Profiling of Serum Metabolites of Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Asymptomatic HMBS Mutation Carriers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design, Setting, and Participants
2.2. Metabolite Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
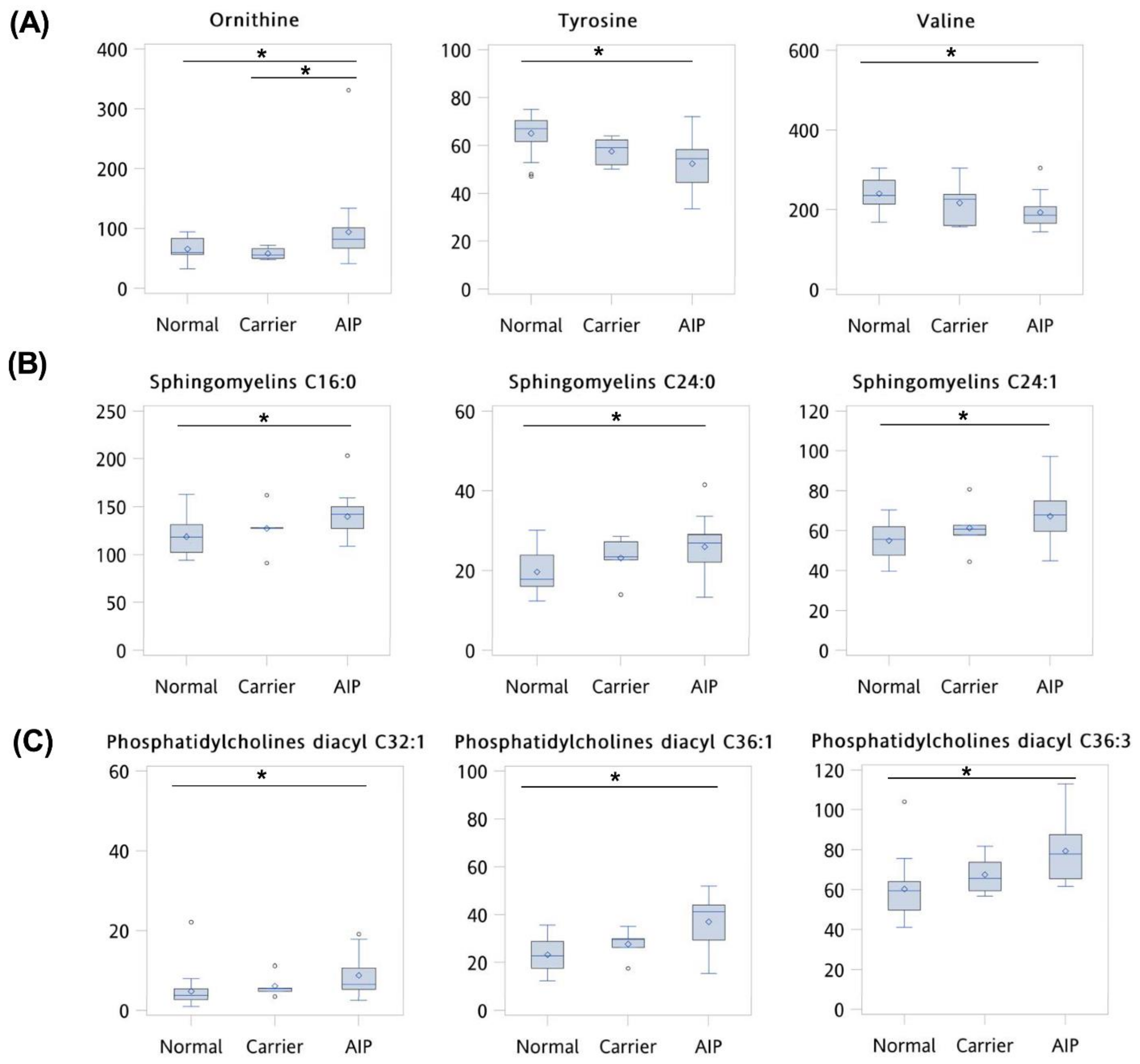
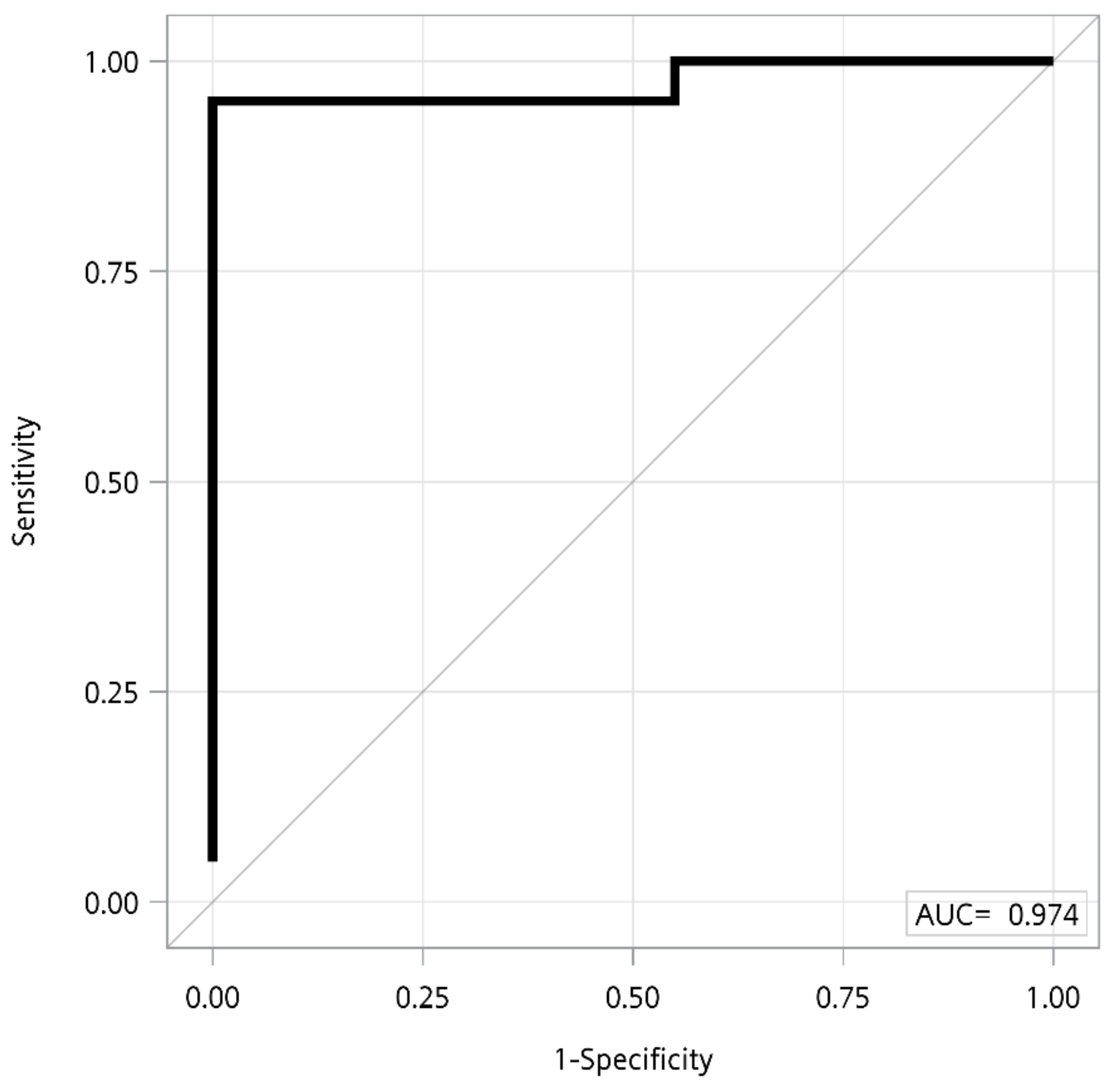
3.2. Comparison of Clinical Variables and Metabolite Levels between Normal, Asymptomatic Carriers, and AIP Patients
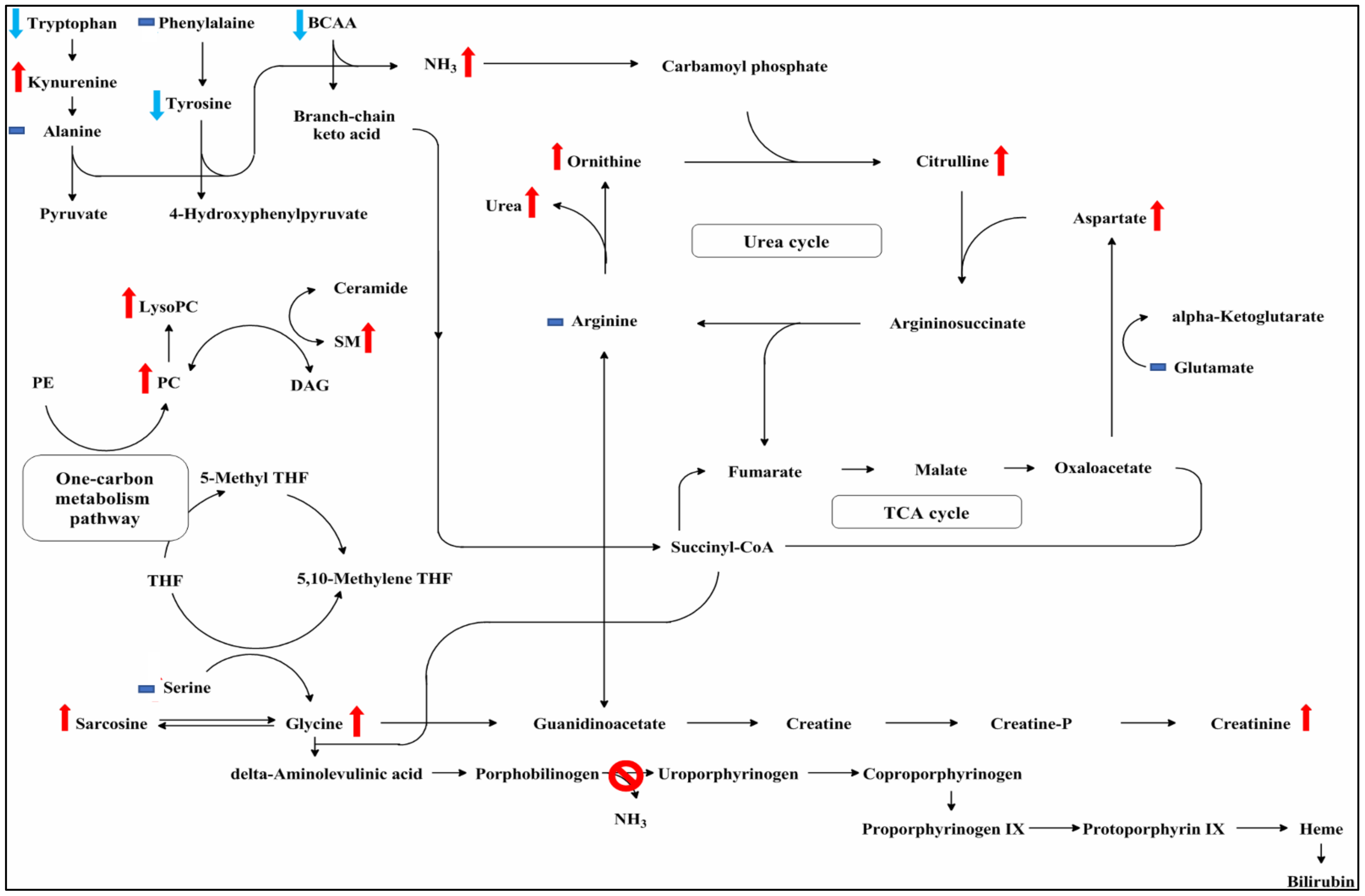
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gill, R.; Kolstoe, S.E.; Mohammed, F.; Al, D.B.A.; Mosely, J.E.; Sarwar, M.; Cooper, J.B.; Wood, S.P.; Shoolingin-Jordan, P.M. Structure of human porphobilinogen deaminase at 2.8 A: The molecular basis of acute intermittent porphyria. Biochem. J. 2009, 420, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Solis-Villa, C.; Erwin, A.L.; Balwani, M.; Nazarenko, I.; Phillips, J.D.; Desnick, R.J.; Yasuda, M. Identification and characterization of 40 novel hydroxymethylbilane synthase mutations that cause acute intermittent porphyria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, J.A.; Dyck, P.J. Porphyria and its neurologic manifestations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 120, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Jia, J.; Yue, L.; Yang, R.; Guo, Y.; Ni, X.; Shi, T. Systematically Analyzing the Pathogenic Variations for Acute Intermittent Porphyria. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, K.E.; Bloomer, J.R.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Kushner, J.P.; Pierach, C.A.; Pimstone, N.R.; Desnick, R.J. Recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of the acute porphyrias. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.E.; Badminton, M.N.; Rees, D.C. Update review of the acute porphyrias. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 176, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carichon, M.; Pallet, N.; Schmitt, C.; Lefebvre, T.; Gouya, L.; Talbi, N.; Deybach, J.C.; Beaune, P.; Vasos, P.; Puy, H.; et al. Urinary metabolic fingerprint of acute intermittent porphyria analyzed by (1)H NMR spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, M.; Schmitt, C.; Talbi, N.; Gouya, L.; Caradeuc, C.; Puy, H.; Bertho, G.; Pallet, N. Urinary metabolic profiling of asymptomatic acute intermittent porphyria using a rule-mining-based algorithm. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semba, R.D.; Gonzalez-Freire, M.; Moaddel, R.; Sun, K.; Fabbri, E.; Zhang, P.; Carlson, O.D.; Khadeer, M.; Chia, C.W.; Salem, N., Jr.; et al. Altered Plasma Amino Acids and Lipids Associated with Abnormal Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Resistance in Older Adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3331–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Cheng, J.; Fan, C.; Shi, X.; Cao, Y.; Sun, B.; Ding, H.; Hu, C.; Dong, F.; Yan, X. Serum Metabolomics to Identify the Liver Disease-Specific Biomarkers for the Progression of Hepatitis to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darshi, M.; Van Espen, B.; Sharma, K. Metabolomics in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Unraveling the Biochemistry of a Silent Killer. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 44, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, G.; Marcos, J.; Pozo, O.J.; Aguilera, P.; Herrero, C.; To-Figueras, J. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry profiling of steroids in urine of patients with acute intermittent porphyria. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holecek, M. Branched-chain amino acids in health and disease: Metabolism, alterations in blood plasma, and as supplements. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, J.E.; Funovics, J.M.; Aguirre, A.; James, J.H.; Keane, J.M.; Wesdorp, R.I.; Yoshimura, N.; Westman, T. The role of plasma amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy. Surgery 1975, 78, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dasarathy, S.; Hatzoglou, M. Hyperammonemia and proteostasis in cirrhosis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, A.; Nair, K.S. Assessment of branched-chain amino Acid status and potential for biomarkers. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 324S–330S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, U.A.; Schuurmans, M.M.; Lindberg, R.L. Acute porphyrias: Pathogenesis of neurological manifestations. Semin. Liver Dis. 1998, 18, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gomez, A.; Marcos, J.; Aguilera, P.; To-Figueras, J.; Pozo, O.J. Comprehensive analysis of the tryptophan metabolome in urine of patients with acute intermittent porphyria. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1060, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puy, H.; Deybach, J.C.; Baudry, P.; Callebert, J.; Touitou, Y.; Nordmann, Y. Decreased nocturnal plasma melatonin levels in patients with recurrent acute intermittent porphyria attacks. Life Sci. 1993, 53, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, C.; Bjersing, L.; Lithner, F. The epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with acute intermittent porphyria. J. Intern. Med. 1996, 240, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallet, N.; Mami, I.; Schmitt, C.; Karim, Z.; Francois, A.; Rabant, M.; Nochy, D.; Gouya, L.; Deybach, J.C.; Xu-Dubois, Y.; et al. High prevalence of and potential mechanisms for chronic kidney disease in patients with acute intermittent porphyria. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, M.; Erwin, A.L.; Liu, L.U.; Balwani, M.; Chen, B.; Kadirvel, S.; Gan, L.; Fiel, M.I.; Gordon, R.E.; Yu, C.; et al. Liver Transplantation for Acute Intermittent Porphyria: Biochemical and Pathologic Studies of the Explanted Liver. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, G. Glycine metabolism in animals and humans: Implications for nutrition and health. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhasly, S.; Naegeli, H.; Baumann, S.; von Bergen, M.; Luch, A.; Jungnickel, H.; Potratz, S.; Gerspach, C. Metabolomic biomarkers correlating with hepatic lipidosis in dairy cows. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goncharova, M.; Pshenichnikova, O.; Luchinina, Y.; Pustovoit, Y.; Karpova, I.; Surin, V. Molecular genetic study of acute intermittent porphyria in Russia: HMBS gene mutation spectrum and problem of penetrance. Clin. Genet. 2019, 96, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieger, C.; Geistlinger, L.; Altmaier, E.; Hrabe de Angelis, M.; Kronenberg, F.; Meitinger, T.; Mewes, H.W.; Wichmann, H.E.; Weinberger, K.M.; Adamski, J.; et al. Genetics meets metabolomics: A genome-wide association study of metabolite profiles in human serum. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Normal | Carrier | AIP | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 20 | N = 5 | N = 21 | ||
| Age (y) | 41 (34.50, 48.00) | 42 (29.00, 45.00) | 43 (34.00, 51.00) | 0.74 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.90 (20.50, 26.80) | 24.10 (22.90, 24.40) | 22.50 (19.50, 24.80) | 0.76 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 12.45 (10.75, 14.60) | 10.50 (10.50, 11.80) | 22.60 (18.40, 30.50) ठ| <0.0001 * |
| AST (U/L) | 21.00 (19.00, 22.00) | 23.00 (22.00, 25.00) | 28.00 (25.00, 30.00) ‡ | 0.0003 * |
| ALT (U/L) | 12.00 (11.00, 16.50) | 18.00 (14.00, 26.00) | 26.00 (19.00, 32.00) ‡ | 0.001 * |
| AC (mg/dL) | 86.50 (81.50, 96.50) | 90.00 (83.00, 90.00) | 88.00 (82.00, 91.00) | 0.98 |
| Hb-Alc (%) | 5.40 (5.20, 5.50) | 5.20 (5.10, 5.50) | 5.40 (5.00, 5.60) | 0.99 |
| T-CHOL (mg/dL) | 183.50 (156.00, 196.50) | 169.00 (161.00, 172.00) | 200.00 (184.00, 217.00) | 0.04 * |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 55.00 (48.50, 67.00) | 66.00 (58.00, 75.00) | 68.00 (60.00, 77.00) ‡ | 0.03 * |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 101.50 (85.00, 118.00) | 95.00 (85.00, 98.00) | 104.00 (100.00, 117.00) | 0.30 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 74.00 (63.00, 120.50) | 51.00 (47.00, 58.00) | 87.00 (68.00, 125.00) | 0.12 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.62 (0.54, 0.68) | 0.51 (0.47, 0.52) | 1.00 (0.80, 1.37) ठ| <0.0001 * |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 108.00 (91.00, 127.50) | 132.00 (127.00, 157.00) | 64.00 (42.00, 77.00) ठ| <0.0001 * |
| Variables (µM) | AUC | p | FDR | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier vs. AIP | |||||
| Blood urea nitrogen | 0.962 | 0.026 | 0.233 | 0.857 | 1.000 |
| Citrulline | 0.910 | 0.049 | 0.233 | 0.810 | 1.000 |
| Normal vs. AIP | |||||
| Blood urea nitrogen | 0.940 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.857 | 0.950 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 0.906 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.762 | 0.950 |
| AST | 0.849 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.810 | 0.850 |
| ALT | 0.838 | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.762 | 0.900 |
| Citrulline | 0.855 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.818 | 0.900 |
| Ornithine | 0.725 | 0.029 | 0.029 | 0.857 | 0.550 |
| Tyrosine | 0.855 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.952 | 0.750 |
| Valine | 0.818 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.810 | 0.750 |
| Sarcosine | 0.875 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.762 | 0.900 |
| Phosphatidylcholines diacyl C32:1 | 0.831 | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.905 | 0.750 |
| Phosphatidylcholines diacyl C36:1 | 0.833 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.619 | 1.000 |
| Phosphatidylcholines diacyl C36:3 | 0.863 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 1.000 | 0.650 |
| SM C16:0 | 0.777 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.714 | 0.750 |
| SM C24:0 | 0.786 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.667 | 0.900 |
| SM C24:1 | 0.788 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.476 | 1.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-N.; Shiao, M.-S.; Cheng, M.-L.; Chen, C.-M.; Kuo, H.-C. Profiling of Serum Metabolites of Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Asymptomatic HMBS Mutation Carriers. Cells 2021, 10, 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102579
Lin C-N, Shiao M-S, Cheng M-L, Chen C-M, Kuo H-C. Profiling of Serum Metabolites of Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Asymptomatic HMBS Mutation Carriers. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102579
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chia-Ni, Ming-Shi Shiao, Mei-Ling Cheng, Chiung-Mei Chen, and Hung-Chou Kuo. 2021. "Profiling of Serum Metabolites of Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Asymptomatic HMBS Mutation Carriers" Cells 10, no. 10: 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102579
APA StyleLin, C.-N., Shiao, M.-S., Cheng, M.-L., Chen, C.-M., & Kuo, H.-C. (2021). Profiling of Serum Metabolites of Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Asymptomatic HMBS Mutation Carriers. Cells, 10(10), 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102579







