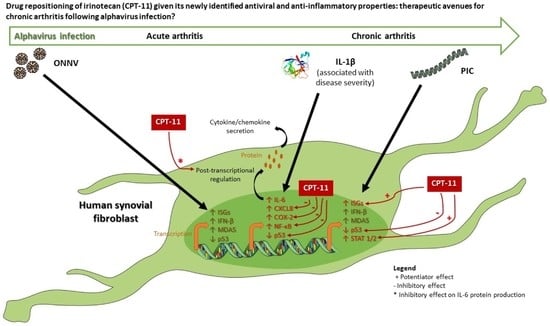
Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.3. MTT Assay
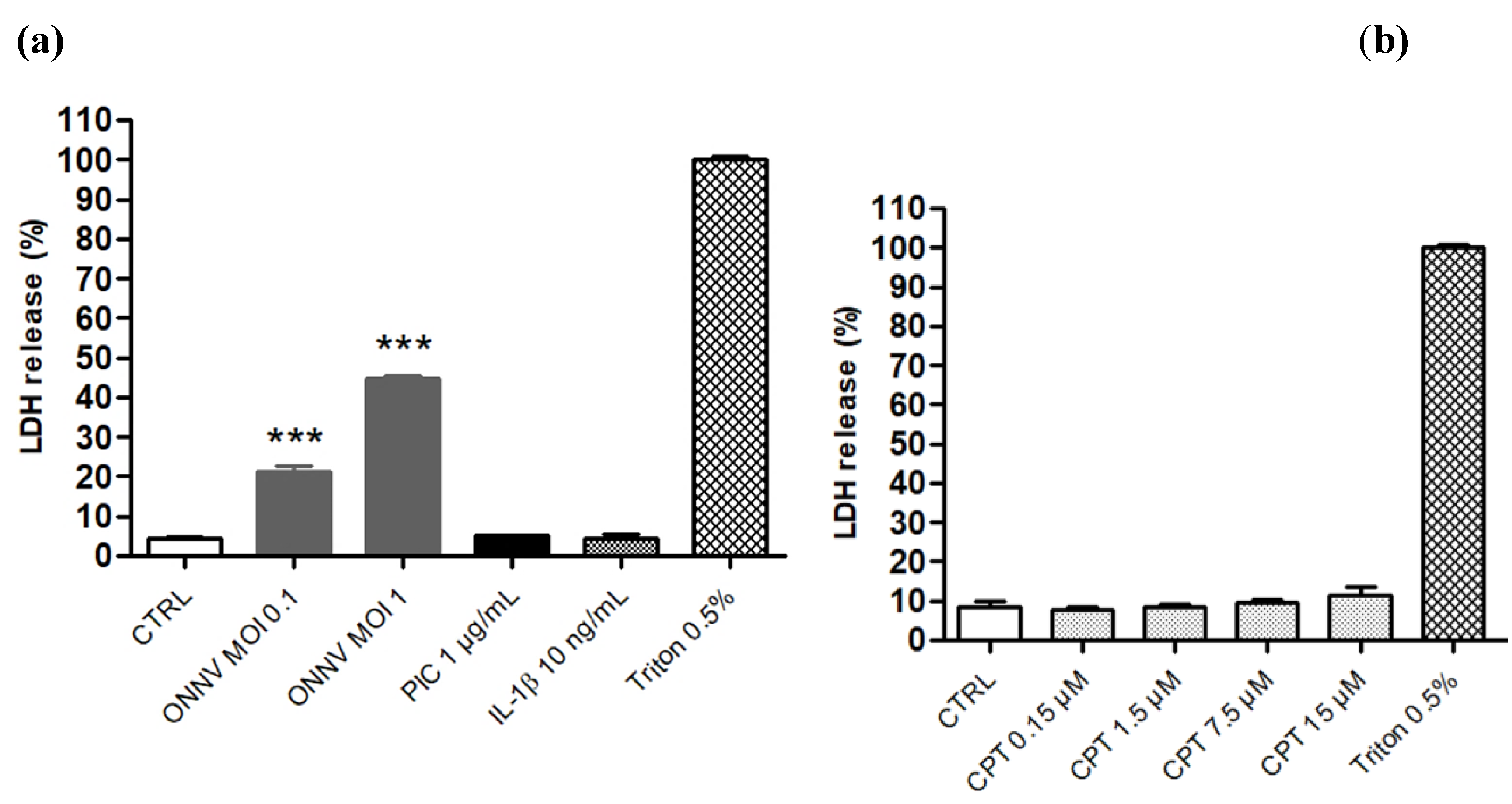
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay (LDH Assay)
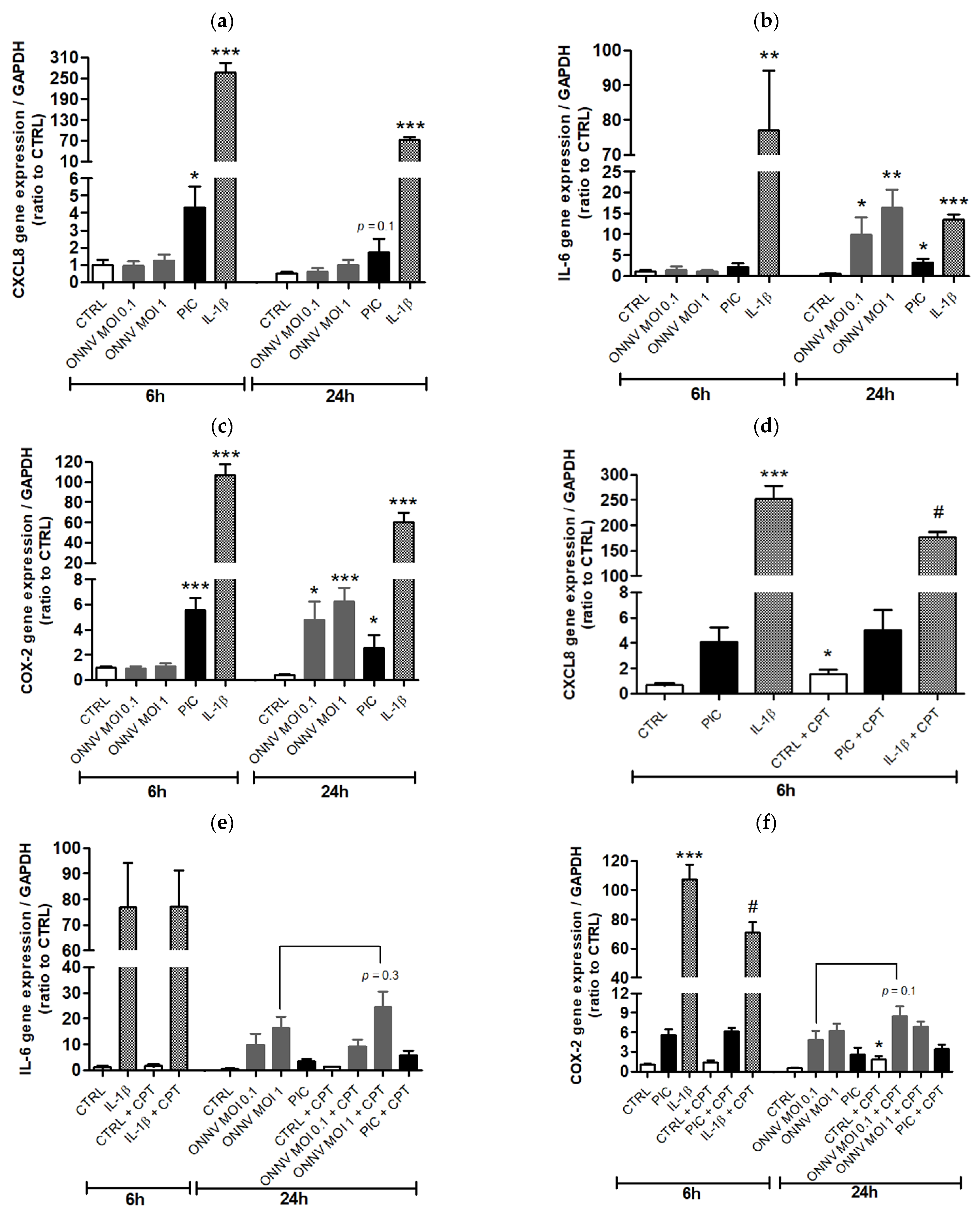
2.5. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
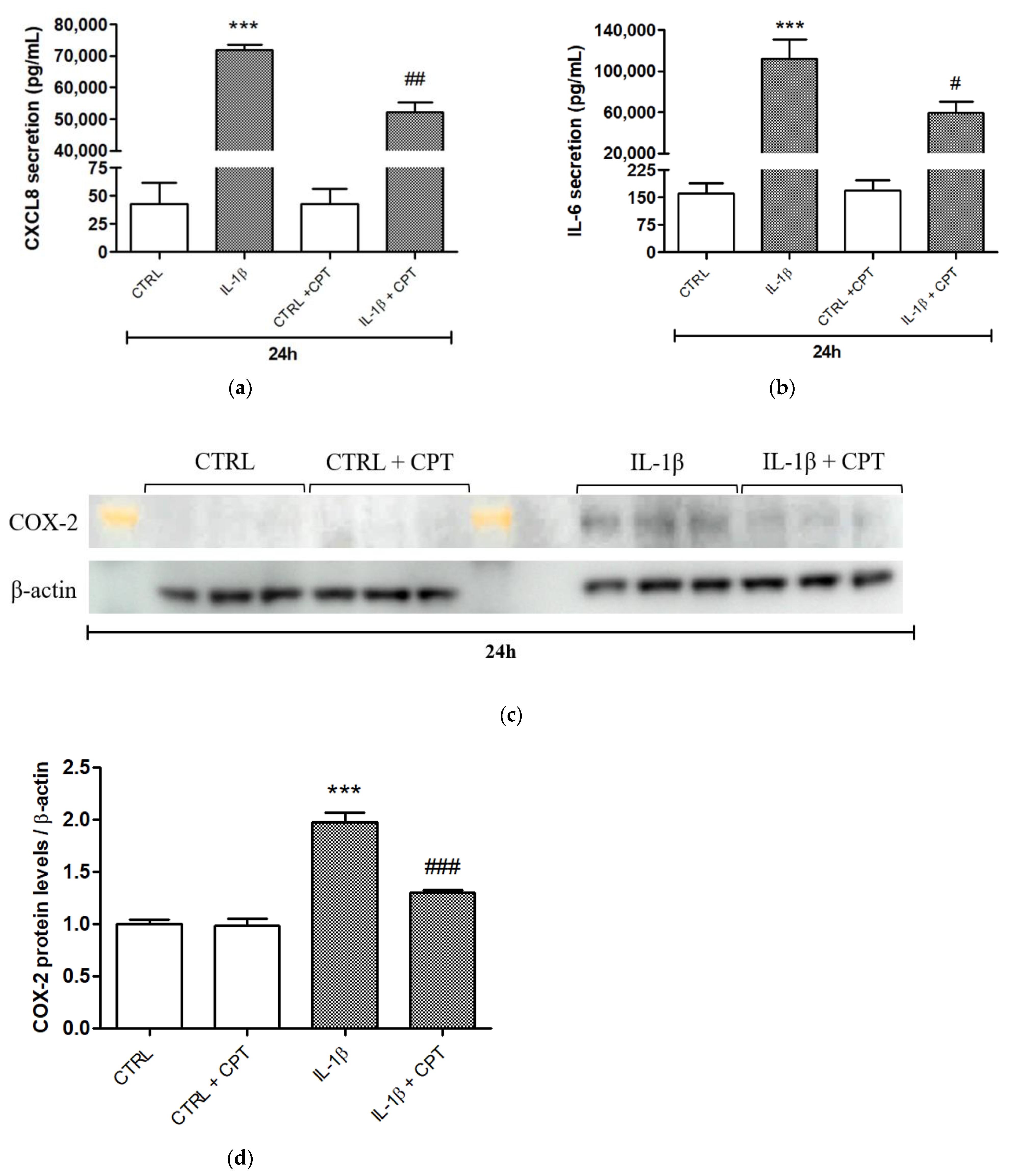
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
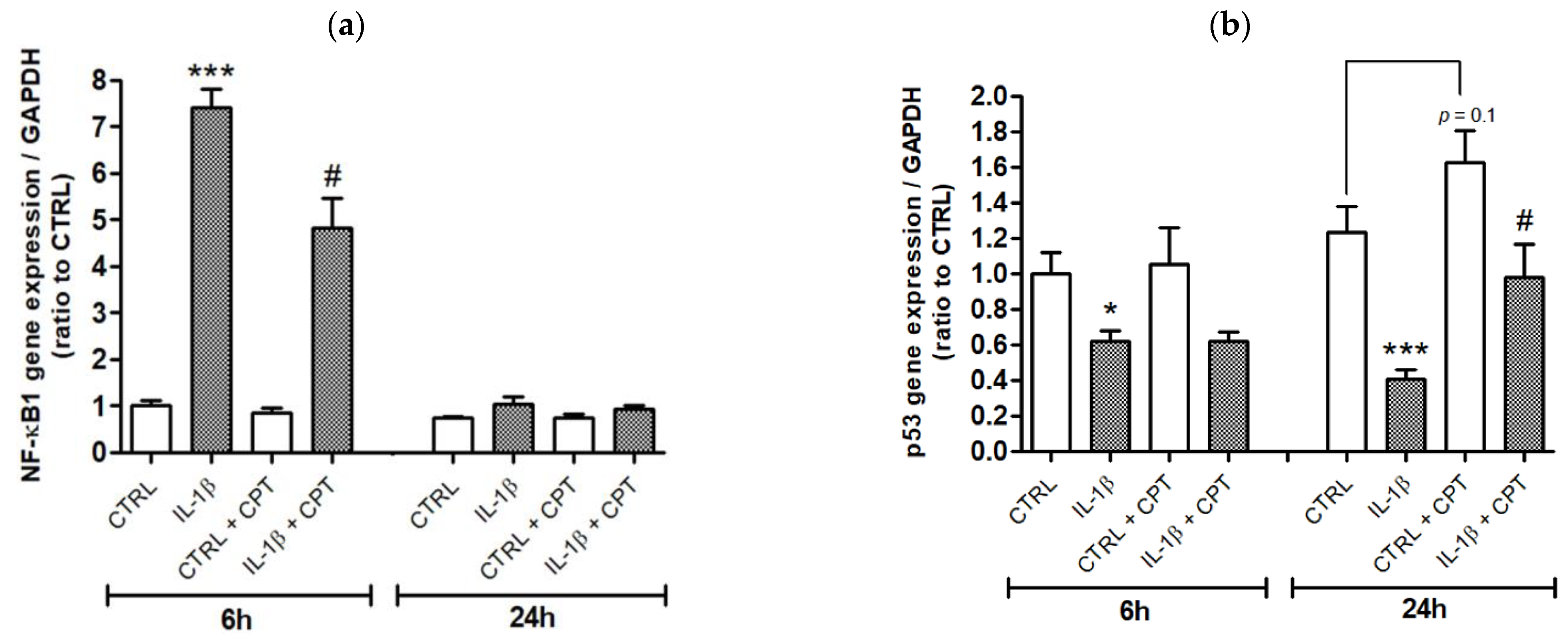
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marks, M.; Marks, J.L. Viral arthritis. Clin. Med. 2016, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, E.A.; Higgs, S. Impact of climate change and other factors on emerging arbovirus diseases. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Lecuit, M. Chikungunya virus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kurkela, S.; Manni, T.; Myllynen, J.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Clinical and laboratory manifestations of Sindbis virus infection: Prospective study, Finland, 2002–2003. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 1820–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgherini, G.; Poubeau, P.; Jossaume, A.; Gouix, A.; Cotte, L.; Michault, A.; Arvin-Berod, C.; Paganin, F. Persistent arthralgia associated with chikungunya virus: A study of 88 adult patients on reunion island. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafavi, H.; Abeyratne, E.; Zaid, A.; Taylor, A. Arthritogenic alphavirus-induced immunopathology and targeting host inflammation as a therapeutic strategy for alphaviral disease. Viruses 2019, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaaitanya, I.K.; Muruganandam, N.; Sundaram, S.G.; Kawalekar, O.; Sugunan, A.P.; Manimunda, S.P.; Ghosal, S.R.; Muthumani, K.; Vijayachari, P. Role of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in chronic arthropathy in CHIKV infection. Viral Immunol. 2011, 24, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuklia, W.; Kasisith, J.; Modhiran, N.; Rodpai, E.; Thannagith, M.; Thongsakulprasert, T.; Smith, D.R.; Ubol, S. Osteoclastogenesis induced by CHIKV-infected fibroblast-like synoviocytes: A possible interplay between synoviocytes and monocytes/macrophages in CHIKV-induced arthralgia/arthritis. Virus Res. 2013, 177, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troost, B.; Mulder, L.M.; Diosa-Toro, M.; van de Pol, D.; Rodenhuis-Zybert, I.A.; Smit, J.M. Tomatidine, a natural steroidal alkaloid shows antiviral activity towards chikungunya virus in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, T.; Liu, M.; Chen, F.; Liu, S.; Yang, J. Anti-influenza a virus activity of dendrobine and its mechanism of action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3665–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitby, K.; Pierson, T.C.; Geiss, B.; Lane, K.; Engle, M.; Zhou, Y.; Doms, R.W.; Diamond, M.S. Castanospermine, a potent inhibitor of dengue virus infection in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8698–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Kang, K.; Ming, G.; Kim, G.J.; Ha, T.-K.-Q.; Choi, H.; Oh, W.K.; Sung, S.H. Jubanines F-J, cyclopeptide alkaloids from the roots of Ziziphus jujuba. Phytochemistry 2015, 119, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantazis, P.; Han, Z.; Chatterjee, D.; Wyche, J. Water-insoluble camptothecin analogues as potential antiviral drugs. J. Biomed. Sci. 1999, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.C.; Avery, R.J.; Dimmock, N.J. Camptothecin: An inhibitor of influenza virus replication. J. Gen. Virol. 1974, 25, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, R.P.; Stewart, R.A.; Hogan, P.A.; Ptak, R.G.; Mankowski, M.K.; Hartman, T.L.; Buckheit, R.W.; Snyder, B.A.; Salter, J.D.; Morales, G.A.; et al. An analog of camptothecin inactive against Topoisomerase I is broadly neutralizing of HIV-1 through inhibition of Vif-dependent APOBEC3G degradation. Antivir. Res. 2016, 136, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, A.; Biewen, B.; Paulsen, M.T.; Berg, N.; Lima, L.C.D.A.; Prasad, J.; Bedi, K.; Magnuson, B.; Wilson, T.E.; Ljungman, M. Genome-wide transcriptional effects of the anti-cancer agent camptothecin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C. Irinotecan: 25 years of cancer treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanLandingham, D.L.; Higgs, S.; Hong, C.; Klingler, K.A.; McElroy, K.L.; Lehane, M.J.; Tsetsarkin, K. Determinants of vector specificity of o’nyong nyong and chikungunya viruses in Anopheles and Aedes mosquitoes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 74, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idili, A.; Arroyo-Curras, N.; Ploense, K.L.; Csordas, A.T.; Kuwahara, M.; Kippin, T.E.; Plaxco, K.W. Seconds-resolved pharmacokinetic measurements of the chemotherapeutic irinotecan in situ in the living body. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 8164–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, G.G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of irinotecan. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1997, 33, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Gale, M., Jr. Differential recognition of double-stranded RNA by RIG-I-like receptors in antiviral immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, K.; Xia, Y.; Zweier, J.L.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature 1997, 389, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assuncão-Miranda, I.; Cruz-Oliveira, C.; Da Poian, A.T. Molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of alphavirus-induced arthritis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 973516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.K.; Taylor, P.C.; Teixeira, M.M.; Morrison, T.E.T.; Schoen, R.T. The clinical features, pathogenesis and methotrexate therapy of chronic chikungunya arthritis. Viruses 2019, 11, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganas, C.; Liu, H.; Perlman, H.; Hoffmann, A.; Thimmapaya, B.; Pope, R.M. Regulation of IL-6 and IL-8 expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts: The dominant role for NF-kappa B but not C/EBP beta or c-Jun. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 7199–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, M.; Kojima, F.; Crofford, L. Arachidonic acid-derived eicosanoids in rheumatoid arthritis: Implications and future targets. Future Rheumatol. 2006, 1, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninla-Aesong, P.; Mitarnun, W.; Noipha, K. Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines as biomarkers of persistent arthralgia and severe disease after chikungunya virus infection: A 5-year follow-up study in Southern Thailand. Viral Immunol. 2019, 32, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, D.; Tang, F.; Zhang, X.; et al. p53 predominantly regulates IL-6 production and suppresses synovial inflammation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes and adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhrbier, A.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Gasque, P. Arthritogenic alphaviruses-an overview. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.; Gérardin, P.; Taylor, A.; Mostafavi, H.; Malvy, D.; Mahalingam, S. Review: Chikungunya arthritis: Implications of acute and chronic inflammation mechanisms on disease management. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoarau, J.J.; Jaffar Bandjee, M.C.; Krejbich Trotot, P.; Das, T.; Li-Pat-Yuen, G.; Dassa, B.; Denizot, M.; Guichard, E.; Ribera, A.; Henni, T.; et al. Persistent chronic inflammation and infection by Chikungunya arthritogenic alphavirus in spite of a robust host immune response. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5914–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokarewa, M.; Tarkowski, A.; Lind, M.; Dahlberg, L.; Magnusson, M. Arthritogenic dsRNA is present in synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis patients with an erosive disease course. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 3237–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoui, Y.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Selambarom, J.; Guiraud, P.; Gasque, P. Immunomodulatory drug methotrexate used to treat patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatisms post-chikungunya does not impair the synovial antiviral and bone repair responses. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fros, J.J.; Pijlman, G.P. Alphavirus infection: Host cell shut-off and inhibition of antiviral responses. Viruses 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hummer, B.T.; Li, X.; Hassel, B.A. Camptothecin induces the ubiquitin-like protein, ISG15, and enhances ISG15 conjugation in response to interferon. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004, 24, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, C.A. Regulating IRFs in IFN driven disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Takaoka, A.; Taniguchi, T. Type I interferon gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity 2006, 25, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornan, D.; Eckert, M.; Wallace, M.; Shimizu, H.; Ramsay, E.; Hupp, T.R.; Ball, K.L. Interferon regulatory factor 1 binding to p300 stimulates DNA-dependent acetylation of p53. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 10083–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Chung, C.H. Interferon-stimulated gene 15 in the control of cellular responses to genotoxic stress. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Verma, U.N.; Gaynor, R.B.; Frenkel, E.P.; Becerra, C.R. Enhanced chemosensitivity to irinotecan by RNA interference-mediated down-regulation of the nuclear factor-kappaB p65 subunit. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3333–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Shin, J.H.; Ham, D.W.; Shin, E.H. Toxoplasma GRA16 inhibits NF-kappaB activation through PP2A-B55 upregulation in non-small-cell lung carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Gales, D.; Valenzuela, P.; Miller, S.; Yehualaeshet, T.; Manne, U.; Francia, G.; Samuel, T. Bromoethylindole (BEI-9) redirects NF-kB signaling induced by camptothecin and TNFα to promote cell death in colon cancer cells. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lou, W.-H.; Xu, X.-F.; Wu, W.; Rong, Y.-F.; Jin, D.-Y. SN38 increases IL-8 expression through the MAPK pathways in HCT8 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 39, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedlinger, T.; Bartkuhn, M.; Zimmermann, T.; Hake, S.B.; Nist, A.; Stiewe, T.; Kracht, M.; Schmitz, M.L. Chemotherapeutic drugs inhibiting topoisomerase 1 activity impede cytokine-induced and NF-kappaB p65-regulated gene expression. Cancers 2019, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.F.; Chow, A.; Sun, Y.J.; Kwek, D.J.; Lim, P.L.; Dimatatac, F.; Ng, L.C.; Ooi, E.E.; Choo, K.H.; Her, Z.; et al. IL-1β, IL-6, and RANTES as biomarkers of Chikungunya severity. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, W.T.; Nassar, N.N.; Ravindra, D.; Li, X.; Meffert, M.K. Multi-level regulatory interactions between NF-kB and the pluripotency factor Lin28. Cells 2020, 9, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; VandenBoom, T.G., II; Kong, D.; Wang, Z.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Up-regulation of miR-200 and let-7 by natural agents leads to the reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6704–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuah, N.H.; Nagoor, N.H. Regulation of MicroRNAs by natural agents: New strategies in cancer therapies. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 804510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet, C.; Catelli, M.-G.; Hecale-Perlemoine, K.; Bricaire, L.; Garcia, C.; Gallet-Dierick, A.; Rodriguez, S.; Cormier, F.; Groussin, L. Dual specificity phosphatase 5, a specific negative regulator of ERK signaling, is induced by serum response factor and Elk-1 transcription factor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharska, A.; Rushworth, L.K.; Staples, C.; Morrice, N.A.; Keyse, S.M. Regulation of the inducible nuclear dual-specificity phosphatase DUSP5 by ERK MAPK. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Cho, Y.C.; Ju, A.; Lee, S.; Park, B.C.; Park, S.G.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.; Cho, S. Dual-specificity phosphatase 5 acts as an anti-inflammatory regulator by inhibiting the ERK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibian, J.S.; Jefic, M.; Bagchi, R.A.; Lane, R.H.; McKnight, R.A.; McKinsey, T.A.; Morrison, R.F.; Ferguson, B.S. DUSP5 functions as a feedback regulator of TNFα-induced ERK1/2 dephosphorylation and inflammatory gene expression in adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Kubota, Y.; Ishida, H.; Sasaki, Y. Irinotecan, a key chemotherapeutic drug for metastatic colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12234–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleiberg, H.; Cvitkovic, E. Characterisation and clinical management of CPT-11 (irinotecan)-induced adverse events: The European perspective. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32, S18–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, D.; Lu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yao, X. Protective effect of curcumin against irinotecan-induced intestinal mucosal injury via attenuation of NFkappaB activation, oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weingart, J.D.; Thompson, R.C.; Tyler, B.; Colvin, O.M.; Brem, H. Local delivery of the topoisomerase I inhibitor camptothecin sodium prolongs survival in the rat intracranial 9L gliosarcoma model. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 62, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Name | Sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|
| GAPDH_F (Forward) | TGTTCGTCATGGGTGTGAAC |
| GAPDH_R (Reverse) | GCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG |
| E1_F | CACCGTCCCCGTACGTAAAA |
| E1_R | GGCTCTGTAGGCTGATGCAA |
| nsP2_F | GCGGAGCAGGTAAAAACGTG |
| nsP2_R | TAGAACACGCCCGTCGTATG |
| ISG15_F | AGATCACCCAGAAGATCGGC |
| ISG15_R | GAGGTTCGTCGCATTTGTCC |
| IFN-β_F | GTTCGTGTTGTCAACATGACCAA |
| IFN-β_R | TCAATTGCCACAGGAGCTTCT |
| MDA5_F | CTGTTTACATTGCCAAGGATC |
| MDA5_R | ACACCAGCATCTTCTCCATTT |
| STAT1_F | TGGTGAAATTGCAAGAGCTG |
| STAT1_R | AGAGGTCGTCTCGAGGTCAA |
| p53_F | GAAGAGAATCTCCGCAAGAAAGG |
| p53_R | TCCATCCAGTGGTTTCTTCTTTG |
| ISG54_F | CTGGTCACCTGGGGAAACTA |
| ISG54_R | GAGCCTTCTCAAAGCACACC |
| OAS1_F | CATGCAAATCAACCATGCCA |
| OAS1_R | ACAACCAGGTCAGCGTCAGATC |
| PKR_F | GTGATGCAGCTCACAATGCT |
| PKR_R | GGCACTGTAAAATGGGTGCT |
| CXCL8_F | CAGAGACAGCAGAGCACACA |
| CXCL8_R | GGCAAAACTGCACCTTCACA |
| IL-6_F | TACAGGGAGAGGGAGCGATAA |
| IL-6_R | TGGACCGAAGGCGCTTGT |
| COX-2_F | TGGCTACAAAAGCTGGGAAG |
| COX-2_R | GGGGATCAGGGATGAACTTT |
| NFKB1_F | CCGGCCCGCCTGAATCATTCTC |
| NFKB1_R | CAGGTGGCGACCGTGATACCT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobi, A.; Gasque, P.; Guiraud, P.; Selambarom, J. Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells 2021, 10, 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061431
Dobi A, Gasque P, Guiraud P, Selambarom J. Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061431
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobi, Anthony, Philippe Gasque, Pascale Guiraud, and Jimmy Selambarom. 2021. "Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts" Cells 10, no. 6: 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061431
APA StyleDobi, A., Gasque, P., Guiraud, P., & Selambarom, J. (2021). Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells, 10(6), 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061431