Porphyromonas gingivalis Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression Leading to Apoptotic Death through the Oxidative Stress/NF-κB Pathway in Brain Endothelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Primary Cell Isolation and Culture
2.4. Bacterial Culture and Preparation
2.5. Bacterial Infection and Antioxidant Treatment
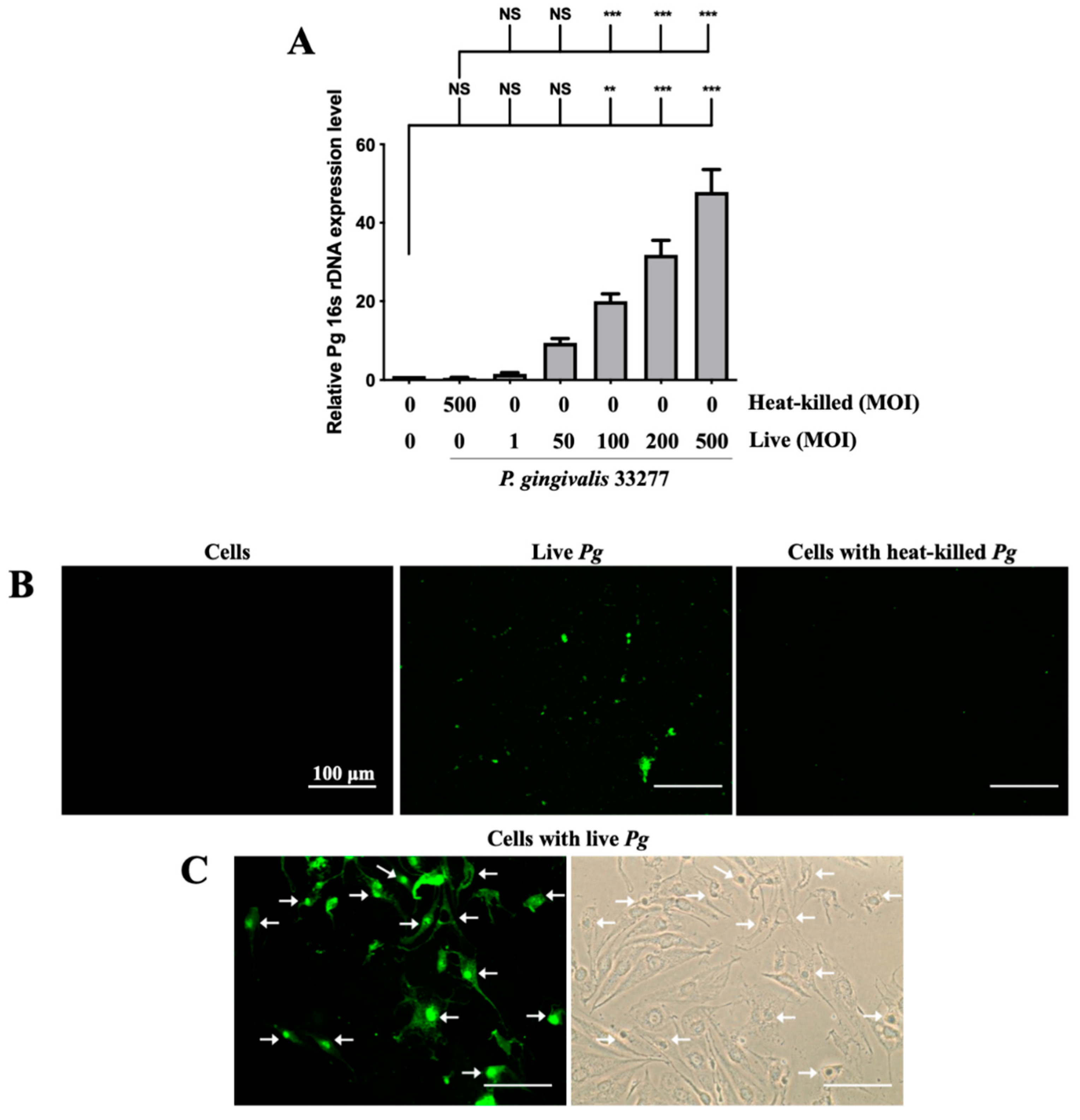
2.6. Adherence of P. gingivalis to Host Cells
2.7. Adherence of FITC-Labeled P. gingivalis to Host Cells
2.8. MTT Assay
2.9. Trypan Blue Exclusion Assay
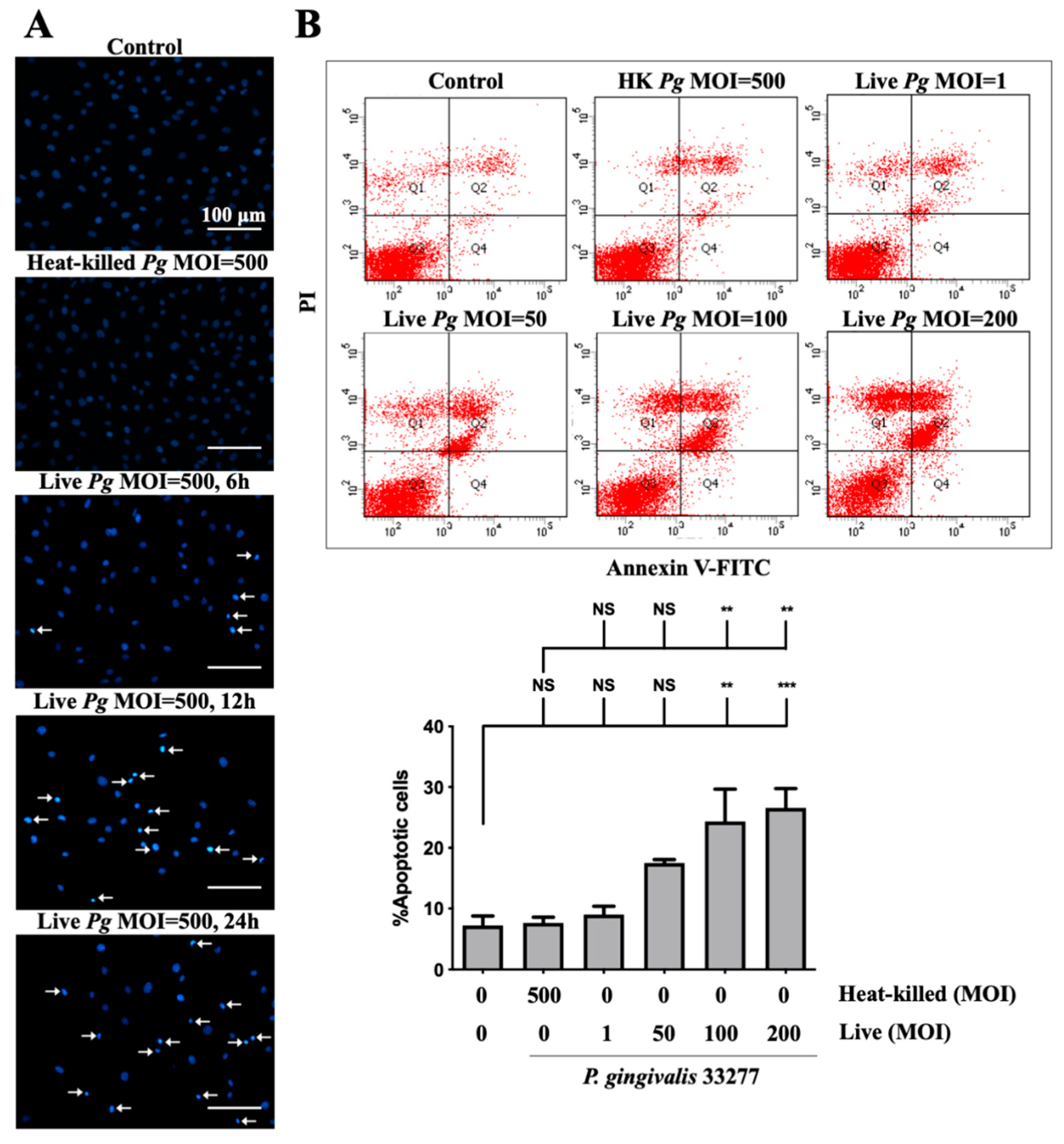
2.10. Nuclear Staining
2.11. FITC Annexin V and PI Staining
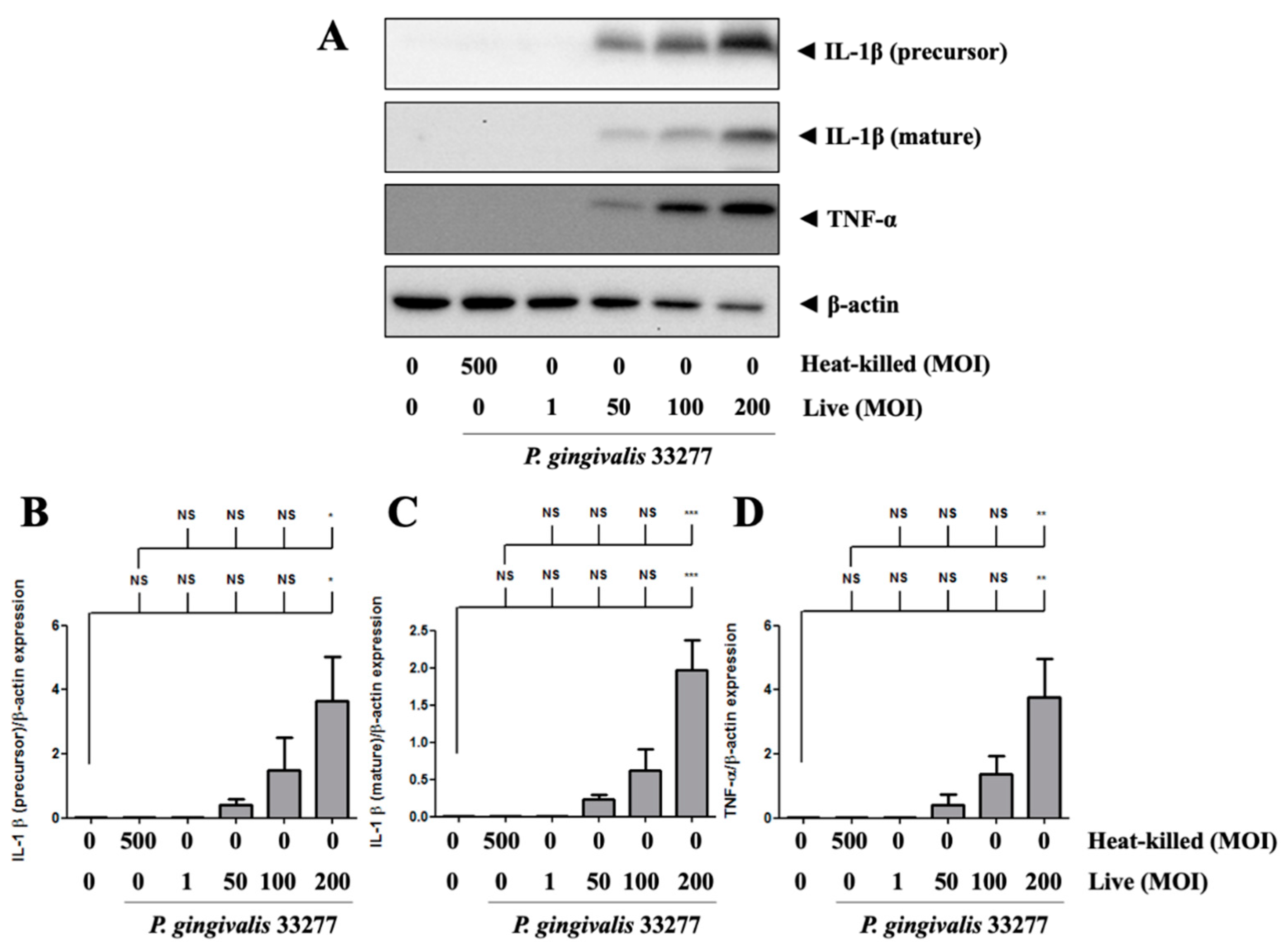
2.12. Western Blot Analysis
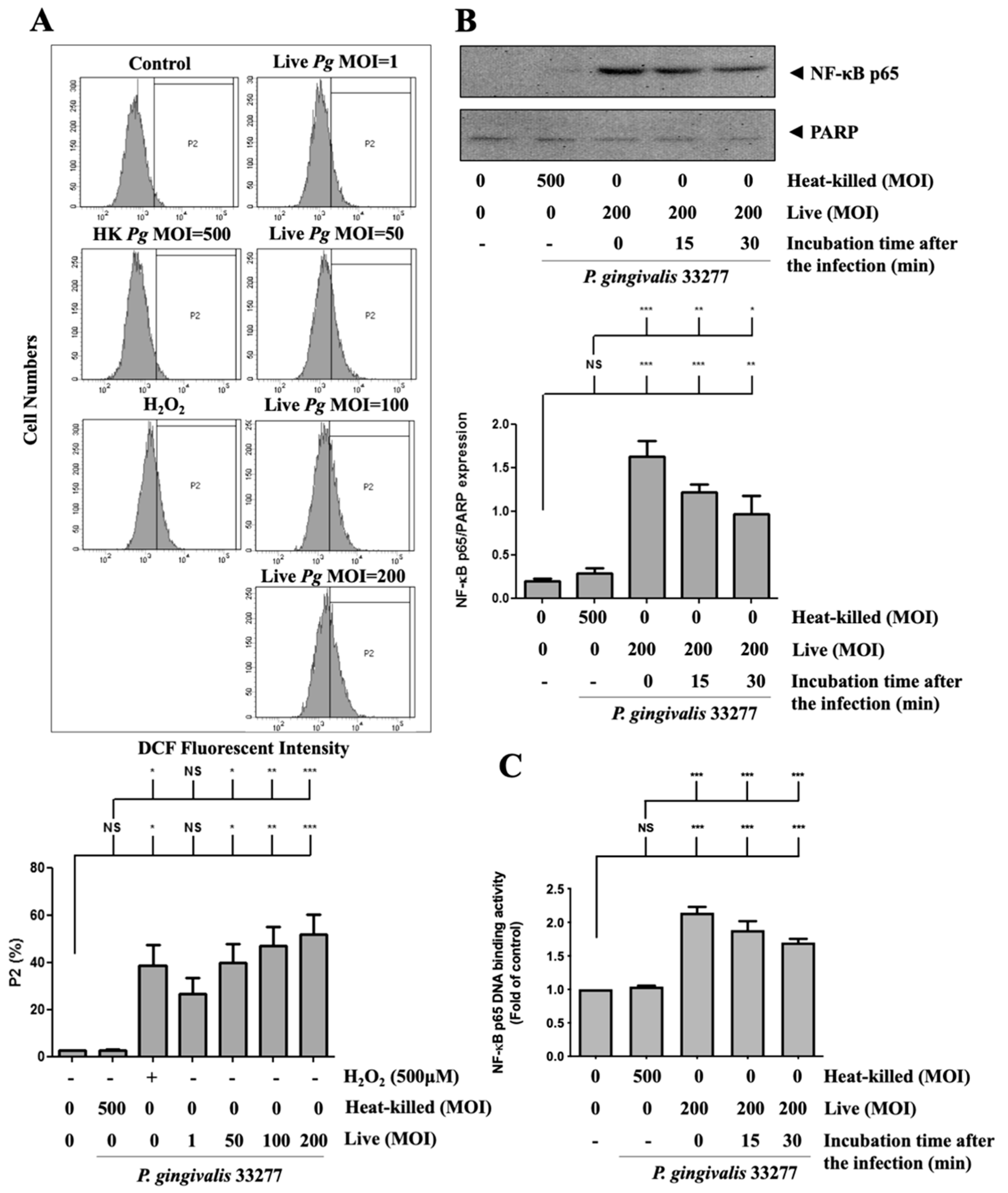
2.13. NF-κB p65 Transcription Factor DNA Binding Activity Assay
2.14. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species Production
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Adherence of P. gingivalis to bEnd.3 Cells Initiated the Infection Process
3.2. P. gingivalis Caused the Alteration of Cell Morphology and Cell Viability in Brain Endothelial Cells
3.3. Infection of P. gingivalis Induces Cell Apoptosis in Brain Endothelial Cells
3.4. Increased Proinflammatory Cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β Expression in P. gingivalis Activated Brain Endothelial Cells
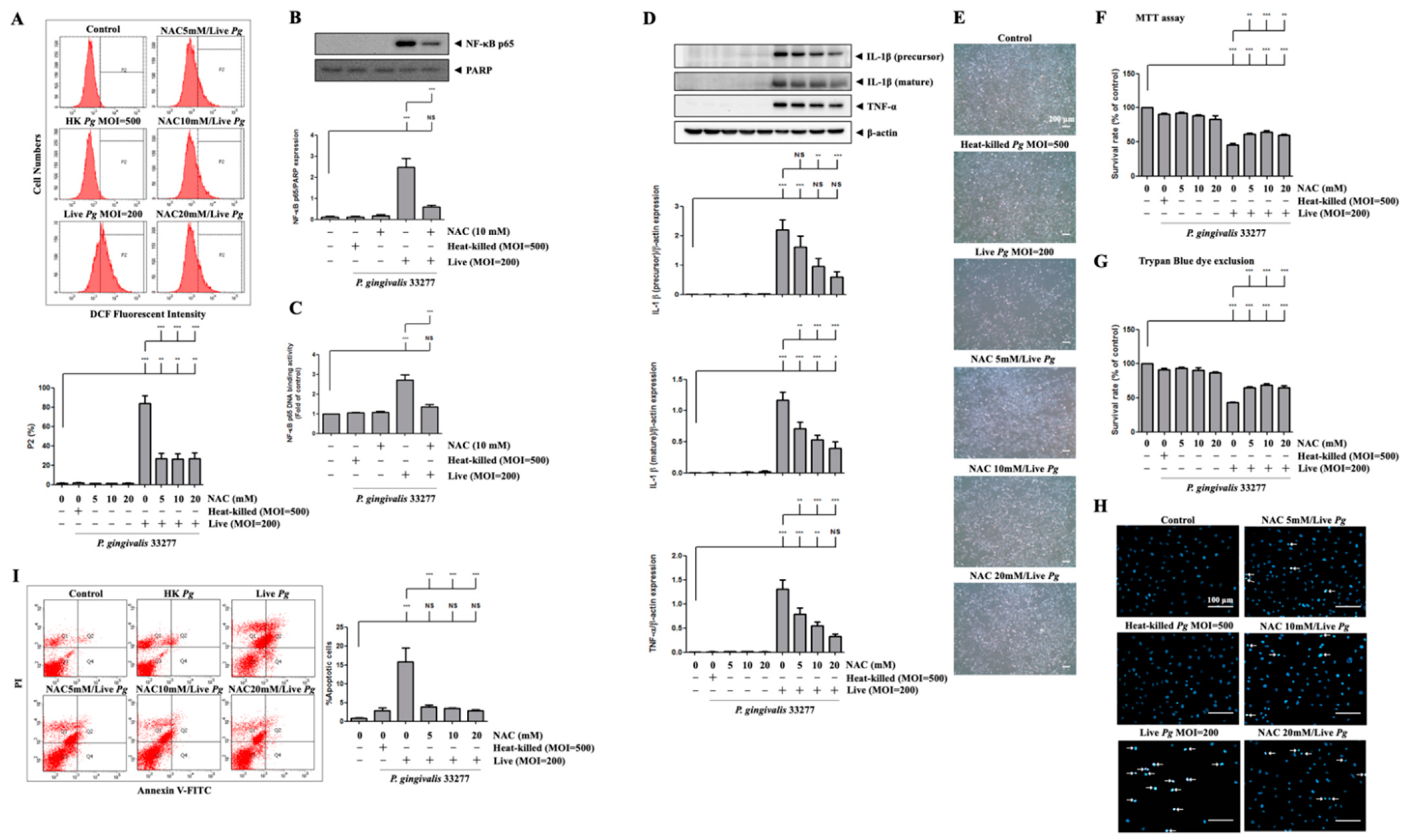
3.5. P. gingivalis Elevated ROS Production and Up-Regulated NF-κB p65 Activation
3.6. P. gingivalis-Induced ROS Production Regulates Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression and Cell Death
3.7. Infection with P. gingivalis in Primary Mouse Brain Endothelial Cells (MBECs) Elevates ROS/NF-κB Activation and Results in Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression and Cell Death
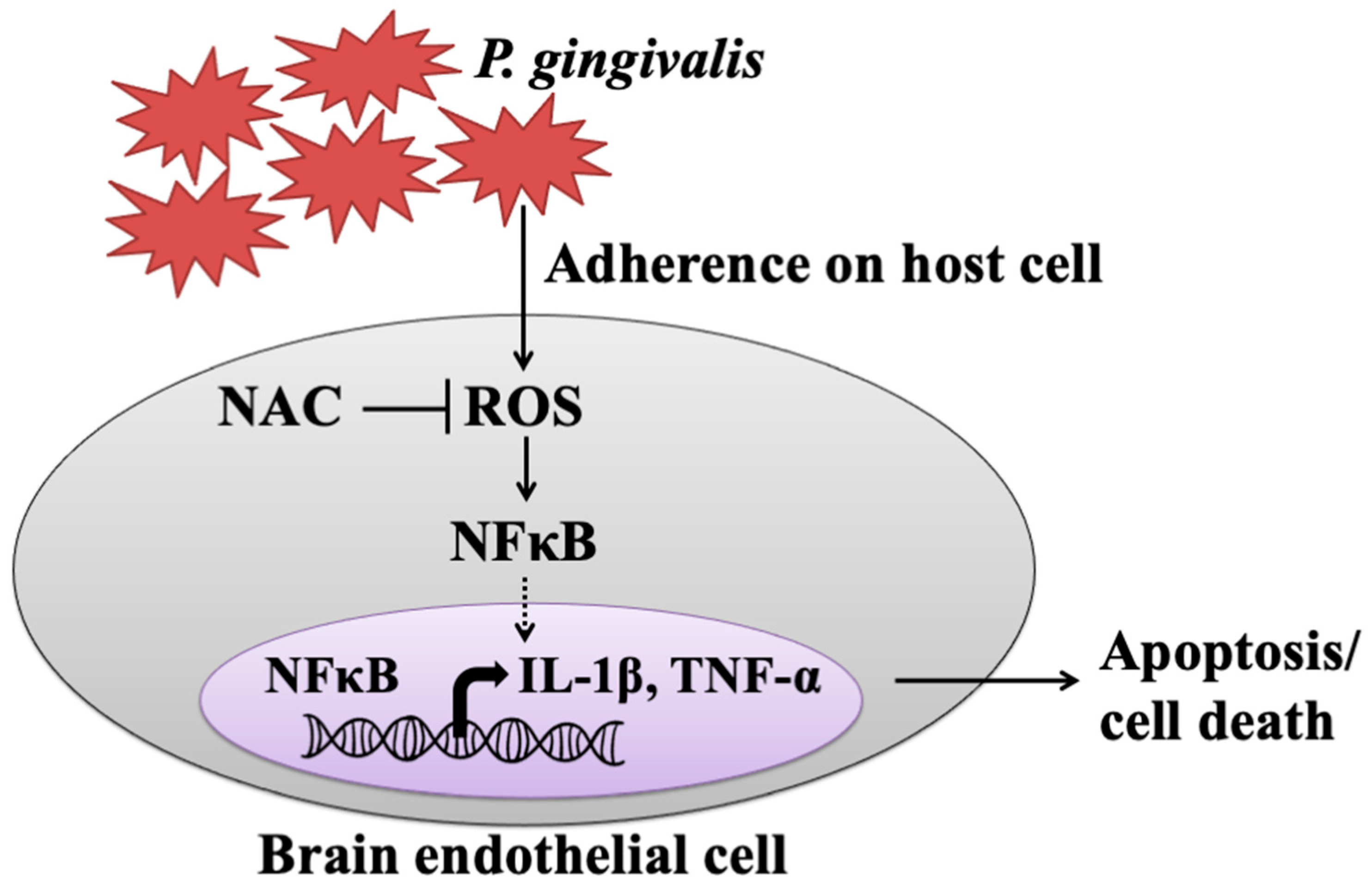
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petersen, P.E.; Ogawa, H. The global burden of periodontal disease: Towards integration with chronic disease prevention and control. Periodontology 2000 2012, 60, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinane, D.F.; Stathopoulou, P.G.; Papapanou, P.N. Periodontal diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlstrom, B.L.; Michalowicz, B.S.; Johnson, N.W. Periodontal diseases. Lancet 2005, 366, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forner, L.; Larsen, T.; Kilian, M.; Holmstrup, P. Incidence of bacteremia after chewing, tooth brushing and scaling in individuals with periodontal inflammation. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2006, 33, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, M.; Harris, M.; Stevens, A.; Sussams, R.; Hopkins, V.; Culliford, D.; Fuller, J.; Ibbett, P.; Raybould, R.; Thomas, R.; et al. Periodontitis and cognitive decline in alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumpio, B.E.; Riley, J.T.; Dardik, A. Cells in focus: Endothelial cell. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 1508–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozarov, E.V.; Dorn, B.R.; Shelburne, C.E.; Dunn, W.A.; Progulske-Fox, A. Human atherosclerotic plaque contains viable invasive actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and porphyromonas gingivalis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, e17–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aarabi, G.; Thomalla, G.; Heydecke, G.; Seedorf, U. Chronic oral infection: An emerging risk factor of cerebral small vessel disease. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G. Periodontitis: From microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballini, A.; Tetè, S.; Scattarella, A.; Cantore, S.; Mastrangelo, F.; Papa, F.; Nardi, G.M.; Perillo, L.; Crincoli, V.; Gherlone, E.; et al. The role of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in periodontal disease. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2010, 23, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullon, P.; Cordero, M.D.; Quiles, J.L.; Morillo, J.M.; Ramirez-Tortosa, M.d.C.; Battino, M. Mitochondrial dysfunction promoted by porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide as a possible link between cardiovascular disease and periodontitis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyajima, S.-i.; Naruse, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Nishikawa, T.; Adachi, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Mitani, A.; Mizutani, M.; et al. Periodontitis-activated monocytes/macrophages cause aortic inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, G.A.; Ankersmit, H.J.; Brown, V.B.; Papapanou, P.N.; Schmidt, A.M.; Lalla, E. Porphyromonas gingivalis infection and cell death in human aortic endothelial cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 272, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, H.; Zelkha, S.; Burkatovskaya, M.; Gupte, R.; Leeman, S.E.; Amar, S. Pivotal role of nod2 in inflammatory processes affecting atherosclerosis and periodontal bone loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E5059–E5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, M.; Stover, C.M.; Dupont, A.P. Gingivalis in periodontal disease and atherosclerosis–scenes of action for antimicrobial peptides and complement. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kebschull, M.; Demmer, R.T.; Papapanou, P.N. “Gum bug, leave my heart alone!”--epidemiologic and mechanistic evidence linking periodontal infections and atherosclerosis. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 879–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Aiuto, F.; Nibali, L.; Parkar, M.; Suvan, J.; Tonetti, M.S. Short-term effects of intensive periodontal therapy on serum inflammatory markers and cholesterol. J. Dent. Res. 2005, 84, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonetti, M.S.; D’Aiuto, F.; Nibali, L.; Donald, A.; Storry, C.; Parkar, M.; Suvan, J.; Hingorani, A.D.; Vallance, P.; Deanfield, J. Treatment of periodontitis and endothelial function. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominy, S.S.; Lynch, C.; Ermini, F.; Benedyk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Konradi, A.; Nguyen, M.; Haditsch, U.; Raha, D.; Griffin, C.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis in alzheimer’s disease brains: Evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singhrao, S.K.; Olsen, I. Assessing the role of porphyromonas gingivalis in periodontitis to determine a causative relationship with alzheimer’s disease. J. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 11, 1563405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palm, F.; Lahdentausta, L.; Sorsa, T.; Tervahartiala, T.; Gokel, P.; Buggle, F.; Safer, A.; Becher, H.; Grau, A.J.; Pussinen, P. Biomarkers of periodontitis and inflammation in ischemic stroke: A case-control study. Innate. Immun. 2014, 20, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pussinen, P.J.; Alfthan, G.; Jousilahti, P.; Paju, S.; Tuomilehto, J. Systemic exposure to porphyromonas gingivalis predicts incident stroke. Atherosclerosis 2007, 193, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pussinen, P.J.; Alfthan, G.; Rissanen, H.; Reunanen, A.; Asikainen, S.; Knekt, P. Antibodies to periodontal pathogens and stroke risk. Stroke 2004, 35, 2020–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghizoni, J.S.; Taveira, L.A.; Garlet, G.P.; Ghizoni, M.F.; Pereira, J.R.; Dionísio, T.J.; Brozoski, D.T.; Santos, C.F.; Sant’Ana, A.C. Increased levels of porphyromonas gingivalis are associated with ischemic and hemorrhagic cerebrovascular disease in humans: An in vivo study. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2012, 20, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashioka, S.; Inoue, K.; Hayashida, M.; Wake, R.; Oh-Nishi, A.; Miyaoka, T. Implications of systemic inflammation and periodontitis for major depression. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, H.; Nonaka, S.; Wu, Z. Microglial cathepsin b and porphyromonas gingivalis gingipains as potential therapeutic targets for sporadic alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2020, 19, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haditsch, U.; Roth, T.; Rodriguez, L.; Hancock, S.; Cecere, T.; Nguyen, M.; Arastu-Kapur, S.; Broce, S.; Raha, D.; Lynch, C.C.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease-like neurodegeneration in porphyromonas gingivalis infected neurons with persistent expression of active gingipains. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2020, 75, 1361–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bhat, M.A. Neuron-glial interactions in blood-brain barrier formation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.Y.; Yu, W.H.; Yeh, W.L.; Tang, C.H.; Leung, Y.M.; Wong, K.L.; Chen, Y.F.; Lai, C.H.; Fu, W.M. Hypoxia-induced matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in astrocytes enhances permeability of brain endothelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2009, 220, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.L.; Lu, D.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Liou, H.C.; Fu, W.M. Inhibition of hypoxia-induced increase of blood-brain barrier permeability by yc-1 through the antagonism of hif-1alpha accumulation and vegf expression. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, E.; Dixit, V.M. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species drive proinflammatory cytokine production. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaprakash, K.; Demirel, I.; Khalaf, H.; Bengtsson, T. Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced inflammatory responses in thp1 cells are altered by native and modified low-density lipoproteins in a strain-dependent manner. Apmis 2018, 126, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, D.; Dai, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Periodontal ligament fibroblasts migration injury via ros/txnip/nlrp3 inflammasome pathway with porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 103, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, G.; Colín-González, A.L.; Rangel-López, E.; Chavarría, A.; Santamaría, A. Redox signaling, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 1626–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.H.; Shen, S.C.; Yang, L.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Chen, Y.C. Gossypol reduction of tumor growth through ros-dependent mitochondria pathway in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Yang, L.-Y.; Shen, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-C. Igf-i plus e2 induces proliferation via activation of ros-dependent erks and jnks in human breast carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 212, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.S.; Chien, C.C.; Cheng, K.T.; Subbaraju, G.V.; Chen, Y.C. Hispolon suppresses lps- or lta-induced inos/no production and apoptosis in bv-2 microglial cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 1649–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, G.; Brunetti, G.; Colucci, S.; Ciccolella, F.; Coricciati, M.; Pignataro, P.; Oranger, A.; Ballini, A.; Farronato, D.; Mastrangelo, F.; et al. Alteration of activity and survival of osteoblasts obtained from human periodontitis patients: Role of trail. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2007, 21, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, G.; Brunetti, G.; Colucci, S.; Oranger, A.; Ciccolella, F.; Sardone, F.; Pignataro, P.; Mori, C.; Karapanou, V.; Ballini, A.; et al. Osteoblast apoptosis in periodontal disease: Role of tnf-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yegla, B.; Foster, T.C. Redox signaling in neurotransmission and cognition during aging. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 1724–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, A.V.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, R.T. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, J.Y.; Chang, P.C.; Shen, Y.C.; Lin, C.; Tsai, C.F.; Chen, J.H.; Yeh, W.L.; Wu, L.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; et al. Regulatory effects of fisetin on microglial activation. Molecules 2014, 19, 8820–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Lin, H.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Tseng, W.P.; Ko, P.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Yeh, W.L.; Lu, D.Y. Effects of paeonol on anti-neuroinflammatory responses in microglial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 8844–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bavarsad Shahripour, R.; Harrigan, M.R.; Alexandrov, A.V. N-acetylcysteine (nac) in neurological disorders: Mechanisms of action and therapeutic opportunities. Brain Behav. 2014, 4, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Sekhon, B.; Jatana, M.; Giri, S.; Gilg, A.G.; Sekhon, C.; Singh, I.; Singh, A.K. Administration of n-acetylcysteine after focal cerebral ischemia protects brain and reduces inflammation in a rat model of experimental stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 76, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Taheri, S.; Liu, K.J.; Shi, H. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 contributes to n-acetylcysteine’s protection in stroke. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 68, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.Y.; Chen, H.C.; Yang, M.S.; Hsu, Y.M.; Lin, H.J.; Tang, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lai, C.K.; Lin, C.J.; Shyu, W.C.; et al. Ceramide and toll-like receptor 4 are mobilized into membrane rafts in response to helicobacter pylori infection in gastric epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lécuyer, M.A.; Saint-Laurent, O.; Bourbonnière, L.; Larouche, S.; Larochelle, C.; Michel, L.; Charabati, M.; Abadier, M.; Zandee, S.; Haghayegh Jahromi, N.; et al. Dual role of alcam in neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E524–E533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puscas, I.; Bernard-Patrzynski, F.; Jutras, M.; Lécuyer, M.A.; Bourbonnière, L.; Prat, A.; Leclair, G.; Roullin, V.G. Ivivc assessment of two mouse brain endothelial cell models for drug screening. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapira, L.; Ayalon, S.; Brenner, T. Effects of porphyromonas gingivalis on the central nervous system: Activation of glial cells and exacerbation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Periodontol. 2002, 73, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative pcr and the 2(-delta delta c(t)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, R.D.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Visvanathan, K.; Hamilton, J.A.; Reynolds, E.C. Flow cytometric analysis of adherence of porphyromonas gingivalis to oral epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2484–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Tonder, A.; Joubert, A.M.; Cromarty, A.D. Limitations of the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2h-tetrazolium bromide (mtt) assay when compared to three commonly used cell enumeration assays. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ju, T.C.; Chen, S.D.; Liu, C.C.; Yang, D.I. Protective effects of s-nitrosoglutathione against amyloid beta-peptide neurotoxicity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Y.; Shen, S.C.; Cheng, K.T.; Subbaraju, G.V.; Chien, C.C.; Chen, Y.C. Hispolon inhibition of inflammatory apoptosis through reduction of inos/no production via ho-1 induction in macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro-Cerdá, J.; Cossart, P. Bacterial adhesion and entry into host cells. Cell 2006, 124, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- How, K.Y.; Song, K.P.; Chan, K.G. Porphyromonas gingivalis: An overview of periodontopathic pathogen below the gum line. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulou, P.G.; Galicia, J.C.; Benakanakere, M.R.; Garcia, C.A.; Potempa, J.; Kinane, D.F. Porphyromonas gingivalis induce apoptosis in human gingival epithelial cells through a gingipain-dependent mechanism. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.R.; Tsai, C.F.; Lin, H.Y.; Tseng, W.P.; Huang, S.S.; Wu, C.R.; Lin, C.; Yeh, W.L.; Lu, D.Y. Interaction of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses in microglia by staphylococcus aureus-derived lipoteichoic acid. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 269, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Wei, I.H.; Chen, J.H.; Lai, C.H.; Lu, D.Y. Peptidoglycan enhances proinflammatory cytokine expression through the tlr2 receptor, myd88, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt and nf-kappab pathways in bv-2 microglia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Chang, C.H.; Maa, M.C.; Fang, S.H.; Hsu, Y.M.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, C.J.; Lee, W.C.; Lin, H.J.; et al. Helicobacter pylori attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production by murine macrophages. Innate. Immun. 2012, 18, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.F.; Yeh, W.L.; Huang, S.M.; Tan, T.W.; Lu, D.Y. Wogonin induces reactive oxygen species production and cell apoptosis in human glioma cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 9877–9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau, A.J.; Becher, H.; Ziegler, C.M.; Lichy, C.; Buggle, F.; Kaiser, C.; Lutz, R.; Bültmann, S.; Preusch, M.; Dörfer, C.E. Periodontal disease as a risk factor for ischemic stroke. Stroke 2004, 35, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Ren, J.; Yu, H.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis, a periodontitis causing bacterium, induces memory impairment and age-dependent neuroinflammation in mice. Immun. Ageing I A 2018, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Casiano, C.A.; Fletcher, H.M. Protease-active extracellular protein preparations from porphyromonas gingivalis w83 induce n-cadherin proteolysis, loss of cell adhesion, and apoptosis in human epithelial cells. J. Periodontol. 2001, 72, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Park, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tribble, G.D.; James, C.E.; Handfield, M.; Stavropoulos, M.F.; Yilmaz, O.; Lamont, R.J. Intrinsic apoptotic pathways of gingival epithelial cells modulated by porphyromonas gingivalis. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desta, T.; Graves, D.T. Fibroblast apoptosis induced by porphyromonas gingivalis is stimulated by a gingipain and caspase-independent pathway that involves apoptosis-inducing factor. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2667–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheets, S.M.; Potempa, J.; Travis, J.; Casiano, C.A.; Fletcher, H.M. Gingipains from porphyromonas gingivalis w83 induce cell adhesion molecule cleavage and apoptosis in endothelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheets, S.M.; Potempa, J.; Travis, J.; Fletcher, H.M.; Casiano, C.A. Gingipains from porphyromonas gingivalis w83 synergistically disrupt endothelial cell adhesion and can induce caspase-independent apoptosis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5667–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maitre, Y.; Micheneau, P.; Delpierre, A.; Mahalli, R.; Guerin, M.; Amador, G.; Denis, F. Did the brain and oral microbiota talk to each other? A review of the literature. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, R.J.; Jenkinson, H.F. Subgingival colonization by porphyromonas gingivalis. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 15, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisvert, H.; Duncan, M.J. Clathrin-dependent entry of a gingipain adhesin peptide and porphyromonas gingivalis into host cells. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2538–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, I.; Amano, A.; Kuboniwa, M.; Nakamura, T.; Kawabata, S.; Hamada, S. Functional differences among fima variants of porphyromonas gingivalis and their effects on adhesion to and invasion of human epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, Y.; Davey, M.; Yumoto, H.; Gibson, F.C., III; Genco, C.A. Fimbria-dependent activation of pro-inflammatory molecules in porphyromonas gingivalis infected human aortic endothelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 738–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, F.; Xie, M.; Huang, X.; Long, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Porphyromonas gingivalis and its systemic impact: Current status. Pathogens 2020, 9, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, A.; Sharma, A.; Sojar, H.T.; Kuramitsu, H.K.; Genco, R.J. Effects of temperature stress on expression of fimbriae and superoxide dismutase by porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 4682–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pöllänen, M.T.; Paino, A.; Ihalin, R. Environmental stimuli shape biofilm formation and the virulence of periodontal pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17221–17237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, K.P.; Simon, R.P.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.; Karin, M. Regulation and function of nf-kappab transcription factors in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 693–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Chen, K.M.; Chiu, P.S.; Lai, S.C.; Su, H.H.; Jan, M.S.; Lin, C.W.; Lu, D.Y.; Fu, Y.T.; Liao, J.M.; et al. Lumbrokinase attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting tlr4 signaling. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 99, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Upadhyay, U.M.; Tamargo, R.J. Inflammation in stroke and focal cerebral ischemia. Surg. Neurol. 2006, 66, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, X.N.; Yenari, M.A. The inflammatory response in stroke. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 184, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quagliarello, V.J.; Wispelwey, B.; Long, W.J., Jr.; Scheld, W.M. Recombinant human interleukin-1 induces meningitis and blood-brain barrier injury in the rat. Characterization and comparison with tumor necrosis factor. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grebe, A.; Hoss, F.; Latz, E. Nlrp3 inflammasome and the il-1 pathway in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1722–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, O. Switching of vascular cells towards atherogenesis, and other factors contributing to atherosclerosis: A systematic review. Thromb. J. 2020, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kralingen, C.; Kho, D.T.; Costa, J.; Angel, C.E.; Graham, E.S. Exposure to inflammatory cytokines il-1β and tnfα induces compromise and death of astrocytes; implications for chronic neuroinflammation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Na, H.S.; Song, Y.R.; Shin, S.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Chung, J. Activation of nlrp3 and aim2 inflammasomes by porphyromonas gingivalis infection. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Desta, T.; Fenton, M.; Graves, D.T.; Amar, S. Cytokine profiling of macrophages exposed to porphyromonas gingivalis, its lipopolysaccharide, or its fima protein. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Duan, X.; Jotwani, R.; Vuddaraju, H.; Liang, S.; Scott, D.A.; Lamont, R.J. Porphyromonas gingivalis induced reactive oxygen species activate jak2 and regulate production of inflammatory cytokines through c-jun. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 4118–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parajuli, B.; Sonobe, Y.; Horiuchi, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Mizuno, T.; Suzumura, A. Oligomeric amyloid β induces il-1β processing via production of ros: Implication in alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z.G. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and nf-κb signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, X.; Qin, Z.; Hua, F. Adiponectin protects obesity-related glomerulopathy by inhibiting ros/nf-κb/nlrp3 inflammation pathway. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.F.; Mei, Q.B.; Zhou, X.G.; Tang, Y.; Xiong, R.; Qiu, W.Q.; Pan, R.; Law, B.Y.; Wong, V.K.; Yu, C.L.; et al. Polyphyllin vi induces caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis via the induction of ros/nf-κb/nlrp3/gsdmd signal axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.Y.; Chang, C.S.; Yeh, W.L.; Tang, C.H.; Cheung, C.W.; Leung, Y.M.; Liu, J.F.; Wong, K.L. The novel phloroglucinol derivative bfp induces apoptosis of glioma cancer through reactive oxygen species and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2012, 19, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, A.; Rochfort, K.D.; McDonnell, C.J.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Cummins, P.M. Staphylococcus aureus-mediated blood-brain barrier injury: An in vitro human brain microvascular endothelial cell model. Cell Microbiol. 2017, 19, e12664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rydkina, E.; Turpin, L.C.; Sahni, A.; Sahni, S.K. Regulation of inducible heme oxygenase and cyclooxygenase isozymes in a mouse model of spotted fever group rickettsiosis. Microb. Pathog. 2012, 53, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paterson, R.L.; Galley, H.F.; Webster, N.R. The effect of n-acetylcysteine on nuclear factor-kappa b activation, interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in patients with sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 2574–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.A.; Yoon, J.C.; Kim, M.; Park, E.M. Activation of classical estrogen receptor subtypes reduces tight junction disruption of brain endothelial cells under ischemia/reperfusion injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 92, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcambal, A.; Taïlé, J.; Rondeau, P.; Viranaïcken, W.; Meilhac, O.; Gonthier, M.P. Hyperglycemia modulates redox, inflammatory and vasoactive markers through specific signaling pathways in cerebral endothelial cells: Insights on insulin protective action. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camós, S.; Mallolas, J. Experimental models for assaying microvascular endothelial cell pathophysiology in stroke. Molecules 2010, 15, 9104–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernard-Patrzynski, F.; Lécuyer, M.A.; Puscas, I.; Boukhatem, I.; Charabati, M.; Bourbonnière, L.; Ramassamy, C.; Leclair, G.; Prat, A.; Roullin, V.G. Isolation of endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes from mouse brain. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charoensaensuk, V.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-H.; Ou, K.-L.; Yang, L.-Y.; Lu, D.-Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression Leading to Apoptotic Death through the Oxidative Stress/NF-κB Pathway in Brain Endothelial Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113033
Charoensaensuk V, Chen Y-C, Lin Y-H, Ou K-L, Yang L-Y, Lu D-Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression Leading to Apoptotic Death through the Oxidative Stress/NF-κB Pathway in Brain Endothelial Cells. Cells. 2021; 10(11):3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113033
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharoensaensuk, Vichuda, Yen-Chou Chen, Yun-Ho Lin, Keng-Liang Ou, Liang-Yo Yang, and Dah-Yuu Lu. 2021. "Porphyromonas gingivalis Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression Leading to Apoptotic Death through the Oxidative Stress/NF-κB Pathway in Brain Endothelial Cells" Cells 10, no. 11: 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113033
APA StyleCharoensaensuk, V., Chen, Y.-C., Lin, Y.-H., Ou, K.-L., Yang, L.-Y., & Lu, D.-Y. (2021). Porphyromonas gingivalis Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression Leading to Apoptotic Death through the Oxidative Stress/NF-κB Pathway in Brain Endothelial Cells. Cells, 10(11), 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113033





