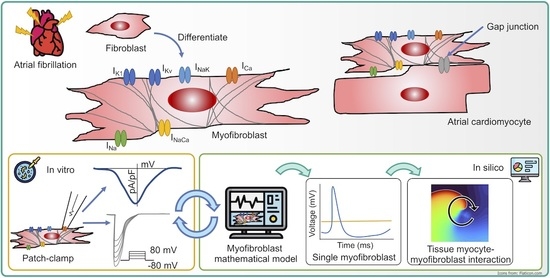
Fibrotic Remodeling during Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: In Silico Investigation of the Role of Calcium for Human Atrial Myofibroblast Electrophysiology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Myocyte Electrophysiology and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Remodeling
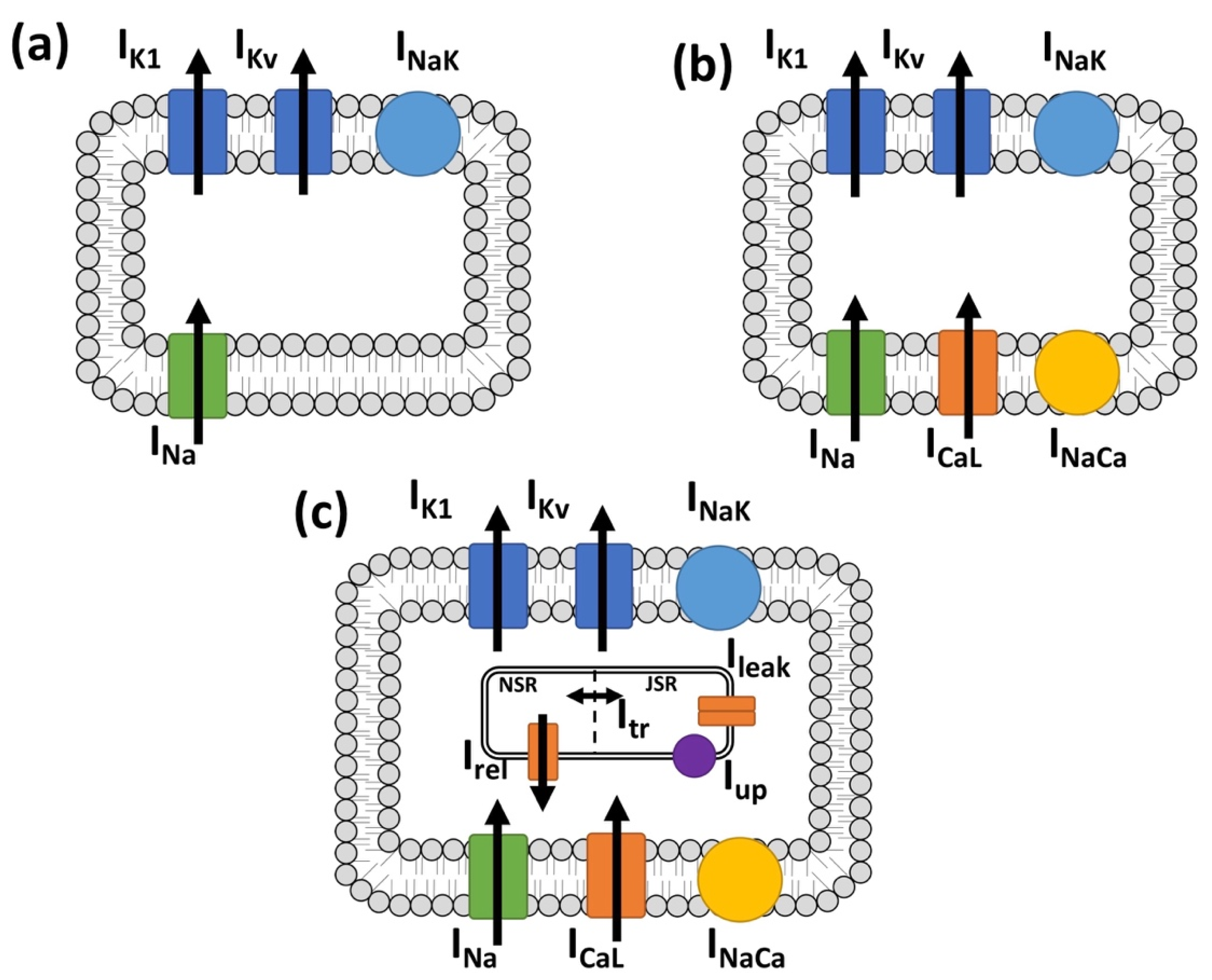
2.2. Myofibroblast Electrophysiology
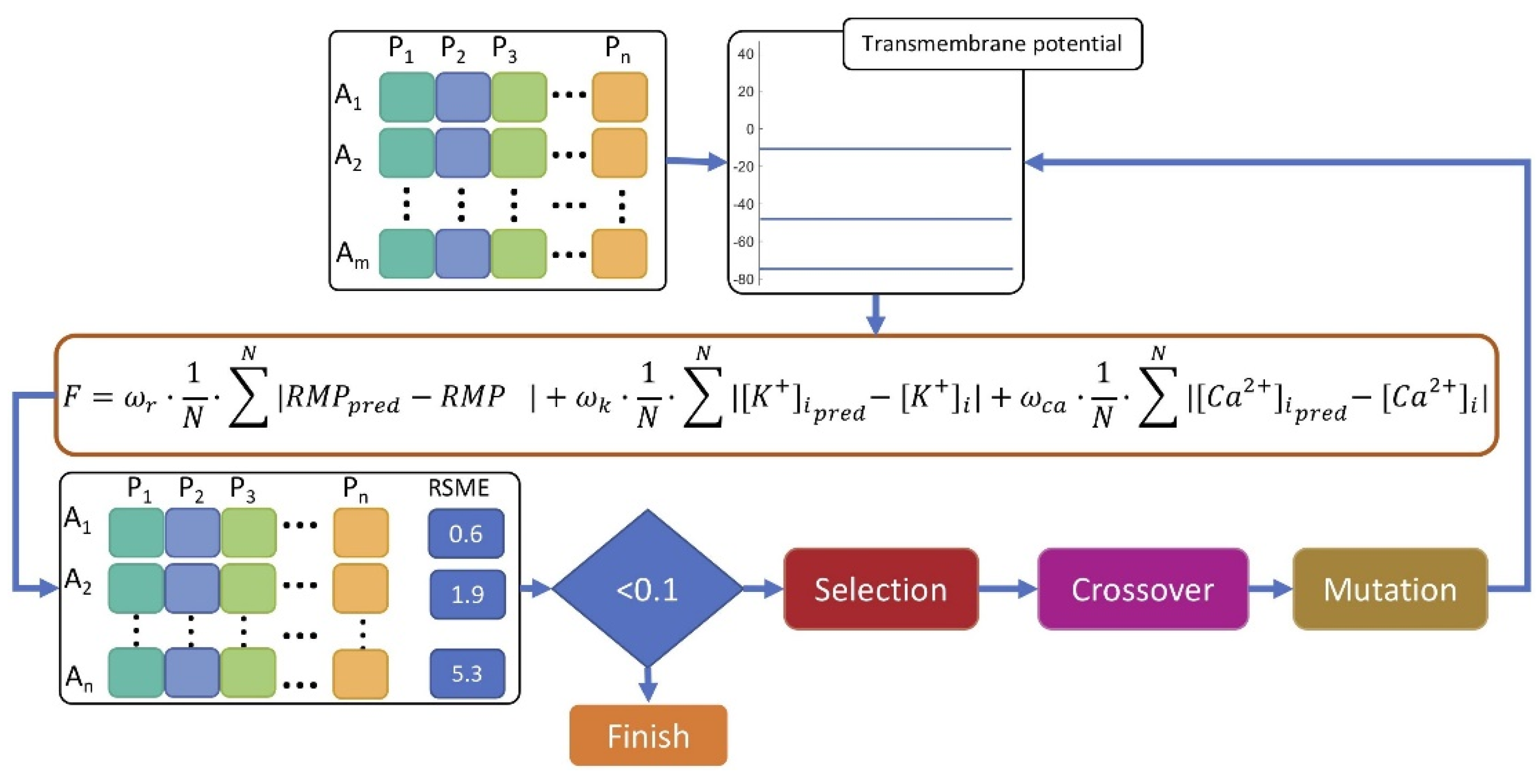
2.3. In Silico Experimental Protocol
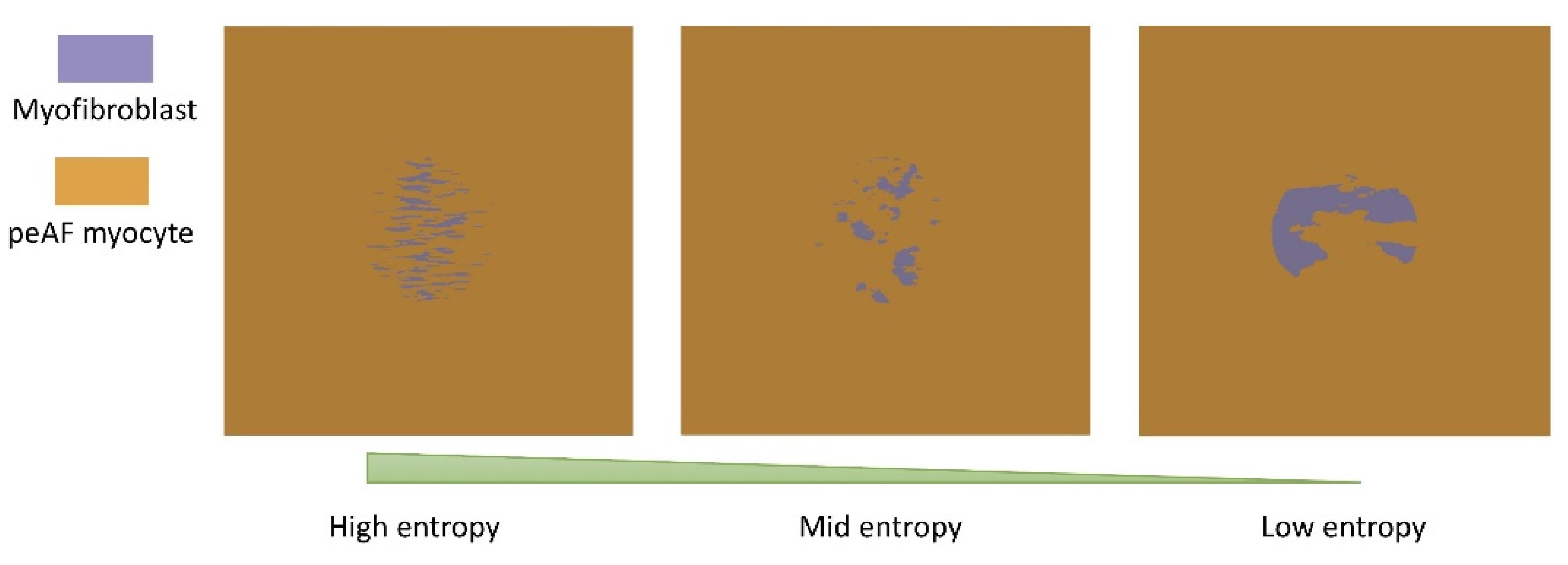
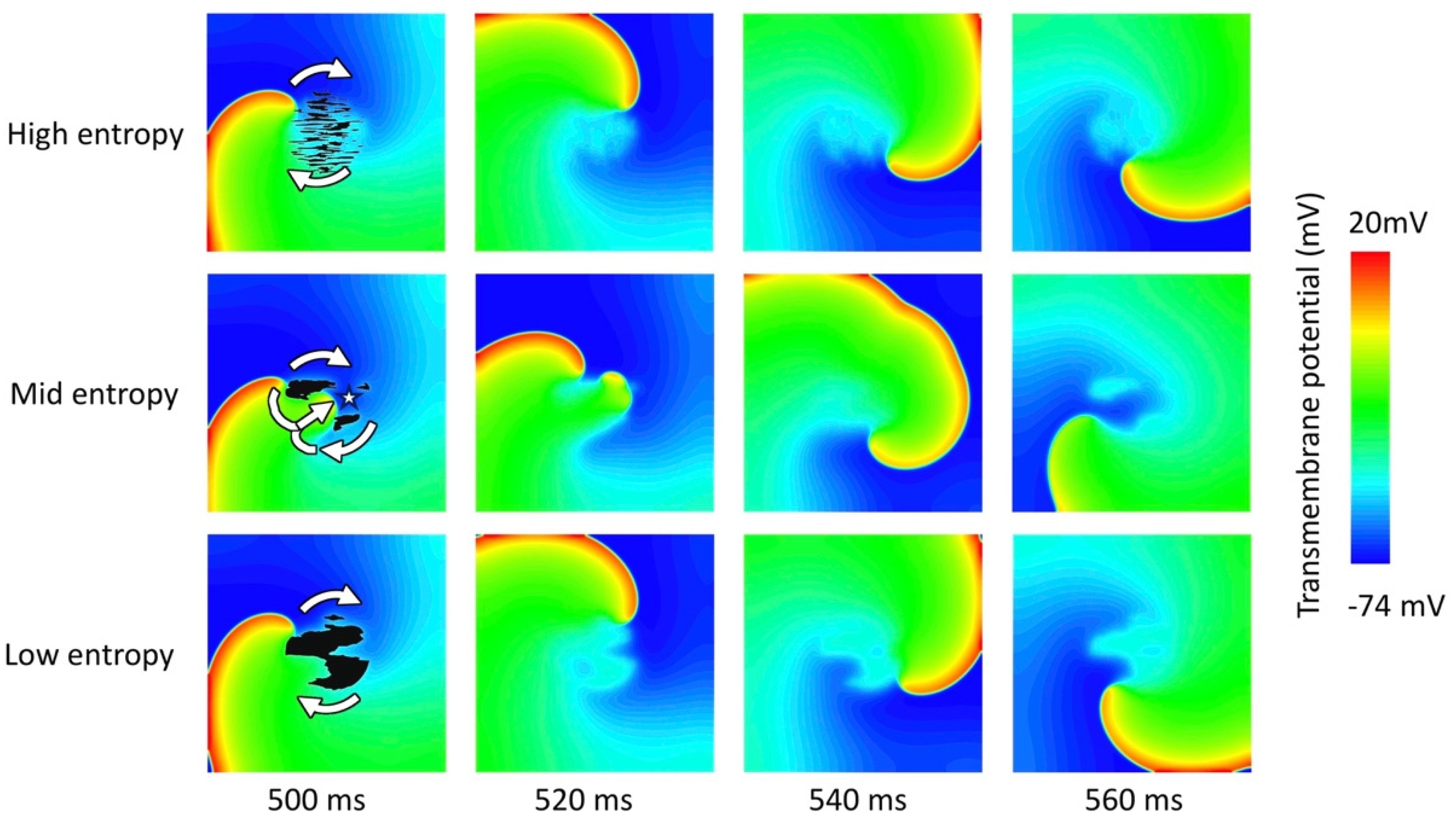
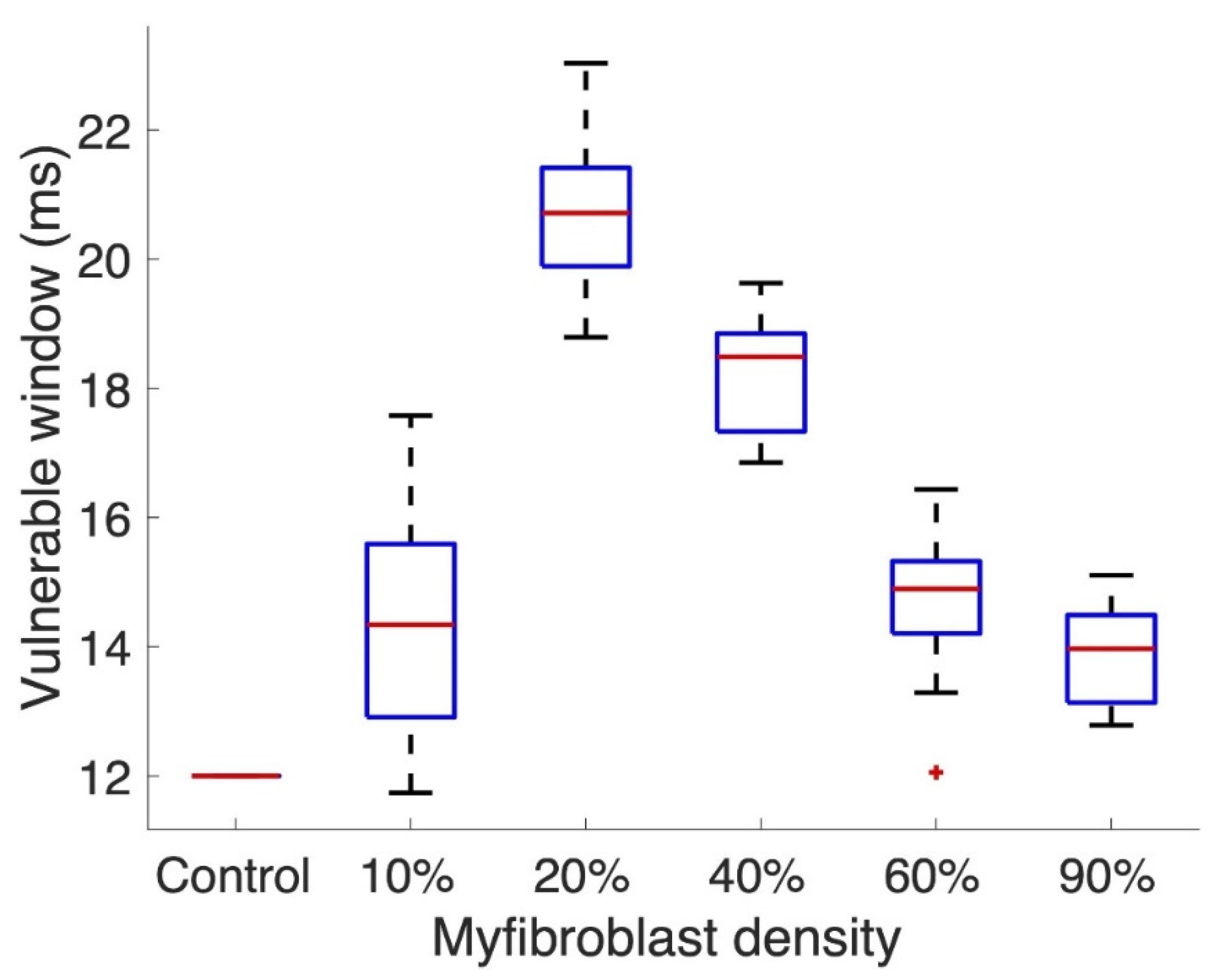
3. Results
3.1. Myofibroblast Electrophysiology
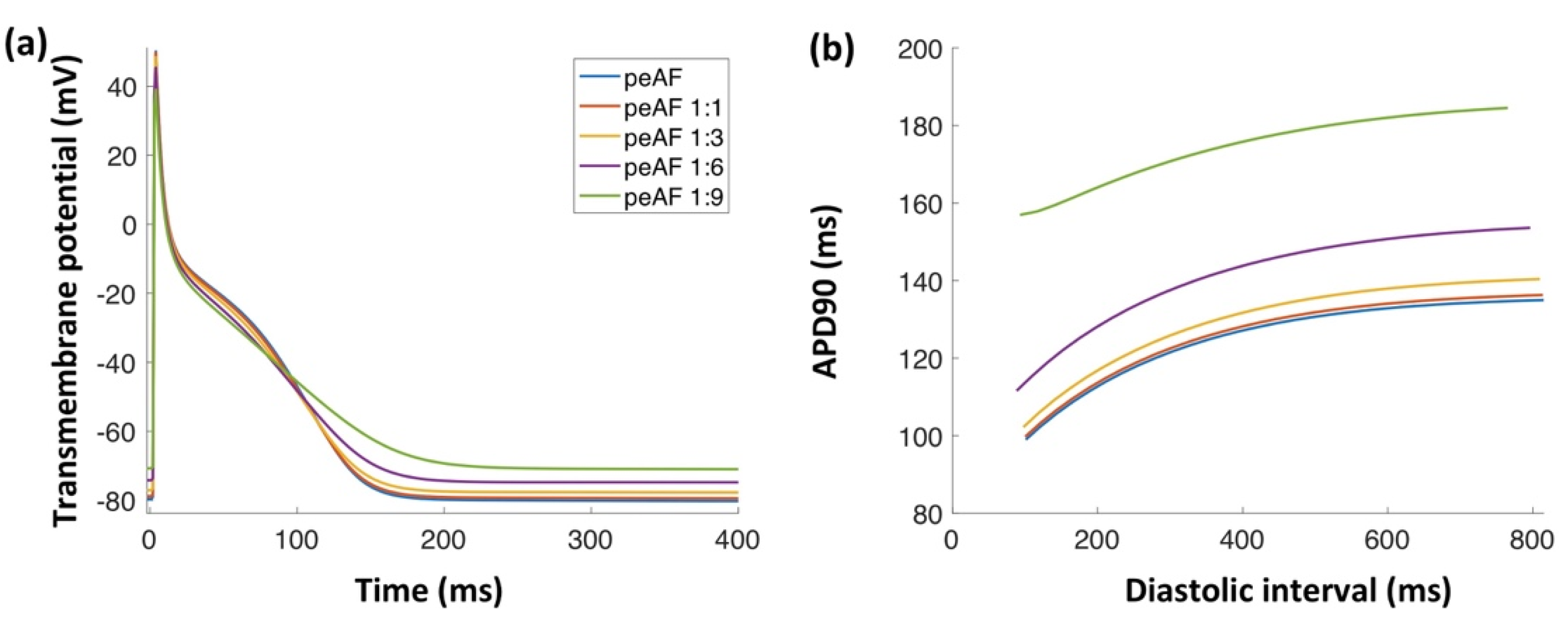
3.2. Tissue Simulations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Camelliti, P.; Borg, T.K.; Kohl, P. Structural and functional characterisation of cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camelliti, P.; Devlin, G.P.; Matthews, K.G.; Kohl, P.; Green, C.R. Spatially and temporally distinct expression of fibroblast connexins after sheep ventricular infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, M.A.; Trafford, A.W. Aging and the cardiac collagen matrix: Novel mediators of fibrotic remodelling. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 93, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plikus, M.V.; Wang, X.; Sinha, S.; Forte, E.; Thompson, S.M.; Herzog, E.L.; Driskell, R.R.; Rosenthal, N.; Biernaskie, J.; Horsley, V. Fibroblasts: Origins, definitions, and functions in health and disease. Cell 2021, 184, 3852–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, D.E.; Boucek, R.J. Quantitation of Collagen in Human Myocardium. Circ. Res. 1957, 5, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platonov, P.G. Atrial fibrosis: An obligatory component of arrhythmia mechanisms in atrial fibrillation? J. Geriatr. Cardiol. JGC 2017, 14, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohns, C.; Marrouche, N.F. Atrial fibrillation and cardiac fibrosis. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelier, A.; Mercier, A.; Tremblier, B.; Thériault, O.; Moubarak, M.; Benamer, N.; Corbi, P.; Bois, P.; Chahine, M.; Faivre, J.F. A distinct de novo expression of Na v 1.5 sodium channels in human atrial fibroblasts differentiated into myofibroblasts. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 4307–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulet, C.; Künzel, S.; Büttner, E.; Lindner, D.; Westermann, D.; Ravens, U. Altered physiological functions and ion currents in atrial fibroblasts from patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivumäki, J.; Clark, R.B.; Belke, D.; Kondo, C.; Fedak, P.; Maleckar, M.M.; Giles, W.R. Na+ current expression in human atrial myofibroblasts: Identity and functional roles. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Kim, T.; Lim, I. Effects of nitric oxide on apoptosis and voltage-gated calcium channels in human cardiac myofibroblasts. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvarani, N.; Maguy, A.; De Simone, S.A.; Miragoli, M.; Jousset, F.; Rohr, S. TGF-β1(Transforming Growth Factor-β1) Plays a Pivotal Role in Cardiac Myofibroblast Arrhythmogenicity. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e004567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Armillei, M.K.; Yu, A.S.; Liang, B.T.; Runnels, L.W.; Yue, L. Ca2+ Signaling in Cardiac Fibroblasts and Fibrosis-Associated Heart Diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2019, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, L.M.; Takawale, A.; Hulsurkar, M.; Menassa, D.A.; Antanaviciute, A.; Lahiri, S.K.; Mehta, N.; Evans, N.; Psarros, C.; Robinson, P.; et al. Paracrine signalling by cardiac calcitonin controls atrial fibrogenesis and arrhythmia. Nature 2020, 587, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raizman, J.E.; Komljenovic, J.; Chang, R.; Deng, C.; Bedosky, K.M.; Rattan, S.G.; Cunnington, R.H.; Freed, D.H.; Dixon, I.M. The participation of the Na+–Ca2+ exchanger in primary cardiac myofibroblast migration, contraction, and proliferation. J.Cell. Physiol. 2007, 213, 5345–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.C.; Lin, Y.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, Y.H.; Yeh, Y.H.; Chen, Y.J. Calcium Regulation on the Atrial Regional Difference of Collagen Production Activity in Atrial Fibrogenesis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.R.; Sun, H.Y.; Chen, J.B.; Zhou, Y.; Tse, H.F.; Lau, C.P. Characterization of Multiple Ion Channels in Cultured Human Cardiac Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.; Qi, X.Y.; Huang, H.; Nattel, S. Fibroblast electrical remodeling in heart failure and potential effects on atrial fibrillation. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 2444–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Benamer, N.; Fares, N.; Bois, P.; Faivre, J.F. Electrophysiological and functional effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate in mouse ventricular fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 408, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamer, N.; Vasquez, C.; Mahoney, V.M.; Steinhardt, M.J.; Coetzee, W.A.; Morley, G.E. Fibroblast K ATP currents modulate myocyte electrophysiology in infarcted hearts. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 304, H1231–H1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, D.; Klesen, A.; Darkow, E.; Kari, F.A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Kohl, P.; Ravens, U.; Peyronnet, R. Heterogeneity and Remodeling of Ion Currents in Cultured Right Atrial Fibroblasts From Patients With Sinus Rhythm or Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 673891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohis, M.; Edwards, S.; Ryan, S.; Rizvi, F.; Tajik, A.J.; Jahangir, A.; Ross, G.R. Aging-related increase in store-operated Ca2+ influx in human ventricular fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H83–H91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, I.M.; Belevych, A.E.; Baine, S.; Stepanov, A.; Mezache, L.; Bodnar, T.; Liu, B.; Volpe, P.; Priori, S.; Weisleder, N.; et al. Enhancement of Cardiac Store Operated Calcium Entry (SOCE) within Novel Intercalated Disk Microdomains in Arrhythmic Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Luo, X.; Qi, X.Y.; Tadevosyan, A.; Maguy, A.; Ordog, B.; Ledoux, J.; Kato, T.; Naud, P.; Voigt, N.; et al. Transient Re- ceptor Potential Canonical-3 Channel–Dependent Fibroblast Regulation in Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2012, 126, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapala, R.K.; Thoppil, R.J.; Luther, D.J.; Paruchuri, S.; Meszaros, J.G.; Chilian, W.M.; Thodeti, C.K. TRPV4 channels mediate cardiac fibroblast differentiation by integrating mechanical and soluble signals. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 54, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tsujikawa, H.; Fusco, D.; Silverman, D.; Liang, B.; Yue, L. TRPM7-Mediated Ca2+ Signals Confer Fibrogenesis in Human Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, A.R. Intracellular calcium-release channels: Regulators of cell life and death. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 1997, 272, H597–H605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grune, J.; Yamazoe, M.; Nahrendorf, M. Electroimmunology and cardiac arrhythmia. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, M.; Kurniawan, N.A. Mechanical and Physical Regulation of Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transition: From Cellular Mechanoresponse to Tissue Pathology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 609653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.H.; Chang, Y.; Reed, N.I.; Sheppard, D. α-Smooth muscle actin is an inconsistent marker of fibroblasts responsible for force-dependent TGFβ activation or collagen production across multiple models of organ fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 310, L824–L836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraju, C.K.; Dries, E.; Gilbert, G.; Abdesselem, M.; Wang, N.; Amoni, M.; Driesen, R.B.; Sipido, K.R. Myofibroblast modulation of cardiac myocyte structure and function. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, A.V.; Humeres, C.; Frangogiannis, N.G. The role of α-smooth muscle actin in fibroblast-mediated matrix contraction and remodeling. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.P.; Perreault, C.L.; Morgan, K.G. The cellular basis of contraction and relaxation in cardiac and vascular smooth muscle. Am. Heart J. 1991, 121, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudesius, G.; Miragoli, M.; Thomas, S.P.; Rohr, S. Coupling of cardiac electrical activity over extended distances by fibroblasts of cardiac origin. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, P.; Gourdie, R.G. Fibroblast-myocyte electrotonic coupling: Does it occur in native cardiac tissue? J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 70, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, T.A.; Camelliti, P.; Rog-Zielinska, E.A.; Siedlecka, U.; Poggioli, T.; O’Toole, E.T.; Knöpfel, T.; Kohl, P. Electrotonic coupling of excitable and nonexcitable cells in the heart revealed by optogenetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14852–14857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, P.M.; Yu, J.; Klimas, A.; Williams, J.C.; Trayanova, N.A.; Entcheva, E. OptoGap is an optogenetics-enabled assay for quantification of cell–cell coupling in multicellular cardiac tissue. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.; Colman, M.A.; Chubb, H.; Seemann, G.; Aslanidi, O.V. Slow conduction in the border zones of patchy fibrosis stabilizes the drivers for atrial fibrillation: Insights from multi-scale human atrial modeling. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Garfinkel, A.; Camelliti, P.; Kohl, P.; Weiss, J.N.; Qu, Z. Effects of fibroblast-myocyte coupling on cardiac conduction and vulnerability to reentry: A computational study. Heart Rhythm. 2009, 6, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, J.; Gomez, J.F.; Martinez-Mateu, L.; Romero, L.; Saiz, J.; Trenor, B. Heterogeneous Effects of Fibroblast-Myocyte Coupling in Different Regions of the Human Atria Under Conditions of Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijman, J.; Sutanto, H.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Nattel, S.; Trayanova, N.A. Computational models of atrial fibrillation: Achievements, challenges, and perspectives for improving clinical care. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1682–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurkiewicz, M.; Korngreen, A. A Numerical Approach to Ion Channel Modelling Using Whole-Cell Voltage-Clamp Recordings and a Genetic Algorithm. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerx, M.; Beattie, K.A.; Gavaghan, D.J.; Mirams, G.R. Four Ways to Fit an Ion Channel Model. Biophys. J. 2019, 117, 2420–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewe, A.; Wilhelms, M.; Schmid, J.; Krause, M.J.; Fischer, F.; Thomas, D.; Scholz, E.P.; Dössel, O.; Seemann, G. Parameter estimation of ion current formulations requires hybrid optimization approach to be both accurate and reliable. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 3, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezlobinsky, T.; Solovyova, O.; Panfilov, A.V. Anisotropic conduction in the myocardium due to fibrosis: The effect of texture on wave propagation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutanto, H.; Cluitmans, M.J.; Dobrev, D.; Volders, P.G.; Bébarová, M.; Heijman, J. Acute effects of alcohol on cardiac electrophysi- ology and arrhythmogenesis: Insights from multiscale in silico analyses. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 146, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skibsbye, L.; Jespersen, T.; Christ, T.; Maleckar, M.M.; van den Brink, J.; Tavi, P.; Koivumäki, J.T. Refractoriness in human atria: Time and voltage dependence of sodium channel availability. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 101, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtemanche, M.; Ramirez, R.J.; Nattel, S. Ionic mechanisms underlying human atrial action potential properties: In-sights from a mathematical model. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 1998, 275, H301–H321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miragoli, M.; Gaudesius, G.; Rohr, S. Electrotonic modulation of cardiac impulse conduction by myofibroblasts. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, G.; Loewe, A.; Neic, A.; Augustin, C.; Huang, Y.L.; Gsell, M.A.; Karabelas, E.; Nothstein, M.; Prassl, A.J.; Sánchez, J.; et al. The openCARP simulation environment for cardiac electrophysiology. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.; Nothstein, M.; Unger, L.; Saiz, J.; Trénor, B.; Dössel, O.; Loewe, A. Influence of Fibrotic Tissue Arrangement on Intracardiac Electrograms During Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. In Proceedings of the 2019 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Singapore, 8–11 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCannell, K.A.; Bazzazi, H.; Chilton, L.; Shibukawa, Y.; Clark, R.B.; Giles, W.R. A mathematical model of electrotonic interactions between ventricular myocytes and fibroblasts. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 4121–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakes, D.; Burrage, K.; Drovandi, C.C.; Burrage, P.; Bueno-Orovio, A.; dos Santos, R.W.; Rodriguez, B.; Lawson, B.A. Perlin noise generation of physiologically realistic patterns of fibrosis. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlin, K. An image synthesizer. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 1985, 19, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.J.; Zhao, J.; Fedorov, V.V. Fibrosis and Atrial Fibrillation: Computerized and Optical Mapping: A View into the Human Atria at Submillimeter Resolution. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoum, N.; Morris, A.; Perry, D.; Cates, J.; Burgon, N.; Kholmovski, E.; Macleod, R.; Marrouche, N. Substrate modification is a better predictor of catheter ablation success in atrial fibrillation than pulmonary vein isolation: An LGE-MRI study. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 2015, 9, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, S.; Whyte, K.N.; Schwarz, E.L.; Blake, R.C.; Boyle, P.M.; Chrispin, J.; Prakosa, A.; Ipek, E.G.; Pashakhanloo, F.; Halperin, H.R.; et al. Feasibility of using patient-specific models and the “minimum cut” algorithm to predict optimal ablation targets for left atrial flutter. Heart Rhythm. 2016, 13, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konings, K.T.; Kirchhof, C.J.; Smeets, J.R.; Wellens, H.J.; Penn, O.C.; Allessie, M.A. High-density mapping of electrically induced atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation 1994, 89, 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, C.; Moreno, a.; Berbari, E. Modeling fibroblast-mediated conduction in the ventricle. Comput. Cardiol. 2004, 2004, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.T.; Qi, X.Y.; Huang, H.; Naud, P.; Dawson, K.; Yeh, Y.H.; Harada, M.; Kuo, C.T.; Nattel, S. Disease and region-related cardiac fibroblast potassium current variations and potential functional significance. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 102, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Weber, K.T.; Sun, Y.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Ahokas, R.A.; Gerling, I.C. Myofibroblast-mediated mechanisms of pathological remodelling of the heart. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2013, 10, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramires, F.J.; Sun, Y.; Weber, K.T. Myocardial Fibrosis Associated with Aldosterone or Angiotensin II Administration: Attenuation by Calcium Channel Blockade. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1998, 30, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colston, J.T.; Chandrasekar, B.; Freeman, G.L. A Novel Peroxide-induced Calcium Transient Regulates Interleukin-6 Expression in Cardiac-derived Fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23477–23483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseleva, I.; Kamkin, A.; Pylaev, A.; Kondratjev, D.; Leiterer, K.; Theres, H.; Wagner, K.; Persson, P.; Günther, J. Electrophysiological Properties of Mechanosensitive Atrial Fibroblasts From Chronic Infarcted Rat Heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1998, 30, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe, A.; Lutz, Y.; Nagy, N.; Fabbri, A.; Schweda, C.; Varro, A.; Severi, S. Inter-Species Differences in the Response of Sinus Node Cellular Pacemaking to Changes of Extracellular Calcium. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkerk, A.O.; van Borren, M.M.G.J.; Wilders, R. Calcium Transient and Sodium-Calcium Exchange Current in Human versus Rabbit Sinoatrial Node Pacemaker Cells. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 507872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, A.; Fantini, M.; Wilders, R.; Severi, S. The Human Sinoatrial Action Potential: An in Silico Model. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 586A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miragoli, M.; Salvarani, N.; Rohr, S. Myofibroblasts Induce Ectopic Activity in Cardiac Tissue. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himeno, Y.; Toyoda, F.; Satoh, H.; Amano, A.; Cha, C.Y.; Matsuura, H.; Noma, A. Minor contribution of cytosolic Ca2+ transients to the pacemaker rhythm in guinea pig sinoatrial node cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohajda, Z.; Loewe, A.; Tóth, N.; Varró, A.; Nagy, N. The Cardiac Pacemaker Story-Fundamental Role of the Na/Ca Exchanger in Spontaneous Automaticity. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattel, S.; Heijman, J.; Zhou, L.; Dobrev, D. Molecular Basis of Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology and Therapy. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roney, C.H.; Bayer, J.D.; Zahid, S.; Meo, M.; Boyle, P.M.J.; Trayanova, N.A.; Haïssaguerre, M.; Dubois, R.; Cochet, H.; Vigmond, E.J. Modelling methodology of atrial fibrosis affects rotor dynamics and electrograms. EP Europace 2016, 18, iv146–iv155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saljic, A.; Friederike Fenner, M.; Winters, J.; Flethøj, M.; Eggert Eggertsen, C.; Carstensen, H.; Dalgas Nissen, S.; Melis Hesselkilde, E.; van Hunnik, A.; Schotten, U.; et al. Increased fibroblast accumulation in the equine heart following persistent atrial fibrillation. IJC Heart Vasc. 2021, 35, 100842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, G.; Halliday, B.P.; Mendonca Costa, C.; Bai, W.; Porter, B.; Rinaldi, C.A.; Plank, G.; Rueckert, D.; Prasad, S.K.; Bishop, M.J. Fibrosis Microstructure Modulates Reentry in Non-ischemic Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Insights From Imaged Guided 2D Computational Modeling. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Vandersickel, N.; Panfilov, A.V. Effect of myocyte-fibroblast coupling on the onset of pathological dynamics in a model of ventricular tissue. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazbanov, I.V.; Ten Tusscher, K.H.; Panfilov, A.V. Effects of Heterogeneous Diffuse Fibrosis on Arrhythmia Dynamics and Mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, J.F.; Cardona, K.; Romero, L.; Ferrero, J.M.; Trenor, B. Electrophysiological and structural remodeling in heart failure modulate arrhythmogenesis. 1D simulation study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, S.; Cochet, H.; Boyle, P.M.; Schwarz, E.L.; Whyte, K.N.; Vigmond, E.J.; Dubois, R.; Hocini, M.; Haïssaguerre, M.; Jaïs, P.; et al. Patient-derived models link re-entrant driver localization in atrial fibrillation to fibrosis spatial pattern. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadidi, A.; Nothstein, M.; Chen, J.; Lehrmann, H.; Dössel, O.; Allgeier, J.; Trenk, D.; Neumann, F.J.; Loewe, A.; Müller-Edenborn, B.; et al. Specific Electrogram Characteristics Identify the Extra-Pulmonary Vein Arrhythmogenic Sources of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation-Characterization of the Arrhythmogenic Electrogram Patterns During Atrial Fibrillation and Sinus Rhythm. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhl, L.; Genové, G.; Leptidis, S.; Liu, J.; He, L.; Mocci, G.; Sun, Y.; Gustafsson, S.; Buyandelger, B.; Chivukula, I.V.; et al. Single-cell analysis uncovers fibroblast heterogeneity and criteria for fibroblast and mural cell identification and discrimination. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.J.; Rognoni, E. Dissecting Fibroblast Heterogeneity in Health and Fibrotic Disease. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künzel, S.R.; Rausch, J.S.E.; Schäffer, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Künzel, K.; Klapproth, E.; Kant, T.; Herzog, N.; Küpper, J.; Lorenz, K.; et al. Modeling atrial fibrosis in vitro —Generation and characterization of a novel human atrial fibroblast cell line. FEBS Open Bio 2020, 10, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Li, M.; Han, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X. Role of TRPM7 in cardiac fibrosis: A potential therapeutic target (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 21, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Lubitz, S.A.; Sullivan, L.M.; Sun, J.X.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Magnani, J.W.; Ellinor, P.T.; Benjamin, E.J.; Wang, T.J. Low Serum Magnesium and the Development of Atrial Fibrillation in the Community. Circulation 2013, 127, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Drca, N.; Michaëlsson, K. Serum Magnesium and Calcium Levels and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, e002349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhle, B.; Trebak, M. Emerging Roles for Native Orai Ca2+ Channels in Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Top. Membr. 2013, 71, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho Londoño, J.E.; Marx, A.; Kraft, A.E.; Schürger, A.; Richter, C.; Dietrich, A.; Lipp, P.; Birnbaumer, L.; Freichel, M. Angiotensin-II-Evoked Ca2+ Entry in Murine Cardiac Fibroblasts Does Not Depend on TRPC Channels. Cells 2020, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roney, C.H.; Cantwell, C.D.; Bayer, J.D.; Qureshi, N.A.; Lim, P.B.; Tweedy, J.H.; Kanagaratnam, P.; Peters, N.S.; Vigmond, E.J.; Ng, F.S. Spatial Resolution Requirements for Accurate Identification of Drivers of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e004899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, J.; Sankarankutty, A.C.; Seemann, G.; Seidel, T.; Sachse, F.B. Confocal Microscopy-Based Estimation of Parameters for Computational Modeling of Electrical Conduction in the Normal and Infarcted Heart. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivumaki, J.T.; Takalo, J.; Korhonen, T.; Tavi, P.; Weckstrom, M. Modelling sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase and its regulation in cardiac myocytes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 2181–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe, A.; Wilhelms, M.; Dössel, O.; Seemann, G. Influence of chronic atrial fibrillation induced remodeling in a computational electrophysiological model. Biomedizinische Technik/Biomedical Engineering; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Boston, 2014; Volume 59, pp. S929–S932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, M.; Valinoti, M.; Unger, L.; Oesterlein, T.; Dössel, O.; Corsi, C.; Loewe, A.; Severi, S. A Computational Framework to Benchmark Basket Catheter Guided Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type of Ion Channel | Ion Channel/Protein | Cell Types |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage-gated Na+ | Nav1.2; Nav1.5; Nav1.9 | Human ventricular fibroblast [17]; human atrial fibroblast [8,9,10] |
| Voltage-gated K+ | Kv4.1, Kv4.2, Kv4.3, Kv6.2 | Human ventricular fibrob last [17]; human atrial fibrob last [9] |
| K+ inward rectifier | Kir2.1 | Human ventricular fibroblast [17]; dog ventricular fibroblast [18] |
| Voltage-gated Ca2+ | Cav1.2, Cav1.3 | Human ventricular fibroblast [11]; human atrial fibroblast [9] |
| ATP-activated K+ | SUR2/Kir6.1 | Mice ventricular fibroblast [19]; rat ventricular fibroblast [20] |
| Ca2+-activated K+ | KCa1.1, KCa3.1 | Human ventricular fibroblast [17]; human atrial fibroblast [21] |
| Voltage-Gated Cl− | ClCN3 | Human ventricular fibroblast [17] |
| Store-operated Ca2+ or Receptor-operated Ca2+ | Orai1/STIM1 | Rat atrial fibroblast [16]; Human ventricular fibroblast [22]; Rat ventricular fibroblast [23] |
| TRP | TRPC3 [24] TRPV4 [25] TRPM1 [9] TRPM7 [12,26] TRPA1 [12] | Rat ventricular fibroblast [24,25]; Human atrial fibrob last [9,12,26] |
| gKv (nS/pF) | gK1 (nS/pF) | gNa (nS/pF) | gNab (nS/pF) | gNaK (nS/pF) | gCaL (nS/pF) | gCab (nS/pF) | kNaCa (nS/pF) | kpCa (nS/pF) | rKv (nS/pF) | sKv (nS/pF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.34 | 1.79 | 0.73 | 2.39 | 0.84 | 0.48 | 0.57 | 2.55 | 1.0 | 14.04 | 16.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez, J.; Trenor, B.; Saiz, J.; Dössel, O.; Loewe, A. Fibrotic Remodeling during Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: In Silico Investigation of the Role of Calcium for Human Atrial Myofibroblast Electrophysiology. Cells 2021, 10, 2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112852
Sánchez J, Trenor B, Saiz J, Dössel O, Loewe A. Fibrotic Remodeling during Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: In Silico Investigation of the Role of Calcium for Human Atrial Myofibroblast Electrophysiology. Cells. 2021; 10(11):2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112852
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez, Jorge, Beatriz Trenor, Javier Saiz, Olaf Dössel, and Axel Loewe. 2021. "Fibrotic Remodeling during Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: In Silico Investigation of the Role of Calcium for Human Atrial Myofibroblast Electrophysiology" Cells 10, no. 11: 2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112852
APA StyleSánchez, J., Trenor, B., Saiz, J., Dössel, O., & Loewe, A. (2021). Fibrotic Remodeling during Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: In Silico Investigation of the Role of Calcium for Human Atrial Myofibroblast Electrophysiology. Cells, 10(11), 2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10112852