV, Gainetdinov RR. Expression of Trace Amine-Associated Receptors in the Murine and Human Hippocampus Based on Public Transcriptomic Data. Cells. 2022; 11(11):1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111813
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatolikova, Nataliia V., Anastasia N. Vaganova, Evgeniya V. Efimova, and Raul R. Gainetdinov. 2022. "Expression of Trace Amine-Associated Receptors in the Murine and Human Hippocampus Based on Public Transcriptomic Data" Cells 11, no. 11: 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111813
APA StyleKatolikova, N. V., Vaganova, A. N., Efimova, E. V., & Gainetdinov, R. R. (2022). Expression of Trace Amine-Associated Receptors in the Murine and Human Hippocampus Based on Public Transcriptomic Data. Cells, 11(11), 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111813









