Disruption of Circadian Rhythms by Ambient Light during Neurodevelopment Leads to Autistic-like Molecular and Behavioral Alterations in Adult Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Circadian Behavioral Assay
2.3. Brain Tissue Processing, Immunostaining, and Microscopic Imaging Analysis
2.4. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting Analysis
2.5. RNA-seq and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.6. Electrophysiological Recording
2.7. Analysis of Neuronal Morphology by Golgi–Cox Staining
2.8. Puromycin Treatment and De Novo Protein Synthesis Analysis
2.9. Mouse Behavioral Tests
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
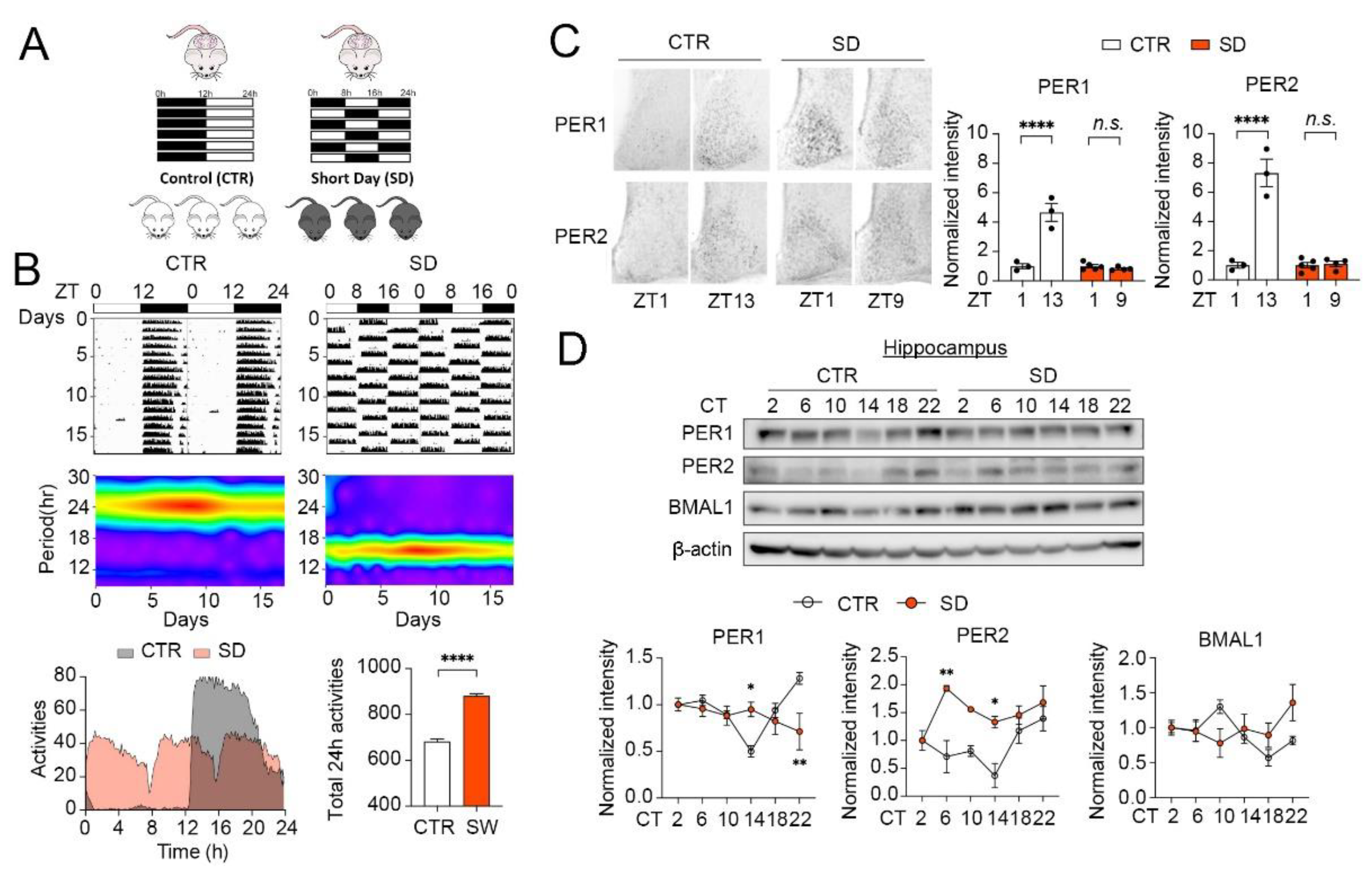
3.1. Daily Rhythms of Animal Locomotor Activity and Clock Gene Expression Are Disrupted in SD Mice
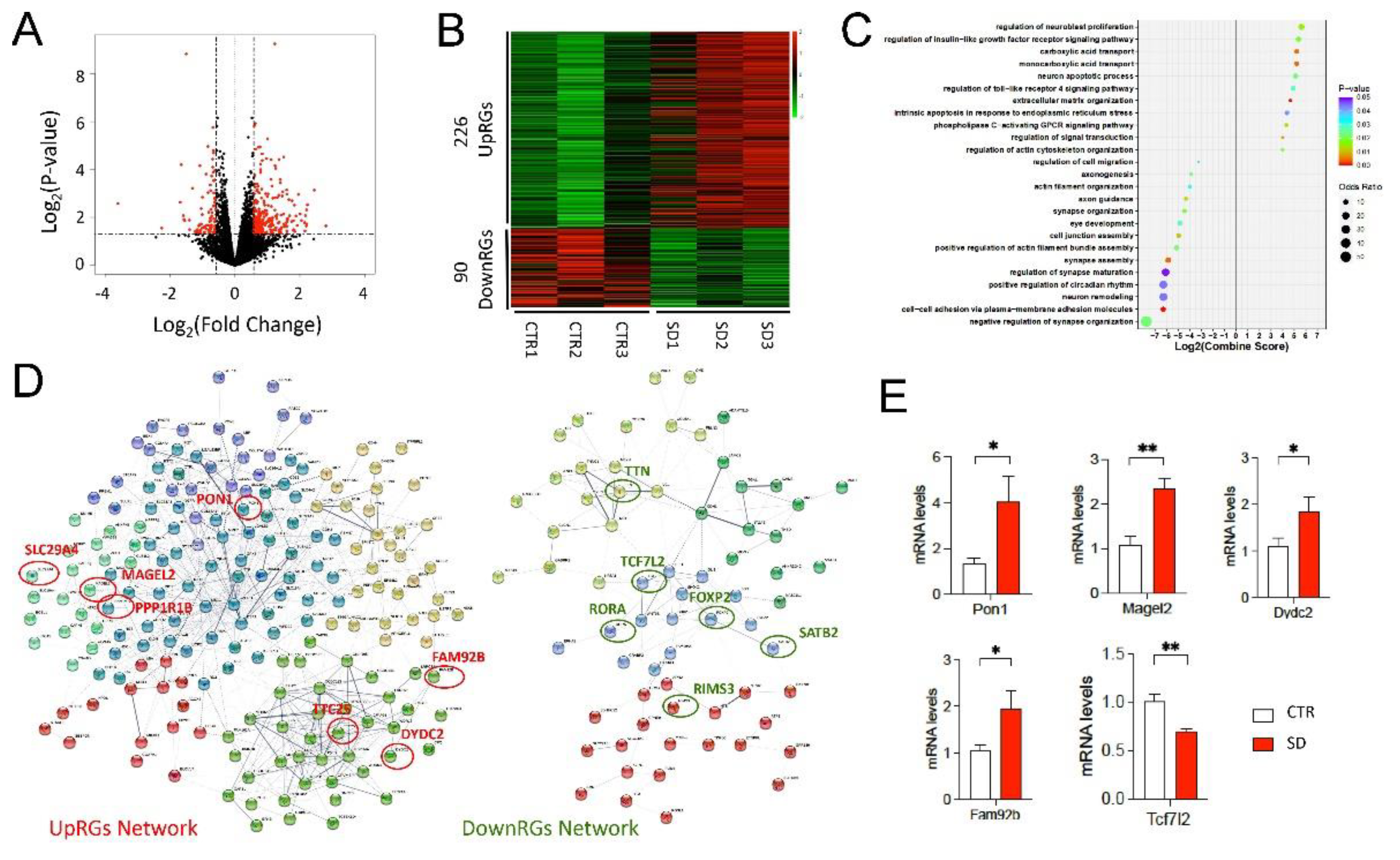
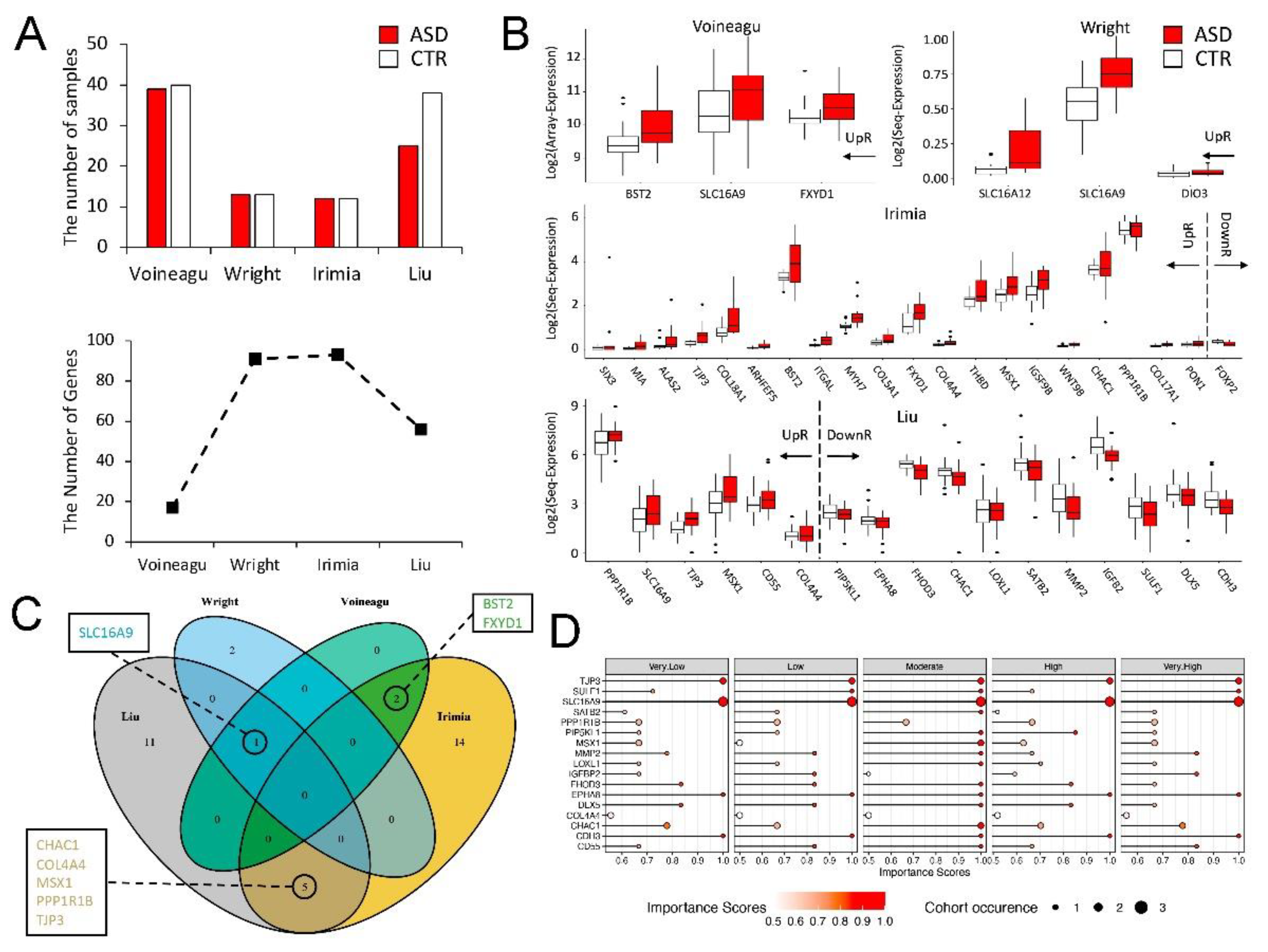
3.2. Genome-Wide Transcriptional Changes in the Hippocampi of SD Mice
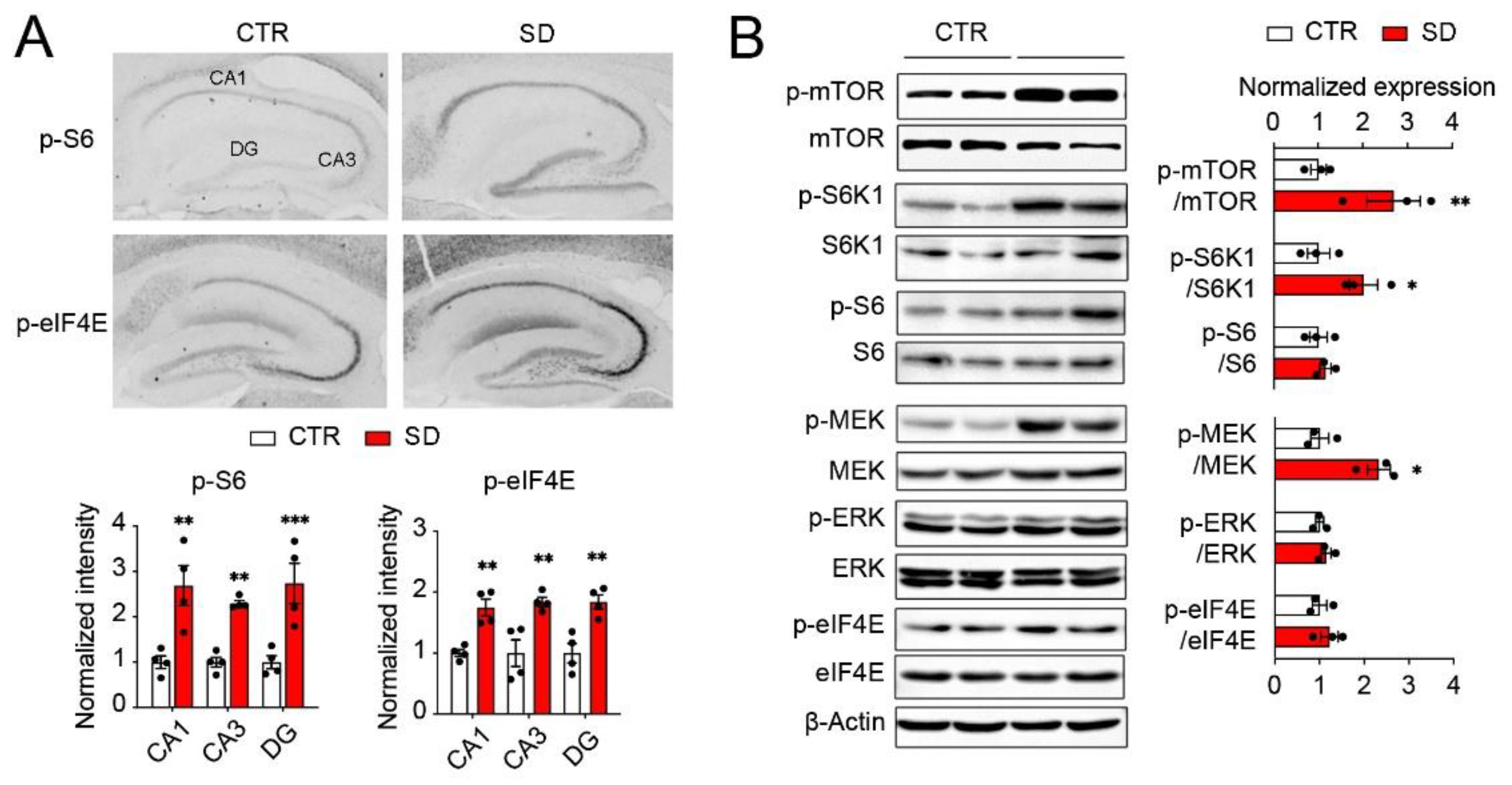
3.3. Hyperactivation of mTOR and ERK MAPK Pathways in the Hippocampi of SD Mice
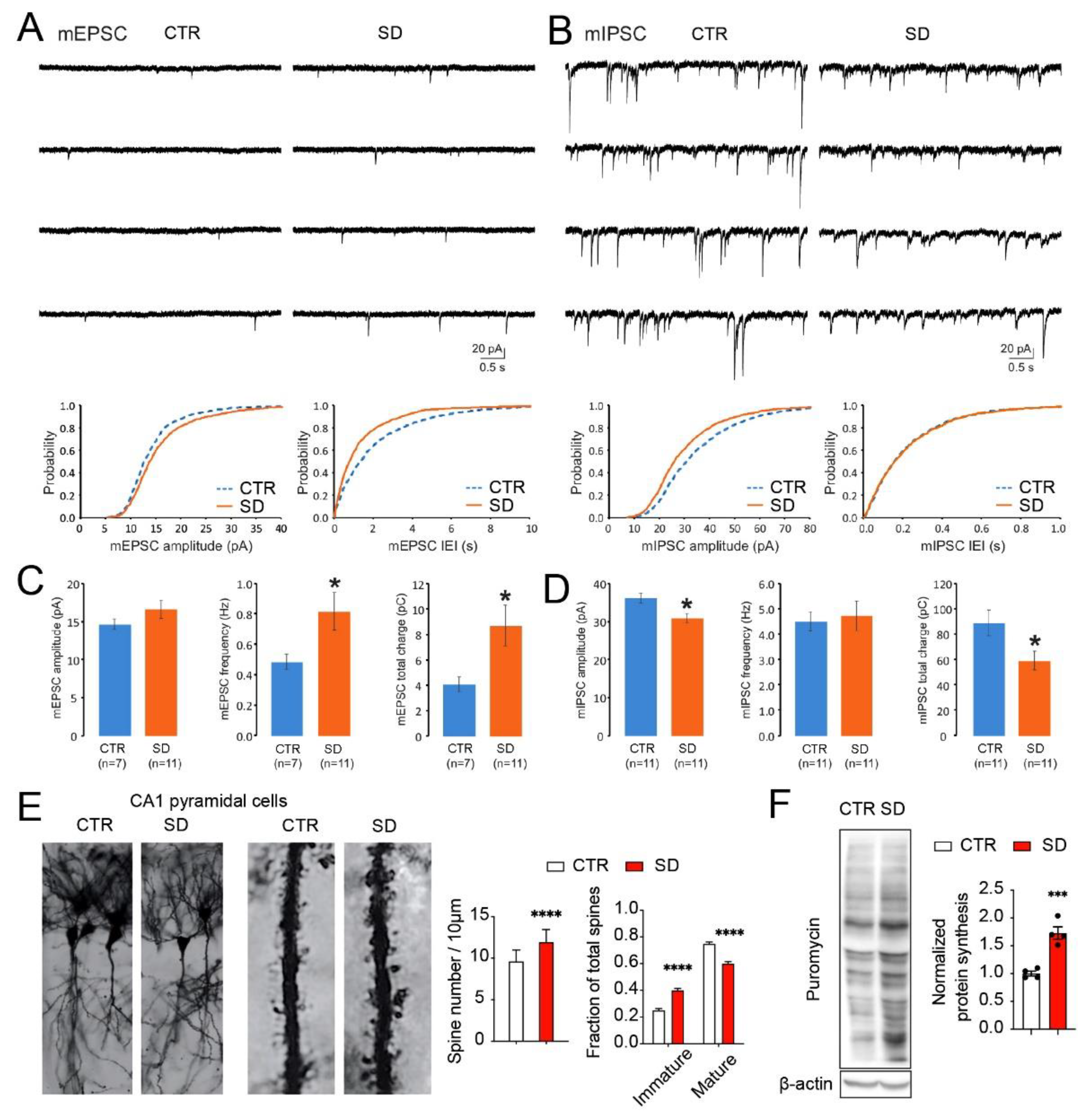
3.4. Aberrant Synaptic Transmission, Dendritic Spine Morphology, and Protein Synthesis in the Hippocampi of SD Mice
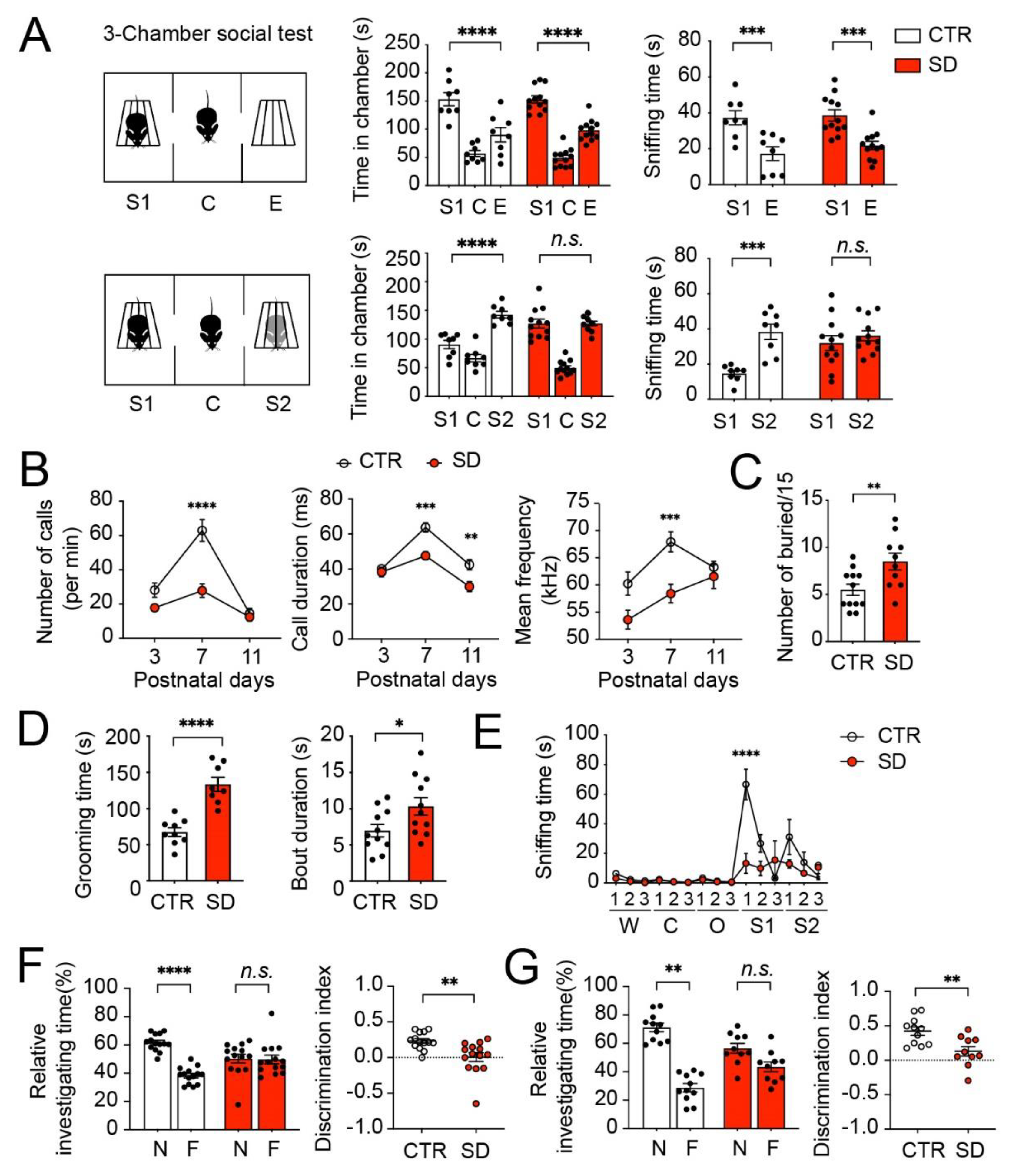
3.5. Autistic-like Behavioral Changes in SD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reppert, S.M.; Weaver, D.R. Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature 2002, 418, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, P.K.; McClung, C.A. Circadian Mechanisms Underlying Reward-Related Neurophysiology and Synaptic Plasticity. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, J.S.; Hong, H.K.; Ko, C.H.; McDearmon, E.L. The genetics of mammalian circadian order and disorder: Implications for physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, E.D.; Hermanstyne, T.; Smyllie, N.J.; Hastings, M.H. Regulating the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) Circadian Clockwork: Interplay between Cell-Autonomous and Circuit-Level Mechanisms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a027706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorsung, E.; Karthikeyan, R.; Cao, R. Biological Timing and Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Role for Circadian Dysfunction in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 642745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, B.; Rudrasingham, V.; Nash, S.; Kirov, G.; Owen, M.J.; Wimpory, D.C. Association of Per1 and Npas2 with autistic disorder: Support for the clock genes/social timing hypothesis. Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iossifov, I.; O’Roak, B.J.; Sanders, S.J.; Ronemus, M.; Krumm, N.; Levy, D.; Stessman, H.A.; Witherspoon, K.T.; Vives, L.; Patterson, K.E.; et al. The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature 2014, 515, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Matsumoto, A.; Nakayama, K.; Jimbo, E.F.; Kojima, K.; Nagata, K.; Iwamoto, S.; Yamagata, T. Circadian-relevant genes are highly polymorphic in autism spectrum disorder patients. Brain Dev. 2016, 38, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Mizuno, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Yang, Z.; Jimbo, E.F.; Tabata, H.; Yamagata, T.; Nagata, K.I. Role of a circadian-relevant gene NR1D1 in brain development: Possible involvement in the pathophysiology of autism spectrum disorders. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takata, A.; Miyake, N.; Tsurusaki, Y.; Fukai, R.; Miyatake, S.; Koshimizu, E.; Kushima, I.; Okada, T.; Morikawa, M.; Uno, Y.; et al. Integrative Analyses of De Novo Mutations Provide Deeper Biological Insights into Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souders, M.C.; Zavodny, S.; Eriksen, W.; Sinko, R.; Connell, J.; Kerns, C.; Schaaf, R.; Pinto-Martin, J. Sleep in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordjman, S.; Anderson, G.M.; Bellissant, E.; Botbol, M.; Charbuy, H.; Camus, F.; Graignic, R.; Kermarrec, S.; Fougerou, C.; Cohen, D.; et al. Day and nighttime excretion of 6-sulphatoxymelatonin in adolescents and young adults with autistic disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 1990–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.L.; Corbett, B.A. A review of rhythm and responsiveness of cortisol in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 49, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, R.; Gkogkas, C.G.; de Zavalia, N.; Blum, I.D.; Yanagiya, A.; Tsukumo, Y.; Xu, H.; Lee, C.; Storch, K.F.; Liu, A.C.; et al. Light-regulated translational control of circadian behavior by eIF4E phosphorylation. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Anderson, F.E.; Jung, Y.J.; Dziema, H.; Obrietan, K. Circadian regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in the mouse suprachiasmatic nucleus. Neuroscience 2011, 181, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolde, R.; Martens, K.; Lokk, K.; Laur, S.; Vilo, J. seqlm: An MDL based method for identifying differentially methylated regions in high density methylation array data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2604–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meijering, E.; Dzyubachyk, O.; Smal, I. Methods for cell and particle tracking. Methods Enzym. 2012, 504, 183–200. [Google Scholar]
- Voineagu, I.; Wang, X.; Johnston, P.; Lowe, J.K.; Tian, Y.; Horvath, S.; Mill, J.; Cantor, R.M.; Blencowe, B.J.; Geschwind, D.H. Transcriptomic analysis of autistic brain reveals convergent molecular pathology. Nature 2011, 474, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.; Shin, J.H.; Rajpurohit, A.; Deep-Soboslay, A.; Collado-Torres, L.; Brandon, N.J.; Hyde, T.M.; Kleinman, J.E.; Jaffe, A.E.; Cross, A.J.; et al. Altered expression of histamine signaling genes in autism spectrum disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irimia, M.; Weatheritt, R.J.; Ellis, J.D.; Parikshak, N.N.; Gonatopoulos-Pournatzis, T.; Babor, M.; Quesnel-Vallières, M.; Tapial, J.; Raj, B.; O’Hanlon, D.; et al. A highly conserved program of neuronal microexons is misregulated in autistic brains. Cell 2014, 159, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Han, D.; Somel, M.; Jiang, X.; Hu, H.; Guijarro, P.; Zhang, N.; Mitchell, A.; Halene, T.; Ely, J.J.; et al. Disruption of an evolutionarily novel synaptic expression pattern in autism. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Kaphzan, H.; Alvarez-Dieppa, A.C.; Murphy, J.P.; Pierre, P.; Klann, E. Genetic removal of p70 S6 kinase 1 corrects molecular, synaptic, and behavioral phenotypes in fragile X syndrome mice. Neuron 2012, 76, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gkogkas, C.G.; Khoutorsky, A.; Cao, R.; Jafarnejad, S.M.; Prager-Khoutorsky, M.; Giannakas, N.; Kaminari, A.; Fragkouli, A.; Nader, K.; Price, T.J.; et al. Pharmacogenetic inhibition of eIF4E-dependent Mmp9 mRNA translation reverses fragile X syndrome-like phenotypes. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1742–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, E.K.; Clavarino, G.; Ceppi, M.; Pierre, P. SUnSET, a nonradioactive method to monitor protein synthesis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawley, J.N. Mouse behavioral assays relevant to the symptoms of autism. Brain Pathol. 2007, 17, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, M.A.; Shair, H.N.; Brunelli, S.A. Ultrasonic vocalizations in rat and mouse pups. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2002, 17, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angoa-Perez, M.; Kane, M.J.; Briggs, D.I.; Francescutti, D.M.; Kuhn, D.M. Marble burying and nestlet shredding as tests of repetitive, compulsive-like behaviors in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 50978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, J.L.; Tolu, S.S.; Barkan, C.L.; Crawley, J.N. Repetitive self-grooming behavior in the BTBR mouse model of autism is blocked by the mGluR5 antagonist MPEP. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel-Ciernia, A.; Wood, M.A. Examining object location and object recognition memory in mice. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2014, 69, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.M.; Dragich, J.M.; Kudo, T.; Odom, I.H.; Welsh, D.K.; O’Dell, T.J.; Colwell, C.S. Expression of the circadian clock gene Period2 in the hippocampus: Possible implications for synaptic plasticity and learned behaviour. ASN Neuro. 2009, 1, AN20090020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wardlaw, S.M.; Phan, T.X.; Saraf, A.; Chen, X.; Storm, D.R. Genetic disruption of the core circadian clock impairs hippocampus-dependent memory. Learn Mem. 2014, 21, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jilg, A.; Lesny, S.; Peruzki, N.; Schwegler, H.; Selbach, O.; Dehghani, F.; Stehle, J.H. Temporal dynamics of mouse hippocampal clock gene expression support memory processing. Hippocampus 2010, 20, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R. mTOR Signaling, Translational Control, and the Circadian Clock. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Robinson, B.; Xu, H.; Gkogkas, C.; Khoutorsky, A.; Alain, T.; Yanagiya, A.; Nevarko, T.; Liu, A.C.; Amir, S.; et al. Translational control of entrainment and synchrony of the suprachiasmatic circadian clock by mTOR/4E-BP1 signaling. Neuron 2013, 79, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crino, P.B. mTOR: A pathogenic signaling pathway in developmental brain malformations. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, J.O.; Sahin, M. The neurology of mTOR. Neuron 2014, 84, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comery, T.A.; Harris, J.B.; Willems, P.J.; Oostra, B.A.; Irwin, S.A.; Weiler, I.J.; Greenough, W.T. Abnormal dendritic spines in fragile X knockout mice: Maturation and pruning deficits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5401–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKinney, B.C.; Grossman, A.W.; Elisseou, N.M.; Greenough, W.T. Dendritic spine abnormalities in the occipital cortex of C57BL/6 Fmr1 knockout mice. Am. J. Med. Genet. B. Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2005, 136B, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantois, I.; Khoutorsky, A.; Popic, J.; Aguilar-Valles, A.; Freemantle, E.; Cao, R.; Sharma, V.; Pooters, T.; Nagpal, A.; Skalecka, A.; et al. Metformin ameliorates core deficits in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, S.; Putignano, E.; Boggio, E.M.; Giustetto, M.; Pizzorusso, T.; Ratto, G.M. The short-time structural plasticity of dendritic spines is altered in a model of Rett syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, M.V.; Du, F.; Felice, C.A.; Shan, X.; Nigam, A.; Mandel, G.; Robinson, J.K.; Ballas, N. MeCP2 is critical for maintaining mature neuronal networks and global brain anatomy during late stages of postnatal brain development and in the mature adult brain. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 10021–10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavazoie, S.F.; Alvarez, V.A.; Ridenour, D.A.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Sabatini, B.L. Regulation of neuronal morphology and function by the tumor suppressors Tsc1 and Tsc2. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haws, M.E.; Jaramillo, T.C.; Espinosa, F.; Widman, A.J.; Stuber, G.D.; Sparta, D.R.; Tye, K.M.; Russo, S.J.; Parada, L.F.; Stavarache, M.; et al. PTEN knockdown alters dendritic spine/protrusion morphology, not density. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 1171–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, M.C.; Chen, H.; Swann, J.W. Loss of mTOR repressors Tsc1 or Pten has divergent effects on excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission in single hippocampal neuron cultures. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, K.; Liu, D.; Pathak, S.S.; Yang, B.; Li, J.; Karthikeyan, R.; Chao, O.Y.; Yang, Y.-M.; Jin, V.X.; Cao, R. Disruption of Circadian Rhythms by Ambient Light during Neurodevelopment Leads to Autistic-like Molecular and Behavioral Alterations in Adult Mice. Cells 2021, 10, 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123314
Fang K, Liu D, Pathak SS, Yang B, Li J, Karthikeyan R, Chao OY, Yang Y-M, Jin VX, Cao R. Disruption of Circadian Rhythms by Ambient Light during Neurodevelopment Leads to Autistic-like Molecular and Behavioral Alterations in Adult Mice. Cells. 2021; 10(12):3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123314
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Kun, Dong Liu, Salil S. Pathak, Bowen Yang, Jin Li, Ramanujam Karthikeyan, Owen Y. Chao, Yi-Mei Yang, Victor X. Jin, and Ruifeng Cao. 2021. "Disruption of Circadian Rhythms by Ambient Light during Neurodevelopment Leads to Autistic-like Molecular and Behavioral Alterations in Adult Mice" Cells 10, no. 12: 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123314
APA StyleFang, K., Liu, D., Pathak, S. S., Yang, B., Li, J., Karthikeyan, R., Chao, O. Y., Yang, Y.-M., Jin, V. X., & Cao, R. (2021). Disruption of Circadian Rhythms by Ambient Light during Neurodevelopment Leads to Autistic-like Molecular and Behavioral Alterations in Adult Mice. Cells, 10(12), 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123314






