TDP-43 Regulation of AChE Expression Can Mediate ALS-Like Phenotype in Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Studies
2.2. Microinjections
2.3. Touch-Evoked Escape Response (TEER)
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Staining for Acetylcholinesterase Activity
2.6. AChE Enzyme Assay and Protein Determination
2.7. RNA Isolation and Analysis of Transcripts by qPCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
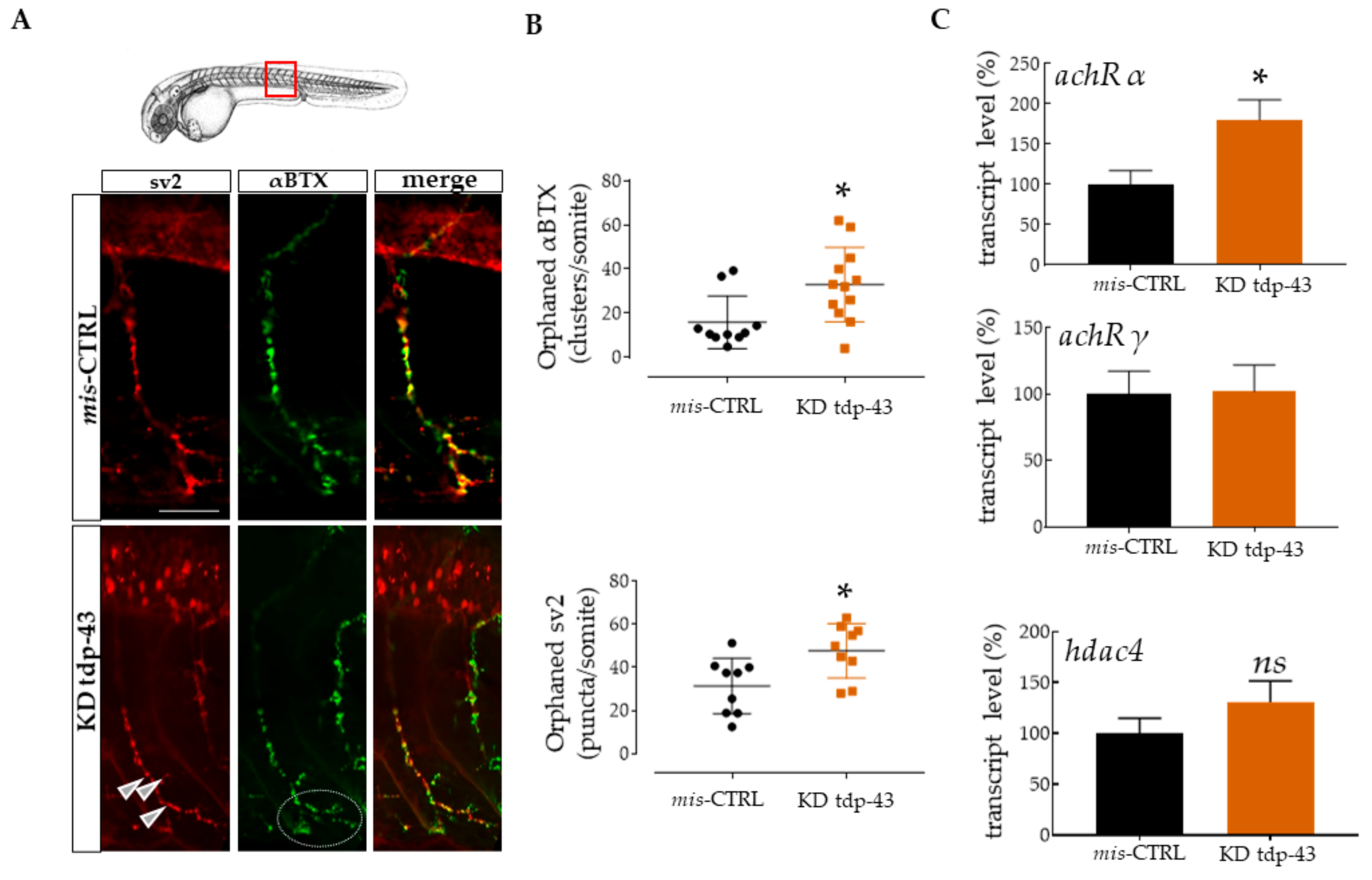
3.1. TDP-43 Knockdown Induced Defective NMJ Structures in Zebrafish
3.2. TDP-43 LoF Caused Decreased Ache Expression
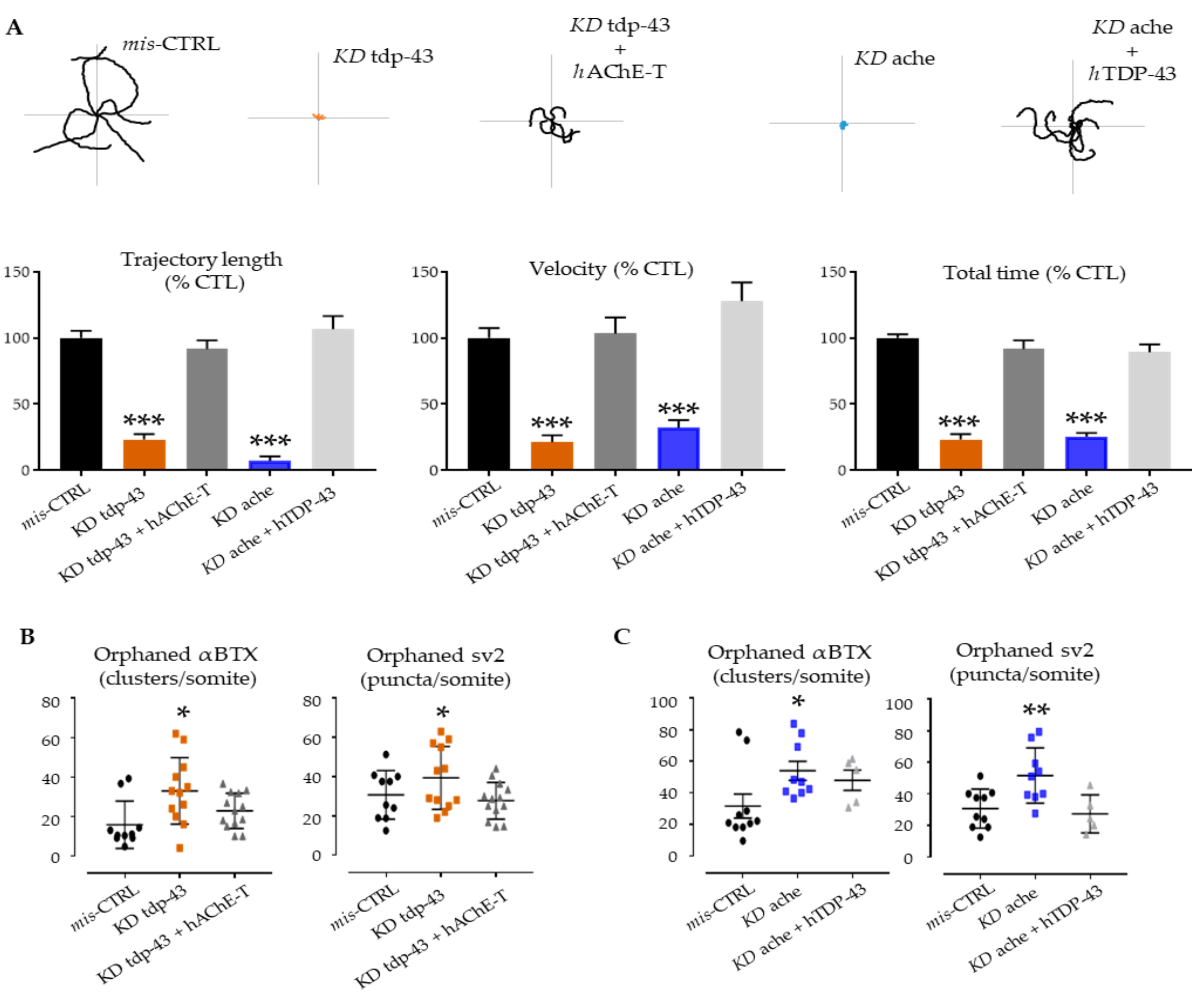
3.3. Functional Interactions between Ache and Tardbp
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, J.P.; Brown, R.H.; Cleveland, D.W. Decoding ALS: From genes to mechanism. Nature 2016, 539, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, M.; Sampathu, D.M.; Kwong, L.K.; Truax, A.C.; Micsenyi, M.C.; Chou, T.T.; Bruce, J.; Schuck, T.; Grossman, M.; Clark, C.M.; et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Science 2006, 314, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Akiyama, H.; Ikeda, K.; Nonaka, T.; Mori, H.; Mann, D.; Tsuchiya, K.; Yoshida, M.; Hashizume, Y.; et al. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, I.R.; Rademakers, R.; Neumann, M. TDP-43 and FUS in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashi, E.; Valdmanis, P.N.; Dion, P.; Spiegelman, D.; McConkey, B.J.; Vande Velde, C.; Bouchard, J.P.; Lacomblez, L.; Pochigaeva, K.; Salachas, F.; et al. TARDBP mutations in individuals with sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedharan, J.; Blair, I.P.; Tripathi, V.B.; Hu, X.; Vance, C.; Rogelj, B.; Ackerley, S.; Durnall, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Buratti, E.; et al. TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2008, 319, 1668–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecic, A.M.; Swanson, M.S. hnRNP complexes: Composition, structure, and function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1999, 11, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, E.; Brindisi, A.; Giombi, M.; Tisminetzky, S.; Ayala, Y.M.; Baralle, F.E. TDP-43 binds heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B through its C-terminal tail: An important region for the inhibition of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator exon 9 splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37572–37584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.-C.; Polymenidou, M.; Cleveland, D.W. Converging Mechanisms in ALS and FTD: Disrupted RNA and Protein Homeostasis. Neuron 2013, 79, 416–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Kim, J.R.; van Bruggen, R.; Park, J. RNA-binding proteins in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 818–829. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, L.R.; Culver, D.G.; Tennant, P.; Davis, A.A.; Wang, M.; Castellano-Sanchez, A.; Khan, J.; Polak, M.A.; Glass, J.D. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a distal axonopathy: Evidence in mice and man. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 185, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killian, J.M.; Wilfong, A.A.; Burnett, L.; Appel, S.H.; Boland, D. Decremental motor responses to repetitive nerve stimulation in ALS. Muscle Nerve 1994, 17, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.A.; Southam, K.A.; Blizzard, C.A.; King, A.E.; Dickson, T.C. Axonal degeneration, distal collateral branching and neuromuscular junction architecture alterations occur prior to symptom onset in the SOD1G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 76, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanari, M.-L.; García-Ayllón, M.-S.; Ciura, S.; Sáez-Valero, J.; Kabashi, E. Neuromuscular Junction Impairment in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Reassessing the Role of Acetylcholinesterase. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Radić, Z. The cholinesterases: From genes to proteins. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1994, 34, 281–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoulié, J. The origin of the molecular diversity and functional anchoring of cholinesterases. NeuroSignals 2002, 11, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshorer, E.; Toiber, D.; Zurel, D.; Sahly, I.; Dori, A.; Cagnano, E.; Schreiber, L.; Grisaru, D.; Tronche, F.; Soreq, H. Combinatorial complexity of 5′ alternative acetylcholinesterase transcripts and protein products. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 29740–29751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, A.L.; Massoulié, J.; Krejci, E. PRiMA: The membrane anchor of acetylcholinesterase in the brain. Neuron 2002, 33, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigoillot, S.M.; Bourgeois, F.; Lambergeon, M.; Strochlic, L.; Legay, C. ColQ controls postsynaptic differentiation at the neuromuscular junction. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudel, J.; Heckmann, M. Desensitization reduces amplitudes of quantal end-plate currents after a single preceding end-plate current in mouse muscle. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1999, 437, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Manley, H.A.; Purcell, A.L.; Deshpande, S.S.; Hamilton, T.A.; Kan, R.K.; Oyler, G.; Lockridge, O.; Duysen, E.G.; Sheridan, R.E. Reduced acetylcholine receptor density, morphological remodeling, and butyrylcholinesterase activity can sustain muscle function in acetylcholinesterase knockout mice. Muscle Nerve 2004, 30, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misgeld, T.; Kummer, T.T.; Lichtman, J.W.; Sanes, J.R. Agrin promotes synaptic differentiation by counteracting an inhibitory effect of neurotransmitter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11088–11093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Dominguez, B.; Yang, J.; Aryal, P.; Brandon, E.P.; Gage, F.H.; Lee, K.-F. Neurotransmitter acetylcholine negatively regulates neuromuscular synapse formation by a Cdk5-dependent mechanism. Neuron 2005, 46, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Holmes, C.; Budd, T.C.; Greenfield, S.A. The effect of acetylcholinesterase on outgrowth of dopaminergic neurons in organotypic slice culture of rat mid-brain. Cell Tissue Res. 1995, 279, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivatsan, M.; Peretz, B. Acetylcholinesterase promotes regeneration of neurites in cultured adult neurons of Aplysia. Neuroscience 1997, 77, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupree, J.L.; Bigbee, J.W. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor treatment delays recovery from axotomy in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Neurocytol. 1996, 25, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisaru, D.; Sternfeld, M.; Eldor, A.; Glick, D.; Soreq, H. Structural roles of acetylcholinesterase variants in biology and pathology. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternfeld, M.; Ming, G.L.; Song, H.J.; Sela, K.; Timberg, R.; Poo, M.M.; Soreq, H. Acetylcholinesterase enhances neurite growth and synapse development through alternative contributions of its hydrolytic capacity, core protein, and variable C termini. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, E.; Bernard, V.; Camp, S.; Taylor, P.; Krejci, E.; Molgó, J. Remodeling of the Neuromuscular Junction in Mice with Deleted Exons 5 and 6 of Acetylcholinesterase. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2006, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, C.; Beeri, R.; Friedman, A.; Lev-Lehman, E.; Henis, S.; Timberg, R.; Shani, M.; Soreq, H. Acetylcholinesterase-transgenic mice display embryonic modulations in spinal cord choline acetyltransferase and neurexin Iβ gene expression followed by late-onset neuromotor deterioration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8173–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, C.; Seidman, S.; Beeri, R.; Timberg, R.; Soreq, H. Transgenic acetylcholinesterase induces enlargement of murine neuromuscular junctions but leaves spinal cord synapses intact. Neurochem. Int. 1998, 32, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvesh, S.; Hopkins, D.A.; Geula, C. Neurobiology of butyrylcholinesterase. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darreh-Shori, T.; Soininen, H. Effects of Cholinesterase Inhibitors on the Activities and Protein Levels of Cholinesterases in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Alzheimers Disease: A Review of Recent Clinical Studies. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2010, 7, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, C.; Chatonnet, A.; Takke, C.; Yan, Y.L.; Postlethwait, J.; Toutant, J.P.; Cousin, X. Zebrafish acetylcholinesterase is encoded by a single gene localized on linkage group 7. Gene structure and polymorphism; molecular forms and expression pattern during development. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behra, M.; Cousin, X.; Bertrand, C.; Vonesch, J.L.; Biellmann, D.; Chatonnet, A.; Strähle, U. Acetylcholinesterase is required for neuronal and muscular development in the zebrafish embryo. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downes, G.B.; Granato, M. Acetylcholinesterase function is dispensable for sensory neurite growth but is critical for neuromuscular synapse stability. Dev. Biol. 2004, 270, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festoff, B.W.; Fernandez, H.L. Plasma and red blood cell acetylcholinesterase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 1981, 4, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, W. Festoff Release of Acetylcholinesterase in Amyotrophic lateral Sclerosis. Adv. Neurol. 1982, 36, 503. [Google Scholar]
- Streichert, L.C.; Sargent, P.B. The role of acetylcholinesterase in denervation supersensitivity in the frog cardiac ganglion. J. Physiol. 1992, 445, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, G.; Leah, R.; Ofira, E.; Oded, A.; Zohar, A.; Hanna, R. Presymptomatic treatment with acetylcholinesterase antisense oligonucleotides prolongs survival in ALS (G93A-SOD1) mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniatis, S.; Äijö, T.; Vickovic, S.; Braine, C.; Kang, K.; Mollbrink, A.; Fagegaltier, D.; Andrusivová, Ž.; Saarenpää, S.; Saiz-Castro, G.; et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of molecular pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2019, 364, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabashi, E.; Lin, L.; Tradewell, M.L.; Dion, P.A.; Bercier, V.; Bourgouin, P.; Rochefort, D.; Bel Hadj, S.; Durham, H.D.; Vande Velde, C.; et al. Gain and loss of function of ALS-related mutations of TARDBP (TDP-43) cause motor deficits in vivo. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 19, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parichy, D.M.; Elizondo, M.R.; Mills, M.G.; Gordon, T.N.; Engeszer, R.E. Normal table of postembryonic zebrafish development: Staging by externally visible anatomy of the living fish. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 2975–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanari, M.-L.; García-Ayllón, M.-S.; Belbin, O.; Galcerán, J.; Lleó, A.; Sáez-Valero, J. Acetylcholinesterase modulates presenilin-1 levels and γ-secretase activity. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2014, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciura, S.; Lattante, S.; Le Ber, I.; Latouche, M.; Tostivint, H.; Brice, A.; Kabashi, E. Loss of function of C9orf72 causes motor deficits in a zebrafish model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Valero, J.; Tornel, P.L.; Muñoz-Delgado, E.; Vidal, C.J. Amphiphilic and hydrophilic forms of acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase in human brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 1993, 35, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, R.; Van Hoecke, A.; Hersmus, N.; Geelen, V.; D’Hollander, I.; Thijs, V.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Carmeliet, P.; Robberecht, W. Overexpression of mutant superoxide dismutase 1 causes a motor axonopathy in the zebrafish. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 2359–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros-Louis, F.; Kriz, J.; Kabashi, E.; McDearmid, J.; Millecamps, S.; Urushitani, M.; Lin, L.; Dion, P.; Zhu, Q.; Drapeau, P.; et al. Als2 mRNA splicing variants detected in KO mice rescue severe motor dysfunction phenotype in Als2 knock-down zebrafish. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 2691–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashi, E.; Bercier, V.; Lissouba, A.; Liao, M.; Brustein, E.; Rouleau, G.A.; Drapeau, P. Fus and tardbp but not sod1 interact in genetic models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, G.A.B.; Drapeau, P. Loss and gain of FUS function impair neuromuscular synaptic transmission in a genetic model of ALS. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 4282–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourefis, A.-R.; Campanari, M.-L.; Buee-Scherrer, V.; Kabashi, E. Functional characterization of a FUS mutant zebrafish line as a novel genetic model for ALS. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maselli, R.A.; Wollman, R.L.; Leung, C.; Distad, B.; Palombi, S.; Richman, D.P.; Salazar-Grueso, E.F.; Roos, R.P. Neuromuscular transmission in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 1993, 16, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruneteau, G.; Simonet, T.; Bauché, S.; Mandjee, N.; Malfatti, E.; Girard, E.; Tanguy, M.L.; Behin, A.; Khiami, F.; Sariali, E.; et al. Muscle histone deacetylase 4 upregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Potential role in reinnervation ability and disease progression. Brain 2013, 136, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.H.; Valdez, G.; Moresi, V.; Qi, X.; McAnally, J.; Elliott, J.L.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Sanes, J.R.; Olson, E.N. MicroRNA-206 delays ALS progression and promotes regeneration of neuromuscular synapses in mice. Science 2009, 326, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigna, E.; Renzini, A.; Greco, E.; Simonazzi, E.; Fulle, S.; Mancinelli, R.; Moresi, V.; Adamo, S. HDAC4 preserves skeletal muscle structure following long-term denervation by mediating distinct cellular responses. Skelet. Muscle 2018, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Macpherson, P.; Marvin, M.; Meadows, E.; Klein, W.H.; Yang, X.-J.J.; Goldman, D. A histone deacetylase 4/myogenin positive feedback loop coordinates denervation-dependent gene induction and suppression. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikoku, E.; Saito, M.; Ono, F. Zebrafish mutants of the neuromuscular junction: Swimming in the gene pool. J. Physiol. Sci. 2015, 65, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renton, A.E.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B.J. State of play in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genetics. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattante, S.; Rouleau, G.A.; Kabashi, E. TARDBP and FUS Mutations Associated with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Summary and Update. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorarú, G.; Orsetti, V.; Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.; Cima, V.; Volpe, M.; D’Ascenzo, C.; Palmieri, A.; Koutsikos, K.; Pegoraro, E.; et al. TDP-43 in skeletal muscle of patients affected with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogler, T.O.; Wheeler, J.R.; Nguyen, E.D.; Hughes, M.P.; Britson, K.A.; Lester, E.; Rao, B.; Betta, N.D.; Whitney, O.N.; Ewachiw, T.E.; et al. TDP-43 and RNA form amyloid-like myo-granules in regenerating muscle. Nature 2018, 563, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afroz, T.; Hock, E.M.; Ernst, P.; Foglieni, C.; Jambeau, M.; Gilhespy, L.A.B.; Laferriere, F.; Maniecka, Z.; Plückthun, A.; Mittl, P.; et al. Functional and dynamic polymerization of the ALS-linked protein TDP-43 antagonizes its pathologic aggregation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feiguin, F.; Godena, V.K.; Romano, G.; D’Ambrogio, A.; Klima, R.; Baralle, F.E. Depletion of TDP-43 affects Drosophila motoneurons terminal synapsis and locomotive behavior. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Acetylcholinesterase: “Classical” and “non-classical” functions and pharmacology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, A.J.; Scobell, A. How China sees America. Foreign Aff. 2012, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soreq, H. Acetylcholinesterase—New roles for an old actor. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Owen, M.B. Acetylcholine as a Regulator of Neurite Outgrowth and Motility in Cultured Embryonic Mouse Spinal Cord. Neuroreport 1995, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D.H.; Reed, G.; Whitefield, B.; Nurcombe, V. Cholinergic regulation of neurite outgrowth from isolated chick sympathetic neurons in culture. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, S.A.; Frosch, M.P.; Phillips, M.D.; Tauck, D.L.; Aizenman, E. Nicotinic antagonists enhance process outgrowth by rat retinal ganglion cells in culture. Science 1988, 239, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüdiger, T.; Bolz, J. Acetylcholine influences growth cone motility and morphology of developing thalamic axons. Cell Adh. Migr. 2008, 2, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichtchenko, K.; Nguyen, T.; Südhof, T.C. Structures, alternative splicing, and neurexin binding of multiple neuroligins. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 2676–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichtchenko, K.; Hata, Y.; Nguyen, T.; Ullrich, B.; Missler, M.; Moomaw, C.; Südhof, T.C. Neuroligin 1: A splice site-specific ligand for β-neurexins. Cell 1995, 81, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constance, W.D.; Mukherjee, A.; Fisher, Y.E.; Pop, S.; Blanc, E.; Toyama, Y.; Williams, D.W. Neurexin and neuroligin-based adhesion complexes drive axonal arborisation growth independent of synaptic activity. Elife 2018, 7, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grifman, M.; Galyam, N.; Seidman, S.; Soreq, H. Functional redundancy of acetylcholinesterase and neuroligin in mammalian neuritogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13935–13940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Xiang, Y.Y.; Farchi, N.; Ju, W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Hochner, B.; Yang, B.; Soreq, H.; et al. Excessive expression of acetylcholinesterase impairs glutamatergic synaptogenesis in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8950–8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejci, E.; Martinez-Pena Y Valenzuela, I.; Ameziane, R.; Akaaboune, M. Acetylcholinesterase dynamics at the neuromuscular junction of live animals. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10347–10354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Brännström, T.; Andersen, P.M.; Pedrosa-Domellöf, F. Distinct Changes in Synaptic Protein Composition at Neuromuscular Junctions of Extraocular Muscles versus Limb Muscles of ALS Donors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, T.J.; Waddell, D.S.; Barrientos, T.; Lu, Z.; Feng, G.; Cox, G.A.; Bodine, S.C.; Yao, T.P. The histone deacetylase HDAC4 connects neural activity to muscle transcriptional reprogramming. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 33752–33759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, E.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Lopergolo, D.; Roseti, C.; Bertollini, C.; Ruffolo, G.; Cifelli, P.; Onesti, E.; Limatola, C.; Miledi, R.; et al. Acetylcholine receptors from human muscle as pharmacological targets for ALS therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3060–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymenidou, M.; Lagier-Tourenne, C.; Hutt, K.R.; Huelga, S.C.; Moran, J.; Liang, T.Y.; Ling, S.C.; Sun, E.; Wancewicz, E.; Mazur, C.; et al. Long pre-mRNA depletion and RNA missplicing contribute to neuronal vulnerability from loss of TDP-43. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombrita, C.; Onesto, E.; Megiorni, F.; Pizzuti, A.; Baralle, F.E.; Buratti, E.; Silani, V.; Ratti, A. TDP-43 and FUS RNA-binding proteins bind distinct sets of cytoplasmic messenger RNAs and differently regulate their post-transcriptional fate in motoneuron-like cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15635–15647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campanari, M.-L.; Marian, A.; Ciura, S.; Kabashi, E. TDP-43 Regulation of AChE Expression Can Mediate ALS-Like Phenotype in Zebrafish. Cells 2021, 10, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020221
Campanari M-L, Marian A, Ciura S, Kabashi E. TDP-43 Regulation of AChE Expression Can Mediate ALS-Like Phenotype in Zebrafish. Cells. 2021; 10(2):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020221
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampanari, Maria-Letizia, Anca Marian, Sorana Ciura, and Edor Kabashi. 2021. "TDP-43 Regulation of AChE Expression Can Mediate ALS-Like Phenotype in Zebrafish" Cells 10, no. 2: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020221
APA StyleCampanari, M.-L., Marian, A., Ciura, S., & Kabashi, E. (2021). TDP-43 Regulation of AChE Expression Can Mediate ALS-Like Phenotype in Zebrafish. Cells, 10(2), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020221





