Hypoxia-Induced Reactivity of Tumor-Associated Astrocytes Affects Glioma Cell Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Murine Gliomas
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.3. Immunofluorescence
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Real-Time qPCR
2.6. Cytokine Array
2.7. Astrocyte-Derived Matrix
2.8. Colony Assay
2.9. Side Population
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
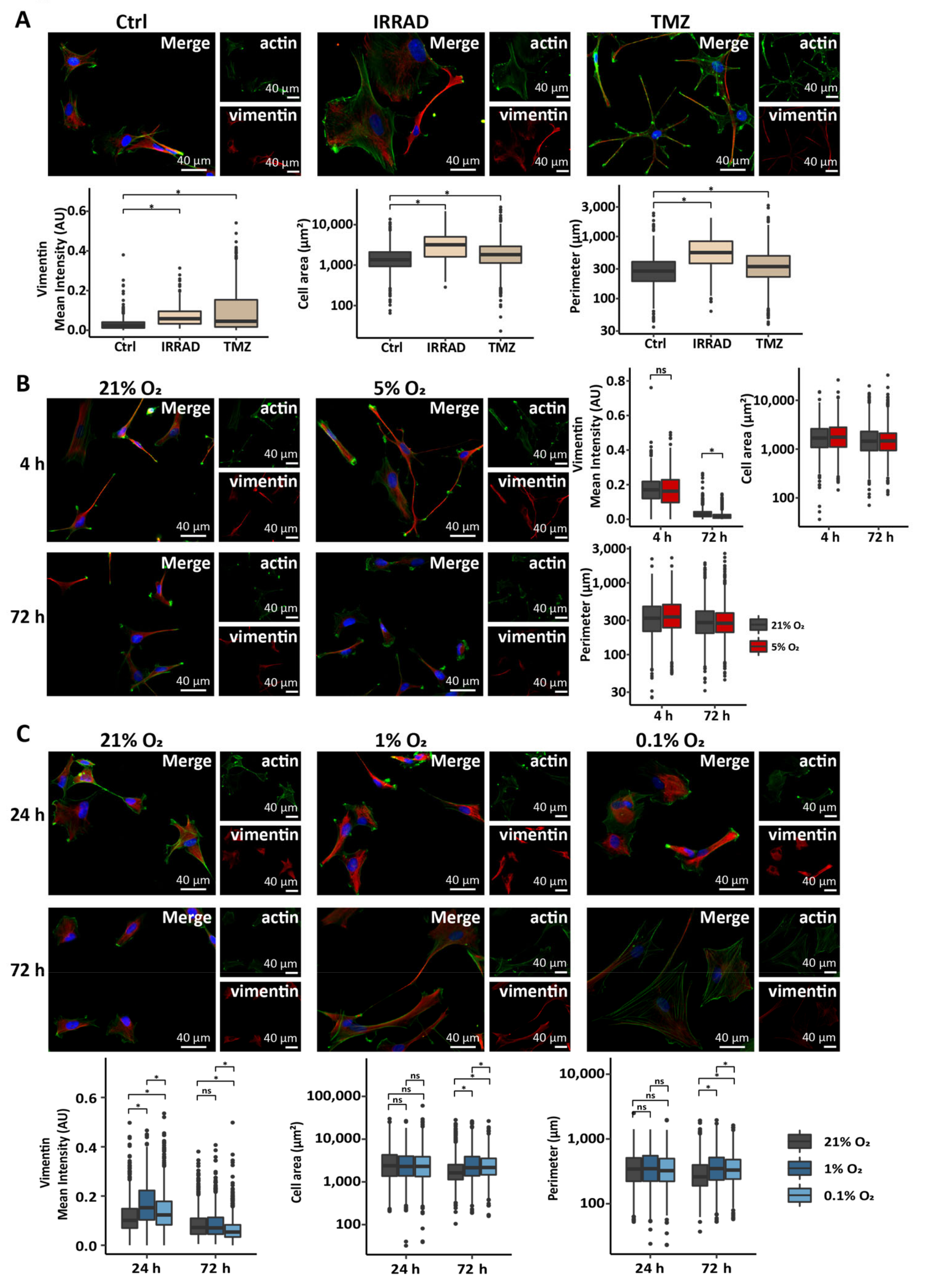
3.1. Astrocytes Adopt a Reactive Phenotype in Response to Stress Related to the Glioma Microenvironment
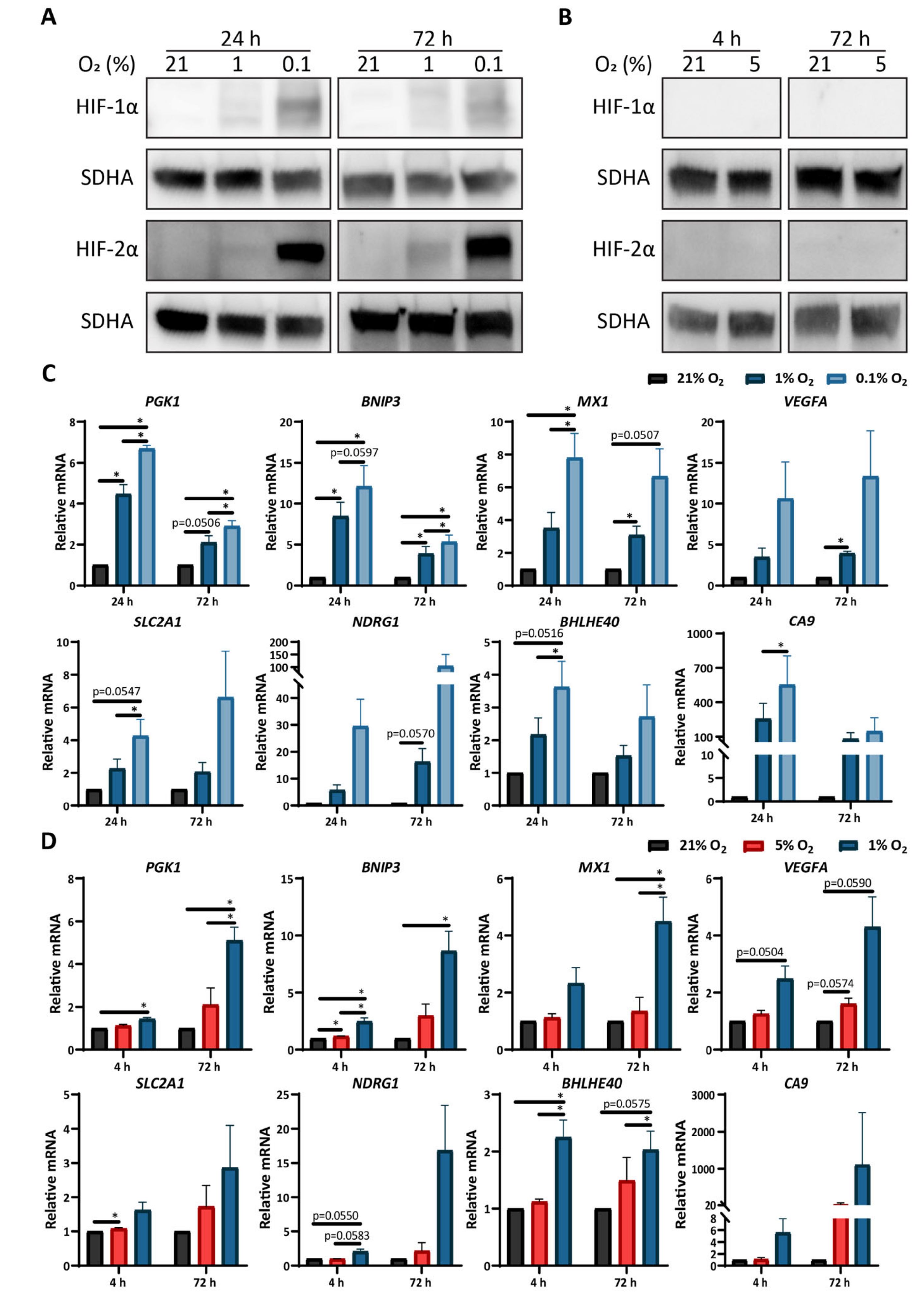
3.2. Low Oxygen Tension Induces a Strong Hypoxic Response in Astrocytes
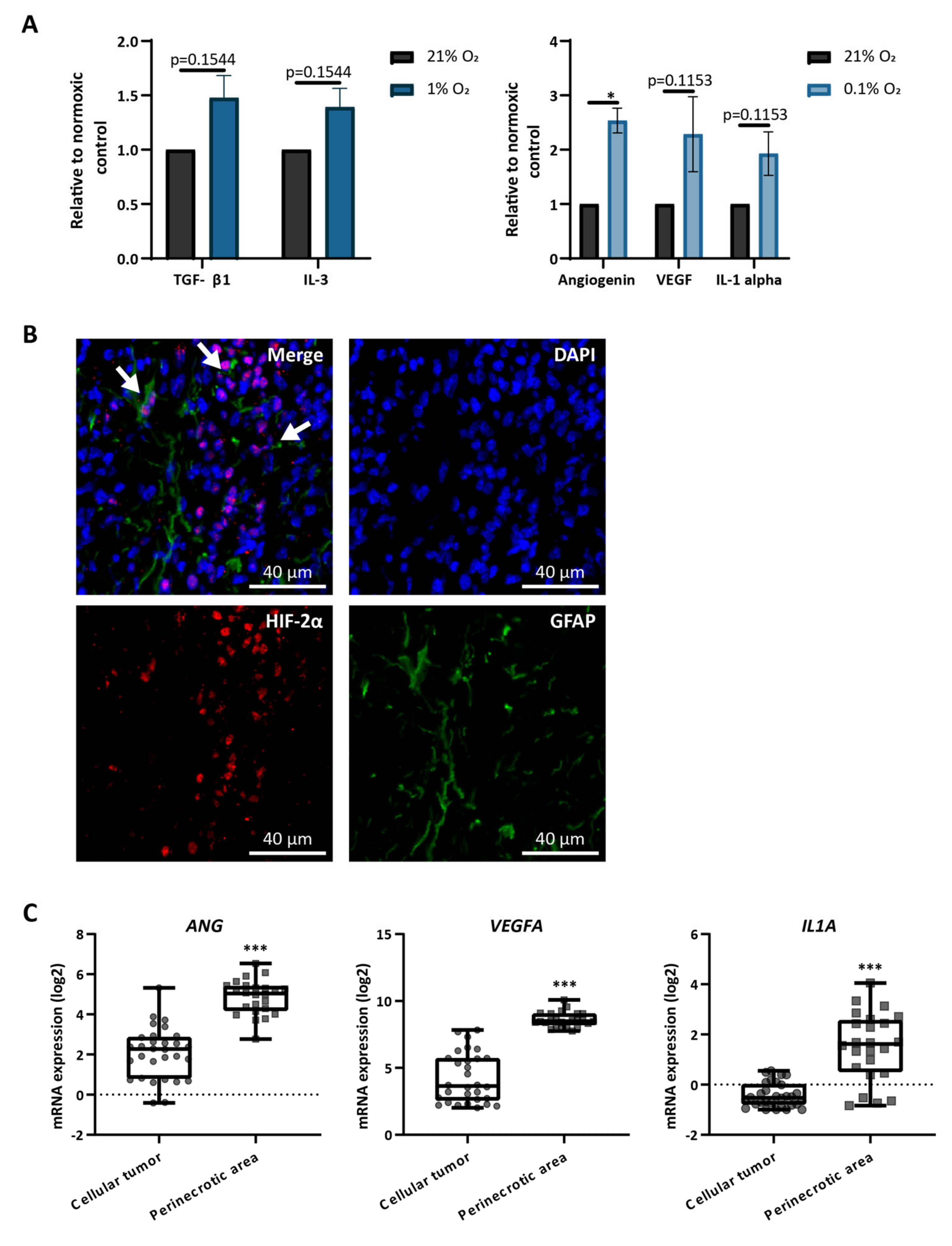
3.3. Astrocytes Produce Hypoxia-Related Cytokines In Vitro and Are Present in Hypoxic Areas In Vivo
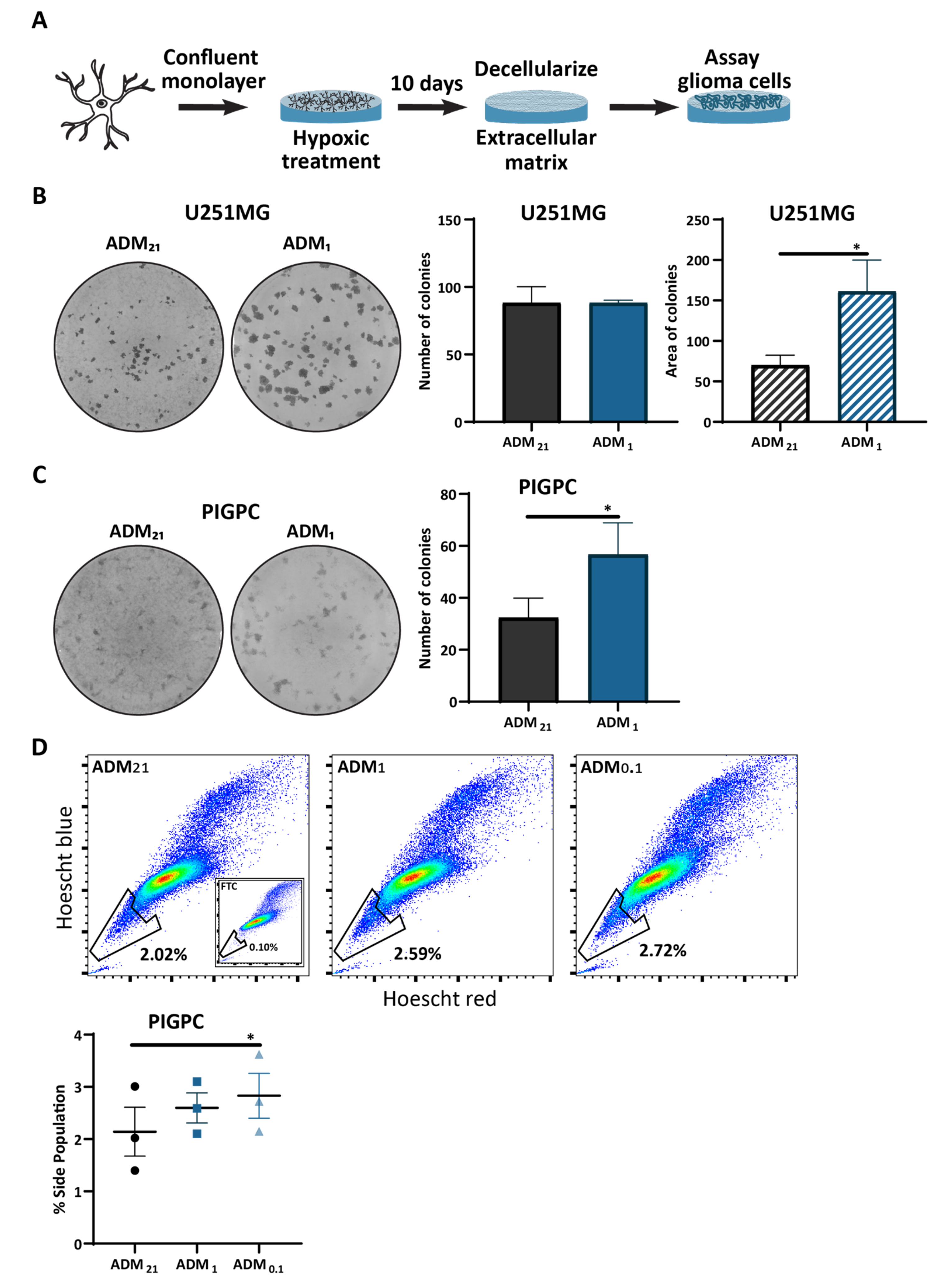
3.4. Extracellular Matrix from Hypoxic Astrocytes Alters the Properties of Glioma Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; Bent, M.J.V.D.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C. Targeting brain cancer: Advances in the molecular pathology of malignant glioma and medulloblastoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathia, J.D.; Mack, S.C.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.; Valentim, C.L.; Rich, J.N. Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Eyler, C.; Sathornsumetee, S.; Shi, Q.; Cao, Y.; Lathia, J.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors Regulate Tumorigenic Capacity of Glioma Stem Cells. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambardzumyan, D.; Bergers, G. Glioblastoma: Defining Tumor Niches. Trends Cancer 2015, 1, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors: Mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C. Hypoxia-inducible factor 3 biology: Complexities and emerging themes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell 2016, 310, C260–C269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivan, M.; Kaelin, W.G. The EGLN-HIF O2-Sensing System: Multiple Inputs and Feedbacks. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.Y.; Powis, G. HAF: The new player in oxygen-independent HIF-1α degradation. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Rich, J.N. Hypoxia and Hypoxia Inducible Factors in Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 345, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heddleston, J.M.; Li, Z.; Lathia, J.D.; Bao, S.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Rich, J.N. Hypoxia inducible factors in cancer stem cells. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, B.; Khwaja, F.W.; Severson, E.A.; Matheny, S.L.; Brat, D.J.; Van Meir, E.G. Hypoxia and the hypoxia-inducible-factor pathway in glioma growth and angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol. 2005, 7, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, H. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1–mediated characteristic features of cancer cells for tumor radioresistance. J. Radiat. Res. 2016, 57, i99–i105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Wei, F.; Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Shi, L.; Xiong, F.; Gong, Z.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Deng, H.; et al. Role of metabolism in cancer cell radioresistance and radiosensitization methods. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Tameemi, W.; Dale, T.P.; Al-Jumaily, R.M.K.; Forsyth, N.R. Hypoxia-Modified Cancer Cell Metabolism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahimi-Horn, M.C.; Pouysségur, J. Hypoxia in cancer cell metabolism and pH regulation. Essays Biochem. 2007, 43, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, E.; Grassi, E.S.; Pantazopoulou, V.; Tong, B.; Lindgren, D.; Berg, T.J.; Pietras, E.J.; Axelson, H.; Pietras, A. CD44 Interacts with HIF-2α to Modulate the Hypoxic Phenotype of Perinecrotic and Perivascular Glioma Cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.; Poppleton, H.; Kocak, M.; Hogg, T.L.; Fuller, C.; Hamner, B.; Oh, E.Y.; Gaber, M.W.; Finklestein, D.; Allen, M.; et al. A Perivascular Niche for Brain Tumor Stem Cells. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, E.S.; Jeannot, P.; Pantazopoulou, V.; Berg, T.J.; Pietras, A. Niche-derived soluble DLK1 promotes glioma growth. Neoplasia 2020, 22, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, E.S.; Pantazopoulou, V.; Pietras, A. Hypoxia-induced release, nuclear translocation, and signaling activity of a DLK1 intracellular fragment in glioma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4028–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, B.; Pantazopoulou, V.; Johansson, E.; Pietras, A. The p75 neurotrophin receptor enhances HIF-dependent signaling in glioma. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 371, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. The Microenvironmental Landscape of Brain Tumors. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mega, A.; Nilsen, M.H.; Leiss, L.W.; Tobin, N.P.; Miletic, H.; Sleire, L.; Strell, C.; Nelander, S.; Krona, C.; Hägerstrand, D.; et al. Astrocytes enhance glioblastoma growth. Glia 2020, 68, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, W.C.; Aftab, Q.; Bechberger, J.F.; Leung, J.H.; Chen, H.; Naus, C.C. Astrocytes promote glioma invasion via the gap junction protein connexin43. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1504–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oushy, S.; Hellwinkel, J.E.; Wang, M.; Nguyen, G.J.; Gunaydin, D.; Harland, T.A.; Anchordoquy, T.J.; Graner, M.W. Glioblastoma multiforme-derived extracellular vesicles drive normal astrocytes towards a tumour-enhancing phenotype. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 373, 20160477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Perez, M.; Voytik-Harbin, S.L.; Rickus, J.L. Extracellular Matrix Properties Regulate the Migratory Response of Glioblastoma Stem Cells in Three-Dimensional Culture. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21, 2572–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, B.H.; Fair, J.M.; Jamal, M.; Camphausen, K.; Tofilon, P.J. Astrocytes Enhance the Invasion Potential of Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, E.S.; Lee, J.-S.; Lin, Q.; Langley, R.R.; Maya, M.; He, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Weihua, Z.; et al. Astrocytes Upregulate Survival Genes in Tumor Cells and Induce Protection from Chemotherapy. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, N.; Du, X.; He, Y.; Chen, S.; Shao, Q.; Ma, C.; Huang, B.; Chen, A.; Zhao, P.; et al. Glioma cells escaped from cytotoxicity of temozolomide and vincristine by communicating with human astrocytes. Med Oncol. 2015, 32, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Balasubramanian, K.; Fan, D.; Kim, S.-J.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Bar-Eli, M.; Aldape, K.D.; Fidler, I.J. Reactive Astrocytes Protect Melanoma Cells from Chemotherapy by Sequestering Intracellular Calcium through Gap Junction Communication Channels. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priego, N.; Valiente, M. The Potential of Astrocytes as Immune Modulators in Brain Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, T.J.; Marques, C.; Pantazopoulou, V.; Johansson, E.; Von Stedingk, K.; Lindgren, D.; Jeannot, P.; Pietras, E.J.; Bergstrom, T.; Swartling, F.J.; et al. The irradiated brain microenvironment supports glioma stemness and survival via astrocyte-derived Transglutaminase 2. Cancer Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, E.C.; Hively, W.P.; Depinho, R.A.; Varmus, H.E. A constitutively active epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with disruption of G1 cell-cycle arrest pathways to induce glioma-like lesions in mice. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3675–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, T.; Riester, M.; Cheng, Y.-K.; Huse, J.T.; Squatrito, M.; Helmy, K.; Charles, N.; Michor, F.; Holland, E.C. Most Human Non-GCIMP Glioblastoma Subtypes Evolve from a Common Proneural-like Precursor Glioma. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietras, A.; Katz, A.M.; Ekström, E.J.; Wee, B.; Halliday, J.J.; Pitter, K.L.; Werbeck, J.L.; Amankulor, N.M.; Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C. Osteopontin-CD44 Signaling in the Glioma Perivascular Niche Enhances Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes and Promotes Aggressive Tumor Growth. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuin, C.; Goodman, A.; Chernyshev, V.; Kamentsky, L.; Cimini, B.A.; Karhohs, K.W.; Doan, M.; Ding, L.; Rafelski, S.M.; Thirstrup, D.; et al. CellProfiler 3.0: Next-generation image processing for biology. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2005970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0034.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleau, A.-M.; Hambardzumyan, D.; Ozawa, T.; Fomchenko, E.I.; Huse, J.T.; Brennan, C.W.; Holland, E.C. PTEN/PI3K/Akt Pathway Regulates the Side Population Phenotype and ABCG2 Activity in Glioma Tumor Stem-like Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Molecular dissection of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, S.R. Defining normoxia, physoxia and hypoxia in tumours—implications for treatment response. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20130676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, T.P.; Mann, G.E. Defining Physiological Normoxia for Improved Translation of Cell Physiology to Animal Models and Humans. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 161–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamerlik, P.; Lathia, J.D.; Rasmussen, R.; Wu, Q.; Bartkova, J.; Lee, M.; Moudry, P.; Bartek, J.; Fischer, W.; Lukas, J.; et al. Autocrine VEGF–VEGFR2–Neuropilin-1 signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell viability and tumor growth. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarassishin, L.; Lim, J.; Weatherly, D.B.; Angeletti, R.H.; Lee, S.C. Interleukin-1-induced changes in the glioblastoma secretome suggest its role in tumor progression. J. Proteom. 2014, 99, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-K.; Jin, X.; Sohn, Y.-W.; Jin, X.; Jeon, H.-Y.; Kim, E.-J.; Ham, S.W.; Jeon, H.-M.; Chang, S.-Y.; Oh, S.-Y.; et al. Tumoral RANKL activates astrocytes that promote glioma cell invasion through cytokine signaling. Cancer Lett. 2014, 353, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Fu, W.; Cai, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Xing, W.; Wang, Y.; Zou, M.; Xu, T.; Xu, N. Angiogenin Promotes U87MG Cell Proliferation by Activating NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Downregulating Its Binding Partner FHL3. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Chung, H.Y.; Ehrlich, L.A.; Jelinek, D.F.; Callander, N.S.; Roodman, G.D.; Choi, S.J. IL-3 expression by myeloma cells increases both osteoclast formation and growth of myeloma cells. Blood 2004, 103, 2308–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, R.B.; Shah, N.; Miller, J.; Dalley, R.; Nomura, S.R.; Yoon, J.-G.; Smith, K.A.; Lankerovich, M.; Bertagnolli, D.; Bickley, K.; et al. An anatomic transcriptional atlas of human glioblastoma. Science 2018, 360, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, B.; Pietras, A.; Ozawa, T.; Bazzoli, E.; Podlaha, O.; Antczak, C.; Westermark, B.; Nelander, S.; Uhrbom, L.; Forsberg-Nilsson, K.; et al. ABCG2 regulates self-renewal and stem cell marker expression but not tumorigenicity or radiation resistance of glioma cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzewska, P.; Christianson, H.C.; Welch, J.E.; Svensson, K.J.; Fredlund, E.; Ringnér, M.; Mörgelin, M.; Bourseau-Guilmain, E.; Bengzon, J.; Belting, M. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7312–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, C.; Yu, Z. Hypoxia enhances CXCR4 expression favoring microglia migration via HIF-1α activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, G.R.; Ding, S. Reactive astrocytes and therapeutic potential in focal ischemic stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 85, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, N.R.; Yew, W.P. Reactive astrogliosis in stroke: Contributions of astrocytes to recovery of neurological function. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 107, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmquist-Mengelbier, L.; Fredlund, E.; Löfstedt, T.; Noguera, R.; Navarro, S.; Nilsson, H.; Pietras, A.; Vallon-Christersson, J.; Borg, Åke; Gradin, K.; et al. Recruitment of HIF-1α and HIF-2α to common target genes is differentially regulated in neuroblastoma: HIF-2α promotes an aggressive phenotype. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfstedt, T.; Fredlund, E.; Holmquist-Mengelbier, L.; Pietras, A.; Ovenberger, M.; Poellinger, L.; Påhlman, S. Hypoxia Inducible Factor-2α in Cancer. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandao, M.; Simon, T.; Critchley, G.; Giamas, G. Astrocytes, the rising stars of the glioblastoma microenvironment. Glia 2019, 67, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mense, S.M.; Sengupta, A.; Zhou, M.; Lan, C.; Bentsman, G.; Volsky, D.J.; Zhang, L. Gene expression profiling reveals the profound upregulation of hypoxia-responsive genes in primary human astrocytes. Physiol. Genom. 2006, 25, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, N.; Wang, L.; Kishimoto, K.; Tsuji, T.; Hu, G.-F. A therapeutic target for prostate cancer based on angiogenin-stimulated angiogenesis and cancer cell proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14519–14524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Weng, C.; Xu, Z. Interaction between angiogenin and fibulin 1: Evidence and implication. Acta Biochim. et Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Jiang, F.; Kalkanis, S.N.; Zhang, Z.G.; Zhang, X.-P.; Decarvalho, A.C.; Katakowski, M.; Bobbitt, K.; Mikkelsen, T.; Chopp, M. SDF-1 and CXCR4 are up-regulated by VEGF and contribute to glioma cell invasion. Cancer Lett. 2006, 236, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagzag, D.; Lukyanov, Y.; Lan, L.; Ali, M.A.; Esencay, M.; Mendez, O.; Yee, H.; Voura, E.B.; Newcomb, E.W. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and VEGF upregulate CXCR4 in glioblastoma: Implications for angiogenesis and glioma cell invasion. Lab. Investig. 2006, 86, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, P.; Shin, S.-H.; Chun, Y.-S.; Shin, H.-W.; Shin, Y.J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.; Nam, D.-H.; Park, J.-W. Astrocyte-derived CCL20 reinforces HIF-1-mediated hypoxic responses in glioblastoma by stimulating the CCR6-NF-κB signaling pathway. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3070–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, A.; E Price, J.; García-Ramirez, M.; Méndez, O.; López, L.; Fabra, A. Astrocyte-derived cytokines contribute to the metastatic brain specificity of breast cancer cells. Lab. Investig. 1997, 77, 357–368. [Google Scholar]
- Batlle, E.; Clevers, H. Cancer stem cells revisited. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirkse, A.; Golebiewska, A.; Buder, T.; Nazarov, P.V.; Muller, A.; Poovathingal, S.; Brons, N.H.C.; Leite, S.; Sauvageot, N.; Sarkisjan, D.; et al. Stem cell-associated heterogeneity in Glioblastoma results from intrinsic tumor plasticity shaped by the microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.; Troike, K.; Silver, D.J.; Lathia, J.D. The evolution of the cancer stem cell state in glioblastoma: Emerging insights into the next generation of functional interactions. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T.; Luque, A.; Lee, S.; Anderson, S.M.; Segura, T.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. Anchorage of VEGF to the extracellular matrix conveys differential signaling responses to endothelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipale, J.; Keski-Oja, J. Growth factors in the extracellular matrix. FASEB J. 1997, 11, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Forward primer (5′-3′) | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| SDHA | TGGGAACAAGAGGGCATCTG | CCACCACTGCATCAAATTCATG |
| UBC | ATTTGGGTCGCGGTTCTT | TGCCTTGACATTCTCGATGGT |
| YWHAZ | ACTTTTGGTACATTGTGGCTTCAA | CCGCCAGGACAAACCAGTAT |
| MXI1 | AGAGGAGATTGAAGTGGATG | CTGGGTTCTATGAAGTGAATG |
| PGK1 | AGATTCAGCTAGTGGCCAAGAGAT | TGCAGTGAAGATGAGCTGAGATG |
| BNIP3 | AAAATATTCCCCCCAAGGAGTTC | ACGCTCGTGTTCCTCATGCT |
| SLC2A1 | CTTCTATCCCAGGAGGTG | AATGGAGCCTGACCCCTA |
| BHLHE40 | CAGTGGCTATGGAGGAGAATCG | GCGTCCGTGGTCACTTTTG |
| VEGFA | CGAAGTGGTGAAGTTCATGGATG | TTCTGTATCAGTCTTTCCTGGTGAG |
| CA9 | CCAGGCCTCACTGGCAACT | TCGCCCAGTGGGTCATCT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantazopoulou, V.; Jeannot, P.; Rosberg, R.; Berg, T.J.; Pietras, A. Hypoxia-Induced Reactivity of Tumor-Associated Astrocytes Affects Glioma Cell Properties. Cells 2021, 10, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030613
Pantazopoulou V, Jeannot P, Rosberg R, Berg TJ, Pietras A. Hypoxia-Induced Reactivity of Tumor-Associated Astrocytes Affects Glioma Cell Properties. Cells. 2021; 10(3):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030613
Chicago/Turabian StylePantazopoulou, Vasiliki, Pauline Jeannot, Rebecca Rosberg, Tracy J. Berg, and Alexander Pietras. 2021. "Hypoxia-Induced Reactivity of Tumor-Associated Astrocytes Affects Glioma Cell Properties" Cells 10, no. 3: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030613
APA StylePantazopoulou, V., Jeannot, P., Rosberg, R., Berg, T. J., & Pietras, A. (2021). Hypoxia-Induced Reactivity of Tumor-Associated Astrocytes Affects Glioma Cell Properties. Cells, 10(3), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030613






