Angiotensin II and Angiotensin Receptors 1 and 2—Multifunctional System in Cells Biology, What Do We Know?
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Angiotensin—A Multi Task Force Peptide Hormone
1.2. RAS in Health and Disease
2. Pituitary Gland
3. Adrenal Gland
4. Prostate Gland
5. Endometrium
6. Other Organs/Cancers
6.1. Brain
6.2. Breast Cancer
6.3. Liver
6.4. Lung
6.5. Ocular Disorders
6.6. Colon Cancer
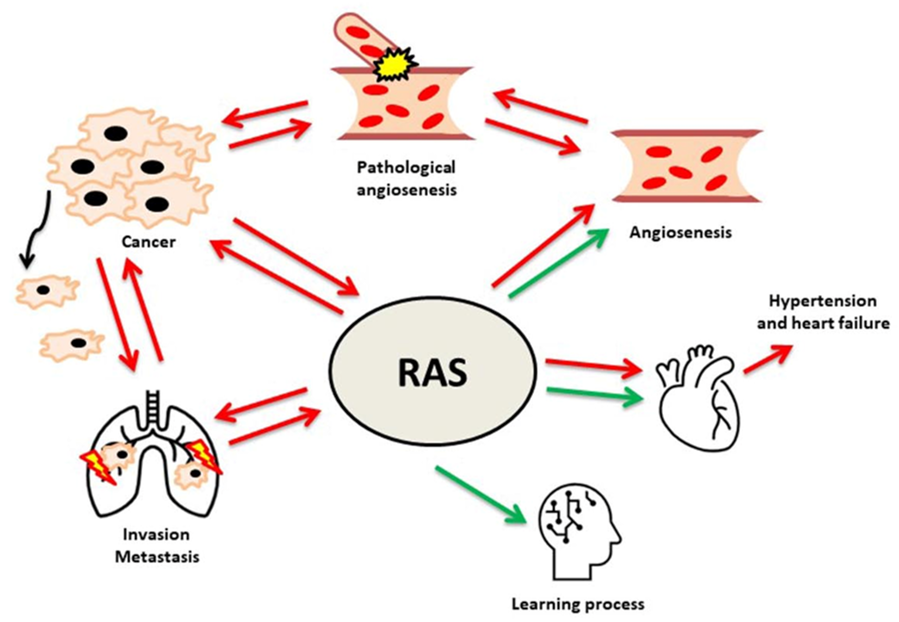
7. Angiogenesis
7.1. Angiotensins Have an Impact on Invasion and Metastasis
7.2. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)
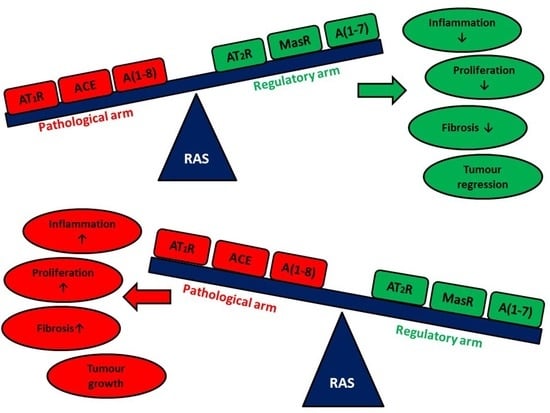
8. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, S.H.; Xiao, L.L.; Cheng, B.; Fu, X.B.; Cui, T.; Liu, H.W. Critical role of the endogenous renin-angiotensin system in maintaining self-renewal and regeneration potential of epidermal stem cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, Y.; An, H.; Lee, N.; Jo, H.; Ban, C.; Seo, J.H. Overexpression of angiotensin II type 1 receptor in breast cancer cells induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition and promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalechi, M.; Dela Cruz, C.; Lima, L.C.; Maciel, L.P.; Pereira, V.M.; Reis, F.M. Angiotensin peptides in the non-gravid uterus: Paracrine actions beyond circulation. Peptides 2018, 101, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, G.; Hyde, C.; Catt, K.J. Angiotensin II binding and prolactin release in pituitary lactotrophs. Clin. Res. 1982, 30, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Deschepper, C.F.; Crumrine, D.A.; Ganong, W.F. Evidence that the gonadotrophs are the likely site of production of angiotensin II in the anterior pituitary of the rat. Endocrinology 1986, 119, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganong, W.F. Blood, pituitary, and brain renin-angiotensin systems and regulation of secretion of anterior pituitary gland. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1993, 14, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.; Podlich, D.; Ritter, M.; Müller, A.; Wanka, H.; Maser-Gluth, C.; Seitz, C.; de Boni, L.; Maier, E.; Gretz, N.; et al. A new transgenic rat model overexpressing the angiotensin II type 2 receptor provides evidence for inhibition of cell proliferation in the outer adrenal cortex. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2012, 302, e1044–e1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, M.; Barker, S.; Puddefoot, J.R.; Vinson, G.P. Localisation of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) components in breast. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianzo, M.; Subir, N. Regulation of Male Fertility by the Renin- Angiotensin System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, D.; Bekes, I.; Wulff, C. Local Renin-Angiotensin System in the Reproductive System. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.; Rezmann, L.; Catt, K.J.; Louis, W.J.; Frauman, A.G.; Nahmias, C.; Louis, S.N.S. Role of the renin—Angiotensin system in prostate cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 302, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.B.; Araújo, F.C.; Pereira, V.M.; Dos Reis, A.M.; Santos, R.A.; Reis, F.M. Angiotensin (1-7) and its receptor Mas are expressed in the human testis: Implications for male infertility. J. Mol. Histol. 2010, 41, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, D.T.; Frauman, A.G.; Johnston, C.I.; Fabiani, M.E. Angiotensin receptors: Distribution, signalling and function. Clin. Sci. 2001, 100, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Wei, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jin, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Song, W.; Huo, J.; et al. ACE2 attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in MLE-12 cells induced by silica. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.Y.; Fernando, R.; Peck, G.; Ye, S.Y.; Mendelsohn, F.A.O.; Jenkins, T.A.; Albiston, A.L. The angiotensin IV/AT4 receptor. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2728–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royea, J.; Zhang, L.; Tong, X.K.; Hamel, E. Angiotensin IV receptors mediate the cognitive and cerebrovascular benefits of losartan in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 5562–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekalski, S.; Chansel, D.; Vandermeersch, S.; Ronco, P.; Ardaillou, R. Evidence for angiotensin IV receptors in human collecting duct cells. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.A.; Krebs, L.T.; Kramár, E.A.; Shaffer, M.J.; Harding, J.W.; Wright, J.W. Autoradiographic identification of brain angiotensin IV binding sites and differential c-Fos expression following intracerebroventricular injection of angiotensin II and IV in rats. Brain Res. 1995, 682, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domińska, K.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W.; Lachowicz-Ochędalska, A.; Ochędalski, T. Similarities and differences between effects of angiotensin III and angiotensin II on human prostate cancer cell migration and proliferation. Peptides 2012, 37, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, S.; Zennaro, C.; Palmisano, S.; Velkoska, E.; Sabato, N.; Toffoli, B.; Giacomel, G.; Buri, L.; Zanconati, F.; Bellini, G.; et al. Characterization and significance of ACE2 and Mas receptor in human colon adenocarcinoma. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012, 13, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, F.M.; Bouissou, D.R.; Pereira, V.M.; Camargos, A.F.; Dos Reis, A.M.; Santos, R.A. Angiotensin-(1-7), its receptor Mas, and the angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2 are expressed in the human ovary. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 95, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Sriramula, S.; Lazartigues, E. ACE2/ANG-(1-7)/Mas pathway in the brain: The axis of good. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Hussain, T. Dimerization of AT 2 and Mas Receptors in Control of Blood Pressure. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolgien, M.C.G.M.; Correa, S.A.A.; Breuel, P.A.F.; Nazário, A.C.P.; Facina, G. Renin Angiotensin System Components and Cancer: Reports of Association. J. Biosci. Med. 2016, 4, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Domińska, K.; Lachowicz-Ochedalska, A. The involvement of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in cancerogenesis. Postepy Biochem. 2008, 54, 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- D’ardes, D.; Boccatonda, A.; Rossi, I.; Guagnano, M.T.; Santilli, F.; Cipollone, F.; Bucci, M. COVID-19 and RAS: Unravelling an unclear relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Oliveira, A.; Nogueira, A.I.; Pereira, R.M.; Vilas Boas, W.W.; Souza dos Santos, R.A.; Simões e Silva, A.C. The renin-angiotensin system and diabetes: An update. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menikdiwela, K.R.; Ramalingam, L.; Rasha, F.; Wang, S.; Dufour, J.M.; Kalupahana, N.S.; Sunahara, K.K.S.; Martins, J.O.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Autophagy in metabolic syndrome: Breaking the wheel by targeting the renin–angiotensin system. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1234567890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.; Kapoor, M.S.; Singh, A.; Bodakhe, S.H. Therapeutic targets of renin-angiotensin system in ocular disorders. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2017, 29, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, D.B.; Molnar, A.; Hosszu, A.; Lakat, T.; Hodrea, J.; Szabo, A.J.; Lenart, L.; Fekete, A. Antidepressant effect in diabetes-associated depression: A novel potential of RAAS inhibition. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 118, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhering Martins, L.; Silva de Miranda, A.; dos Santos Rodrigues, A.M.; Braga Tibaes, J.R.; Gomez, R.S.; Ferreira, A.V.M.; Teixeira, A.L. Altered Serum Levels of Renin-Angiotensin System Markers in Migraine. Headache 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshayes, F.; Nahmias, C. Angiotensin receptors: A new role in cancer? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 16, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczuk, P.; Szczylik, C.; Porta, C.; Czarnecka, A. Renin angiotensin system deregulation as renal cancer risk factor (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, B.; Trivedi, M.; Speth, R.C. Alterations in Gene Expression of Components of the Renin-Angiotensin System and Its Related Enzymes in Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer Int. 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Ni, L.; Wan, H.; Fan, L.; Fei, X.; Ma, Q.; Gao, B.; Xiang, Y.; Che, J.; Li, Q. Overexpression of ACE2 produces antitumor effects via inhibition of angiogenesis and tumor cell invasion in vivo and in vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, J.; Wan, H.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y. ACE2 overexpression inhibits acquired platinum resistance-induced tumor angiogenesis in NSCLC. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Sun, J.F.; Hu, S.Q. The renin-angiotensin system blockers as adjunctive therapy for cancer: A meta-analysis of survival outcome. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, D.S.; Xin, L.; Zhou, L.Q.; Zhang, H.T.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Y.W.; Li, S.H. The renin-angiotensin system blockers and survival in digestive system malignancies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, T.; Zhuang, R.; Cai, W.; Zheng, Y. Do renin—Angiotensin system inhibitors influence the recurrence, metastasis, and survival in cancer patients? Medicine 2017, 96, e6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, M.; Weinmann, A.; Wörns, M.-A.; Hucke, F.; Bota, S.; Marquardt, J.U.; Duda, D.G.; Jain, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Trauner, M.; et al. Use of inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin system is associated with longer survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datzmann, T.; Fuchs, S.; Andree, D.; Hohenstein, B.; Schmitt, J.; Schindler, C. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled clinical trial evidence refutes relationship between pharmacotherapy with angiotensin-receptor blockers and an increased risk of cancer. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 64, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipahi, I.; Debanne, S.M.; Rowland, D.Y.; Simon, D.I.; Fang, J.C. Angiotensin-receptor blockade and risk of cancer: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangalore, S.; Kumar, S.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Makani, H.; Grossman, E.; Wetterslev, J.; Gupta, A.K.; Sever, P.S.; Gluud, C.; Messerli, F.H. Antihypertensive drugs and risk of cancer: Network meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses of 324 168 participants from randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganong, W.F.; Deschepper, C.F.; Steele, M.K.; Intebi, A. Renin-Angiotensin System in the Anterior Pituitary of the Rat. Am. J. Hypertens. 1989, 2, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschepper, C.F. The renin-angiotensin system in the pituitary gland. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 2, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, G.; Hyde, C.L.; Catt, K.J. Angiotensin II receptors and prolactin release in pituitary lactotrophs. Endocrinology 1982, 111, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.K.; Negro-Vilar, A.; McCann, S.M. Effect of central injection of bradykinin and bradykinin potentiating factor upon release of anterior pituitary hormones in ovariectomized female rats. Peptides 1980, 1, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowski, M.; Kunert-Radek, J. Angiotensin IV Stimulates the Proliferation of Rat Anterior Pituitary Cells in Vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 232, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlikowski, M. Immunohistochemical detection of angiotensin receptors AT1 and AT2 in normal rat pituitary gland, estrogen-induced rat pituitary tumor and human pituitary adenomas. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2006, 44, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlikowski, M.; Mucha, S.; Kunert-Radek, J.; Sępień, H.; Pisarek, H.; Stawowy, A. Is Estrogen-Induced Pituitary Hyperplasia and Hyperprolactinaemia Mediated by Angiotensin II? In Advances in experimental medicine and biology. In Tissue Renin-Angiotensin Systems; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 377, pp. 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowski, M. Endocrine/paracrine control of pituitary cell proliferation and its involvement in pituitary tumorigenesis. Pituitary 1999, 1, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebas, E.; Lachowicz-Ochedalska, A.; Pawlikowski, M. Angiotensin IV stimulates the activity of tyrosine kinases in rat anterior pituitary gland acting via AT1-like receptors? J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2004, 55, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ptasinska-Wnuk, D.; Kunert-Radek, J.; Pawlikowski, M. Angiotensins II and IV stimulate the rat anterior pituitary cell proliferation independently of the AT1 receptor subtype. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2003, 24, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Lawnicka, H.; Ptasinska-Wnuk, D.; Mucha, S.; Kunert-Radek, J.; Pawlikowski, M.; Stepien, H. The Involvement of Angiotensin Type 1 and Type 2 Receptors in Estrogen-Induced Cell Proliferation and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in the Rat Anterior Pituitary. Sci. World J. 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptasinska-Wnuk, D.; Lawnicka, H.; Mucha, S.; Kunert-Radek, J.; Pawlikowski, M.; Stepien, H. Angiotensins Inhibit Cell Growth in GH3 Lactosomatotroph Pituitary Tumor Cell Culture: A Possible Involvement of the p44/42 and p38 MAPK Pathways. Sci. World J. 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptasinska-Wnuk, D.; Mucha, S.A.; Lawnicka, H.; Fryczak, J.; Kunert-Radek, J.; Pawlikowski, M.; Stepien, H. The effects of angiotensin peptides and angiotensin receptor antagonists on the cell growth and angiogenic activity of GH3 lactosomatotroph cells in vitro. Endocrine 2012, 42, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunert-Radek, J.; Pawlikowski, M. Angiotensin II stimulation of the rat pituitary tumoral cell proliferation in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 183, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert-Radek, J.; Stepien, H.; Komorowski, J.; Pawlikowski, M. Stimulatory Effect of Angiotensin II on the Proliferation of Mouse Spleen Lymphocytes in vitro Is Mediated via Both Types of Angiotensin II Receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 198, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkai, T.; Ooka, H. Effect of angiotensin II on the proliferation of mammotrophs from the adult rat anterior pituitary in culture. Peptides 1995, 16, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochedalska, A.L.; Rebas, E.; Kunert-Radek, J.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.-C.; Pawlikowski, M. Angiotensins II and IV stimulate the activity of tyrosine kinases in estrogen-induced rat pituitary tumors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 297, 931–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haendeler, J.; Berk, B.C. Angiotensin II mediated signal transduction. Important role of tyrosine kinases. Regul. Pept. 2000, 95, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Yan, C.; Berk, B.C. Angiotensin II signaling pathways mediated by tyrosine kinases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rębas, E.; Lachowicz-Ochędalska, A. The effect of angiotensin III on protein tyrosine kinase activity in rat pituitary. Regul. Pept. 2005, 130, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, A.; Ochedalski, T.; Pawlikowski, M.; Rebas, E. Effect of 17-β-Estradiol and Progesterone on Angiotensin II-Induced Changes in Inositol-1,4,5-Trisphosphate Content and Protein Kinase C Activity in Anterior Pituitary. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachowicz, A.; Pawlikowski, M.; Rębas, E. Pregnenolone Sulfate Modulates Angiotensin II-Induced Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Changes in the Anterior Pituitary of Female Rat. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 287, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Klein, J.; Yun, C.C. Activation of Na + /H + Exchanger NHE3 by Angiotensin II Is Mediated by Inositol 1,4,5-Triphosphate (IP 3) Receptor-binding Protein Released with IP 3 (IRBIT) and Ca 2+ /Calmodulin-dependent Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27869–27878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, A.; Rebas, E.; Ochedalski, T.; Pawlikowski, M. Angiotensin II changes inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate content in the pituitary and hypothalamus but not in cerebral cortex of the rat brain. Biol. Signals 1995, 4, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J. Local renin–angiotensin systems in the adrenal gland. Peptides 2012, 34, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, N.; Weissenberger, J.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Höfliger, M.; Weis, J.; Imboden, H. Immunocytochemical localization of angiotensin II receptor subtypes and angiotensin II with monoclonal antibodies in the rat adrenal gland. Regul. Pept. 2001, 101, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowski, M.; Winczyk, K.; Sledź, B. Immunohistochemical detection of angiotensin receptors AT1 and AT2 in adrenal tumors. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2008, 46, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowski, M.; Lewiński, A.; Sewerynek, E.; Szkudliński, M.; Kunert-Radek, J.; Wajs, E. Somatostatin analog (SMS 201-995) inhibits the basal and angiotensin II-stimulated 3H-thymidine uptake by rat adrenal glands. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 166, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siejka, A.; Mełeń-Mucha, G.; Mucha, S.A.; Pawlikowski, M. Angiotensins II and IV modulate adrenocortical cell proliferation in ovariectomized rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otis, M.; Campbell, S.; Payet, M.D.; Gallo-Payet, N. Angiotensin II Stimulates Protein Synthesis and Inhibits Proliferation in Primary Cultures of Rat Adrenal Glomerulosa Cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otis, M.; Campbell, S.; Payet, M.D.; Gallo-Payet, N. In Adrenal Glomerulosa Cells, Angiotensin II Inhibits Proliferation by Interfering with Fibronectin-Integrin Signaling. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3435–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowski, M.; Meleń-Mucha, G.; Mucha, S. The involvement of the renin-angiotensin system in the regulation of cell proliferation in the rat endometrium. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 55, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ławnicka, H.; Potocka, A.M.; Juzala, A.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Pawlikowski, M. Angiotensin II and its fragments (angiotensins III and IV) decrease the growth of DU-145 prostate cancer in vitro. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, BR410-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sidorkiewicz, M.; Rebas, E.; Szymajda, M.; Ławnicka, H.; Pawlikowski, M.; Lachowicz, A. Angiotensin receptors in hormone-independent prostate cancer cell line DU145: Presence of two variants of angiotensin type 1 receptor. Med. Sci. Monit. 2009, 15, BR106-10. [Google Scholar]
- Domińska, K.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W.; Płuciennik, E.; Lachowicz-Ochȩdalska, A.; Ochȩdalski, T. A comparison of the effects of Angiotensin IV on androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer cell lines. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2013, 14, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domińska, K.; Ochędalski, T.; Kowalska, K.; Matysiak-Burzyńska, Z.E.; Płuciennik, E.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Interaction between angiotensin II and relaxin 2 in the progress of growth and spread of prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domińska, K.; Kowalska, K.; Matysiak, Z.E.; Płuciennik, E.; Ochędalski, T.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Regulation of mRNA gene expression of members of the NF-κB transcription factor gene family by angiotensin II and relaxin 2 in normal and cancer prostate cell lines. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 4352–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domińska, K.; Ochędalski, T.; Kowalska, K.; Matysiak-Burzyńska, Z.E.; Płuciennik, E.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. A common effect of angiotensin II and relaxin 2 on the PNT1A normal prostate epithelial cell line. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 72, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, H.; Ishiguro, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Nakaigawa, N.; Hasumi, H.; Kato, S.; Kubota, Y. Antiproliferative activity of angiotensin II receptor blocker through cross-talk between stromal and epithelial prostate cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1699–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domińska, K.; Piastowska, A.W.; Rębas, E.; Lachowicz-Ochędalska, A. The influence of peptides from the angiotensin family on tyrosine kinase activity and cell viability in a human hormone-dependent prostate cancer line. Endokrynol. Pol. 2009, 60, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Domińska, K.; Kowalski, A.; Ochędalski, T.; Rębas, E. Effects of testosterone and 17β-estradiol on angiotensin-induced changes in tyrosine kinase activity in the androgen-independent human prostate cancer cell line, DU145. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Naiki-Ito, A.; Kato, H.; Suzuki, S.; Kuno, T.; Ishiguro, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Uemura, H. Chemopreventive effects of angiotensin II receptor type 2 agonist on prostate carcinogenesis by the down-regulation of the androgen receptor. Oncotarget 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, Y.; Jung, Y.-J. Angiotensin II receptor blockers induce autophagy in prostate cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3579–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W.; Drobnik, J.; Zarzyńska, J.; Domińska, K.; Russell, J.A.; Ochedalski, T. Influence of myocardial infarction on changes in the expression of angiotensin type 1 receptor in the rat prostate. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2011, 49, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowska, M.; Matysiak-Burzyńska, Z.; Kowalska, K.; Płuciennik, E.; Domińska, K.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Angiotensin II promotes endometrial cancer cell survival. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Shang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Effect of angiotensin-(1-7) and angiotensin II on the proliferation and activation of human endometrial stromal cells in vitro. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 8948–8957. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, N.; Nishida, Y.; Ishii, T.; Yoshida, T.; Furukawa, Y.; Narahara, H. Telmisartan Induces Growth Inhibition, DNA Double-Strand Breaks and Apoptosis in Human Endometrial Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W.; Płuciennik, E.; Wójcik-Krowiranda, K.; Bieńkiewicz, A.; Bednarek, A.; Ochędalski, T. Analysis of the expression of angiotensin II type 1 receptor and VEGF in endometrial adenocarcinoma with different clinicopathological characteristics. Tumor Biol. 2012, 33, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysiak, Z.E.; Ochędalski, T.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. The evaluation of involvement of angiotensin II, its receptors, and androgen receptor in endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2015, 31, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforce, S.J.; Lumbers, E.R.; Corbisier de Meaultsart, C.; Wang, Y.; Proietto, A.; Otton, G.; Scurry, J.; Verrills, N.M.; Scott, R.J.; Pringle, K.G. Expression of renin–angiotensin system (RAS) components in endometrial cancer. Endocr. Connect. 2017, 6, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszko, J.J.; Kupryszewski, G.; Witczuk, B.; Wiśniewski, K. Angiotensin ii-(3-8)-hexapeptide affects motor activity, performance of passive avoidance and a conditioned avoidance response in rats. Neuroscience 1988, 27, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszko, J.J.; Winnicka, M.M. Effects of Angiotensin II and Its Receptor Antagonists on. Control 2003, 2, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama, S.; Sakagawa, T.; Chaki, S.; Imagawa, Y.; Ichiki, T.; Inagami, T. Anxiety-like behavior in mice lacking the angiotensin II type-2 receptor. Brain Res. 1999, 821, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzsimons, J.T. Drinking Induced By Injection Of Angiotensin. J. Physiol. 1970, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Julio, A.N.A.; Hayduk, K.; Karswnky, K.P. Renin in dog brain. Am. J. Physiol. 2018, 221, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, K.; Bickerton, J.P.B. Central Pressor Effects Of Angiotensin. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1961, 106, 834–836. [Google Scholar]
- Gebre, A.K.; Altaye, B.M.; Atey, T.M.; Tuem, K.B.; Berhe, D.F. Targeting Renin-Angiotensin System Against Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, S.; Akaike, M.; Ise, T.; Ueda, Y.; Iwase, T.; Sata, M. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system has a pivotal role in cognitive impairment. Hypertens. Res. 2013, 36, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, R.; Rincón, J.; Pedreañez, A.; Viera, N.; Hernández-Fonseca, J.P.; Peña, C.; Mosquera, J. Role of angiotensin II in the brain inflammatory events during experimental diabetes in rats. Brain Res. 2012, 1453, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, R.; Igarashi, A.; Kamata, M.; Nagata, K.; Takano, S.; Nakagawa, H. The N-terminal active centre of human angiotensin-converting enzyme degrades Alzheimer amyloid β-peptide. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Igarashi, A.; Kamata, M.; Nakagawa, H. Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Degrades Alzheimer Amyloid β-Peptide (Aβ); Retards Aβ Aggregation, Deposition, Fibril Formation; and Inhibits Cytotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 47863–47868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronvik, E.; Stovner, L.J.; Helde, G.; Sand, T.; Bovim, G. Prophylactic treatment of migraine with an angiotensin II receptor blocker: A randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2003, 289, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, H.C.; Gendolla, A.; Feuersenger, A.; Evers, S.; Straube, A.; Schumacher, H.; Davidai, G. Telmisartan in migraine prophylaxis: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, H.; Stovner, L.J.; Helde, G.; Sand, T.; Bovim, G. Prophylactic treatment of migraine with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (lisinopril): Randomised, placebo controlled, crossover study. Br. Med. J. 2001, 322, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, I.; Paxinos, G.; Mendelsohn, A.O.; Aldred, G.P.; Casley, D.; Yeen, S. Distribution of AT 4 receptors in the Macaca fascicularis brain. Brain Res. 1996, 712, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, O.; Villarreal-Garza, C.; Vizcaíno, G.; Pineda, B.; Hernández-Pedro, N.; Guevara-Salazar, P.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Villanueva-Rodríguez, G.; Gamboa-Domínguez, A. Association between AT1 and AT2 angiotensin II receptor expression with cell proliferation and angiogenesis in operable breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 5627–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jethon, A.; Pula, B.; Piotrowska, A.; Wojnar, A.; Rys, J.; Dziegiel, P.; Podhorska-Okolow, M. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT-1R) expression correlates with VEGF-A and VEGF-D expression in invasive ductal breast cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2012, 18, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska, U.; Lachowicz-Ochędalska, A.; Domińska, K.; Kaszewska, D.; Rębas, E. Angiotensin II as a factor modulating protein tyrosine kinase activity in two breast cancer lines—MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. Endokrynol. Pol. 2011, 62, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ping, H.; Guo, L.; Xi, J.; Wang, D. Angiotensin II type 2 receptor-interacting protein 3a inhibits ovarian carcinoma metastasis via the extracellular HMGA2-mediated ERK/EMT pathway. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiji, H.; Kuriyama, S.; Fukui, H. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitors may be an alternative anti-angiogenic strategy in the treatment of liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Possible role of vascular endothelial growth factor. Tumour Biol. 2002, 23, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rahman, S.S.; Fayed, H.M. Targeting AngII/AT1R signaling pathway by perindopril inhibits ongoing liver fibrosis in rat. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paizis, G.; Gilbert, R.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Murthi, P.; Schembri, J.M.; Wu, L.L.; Rumble, J.R.; Kelly, D.J.; Tikellis, C.; Cox, A.; et al. Effect of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade on experimental hepatic fibrogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samukawa, E.; Fujihara, S.; Oura, K.; Iwama, H.; Yamana, Y.; Tadokoro, T.; Chiyo, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Morishita, A.; Nakahara, M.; et al. Angiotensin receptor blocker telmisartan inhibits cell proliferation and tumor growth of cholangiocarcinoma through cell cycle arrest. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Fujihara, S.; Morishita, A.; Chiyo, T.; Samukawa, E.; Yamana, Y.; Fujita, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Nomura, T.; et al. Telmisartan inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation in vitro by inducing cell cycle arrest. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2825–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, M.-C.; Zhang, J.-F.; Wang, J.-Y.; Hu, R.-H.; Lee, P.-H. Comparative effectiveness of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers in chemoprevention of hepatocellular carcinoma: A nationwide high-risk cohort study. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, J.; Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Callahan, M.F.; Cline, J.M.; Ferrario, C.M.; Tallant, E.A.; Gallagher, P.E. Angiotensin-(1-7) inhibits growth of human lung adenocarcinoma xenografts in nude mice through a reduction in cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Pei, N.; Mao, Y.; Wang, S.; Yan, R.; Bai, N.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y.; Du, H.; et al. AAV-Mediated angiotensin 1-7 overexpression inhibits tumor growth of lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Telmisartan inhibits NSCLC A549 cell proliferation and migration by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5859–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Feng, Y.; Wan, H.; Ma, Q.; Fan, L.; Qian, Y.; Li, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Gao, B. Angiotensin-(1-7) inhibits the migration and invasion of A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells through inactivation of the PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, A.; Ishida, S. (Pro)renin receptor: Involvement in diabetic retinopathy and development of molecular targeted therapy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Mori, N.; Totsune, K.; Morimoto, R.; Maejima, T.; Kawamura, T.; Metoki, H.; Asayama, K.; Kikuya, M.; Ohkubo, T.; et al. Gene expression of (pro)renin receptor is upregulated in hearts and kidneys of rats with congestive heart failure. Peptides 2009, 30, 2316–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satofuka, S.; Ichihara, A.; Nagai, N.; Yamashiro, K.; Koto, T.; Shinoda, H.; Noda, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Inoue, M.; Tsubota, K.; et al. Suppression of ocular inflammation in endotoxin-induced uveitis by inhibiting nonproteolytic activation of prorenin. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 2686–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, K.A.; Advani, A.; Kim, S.; Advani, S.L.; Zhang, M.; White, K.E.; Kim, Y.M.; Parker, C.; Thai, K.; Krum, H.; et al. The cardiac (pro)renin receptor is primarily expressed in myocyte transverse tubules and is increased in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, S.M.; Wong, W.T. Microglia in the retina: Roles in development, maturity, and disease. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2018, 4, 45–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, N.; Mitchell, P.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet 2010, 376, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, A.; Mahdi, L.; Musat, O. Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 59, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Danser, A.H.J.; Derkx, F.H.M.; Admiraal, P.J.J.; Deinum, J.; De Jong, P.T.V.M.; Schalekamp, M.A.D.H. Angiotensin levels in the eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, C.R.; Pumfery, A.M.; Micales, B.; Bindley, C.D.; Lyons, G.E.; Sramek, S.J.; Wallow, I.H.L. Renin mRNA is synthesized locally in rat ocular tissues. Curr. Eye Res. 1994, 13, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.; Delarue, F.; Burcklé, C.; Bouzhir, L.; Giller, T.; Sraer, J.D. Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Riet, L.; van den Heuvel, M.; Peutz-Kootstra, C.J.; van Esch, J.H.M.; van Veghel, R.; Garrelds, I.M.; Musterd-Bhaggoe, U.; Bouhuizen, A.M.; Leijten, F.P.J.; Jan Danser, A.H.; et al. Deterioration of kidney function by the (pro)renin receptor blocker handle region peptide in aliskiren-treated diabetic transgenic (mRen2)27 rats. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 306, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, D.B.; Li, X.N.; Tan, X.; Qi, X.; Zhang, B. Protective effect of benazepril on diabetic retinopathy in rats. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 11, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogeboom Van Buggenum, I.M.; Polak, B.C.P.; Reichert-Thoen, J.W.M.; De Vries-Knoppert, W.A.E.J.; Van Hinsbergh, V.W.M.; Tangelder, G.J. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibiting therapy is associated with lower vitreous vascular endothelial growth factor concentrations in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miller, A.G.; Tan, G.; Binger, K.J.; Pickering, R.J.; Thomas, M.C.; Nagaraj, R.H.; Cooper, M.E.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L. Candesartan attenuates diabetic retinal vascular pathology by restoring glyoxalase-I function. Diabetes 2010, 59, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, M.S.; Ahmed, M.M.; Abuohashish, H.M.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Alhomida, A.S. Telmisartan ameliorates neurotrophic support and oxidative stress in the retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagisa, Y.; Shintani, A.; Nakagawa, S. The angiotensin II receptor antagonist candesartan cilexetil (TCV-116) ameliorates retinal disorders in rats. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravski, C.J.; Kelly, D.J.; Cooper, M.E.; Gilbert, R.E.; Bertram, J.F.; Shahinfar, S.; Skinner, S.L.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L. Retinal neovascularization is prevented by blockade of the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension 2000, 36, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.E.; Kelly, D.J.; Cox, A.J.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L.; Rumble, J.R.; Osicka, T.; Panagiotopoulos, S.; Lee, V.; Hendrich, E.C.; Jerums, G.; et al. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition reduces retinal overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor and hyperpermeability in experimental diabetes. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Hur, E.H.; Farrell, A.N.; Iuvone, P.M.; Howell, J.C. MicroRNA-152 represses VEGF and TGFβ1 expressions through post-transcriptional inhibition of (Pro)renin receptor in human retinal endothelial cells. Mol. Vis. 2015, 21, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagai, N.; Izumi-Nagai, K.; Oike, Y.; Koto, T.; Satofuka, S.; Ozawa, Y.; Yamashiro, K.; Inoue, M.; Tsubota, K.; Umezawa, K.; et al. Suppression of diabetes-induced retinal inflammation by blocking the angiotensin II type 1 receptor or its downstream nuclear factor-κB pathway. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 4342–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T.; Okuno, T.; Fukuhara, M.; Oku, H.; Ikeda, T.; Obayashi, H.; Ohta, M.; Fukui, M.; Hasegawa, G.; Nakamura, N. Angiotensin II receptor blocker inhibits abnormal accumulation of advanced glycation end products and retinal damage in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Exp. Eye Res. 2007, 85, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, S. Lifestyle-related diseases and anti-aging ophthalmology: Suppression of retinal and choroidal pathologies by inhibiting renin-angiotensin system and inflammation. Nihon. Ganka Gakkai Zasshi 2009, 113, 403–422, discussion 423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pons, M.; Cousins, S.W.; Alcazar, O.; Striker, G.E.; Marin-Castaño, M.E. Angiotensin II-induced MMP-2 activity and MMP-14 and basigin protein expression are mediated via the angiotensin ii receptor type 1-mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 pathway in retinal pigment epithelium: Implications for age-related macular degeneration. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 2665–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, N.; Oike, Y.; Izumi-Nagai, K.; Koto, T.; Satofuka, S.; Shinoda, H.; Noda, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Inoue, M.; Tsubota, K.; et al. Suppression of choroidal neovascularization hy inhibiting angiotensin-converting enzyme: Minimal role of bradykinin. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 2321–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, N.; Oike, Y.; Izumi-Nagai, K.; Urano, T.; Kubota, Y.; Noda, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Inoue, M.; Tsubota, K.; Suda, T.; et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated inflammation is required for choroidal neovascularization. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2252–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satofuka, S.; Ichihara, A.; Nagai, N.; Noda, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Fukamizu, A.; Tsubota, K.; Itoh, H.; Oike, Y.; Ishida, S. (Pro)renin receptor promotes choroidal neovascularization by activating its signal transduction and tissue renin-angiotensin system. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.F.; Podos, S.M.; Mittag, T.W.; Yokoyoma, T. Effect of CS-088, an angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist, on intraocular pressure in glaucomatous monkey eyes. Exp. Eye Res. 2005, 80, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costagliola, C.; Verolino, M.; Leonarda De Rosa, M.; Iaccarino, G.; Ciancaglini, M.; Mastropasqua, L. Effect of oral losartan potassium administration on intraocular pressure in normotensive and glaucomatous human subjects. Exp. Eye Res. 2000, 71, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Iyer, L.; Parmar, S.; Shah, G.; Goyal, R. Oculohypotensive effect of perindopril in acute and chronic models of glaucoma in rabbits. Can. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2010, 88, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinane, A.B.; Leung, P.S.; Ortego, J.; Coca-Prados, M.; Harvey, B.J. Renin-angiotensin system expression and secretory function in cultured human ciliary body non-pigmented epithelium. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 86, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foureaux, G.; Nogueira, B.S.; Coutinho, D.C.O.; Raizada, M.K.; Nogueira, J.C.; Ferreira, A.J. Activation of endogenous angiotensin converting enzyme 2 prevents early injuries induced by hyperglycemia in rat retina. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaajanen, A.; Vapaatalo, H.; Kautiainen, H.; Oksala, O. Angiotensin (1-7) reduces intraocular pressure in the normotensive rabbit eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 2557–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotti, V.J.; Pawlowski, N. Prostaglandins Mediate the Ocular Hypotensive Action of the Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor MK-422 (Enalaprilat) in African Green Monkeys. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. 1990, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T. Effects of angiotensin II on the 3H-TdR incorporation and synthesis of collagen in cultured bovine trabecular meshwork cells. Yan Ke Xue Bao 2001, 17, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, T.; Yokoyoma, T.; Koike, H. The effect of angiotensin II on uveoscleral outflow in rabbits. Curr. Eye Res. 2001, 23, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuniyasu, H. Multiple roles of angiotensin in colorectal cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 3, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomoto, T.; Ohmori, H.; Luo, Y.; Chihara, Y.; Denda, A.; Sasahira, T.; Tatsumoto, N.; Fujii, K.; Kuniyasu, H. Diabetes-associated angiotensin activation enhances liver metastasis of colon cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2012, 29, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belova, L.A. Angiotensin II-generating enzymes. Biochemistry 2000, 65, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yisireyili, M.; Uchida, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakayama, T.; Cheng, X.W.; Matsushita, T.; Nakamura, S.; Murohara, T.; Takeshita, K. Angiotensin receptor blocker irbesartan reduces stress-induced intestinal inflammation via AT1a signaling and ACE2-dependent mechanism in mice. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmenkari, H.; Pasanen, L.; Linden, J.; Korpela, R.; Vapaatalo, H. Beneficial anti-inflammatory effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin receptor blocker in the treatment of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2018, 69, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allin, K.H.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Elevated C-reactive protein in the diagnosis, prognosis, and cause of cancer. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2011, 48, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakoshi, S.; Nakamura, T.; Mori, N.; Suda, C.; Kohzuki, M.; Ito, O. Effects of exercise training on renal interstitial fibrosis and renin–angiotensin system in rats with chronic renal failure. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armando, I.; Jezova, M.; Juorio, A.V.; Terrón, J.A.; Falcón-Neri, A.; Semino-Mora, C.; Imboden, H.; Saavedra, J.M. Estrogen upregulates renal angiotensin II AT2 receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2002, 283, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, K.; Tajima, H.; Nakanuma, S.; Sakai, S.; Makino, I.; Kinoshita, J.; Hayashi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Oyama, K.; Nakagawara, H.; et al. Angiotensin II enhances epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through the interaction between activated hepatic stellate cells and the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 axis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenter, K.; Dashwood, M.R. Blockade of the renin-angiotensin and endothelin systems on progressive renal injury. Hypertension 2001, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.W.; Wright, J.W.; Swanson, G.N.; Hanesworth, J.M.; Krebs, L.T. AT4 receptors: Specificity and distribution. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 1510–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, T.A.; Handa, R.K.; Harding, J.W.; Wright, J.W. A role for the angiotensin IV/AT4 system in mediating natriuresis in the rat. Peptides 2001, 22, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, H.; Yin, B.; Zhou, H.; Cai, D.; Ma, B.; Xiang, Y. Loss of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 promotes growth of gallbladder cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 5171–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, Z.L.; Ren, X.; Zou, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, L.; Chen, M.; Chen, S. ACE2 and FZD1 are prognosis markers in squamous cell/adenosquamous carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of gallbladder. J. Mol. Histol. 2014, 45, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Eberhard, M.; Erne, P. Stimulation of DNA and RNA synthesis in cultured rabbit cardiac fibroblasts by angiotensin IV. Clin. Sci. 1995, 88, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, H.; Ishiguro, H.; Nakaigawa, N.; Nagashima, Y.; Miyoshi, Y.; Fujinami, K.; Sakaguchi, A.; Kubota, Y. Angiotensin II receptor blocker shows antiproliferative activity in prostate cancer cells: A possibility of tyrosine kinase inhibitor of growth factor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2003, 2, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, L.; Barsh, G.S.; Pratt, R.E.; Dzau, V.J.; Kobilka, B.K. Behavioural and cardiovascular effects of disrupting the angiotensin II type-2 receptor gene in mice. Nature 1995, 377, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, Y.; Matsubara, H.; Masaki, H.; Kurihara, H.; Murasawa, S.; Takai, S.; Miyazaki, M.; Nozawa, Y.; Ozono, R.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Angiotensin II type 2 receptor overexpression activates the vascular kinin system and causes vasodilation. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 104, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.H.; Wen, C.H.; Lin, C.S. Interplay of angiotensin II and angiotensin(1-7) in the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases of human cardiocytes. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWhinney, C.D.; Hunt, R.A.; Conrad, K.M.; Dostal, D.E.; Baker, K.M. The type I angiotensin II receptor couples to Stat1 and Stat3 activation through Jak2 kinase in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1997, 29, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munzenmaier, D.H.; Greene, A.S. Opposing actions of angiotensin II on microvascular growth and arterial blood pressure. Hypertension 1996, 27, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W.; Kozłowski, M.; Wagner, W.; Domińska, K.; Ochędalski, T. Effect of an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker on caveolin-1 expression in prostate cancer cells. Arch. Med. Sci. 2013, 9, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Hayashi, I.; Yamashina, S.; Itoman, M.; Majima, M. Blockade of angiotensin AT1a receptor signaling reduces tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 294, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Park, K.H.; Oh, S.C.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, S.W.; Kim, Y.H. How does inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system affect the prognosis of advanced gastric cancer patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy? Oncology 2012, 83, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, R.; Tanrikut, C. Manipulation of a locally expressed renin-angiotensin system in the testis: Implications for steroidogenesis. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 1599–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, S.; Lam, M.M.T.; Poon, T.C.W.; Sun, L.; Jiao, Y.; Wong, A.S.T.; Lee, L.T.O. Angiotensin II promotes ovarian cancer spheroid formation and metastasis by upregulation of lipid desaturation and suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakoo, A.Y.; Sidman, R.L.; Pasqualini, R.; Arap, W. Does the Renin-Angiotensin System Participate in Regulation of Human Vasculogenesis and Angiogenesis? Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9112–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinter, M.; Jain, R.K. Targeting the renin-angiotensin system to improve cancer treatment: Implications for immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanishi, T.; Hano, T.; Nishio, I. Angiotensin II potentiates vascular endothelial growth factor-induced proliferation and network formation of endothelial progenitor cells. Hypertens. Res. 2004, 27, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Otani, A.; Takagi, H.; Oh, H.; Suzuma, K.; Matsumura, M.; Ikeda, E.; Honda, Y. Angiotensin II-stimulated vascular endothelial growth factor expression in bovine retinal pericytes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Pupilli, C.; Lasagni, L.; Romagnani, P.; Bellini, F.; Mannelli, M.; Misciglia, N.; Mavilia, C.; Vellei, U.; Villari, D.; Serio, M. Angiotensin II stimulates the synthesis and secretion of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor in human mesangial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Baker, A.Q.; Gallacher, B.; Lodwick, D. Angiotensin II increases vascular permeability factor gene expression by human vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 1995, 25, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptasińska-Wnuk, D.; Ławnicka, H.; Fryczak, J.; Kunert-Radek, J.; Pawlikowski, M. Angiotensin peptides regulate angiogenic activity in rat anterior pituitary tumour cell cultures. Endokrynol. Pol. 2007, 58, 478–486. [Google Scholar]
- Cambados, N.; Walther, T.; Nahmod, K.; Tocci, J.M.; Rubinstein, N.; Böhme, I.; Simian, M.; Sampayo, R.; Suberbordes, M.D.V.; Kordon, E.C.; et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) counteracts the transforming effects triggered by angiotensin II in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88475–88487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, N.; Wan, R.; Chen, X.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Du, H.; Chen, B.; Wei, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) Decreases Cell Growth and Angiogenesis of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Xenografts. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Meng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Sun, L.; Sui, G.; Cai, L.; Dong, X. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists inhibit cell proliferation and angiogenesis in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 328, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W.; Płuciennik, E.; Wójcik-Krowiranda, K.; Bieńkiewicz, A.; Nowakowska, M.; Pospiech, K.; Bednarek, A.K.; Domińska, K.; Ochedalski, T. Correlation between VEGFR-2 receptor kinase domain-containing receptor (KDR) mRNA and angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1-R) mRNA in endometrial cancer. Cytokine 2013, 61, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka, B.; Terlikowski, S.J.; Kowalczuk, O.; Kulikowski, M.; Niklinski, J. Serum levels of VEGF and VEGF-C in patients with endometrial cancer. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2011, 22, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukourakis, M.I.; Limberis, V.; Tentes, I.; Kontomanolis, E.; Kortsaris, A.; Sivridis, E.; Giatromanolaki, A. Serum VEGF levels and tissue activation of VEGFR2/KDR receptors in patients with breast and gynecologic cancer. Cytokine 2011, 53, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.K.; Brosseau, S.; Cook, A.; Zalcman, G. Antiangiogeneic Strategies in Mesothelioma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Chen, Q.; Rao, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Ge, H.; Wei, Q. OVA66 promotes tumour angiogenesis and progression through enhancing autocrine VEGF-VEGFR2 signalling. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.B.; Giri, U.; Gudikote, J.; Tang, X.; Lu, W.; Tran, H.; Fan, Y.; Koo, A.; Diao, L.; Tong, P.; et al. KDR amplification is associated with VEGF-induced activation of the mTOR and invasion pathways but does not predict clinical benefit to the VEGFR TKI vandetanib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, I.; Adham, S.A.; Petrik, J.; Coomber, B.L. Autocrine VEGF-A/KDR loop protects epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells from anoikis. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikane, S.; Takahashi-Yanaga, F. The role of angiotensin II in cancer metastasis: Potential of renin-angiotensin system blockade as a treatment for cancer metastasis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alvarenga, E.C.; De Castro Fonseca, M.; Carvalho, C.C.; Florentino, R.M.; França, A.; Matias, E.; Guimarães, P.B.; Batista, C.; Freire, V.; Carmona, A.K.; et al. Angiotensin converting enzyme regulates cell proliferation and migration. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olschewski, D.N.; Hofschröer, V.; Nielsen, N.; Seidler, D.G.; Schwab, A.; Stock, C. The Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antagonist Losartan Affects NHE1-Dependent Melanoma Cell Behavior. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 2560–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Luo, Y.; Sato, S.; Tanabe, E.; Kitayoshi, M.; Fujiwara, R.; Sasaki, T.; Fujii, K.; Ohmori, H.; Kuniyasu, H. Role of Two Types of Angiotensin II Receptors in Colorectal Carcinoma Progression. Pathobiology 2014, 81, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gu, C. MicroRNA-410 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting angiotensin II type 1 receptor in pancreatic cancer. Iubmb Life 2015, 67, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhekadur, P.K.; Akiel, M.; Emdad, L.; Gredler, R.; Srivastava, J.; Rajasekaran, D.; Robertson, C.L.; Mukhopadhyay, N.D.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Staphylococcal nuclease domain containing-1 (SND1) promotes migration and invasion via angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and TGFβ signaling. Febs Open Bio 2014, 4, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W.; Domińska, K.; Nowakowska, M.; Gajewska, M.; Gajos-Michniewicz, A.; Ochędalski, T. Angiotensin modulates human mammary epithelial cell motility. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2014, 15, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Yan, S.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, W. The influence of TNF-α and Ang II on the proliferation, migration and invasion of HepG2 cells by regulating the expression of GRK2. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Ager, E.I.; Neo, J.; Christophi, C. Regulation of colorectal cancer cell epithelial to mesenchymal transition by the renin angiotensin system. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Ferreira, S.; Abdelkarim, M.; Dillenburg-Pilla, P.; Luissint, A.-C.; di-Tommaso, A.; Deshayes, F.; Pontes, C.L.S.; Molina, A.; Cagnard, N.; Letourneur, F.; et al. Angiotensin II Facilitates Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Metastasis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinsley, E.E.; de Oliveira, C.E.; Hunt, S.; Coletta, R.D.; Lambert, D.W. Angiotensin 1-7 inhibits angiotensin II-stimulated head and neck cancer progression. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 125, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, K.; Nowakowska, M.; Domińska, K.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Coexpression of CAV-1, AT1-R and FOXM1 in prostate and breast cancer and normal cell lines and their influence on metastatic properties. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klymkowsky, M.W.; Savagner, P. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Wen, Z.B.; Yang, H.H.; Zhang, C.Y.; Xiong, J.B.; Guan, X.X.; Zhong, W.J.; Jiang, H.L.; Sun, C.C.; Luo, X.Q.; et al. Exogenous angiotensin (1-7) directly inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transformation induced by transforming growth factor-β1 in alveolar epithelial cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Organs | Data |
|---|---|
| Kidney | •Exercise training attenuates the progression of glomerular sclerosis and renal interstitial fibrosis in chronic renal failure rats by increasing expression of RAS components such as angiotensinogen and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) [164]. •Increase in AT2R expression after estrogen treatment in the mouse kidney [165]. •Estrogen treatment in OVX mice dramatically decreased the AT1R to AT2Rratio by upregulation of AT2R expression [165]. •Ang II actively participates in renal fibrosis and in the parts mediated by TGF- β [166]. •Irbesartan reduces the expression of TGF-β1 mRNA [166]. •In the rat kidney, the distribution of the AT4R was reported to occur in high levels in the proximal tubules [167]. •Infusion of Ang IV into the renal artery of rats resulted in increased renal cortical blood flow and urinary sodium excretion [168]. •AT2R mRNA has been reported to have a widespread distribution within the rat kidney [169]. |
| Gallbladder | •ACE2 suppressed tumor growth in gallbladder cancer [170]. •Lowered ACE2 expression was correlated with larger tumor size, high TNM stage, lymph node metastasis, and invasion in squamous cell/adenosquamous carcinoma patients [171]. |
| Heart | •Ang IV stimulated DNA and RNA synthesis in cultured rabbit cardiac fibroblast [172]. •The activation of ERK1/2 was critical for the growth-promoting actions of ang II in cardiac fibroblasts or prostate cancer cell subcultures [173]. •Enhanced vasoconstrictive effect of Ang II in AT2R-knockout mice [174]. •Vasodilatation due to AT2R overexpression in vascular smooth muscle cells [175]. •Ang IV stimulates protein synthesis in rabbit cardiac fibroblasts [172]. •Ang (1-7) treatment leads to decrease the ratio of expression of MMPs/TIMPs in human cardiocytes [176]. •Ang II induces SIF complex formation in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes in a time- and dose-dependent manner [177]. |
| Muscle | •Ang II stimulated angiogenesis in the rat cremaster muscle [178]. •Janus tyrosine kinase-STAT pathway directly through the AT1R in smooth muscle cells and cardiac myocytes [177]. •Cav-1 plays a critical role in the key signaling step in which angiotensin II induces the transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), leading to the hypertrophy and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells [179]. •Blockade of AT1R signaling reduced tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis in the model of murine sarcoma and fibrosarcoma cells [180]. |
| Stomach | •The local production of Ang II in gastric cancer has been indicated to promote lymph node metastasis and cancer progression [180]. •Increased OS median in ACEI/ARB group compared to the non-ACEI /ARB group [181]. |
| Testicles | •Ang III and IV, and ACE2 may serve as the regulators of testicular steroidogenesis [182]. •Ang 1-7 can bind to a third receptor, specific to Ang 1-7 only (AT1-7/Mas receptor), which is also found in testes of fertile and infertile men [12]. •Main localization of Ang (1–7) and Mas receptor is observed in the Leydig cells [12]. •In non-obstructive azoospermia biopsies samples, Mas mRNA, protein, and ACE2 mRNA were lowered compared with biopsies from men with obstructive azoospermia [12]. |
| Ovaries | •Ang II increases the invasive potential of the highly-metastatic ovarian cancer cell line SKOV3 [183]. •RAS components like Ang (1-7) and Mas were localized to primordial, primary, secondary, and antral follicles, stroma, and corpora lutea of reproductive-age ovaries [21]. •High expression of AT1 predicted a shorter survival time for Grade 1 and Grade 2 ovary tumor patients [183]. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziaja, M.; Urbanek, K.A.; Kowalska, K.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Angiotensin II and Angiotensin Receptors 1 and 2—Multifunctional System in Cells Biology, What Do We Know? Cells 2021, 10, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020381
Ziaja M, Urbanek KA, Kowalska K, Piastowska-Ciesielska AW. Angiotensin II and Angiotensin Receptors 1 and 2—Multifunctional System in Cells Biology, What Do We Know? Cells. 2021; 10(2):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020381
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiaja, Maksymilian, Kinga Anna Urbanek, Karolina Kowalska, and Agnieszka Wanda Piastowska-Ciesielska. 2021. "Angiotensin II and Angiotensin Receptors 1 and 2—Multifunctional System in Cells Biology, What Do We Know?" Cells 10, no. 2: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020381
APA StyleZiaja, M., Urbanek, K. A., Kowalska, K., & Piastowska-Ciesielska, A. W. (2021). Angiotensin II and Angiotensin Receptors 1 and 2—Multifunctional System in Cells Biology, What Do We Know? Cells, 10(2), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020381