Downregulation of Mcl-1 by Panobinostat Potentiates Proton Beam Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Drug Treatment
2.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.3. Irradiation
2.4. Clonogenic Survival Assay
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. siRNA Transfection
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Panobinostat Sensitizes HCC Cells to Proton and X-ray Irradiation
3.2. Panobinostat Increased Sub-G1 Population When Combined with Protons in Huh7 Cells
3.3. Panobinostat Augments Proton-Induced ROS Production in Huh7 Cells
3.4. Panobinostat Enhances Proton-Induced DNA Damage in Huh7 Cells
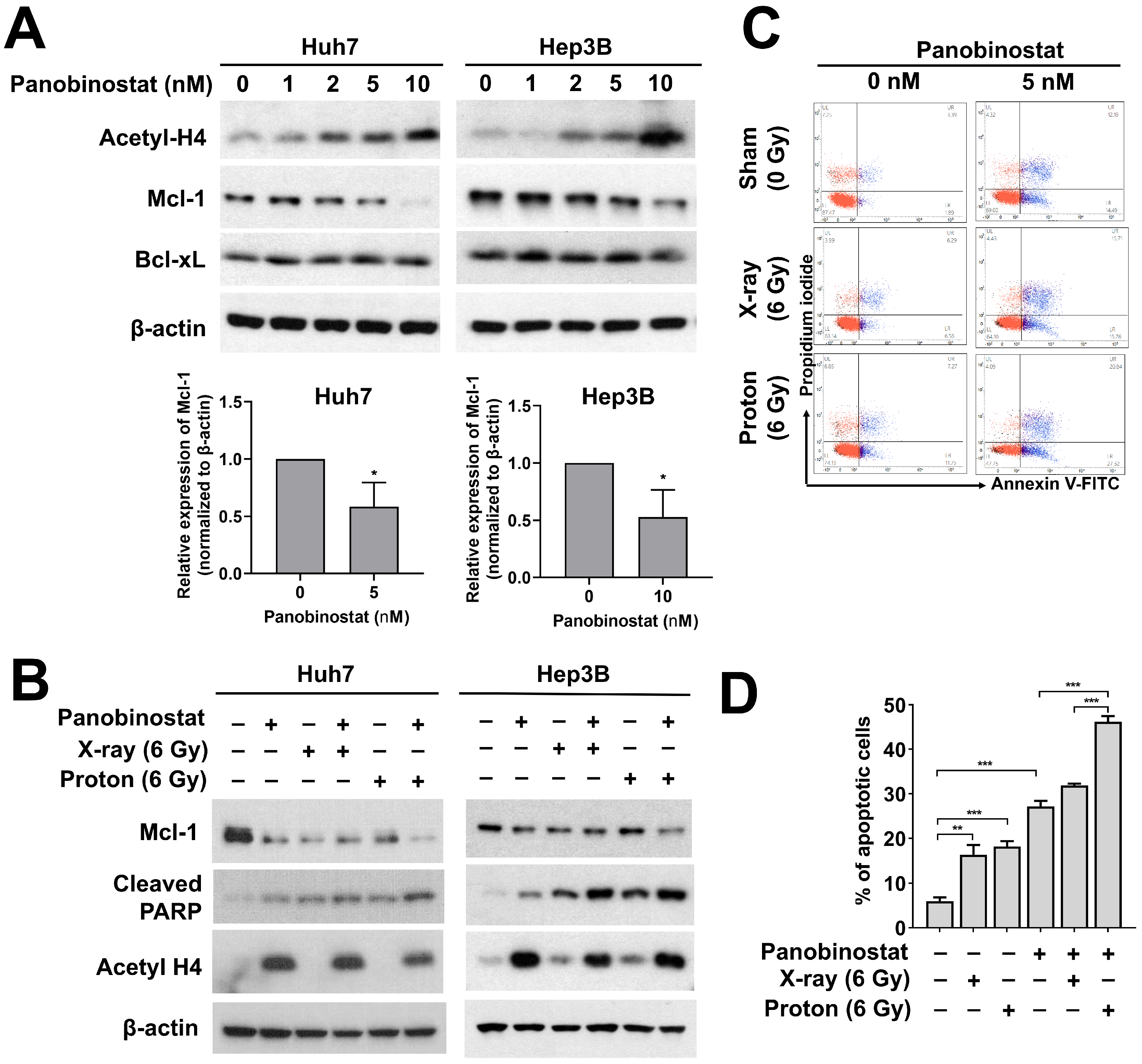
3.5. Panobinostat Enhances Proton-Induced Apoptosis Possibly through Downregulation of Mcl-1 Expression in HCC Cells
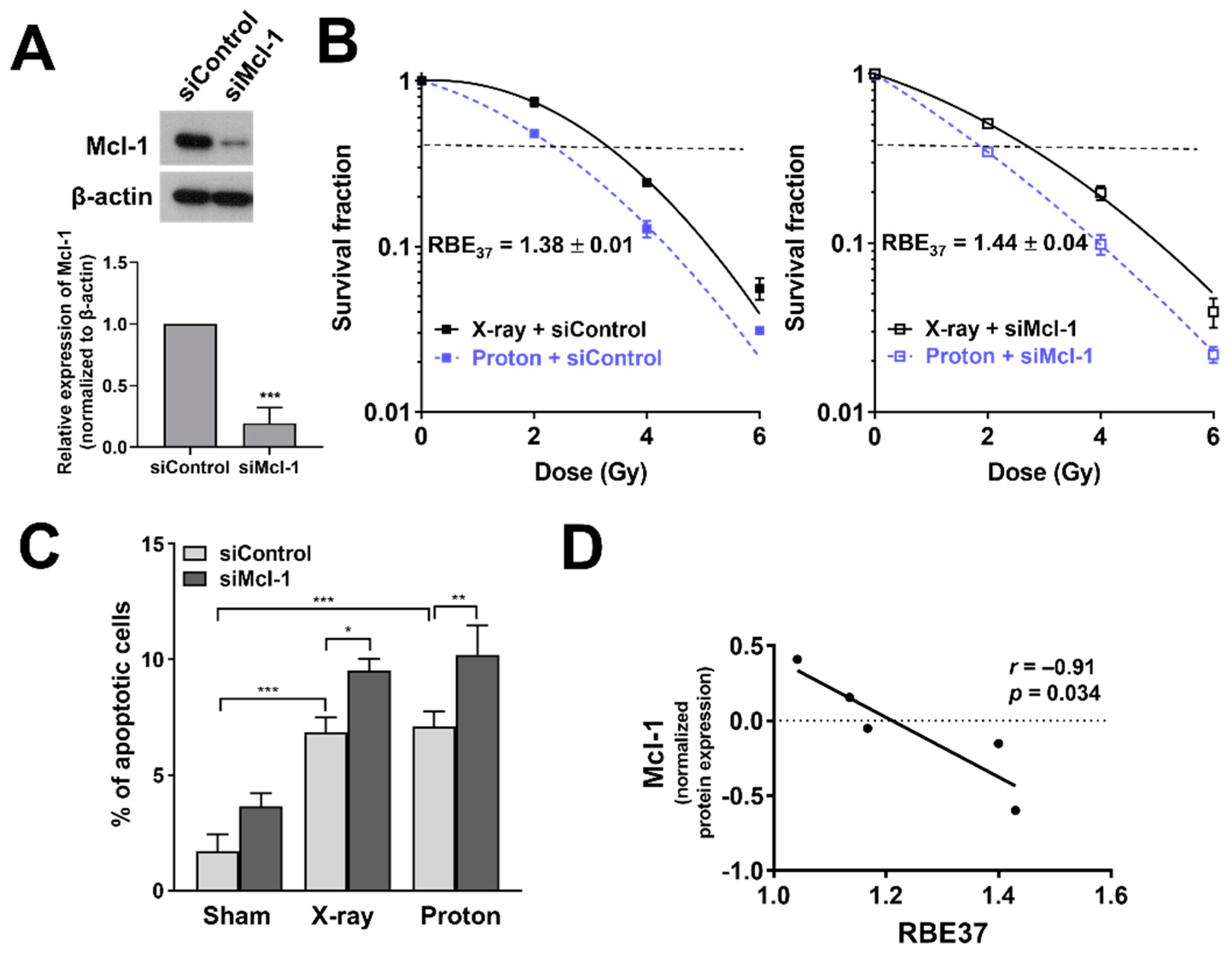
3.6. Depletion of Mcl-1 Increases Proton Sensitivity in Huh7 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalogeridi, M.A.; Zygogianni, A.; Kyrgias, G.; Kouvaris, J.; Chatziioannou, S.; Kelekis, N.; Kouloulias, V. Role of radiotherapy in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Dawson, L.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma radiation therapy: Review of evidence and future opportunities. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, M.; Orecchia, R.; Loeffler, J.S. Charged-particle therapy in cancer: Clinical uses and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; Overgaard, J.; Debus, J.; Bentzen, S.M.; Daartz, J.; Richter, C.; Zips, D.; Bortfeld, T. Radiation oncology in the era of precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.Y.; Liu, C.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Hsu, H.C.; Huang, E.Y.; Huang, T.T.; Lee, C.H.; Hung, S.P.; Huang, B.S. Proton versus photon radiotherapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity-matched analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, B.; Park, J.W. Proton beam radiotherapy vs. radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized phase III trial. J. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, G.S.; Yu, J.I.; Park, H.C.; Hyun, D.; Jeong, W.K.; Lim, H.Y.; Choi, M.S.; Ha, S.Y. Do Biliary Complications after Proton Beam Therapy for Perihilar Hepatocellular Carcinoma Matter? Cancers 2020, 12, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Son, A.; Lee, G.H.; Shin, S.W.; Park, S.; Ahn, S.H.; Chung, Y.; Yu, J.I.; Park, H.C. Targeting DNA-dependent protein kinase sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to proton beam irradiation through apoptosis induction. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.A.; Chabner, B.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5459–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.M.; Hackanson, B.; Lubbert, M.; Jung, M. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors in recent clinical trials for cancer therapy. Clin. Epigenetics 2010, 1, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.C.; Johnstone, R.W. New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groselj, B.; Sharma, N.L.; Hamdy, F.C.; Kerr, M.; Kiltie, A.E. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as radiosensitisers: Effects on DNA damage signalling and repair. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnaiyan, P.; Vallabhaneni, G.; Armstrong, E.; Huang, S.M.; Harari, P.M. Modulation of radiation response by histone deacetylase inhibition. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 62, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, A.; Tanaka, T.; Hobbs, M.L.; Tucker, S.L.; Richon, V.M.; Meyn, R.E. Vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances the response of human tumor cells to ionizing radiation through prolongation of gamma-H2AX foci. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, A.; Kurland, J.F.; Nishikawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Hobbs, M.L.; Tucker, S.L.; Ismail, S.; Stevens, C.; Meyn, R.E. Histone deacetylase inhibitors radiosensitize human melanoma cells by suppressing DNA repair activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4912–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattmann, C.; Oertel, S.; Ehemann, V.; Thiemann, M.; Huber, P.E.; Bischof, M.; Witt, O.; Deubzer, H.E.; Kulozik, A.E.; Debus, J.; et al. Enhancement of radiation response in osteosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines by histone deacetylase inhibition. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 78, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdhani, S.; Sachs, R.; Hlatky, L. Biological effects of proton radiation: What we know and don’t know. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, K.D.; Kawamura, H.; Kaminuma, T.; Paz, A.E.; Yoshida, Y.; Liu, Q.; Willers, H.; Takahashi, A. Effects of Charged Particles on Human Tumor Cells. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H. Relating proton treatments to photon treatments via the relative biological effectiveness-should we revise current clinical practice? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 892–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasino, F.; Durante, M. Proton radiobiology. Cancers 2015, 7, 353–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.I.; Choi, C.; Shin, S.W.; Son, A.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.C. Valproic Acid Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Proton Therapy by Suppressing NRF2 Activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Graham, P.H.; Hao, J.; Chang, L.; Ni, J.; Power, C.A.; Dong, Q.; Kearsley, J.H.; Li, Y. Combination therapy with the histone deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 and radiation is an effective regimen for prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Cuneo, K.C.; Fu, A.; Tu, T.; Atadja, P.W.; Hallahan, D.E. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor LBH589 increases duration of gamma-H2AX foci and confines HDAC4 to the cytoplasm in irradiated non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11298–11304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groselj, B.; Kerr, M.; Kiltie, A.E. Radiosensitisation of bladder cancer cells by panobinostat is modulated by Ku80 expression. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 108, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmayer, A.; Toffanin, S.; Cabellos, L.; Alsinet, C.; Hoshida, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Minguez, B.; Tsai, H.W.; Ward, S.C.; Thung, S.; et al. Combination therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Additive preclinical efficacy of the HDAC inhibitor panobinostat with sorafenib. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zopf, S.; Ocker, M.; Neureiter, D.; Alinger, B.; Gahr, S.; Neurath, M.F.; Di Fazio, P. Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase activity and expression by treatment with the pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Song, R.; Liang, Y.; Bhatta, N.; Yin, D.; Pan, S.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; et al. LBH589 Inhibits proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibition of gankyrin/STAT3/Akt pathway. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbano, R.; Waldegger, P.; Quint, K.; Jabari, S.; Neureiter, D.; Illig, R.; Ocker, M.; Di Fazio, P. Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays a pivotal role in cell death mediated by the pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat in human hepatocellular cancer cells. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Son, A.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, H.C. Radiosensitization by Marine Sponge Agelas sp. Extracts in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells with Autophagy Induction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Choi, C.; Lee, G.H.; Son, A.; Kim, S.H.; Park, H.C.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Park, W. Mechanism of the Antitumor and Radiosensitizing Effects of a Manganese Porphyrin, MnHex-2-PyP. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2017, 27, 1067–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, A.L.; Schuemann, J.; Paganetti, H. A phenomenological relative biological effectiveness (RBE) model for proton therapy based on all published in vitro cell survival data. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 8399–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Suzuki, A.; Borlak, J.; Andrade, R.J.; Lucena, M.I. Drug-induced liver injury: Interactions between drug properties and host factors. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fazio, P.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Neureiter, D.; Okamoto, K.; Wissniowski, T.; Gahr, S.; Quint, K.; Meissnitzer, M.; Alinger, B.; Montalbano, R.; et al. The pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma models by alternative pathways of apoptosis. Cell Oncol. 2010, 32, 285–300. [Google Scholar]
- Brazelle, W.; Kreahling, J.M.; Gemmer, J.; Ma, Y.; Cress, W.D.; Haura, E.; Altiok, S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors downregulate checkpoint kinase 1 expression to induce cell death in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasim, L.; Chopra, M. Panobinostat induces apoptosis via production of reactive oxygen species and synergizes with topoisomerase inhibitors in cervical cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Cho, W.K.; Park, S.; Shin, S.W.; Park, W.; Kim, H.; Choi, D.H. Checkpoint Kinase 1 (CHK1) Inhibition Enhances the Sensitivity of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Proton Irradiation via Rad51 Downregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barazzuol, L.; Jeynes, J.C.; Merchant, M.J.; Wera, A.C.; Barry, M.A.; Kirkby, K.J.; Suzuki, M. Radiosensitization of glioblastoma cells using a histone deacetylase inhibitor (SAHA) comparing carbon ions with X-rays. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 91, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerelchuluun, A.; Maeda, J.; Manabe, E.; Brents, C.A.; Sakae, T.; Fujimori, A.; Chen, D.J.; Tsuboi, K.; Kato, T.A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Induced Radiation Sensitization Effects on Human Cancer Cells after Photon and Hadron Radiation Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, M.; Yamada, S.; Hoshino, I.; Murakami, K.; Akutsu, Y.; Sakata, H.; Nishimori, T.; Usui, A.; Miyazawa, Y.; Kamada, T.; et al. Effects of carbon-ion radiotherapy combined with a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, cyclic hydroxamic-acid-containing peptide 31 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 4433–4438. [Google Scholar]
- Oertel, S.; Thiemann, M.; Richter, K.; Weber, K.J.; Huber, P.E.; Perez, R.L.; Brons, S.; Bischof, M.; Kulozik, A.E.; Ehemann, V.; et al. Combination of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid with heavy ion therapy shows promising effects in infantile sarcoma cell lines. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Funayama, T.; Yokota, Y.; Murakami, T.; Kobayashi, Y. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Sensitize Murine B16F10 Melanoma Cells to Carbon Ion Irradiation by Inducing G1 Phase Arrest. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Ko, S.M.; Cho, J.H.; Chae, J.I.; Shim, J.H. The HDAC inhibitor, panobinostat, induces apoptosis by suppressing the expresssion of specificity protein 1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shao, W.; Growney, J.D.; Feng, Y.; O’Connor, G.; Pu, M.; Zhu, W.; Yao, Y.M.; Kwon, P.; Fawell, S.; Atadja, P. Activity of deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589) in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma models: Defining molecular mechanisms of resistance. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattoo, A.R.; Pandita, R.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Charaka, V.; Mujoo, K.; Hunt, C.R.; Pandita, T.K. MCL-1 Depletion Impairs DNA Double-Strand Break Repair and Reinitiation of Stalled DNA Replication Forks. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, N.; Fontana, A.O.; Hug, E.B.; Lomax, A.; Coray, A.; Augsburger, M.; Paganetti, H.; Sartori, A.A.; Pruschy, M. Deficiency in homologous recombination renders Mammalian cells more sensitive to proton versus photon irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 88, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymonowicz, K.; Krysztofiak, A.; Linden, J.V.; Kern, A.; Deycmar, S.; Oeck, S.; Squire, A.; Koska, B.; Hlouschek, J.; Vullings, M.; et al. Proton Irradiation Increases the Necessity for Homologous Recombination Repair Along with the Indispensability of Non-Homologous End Joining. Cells 2020, 9, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
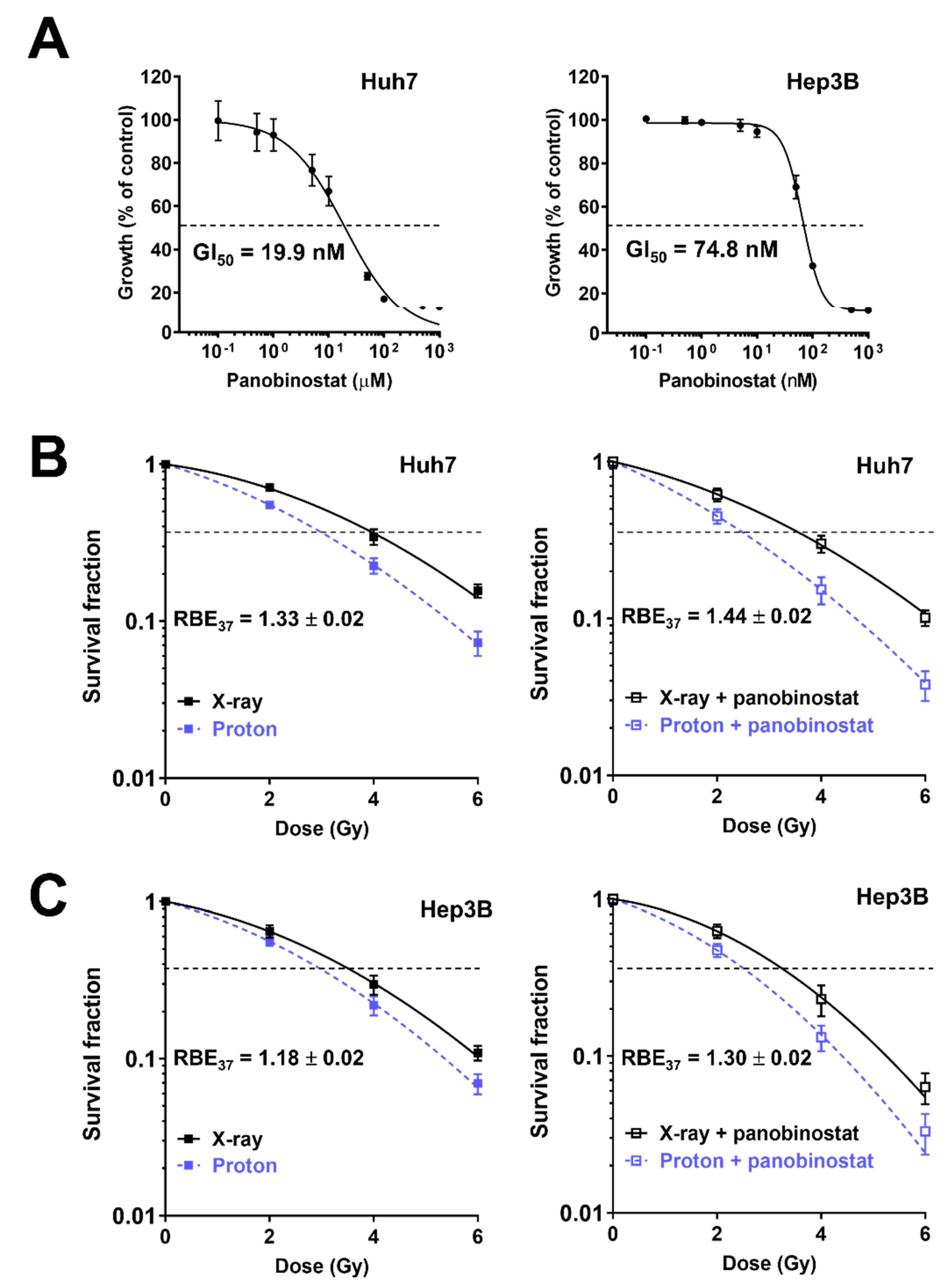
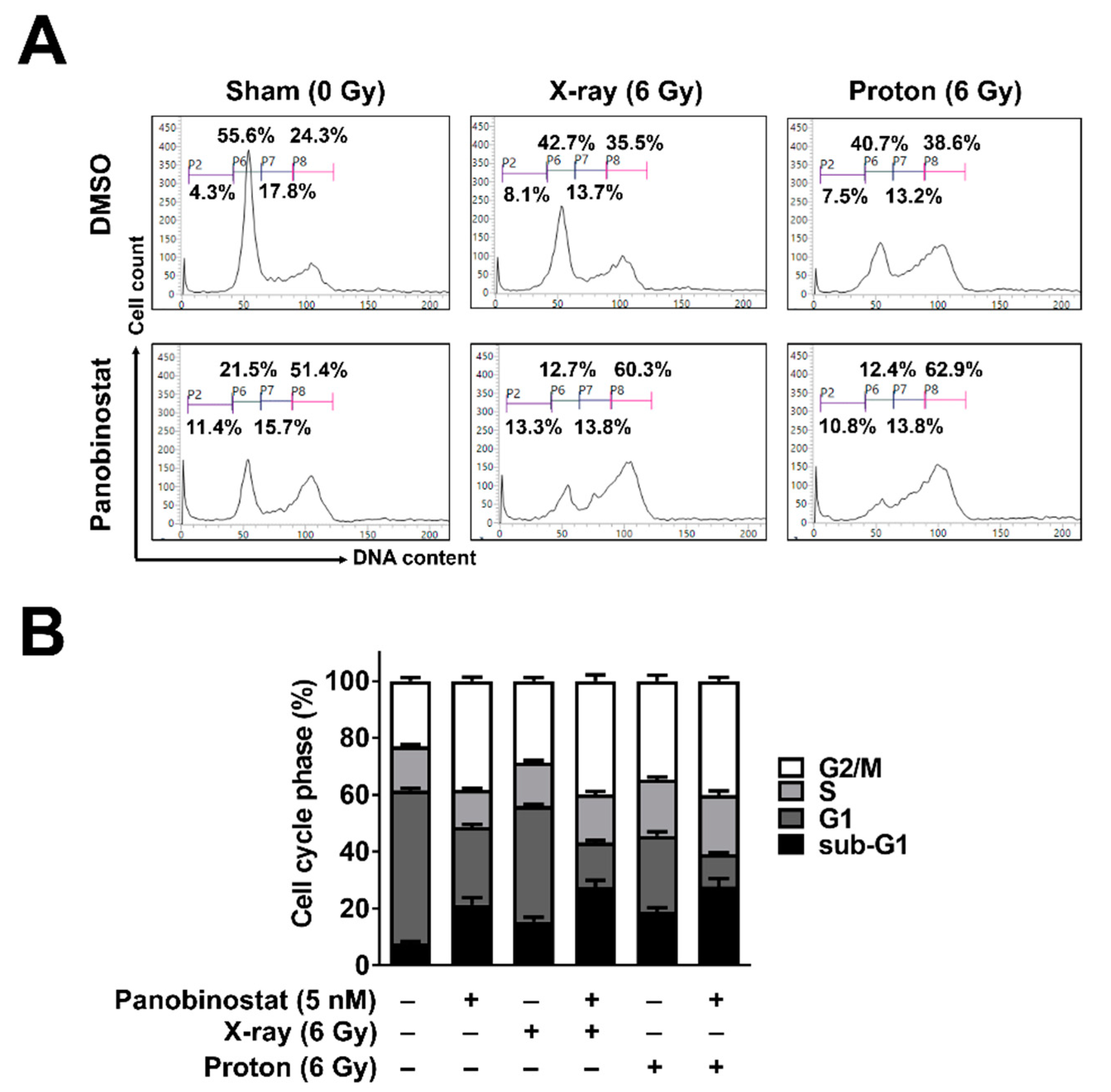
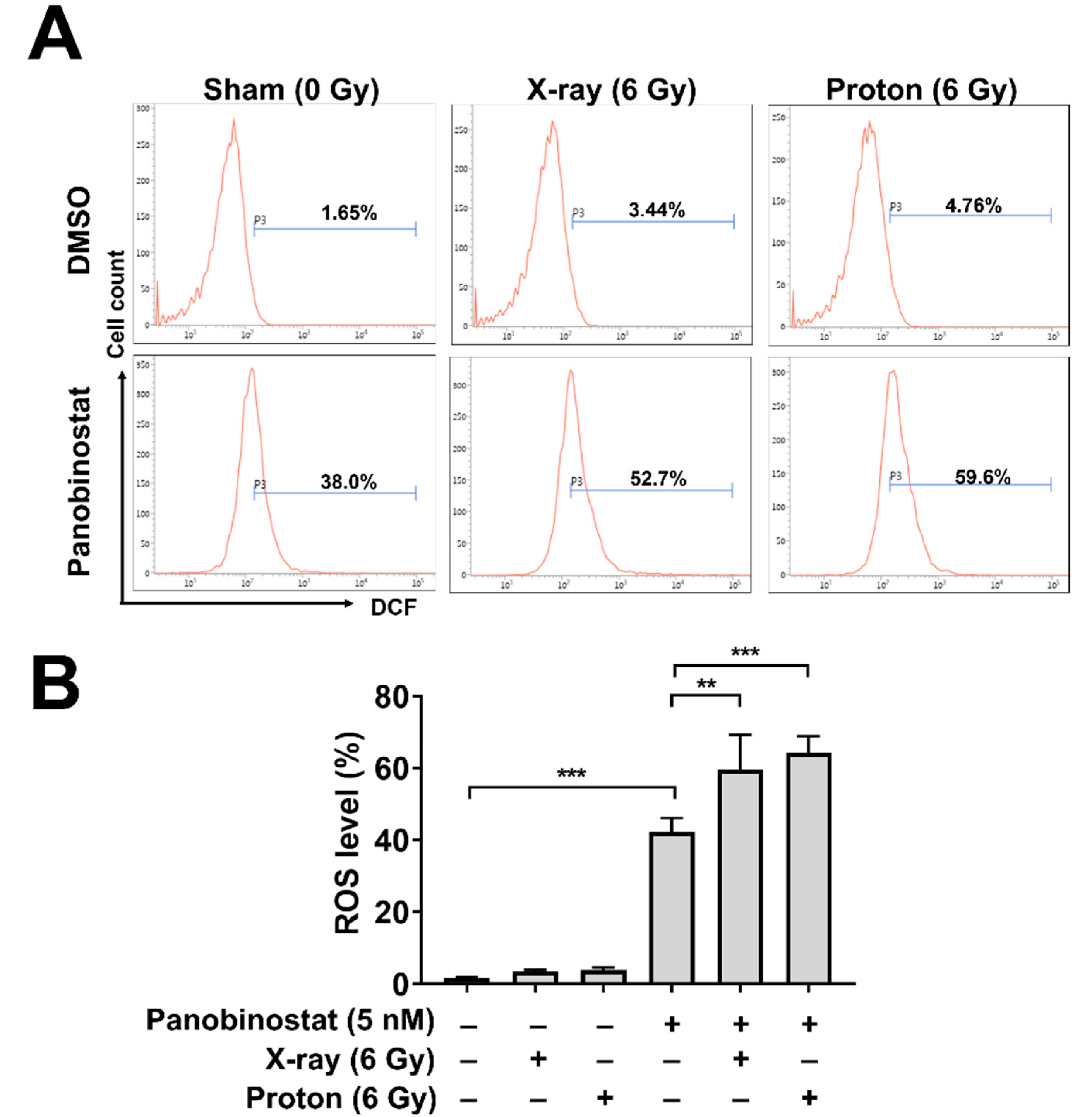
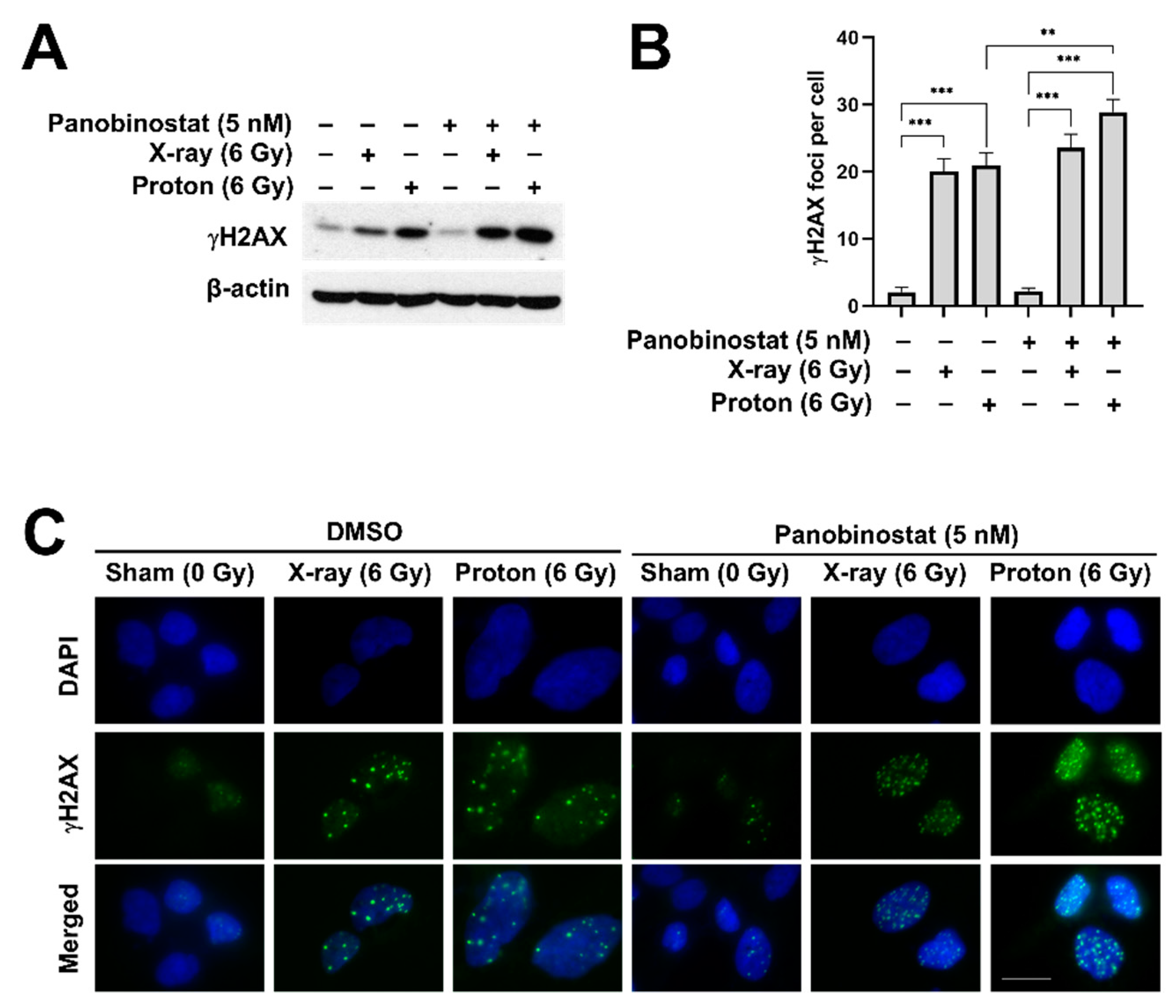
| Cell Line/Treatment | D37 (Gy) | SER37 (DMSO Versus Panobinostat) | RBE37 (X-ray Versus Proton) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huh7 | |||
| X-ray, DMSO | 3.96 ± 0.21 | ||
| X-ray, panobinostat | 3.45 ± 0.30 | 1.15 ± 0.04 | |
| Proton, DMSO | 2.99 ± 0.12 | 1.33 ± 0.02 | |
| Proton, panobinostat | 2.41 ± 0.25 | 1.25 ± 0.08 | 1.44 ± 0.02 ** |
| Hep3B | |||
| X-ray, DMSO | 3.54 ± 0.30 | ||
| X-ray, panobinostat | 3.20 ± 0.32 | 1.11 ± 0.02 | |
| Proton, DMSO | 3.00 ± 0.21 | 1.18 ± 0.02 | |
| Proton, panobinostat | 2.47 ± 0.21 | 1.21 ± 0.02 ** | 1.30 ± 0.02 ** |
| Cell Line/Treatment | D37 (Gy) | SER37 (siControl versus siMcl-1) | RBE37 (X-ray versus Proton) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huh7 | |||
| X-ray, siControl | 3.44 ± 0.06 | ||
| X-ray, siMcl-1 | 2.74 ± 0.04 | 1.26 ± 0.02 | |
| Proton, siControl | 2.50 ± 0.04 | 1.38 ± 0.01 | |
| Proton, siMcl-1 | 1.90 ± 0.05 | 1.31 ± 0.04 | 1.44 ± 0.04 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, C.; Lee, G.H.; Son, A.; Yoo, G.S.; Yu, J.I.; Park, H.C. Downregulation of Mcl-1 by Panobinostat Potentiates Proton Beam Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030554
Choi C, Lee GH, Son A, Yoo GS, Yu JI, Park HC. Downregulation of Mcl-1 by Panobinostat Potentiates Proton Beam Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cells. 2021; 10(3):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030554
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Changhoon, Ga Haeng Lee, Arang Son, Gyu Sang Yoo, Jeong Il Yu, and Hee Chul Park. 2021. "Downregulation of Mcl-1 by Panobinostat Potentiates Proton Beam Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells" Cells 10, no. 3: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030554
APA StyleChoi, C., Lee, G. H., Son, A., Yoo, G. S., Yu, J. I., & Park, H. C. (2021). Downregulation of Mcl-1 by Panobinostat Potentiates Proton Beam Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cells, 10(3), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030554






