Inhibition of Cellular and Animal Inflammatory Disease Models by NF-κB Inhibitor DHMEQ
Abstract
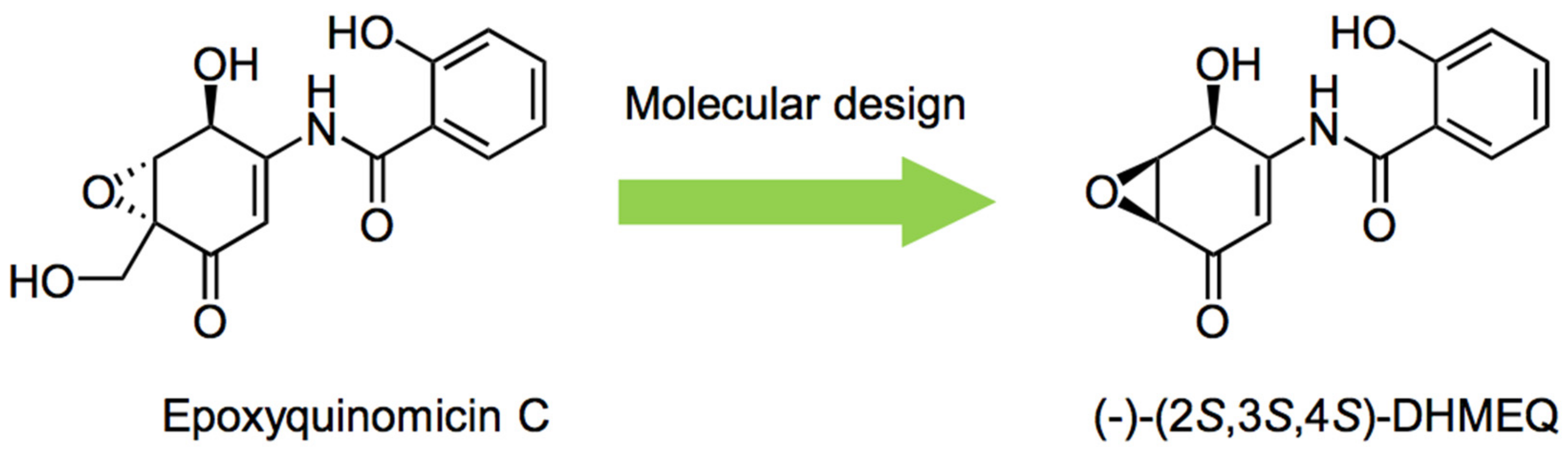
1. Introduction
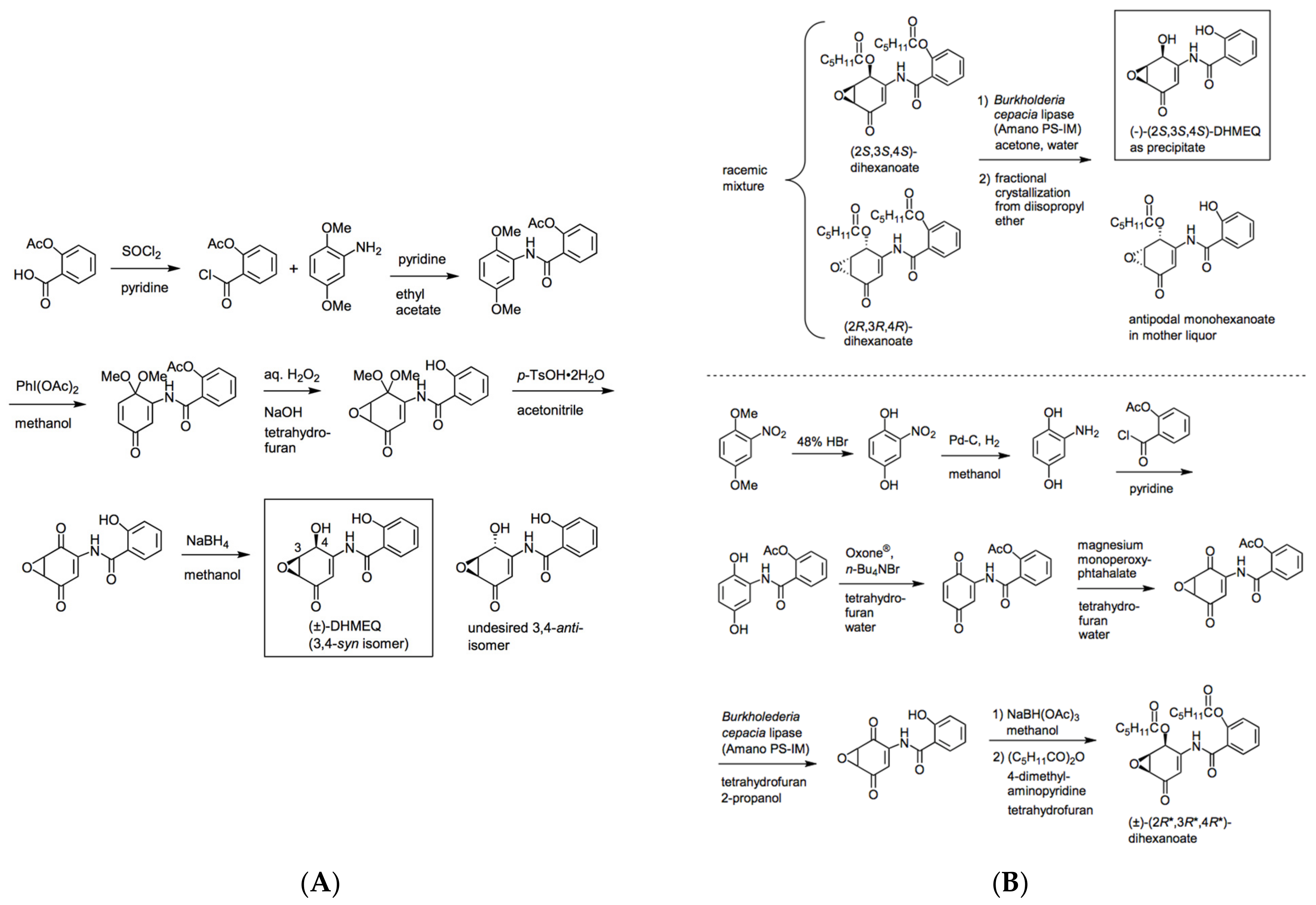
2. Preparation of Racemic and Enantiomerically Pure DHMEQ
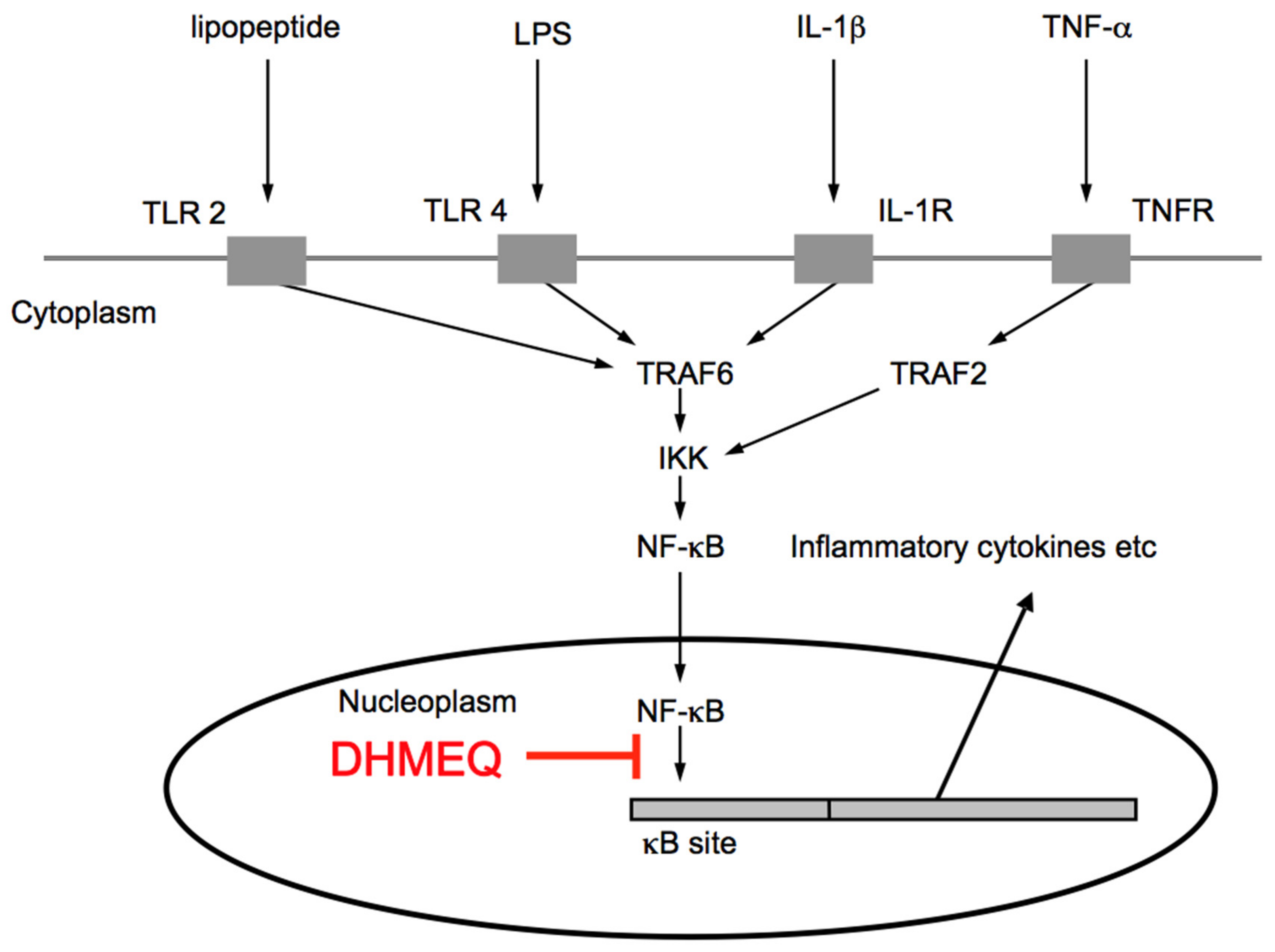
3. Mechanism of NF-κB Inhibition by DHMEQ
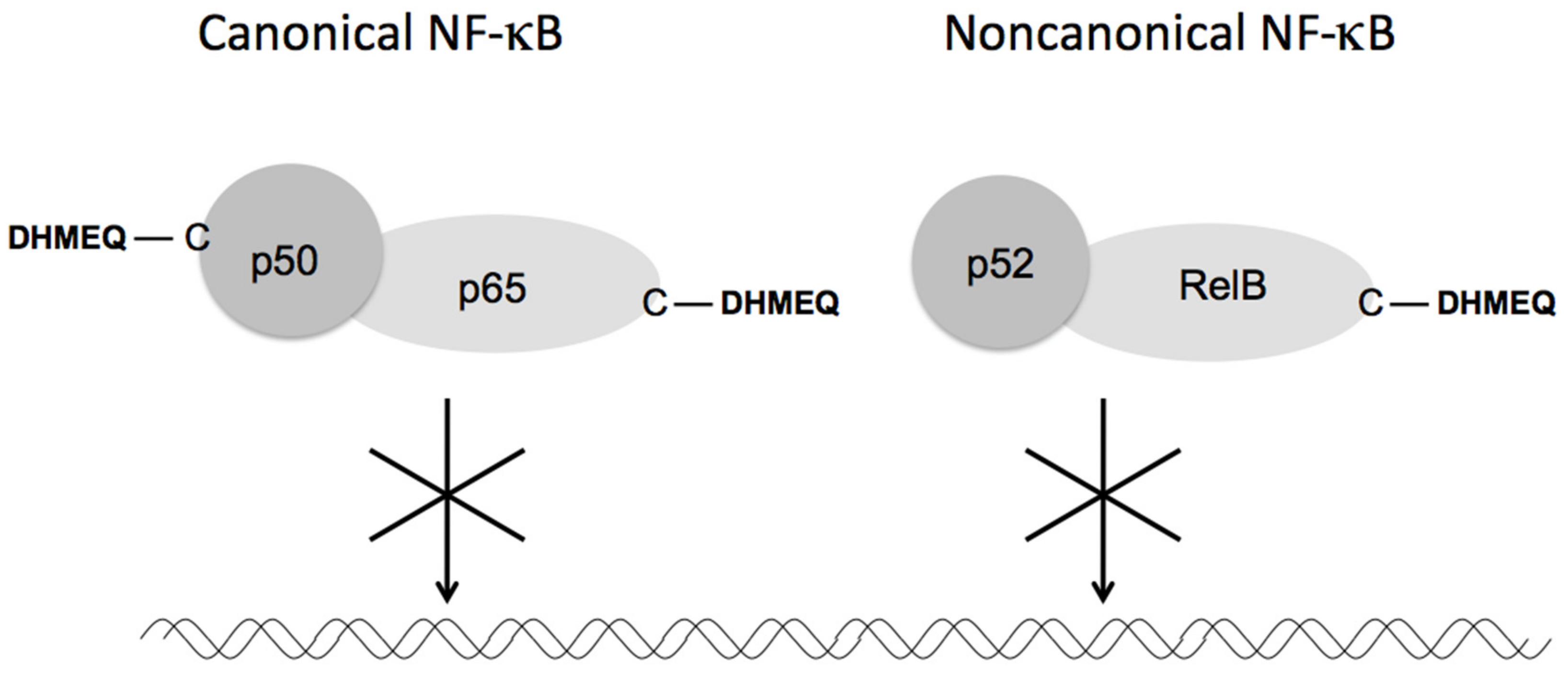
3.1. Direct Inactivation of NF-κB Components
3.2. Alternative Mechanism; ROS-Mediated Inhibition of NF-κB
4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of DHMEQ
4.1. Cellular Anti-Inflammatory Activity
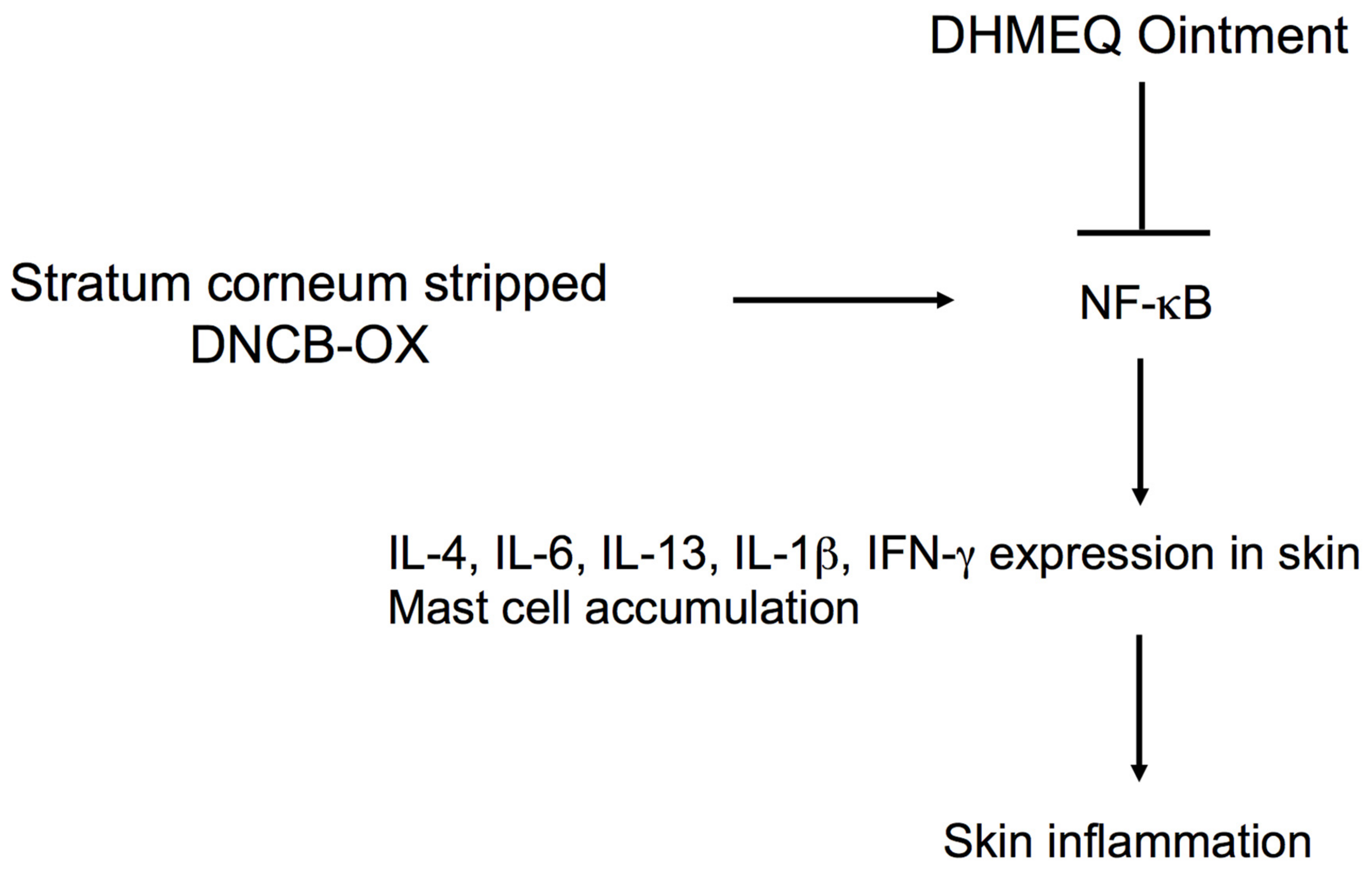
4.2. Inhibition of Skin and Nasal Inflammations
4.3. Amelioration of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Rheumatoid Arthritis
4.4. Inhibition of Ophthalmic Inflammations
4.5. Inhibition of Digestive Tract Inflammation
4.6. Inhibition of Renal Inflammation
4.7. Inhibition of Graft Rejection in Organ Transplantation
4.8. Amelioration of Endotoxin Shock, Asthma, and Other Inflammatory Diseases
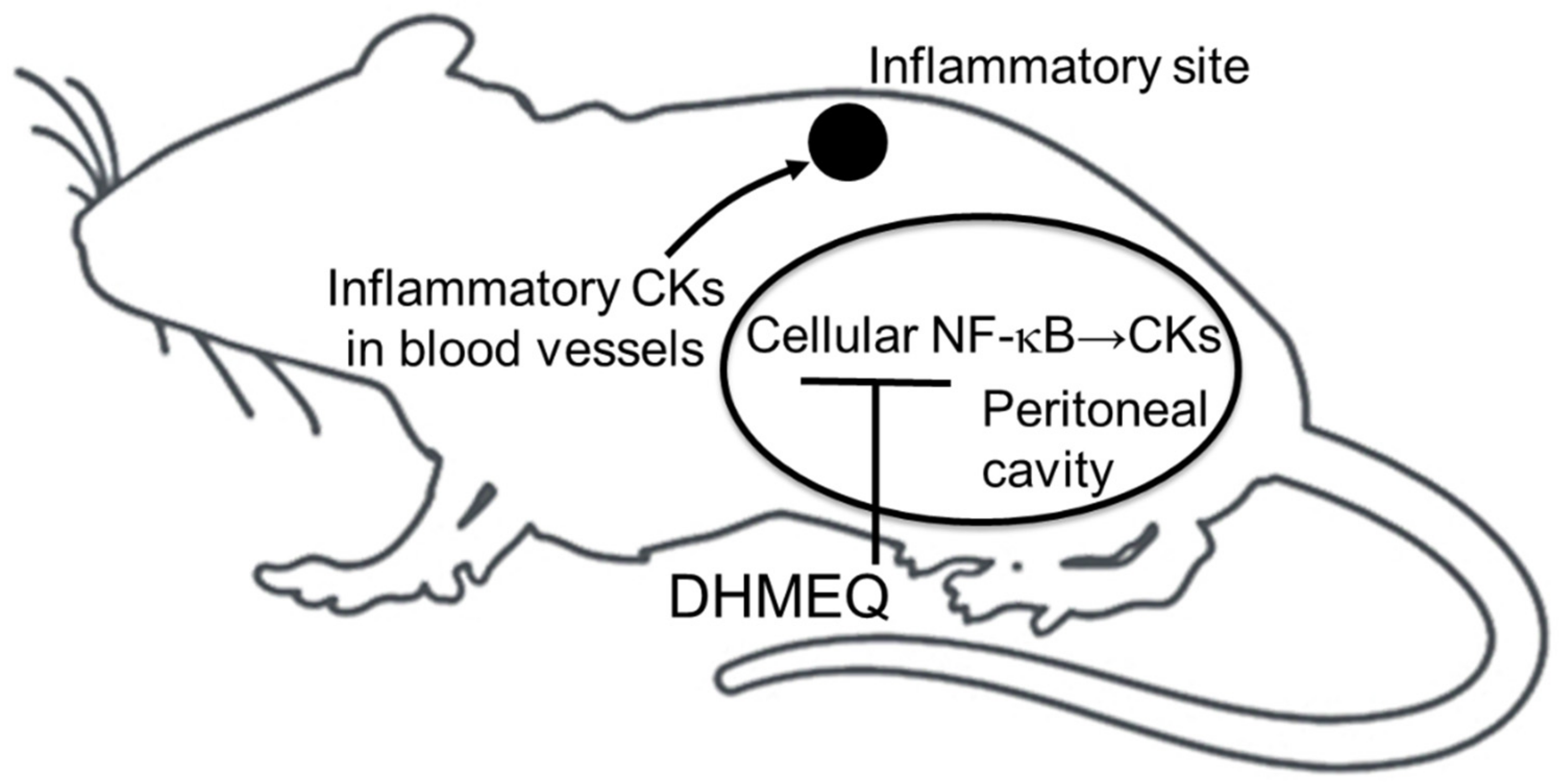
5. Possible Mechanism of Action for Intraperitoneal DHMEQ Therapy
6. Discussion and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sen, R.; Baltimore, D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell 1986, 46, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Dai, J.; Keller, E.T.; Giordano, T.; Gu, K.; Shah, V.; Pei, L.; Zarbo, R.J.; et al. NF-κB in breast cancer cells promotes osteolytic bone metastasis by inducing osteoclastogenesis via GM-CSF. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zins, K.; Abraham, D.; Sioud, M.; Aharinejad, S. Colon cancer cell-derived tumor necrosis factor-α mediates the tumor growth-promoting response in macrophages by up-regulating the colony-stimulating factor-1 pathway. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Tsuchida, T.; Umekita, M.; Kinoshita, N.; Iinuma, H.; Sawa, T.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T. Epoxyquinomicins A, B, C and D, new antibiotics from Amycolatopsis. J. Antibiot. 1997, 50, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erkel, G.; Anke, T.; Sterner, O. Inhibition of NF-κB activation by panepoxydone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996, 226, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrt, A.; Erkel, G.; Anke, T.; Sterner, O.A. Cycloepoxydon: 1-hydroxy-2-hydroxymethyl-3-pent-1-enylbenzene1-hydroxy-2-hydroxymethyl-3-pent-1, 3-dienylbenzene, new inhibitors of eukaryotic signal transduction. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsumoto, N.; Ariga, A.; To-e, S.; Nakamura, H.; Agata, N.; Hirano, S.; Inoue, J.; Umezawa, K. Synthesis of NF-κB activation inhibitors derived from epoxyquinomicin C. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Sugiyama, C.; Ohno, O.; Umezawa, K. Preparation and biological activities of optically active dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, a novel NF-κB inhibitor. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 7061–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaicharoenpong, C.; Kato, K.; Umezawa, K. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin analogues as inhibitors of NF-κB functions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 3933–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Hanaya, K.; Shoji, M.; Umezawa, K.; Sugai, T. A chemo-enzymatic expeditious route to racemic dihexanoyl (2R*,3R*,4R*)-DHMEQ (dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomycin), the precursor for lipase-catalyzed synthesis of (2S,3S,4S)-DHMEQ, a potent NF-κB inhibitor. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niitsu, Y.; Hakamata, M.; Goto, Y.; Higashi, T.; Shoji, M.; Sugai, T.; Umezawa, K. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of (2R,3R,4R)-dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin (DHMEQ), a new activator of antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4635–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Qu, J.; Shen, X. NF-κB/p65 antagonizes Nrf2-ARE pathway by depriving CBP from Nrf2 and facilitating recruitment of HDAC3 to MafK. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 713–727. [Google Scholar]
- Lampiasi, N.; Azzolina, A.; D’Alessandro, N.; Umezawa, K.; McCubrey, J.A.; Montalto, G.; Cervello, M. Antitumor effects of DHMEQ, a novel NF-κB inhibitor, in human liver cancer cells is mediated through a reactive oxygen species-dependent mechanism. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, A.; Namekawa, J.; Matsumoto, N.; Inoue, J.; Umezawa, K. Inhibition of TNF-α-induced nuclear translocation and activation of NF-κB by dehydroxymethyl-epoxyquinomicin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27625–27630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Horie, R.; Takeiri, M.; Kozawa, I.; Umezawa, K. Inactivation of nuclear factor kappa B components by covalent binding of (–)-dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin to specific cysteine residues. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5780–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, K.; Ma, J.; Umezawa, K. Inhibition of canonical NF-κB nuclear localization by (–)-DHMEQ via impairment of DNA binding. Oncol. Res. 2015, 22, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozawa, I.; Kato, K.; Teruya, T.; Suenaga, K.; Umezawa, K. Unusual intramolecular N→O acyl group migration occurring during conjugation of (–)-DHMEQ with cysteine. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5380–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, C.; Ninomiya, Y.; Suzuki, E.; Umezawa, K. Efficient cellular uptake of the novel NF-κB inhibitor (−)-DHMEQ and irreversible inhibition of NF-κB in neoplastic cells. Oncol. Res. 2010, 18, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeiri, M.; Horie, K.; Takahashi, D.; Watanabe, M.; Horie, R.; Simizu, S.; Umezawa, K. Involvement of DNA binding domain in the cellular stability and importin affinity of NF-κB component RelB. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 3053–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S.; Kitamura, M. Bidirectional regulation of NF-κB by reactive oxygen species: A role of unfolded protein response. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, S.; Kato, H.; Gu, L.; Takahashi, S.; Johno, H.; Umezawa, K.; Kitamura, M. Pleiotropic potential of dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin for NF-κB suppression via reactive oxygen species and unfolded protein response. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6559–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, E.; Umezawa, K. Inhibition of macrophage activation and phagocytosis by a novel NF-κB inhibitor, dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2006, 60, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, E.; Ninomiya, Y.; Umezawa, K. Induction of hisitidine decarboxylase in macrophages inhibited by the novel NF-kappa B inhibitor (–)-DHMEQ. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, B.; Cogswell, P.C.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. Functional and physical associations between NF-kappa B and C/EBP family members: A Rel domain-bZIP interaction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 3964–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, E.; Sugiyama, C.; Umezawa, K. Inhibition of inflammatory mediator secretion by (–)-DHMEQ in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2009, 63, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuna, H.; Morita, S.; Nagatsu, T.; Sawada, M.; Umezawa, K. Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine secretion from mouse microglia cells by DHMEQ, an NF-κB inhibitor. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005, 59, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noma, N.; Asagiri, M.; Takeiri, M.; Ohmae, S.; Takemoto, K.; Iwaisako, K.; Simizu, S.; Umezawa, K. Inhibition of MMP-2-mediated mast cell invasion by NF-κB inhibitor DHMEQ in mast cells. Int. Ach. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 166, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaka, A.; Yoshioka, N.; Abe, R.; Kishino, S.; Umezawa, K.; Ozaki, M.; Todo, S.; Shimizu, H. Topical application of DHMEQ improves allergic inflammation via NF-κB inhibition. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wei, B.; Lan, Y.; Dai, C.; Gu, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Umezawa, K.; Zhang, Y. External application of NF-κB inhibitor DHMEQ suppresses development of atopic dermatitis-like lesions induced with DNCB/OX in BALB/c mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2017, 39, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; He, H.; Xie, Z.; Wen, H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Umezawa, K.; Zhang, Y. Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin suppresses atopic dermatitis-like lesions in a stratum corneum-removed murine model through NF-κB inhibition. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2019, 41, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Xie, Z.; Ma, K.; Ma, J.; Umezawa, K.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of anti-atopic dermatitis activities between DHMEQ and tacrolimus ointments in mouse model without stratum corneum. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 71, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardile, V.; Libra, M.; Caggia, S.; Frasca, G.; Umezawa, K.; Stivala, F.; Mazzarino, M.C.; Bevelacqua, Y.; Coco, M.; Malaponte, G. Dehydroxyquinomicin, a novel NF-kappa B inhibitor, prevents inflammatory injury induced by IFN-γ and histamine in keratinocytes NCTC 2544. Cell. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, S.; Mitsutake, N.; Nakashima, M.; Saenko, V.A.; Ohtsuru, A.; Umezawa, K.; Tanaka, K.; Hirano, A.; Yamashita, S. DHMEQ, a novel NF-kappaB inhibitor, suppresses growth and type I collagen accumulation in keloid fibroblasts. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 51, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, F.C.P.; Queiroz, R.; Scrideli, C.; Tone, L.G.; Anselmo-Lima, W.T. Expression of transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1 in nasal polyposis. Clin Exp Allergy 2008, 38, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, F.C.P.; Queiroz, R.; Scrideli, C.; Tone, L.G.; Anselmo-Lima, W.T. Evaluating budesonide efficacy in nasal polyposis and predicting the resistance to treatment. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, F.C.P.; Umezawa, K.; Brassesco, M.S.; Gamero, A.M.C.; Queiro, R.G.P.; Scrideli, C.A.; Tone, L.G.; Anselmo-Lima, W.T. Suppression of inflammatory cytokine secretion by an NF-κB inhibitor in nasal polyps fibroblasts. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, K.; Nanki, T.; Miyasaka, N.; Umezawa, K.; Kubota, T. Effect of a small molecule inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB nuclear translocation in a murine model of arthritis and cultured human synovial cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, 1348–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Umezawa, K. Suppression of erosive arthritis by NF-κB Inhibitors. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2011, 7, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuna, H.; Asagiri, M.; Kubota, T.; Oka, K.; Osada, T.; Sugiyama, C.; Saito, H.; Aoki, K.; Ohya, K.; Takayanagi, H.; et al. Inhibition of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by (–)-DHMEQ, a novel NF-κB inhibitor, through downregulation of NFATc1. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Hoshino, M.; Aoki, K.; Ohya, K.; Komano, Y.; Nanki, T.; Miyasaka, N.; Umezawa, K. NF-κB inhibitor DHMEQ suppresses osteoclastogenesis and expression of NFATc1 in mouse arthritis without affecting expression of RANCL, OPG or M-CSF. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2007, 9, R97. Available online: http://arthritis-research.com/content/9/5//R97 (accessed on 30 August 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimi, E.; Aoki, K.; Saito, H.; D’Acquisto, F.; May, M.J.; Nakamura, I.; Sudo, T.; Kojima, T.; Okamoto, F.; Fukushima, H.; et al. Selective inhibition of NF-κB blocks osteoclastogenesis and prevents inflammatory bone destruction in vivo. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardile, V.; Frasca, G.; Libra, M.; Caggia, S.; Umezawa, K.; Panico, A.; Malaponte, G. Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin inhibits expression and production of inflammatory mediators in interleukin-1β-induced human chondrocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 25, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Fukuya, Y.; Hashimoto, R.; Kanda, T.; Suzuki, H.; Okamura, Y.; Nanki, T.; Miyasaka, N.; Umezawa, K. Possible involvement of chemokine-induced platelet activation in thrombophilic diathesis of antiphospholipid syndrome: An attractive target for the NF-κB-specific inhibitor DHMEQ. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1173, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Nii, T.; Trimova, G.; Miura, S.; Umezawa, K.; Ushiyama, A.; Kubota, T. The NF-κB specific inhibitor DHMEQ prevents thrombosis formation in a mouse model of antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Nephropathol. 2013, 2, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ando, Y.; Keino, H.; Kudo, A.; Hitrakata, A.; Okada, A.A.; Umezawa, K. Anti-inflammatory effect of dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, a nuclear factor–κB inhibitor, on endotoxin-induced uveitis in rats in vivo and in vitro. Occular Immunol. Inflamm. 2019, 28, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, D.; Kitaichi, N.; Ebihara, A.; Iwabuchi, K.; Yoshida, K.; Namba, K.; Ozaki, M.; Ohno, S.; Umezawa, K.; Yamashita, K.; et al. Nuclear factor-κB inhibitor, dehydroxy methyl epoxyquinomicin ameliorates experimental autoimmune uveoreitinitis (EAU) in mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kudo, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hirakata, A.; Okada, A.A.; Umezawa, K.; Keino, H. Anti-inflammatory effects of the NF-κB inhibitor dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin on ARPE-19 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Kamoshita, M.; Osada, H.; Toda, E.; Kurihara, T.; Nagai, N.; Umezawa, K.; Tsubota, K. The neuroprotective effect of rapamycin as a modulator of the mTOR-NF-κB axis during retinal Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoshita, M.; Ozawa, Y.; Kubota, S.; Miyake, S.; Tsuda, C.; Nagai, N.; Yuki, K.; Shimmura, S.; Umezawa, K.; Tsubota, K. AMPK-NF-κB axis in the photoreceptor disorder during retinal inflammation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, N.; Oike, Y.; Izumi-Nagai, K.; Koto, T.; Satofuka, S.; Ozawa, Y.; Yamashiro, K.; Inoue, M.; Tsubota, K.; Umezawa, K.; et al. Suppression of diabetes-induced retinal inflammation by blocking angiotensin II type 1 receptor or its downstream NF-κB pathway. Investig. Ohthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 4342–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirasawa, M.; Takubo, K.; Osada, H.; Miyake, S.; Toda, E.; Endo, M.; Umezawa, K.; Tsubota, K.; Oike, Y.; Ozawa, Y. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 is a multistep regulator of inflammatory neovascularization in a murine model of age-related macular degeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 7373–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inokawa, S.; Watanabe, T.; Keino, H.; Sato, Y.; Hirakata, A.; Okada, A.A.; Fukuda, K.; Fukushima, A.; Umezawa, K. Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, a novel nuclear factor–κB inhibitor, reduces chemokines and adhesion molecule expression induced by IL-1β in human corneal fibroblasts. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, M.; Shimmura, S.; Kubota, S.; Miyashita, H.; Kato, N.; Noda, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Usui, T.; Ishida, S.; Umezawa, K.; et al. Hydrogen and N-acetyl-l-cysteine rescue oxidative stress-induced angiogenesis in a mouse corneal alkali-burn model. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salhy, M.; Umezawa, K.; Gilja, O.-H.; Hatlebakk, J.G.; Gundersen, D.; Hausken, T. Amelioration of severe TNBS induced colitis by novel AP-1 and NF-κB inhibitors in rats. Sci. World 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salhy, M.; Umezawa, K. Treatment with novel AP-1 and NF-κB inhibitors restores the colonic endocrine cells to normal levels in rats with DSS-induced colitis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salhy, M.; Umezawa, K. Anti-inflammatory effects of novel AP-1 and NF-κB inhibitors in dextran-sulfate-sodium-induced colitis in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Salhy, M.; Umezawa, K. Effects of AP-1 and NF-kappa B inhibitors on colonic endocrine cells in rats with TNBS-induced colitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Funakoshi, T.; Yamashita, K.; Ichikawa, N.; Fukai, M.; Suzuki, T.; Goto, R.; Oura, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Katsurada, T.; Ichihara, S.; et al. A novel NF-κB inhibitor, dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, ameliorates inflammatory colonic injury in mice. J. Crohn’s Colotis 2012, 6, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamashita, K.; Jomen, W.; Ueki, S.; Aoyagi, T.; Fukai, M.; Furukawa, H.; Umezawa, K.; Ozaki, M.; Todo, S. The novel NF-κB inhibitor, dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, prevents local and remote organ injury following intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 149, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, A.; Kosaka, T.; Seta, K.; Asano, T.; Umezawa, K.; Hayakawa, M. Novel NF-κB activation inhibitor prevents inflammatory injury in unilateral urethral obstruction. J. Urol. 2003, 169, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; Miyajima, A.; Kikuchi, E.; Horiguchi, Y.; Umezawa, K.; Ohigashi, T.; Nakashima, J.; Asano, T.; Oya, M. The novel NF-κB activation inhibitor dehydroxymethyl-epoxyquinomicin suppresses anti-Thy1.1-induced glomerulonephritis in rats. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2008, 110, e17–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimo, T.; Adachi, Y.; Yamanouchi, S.; Tsuji, S.; Kimata, T.; Umezawa, K.; Okigaki, M.; Takaya, J.; Ikehara, S.; Kaneko, K. A novel NF- kappaB inhibitor DHMEQ ameliorates puromycin aminonucleoside induced nephrosis in mice. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 37, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.; Shinoda, K.; Yoshida, T.; Shimoda, M.; Kanno, Y.; Mizuno, R.; Kono, H.; Asanuma, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Umezawa, K.; et al. Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, a novel nuclear factor-κB inhibitor, prevents the development of cyclosporine A nephrotoxicity in a rat model. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 21, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Yamashita, K.; Aoyagi, T.; Haga, S.; Suzuki, T.; Itoh, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Shimamura, T.; Furukawa, H.; Ozaki, M.; et al. Control of allograft rejection by applying a novel NF-κB inhibitor, dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin. Transplantation 2006, 82, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, R.; Yamashita, K.; Aoyagi, T.; Ueki, S.; Uno, M.; Oura, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Igarashi, R.; Shibasaki, S.; Wakayama, K.; et al. The immunomodulatory effect of nuclear factor-κB inhibition by dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin in combination with donor-specific blood transfusion. Transplantation 2012, 93, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraya, D.; Watanabe, M.; Koshizuka, Y.; Ogura, M.; Yoshida, T.; Asahi, Y.; Kamachi, H.; Nakamura, T.; Harashima, H.; Ozaki, M.; et al. Efficacy of DHMEQ, a NF-κB Inhibitor, in islet transplantation: I. HMGB1 suppression by DHMEQ prevents early islet graft damage. Transplantation 2013, 96, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Yamashita, K.; Kamachi, H.; Kuraya, D.; Koshizuka, Y.; Shibasaki, S.; Asahi, Y.; Ono, H.; Emoto, S.; Ogura, M.; et al. Efficacy of DHMEQ, a NF-κB inhibitor, in islet transplantation: II. Induction DHMEQ treatment ameliorates subsequent alloimmune responses and permits long-term islet allograft acceptance. Transplantation 2013, 96, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Matsushita, M.; Kamachi, H.; Tsuruga, Y.; Kasai, H.; Watanabe, M.; Ozaki, M.; Furukawa, H.; Umezawa, K.; et al. Donor pretreatment with DHMEQ improves islet transplantation. J. Surg. Res. 2010, 163, e23–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanouchi, S.; Adachi, Y.; Shimo, T.; Umezawa, K.; Okigaki, M.; Tsuji, S.; Li, M.; Takaya, J.; Kuge, T.; Ikehara, S.; et al. A nuclear factor-κB inhibitor, dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, ameliorates GVHD in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimo, T.; Adachi, Y.; Umezawa, K.; Okigaki, M.; Takaya, J.; Taniuchi, S.; Ikehara, S.; Kaneko, K. Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin (DHMEQ) can suppress tumour necrosis factor-a production in lipopolysaccharide-injected mice, resulting in rescuing mice from death in vivo. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 166, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shimizu, K.; Konno, S.; Ozaki, M.; Umezawa, K.; Yamashita, K.; Todo, S.; Nishimura, M. Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin (DHMEQ), a novel NF-kappaB inhibitor, inhibits allergic inflammation and airway remodelling in murine models of asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Kondo, Y.; Shinozaki, S.; Kaneko, E.; Ishigami, A.; Maruyama, N.; Umezawa, K.; Shimokado, K. A selective NF-κB inhibitor, DHMEQ, reduced atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2006, 13, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, O.; Shima, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Kawai, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Watanabe, K.; Umezawa, K. Inhibition of cellular adhesion in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by NF-κB inhibitor DHMEQ under flow. Oncol. Res. 2005, 15, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Umezawa, K.; Yasui, M. Apoptosis in mouse amniotic epithelium is induced by activated macrophages through the TNF receptor type 1/TNF pathway. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, K. Possible role of peritoneal NF-κB in peripheral inflammation and cancer: Lessons from the inhibitor DHMEQ. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2011, 65, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Horiguchi, Y.; Nakashima, J.; Kikuchi, E.; Kanao, K.; Miyajima, A.; Ohigashi, T.; Umezawa, K.; Murai, M. Prevention of cancer cachexia by a novel nuclear factor κB inhibitor in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5590–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vernon-Roberts, B. Lymphocyte to macrophage transformation in the peritoneal cavity preceding the mobilization of peritoneal macrophages to inflamed areas. Nature 1969, 222, 1286–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosińska, P.; Maćkowiak, B.; Staniszewski, R.; Umezawa, K.; Bręborowicz, A. Inhibition of NF-κB with dehydroxyepoxiquinomicin modifies function of human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5756–5765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Umezawa, K.; Breborowicz, A.; Gantsev, S. Anticancer activity of novel NF-κB inhibitor DHMEQ by intraperitoneal administration. Oncol. Res. 2020, 28, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disease or Treatment | Key Findings | Route | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atopic dermatitis | Amelioration of inflammatory score | Ointment | [29,30,31,32] |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Amelioration of arthritic score | IP | [8] |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Inhibition of paw swelling and bone destruction | SC | [38,39,41] |
| Anti-phospholipid disease | Inhibition of thrombus formation | IP | [45] |
| Uveitis | Reduction of infiltrating cells | IP | [46,47] |
| Retinal inflammation | Reduction of infiltrating cells and preservation of rhodopsin | IP | [49,50,51,52] |
| Corneal inflammation | Inhibition of angiogenesis | IP | [54] |
| Inflammatory bowel diseases | Amelioration of inflammatory score | IP | [55,56,57,58,59] |
| Intestinal ischemia/reperfusion | Amelioration of mucosal damage | IP | [60] |
| Kidney inflammation | Preservation of creatinine clearance and reduction of fibrosis | IP | [61,62,63,64] |
| Heart transplantation | Prolongation of graft survival | IP | [65,66] |
| Islet transplantation | Prolongation of graft survival | IP | [67,68,69] |
| Bone marrow transplantation | Amelioration of GVHD | IP | [70] |
| Sepsis | Prolongation of survival | IP | [71] |
| Asthma | Amelioration of airway remodeling | IP | [72] |
| Atherosclerosis | IP | [73] | |
| Premature birth | IP | [75] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sugai, T.; Kubota, T.; Keino, H.; El-Salhy, M.; Ozaki, M.; Umezawa, K. Inhibition of Cellular and Animal Inflammatory Disease Models by NF-κB Inhibitor DHMEQ. Cells 2021, 10, 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092271
Ma J, Zhang Y, Sugai T, Kubota T, Keino H, El-Salhy M, Ozaki M, Umezawa K. Inhibition of Cellular and Animal Inflammatory Disease Models by NF-κB Inhibitor DHMEQ. Cells. 2021; 10(9):2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092271
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jun, Yuyang Zhang, Takeshi Sugai, Tetsuo Kubota, Hiroshi Keino, Magdy El-Salhy, Michitaka Ozaki, and Kazuo Umezawa. 2021. "Inhibition of Cellular and Animal Inflammatory Disease Models by NF-κB Inhibitor DHMEQ" Cells 10, no. 9: 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092271
APA StyleMa, J., Zhang, Y., Sugai, T., Kubota, T., Keino, H., El-Salhy, M., Ozaki, M., & Umezawa, K. (2021). Inhibition of Cellular and Animal Inflammatory Disease Models by NF-κB Inhibitor DHMEQ. Cells, 10(9), 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092271







