Circular RNA circMYL1 Inhibit Proliferation and Promote Differentiation of Myoblasts by Sponging miR-2400
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Samples Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and Real-Time qPCR
2.3. Plasmid Construction
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Cell Transfection
2.6. RNA Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (RNA-FISH)
2.7. 5-Ethynyl 2′-Deoxyuridine Assay (EdU)
2.8. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) Assay
2.9. Cell Cycle Assay by Flow Cytometry
2.10. Luciferase Activity Assay
2.11. Western Blotting Analysis
2.12. Immunofluorescent Staining
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
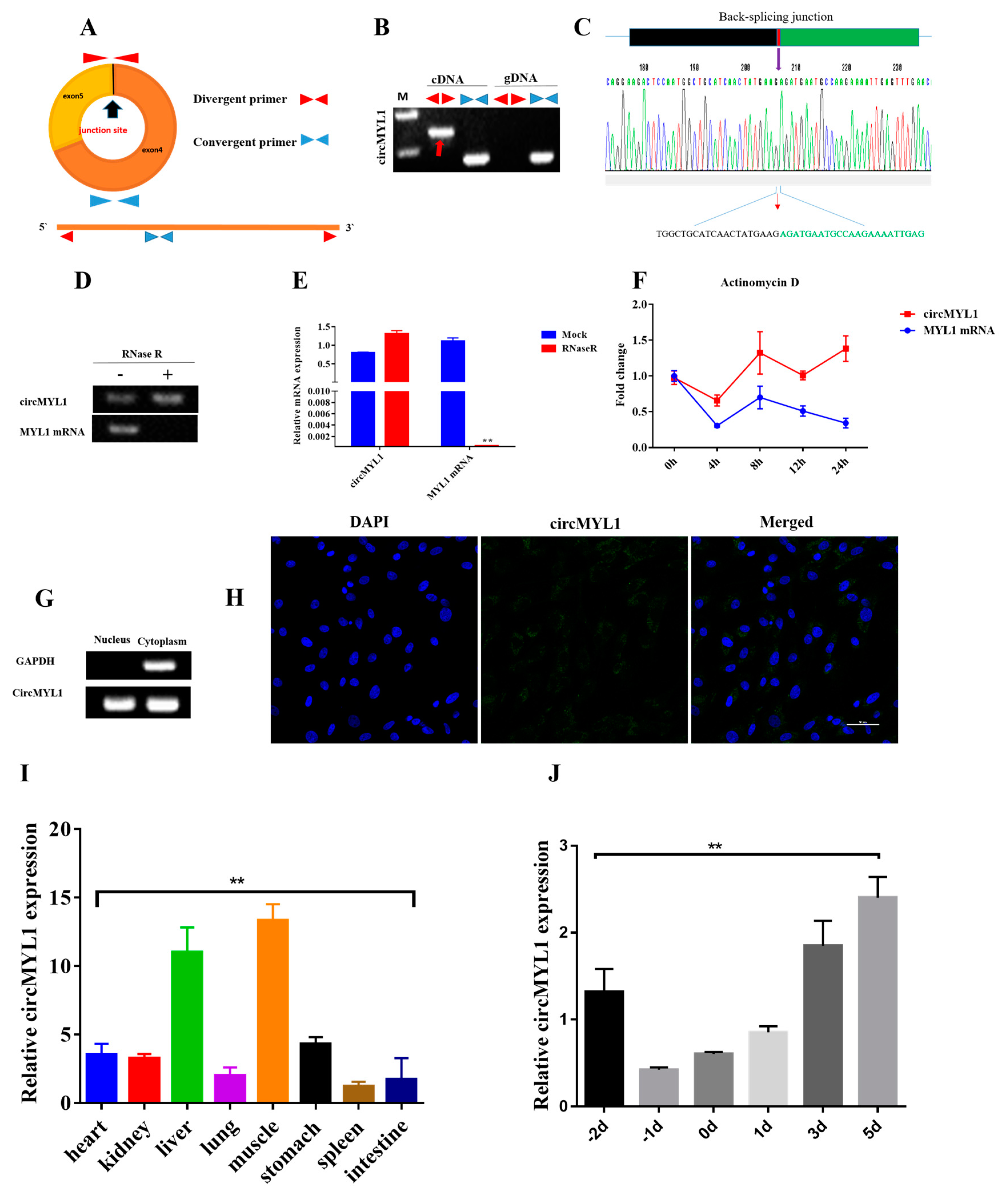
3.1. Characterization of circMYL1
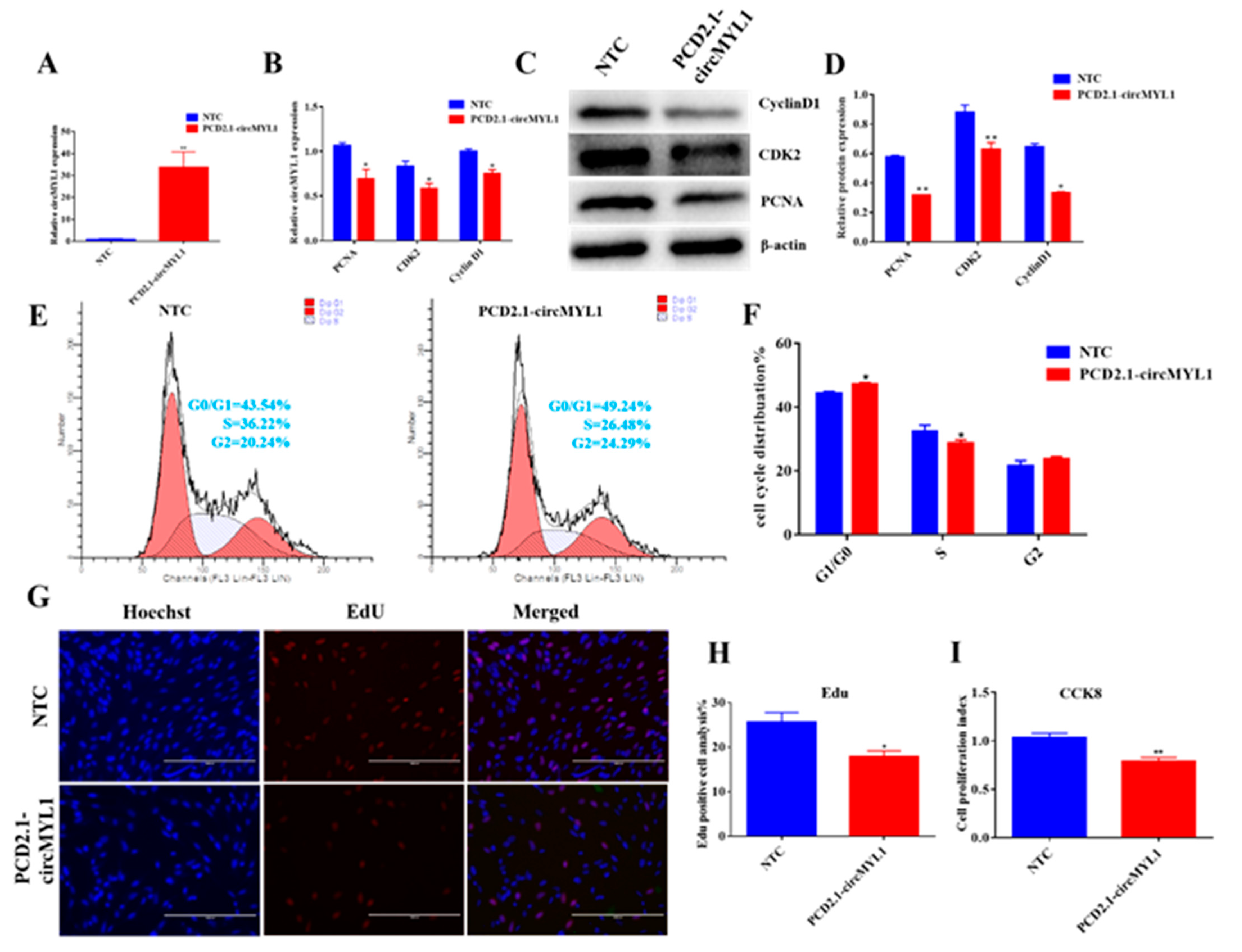
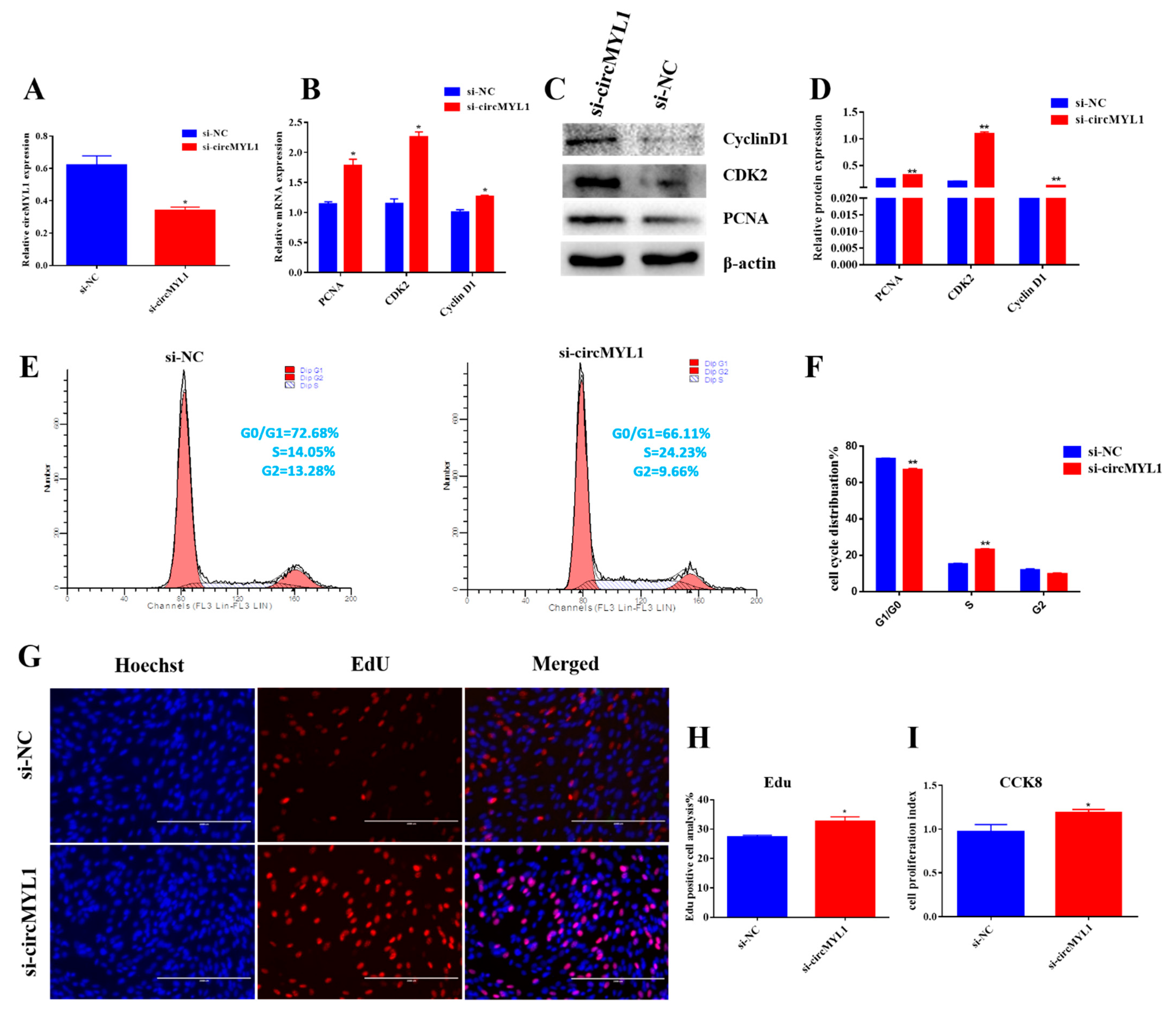
3.2. circMYL1 Inhibits Myoblasts Proliferation
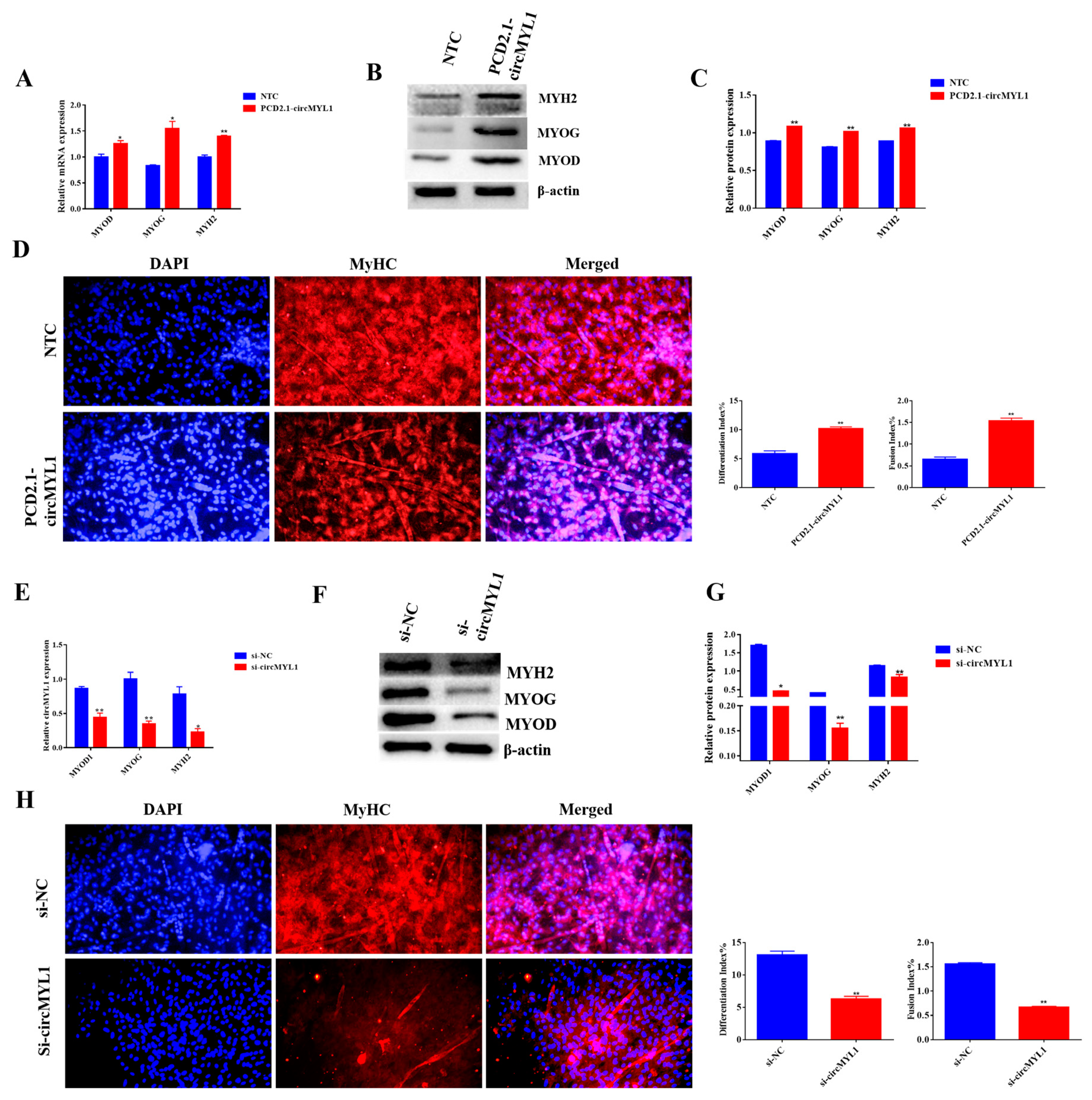
3.3. circMYL1 Promotes Myoblasts Differentiation
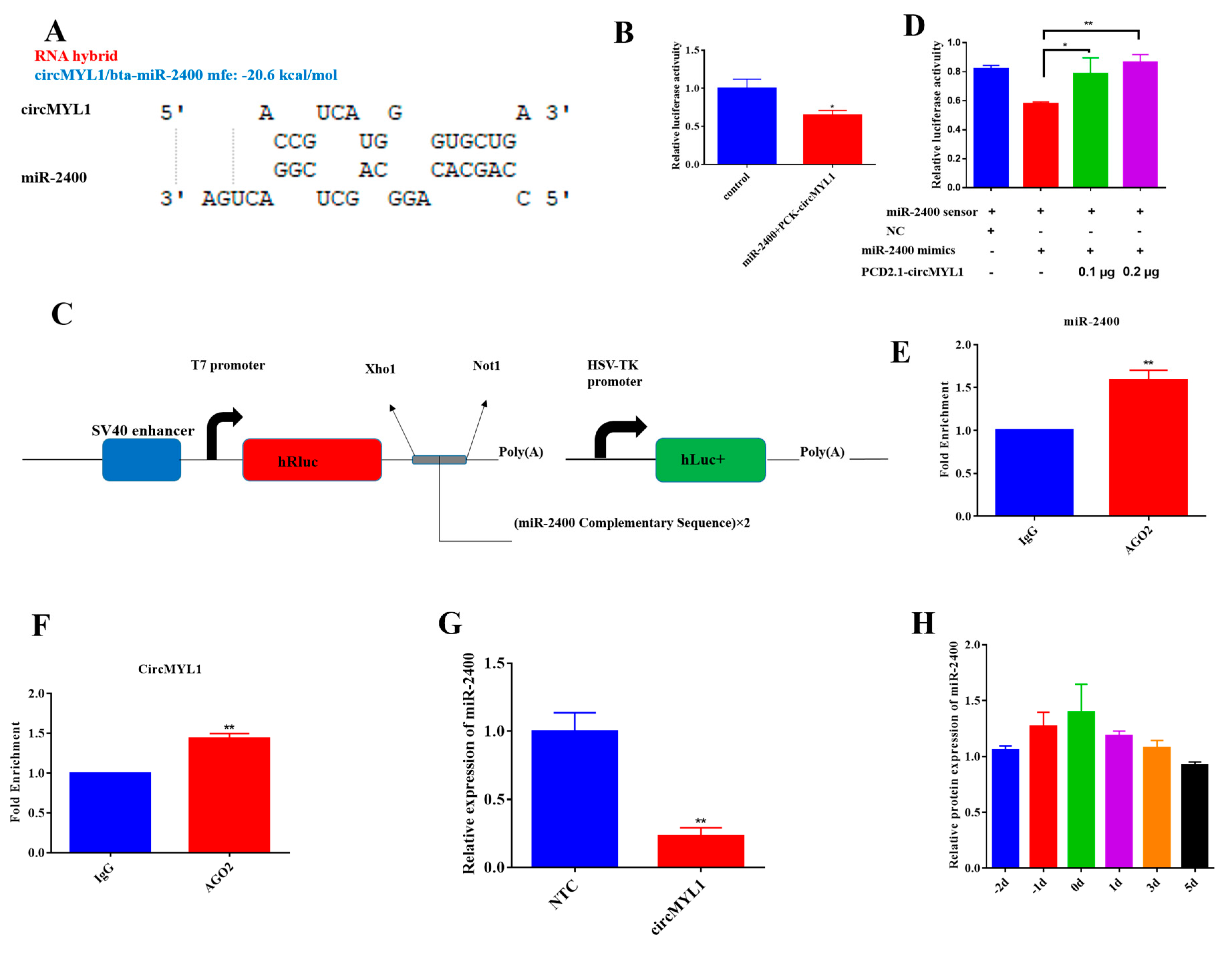
3.4. circMYL1 Acts as A Sponge for miR-2400
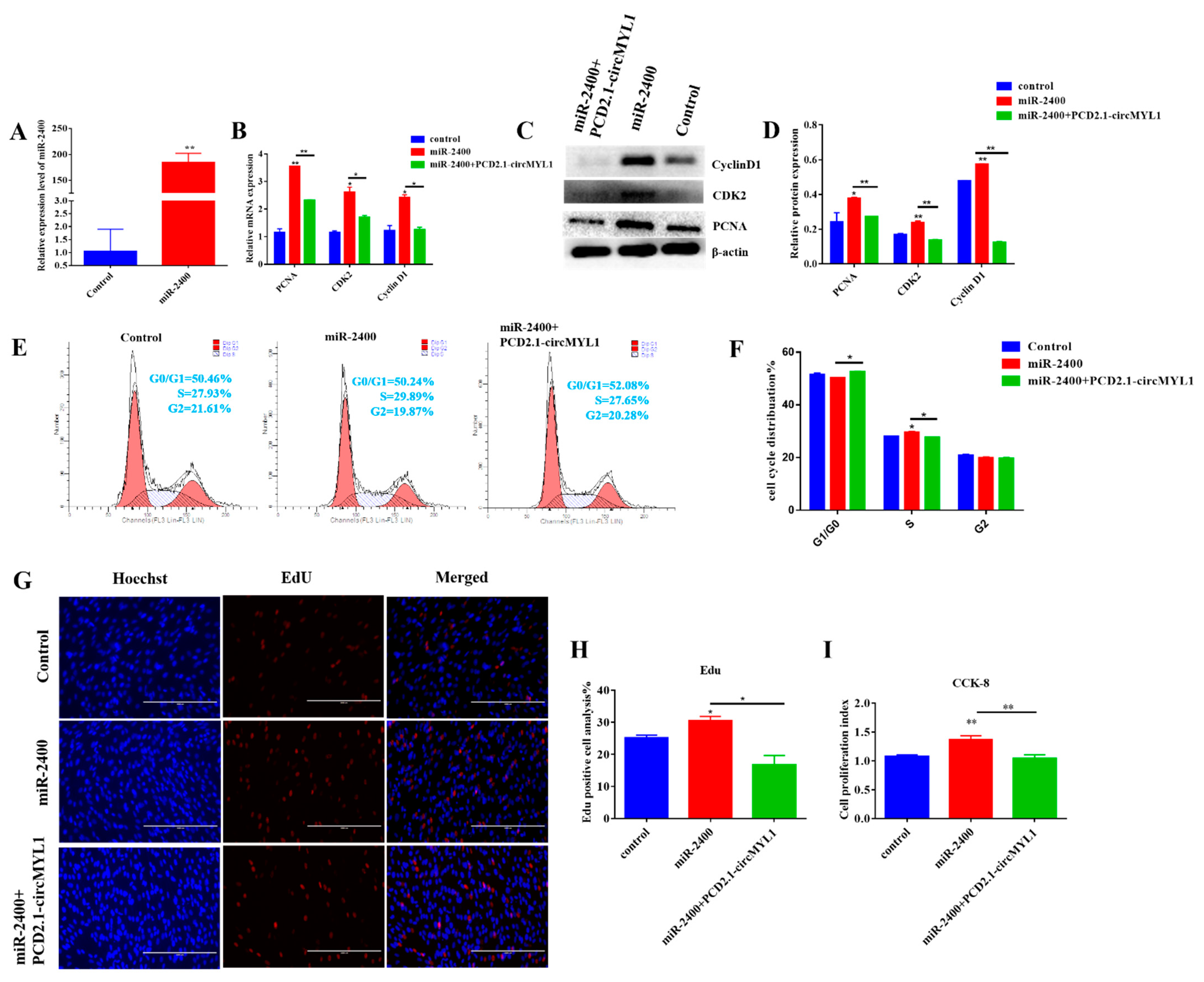
3.5. miR-2400 Promotes Myoblast Proliferation
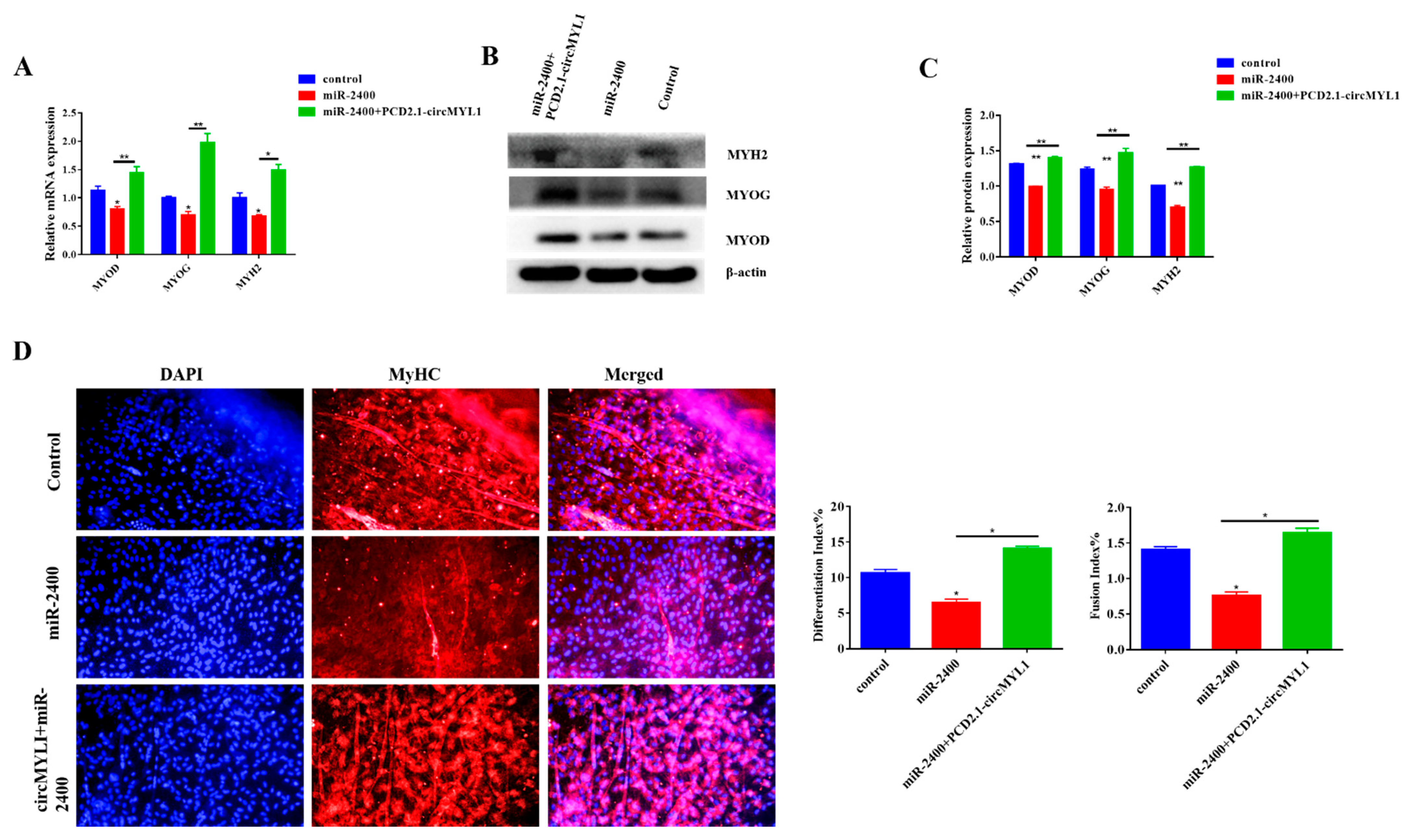
3.6. miR-2400 Inhibits Myoblast Differentiation
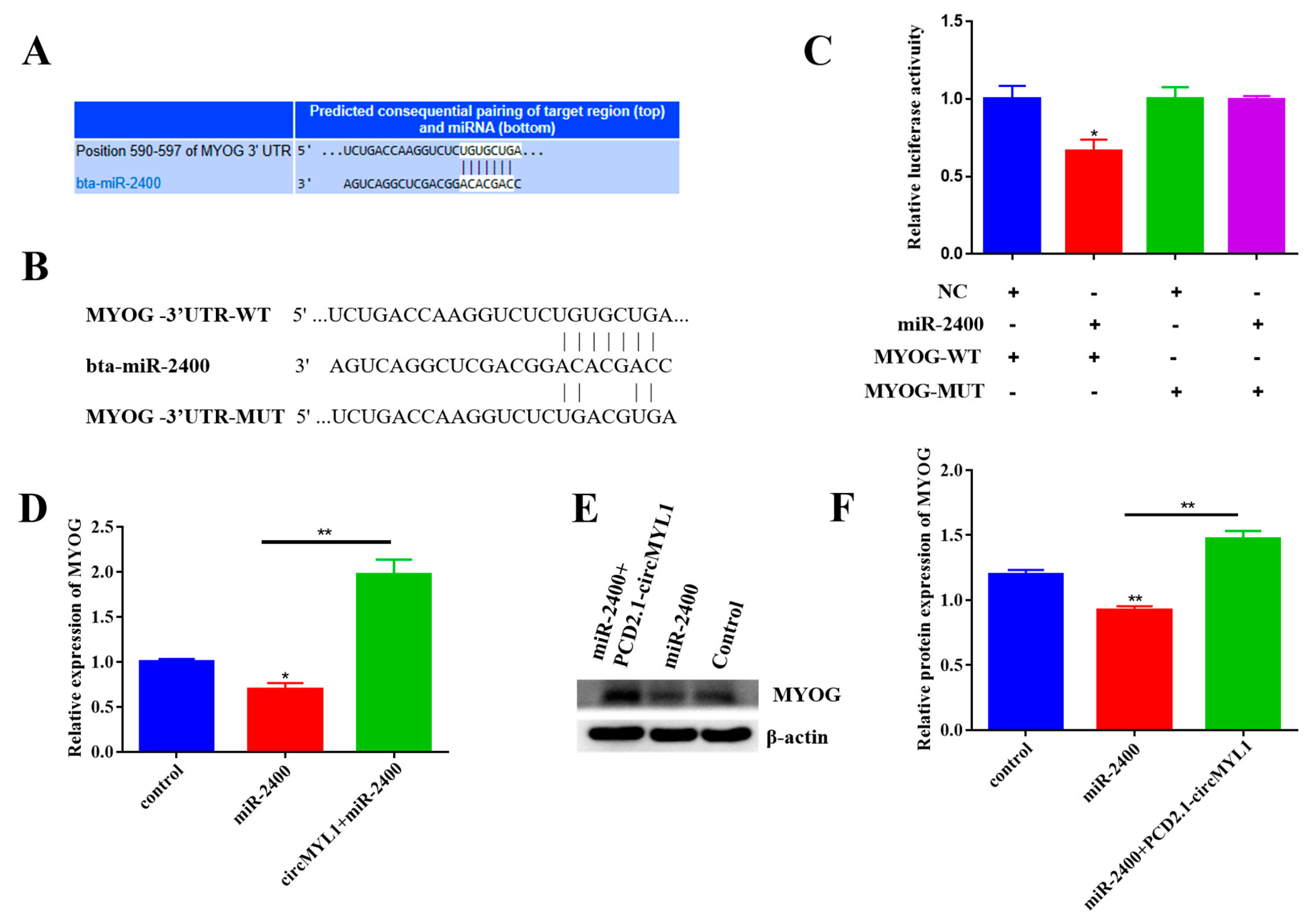
3.7. circMYL1 Acts as a ceRNA for miR-2400 to Activate MYOG
4. Discussion
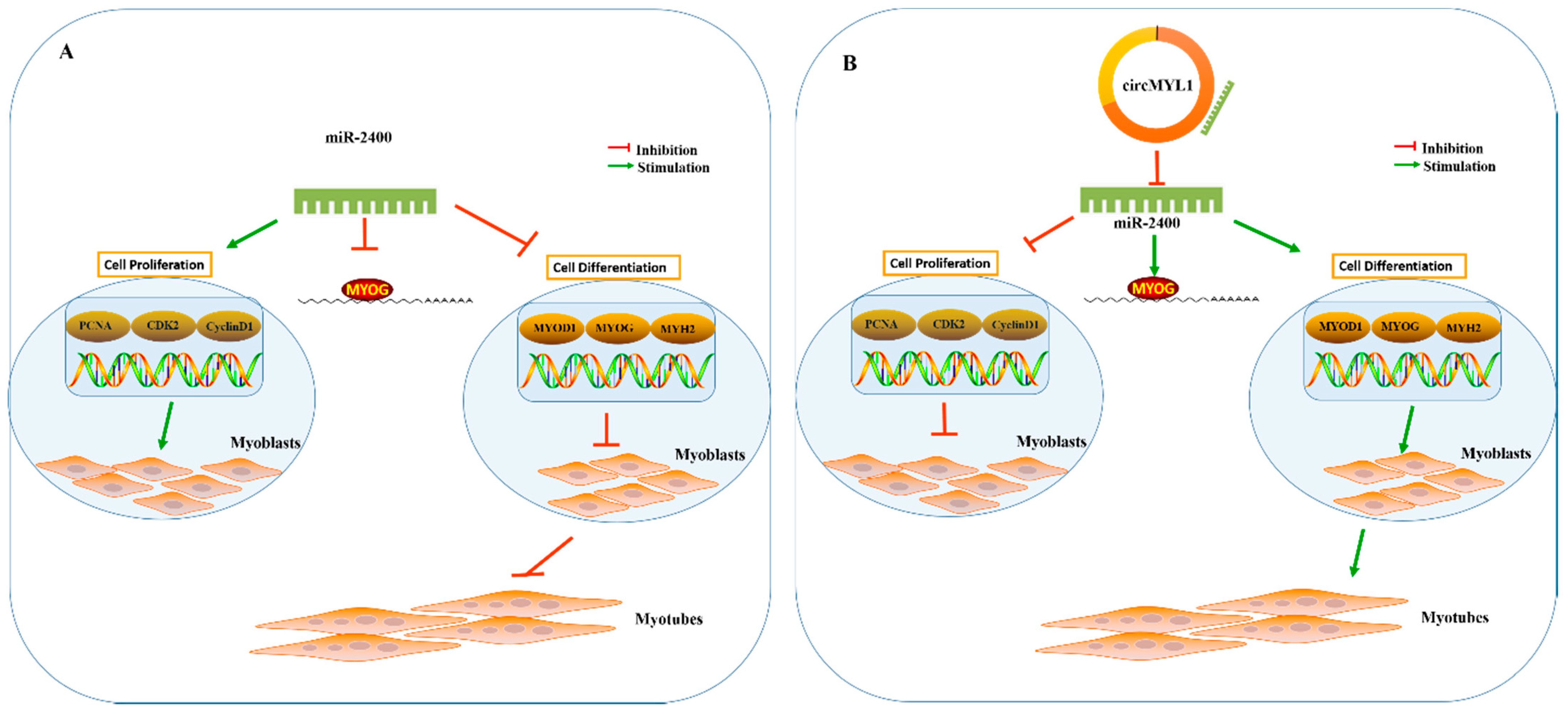
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Grand, F.; Rudnicki, M.A. Skeletal muscle satellite cells and adult myogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M. Gene regulatory networks and cell lineages that underlie the formation of skeletal muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5830–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M.E. Myogenic progenitor cells and skeletal myogenesis in vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2006, 16, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismuth, K.; Relaix, F. Genetic regulation of skeletal muscle development. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 3081–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentzinger, C.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Rudnicki, M.A. Building Muscle: Molecular Regulation of Myogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ge, Y.; Drnevich, J.; Zhao, Y.; Band, M.; Chen, J. Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates miRNA-1 and follistatin in skeletal myogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legnini, I.; Morlando, M.; Mangiavacchi, A.; Fatica, A.; Bozzoni, I. A Feedforward Regulatory Loop between HuR and the Long Noncoding RNA linc-MD1 Controls Early Phases of Myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, X. Circular RNA circSVIL Promotes Myoblast Proliferation and Differentiation by Sponging miR-203 in Chicken. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pas, M.F.W.T.; Keuning, E.; Hulsegge, B.; Hoving-Bolink, A.H.; Evans, G.; Mulder, H. Longissimus muscle transcriptome profiles related to carcass and meat quality traits in fresh meat Piétrain carcasses1. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 4044–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Tsukahara, T. A View of Pre-mRNA Splicing from RNase R Resistant RNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 9331–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, D.; Sun, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Dong, C.; Fu, K.; Tang, W.; Cao, H. An emerging function of circRNA-miRNAs-mRNA axis in human diseases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73271–73281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2012, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs Are the Predominant Transcript Isoform from Hundreds of Human Genes in Diverse Cell Types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA Biogenesis Competes with Pre-mRNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.-O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.-F.; Yin, Q.-F.; Xing, Y.-H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. Circular Intronic Long Noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Mao, M.; Song, X.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N6-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, X.; Mo, Y.; Fan, C.; Xiong, F.; Ren, D.; Ye, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Kuwano, Y.; Srikantan, S.; Lee, E.K.; Martindale, J.L.; Gorospe, M. HuR recruits let-7/RISC to repress c-Myc expression. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J.; Damgaard, C.K. Circular RNA and miR-7 in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5609–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.L.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentze, M.W.; Preiss, T. Circular RNAs: Splicing’s enigma variations. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 923–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, X.; Yang, J.; Dong, D.; Hao, D.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Plath, M.; Lei, C.; Ma, Y.; et al. circFGFR4 Promotes Differentiation of Myoblasts via Binding miR-107 to Relieve Its Inhibition of Wnt3a. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Fang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C. A Zfp609 circular RNA regulates myoblast differentiation by sponging miR-194-5p. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Hao, D.; Dong, D.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Plath, M.; Lei, C.; Lin, F.; et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circLMO7 that regulates myoblasts differentiation and survival by sponging miR-378a-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Wei, X.; Song, C.; Dong, D.; Huang, Y.-Z.; Lan, X.; Plath, M.; Lei, C.; Ma, Y.; et al. CircFUT10 reduces proliferation and facilitates differentiation of myoblasts by sponging miR-133a. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 4643–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Song, C.; Li, H.; Cao, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Chaogetu, B.; et al. Circular RNA SNX29 Sponges miR-744 to Regulate Proliferation and Differentiation of Myoblasts by Activating the Wnt5a/Ca2+ Signaling Pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloosterman, W.P.; Plasterk, R.H. The Diverse Functions of MicroRNAs in Animal Development and Disease. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Mo, W.-C.; Qiu, R.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.Y.; He, R. MiR-124 regulates early neurogenesis in the optic vesicle and forebrain, targeting NeuroD1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, 2869–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazov, E.A.; Kongsuwan, K.; Assavalapsakul, W.; Horwood, P.; Mitter, N.; Mahony, T.J. Repertoire of Bovine miRNA and miRNA-Like Small Regulatory RNAs Expressed upon Viral Infection. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-W.; Tong, H.; Sun, X.F.; Hu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.F.; Yan, Y.Q.; Li, G.-P. Identification of miR-2400 gene as a novel regulator in skeletal muscle satellite cells proliferation by targeting MYOG gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Cai, H.; Lan, X.; Huang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Qi, X.; Chen, H. The developmental transcriptome sequencing of bovine skeletal muscle reveals a long noncoding RNA, lncMD, promotes muscle differentiation by sponging miR-125b. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2016, 1863, 2835–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venø, M.T.; Hansen, T.B.; Venø, S.T.; Clausen, B.H.; Grebing, M.; Finsen, B.; Holm, I.E.; Kjems, J. Spatio-temporal regulation of circular RNA expression during porcine embryonic brain development. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, S.; Cardinali, B.; Falcone, G.; Martelli, F. Circular RNAs in Muscle Function and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Han, J.S.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, S.-J.; Park, T.S. Muscle differentiation induced up-regulation of calcium-related gene expression in quail myoblasts. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenscroft, G.; Zaharieva, I.T.; A Bortolotti, C.; Lambrughi, M.; Pignataro, M.; Borsari, M.; A Sewry, C.; Phadke, R.; Haliloglu, G.; Ong, R.; et al. Bi-allelic mutations in MYL1 cause a severe congenital myopathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 4263–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Nie, Q. A Novel Circular RNA Generated by FGFR2 Gene Promotes Myoblast Proliferation and Differentiation by Sponging miR-133a-5p and miR-29b-1-5p. Cells 2018, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, X.; Dong, D.; Shen, X.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, R.; Yang, Z.; Peng, S.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; et al. Circular RNA TTN Acts As a miR-432 Sponge to Facilitate Proliferation and Differentiation of Myoblasts via the IGF2/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elnour, I.E.; Wang, X.; Zhansaya, T.; Akhatayeva, Z.; Khan, R.; Cheng, J.; Hung, Y.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Chen, H. Circular RNA circMYL1 Inhibit Proliferation and Promote Differentiation of Myoblasts by Sponging miR-2400. Cells 2021, 10, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010176
Elnour IE, Wang X, Zhansaya T, Akhatayeva Z, Khan R, Cheng J, Hung Y, Lan X, Lei C, Chen H. Circular RNA circMYL1 Inhibit Proliferation and Promote Differentiation of Myoblasts by Sponging miR-2400. Cells. 2021; 10(1):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010176
Chicago/Turabian StyleElnour, Ibrahim Elsaeid, Xiaogang Wang, Toremurat Zhansaya, Zhanerke Akhatayeva, Rajwali Khan, Jie Cheng, Yongzhen Hung, Xianyong Lan, Chuzhao Lei, and Hong Chen. 2021. "Circular RNA circMYL1 Inhibit Proliferation and Promote Differentiation of Myoblasts by Sponging miR-2400" Cells 10, no. 1: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010176
APA StyleElnour, I. E., Wang, X., Zhansaya, T., Akhatayeva, Z., Khan, R., Cheng, J., Hung, Y., Lan, X., Lei, C., & Chen, H. (2021). Circular RNA circMYL1 Inhibit Proliferation and Promote Differentiation of Myoblasts by Sponging miR-2400. Cells, 10(1), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010176





