Research Progress and Challenges in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
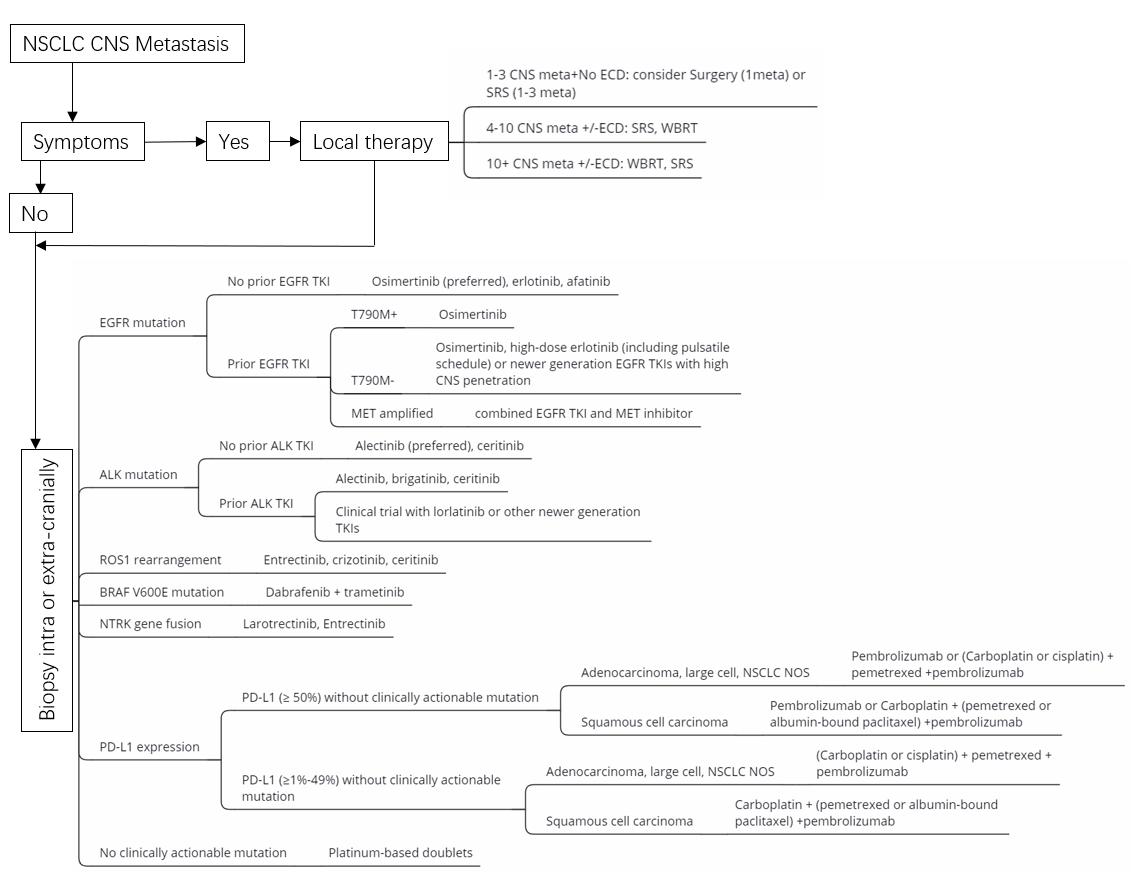
:1. Introduction
2. Local Treatment
2.1. Surgery
2.2. Whole Brain Radiotherapy
2.3. Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Radiotherapy
2.4. Exploration of New Local Treatment Methods
3. Chemotherapy
4. Targeted Therapy
4.1. Targeted Therapy with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
4.2. Targeted Therapy with ALK-TKI
4.3. Other Targeted Therapies
5. Immunotherapy
5.1. Treatment Progress of ICI Monotherapy in NSCLC CNS Metastasis
5.2. Treatment Progress of ICI Monotherapy Combined with Chemotherapy/Radiotherapy for NSCLC CNS Metastasis
6. Discussion
6.1. Choice of Clinical Treatment Model for NSCLC CNS Metastasis with Driver Mutations
6.2. Prognostic Factors of NSCLC CNS Metastasis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proescholdt, M.A.; Schödel, P.; Doenitz, C.; Pukrop, T.; Höhne, J.; Schmidt, N.O.; Schebesch, K.M. The Management of Brain Metastases-Systematic Review of Neurosurgical Aspects. Cancers 2021, 13, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, P.H.; Peterson, S.L.; Vigneau, F.D.; Shore, R.D.; Quarshie, W.O.; Islam, K.; Schwartz, A.G.; Wozniak, A.J.; Gadgeel, S.M. Risk of brain metastases in patients with nonmetastatic lung cancer: Analysis of the Metropolitan Detroit Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data. Cancer 2016, 122, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakonas, G.; De Petris, L.; Ekman, S. Management of brain metastasized non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)—From local treatment to new systemic therapies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 54, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Wright, C.H.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Brain metastases: Epidemiology. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 149, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.; Rathnum, K.K. Management of leptomeningeal metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Indian J. Cancer 2019, 56 (Suppl. S1), S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, S.R.; Molitoris, J.K.; Vyfhuis, M.A.L.; Edelman, M.J.; Burrows, W.M.; Feliciano, J.; Nichols, E.M.; Suntharalingam, M.; Donahue, J.; Carr, S.R.; et al. Lymph Node Size Predicts for Asymptomatic Brain Metastases in Patients With Non-small-cell Lung Cancer at Diagnosis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e107–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Luo, S.; Lin, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Liao, Z.; Lin, W.; Zheng, W.; Xie, X. Correlation between EGFR mutation status and the incidence of brain metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barlesi, F.; Mazieres, J.; Merlio, J.P.; Debieuvre, D.; Mosser, J.; Lena, H.; Ouafik, L.; Besse, B.; Rouquette, I.; Westeel, V.; et al. Routine molecular profiling of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Results of a 1-year nationwide programme of the French Cooperative Thoracic Intergroup (IFCT). Lancet 2016, 387, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, R.; Liang, X.; Zhan, Q. High probability and frequency of EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 135, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Ou, S.H.; Logan, J.; Borges, L.F.; Shaw, A.T. The central nervous system as a sanctuary site in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2013, 8, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, J.S.; Kim, S.H. EGFR and HER-2 status of non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis and corresponding primary tumor. Neoplasma 2011, 58, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, C.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. China Experts Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Brain Metastases of Lung Cancer (2017 version). Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi Chin. J. Lung Cancer 2017, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: An accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dempke, W.C.; Edvardsen, K.; Lu, S.; Reinmuth, N.; Reck, M.; Inoue, A. Brain Metastases in NSCLC—Are TKIs Changing the Treatment Strategy? Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 5797–5806. [Google Scholar]
- Tsao, M.; Xu, W.; Sahgal, A. A meta-analysis evaluating stereotactic radiosurgery, whole-brain radiotherapy, or both for patients presenting with a limited number of brain metastases. Cancer 2012, 118, 2486–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Ballman, K.V.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Whitton, A.C.; Greenspoon, J.; Parney, I.F.; Laack, N.N.I.; Ashman, J.B.; et al. Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC·3): A multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Abbas, M.; Li, Y.; Teng, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yu, S.; Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, M. Comparative Effectiveness of Pemetrexed-platinum Doublet Chemotherapy With or Without Bevacizumab as First-line Therapy for Treatment-naive Patients With Advanced Nonsquamous Non-small-cell Lung Cancer in China. Clin. Ther. 2019, 41, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, S.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Peters, S. Indications and limitations of chemotherapy and targeted agents in non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, S.W.; Suh, C.; Lee, J.S. Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring either exon 19 or 21 mutation. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffknecht, P.; Tufman, A.; Wehler, T.; Pelzer, T.; Wiewrodt, R.; Schütz, M.; Serke, M.; Stöhlmacher-Williams, J.; Märten, A.; Maria Huber, R.; et al. Efficacy of the irreversible ErbB family blocker afatinib in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-pretreated non-small-cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases or leptomeningeal disease. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2015, 10, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabari, J.K.; Santini, F.C.; Schram, A.M.; Bergagnini, I.; Chen, R.; Mrad, C.; Lai, W.V.; Arbour, K.C.; Drilon, A. The activity, safety, and evolving role of brigatinib in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancers. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garon, E.B.; Hellmann, M.D.; Rizvi, N.A.; Carcereny, E.; Leighl, N.B.; Ahn, M.J.; Eder, J.P.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Aggarwal, C.; Horn, L.; et al. Five-Year Overall Survival for Patients With Advanced Non‒Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Pembrolizumab: Results From the Phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2518–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindl, A.; Yadavalli, S.; Gruber, K.; Seiwald, M.; Gatterbauer, B.; Dieckmann, K.; Frischer, J.; Klikovits, T.; Zöchbauer-Müller, S.; Grisold, A.; et al. Neurological symptom burden impacts survival prognosis in patients with newly diagnosed non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. Cancer 2020, 126, 4341–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Kotecha, R.; Chao, S.; Ahluwalia, M.; Sahgal, A.; Chang, E. Current approaches to the management of brain metastases. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaal, E.; Niël, C.; Vecht, C. Therapeutic management of brain metastasis. Lancet Neurol. 2005, 4, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchino, F.; Rudà, R.; Soffietti, R. Mechanisms and Therapy for Cancer Metastasis to the Brain. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatiboglu, M.A.; Akdur, K.; Sawaya, R. Neurosurgical management of patients with brain metastasis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 43, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Adeni, A.; Sholl, L.M.; Nishino, M.; Awad, M.M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Outcomes for Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Receiving Baseline Corticosteroids for Palliative Versus Nonpalliative Indications. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, E.Y.; Merl, M.Y.; Lin, K. The impact of corticosteroid use during anti-PD1 treatment. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 26, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, H.; Ruschin, M.; Angelov, L.; Brown, P.D.; Chiang, V.L.S.; Kirkpatrick, J.P.; Lo, S.S.; Mahajan, A.; Oh, K.S.; Sheehan, J.P.; et al. Consensus Contouring Guidelines for Postoperative Completely Resected Cavity Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuntia, D.; Brown, P.; Li, J.; Mehta, M.P. Whole-brain radiotherapy in the management of brain metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrona, A. Management of CNS disease in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: Is whole brain radiotherapy still needed? Cancer Radiother. J. Soc. Fr. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 23, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, R.E.; Stephens, R.J.; Nankivell, M.; Pugh, C.; Moore, B.; Navani, N.; Wilson, P.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Barton, R.; Parmar, M.K.; et al. Interim data from the Medical Research Council QUARTZ Trial: Does whole brain radiotherapy affect the survival and quality of life of patients with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer? Clin. Oncol. 2013, 25, e23–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Pugh, S.; Laack, N.N.; Wefel, J.S.; Khuntia, D.; Meyers, C.; Choucair, A.; Fox, S.; Suh, J.H.; Roberge, D.; et al. Memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, S.R.; Case, L.D.; Peiffer, A.; Naughton, M.M.; Chan, M.D.; Stieber, V.W.; Moore, D.F., Jr.; Falchuk, S.C.; Piephoff, J.V.; Edenfield, W.J.; et al. Donepezil for Irradiated Brain Tumor Survivors: A Phase III Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G., 2nd; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of Radiosurgery Alone vs Radiosurgery With Whole Brain Radiation Therapy on Cognitive Function in Patients With 1 to 3 Brain Metastases: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGranahan, T.; Nagpal, S. A Neuro-oncologist’s Perspective on Management of Brain Metastases in Patients with EGFR Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2017, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golding, B.; Luu, A.; Jones, R.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. The function and therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muacevic, A.; Wowra, B.; Siefert, A.; Tonn, J.C.; Steiger, H.J.; Kreth, F.W. Microsurgery plus whole brain irradiation versus Gamma Knife surgery alone for treatment of single metastases to the brain: A randomized controlled multicentre phase III trial. J. Neuro Oncol. 2008, 87, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): A multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Multiinstitutional prospective observational study of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer (JLGK0901 study-NSCLC). J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Ludmir, E.B.; Wang, Y.; Guha-Thakurta, N.; McAleer, M.F.; Settle, S.H.; Yeboa, D.N.; Ghia, A.J.; McGovern, S.L.; Chung, C.; et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery versus Whole-brain Radiation Therapy for Patients with 4-15 Brain Metastases: A Phase III Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, S21–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulahannan, D.; Khalifa, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Lee, S.M. Emerging treatment paradigms for brain metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer: An overview of the current landscape and challenges ahead. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.L.; Tome, W.A.; Caine, C.; Corn, B.; Kanner, A.; Rowley, H.; Kundapur, V.; DeNittis, A.; Greenspoon, J.N.; et al. Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): A phase II multi-institutional trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3810–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, J.C.; Herskovic, A.M.; Gielda, B.T.; Hughes, F.F.; Hoeppner, T.; Turian, J.; Abrams, R.A. Intracranial metastatic disease spares the limbic circuit: A review of 697 metastatic lesions in 107 patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayenbuehl, J.; Di Martino, M.; Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N. Improved plan quality with automated radiotherapy planning for whole brain with hippocampus sparing: A comparison to the RTOG 0933 trial. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, A.; Sun, W.; Zhao, F.; Wu, Z.; Shang, D.; Yu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; Yang, F.; Yuan, S. Dosimetric evaluation of four whole brain radiation therapy approaches with hippocampus and inner ear avoidance and simultaneous integrated boost for limited brain metastases. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlesi, F.; Gervais, R.; Lena, H.; Hureaux, J.; Berard, H.; Paillotin, D.; Bota, S.; Monnet, I.; Chajara, A.; Robinet, G. Pemetrexed and cisplatin as first-line chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with asymptomatic inoperable brain metastases: A multicenter phase II trial (GFPC 07-01). Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2011, 22, 2466–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zou, P.; Wang, Y.; Xiu, C.; Zhang, H.; Chi, N.; Zou, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, S.; et al. Phase II Study of High-Dose Pemetrexed Plus Cisplatin as First-Line Chemotherapy In the Treatment of Patients with Brain Metastases from Lung Adenocarcinoma. World Neurosurg. 2017, 99, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Qin, Q.; Jinglong, S.; Dan, H.; Zhongtang, W.; Junjie, T.; Baosheng, L.; Shian-Ying, S. Brain Radiotherapy plus Concurrent Temozolomide versus Radiotherapy Alone for Patients with Brain Metastases: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150419. [Google Scholar]
- Rotow, J.; Bivona, T.G. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 4), iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, C.; Sugimoto, M.; Wakita, D.; Monnai, M.; Ishimaru, C.; Nakamura, R.; Kinoshita, M.; Yorozu, K.; Kurasawa, M.; Kondoh, O.; et al. Bevacizumab suppresses the growth of established non-small-cell lung cancer brain metastases in a hematogenous brain metastasis model. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2020, 37, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Braganca, K.C.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Azzoli, C.G.; Kris, M.G.; Pietanza, M.C.; Nolan, C.P.; Omuro, A.M.; Holodny, A.I.; Lassman, A.B. Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in active brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2010, 100, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schettino, C.; Bareschino, M.A.; Rossi, A.; Maione, P.; Sacco, P.C.; Colantuoni, G.; Rossi, E.; Gridelli, C. Targeting angiogenesis for treatment of NSCLC brain metastases. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2012, 12, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C.; Qin, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren-Heidenreich, L.; Shi, B.; Ren, H.; Chu, X.; et al. Coexistence of EGFR with KRAS, or BRAF, or PIK3CA somatic mutations in lung cancer: A comprehensive mutation profiling from 5125 Chinese cohorts. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2812–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Zhao, T.T.; Xu, H.M.; Wang, Z.N.; Xu, Y.Y.; Han, Y.; Song, Y.X.; Wu, J.H.; Xu, H.; Yin, S.C.; et al. The role of EGFR mutation as a prognostic factor in survival after diagnosis of brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, A.F.; Kahle, K.T.; Wang, D.L.; Joshi, V.A.; Willers, H.; Engelman, J.A.; Lynch, T.J.; Sequist, L.V. EGFR mutation status and survival after diagnosis of brain metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Neuro-Oncology 2010, 12, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.J.; Zhou, C.; Huang, Y.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Song, Y.; Huang, C.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Icotinib versus whole-brain irradiation in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer and multiple brain metastases (BRAIN): A multicentre, phase 3, open-label, parallel, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, J.; Okuma, Y.; Miwa, M.; Hosomi, Y. Survival of patients with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations treated with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, A.; Li, Z.; Jia, J. Icotinib is as efficacious as gefitinib for brain metastasis of EGFR mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Li, J. Second-generation EGFR and ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitors as first-line treatments for non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 6535–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.; Wu, Y.L.; Hirsh, V.; O’Byrne, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Mok, T.; Popat, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Massey, D.; Zazulina, V.; et al. First-Line Afatinib versus Chemotherapy in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Common Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutations and Brain Metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shriyan, B.; Patil, D.; Gurjar, M.; Nookala, M.; Patil, A.; Kannan, S.; Patil, V.; Joshi, A.; Noronha, V.; Prabhash, K.; et al. Safety and CSF distribution of high-dose erlotinib and gefitinib in patients of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with brain metastases. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 76, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.E.; Rodriguez-Cruz, V.; Felmlee, M.A. SLC and ABC Transporters: Expression, Localization, and Species Differences at the Blood-Brain and the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barriers. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; Oxnard, G.R.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Pao, W.; Holodny, A.I.; Clarke, J.L.; Lassman, A.B. “Pulsatile” high-dose weekly erlotinib for CNS metastases from EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, J.L.; Pao, W.; Wu, N.; Miller, V.A.; Lassman, A.B. High dose weekly erlotinib achieves therapeutic concentrations in CSF and is effective in leptomeningeal metastases from epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung cancer. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2010, 99, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhruva, N.; Socinski, M.A. Carcinomatous meningitis in non-small-cell lung cancer: Response to high-dose erlotinib. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, e31–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Kiura, K.; Ueoka, H.; Tabata, M.; Fujiwara, K.; Kozuki, T.; Okada, T.; Hisamoto, A.; Tanimoto, M. Effect of gefitinib (‘Iressa’, ZD1839) on brain metastases in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2004, 46, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colclough, N.; Chen, K.; Johnström, P.; Strittmatter, N.; Yan, Y.; Wrigley, G.L.; Schou, M.; Goodwin, R.; Varnäs, K.; Adua, S.J.; et al. Preclinical Comparison of the Blood-brain barrier Permeability of Osimertinib with Other EGFR TKIs. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Cho, B.C.; Cobo Dols, M.A.; Cho, E.K.; Bertolini, A.; Bohnet, S.; Zhou, C.; Lee, K.H.; et al. CNS response to osimertinib vs standard of care (SoC) EGFR-TKI as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with EGFR-TKI sensitising mutation (EGFRm)-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Data from the FLAURA study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2017, 28, x189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Cho, B.C.; Cobo, M.; Cho, E.K.; Bertolini, A.; Bohnet, S.; Zhou, C.; Lee, K.H.; Nogami, N.; et al. CNS Response to Osimertinib Versus Standard Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients With Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.; Gray, J.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. EGFROverall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, -Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Choi, Y.L.; Han, J.; Park, S.; Ahn, M.J. Osimertinib improves overall survival in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal metastases regardless of T790M mutational status. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhong, D. Simultaneous determination of alflutinib and its active metabolite in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 176, 112735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S.; Lv, D.; Wu, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and genetic analysis of furmonertinib (AST2818) in patients with EGFR T790M mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase 2b, multicentre, single-arm, open-label study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Feng, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yang, N.; Wu, L.; Liao, W.; Zhong, D.; et al. Safety, Clinical Activity, and Pharmacokinetics of Alflutinib (AST2818) in Patients With Advanced NSCLC With EGFR T790M Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwak, E.L.; Bang, Y.J.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.; Maki, R.G.; Ou, S.H.; Dezube, B.J.; Jänne, P.A.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rangachari, D.; Yamaguchi, N.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Folch, E.; Mahadevan, A.; Floyd, S.R.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Wong, E.T.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Huberman, M.S.; et al. Brain metastases in patients with EGFR-mutated or ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metro, G.; Lunardi, G.; Floridi, P.; Pascali, J.P.; Marcomigni, L.; Chiari, R.; Ludovini, V.; Crinò, L.; Gori, S. CSF Concentration of Crizotinib in Two ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with CNS Metastases Deriving Clinical Benefit from Treatment. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2015, 10, e26–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.B.; Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.H.; Solomon, B.J.; Riely, G.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Zhou, C.; Shreeve, S.M.; Selaru, P.; Polli, A.; et al. Clinical Experience With Crizotinib in Patients With Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gourd, E. Alectinib shows CNS efficacy in ALK-positive NSCLC. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Nokihara, H.; Kondo, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Azuma, K.; Seto, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Yoshioka, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, S.; Mazières, J.; Oh, I.J.; de Castro, J.; Migliorino, M.R.; Helland, Å.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Griesinger, F.; Kotb, A.; Zeaiter, A.; et al. Alectinib versus chemotherapy in crizotinib-pretreated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from the phase III ALUR study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Pérol, M.; Wrona, A.; Novello, S.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in treatment-naive anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive (ALK+) non-small-cell lung cancer: CNS efficacy results from the ALEX study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Shaw, A.T.; Govindan, R.; Gandhi, L.; Socinski, M.A.; Camidge, D.R.; De Petris, L.; Kim, D.W.; Chiappori, A.; Moro-Sibilot, D.L.; et al. Pooled Analysis of CNS Response to Alectinib in Two Studies of Pretreated Patients With ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4079–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Tanaka, T.; Kuriki, H.; Zeaiter, A.; Tamura, T. Analysis of central nervous system efficacy in the J-ALEX study of alectinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 121, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, D.W.; Tiseo, M.; Langer, C.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Shaw, A.T.; Huber, R.M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Lee, D.H.; Bazhenova, L.A.; et al. Exploratory Analysis of Brigatinib Activity in Patients With Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases in Two Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, T.M.; Crinò, L.; Gridelli, C.; Kiura, K.; Liu, G.; Novello, S.; Bearz, A.; Gautschi, O.; Mok, T.; et al. Ceritinib versus chemotherapy in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer previously given chemotherapy and crizotinib (ASCEND-5): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crinò, L.; Ahn, M.J.; De Marinis, F.; Groen, H.J.; Wakelee, H.; Hida, T.; Mok, T.; Spigel, D.; Felip, E.; Nishio, M.; et al. Multicenter Phase II Study of Whole-Body and Intracranial Activity With Ceritinib in Patients With ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Previously Treated With Chemotherapy and Crizotinib: Results From ASCEND-2. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2866–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Felip, E.; Bauer, T.M.; Besse, B.; Navarro, A.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Gainor, J.F.; Johnson, M.; Dietrich, J.; James, L.P.; et al. Lorlatinib in non-small-cell lung cancer with ALK or ROS1 rearrangement: An international, multicentre, open-label, single-arm first-in-man phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johung, K.L.; Yeh, N.; Desai, N.B.; Williams, T.M.; Lautenschlaeger, T.; Arvold, N.D.; Ning, M.S.; Attia, A.; Lovly, C.M.; Goldberg, S.; et al. Extended Survival and Prognostic Factors for Patients With ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Soo, R.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Chiari, R.; Bearz, A.; Lin, C.C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, R. Effectiveness and Safety of Adding Bevacizumab to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 616380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagstaff, A.; Keam, S.; McCormack, P. Bevacizumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy: In advanced non-small cell lung cancer. BioDrugs Clin. Immunother. Biopharm. Gene Ther. 2009, 23, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Hu, J.; Du, N.; Jiao, S.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Zhao, H.; Kang, H. Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for preventing brain metastasis derived from advanced lung cancer. J. Chemother. 2016, 28, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Greater efficacy of chemotherapy plus bevacizumab compared to chemo- and targeted therapy alone on non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3635–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azelby, C.; Sakamoto, M.; Bowles, D. ROS1 Targeted Therapies: Current Status. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazières, J.; Barlesi, F.; Filleron, T.; Besse, B.; Monnet, I.; Beau-Faller, M.; Peters, S.; Dansin, E.; Früh, M.; Pless, M.; et al. Lung cancer patients with HER2 mutations treated with chemotherapy and HER2-targeted drugs: Results from the European EUHER2 cohort. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2016, 27, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Oxnard, G.R.; Jackman, D.M.; Savukoski, D.O.; Hall, D.; Shivdasani, P.; Heng, J.C.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Jänne, P.A.; Verma, S.; et al. MET Exon 14 Mutations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Are Associated With Advanced Age and Stage-Dependent MET Genomic Amplification and c-Met Overexpression. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taggart, D.; Andreou, T.; Scott, K.J.; Williams, J.; Rippaus, N.; Brownlie, R.J.; Ilett, E.J.; Salmond, R.J.; Melcher, A.; Lorger, M. Anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4 efficacy in melanoma brain metastases depends on extracranial disease and augmentation of CD8(+) T cell trafficking. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1540–E1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendriks, L.E.L.; Henon, C.; Auclin, E.; Mezquita, L.; Ferrara, R.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Mazieres, J.; Lefebvre, C.; Rabeau, A.; Le Moulec, S.; et al. Outcome of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases Treated with Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2019, 14, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.W.; Felip, E.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.B.; Schalper, K.A.; Gettinger, S.N.; Mahajan, A.; Herbst, R.S.; Chiang, A.C.; Lilenbaum, R.; Wilson, F.H.; Omay, S.B.; Yu, J.B.; et al. Pembrolizumab for management of patients with NSCLC and brain metastases: Long-term results and biomarker analysis from a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, C.J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Borghaei, H.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Patnaik, A.; Powell, S.F.; Gentzler, R.D.; Martins, R.G.; Stevenson, J.P.; Jalal, S.I.; et al. Carboplatin and pemetrexed with or without pembrolizumab for advanced, non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: A randomised, phase 2 cohort of the open-label KEYNOTE-021 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ott, P.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Razak, A.R.A.; Bennouna, J.; Soria, J.C.; Rugo, H.S.; Cohen, R.B.; O’Neil, B.H.; Mehnert, J.M.; et al. T-Cell-Inflamed Gene-Expression Profile, Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression, and Tumor Mutational Burden Predict Efficacy in Patients Treated With Pembrolizumab Across 20 Cancers: KEYNOTE-028. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Mazières, J.; Planchard, D.; Stinchcombe, T.E.; Dy, G.K.; Antonia, S.J.; Horn, L.; Lena, H.; Minenza, E.; Mennecier, B.; et al. Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): A phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Rizvi, N.A.; Goldman, J.W.; Gettinger, S.N.; Borghaei, H.; Brahmer, J.R.; Ready, N.E.; Gerber, D.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Juergens, R.A.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 012): Results of an open-label, phase 1, multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gettinger, S.; Rizvi, N.A.; Chow, L.Q.; Borghaei, H.; Brahmer, J.; Ready, N.; Gerber, D.E.; Shepherd, F.A.; Antonia, S.; Goldman, J.W.; et al. Nivolumab Monotherapy for First-Line Treatment of Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2980–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Brahmer, J.R.; Juergens, R.A.; Borghaei, H.; Gettinger, S.; Chow, L.Q.; Gerber, D.E.; Laurie, S.A.; Goldman, J.W.; et al. Nivolumab in Combination With Platinum-Based Doublet Chemotherapy for First-Line Treatment of Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2969–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Chaft, J.E.; Gettinger, S.; Chao, B.H.; Dirix, L.; Schmid, P.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Hicks, R.J.; Leon, L.; Fredrickson, J.; et al. FIR: Efficacy, Safety, and Biomarker Analysis of a Phase II Open-Label Study of Atezolizumab in PD-L1-Selected Patients with NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2018, 13, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalabi, M.; Cardona, A.; Nagarkar, D.R.; Dhawahir Scala, A.; Gandara, D.R.; Rittmeyer, A.; Albert, M.L.; Powles, T.; Kok, M.; Herrera, F.G. Efficacy of chemotherapy and atezolizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer receiving antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors: Pooled post hoc analyses of the OAK and POPLAR trials. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2020, 31, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Socinski, M.A.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.A.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jotte, R.; Cappuzzo, F.; Vynnychenko, I.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Hussein, M.; Soo, R.; Conter, H.J.; Kozuki, T.; Huang, K.C.; et al. Atezolizumab in Combination With Carboplatin and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Squamous NSCLC (IMpower131): Results From a Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2020, 15, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Kurata, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Overall Survival with Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.J.; Balmanoukian, A.; Brahmer, J.; Ou, S.I.; Hellmann, M.D.; Kim, S.W.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Gutierrez, M.; Liu, S.V.; et al. Clinical Activity, Tolerability, and Long-Term Follow-Up of Durvalumab in Patients With Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2019, 14, 1794–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garassino, M.C.; Cho, B.C.; Kim, J.H.; Mazières, J.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Lena, H.; Jaime, J.C.; Gray, J.E.; Powderly, J.; Chouaid, C.; et al. Final overall survival and safety update for durvalumab in third- or later-line advanced NSCLC: The phase II ATLANTIC study. Lung Cancer 2020, 147, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Shepherd, F.A.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, G.W.; Lee, J.S.; Chang, G.C.; Lee, S.S.; Wei, Y.F.; Lee, Y.G.; Laus, G.; et al. Osimertinib Plus Durvalumab versus Osimertinib Monotherapy in EGFR T790M-Positive NSCLC following Previous EGFR TKI Therapy: CAURAL Brief Report. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2019, 14, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Yang, J.C.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.W.; Saka, H.; Horn, L.; Goto, K.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Thress, K.S.; et al. TATTON: A multi-arm, phase Ib trial of osimertinib combined with selumetinib, savolitinib, or durvalumab in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2020, 31, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonia, S.; Goldberg, S.B.; Balmanoukian, A.; Chaft, J.E.; Sanborn, R.E.; Gupta, A.; Narwal, R.; Steele, K.; Gu, Y.; Karakunnel, J.J.; et al. Safety and antitumour activity of durvalumab plus tremelimumab in non-small cell lung cancer: A multicentre, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planchard, D.; Reinmuth, N.; Orlov, S.; Fischer, J.R.; Sugawara, S.; Mandziuk, S.; Marquez-Medina, D.; Novello, S.; Takeda, Y.; Soo, R.; et al. ARCTIC: Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab as third-line or later treatment of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2020, 31, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juergens, R.A.; Hao, D.; Ellis, P.M.; Tu, D.; Mates, M.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Bradbury, P.A.; Tehfe, M.; Wheatley-Price, P.; Robinson, A.; et al. A phase IB study of durvalumab with or without tremelimumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy in advanced solid tumours: Canadian Cancer Trials Group Study IND226. Lung Cancer 2020, 143, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, C.; Xie, F.; Liu, Y. Use of Programmed Death Receptor-1 and/or Programmed Death Ligand 1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Brain Metastasis of Lung Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, S.B.; Gettinger, S.N.; Mahajan, A.; Chiang, A.C.; Herbst, R.S.; Sznol, M.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Cohen, J.; Vortmeyer, A.; Jilaveanu, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with melanoma or non-small-cell lung cancer and untreated brain metastases: Early analysis of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldman, J.W.; Crino, L.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; Brahmer, J.R. Nivolumab (nivo) in patients (pts) with advanced (adv) NSCLC and central nervous system (CNS) metastases (mets). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 9038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinovis, D.; Delmonte, A.; Chiari, R.; Catino, A.; Grossi, F.; Noberasco, C.; Gelsomino, F.; Gilli, M.; Proto, C.; Parra, H.; et al. P3.02c-094 Italian Nivolumab Advanced Squamous NSCLC Expanded Access Program: Efficacy and Safety in Patients with Brain Metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Lukas, R.V.; Goldschmidt, J.; Conkling, P.; Park, K.; Cortinovis, D.; de Marinis, F.; Rittmeyer, A.; Patel, J.D.; von Pawel, J.; et al. Atezolizumab in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and history of asymptomatic, treated brain metastases: Exploratory analyses of the phase III OAK study. Lung Cancer 2019, 128, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, M.Z.; Dragnev, K.; Shirai, K. A tertiary care cancer center experience with carboplatin and pemetrexed in combination with pembrolizumab in comparison with carboplatin and pemetrexed alone in non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3575–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadgeel, S.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Speranza, G.; Esteban, E.; Felip, E.; Dómine, M.; Hui, R.; Hochmair, M.J.; Clingan, P.; Powell, S.F.; et al. Updated Analysis From KEYNOTE-189: Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Pemetrexed and Platinum for Previously Untreated Metastatic Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, S.; Nomura, R.; Sato, K.; Awano, N.; Kuse, N.; Inomata, M.; Izumo, T.; Terada, Y.; Furuhata, Y.; Bae, Y.; et al. Nivolumab and stereotactic radiation therapy for the treatment of patients with Stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Douglass, J.; Kleinberg, L.; Ye, X.; Marciscano, A.E.; Forde, P.M.; Brahmer, J.; Lipson, E.; Sharfman, W.; Hammers, H. Concurrent Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Melanoma, and Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.A.; Kim, S.; Arrington, J.; Naghavi, A.O.; Dilling, T.J.; Creelan, B.C.; Antonia, S.J.; Caudell, J.J.; Harrison, L.B.; Sahebjam, S.; et al. Outcomes targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in conjunction with stereotactic radiation for patients with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 133, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, M.J.; Xu, Z.; Donahue, J.; Eluvathingal Muttikkal, T.J.; Cordeiro, D.; Hansen, L.; Mohammed, N.; Gentzler, R.D.; Larner, J.; Fadul, C.E.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery with and without checkpoint inhibition for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer to the brain: A matched cohort study. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.M.; Cagney, D.N.; Catalano, P.J.; Alexander, B.M.; Redig, A.J.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Aizer, A.A. Immunotherapy and Symptomatic Radiation Necrosis in Patients With Brain Metastases Treated With Stereotactic Radiation. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, Y.; Masago, K.; Masuda, S.; Mizuno, T.; Fukudo, M.; Ikemi, Y.; Sakamori, Y.; Nagai, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Katsura, T.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 70, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nosaki, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Hamada, A.; Shiraishi, Y.; Harada, T.; Himeji, D.; Kitazaki, T.; Ebi, N.; Shimose, T.; Seto, T.; et al. Erlotinib for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Leptomeningeal Metastases: A Phase II Study (LOGIK1101). Oncologist 2020, 25, e1869–e1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamiyam, A.; Tamiya, M.; Nishihara, T.; Shiroyama, T.; Nakao, K.; Tsuji, T.; Takeuchi, N.; Isa, S.; Omachi, N.; Okamoto, N.; et al. OA08.05 Efficacy and Cerebrospinal Fluid Concentration of Afatinib in NSCLC Patients with EGFR Mutation Developing Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2017, 12, S273. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Cho, B.C.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; Su, W.-C.; John, T.; Kao, S.C.-H.; Natale, R.; Goldman, J.W.; et al. Osimertinib for patients (pts) with leptomeningeal metastases (LM) from EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Updated results from the BLOOM study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjo, S.; Hata, A.; Okuda, C.; Kaji, R.; Okada, H.; Tamura, D.; Irie, K.; Okada, H.; Fukushima, S.; Katakami, N. Standard-dose osimertinib for refractory leptomeningeal metastases in T790M-positive EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, T.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Ratnayake, J.; Carlie, D.J.; Yin, X.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.C.-H. Phase I study of AZD3759, a CNS penetrable EGFR inhibitor, for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with brain metastasis (BM) and leptomeningeal metastasis (LM). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Mehra, R.; Tan, D.; Felip, E.; Chow, L.; Camidge, D.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Sharma, S.; De Pas, T.; Riely, G.; et al. Activity and safety of ceritinib in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-1): Updated results from the multicentre, open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, I.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Palmer, J.D.; Mehra, R.; Lu, B. Targeting brain metastases in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e510–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.; Gandhi, L.; Riely, G.; Chiappori, A.; West, H.; Azada, M.; Morcos, P.; Lee, R.; Garcia, L.; Yu, L.; et al. Safety and activity of alectinib against systemic disease and brain metastases in patients with crizotinib-resistant ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-002JG): Results from the dose-finding portion of a phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takanashi, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Kondoh, O.; Sakamoto, H. Antitumor activity of the selective ALK inhibitor alectinib in models of intracranial metastases. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Besse, B.; James, L.P.; Clancy, J.S.; Klamerus, K.J.; Martini, J.-F.; Abbattista, A.; Shaw, A.T. Safety and efficacy of lorlatinib (PF-06463922) from the dose-escalation component of a study in patients with advanced ALK+ or ROS1+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoach, C.E.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Zhang, L.; Myers, A.; Tang, S.; Sridhara, R.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R.; Doebele, R.C.; Kazandjian, D. Exploratory analysis of the association of depth of response and survival in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer treated with a targeted therapy or immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wujanto, C.; Vellayappan, B.; Siva, S.; Louie, A.V.; Guckenberger, M.; Slotman, B.J.; Onishi, H.; Nagata, Y.; Liu, M.; Lo, S.S. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Disease in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Yang, T.J.; Beal, K.; Pan, H.; Brown, P.D.; Bangdiwala, A.; Shanley, R.; Yeh, N.; Gaspar, L.E.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Estimating Survival in Patients With Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases: An Update of the Graded Prognostic Assessment for Lung Cancer Using Molecular Markers (Lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Su, P.L.; Yang, S.C.; Lin, C.C.; Su, W.C. The impact of EGFR mutations on the incidence and survival of stages I to III NSCLC patients with subsequent brain metastasis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Bian, Y.; Wu, C.C.; Saraf, A.; Tai, C.H.; Nanda, T.; Yaeh, A.; Lapa, M.E.; Andrews, J.I.S.; Cheng, S.K.; et al. Natural history, clinical course and predictors of interval time from initial diagnosis to development of subsequent NSCLC brain metastases. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2019, 143, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhangoo, S.; Linskey, M.; Kalkanis, S. Evidence-based guidelines for the management of brain metastases. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 22, 97–104, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.K.; Yu, W.S.; Byun, G.E.; Lee, C.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, D.J.; Chung, K.Y. Prognostic factors for cases with no extracranial metastasis in whom brain metastasis is detected after resection of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, C.; Wang, R.; Lu, C.; Sun, Z.; Li, P.; Yin, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Prognostic factors and outcome of surgically treated patients with brain metastases of non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pojskic, M.; Bopp, M.H.A.; Schymalla, M.; Nimsky, C.; Carl, B. Retrospective study of 229 surgically treated patients with brain metastases: Prognostic factors, outcome and comparison of recursive partitioning analysis and diagnosis-specific graded prognostic assessment. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2017, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Trials/NCT Numbers | Drugs | Phase | Sample Size | OS (Months) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEYNOTE-001/NCT01295827 | Pembrolizumab | I | 1260 | 12 | [107] |
| KEYNOTE-010/NCT01905657 | Pembrolizumab | II–III | 1034 | 11.8 | [108] |
| IND-121564/NCT02085070 | Pembrolizumab | II | 65 | 7.7 | [109] |
| KEYNOTE-021/NCT02039674 | Pembrolizumab | I–II | 267 | 16.7 | [110] |
| Pembrolizumab combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel | 21.4 | ||||
| Pembrolizumab combined with carboplatin, paclitaxel, and bevacizumab | 16.7 | ||||
| Pembrolizumab combined with carboplatin and pemetrexed | 16.7 | ||||
| KEYNOTE-024/NCT02142738 | Pembrolizumab | III | 305 | 30 | [111] |
| KEYNOTE-028/NCT02054806 | Pembrolizumab | I | 477 | 11.3 | [112] |
| CheckMate-017/NCT01642004 | Nivolumab | III | 352 | 9.2 | [113] |
| CheckMate-057/NCT01673867 | Nivolumab | III | 792 | 12.2 | [114] |
| CheckMate-063/NCT01721759 | Nivolumab | II | 140 | 8.2 | [115] |
| CheckMate-227/NCT02477826 | Nivolumab plus ipilimumab | III | 2220 | 17.1 | [116] |
| CheckMate-012/NCT01454102 | Nivolumab plus erlotinib | I | 472 | 19.2 | [117,118,119] |
| Nivolumab | 19.4 | ||||
| FIR/NCT01846416 | Atezolizumab | II | 138 | 6.3 | [120] |
| OAK/NCT02008227 | Atezolizumab | III | 1225 | 13.8 | [121] |
| POPLAR/NCT01903993 | Atezolizumab | III | 287 | 12.6 | [122] |
| IMpower150/NCT02366143 | Atezolizumab combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel | III | 1202 | 14.4 | [123] |
| Atezolizumab combined with bevacizumab, carboplatin, and paclitaxel | 19.2 | ||||
| IMPower-131/NCT02367794 | Atezolizumab combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel | III | 1021 | 14 | [124] |
| PACIFIC/NCT02125461 | Durvalumab | III | 713 | 28.3 | [125] |
| Study 1108/NCT01693562 | Durvalumab | I-II | 1022 | 12.4 | [126] |
| ATLANTIC/NCT02087423 | Durvalumab | II | 446 | 13.2 | [127] |
| CAURAL/NCT02454933 | Durvalumab and osimertinib | III | 29 | Not reported | [128] |
| TATTON/NCT02143466 | Durvalumab and osimertinib | I | 344 | Not reported | [129] |
| NCT02000947 | Durvalumab and tremelimumab | I | 459 | Not reported | [130] |
| ARCTIC/NCT02352948 | Durvalumab | II | 597 | 11.7 | [131] |
| Durvalumab and tremelimumab | 11.5 | ||||
| IND226/NCT02537418 | Durvalumab | I | 153 | 19.8 | [132] |
| Drug Name | Cerebrospinal Fluid Concentration | Cerebrospinal Penetration Rate | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR-targeted therapies | |||
| Erlotinib | 28.7 ng/mL (66.9 nM) | 2.8–3.3% | [145,146] |
| Gefitinib | 3.7 ng/mL (8.2 nM) | 1.13% | [145] |
| Afatinib | 1.4 ng/mL (2.9 nM); 1 nM | 1.65% | [147] |
| Osimertinib | 7.51 nM | 2.5–16% | [148,149] |
| AZD3759 | 25.2 nM | 100% | [150] |
| ALK-targeted therapies | |||
| Crizotinib | 0.616 ng/mL (0.14 nM) | 0.26% | [84] |
| Ceritinib | No data | 15% | [151,152] |
| Alectinib | 2.69 nM | 63–94% | [153,154] |
| Lorlatinib | 2.64–125 ng/mL (6.5–308 nM) | 20–96% | [95,152,155] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Guo, H.; Xu, H.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G. Research Progress and Challenges in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102620
Wang B, Guo H, Xu H, Yu H, Chen Y, Zhao G. Research Progress and Challenges in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102620
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bin, Hanfei Guo, Haiyang Xu, Hongquan Yu, Yong Chen, and Gang Zhao. 2021. "Research Progress and Challenges in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Cells 10, no. 10: 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102620
APA StyleWang, B., Guo, H., Xu, H., Yu, H., Chen, Y., & Zhao, G. (2021). Research Progress and Challenges in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cells, 10(10), 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102620






