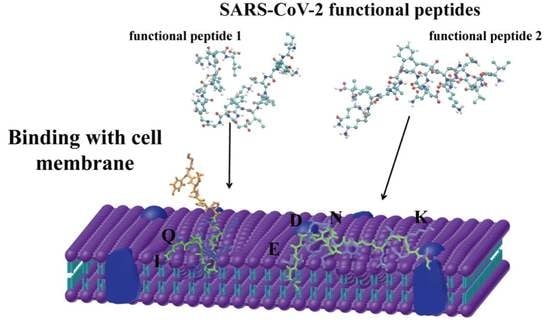
Functional Peptides from SARS-CoV-2 Binding with Cell Membrane: From Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Cell Demonstration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Details
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Preparation and Characterization of Functional Peptides
2.1.3. Preparation of DPPC Liposomes
2.1.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.1.5. Calcein-Release Assay
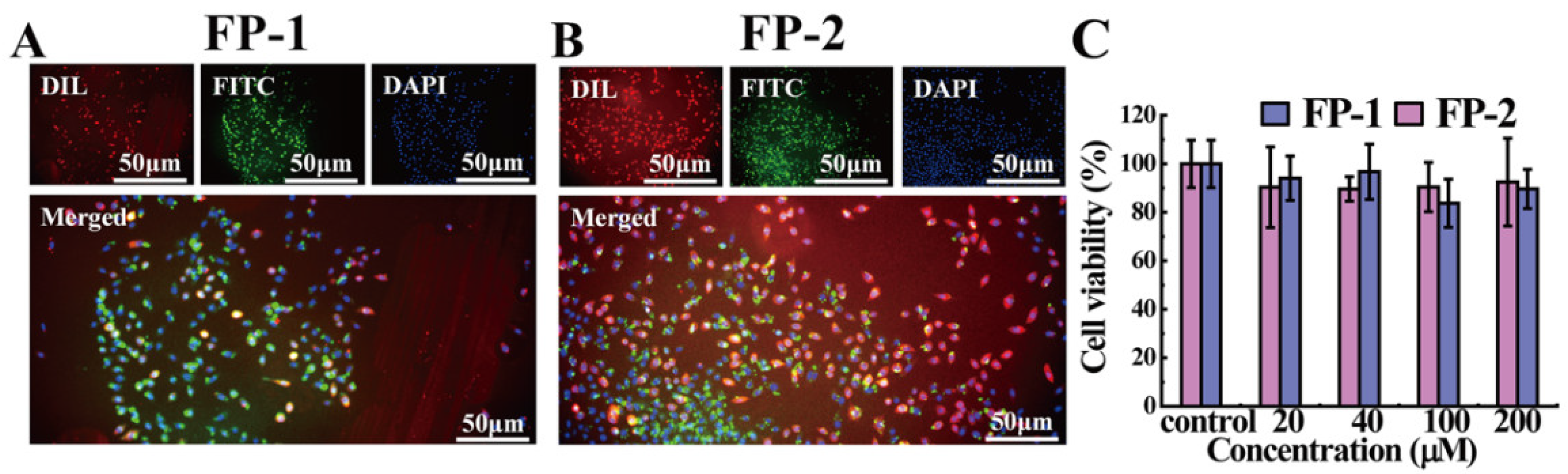
2.1.6. Liposome Localization of the Functional Peptides
2.1.7. Cell-Membrane-Localization Assay
2.1.8. Cytotoxicity Measurement
2.1.9. Statistical Analysis
2.2. Simulation Details
2.2.1. Set Up of the Functional Peptide and Membrane Systems
2.2.2. All-Atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.2.3. Lateral Diffusion Coefficients
2.2.4. Umbrella Sampling
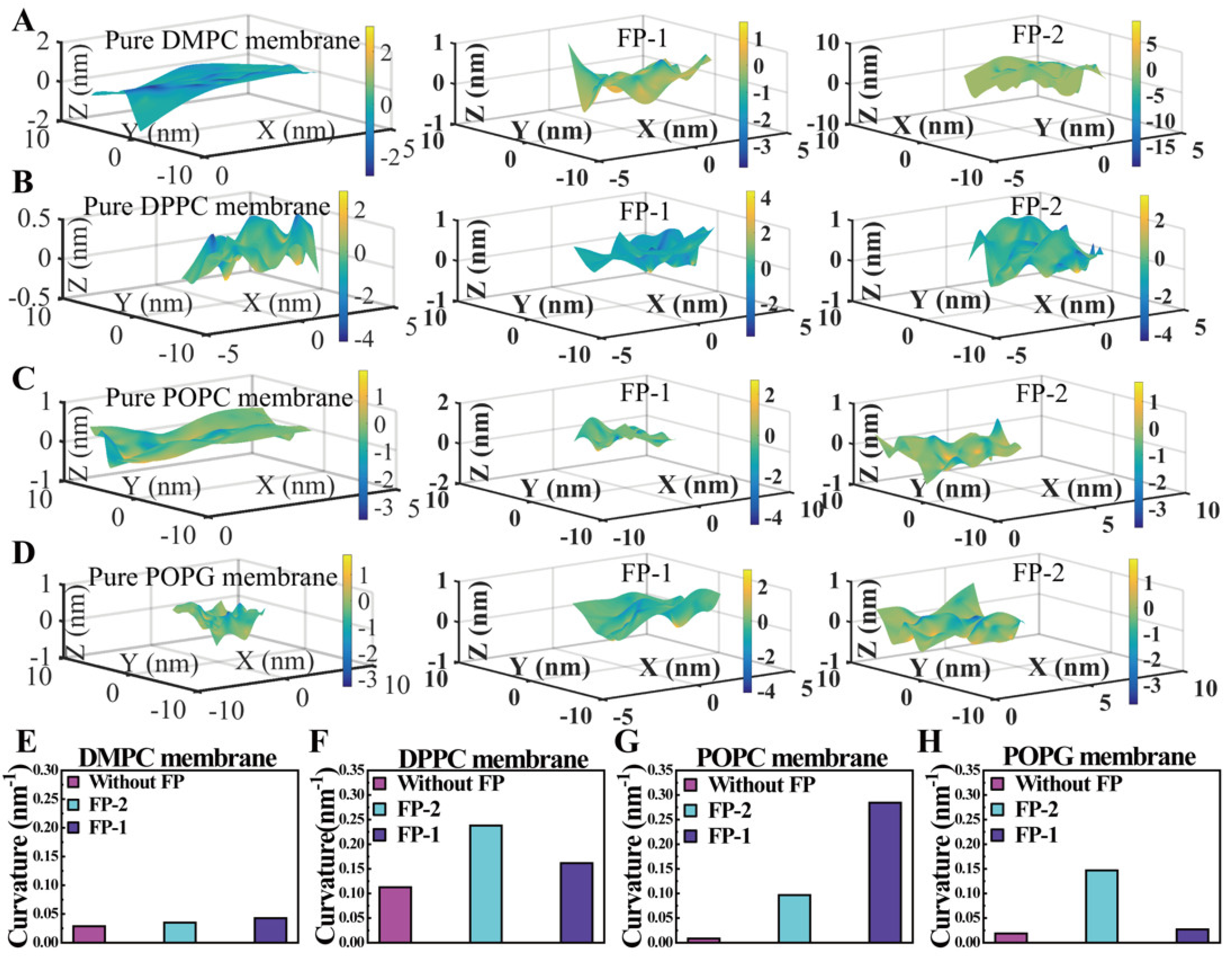
2.2.5. Curvature Analysis of Lipid Membrane
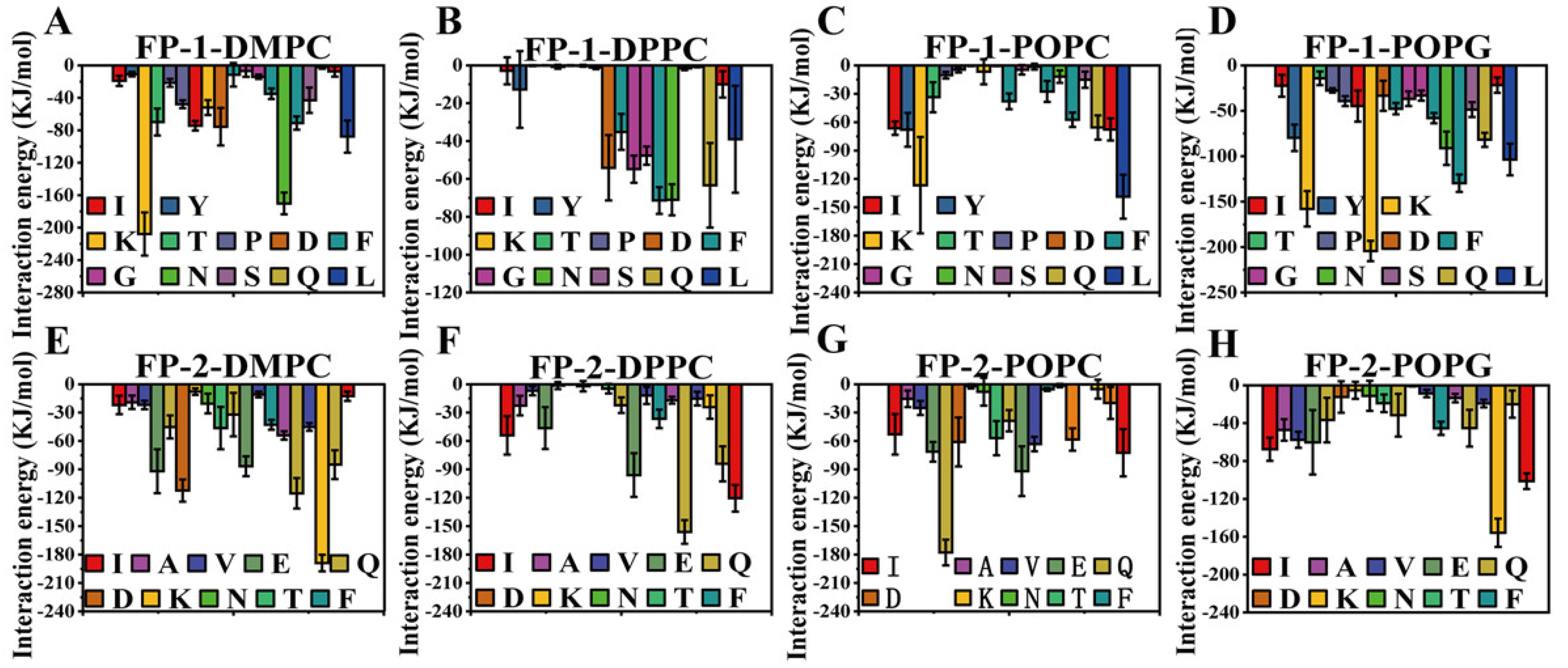
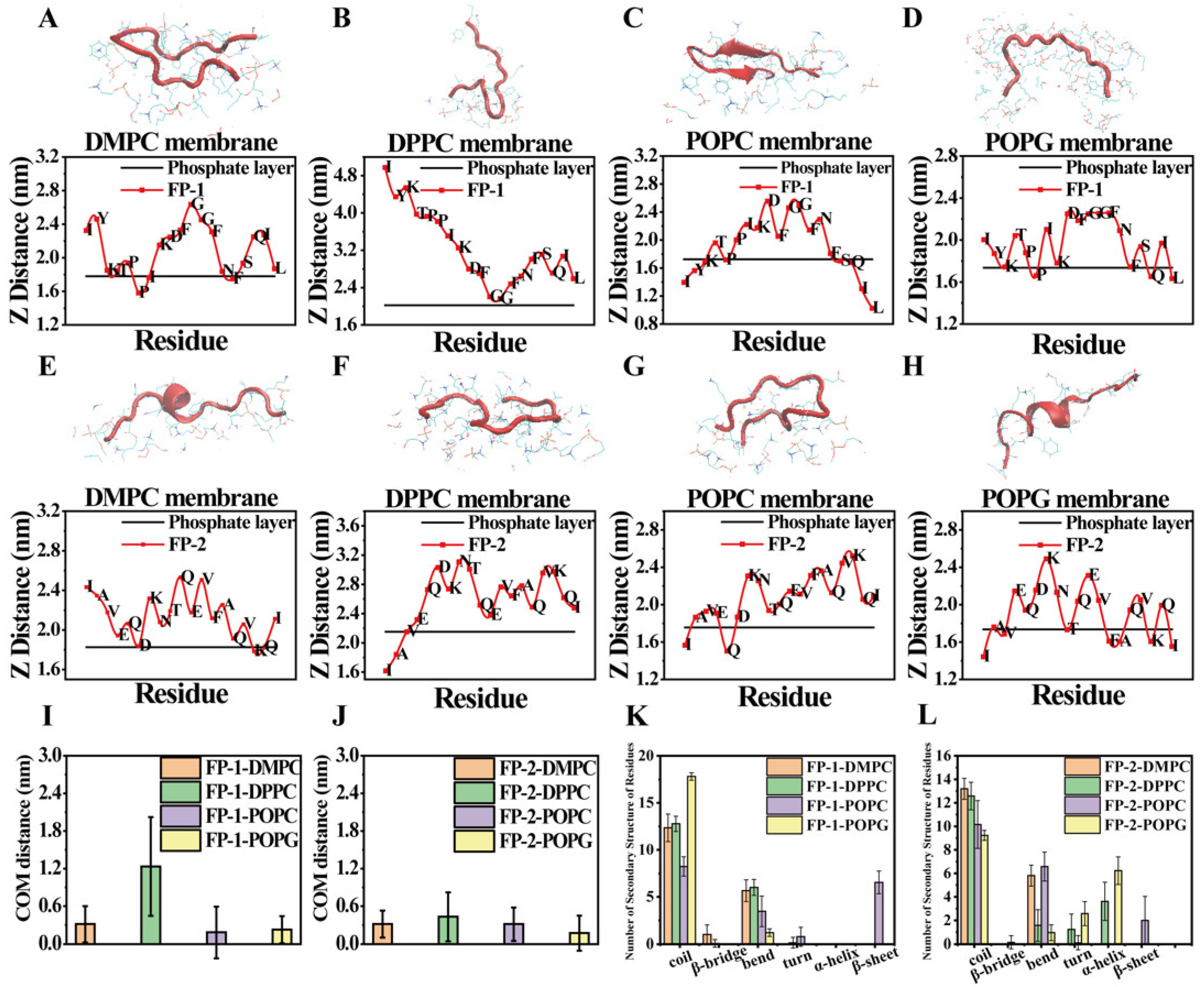
3. Results and Discussion

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.-Y.; You, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.-J.; Qiu, Y.; Luo, R.; Ge, X.-Y. The epidemic of 2019-novel-coronavirus (2019-nCoV) pneumonia and insights for emerging infectious diseases in the future. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.C.; Shih, T.P.; Ko, W.C.; Tang, H.J.; Hsueh, P.R. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Ye, G.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 202003138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, Z.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Ye, Q.; Cao, L.; Sun, C.-Y.; Fan, C.; Huang, W.; Sun, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. Structural basis for neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV by a potent therapeutic antibody. Science 2020, 369, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Receptor Binding and Membrane Fusion in Virus Entry: The Influenza Hemagglutinin. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 531–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earp, L.J.; Delos, S.E.; Park, H.E.; White, J.M. The Many Mechanisms of Viral Membrane Fusion Proteins. In Membrane Trafficking in Viral Replication; Marsh, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 25–66. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, L.G.M.; Vicente, E.F.; Crusca, E.; Cilli, E.M.; Costa-Filho, A.J. SARS-CoV fusion peptides induce membrane surface ordering and curvature. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsaadi, E.; Neuman, B.W.; Jones, I.M. A Fusion Peptide in the Spike Protein of MERS Coronavirus. Viruses 2019, 11, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Victor, B.L.; Lousa, D.; Antunes, J.M.; Soares, C.M. Self-assembly molecular dynamics simulations shed light into the interaction of the influenza fusion Peptide with a membrane bilayer. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2015, 55, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.M.; Delos, S.E.; Brecher, M.; Schornberg, K. Structures and Mechanisms of Viral Membrane Fusion Proteins: Multiple Variations on a Common Theme. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 43, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamm, L.K.; Xing, H. Viral Fusion Peptides: A Tool Set to Disrupt and Connect Biological Membranes. Biosci. Rep. 2000, 20, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, G.P.; Bhattacharjya, S.; Chakraborty, H. Enhanced Cholesterol-Dependent Hemifusion by Internal Fusion Peptide 1 of SARS Coronavirus-2 Compared to Its N-Terminal Counterpart. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppisetti, R.K.; Fulcher, Y.G.; Van Doren, S.R. Fusion Peptide of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Rearranges into a Wedge Inserted in Bilayered Micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 13205–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birtles, D.; Lee, J. Identifying Distinct Structural Features of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Fusion Domain Essential for Membrane Interaction. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 2978–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, S.L.; Jung, H.; Hummer, G. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Fusion Peptide to Host Endosome and Plasma Membrane. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 7732–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Lan, Q.; Feng, S.; Qi, F.; Bao, L.; Du, L.; Liu, S.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boopathi, S.; Poma, A.B.; Kolandaivel, P. Novel 2019 coronavirus structure, mechanism of action, antiviral drug promises and rule out against its treatment. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 3409–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.; Ou, X.; Tian, R.; Zhang, J.; Jin, H.; Dong, M.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Membrane destruction and phospholipid extraction by using two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 20162–20170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Lang, J.C.; Mao, C.; Kroll, P.; Tang, L.; Dong, H. Self-Assembled Peptide Nanofibers Display Natural Antimicrobial Peptides to Selectively Kill Bacteria without Compromising Cytocompatibility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28681–28689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainz, B.; Rausch Joshua, M.; Gallaher William, R.; Garry Robert, F.; Wimley William, C. Identification and Characterization of the Putative Fusion Peptide of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Associated Coronavirus Spike Protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7195–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, P.; Yuan, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Mao, X.; Liu, L. Deformation of stable and toxic hIAPP oligomers by liposomes with distinct nanomechanical features and reduced cytotoxicity. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 14359–14362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukol, A. Lipid Models for United-Atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzinek, J.K.; Bag, N.; Huber, R.G.; Holdbrook, D.A.; Wohland, T.; Verma, C.S.; Bond, P.J. A Funneled Conformational Landscape Governs Flavivirus Fusion Peptide Interaction with Lipid Membranes. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2018, 14, 3920–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameselle, J.C.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Sillero, A. Derivation and use of a formula to calculate the net charge of acid-base compounds. Its application to amino acids, proteins and nucleotides. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 1986, 14, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.S. Amino acid and peptide net charges: A simple calculational procedure. Biochem. Educ. 1985, 13, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.J.; Ramalli, S.G.; Wallace, B.A. DichroWeb, a Website for Calculating Protein Secondary Structure from Circular Dichroism Spectroscopic Data. Protein Sci. 2021, 31, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieva, J.L.; Nir, S.; Muga, A.; Goni, F.M.; Wilschut, J. Interaction of the HIV-1 Fusion Peptide with Phospholipid Vesicles: Different Structural Requirements for Fusion and Leakage. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 3201–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgun, D.; Lihan, M.; Kapoor, K.; Tajkhorshid, E. Binding Mode of SARS-CoV2 Fusion Peptide to Human Cellular Membrane. bioRxiv 2021, 120, 2914–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bennett, W.F.D.; Zheng, T.; Ouyang, P.-K.; Ouyang, X.; Qiu, X.; Luo, A.; Karttunen, M.; Chen, P. Effect of Cholesterol on Cellular Uptake of Cancer Drugs Pirarubicin and Ellipticine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 3148–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Ding, Y.; Wang, T.; Jin, G.; Martz, M.; Gui, Z.; Ouyang, P.; Chen, P. Histidine-Rich Cell-Penetrating Peptide for Cancer Drug Delivery and Its Uptake Mechanism. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2019, 35, 3513–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, H.; Ganjali Koli, M.; Ranjbar, R.; Pooshang Bagheri, K. Interactions of GF-17 derived from LL-37 antimicrobial peptide with bacterial membranes: A molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2020, 34, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaspina, T.; Colherinhas, G.; de Oliveira Outi, F.; Fileti, E.E. Assessing the interaction between surfactant-like peptides and lipid membranes. RSC Advances 2017, 7, 35973–35981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blood, P.D.; Voth, G.A. Direct observation of Bin/amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) domain-induced membrane curvature by means of molecular dynamics simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15068–15072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuhrmans, M.; Marrink, S.J. Molecular View of the Role of Fusion Peptides in Promoting Positive Membrane Curvature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Functional Peptide | Lipid Bilayer | DMDmem (μm2 s−1) | DMDmem+functional peptide (μm2·s−1) | DMDmem+functional peptide/DMDmem | No. of Clusters Obtained | PMF (kcal·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP-1 | DMPC | 1.75 ± 0.047 | 1.4 ± 0.047 | 0.8 | 2 | 22.515 ± 0.531 |
| DPPC | 4.1 ± 0.029 | 3.82 ± 0.029 | 0.932 | 4 | 28.369 ± 1.10 | |
| POPC | 1.3 ± 0.019 | 1.07 ± 0.019 | 0.826 | 2 | 20.030 ± 1.396 | |
| POPG | 2.1 ± 0.066 | 1.26 ± 0.066 | 0.602 | 4 | 48.458 ± 0.922 | |
| FP-2 | DMPC | 1.75 ± 0.047 | 1.225 ± 0.042 | 0.7 | 9 | 41.022 ± 0.578 |
| DPPC | 4.1 ± 0.029 | 1.425 ± 0.274 | 0.347 | 3 | 44.260 ± 0.902 | |
| POPC | 1.3 ± 0.0019 | 1.0 ± 0.018 | 0.769 | 3 | 24.458 ± 1.266 | |
| POPG | 2.1 ± 0.0066 | 1.7 ± 0.075 | 0.818 | 4 | 28.737 ± 0.729 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, Y.; Wu, R.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Song, X.; Liu, L. Functional Peptides from SARS-CoV-2 Binding with Cell Membrane: From Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Cell Demonstration. Cells 2022, 11, 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111738
Hao Y, Wu R, Wang F, Zhang L, Wang Z, Song X, Liu L. Functional Peptides from SARS-CoV-2 Binding with Cell Membrane: From Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Cell Demonstration. Cells. 2022; 11(11):1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111738
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Yun, Rongrong Wu, Fenghua Wang, Liwei Zhang, Zengkai Wang, Xiaolu Song, and Lei Liu. 2022. "Functional Peptides from SARS-CoV-2 Binding with Cell Membrane: From Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Cell Demonstration" Cells 11, no. 11: 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111738
APA StyleHao, Y., Wu, R., Wang, F., Zhang, L., Wang, Z., Song, X., & Liu, L. (2022). Functional Peptides from SARS-CoV-2 Binding with Cell Membrane: From Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Cell Demonstration. Cells, 11(11), 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111738