Altered TGFβ/SMAD Signaling in Human and Rat Models of Pulmonary Hypertension: An Old Target Needs Attention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collecting Human Tissue Samples
2.2. Preparing PAH Animal Models
2.3. Reagents
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining and Quantification Analysis
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Isolation of mRNA and qPCR
2.7. Measurement of TGF-β1 by ELISA
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
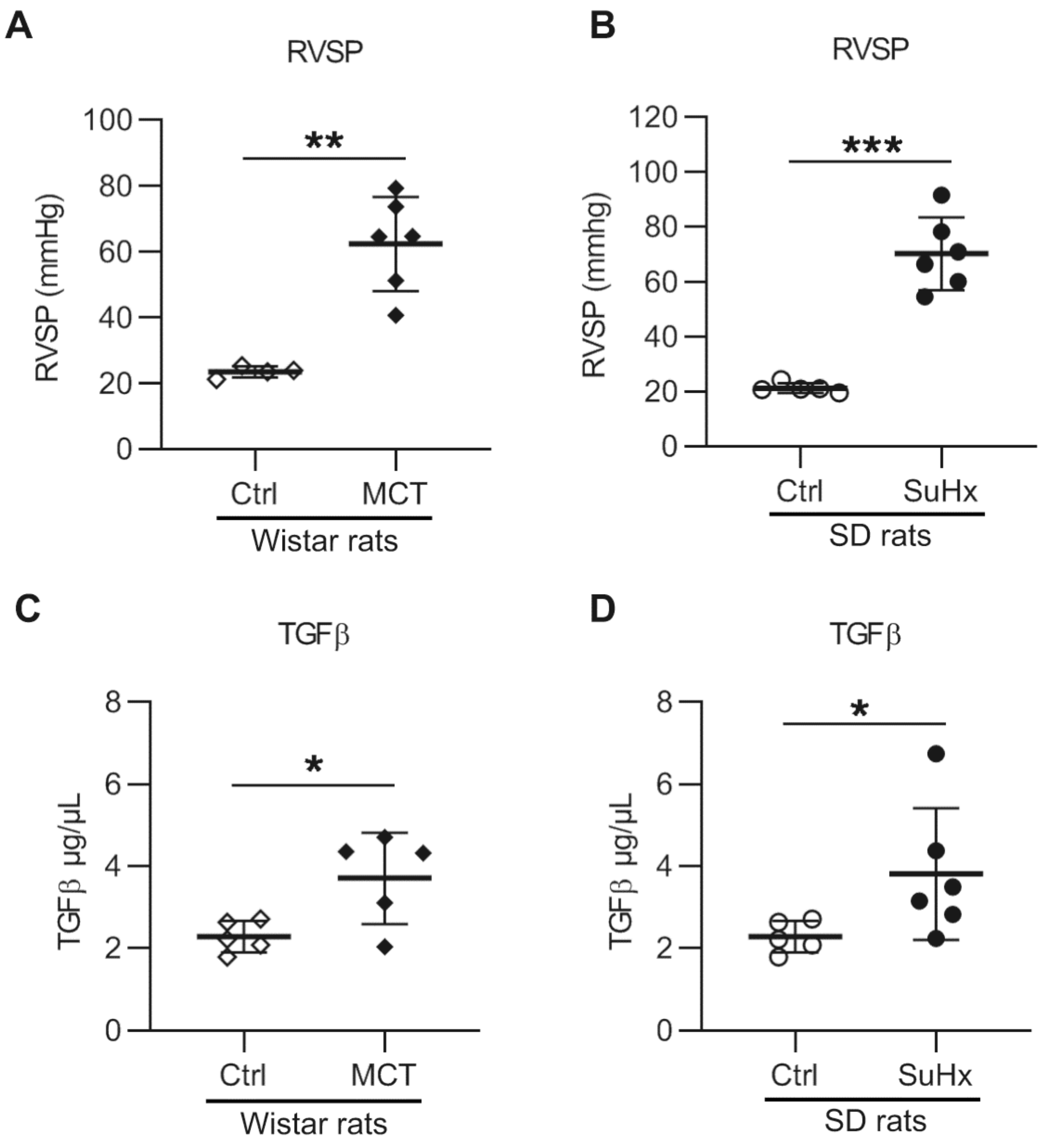
3.1. Increased TGF-β1 in PAH Animal Models
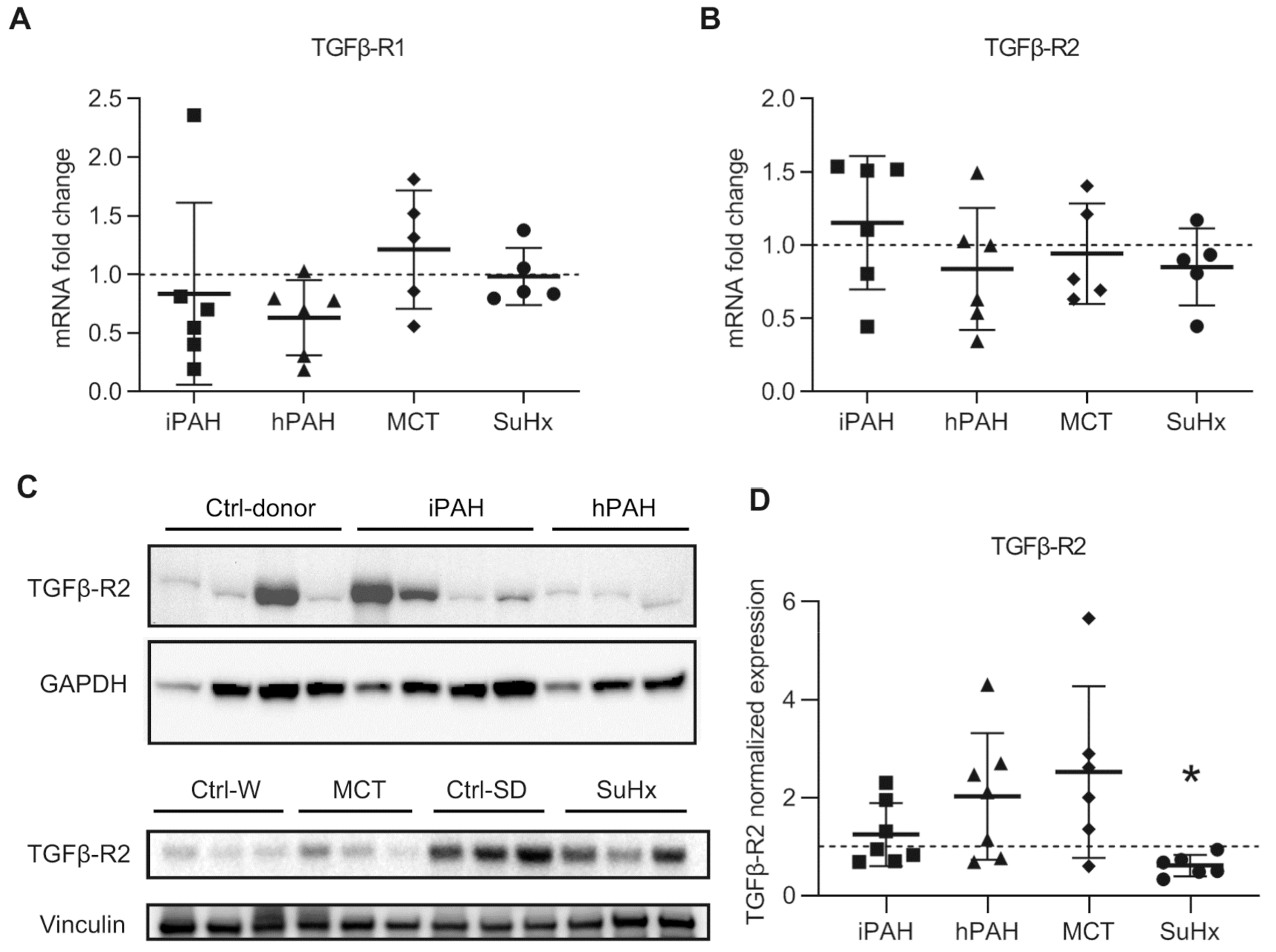
3.2. Increased Levels of TGFβR2 in Pulmonary Vasculature of Animal PAH Models
3.3. Differential Expressions Levels of TGF-β Receptors in Lungs of PAH Patients and PAH Animal Models
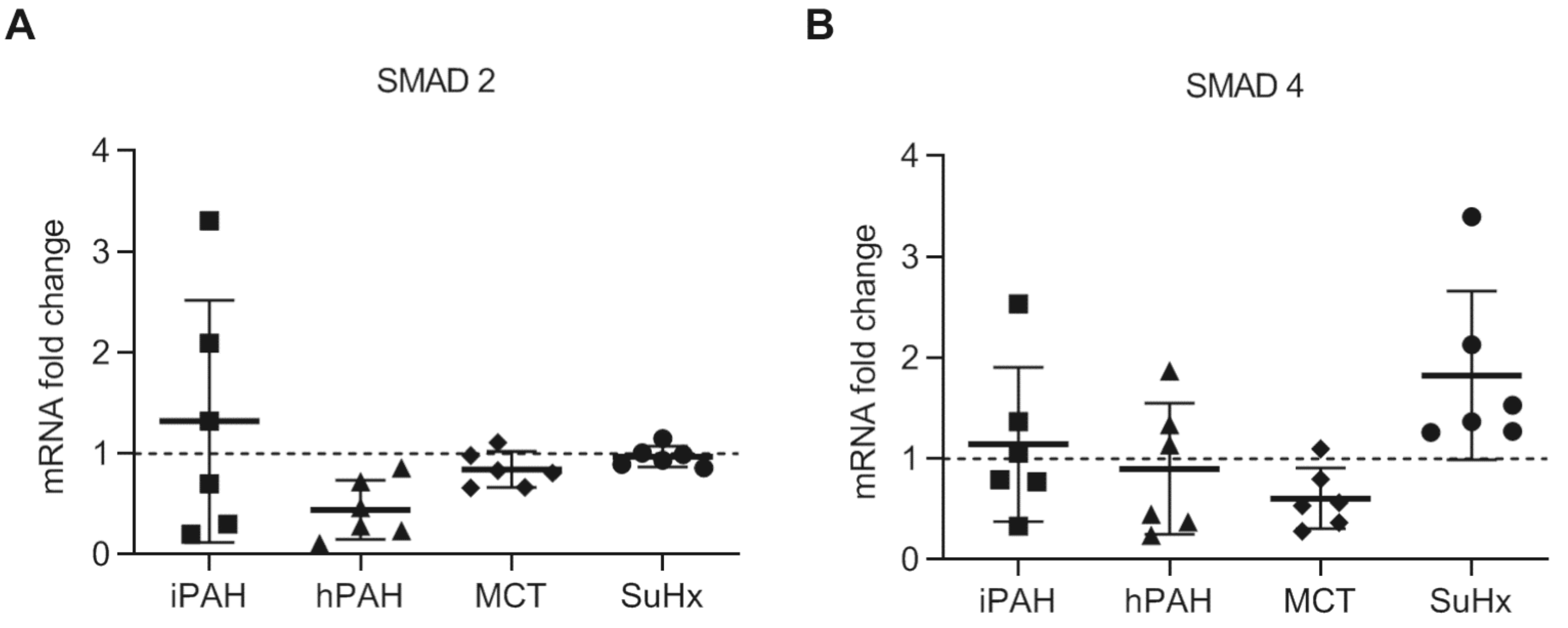
3.4. No Changes in Levels of SMAD2 and SMAD4 in PAH Patients and Animal PAH Models
3.5. Discrapancies in pSMAD2/3 Levels in the Lungs of PAH Patients and Animal Models of PAH
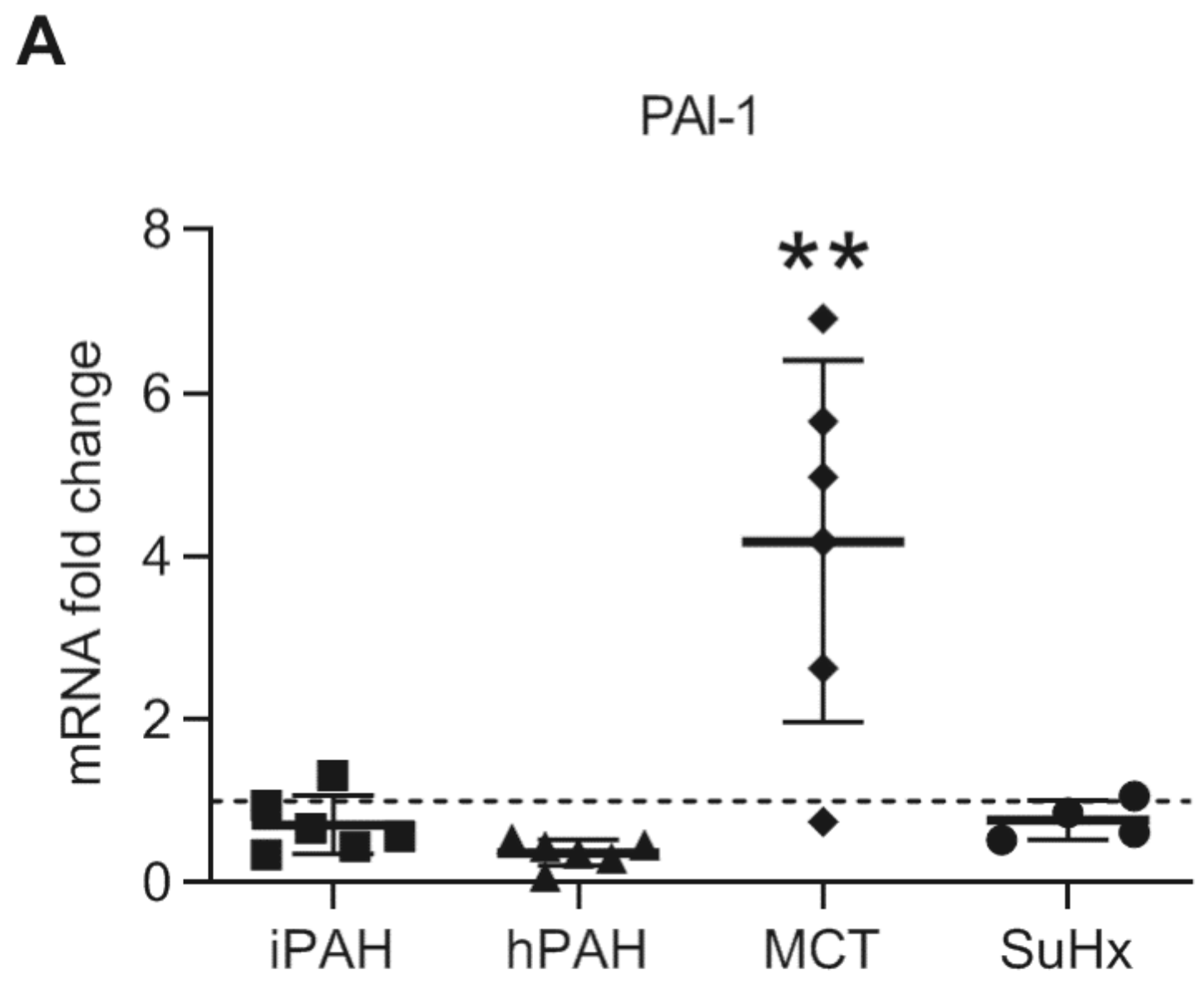
3.6. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Lungs in PAH Patients and Animal PAH Rats
4. Discussion
4.1. Altered TGFβ-SMAD2/3 Signaling in Experimentally Induced PAH Animal Models
4.2. Unaltered TGFβ-SMAD2/3 Signaling in the Lungs of PAH Patients
4.3. Differential Regulation of TGF-β-SMAD2/3 Signaling Levels in PAH Patients and Animal PAH Models
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.-L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2015, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, D.; Edwards, J.E. The pathology of hypertensive pulmonary vascular disease: A description of six grades of structural changes in the pulmonary arteries with special reference to congenital cardiac septal defects. Circulation 1958, 18, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Guignabert, C.; Bonnet, S.; Dorfmuller, P.; Klinger, J.R.; Nicolls, M.R.; Olschewski, A.J.; Pullamsetti, S.S.; Schermuly, R.T.; Stenmark, K.R.; et al. Pathology and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension: State of the art and research perspectives. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rol, N.; Kurakula, K.B.; Happe, C.; Bogaard, H.J.; Goumans, M.J. TGF-beta and BMPR2 signaling in PAH: Two black sheep in one family. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2018, 19, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimovic, N.; Bergh, C.H.; Andersson, B.; Sakiniene, E.; Carlsten, H.; Rundqvist, B. Growth factors and interleukin-6 across the lung circulation in pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Han, W.; Greer, P.A.; Tuder, R.M.; Toque, H.A.; Wang, K.K.; Caldwell, R.W.; Su, Y. Calpain mediates pulmonary vascular remodeling in rodent models of pulmonary hypertension, and its inhibition attenuates pathologic features of disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4548–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, N.W.; Aldred, M.A.; Chung, W.K.; Elliott, C.G.; Nichols, W.C.; Soubrier, F.; Trembath, R.C.; Loyd, J.E. Genetics and genomics of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhurst, R.J.; Hata, A. Targeting the TGFbeta signalling pathway in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2012, 11, 790–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.Y.; S, D.C.; Luo, F.; Weng, T.; Le, T.T.; A, M.H.; Philip, K.; Molina, J.G.; Garcia-Morales, L.J.; Cao, Y.; et al. Macrophage bone morphogenic protein receptor 2 depletion in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and Group III pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell Mol. Physiol. 2016, 311, L238–L254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Liu, J.; Derynck, R. Post-translational regulation of TGF-β receptor and Smad signaling. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiman, A.L.; Podowski, M.; Medicherla, S.; Gordy, K.; Xu, F.; Zhen, L.; Shimoda, L.A.; Neptune, E.; Higgins, L.; Murphy, A.; et al. Role of the TGF-beta/Alk5 signaling pathway in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2008, 177, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Docx, C.; Holmes, A.M.; Beach, S.; Duggan, N.; England, K.; Leblanc, C.; Lebret, C.; Schindler, F.; Raza, F.; et al. Activin-like kinase 5 (ALK5) mediates abnormal proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells from patients with familial pulmonary arterial hypertension and is involved in the progression of experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension induced by monocrotaline. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Crosby, A.; Yang, X.; Southwood, M.; Upton, P.D.; Kim, D.K.; Morrell, N.W. Altered bone morphogenetic protein and transforming growth factor-beta signaling in rat models of pulmonary hypertension: Potential for activin receptor-like kinase-5 inhibition in prevention and progression of disease. Circulation 2009, 119, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, L.M.; Nikolic, I.; Paskin-Flerlage, S.D.; Pearsall, R.S.; Kumar, R.; Yu, P.B. A Selective Transforming Growth Factor-β Ligand Trap Attenuates Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2016, 194, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badesch, D.B.; McLaughlin, V.; Gibbs, S.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Hoeper, M.M.; Preston, I.; Souza, R.; Waxman, A.; Mutyaba, M.; Manimaran, S.; et al. Sotatercept for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Available online: https://conference.thoracic.org/program/session-information/virtual-clinical-trials.php (accessed on 12 September 2020).
- Kay, J.M.; Harris, P.; Heath, D. Pulmonary hypertension produced in rats by ingestion of Crotalaria spectabilis seeds. Thorax 1967, 22, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattocks, A.R. Toxicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Nature 1968, 217, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraseviciene-Stewart, L.; Kasahara, Y.; Alger, L.; Hirth, P.; Mc Mahon, G.; Waltenberger, J.; Voelkel, N.F.; Tuder, R.M. Inhibition of the VEGF receptor 2 combined with chronic hypoxia causes cell death-dependent pulmonary endothelial cell proliferation and severe pulmonary hypertension. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztuka, K.; Jasińska-Stroschein, M. Animal models of pulmonary arterial hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of data from 6126 animals. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 125, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, M.; Alzoubi, A.; O’Neill, K.D.; Gairhe, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Oshima, K.; Abe, K.; Oka, M.; McMurtry, I.F. Temporal hemodynamic and histological progression in Sugen5416/hypoxia/normoxia-exposed pulmonary arterial hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 306, H243–H250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewicz, A.; Kouri, F.M.; Nejman, B.; Kwapiszewska, G.; Hecker, M.; Sandu, R.; Dony, E.; Seeger, W.; Schermuly, R.T.; Eickelberg, O.; et al. The transforming growth factor-beta/Smad2,3 signalling axis is impaired in experimental pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.F.; Lame, M.W.; Segall, H.J.; Wilson, D.W. Smad signaling in the rat model of monocrotaline pulmonary hypertension. Toxicol Pathol. 2008, 36, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morty, R.E.; Nejman, B.; Kwapiszewska, G.; Hecker, M.; Zakrzewicz, A.; Kouri, F.M.; Peters, D.M.; Dumitrascu, R.; Seeger, W.; Knaus, P.; et al. Dysregulated bone morphogenetic protein signaling in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogo, T.; Chowdhury, H.M.; Yang, J.; Long, L.; Li, X.; Torres Cleuren, Y.N.; Morrell, N.W.; Schermuly, R.T.; Trembath, R.C.; Nasim, M.T. Inhibition of overactive transforming growth factor-beta signaling by prostacyclin analogs in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overbeek, M.J.; Mouchaers, K.T.; Niessen, H.M.; Hadi, A.M.; Kupreishvili, K.; Boonstra, A.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Belien, J.A.; Smit, E.F.; Dijkmans, B.C.; et al. Characteristics of interstitial fibrosis and inflammatory cell infiltration in right ventricles of systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 2010, 604615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Raaf, M.A.; Schalij, I.; Gomez-Arroyo, J.; Rol, N.; Happe, C.; de Man, F.S.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; Westerhof, N.; Voelkel, N.F.; Bogaard, H.J. SuHx rat model: Partly reversible pulmonary hypertension and progressive intima obstruction. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happé, C.; Kurakula, K.; Sun, X.Q.; da Silva Goncalves Bos, D.; Rol, N.; Guignabert, C.; Tu, L.; Schalij, I.; Wiesmeijer, K.C.; Tura-Ceide, O.; et al. The BMP Receptor 2 in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: When and Where the Animal Model Matches the Patient. Cells 2020, 9, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurakula, K.; Sun, X.Q.; Happe, C.; da Silva Goncalves Bos, D.; Szulcek, R.; Schalij, I.; Wiesmeijer, K.C.; Lodder, K.; Tu, L.; Guignabert, C.; et al. Prevention of progression of pulmonary hypertension by the Nur77 agonist 6-mercaptopurine: Role of BMP signalling. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1802400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabini, D.; Granton, E.; Hu, Y.; Miranda, M.Z.; Weichelt, U.; Breuils Bonnet, S.; Bonnet, S.; Morrell, N.W.; Connelly, K.A.; Provencher, S.; et al. Loss of SMAD3 Promotes Vascular Remodeling in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension via MRTF Disinhibition. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care. Med. 2018, 197, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, L.A.; Obaid, A.A.; Zaki, H.F.; Agha, A.M. Role of oxidative stress, inflammation, nitric oxide and transforming growth factor-beta in the protective effect of diosgenin in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasim, M.T.; Ogo, T.; Chowdhury, H.M.; Zhao, L.; Chen, C.N.; Rhodes, C.; Trembath, R.C. BMPR-II deficiency elicits pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic responses through the activation of TGFβ-TAK1-MAPK pathways in PAH. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 2548–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, P.D.; Morrell, N.W. The transforming growth factor-β-bone morphogenetic protein type signalling pathway in pulmonary vascular homeostasis and disease. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botney, M.D.; Bahadori, L.; Gold, L.I. Vascular remodeling in primary pulmonary hypertension. Potential role for transforming growth factor-beta. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 144, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gore, B.; Izikki, M.; Mercier, O.; Dewachter, L.; Fadel, E.; Humbert, M.; Dartevelle, P.; Simonneau, G.; Naeije, R.; Lebrin, F.; et al. Key role of the endothelial TGF-β/ALK1/endoglin signaling pathway in humans and rodents pulmonary hypertension. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, A.; Yeager, M.E.; Zaiman, A.; Cool, C.D.; Voelkel, N.F.; Tuder, R.M. Impaired transforming growth factor-beta signaling in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2004, 170, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Long, L.; Reynolds, P.N.; Morrell, N.W. Expression of mutant BMPR-II in pulmonary endothelial cells promotes apoptosis and a release of factors that stimulate proliferation of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Pulm. Circ. 2011, 1, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordenave, J.; Tu, L.; Berrebeh, N.; Thuillet, R.; Cumont, A.; Le Vely, B.; Fadel, E.; Nadaud, S.; Savale, L.; Humbert, M.; et al. Lineage Tracing Reveals the Dynamic Contribution of Pericytes to the Blood Vessel Remodeling in Pulmonary Hypertension. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanada, T.J.; Sun, X.-Q.; Happé, C.; Guignabert, C.; Tu, L.; Schalij, I.; Bogaard, H.-J.; Goumans, M.-J.; Kurakula, K. Altered TGFβ/SMAD Signaling in Human and Rat Models of Pulmonary Hypertension: An Old Target Needs Attention. Cells 2021, 10, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010084
Sanada TJ, Sun X-Q, Happé C, Guignabert C, Tu L, Schalij I, Bogaard H-J, Goumans M-J, Kurakula K. Altered TGFβ/SMAD Signaling in Human and Rat Models of Pulmonary Hypertension: An Old Target Needs Attention. Cells. 2021; 10(1):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010084
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanada, Takayuki Jujo, Xiao-Qing Sun, Chris Happé, Christophe Guignabert, Ly Tu, Ingrid Schalij, Harm-Jan Bogaard, Marie-José Goumans, and Kondababu Kurakula. 2021. "Altered TGFβ/SMAD Signaling in Human and Rat Models of Pulmonary Hypertension: An Old Target Needs Attention" Cells 10, no. 1: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010084
APA StyleSanada, T. J., Sun, X.-Q., Happé, C., Guignabert, C., Tu, L., Schalij, I., Bogaard, H.-J., Goumans, M.-J., & Kurakula, K. (2021). Altered TGFβ/SMAD Signaling in Human and Rat Models of Pulmonary Hypertension: An Old Target Needs Attention. Cells, 10(1), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010084





