Adiponectin Promotes VEGF Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts and Induces Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis by Inhibiting miR-106a-5p
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. qRT-PCR Gene Expression Analysis of mRNA and miRNA
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. EPC Tube Formation
2.6. Transwell Migration Assay
2.7. Plasmid Construction and Luciferase Assay
2.8. The Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay
2.9. In Vivo Matrigel Plug Assay
2.10. Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model
2.11. Ethics Statement
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
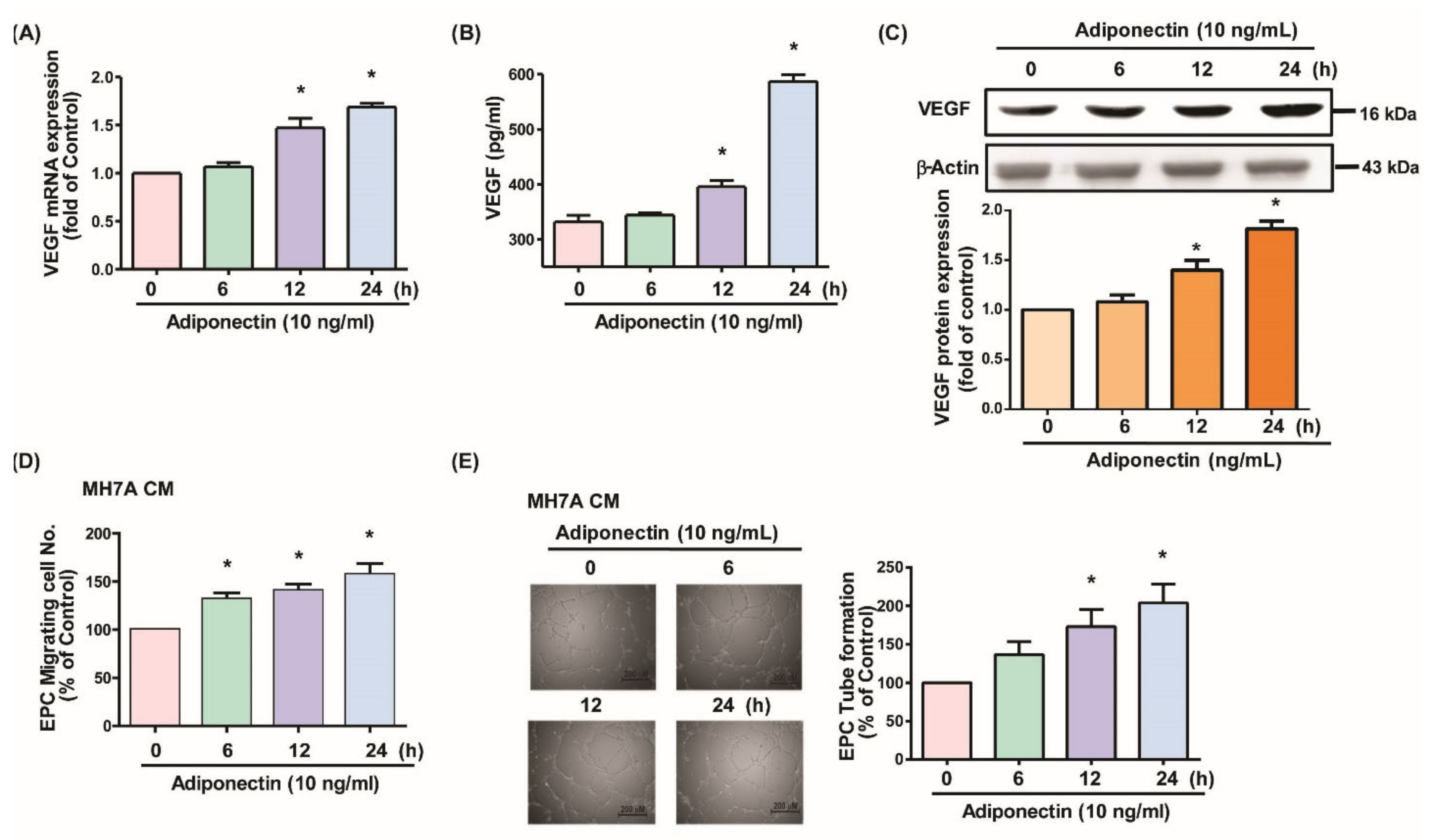
3.1. Adiponectin Increases VEGF-Dependent EPC Angiogenesis in MH7A Cells
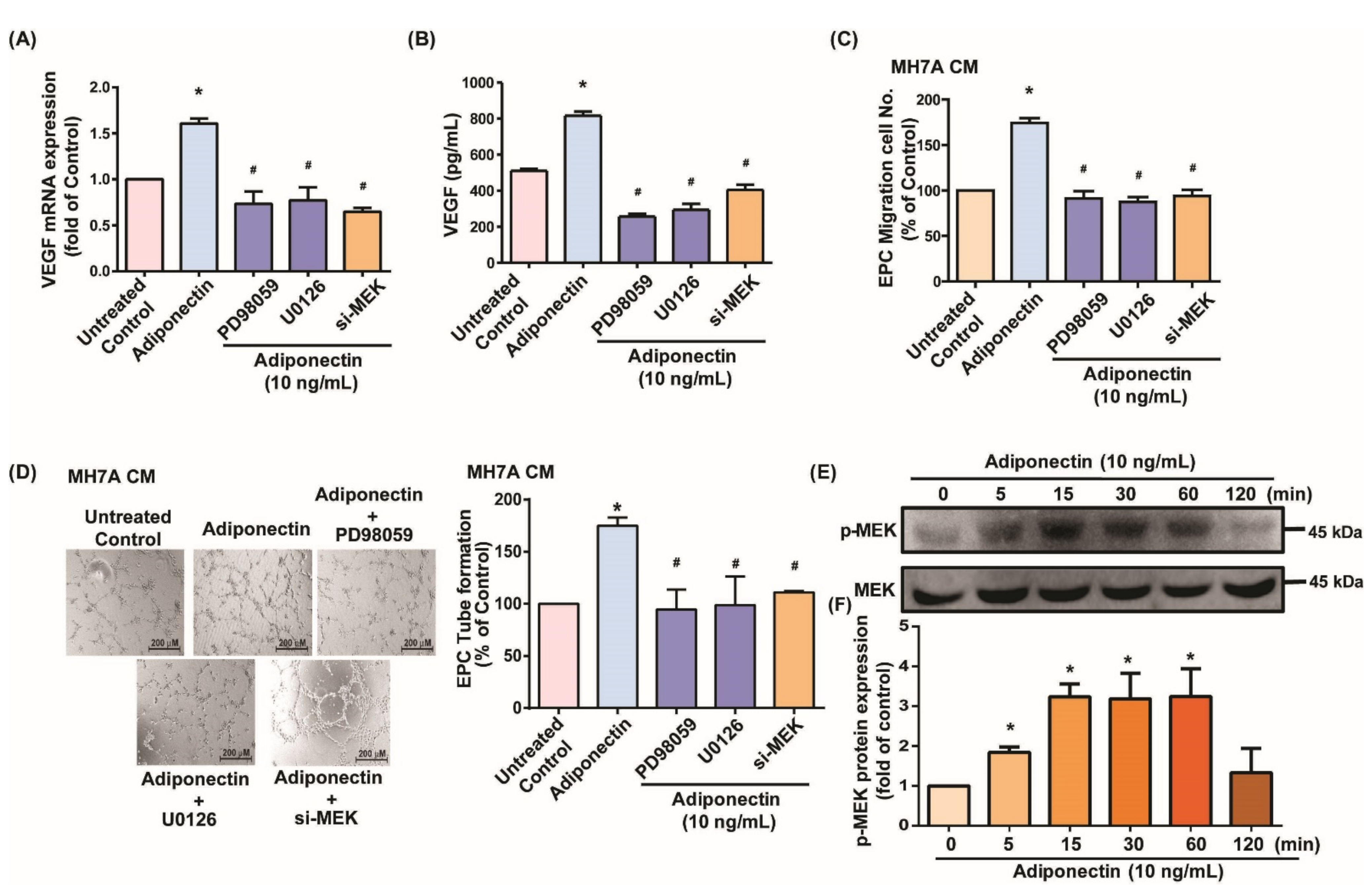
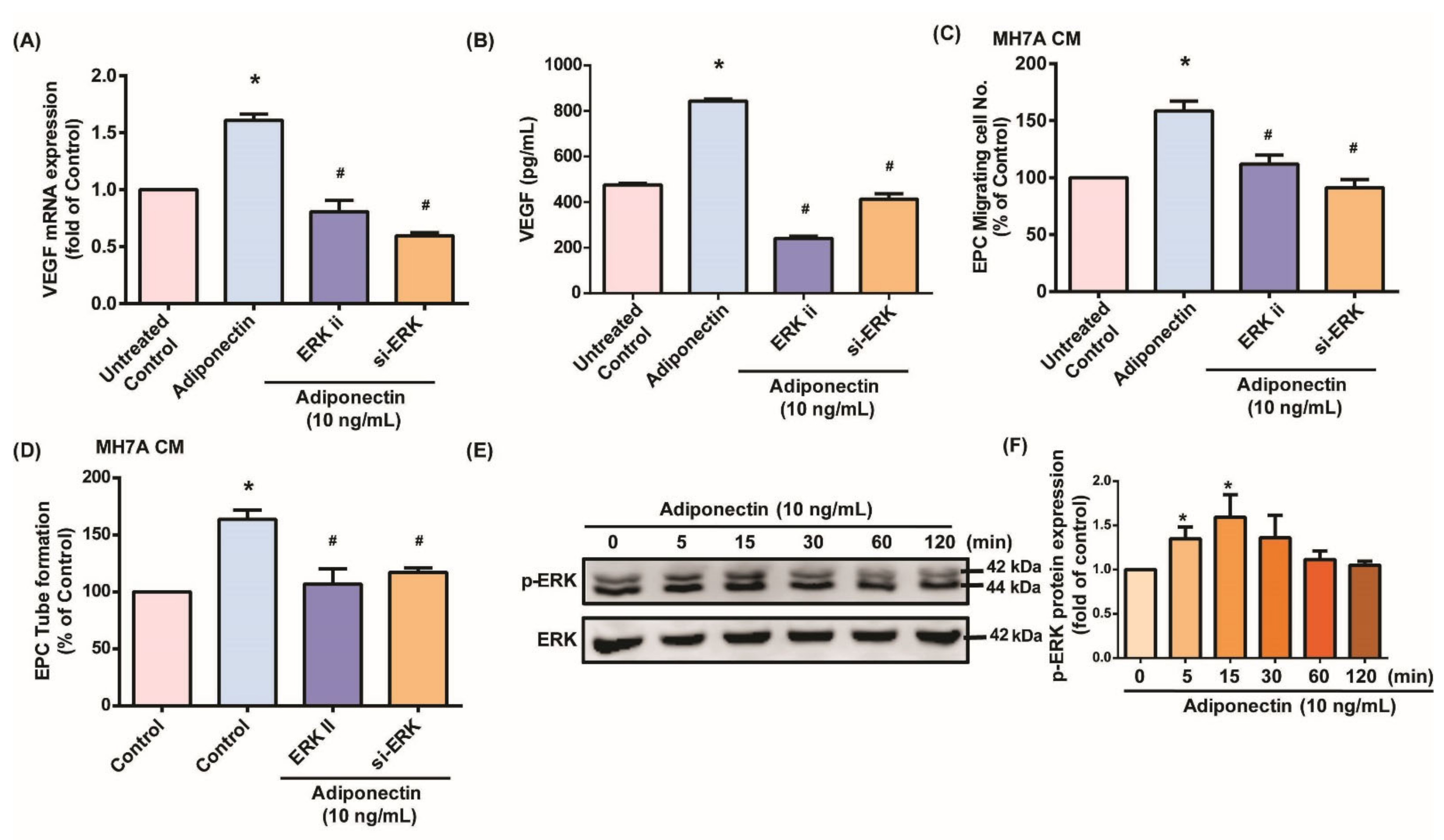
3.2. MEK/ERK Signaling Is Critical for Adiponectin-Dependent EPC Angiogenesis
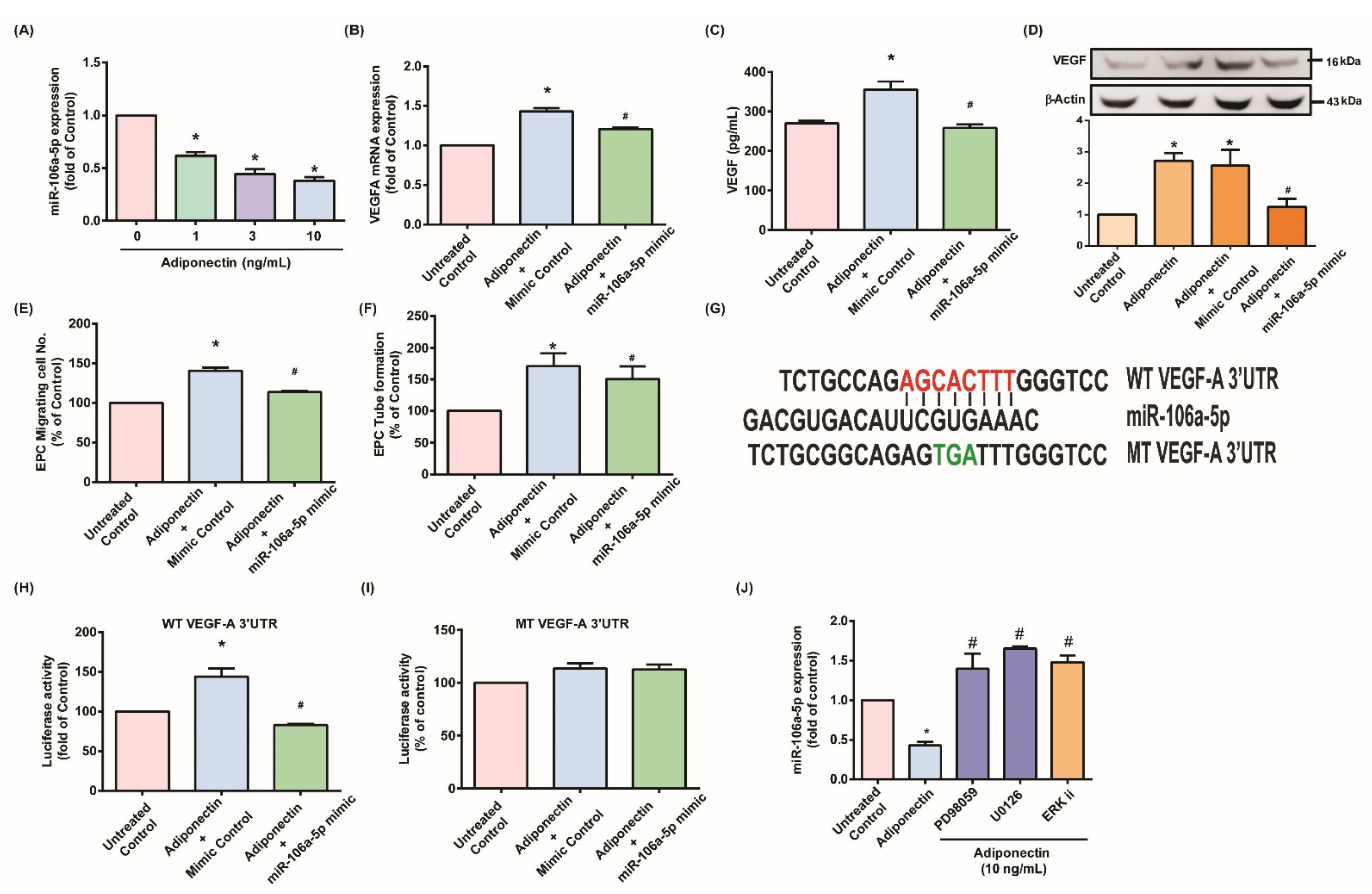
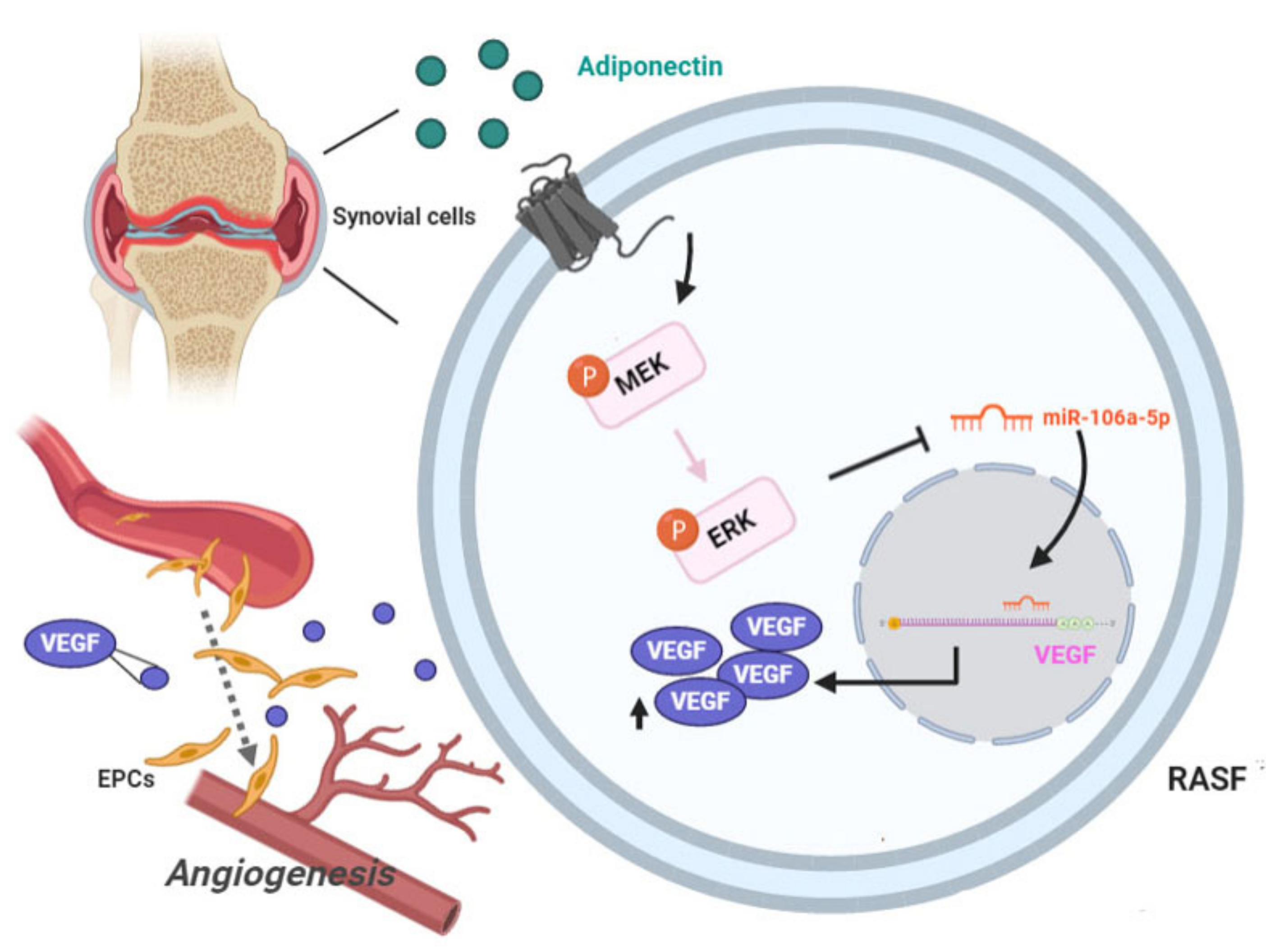
3.3. Adiponectin Enhanced VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis via Downregulation of Adiponectin-Mediated miR-106a-5p Expression
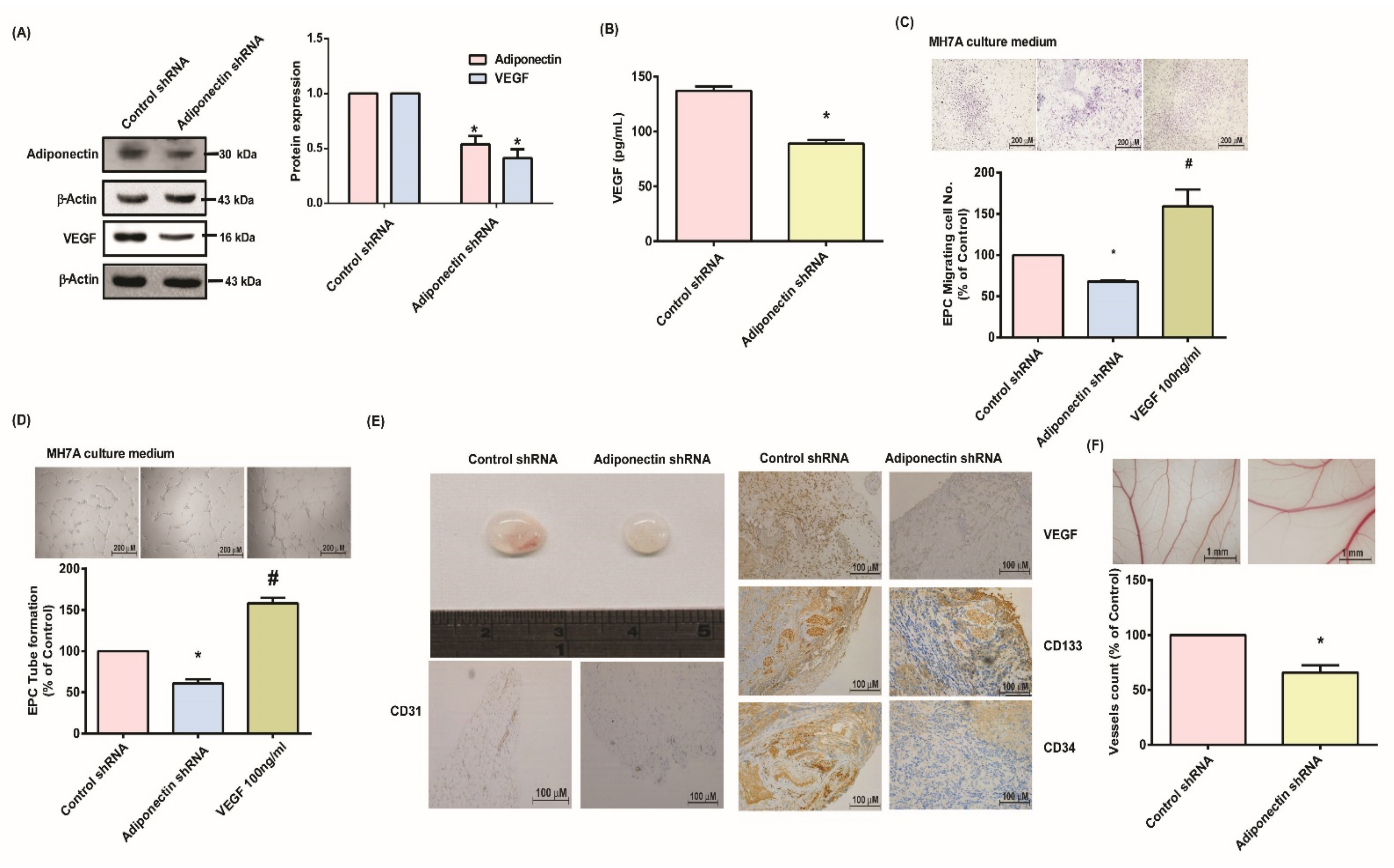
3.4. Suppressing Adiponectin Reduces RA Angiogenesis
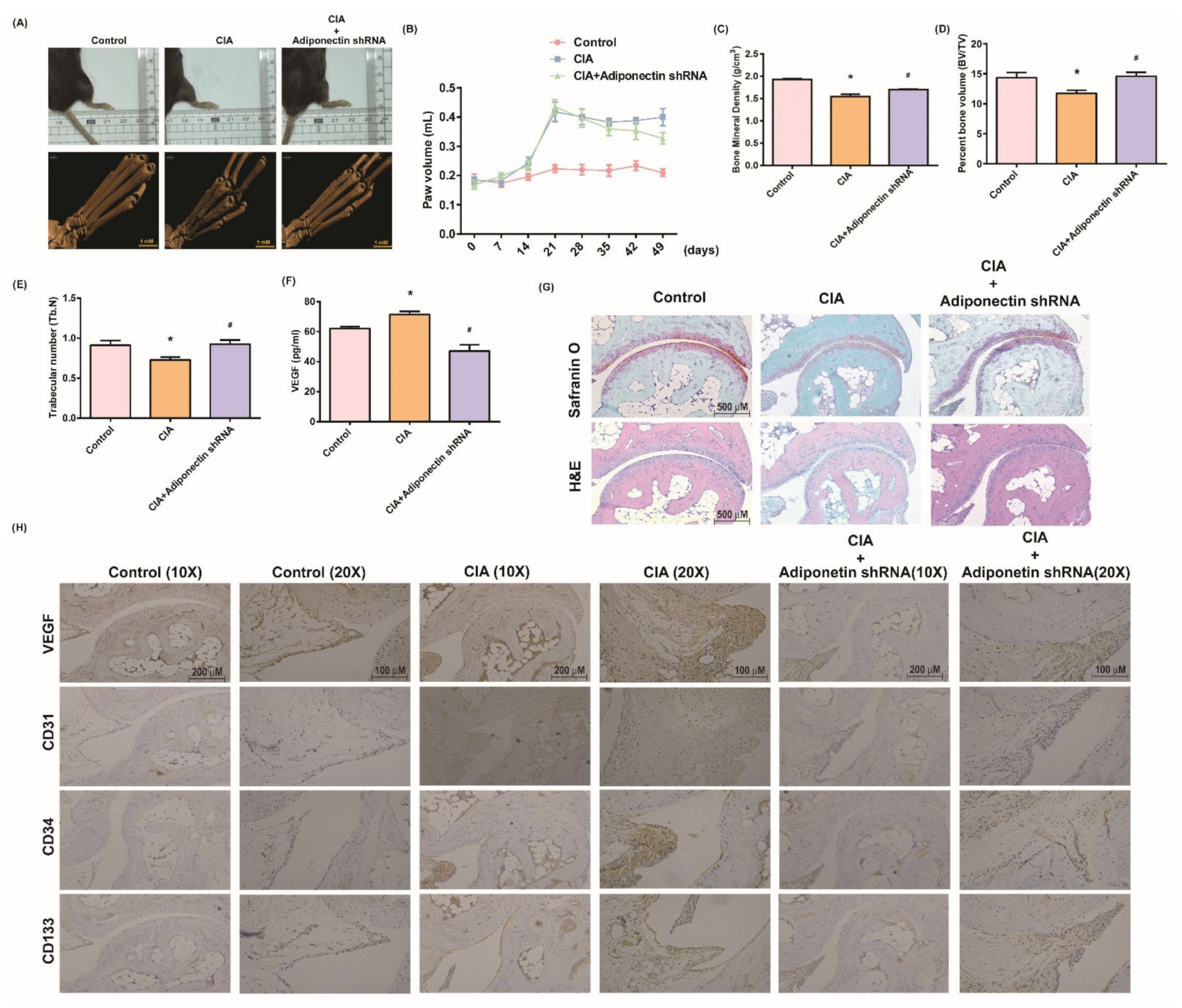
3.5. Attenuating Bone Damage and Angiogenesis by Targeting Adiponectin in CIA Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.E. Review: Angiogenesis: Implications for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshabrawy, H.A.; Chen, Z.; Volin, M.V.; Ravella, S.; Virupannavar, S.; Shahrara, S. The pathogenic role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Da, G.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y. Avastin exhibits therapeutic effects on collagen-induced arthritis in rat model. Inflammation 2013, 36, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xun, K.; Wang, C.; Zhao, H.; Bi, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Adiponectin, an unlocking adipocytokine. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2009, 27, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, F. Regulation of adiponectin multimerization, signaling and function. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, M. Adiponectin: A versatile player of innate immunity. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.T.; Allison, M.; Bingham, C.O., III; Scott, W.M., Jr.; Bathon, J.M. Adiponectin is a mediator of the inverse association of adiposity with radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rho, Y.H.; Solus, J.; Sokka, T.; Oeser, A.; Chung, C.P.; Gebretsadik, T.; Shintani, A.; Pincus, T.; Stein, C.M. Adipocytokines are associated with radiographic joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Lu, J.; Bao, J.; Guo, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y. Adiponectin: A biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotece, M.; Conde, J.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Koskinen, A.; López, V.; Gómez-Reino, J.; Lago, F.; Moilanen, E.; Gualillo, O. Adipokines as drug targets in joint and bone disease. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.M.; Lee, Y.A.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, S.J.; Hahm, D.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Yang, H.I.; Yoo, M.C.; Kim, K.S. Adiponectin may contribute to synovitis and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis by stimulating vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix metalloproteinase-1, and matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in fibroblast-like synoviocytes more than proinflammatory mediators. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R161. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.A.; Choi, H.M.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, H.I.; Yoo, M.C.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, K.S. Synergy between adiponectin and interleukin-1β on the expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and cyclooxygenase-2 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2012, 44, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Ji, H.I.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, S.J.; Yang, H.I.; Chul Yoo, M.; Kim, K.S. The role of adiponectin in the production of IL-6, IL-8, VEGF and MMPs in human endothelial cells and osteoblasts: Implications for arthritic joints. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.A.; Ji, H.I.; Song, R.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, S.J.; Yoo, M.C.; Yang, H.I. Increased expression of endocan in arthritic synovial tissues: Effects of adiponectin on the expression of endocan in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asahara, T.; Murohara, T.; Sullivan, A.; Silver, M.; van der Zee, R.; Li, T.; Witzenbichler, B.; Schatteman, G.; Isner, J.M. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 1997, 275, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadini, G.P.; Losordo, D.; Dimmeler, S. Critical reevaluation of endothelial progenitor cell phenotypes for therapeutic and diagnostic use. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rüger, B.; Giurea, A.; Wanivenhaus, A.H.; Zehetgruber, H.; Hollemann, D.; Yanagida, G.; Groger, M.; Petzelbauer, P.; Smolen, J.S.; Hoecker, P.; et al. Endothelial precursor cells in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Villeroché, V.J.; Avouac, J.; Ponceau, A.; Ruiz, B.; Kahan, A.; Boileau, C.; Uzan, G.; Allanore, Y. Enhanced late-outgrowth circulating endothelial progenitor cell levels in rheumatoid arthritis and correlation with disease activity. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavi, M.J.; Jamshidi, A.; Chopra, A.; Aslani, S.; Akhlaghi, M.; Mahmoudi, M. Implications of the noncoding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 234, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.M.; Huang, Q.C.; Yang, S.L.; Chu, Y.L.; Yan, Y.H.; Han, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, R.Y. Role of Micro RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Novel Perspectives Based on Review of the Literature. Medicine 2015, 94, e1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawaf, H.A. Circulating microRNAs and adipokines as markers of metabolic syndrome in adolescents with obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santovito, D.; De Nardis, V.; Marcantonio, P.; Mandolini, C.; Paganelli, C.; Vitale, E.; Buttitta, F.; Bucci, M.; Mezzetti, A.; Consoli, A.; et al. Plasma exosome microRNA profiling unravels a new potential modulator of adiponectin pathway in diabetes: Effect of glycemic control. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1681–E1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Li, L. Down-regulation of microRNA-375 regulates adipokines and inhibits inflammatory cytokines by targeting AdipoR2 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Chang, A.C.; Chen, H.T.; Wang, S.W.; Lo, Y.S.; Tang, C.H. Adiponectin promotes VEGF-C-dependent lymphangiogenesis by inhibiting miR-27b through a CaMKII/AMPK/p38 signaling pathway in human chondrosarcoma cells. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.L.; Chang, A.C.; Huang, C.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Lin, C.C.; Tang, C.H. Myostatin Promotes Interleukin-1β Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts through Inhibition of miR-21-5p. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-P.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chen, B.-C.; Liu, S.-C.; Li, T.-M.; Huang, W.-C.; Hsu, C.-J.; Tang, C.-H. Soya-cerebroside reduces interleukin production in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting the ERK, NF-κB and AP-1 signalling pathways. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-P.; Chen, P.-C.; Wang, S.-W.; Fong, Y.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Tsai, F.-J.; Chung, J.-G.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Hsu, Y.-M.; et al. Plumbagin suppresses endothelial progenitor cell-related angiogenesis in vitro and In Vivo. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-P.; Wang, S.-W.; Wu, Y.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Tsai, F.-J.; Chung, J.-G.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Yin, M.-C.; et al. Glucocerebroside reduces endothelial progenitor cell-induced angiogenesis. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-P.; Wang, S.-W.; Wu, Y.-C.; Lin, L.-W.; Tsai, F.-J.; Yang, J.-S.; Li, T.-M.; Tang, C.-H. Soya-cerebroside inhibits VEGF-facilitated angiogenesis in endothelial progenitor cells. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.C.; Chiu, C.P.; Tsai, C.H.; Hung, C.Y.; Li, T.M.; Wu, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. Soya-cerebroside, an extract of Cordyceps militaris, suppresses monocyte migration and prevents cartilage degradation in inflammatory animal models. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Wu, T.-Y.; Tsai, C.-H.; Tsai, F.-J.; Chung, J.-G.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Yin, M.-C.; et al. Soya-cerebroside reduces IL-1β-induced MMP-1 production in chondrocytes and inhibits cartilage degradation: Implications for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Hsu, C.J.; Fong, Y.C. The CCL5/CCR5 axis promotes interleukin-6 production in human synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3615–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-P.; Liu, S.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, B.-C.; Chen, H.-T.; Li, T.-M.; Huang, W.-C.; Hsu, C.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Tang, C.-H. Cordycerebroside A suppresses VCAM-dependent monocyte adhesion in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting MEK/ERK/AP-1 signaling. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 86, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tsai, C.-H.; Lee, H.-P.; Lo, L.-C.; Huang, W.-C.; Wu, Y.-C.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Tang, C.-H. Betulin suppresses TNF-α and IL-1β production in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting the MEK/ERK/NF-κB pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 86, 2411–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Su, C.M.; Hsu, C.J.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, S.W.; Liu, S.C.; Chen, W.C.; Fuh, L.J.; Tang, C.H. CCN1 Promotes VEGF Production in Osteoblasts and Induces Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis by Inhibiting miR-126 Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storgard, C.; Mikolon, D.; Stupack, D.G. Angiogenesis assays in the chick CAM. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 294, 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Lin, J.A.; Wang, S.W.; Peng, C.Y.; Cheng, H.C.; Tang, C.H. Endothelin-1 promotes vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent angiogenesis in human chondrosarcoma cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bäcklund, J.; Li, C.; Jansson, E.; Carlsen, S.; Merky, P.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Haag, S.; Ytterberg, J.; Zubarev, R.A.; Holmdahl, R. C57BL/6 mice need MHC class II Aq to develop collagen-induced arthritis dependent on autoreactive T cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamio, N.; Akifusa, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Yamashita, Y. Induction of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor by globular adiponectin via the MEK-ERK pathway. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2008, 292, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, N.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Suhail, A.; Sweeney, G.; Wheeler, M.B. Adiponectin-induced ERK and Akt phosphorylation protects against pancreatic beta cell apoptosis and increases insulin gene expression and secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33623–33631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Jian, X.; Zou, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Le, Q.; Chen, H.; Gao, X.; He, C. Adiponectin Is Involved in Connective Tissue Growth Factor-Induced Proliferation, Migration and Overproduction of the Extracellular Matrix in Keloid Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.Y.; Tsai, H.C.; Chou, P.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Chen, H.T.; Lin, Y.M.; Chiang, I.P.; Chang, T.M.; Hsu, S.K.; Chou, M.C.; et al. CCL3 promotes angiogenesis by dysregulation of miR-374b/VEGF-A axis in human osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 4310–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartok, B.; Firestein, G.S. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashiri, S.Y.; Suzuki, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Horai, Y.; Okada, A.; Iwamoto, N.; Ichinose, K.; Tamai, M.; Arima, K.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Ultrasonographic examination of rheumatoid arthritis patients who are free of physical synovitis: Power Doppler subclinical synovitis is associated with bone erosion. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitchen, J.; Kane, D. Greyscale and power Doppler ultrasonographic evaluation of normal synovial joints: Correlation with pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and angiogenic factors. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tas, S.W.; Maracle, C.X.; Balogh, E.; Szekanecz, Z. Targeting of proangiogenic signalling pathways in chronic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrion, M.; Frommer, K.W.; Perez-Garcia, S.; Muller-Ladner, U.; Gomariz, R.P.; Neumann, E. The Adipokine Network in Rheumatic Joint Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minamino, H.; Katsushima, M.; Yoshida, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Fujita, Y.; Shirakashi, M.; Yamamoto, W.; Murakami, K.; Murata, K.; Nishitani, K.; et al. Increased circulating adiponectin is an independent disease activity marker in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study using the KURAMA database. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Luo, S.; Li, Z. Multifaceted roles of adiponectin in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Q.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X. Endocan: A new marker for cancer and a target for cancer therapy. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, I.J.; Liu, S.C.; Su, C.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Tang, C.H. Implications of Angiogenesis Involvement in Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavasolian, F.; Abdollahi, E.; Rezaei, R.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Henrotin, Y.; Sahebkar, A. Altered Expression of MicroRNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.X.; Chen, H.X.; Mou, X.J.; Zhu, X.K.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.G. GZMB gene silencing confers protection against synovial tissue hyperplasia and articular cartilage tissue injury in rheumatoid arthritis through the MAPK signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, B.; Sun, B.; Liu, C.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, D.; Yu, F.; Yan, D. Long non-coding RNA Fer-1-like protein 4 suppresses oncogenesis and exhibits prognostic value by associating with miR-106a-5p in colon cancer. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Cai, H.; Zheng, R.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Tu, J. Long non-coding RNA 657 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-106a-5p to regulate PTEN expression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 92, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.J.; Wei, L.L.; Wu, X.J.; Huo, F.C.; Mou, J.; Pei, D.S. MiR-106a-5p inhibits the cell migration and invasion of renal cell carcinoma through targeting PAK5. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Qi, D.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Goodman, S.B.; Kang, L.; Song, Q.; Fan, Z.; Maloney, W.J.; Wang, Y. Cryptotanshinone Protects Cartilage against Developing Osteoarthritis through the miR-106a-5p/GLIS3 Axis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Ni, X.; Feng, P.; Wang, Y.U. Long non-coding RNA H19 modulates proliferation and apoptosis in osteoarthritis via regulating miR-106a-5p. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Park, M.C.; Park, Y.B.; Lee, S.K. Adiponectin mitigates the severity of arthritis in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 37, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Hua, B.; Fang, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, N.; Ma, Y. Adiponectin exerts a potent anti-arthritic effect and insulin resistance in collagen-induced arthritic rats. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Feng, X.; Tan, W.; Lin, N.; Hua, M.; Wei, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, N.; Zhang, M. Adiponectin exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis via enhancing Th17 response and prompting RANKL expression. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Xuan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, P.; Wu, Q.; Liu, R.; Che, N.; et al. Adiponectin aggravates bone erosion by promoting osteopontin production in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebina, K.; Oshima, K.; Matsuda, M.; Fukuhara, A.; Maeda, K.; Kihara, S.; Hashimoto, J.; Ochi, T.; Banda, N.K.; Yoshikawa, H.; et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of adiponectin reduces the severity of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 378, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Hahm, D.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Sur, B.; Lee, H.M.; Ryu, C.J.; Yang, H.I.; Kim, K.S. Potential therapeutic antibodies targeting specific adiponectin isoforms in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.M.; Doss, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in Inflammation and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-C.; Law, Y.-Y.; Liu, S.-C.; Hu, S.-L.; Lin, J.-A.; Chen, C.-J.; Wang, S.-W.; Tang, C.-H. Adiponectin Promotes VEGF Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts and Induces Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis by Inhibiting miR-106a-5p. Cells 2021, 10, 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102627
Huang C-C, Law Y-Y, Liu S-C, Hu S-L, Lin J-A, Chen C-J, Wang S-W, Tang C-H. Adiponectin Promotes VEGF Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts and Induces Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis by Inhibiting miR-106a-5p. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102627
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chien-Chung, Yat-Yin Law, Shan-Chi Liu, Sung-Lin Hu, Jun-An Lin, Chao-Ju Chen, Shih-Wei Wang, and Chih-Hsin Tang. 2021. "Adiponectin Promotes VEGF Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts and Induces Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis by Inhibiting miR-106a-5p" Cells 10, no. 10: 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102627
APA StyleHuang, C.-C., Law, Y.-Y., Liu, S.-C., Hu, S.-L., Lin, J.-A., Chen, C.-J., Wang, S.-W., & Tang, C.-H. (2021). Adiponectin Promotes VEGF Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts and Induces Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis by Inhibiting miR-106a-5p. Cells, 10(10), 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102627





