Expression of CD38 in Mast Cells: Cytological and Histotopographic Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Selection
2.2. Tissue Probe Staining
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Assessment of CD38 Expression in the Mast Cell Population
3. Results
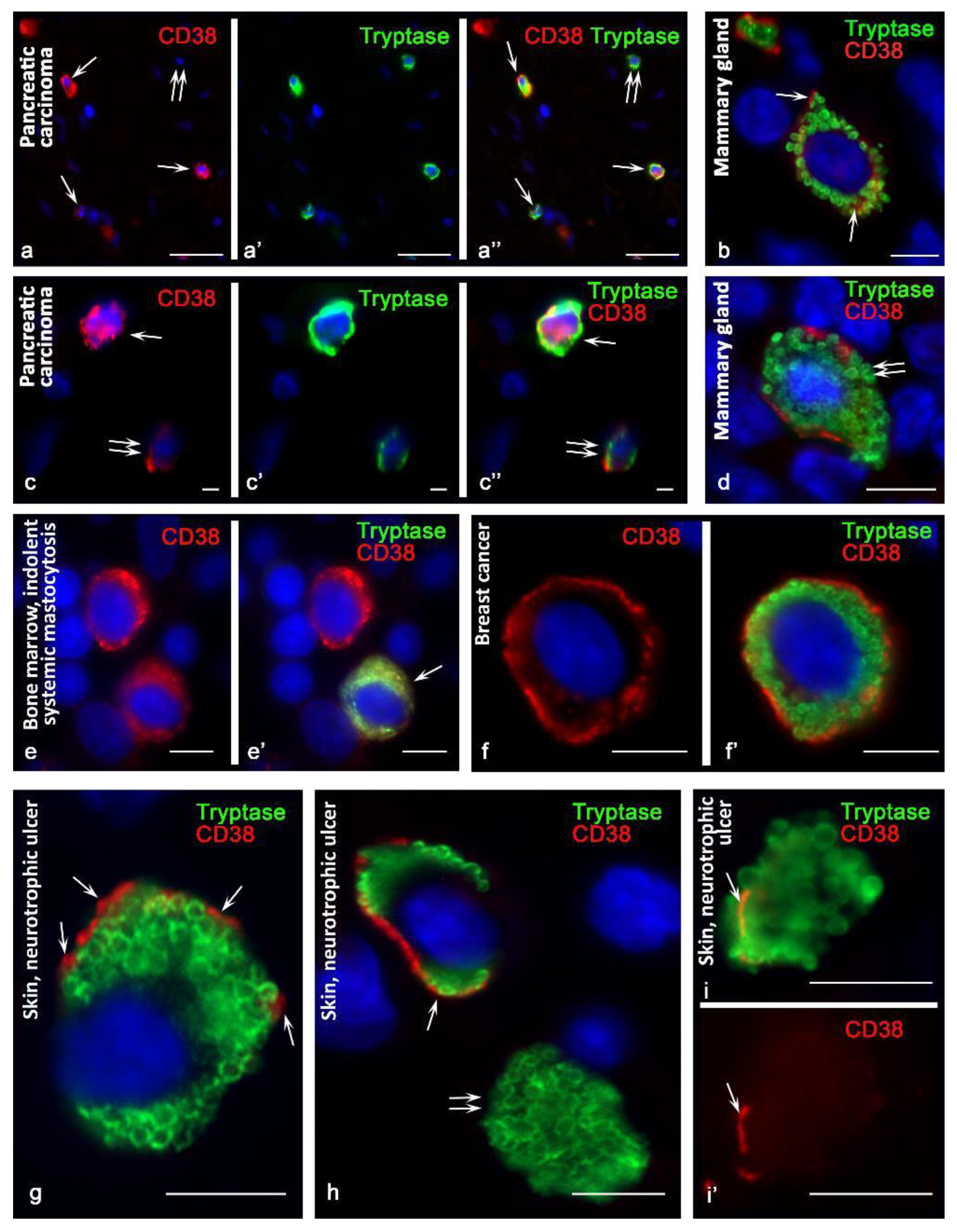
3.1. The Effectiveness of Antibodies in the Detection of CD38 in MCs
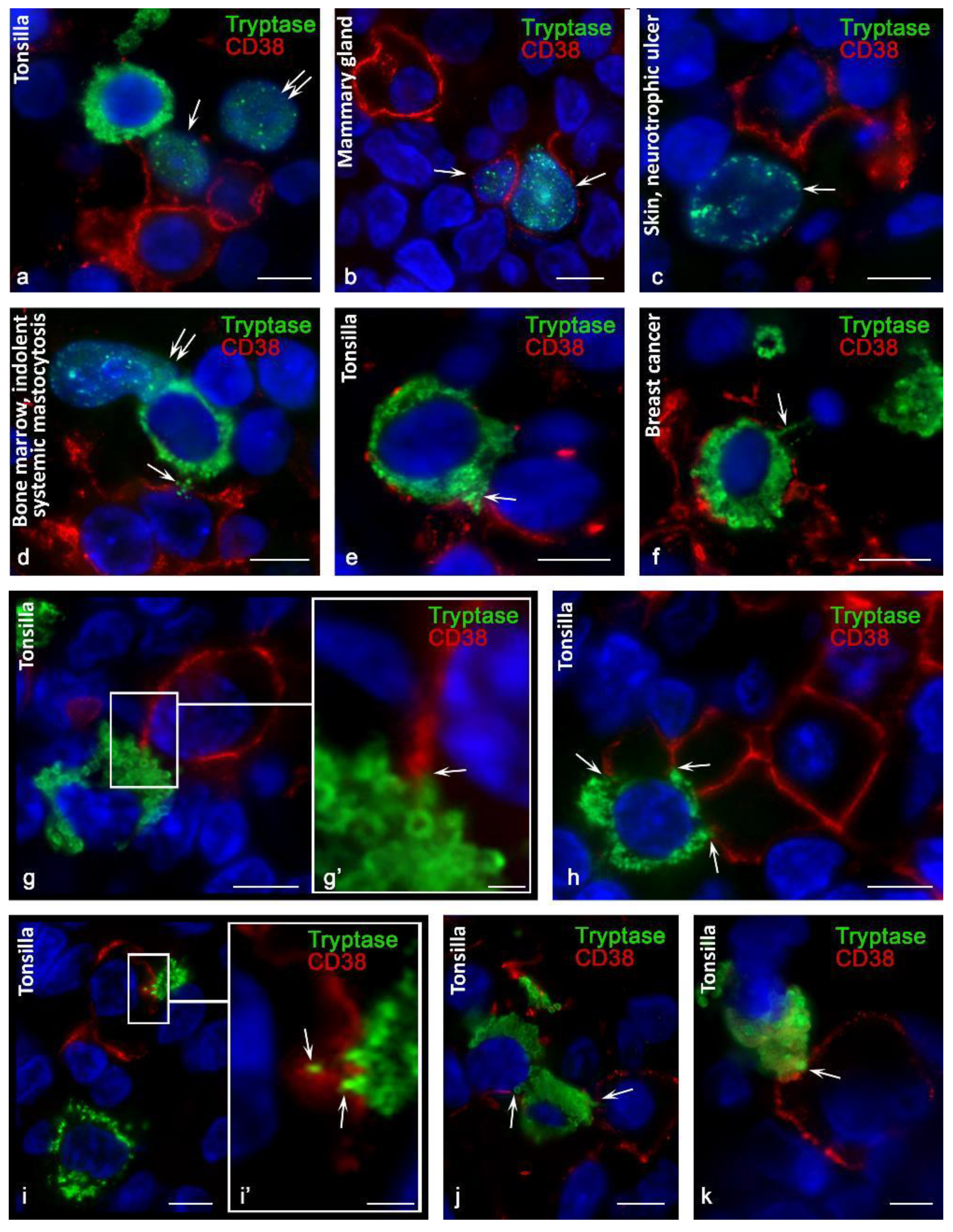
3.2. CD38 Cytotopography in Mast Cells
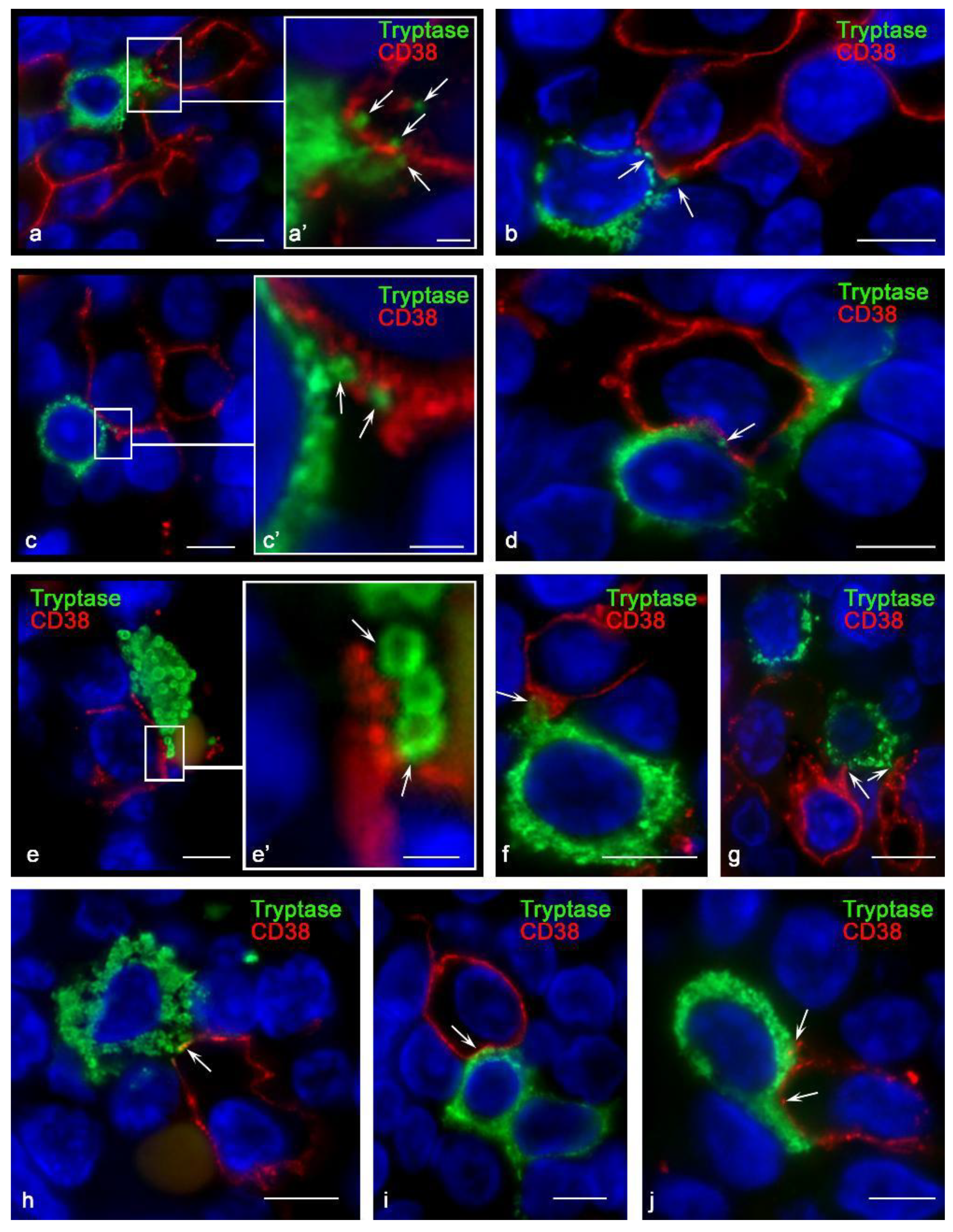
3.3. Histotopographic Features of Co-Localization of Mast Cells and CD38+ Cells in a Specific Tissue Microenvironment
3.4. Content of Tryptase in Nuclei of CD38+ Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhan, A.K.; Reinherz, E.L.; Poppema, S.; McCluskey, R.T.; Schlossman, S.F. Location of T cell and major histocompatibility complex antigens in the human thymus. J. Exp. Med. 1980, 152, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reinherz, E.L.; Kung, P.C.; Goldstein, G.; Levey, R.H.; Schlossman, S.F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: Analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Read, S.; Mauze, S.; Asseman, C.; Bean, A.; Coffman, R.; Powrie, F. CD38+ CD45RB(low) CD4+ T cells: A population of T cells with immune regulatory activities in vitro. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 3435–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavasi, F.; Funaro, A.; Roggero, S.; Horenstein, A.; Calosso, L.; Mehta, K. Human CD38: A glycoprotein in search of a function. Immunol. Today 1994, 15, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavasi, F.; Deaglio, S.; Funaro, A.; Ferrero, E.; Horenstein, A.L.; Ortolan, E.; Vaisitti, T.; Aydin, S. Evolution and function of the ADP ribosyl cyclase/CD38 gene family in physiology and pathology. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 841–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quarona, V.; Zaccarello, G.; Chillemi, A.; Brunetti, E.; Singh, V.K.; Ferrero, E.; Funaro, A.; Horenstein, A.L.; Malavasi, F. CD38 and CD157: A long journey from activation markers to multifunctional molecules. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2013, 84, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavasi, F.; Funaro, A.; Alessio, M.; De Monte, L.; Ausiello, C.M.; Dianzani, U.; Lanza, F.; Magrini, E.; Momo, M.; Roggero, S. CD38: A multi-lineage cell activation molecule with a split personality. Int. J. Clin. Lab. Res. 1992, 22, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, F.; Airoldi, I.; Marimpietri, D.; Bracci, C.; Faini, A.C.; Gramignoli, R. CD38, a Receptor with Multifunctional Activities: From Modulatory Functions on Regulatory Cell Subsets and Extracellular Vesicles, to a Target for Therapeutic Strategies. Cells 2019, 8, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steiniger, B.S.; Raimer, L.; Ecke, A.; Stuck, B.A.; Cetin, Y. Plasma cells, plasmablasts, and AID(+)/CD30(+) B lymphoblasts inside and outside germinal centres: Details of the basal light zone and the outer zone in human palatine tonsils. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 154, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deaglio, S.; Mehta, K.; Malavasi, F. Human CD38: A (r)evolutionary story of enzymes and receptors. Leuk. Res. 2001, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiepe, F.; Radbruch, A. Plasma cells as an innovative target in autoimmune disease with renal manifestations. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfaremo, D.; Gabrielli, A. Is There a Future for Anti-CD38 Antibody Therapy in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases? Cells 2019, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reinis, M.; Morra, M.; Funaro, A.; di Primio, R.; Malavasi, F. Functional associations of CD38 with CD3 on the T-cell membrane. J. Boil. Regul. Homeost. Agents 1998, 11, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz, P.; Navarro, M.D.; Pavon, E.J.; Salmeron, J.; Malavasi, F.; Sancho, J.; Zubiaur, M. CD38 signaling in T cells is initiated within a subset of membrane rafts containing Lck and the CD3-zeta subunit of the T cell antigen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50791–50802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sconocchia, G.; Titus, J.A.; Mazzoni, A.; Visintin, A.; Pericle, F.; Hicks, S.W.; Malavasi, F.; Segal, D.M. CD38 triggers cytotoxic responses in activated human natural killer cells. Blood 1999, 94, 3864–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aponte-López, A.; Muñoz-Cruz, S. Mast Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1273, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komi, D.E.A.; Redegeld, F.A. Role of Mast Cells in Shaping the Tumor Microenvironment. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 58, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valent, P.; Akin, C.; Metcalfe, D.D. Mastocytosis: 2016 updated WHO classification and novel emerging treatment concepts. Blood 2017, 129, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribano, L.; Orfao, A.; Diaz Agustin, B.; Cervero, C.; Herrero, S.; Villarrubia, J.; Bravo, P.; Torrelo, A.; Montero, T.; Valdemoro, M.; et al. Human bone marrow mast cells from indolent systemic mast cell disease constitutively express increased amounts of the CD63 protein on their surface. Cytometry 1998, 34, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribano, L.; Orfao, A.; Díaz-Agustin, B.; Villarrubia, J.; Cerveró, C.; López, A.; Marcos, M.A.G.; Bellas, C.; Fernández-Cañadas, S.; Cuevas, M.; et al. Indolent systemic mast cell disease in adults: Immunophenotypic characterization of bone marrow mast cells and its diagnostic implications. Blood 1998, 91, 2731–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, D.F.; Ordovas-Montanes, J.; Allon, S.J.; Buchheit, K.M.; Vukovic, M.; Derakhshan, T.; Feng, C.; Lai, J.; Hughes, T.K.; Nyquist, S.K.; et al. Human airway mast cells proliferate and acquire distinct inflammation-driven phenotypes during type 2 inflammation. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabb7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchwalow, I.B.; Boecker, W. Immunohistochemistry: Basics and Methods, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Buchwalow, I.B.; Samoilova, V.; Boecker, W.; Tiemann, M. Non-specific binding of antibodies in immunohistochemistry: Fallacies and facts. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buchwalow, I.; Samoilova, V.; Boecker, W.; Tiemann, M. Multiple immunolabeling with antibodies from the same host species in combination with tyramide signal amplification. Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atiakshin, D.A.; Shishkina, V.V.; Gerasimova, O.A.; Meshkova, V.Y.; Samodurova, N.Y.; Samoilenko, T.V.; Buchwalow, I.B.; Samoilova, V.E.; Tiemann, M. Combined histochemical approach in assessing tryptase expression in the mast cell population. Acta Histochem. 2021, 123, 151711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, E.; Valitutti, S.; Laroche, M.; Laurent, C.; Apoil, P.A.; Hermine, O.; Lavit, M.; Paul, C.; Livideanu, C.B. Hydroxychloroquine as a novel therapeutic approach in mast cell activation diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 194, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanazi, S.; Grujic, M.; Lampinen, M.; Rollman, O.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Pejler, G.; Melo, F.R. Mast Cell beta-Tryptase Is Enzymatically Stabilized by DNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.R.; Wallerman, O.; Paivandy, A.; Calounova, G.; Gustafson, A.-M.; Sabari, B.R.; Zabucchi, G.; Allis, C.D.; Pejler, G. Tryptase-catalyzed core histone truncation: A novel epigenetic regulatory mechanism in mast cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, D.; Liu, J.; Xia, M.; Yi, L.; Shen, Q.; Xu, S.; et al. Adult Connective Tissue-Resident Mast Cells Originate from Late Erythro-Myeloid Progenitors. Immunity 2018, 49, 640–653.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakahata, T.; Toru, H. Cytokines regulate development of human mast cells from hematopoietic progenitors. Int. J. Hematol. 2002, 75, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiohara, M.; Koike, K. Regulation of mast cell development. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2005, 87, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, M.; Atiakshin, D.; Samoilova, V.; Buchwalow, I. Identification of CTLA-4-Positive Cells in the Human Tonsil. Cells 2021, 10, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.G.; Corzo, K.; Chiron, M.; Van De Velde, H.; Abbadessa, G.; Campana, F.; Solanki, M.; Meng, R.; Lee, H.; Wiederschain, D.; et al. Therapeutic Opportunities with Pharmacological Inhibition of CD38 with Isatuximab. Cells 2019, 8, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van de Donk, N.; Usmani, S.Z. CD38 Antibodies in Multiple Myeloma: Mechanisms of Action and Modes of Resistance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejcik, J.; Frerichs, K.A.; Nijhof, I.S.; van Kessel, B.; van Velzen, J.F.; Bloem, A.C.; Broekmans, M.E.C.; Zweegman, S.; van Meerloo, J.; Musters, R.J.P.; et al. Monocytes and Granulocytes Reduce CD38 Expression Levels on Myeloma Cells in Patients Treated with Daratumumab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 7498–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wo, Y.J.; Gan, A.S.P.; Lim, X.; Tay, I.S.Y.; Lim, S.; Lim, J.C.T.; Yeong, J.P.S. The Roles of CD38 and CD157 in the Solid Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Immunotherapy. Cells 2019, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krejcik, J.; Casneuf, T.; Nijhof, I.S.; Verbist, B.; Bald, J.; Plesner, T.; Syed, K.; Liu, K.; Van De Donk, N.W.C.J.; Weiss, B.M.; et al. Daratumumab depletes CD38+ immune regulatory cells, promotes T-cell expansion, and skews T-cell repertoire in multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konen, J.M.; Fradette, J.J.; Gibbons, D.L. The Good, the Bad and the Unknown of CD38 in the Metabolic Microenvironment and Immune Cell Functionality of Solid Tumors. Cells 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glaría, E.; Valledor, A.F. Roles of CD38 in the Immune Response to Infection. Cells 2020, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll-Portillo, A.; Surviladze, Z.; Cambi, A.; Lidke, D.S.; Wilson, B.S.P. Mast cell synapses and exosomes: Membrane contacts for information exchange. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zambello, R.; Barila, G.; Manni, S.; Piazza, F.; Semenzato, G. NK cells and CD38: Implication for (Immuno)Therapy in Plasma Cell Dyscrasias. Cells 2020, 9, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Antibody/Clone | Host | Source | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD38 (SP149) | Rabbit monoclonal | Cell Marque, Rocklin, USA | 1:300 |
| CD38 (IB4; IB6, SUN-4B7) | Mouse monoclonal | Antibody kindly made available by Fabio Malavasi, University of Torino, Torino, Italy | 1:200 |
| Anti-mast cell tryptase antibody [AA1] #ab2378 | Mouse monoclonal | Abcam, UK | 1:3000 |
| Anti-mast cell tryptase antibody [EPR9522] #ab151757 | Rabbit monoclonal | Abcam, UK | 1:2000 |
| Antibodies and Other Reagents | Source | Dilution | Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goat anti-mouse IgG Ab (#115-165-166) | Jackson ImmunoResearch, Ely, United Kingdom | 1/200 | Cy3 |
| Goat anti-rabbit IgG Ab (#A-11034) | Invitrogen, Darmstadt, Germany | 1/200 | Cy3 |
| Goat anti-mouse IgG Ab (#A-11029) | Invitrogen, Darmstadt, Germany | 1/200 | Alexa Fluor 488 |
| Goat anti-rabbit IgG Ab (#A-11034) | Invitrogen, Darmstadt, Germany | 1/200 | Alexa Fluor 488 |
| CC2 solution (#950-223) | Ventana Medical Systems, Lund Sweden | Ready-to-use | w/o |
| VECTASHIELD mounting medium (#H-1000) | Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA | Ready-to-use | w/o |
| TSA plus fluorescein (#NEL741E001K) | PerkinElmer, Rodgau, Germany | 1/200 | Fluorescein |
| TSA plus cyanine 3 (#NEL744E001KT) | PerkinElmer, Rodgau, Germany | 1/200 | Cyanine 3 |
| Organ | Primary Antibodies to CD38 (SP149) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Cell Marque, USA) | Primary Murine Antibodies to CD38 (Kindly Provided by Fabio Malavasi, University of Torino, Italy) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number CD38+ MC (%, M ± m) | Expression Intensity (%) | Number CD38+ MC (%, M ± m) | Expression Intensity (%) | |||||
| + (M ± m) | ++ (M ± m) | +++ (M ± m) | + (M ± m) | ++ (M ± m) | +++ (M ± m) | |||
| Skin (normal; n = 5) | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 65.2 ± 3.1 | 22.3 ± 1.9 | 12.5 ± 1.1 | 8.8 ± 0.5 | 52.4 ± 4.2 | 39.2 ± 2.5 | 8.4 ± 0.5 |
| Skin (neurotrophic ulcers; n = 6) | 7.3 ± 0.6 ∆ | 13.2 ± 0.8 ∆ | 62 ± 4.3 ∆ | 24.8 ± 1.6 ∆ | 14.1 ± 1.2 ∆ | 15.6 ± 1.1 ∆ | 66.7 ± 4.3 ∆ | 17.7 ± 1.3 ∆ |
| Breast (normal; n = 5) | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 58.9 ± 5.1 | 32.7 ± 2.8 | 8.4 ± 0.9 | 8.4 ± 0.6 | 45.6 ± 3.4 | 47.1 ± 3.1 | 7.3 ± 0.5 |
| Mammary cancer (n = 6) | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 23.5 ± 1.9 ∆ | 61.3 ± 5.3 ∆ | 15.2 ± 1.4 ∆ | 12.3 ± 1.3 ∆ | 35.6 ± 2.2 ∆ | 55.6 ± 3.2 ∆ | 8.8 ± 0.4 |
| Bone marrow (mastocytosis; n = 4) | * | - | - | - | 8.2 ± 0.6 | 65.2 ± 4.3 | 29.5 ± 1.8 | 5.3 ± 0.3 |
| Tonsilla (recurrent tonsillitis; n = 10) | * | - | - | - | 9.7 ± 0.5 | 59.4 ± 4.1 | 35.9 ± 2.2 | 4.7 ± 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atiakshin, D.; Samoilova, V.; Buchwalow, I.; Tiemann, M. Expression of CD38 in Mast Cells: Cytological and Histotopographic Features. Cells 2021, 10, 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102511
Atiakshin D, Samoilova V, Buchwalow I, Tiemann M. Expression of CD38 in Mast Cells: Cytological and Histotopographic Features. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102511
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtiakshin, Dmitri, Vera Samoilova, Igor Buchwalow, and Markus Tiemann. 2021. "Expression of CD38 in Mast Cells: Cytological and Histotopographic Features" Cells 10, no. 10: 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102511
APA StyleAtiakshin, D., Samoilova, V., Buchwalow, I., & Tiemann, M. (2021). Expression of CD38 in Mast Cells: Cytological and Histotopographic Features. Cells, 10(10), 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102511






