Complement as a Therapeutic Target in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
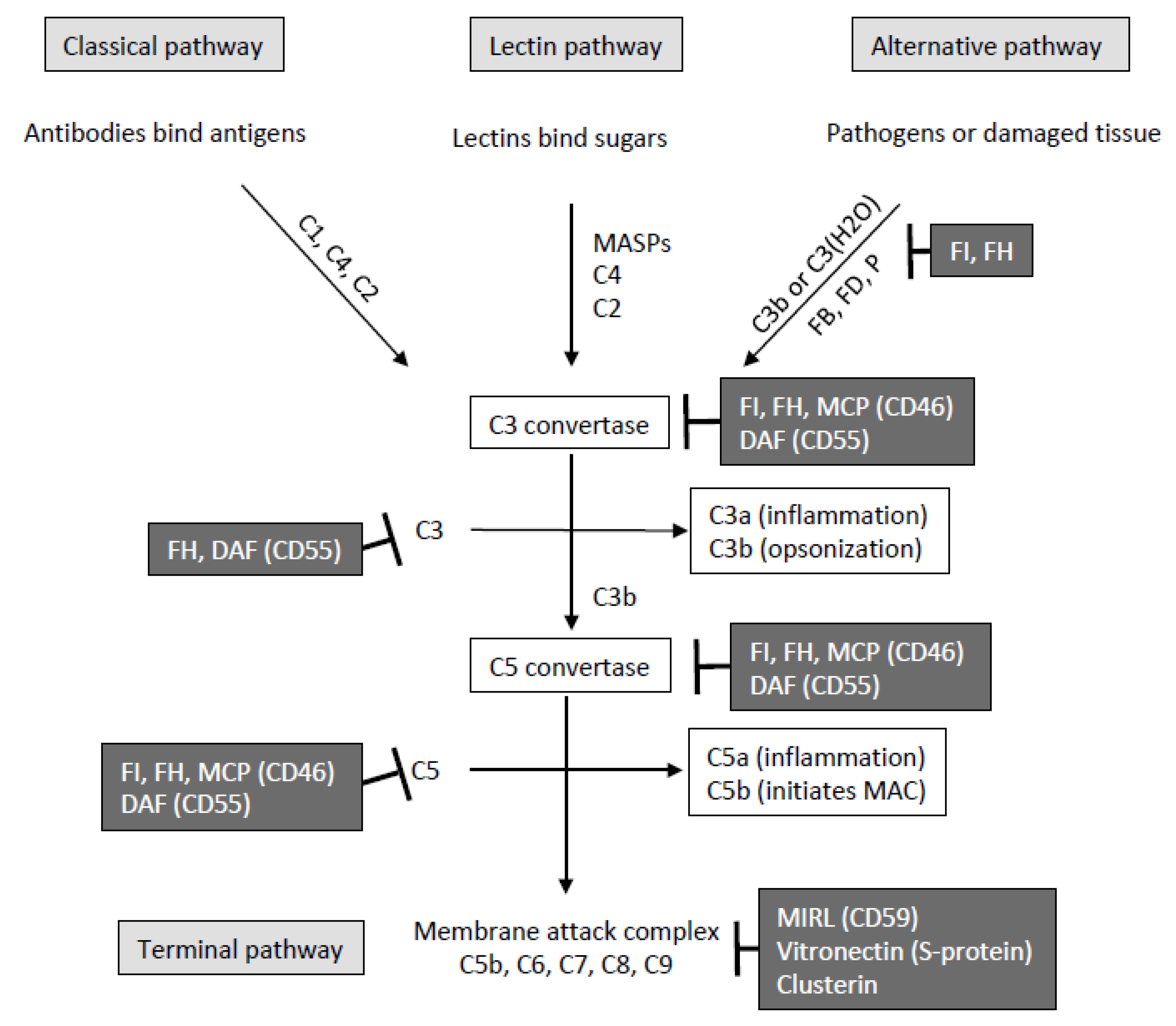
1. Introduction
2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
3. Antiphospholipid Syndrome
4. Sjögren’s Syndrome
5. Rheumatoid Arthritis
6. ANCA Associated Vasculitis
7. Other
8. The Complement System as a Therapeutic Target
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajic, G.; Degn, S.E.; Thiel, S.; Andersen, G.R. Complement Activation, Regulation, and Molecular Basis for Complement-Related Diseases. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2735–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricklin, D.; Reis, E.S.; Lambris, J.D. Complement in Disease: A Defence System Turning Offensive. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-H.; Tan, L.A.; Carroll, M.V.; Gentle, M.E.; Sim, R.B. Target Pattern Recognition by Complement Proteins of the Classical and Alternative Pathways. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 653, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, A.W.; Sim, R.B.; Porter, R.R.; Kerr, M.A. Activation of the First Component of Human Complement (C1) by Antibody-Antigen Aggregates. Biochem. J. 1978, 175, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlaud, G.J.; Gaboriaud, C.; Thielens, N.M.; Rossi, V. Structural Biology of C1. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002, 30, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaer, T.R.; Thiel, S.; Andersen, G.R. Toward a Structure-Based Comprehension of the Lectin Pathway of Complement. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 56, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobó, J.; Kocsis, A.; Gál, P. Be on Target: Strategies of Targeting Alternative and Lectin Pathway Components in Complement-Mediated Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troldborg, A.; Hansen, A.; Hansen, S.W.K.; Jensenius, J.C.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K.; Thiel, S. Lectin Complement Pathway Proteins in Healthy Individuals. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 188, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, J.M.; Holers, V.M. The Central Role of the Alternative Complement Pathway in Human Disease. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2006, 176, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, P.J. The Amplification Loop of the Complement Pathways. Adv. Immunol. 2009, 104, 115–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klos, A.; Tenner, A.J.; Johswich, K.-O.; Ager, R.R.; Reis, E.S.; Köhl, J. The Role of the Anaphylatoxins in Health and Disease. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2753–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewski, M.M.; Lambris, J.D. The Role of Complement in Inflammatory Diseases from behind the Scenes into the Spotlight. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipfel, P.F.; Skerka, C. Complement Regulators and Inhibitory Proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesher, A.M.; Song, W.-C. Review: Complement and Its Regulatory Proteins in Kidney Diseases. Nephrol. Carlton Vic. 2010, 15, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A Key System for Immune Surveillance and Homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaboriaud, C.; Ling, W.L.; Thielens, N.M.; Bally, I.; Rossi, V. Deciphering the Fine Details of C1 Assembly and Activation Mechanisms: “Mission Impossible”? Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero-Esparza, A.; Kalchishkova, N.; Kurbasic, E.; Jiang, W.G.; Blom, A.M. The Novel Complement Inhibitor Human CUB and Sushi Multiple Domains 1 (CSMD1) Protein Promotes Factor I-Mediated Degradation of C4b and C3b and Inhibits the Membrane Attack Complex Assembly. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2013, 27, 5083–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna, M.; Giles, J.L.; Morgan, B.P.; Bubeck, D. Structural Basis of Complement Membrane Attack Complex Formation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabib, A.; Karbian, N.; Mevorach, D. Demyelination, Strokes, and Eculizumab: Lessons from the Congenital CD59 Gene Mutations. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 89, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, C.; Köhl, J. Novel Roles for Complement Receptors in T Cell Regulation and Beyond. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 56, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holers, V.M. Complement and Its Receptors: New Insights into Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lintner, K.E.; Wu, Y.L.; Yang, Y.; Spencer, C.H.; Hauptmann, G.; Hebert, L.A.; Atkinson, J.P.; Yu, C.Y. Early Components of the Complement Classical Activation Pathway in Human Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botto, M.; Dell’Agnola, C.; Bygrave, A.E.; Thompson, E.M.; Cook, H.T.; Petry, F.; Loos, M.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Walport, M.J. Homozygous C1q Deficiency Causes Glomerulonephritis Associated with Multiple Apoptotic Bodies. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, G.S.; Crawford, G.; Buang, N.; Bartok, I.; Tian, K.; Thielens, N.M.; Bally, I.; Harker, J.A.; Ashton-Rickardt, P.G.; Rutschmann, S.; et al. C1q Restrains Autoimmunity and Viral Infection by Regulating CD8+ T Cell Metabolism. Science 2018, 360, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.; Norsworthy, P.J.; Hall, A.E.; Kelly, S.J.; Walport, M.J.; Botto, M.; Pickering, M.C. SLE with C1q Deficiency Treated with Fresh Frozen Plasma: A 10-Year Experience. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2010, 49, 823–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, A.C.L.; Isaac, L. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Deficiencies of Early Components of the Complement Classical Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degn, S.E.; Jensenius, J.C.; Thiel, S. Disease-Causing Mutations in Genes of the Complement System. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayilyan, K.R. Complement Genetics, Deficiencies, and Disease Associations. Protein Cell 2012, 3, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skare, T.L.; Nisihara, R.; Cieslinski, J.Z.; Zeni, J.O.; Rasera, H.N.; Messias-Reason, I.; Utiyama, S.R.R. Mannose-Binding Lectin Deficiency in Brazilian Patients with Spondyloarthritis. Immunol. Investig. 2017, 46, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-D.; Peng, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.-Z.; Pan, H.-F.; Ye, D.-Q. Association of RANTES and MBL Gene Polymorphisms with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troldborg, A.; Thiel, S.; Trendelenburg, M.; Friebus-Kardash, J.; Nehring, J.; Steffensen, R.; Hansen, S.W.K.; Laska, M.J.; Deleuran, B.; Jensenius, J.C.; et al. The Lectin Pathway of Complement Activation in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S Reis, E.; Falcão, D.A.; Isaac, L. Clinical Aspects and Molecular Basis of Primary Deficiencies of Complement Component C3 and Its Regulatory Proteins Factor I and Factor H. Scand. J. Immunol. 2006, 63, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, J.H.; Bayles, T.B.; Favour, C.B. The Response of Serum Gamma Globulin Level and Complement Titer to Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Therapy in Lupus Erythematosus Disseminatus. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1951, 37, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schur, P.H.; Sandson, J. Immunologic Factors and Clinical Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1968, 278, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentijn, R.M.; van Overhagen, H.; Hazevoet, H.M.; Hermans, J.; Cats, A.; Daha, M.R.; van ES, L.A. The Value of Complement and Immune Complex Determinations in Monitoring Disease Activity in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1985, 28, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmasso, A.P. Complement in the Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Human Diseases. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1986, 24, 123–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi, S.; Rairie, J.E.; Carpenter, A.B.; Kelly, R.H.; Jagarlapudi, S.P.; Sereika, S.M.; Medsger, T.A.; Ramsey-Goldman, R. Sensitivity and Specificity of Plasma and Urine Complement Split Products as Indicators of Lupus Disease Activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojan, G.; Petri, M. Anti-C1q in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus 2016, 25, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, M.; van Schaarenburg, R.A.; Trouw, L.A. Anti-C1q Autoantibodies, Novel Tests, and Clinical Consequences. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelen, M.A.; Trouw, L.A.; van der Hoorn, J.W.A.; Fallaux-van den Houten, F.C.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Daha, M.R.; Roos, A. Autoantibodies against Mannose-Binding Lectin in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 134, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plawecki, M.; Lheritier, E.; Clavarino, G.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Ouili, S.; Paul, S.; Gout, E.; Sarrot-Reynauld, F.; Bardin, N.; Boëlle, P.-Y.; et al. Association between the Presence of Autoantibodies Targeting Ficolin-3 and Active Nephritis in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wu, X.; Shan, G.; Zhang, X. Diagnostic Value of Serum Anti-C1q Antibodies in Patients with Lupus Nephritis: A Meta-Analysis. Lupus 2012, 21, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, C.T.; Østergaard, O.; Stener, L.; Iversen, L.V.; Truedsson, L.; Gullstrand, B.; Jacobsen, S.; Heegaard, N.H.H. Increased IgG on Cell-Derived Plasma Microparticles in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Is Associated with Autoantibodies and Complement Activation. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, C.G.; Burge, J.J. A New Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for Measuring Immunoconglutinins Directed against the Third Component of Human Complement. Findings in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. Methods 1984, 73, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, K.D.; Cole, C.; Crawford, F.; Kappler, J.W.; Thurman, J.M.; Bratton, D.L.; Boackle, S.A.; Henson, P.M. IgG Autoantibodies against Deposited C3 Inhibit Macrophage-Mediated Apoptotic Cell Engulfment in Systemic Autoimmunity. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2011, 187, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmingham, D.J.; Bitter, J.E.; Ndukwe, E.G.; Dials, S.; Gullo, T.R.; Conroy, S.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Rovin, B.H.; Hebert, L.A. Relationship of Circulating Anti-C3b and Anti-C1q IgG to Lupus Nephritis and Its Flare. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2016, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmingham, D.J.; Merchant, M.; Waikar, S.S.; Nagaraja, H.; Klein, J.B.; Rovin, B.H. Biomarkers of Lupus Nephritis Histology and Flare: Deciphering the Relevant amidst the Noise. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2017, 32, i71–i79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilev, V.V.; Noe, R.; Dragon-Durey, M.-A.; Chauvet, S.; Lazarov, V.J.; Deliyska, B.P.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Dimitrov, J.D.; Roumenina, L.T. Functional Characterization of Autoantibodies against Complement Component C3 in Patients with Lupus Nephritis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 25343–25355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészáros, T.; Füst, G.; Farkas, H.; Jakab, L.; Temesszentandrási, G.; Nagy, G.; Kiss, E.; Gergely, P.; Zeher, M.; Griger, Z.; et al. C1-Inhibitor Autoantibodies in SLE. Lupus 2010, 19, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavai, M. Immune Complex Clearance by Complement Receptor Type 1 in SLE. Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 8, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richaud-Patin, Y.; Pérez-Romano, B.; Carrillo-Maravilla, E.; Rodriguez, A.B.; Simon, A.J.; Cabiedes, J.; Jakez-Ocampo, J.; Llorente, L.; Ruiz-Argüelles, A. Deficiency of Red Cell Bound CD55 and CD59 in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunol. Lett. 2003, 88, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegretti, A.P.; Mucenic, T.; Merzoni, J.; Faulhaber, G.A.; Silla, L.M.; Xavier, R.M. Expression of CD55 and CD59 on Peripheral Blood Cells from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Patients. Cell. Immunol. 2010, 265, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, M.; Seya, T.; Koni, I.; Mabuchi, H. Elevated Serum Levels of Soluble Membrane Cofactor Protein (CD46, MCP) in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1999, 116, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, M.-H.; Lin, S.-H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chien, H.-P.; Yang, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chou, Y.-C.; Huang, J.-L. Serum Complement Factor I Is Associated with Disease Activity of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8502–8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hein, E.; Nielsen, L.A.; Nielsen, C.T.; Munthe-Fog, L.; Skjoedt, M.-O.; Jacobsen, S.; Garred, P. Ficolins and the Lectin Pathway of Complement in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 63, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, S.B.; Given, W.P.; Edelson, H.S.; Weissmann, G. Neutrophil Aggregation Induced by Sera from Patients with Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1983, 26, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpman, D.; Kahn, R. The Contact/Kinin and Complement Systems in Vasculitis. APMIS. Suppl. 2009, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, S.; Vives, G.; Ferré, R.; González, M.; Guardiola, M.; Ribalta, J.; Castro, A. Complement System and Small HDL Particles Are Associated with Subclinical Atherosclerosis in SLE Patients. Atherosclerosis 2012, 225, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holers, V.M.; Girardi, G.; Mo, L.; Guthridge, J.M.; Molina, H.; Pierangeli, S.S.; Espinola, R.; Xiaowei, L.E.; Mao, D.; Vialpando, C.G.; et al. Complement C3 Activation Is Required for Antiphospholipid Antibody-Induced Fetal Loss. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, G.; Berman, J.; Redecha, P.; Spruce, L.; Thurman, J.M.; Kraus, D.; Hollmann, T.J.; Casali, P.; Caroll, M.C.; Wetsel, R.A.; et al. Complement C5a Receptors and Neutrophils Mediate Fetal Injury in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischetti, F.; Durigutto, P.; Pellis, V.; Debeus, A.; Macor, P.; Bulla, R.; Bossi, F.; Ziller, F.; Sblattero, D.; Meroni, P.; et al. Thrombus Formation Induced by Antibodies to Beta2-Glycoprotein I Is Complement Dependent and Requires a Priming Factor. Blood 2005, 106, 2340–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, A.M.; Gibbs, R.S.; Murphy, J.R.; Giclas, P.C.; Salmon, J.E.; Holers, V.M. Early Elevations of the Complement Activation Fragment C3a and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 117, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurman, J.M.; Kraus, D.M.; Girardi, G.; Hourcade, D.; Kang, H.J.; Royer, P.A.; Mitchell, L.M.; Giclas, P.C.; Salmon, J.; Gilkeson, G.; et al. A Novel Inhibitor of the Alternative Complement Pathway Prevents Antiphospholipid Antibody-Induced Pregnancy Loss in Mice. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nangaku, M.; Alpers, C.E.; Pippin, J.; Shankland, S.J.; Kurokawa, K.; Adler, S.; Morgan, B.P.; Johnson, R.J.; Couser, W.G. CD59 Protects Glomerular Endothelial Cells from Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 1998, 9, 590–597. [Google Scholar]
- Pierangeli, S.S.; Girardi, G.; Vega-Ostertag, M.; Liu, X.; Espinola, R.G.; Salmon, J. Requirement of Activation of Complement C3 and C5 for Antiphospholipid Antibody-Mediated Thrombophilia. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.D.; Brey, R.L. Antiphospholipid Antibodies and Complement Activation in Patients with Cerebral Ischemia. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1992, 10, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Breen, K.A.; Seed, P.; Parmar, K.; Moore, G.W.; Stuart-Smith, S.E.; Hunt, B.J. Complement Activation in Patients with Isolated Antiphospholipid Antibodies or Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 107, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, P.L.; Macor, P.; Durigutto, P.; De Maso, L.; Gerosa, M.; Ferraresso, M.; Borghi, M.O.; Mollnes, T.E.; Tedesco, F. Complement Activation in Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Its Inhibition to Prevent Rethrombosis after Arterial Surgery. Blood 2016, 127, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropp, K.; Weber, N.; Reuter, M.; Micklisch, S.; Kopka, I.; Hallström, T.; Skerka, C. Β₂-Glycoprotein I, the Major Target in Antiphospholipid Syndrome, Is a Special Human Complement Regulator. Blood 2011, 118, 2774–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Brodsky, R.A.; McCrae, K.R. Complement in the Pathophysiology of the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, J.E.; Girardi, G. Antiphospholipid Antibodies and Pregnancy Loss: A Disorder of Inflammation. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2008, 77, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, K.; Atsumi, T.; Bohgaki, M.; Amengual, O.; Kataoka, H.; Horita, T.; Yasuda, S.; Koike, T. Complement Activation in Patients with Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, M.; Watson, R.; Winkelstein, J.A.; McLean, R.H. Clinical Expression of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Patients with C4A Deficiency. Med. (Baltim.) 1993, 72, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturfelt, G.; Sjöholm, A.G.; Svensson, B. Complement Components, C1 Activation and Disease Activity in SLE. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1983, 70, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brito-Zerón, P.; Yagüe, J.; Akasbi, M.; Bautista, R.; Ruano, M.; Claver, G.; Gil, V.; Font, J. Hypocomplementaemia as an Immunological Marker of Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2005, 44, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, G.J.; Lappin, D.; Birnie, G.D.; Whaley, K. Complement Biosynthesis in Human Synovial Tissue. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1989, 78, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, S.M.; Morgan, B.P. Complement Activation and Inhibition in Experimental Models of Arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 1999, 36, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, E.; Barnum, S.R.; Tarner, I.H.; Echols, J.; Fleck, M.; Judex, M.; Kullmann, F.; Mountz, J.D.; Schölmerich, J.; Gay, S.; et al. Local Production of Complement Proteins in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, R.D.; Harpel, P.C. C1 Inactivator-C1s Complexes in Inflammatory Joint Disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1983, 53, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Moxley, G.; Ruddy, S. Elevated C3 Anaphylatoxin Levels in Synovial Fluids from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985, 28, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollnes, T.E.; Paus, A. Complement Activation in Synovial Fluid and Tissue from Patients with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaak, A.J.; Van Rooyen, A.; Planten, O.; Han, H.; Hattink, O.; Hack, E. An Analysis of the Levels of Complement Components in the Synovial Fluid in Rheumatic Diseases. Clin. Rheumatol. 1987, 6, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodeur, J.P.; Ruddy, S.; Schwartz, L.B.; Moxley, G. Synovial Fluid Levels of Complement SC5b-9 and Fragment Bb Are Elevated in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 34, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingu, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Tomooka, K.; Yoshioka, K.; Ohtsuka, E.; Nobunaga, M. Complement Degradation Products in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fluid. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 33, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, M.; Richards, N.; Hornby, J.; Powell, R. Relation between Synovial Fluid C3 Degradation Products and Local Joint Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis, and Crystal Associated Arthropathy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1988, 47, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, P.J.; Moss, I.K.; Maini, R.N.; Williams, T.J. Measurement of the Chemotactic Complement Fragment C5a in Rheumatoid Synovial Fluids by Radioimmunoassay: Role of C5a in the Acute Inflammatory Phase. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1990, 49, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konttinen, Y.T.; Ceponis, A.; Meri, S.; Vuorikoski, A.; Kortekangas, P.; Sorsa, T.; Sukura, A.; Santavirta, S. Complement in Acute and Chronic Arthritides: Assessment of C3c, C9, and Protectin (CD59) in Synovial Membrane. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1996, 55, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöholm, A.G.; Berglund, K.; Johnson, U.; Laurell, A.B.; Sturfelt, G. C1 Activation, with C1q in Excess of Functional C1 in Synovial Fluid from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1986, 79, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okroj, M.; Heinegård, D.; Holmdahl, R.; Blom, A.M. Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Complement System. Ann. Med. 2007, 39, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, D.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Molenaar, E.T.H.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Hack, C.E. Evaluation of Classical Complement Pathway Activation in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Measurement of C1q-C4 Complexes as Novel Activation Products. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, A.; Onnerfjord, P.; Mörgelin, M.; Heinegård, D.; Blom, A.M. The Extracellular Matrix and Inflammation: Fibromodulin Activates the Classical Pathway of Complement by Directly Binding C1q. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 32301–32308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöberg, A.P.; Manderson, G.A.; Mörgelin, M.; Day, A.J.; Heinegård, D.; Blom, A.M. Short Leucine-Rich Glycoproteins of the Extracellular Matrix Display Diverse Patterns of Complement Interaction and Activation. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happonen, K.E.; Saxne, T.; Aspberg, A.; Mörgelin, M.; Heinegård, D.; Blom, A.M. Regulation of Complement by Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein Allows for a Novel Molecular Diagnostic Principle in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3574–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin Fürst, C.; Mörgelin, M.; Vadstrup, K.; Heinegård, D.; Aspberg, A.; Blom, A.M. The C-Type Lectin of the Aggrecan G3 Domain Activates Complement. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, N.K.; Kraus, D.; Vondracek, A.; Huynh, L.H.; Bendele, A.; Holers, V.M.; Arend, W.P. Mechanisms of Effects of Complement Inhibition in Murine Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietala, M.A.; Jonsson, I.-M.; Tarkowski, A.; Kleinau, S.; Pekna, M. Complement Deficiency Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2002, 169, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietala, M.A.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Persson, L.; Fahlén, S.; Holmdahl, R.; Pekna, M. Complement Activation by Both Classical and Alternative Pathways Is Critical for the Effector Phase of Arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holers, V.M.; Banda, N.K. Complement in the Initiation and Evolution of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Ohmura, K.; Mahmood, U.; Lee, D.M.; Hofhuis, F.M.A.; Boackle, S.A.; Takahashi, K.; Holers, V.M.; Walport, M.; Gerard, C.; et al. Arthritis Critically Dependent on Innate Immune System Players. Immunity 2002, 16, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, N.K.; Thurman, J.M.; Kraus, D.; Wood, A.; Carroll, M.C.; Arend, W.P.; Holers, V.M. Alternative Complement Pathway Activation Is Essential for Inflammation and Joint Destruction in the Passive Transfer Model of Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2006, 177, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, N.K.; Takahashi, K.; Wood, A.K.; Holers, V.M.; Arend, W.P. Pathogenic Complement Activation in Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis in Mice Requires Amplification by the Alternative Pathway. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2007, 179, 4101–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferluga, J.; Kouser, L.; Murugaiah, V.; Sim, R.B.; Kishore, U. Potential Influences of Complement Factor H in Autoimmune Inflammatory and Thrombotic Disorders. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 84, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, N.K.; Levitt, B.; Glogowska, M.J.; Thurman, J.M.; Takahashi, K.; Stahl, G.L.; Tomlinson, S.; Arend, W.P.; Holers, V.M. Targeted Inhibition of the Complement Alternative Pathway with Complement Receptor 2 and Factor H Attenuates Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis in Mice. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2009, 183, 5928–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltyn Zadura, A.; Zipfel, P.F.; Bokarewa, M.I.; Sturfelt, G.; Jönsen, A.; Nilsson, S.C.; Hillarp, A.; Saxne, T.; Trouw, L.A.; Blom, A.M. Factor H Autoantibodies and Deletion of Complement Factor H-Related Protein-1 in Rheumatic Diseases in Comparison to Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamann, J.; Wishaupt, J.O.; van Lier, R.A.; Smeets, T.J.; Breedveld, F.C.; Tak, P.P. Expression of the Activation Antigen CD97 and Its Ligand CD55 in Rheumatoid Synovial Tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, R.M.; de Launay, D.; Kop, E.N.; Yilmaz-Elis, A.S.; Lin, F.; Reedquist, K.A.; Verbeek, J.S.; Medof, M.E.; Tak, P.P.; Hamann, J. Deletion of Either CD55 or CD97 Ameliorates Arthritis in Mouse Models. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouskoff, V.; Korganow, A.S.; Duchatelle, V.; Degott, C.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Organ-Specific Disease Provoked by Systemic Autoimmunity. Cell 1996, 87, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Marin, E.; Shimizu, J.; Kanagawa, O.; Unanue, E.R. The Class II MHC I-Ag7 Molecules from Non-Obese Diabetic Mice Are Poor Peptide Binders. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 1996, 156, 450–458. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, I.; Staub, A.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Arthritis Provoked by Linked T and B Cell Recognition of a Glycolytic Enzyme. Science 1999, 286, 1732–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Horvath, S.; Matsumoto, I.; Fremont, D.H.; Allen, P.M. Molecular Basis for Recognition of an Arthritic Peptide and a Foreign Epitope on Distinct MHC Molecules by a Single TCR. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2000, 164, 5788–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korganow, A.S.; Ji, H.; Mangialaio, S.; Duchatelle, V.; Pelanda, R.; Martin, T.; Degott, C.; Kikutani, H.; Rajewsky, K.; Pasquali, J.L.; et al. From Systemic T Cell Self-Reactivity to Organ-Specific Autoimmune Disease via Immunoglobulins. Immunity 1999, 10, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Gauguier, D.; Ohmura, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Duchatelle, V.; Danoy, P.; Garchon, H.J.; Degott, C.; Lathrop, M.; Benoist, C.; et al. Genetic Influences on the End-Stage Effector Phase of Arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, I.; Maccioni, M.; Lee, D.M.; Maurice, M.; Simmons, B.; Brenner, M.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. How Antibodies to a Ubiquitous Cytoplasmic Enzyme May Provoke Joint-Specific Autoimmune Disease. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monach, P.A.; Verschoor, A.; Jacobs, J.P.; Carroll, M.C.; Wagers, A.J.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Circulating C3 Is Necessary and Sufficient for Induction of Autoantibody-Mediated Arthritis in a Mouse Model. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2968–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, P.Y.; Arora, V.; Ji, M.Q.; Wright, A.C.; Eisenberg, R.A. KRN/I-Ag7 Mouse Arthritis Is Independent of Complement C3. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Solomon, S.; Kolb, C.; Mohanty, S.; Jeisy-Walder, E.; Preyer, R.; Schöllhorn, V.; Illges, H. Transmission of Antibody-Induced Arthritis Is Independent of Complement Component 4 (C4) and the Complement Receptors 1 and 2 (CD21/35). Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubart, A.; Anderson, K.; Mainolfi, N.; Sellner, H.; Ehara, T.; Adams, C.M.; Mac Sweeney, A.; Liao, S.-M.; Crowley, M.; Littlewood-Evans, A.; et al. Small-Molecule Factor B Inhibitor for the Treatment of Complement-Mediated Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7926–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornum, L.; Hansen, A.J.; Tornehave, D.; Fjording, M.S.; Colmenero, P.; Wätjen, I.F.; Søe Nielsen, N.H.; Bliddal, H.; Bartels, E.M. C5a and C5aR Are Elevated in Joints of Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Patients, and C5aR Blockade Attenuates Leukocyte Migration to Synovial Fluid. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Zhao, M.-H. Complement in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Mechanisms and Implications for Management. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, L.; Haroche, J.; Mathian, A.; Gorochov, G.; Amoura, Z. Pathogenesis of Takayasu’s Arteritis: A 2011 Update. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 11, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimenti, M.S.; Ballanti, E.; Triggianese, P.; Perricone, R. Vasculitides and the Complement System: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 49, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Schreiber, A.; Heeringa, P.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Alternative Complement Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Disease Mediated by Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Heeringa, P.; Hu, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Aratani, Y.; Maeda, N.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies Specific for Myeloperoxidase Cause Glomerulonephritis and Vasculitis in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Dairaghi, D.J.; Powers, J.P.; Ertl, L.S.; Baumgart, T.; Wang, Y.; Seitz, L.C.; Penfold, M.E.T.; Gan, L.; Hu, P.; et al. C5a Receptor (CD88) Blockade Protects against MPO-ANCA GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2014, 25, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.; Chen, M.; Liu, G.; Heeringa, P.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; Jie, E.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; Zhao, M. Complement Activation Is Involved in Renal Damage in Human Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody Associated Pauci-Immune Vasculitis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Li, D.-Y.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.-H. Platelets Are Activated in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis via Thrombin-PARs Pathway and Can Activate the Alternative Complement Pathway. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-F.; Wang, F.-M.; Li, Z.-Y.; Yu, F.; Zhao, M.-H.; Chen, M. Plasma Complement Factor H Is Associated with Disease Activity of Patients with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-F.; Wang, F.-M.; Li, Z.-Y.; Yu, F.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.-H. The Functional Activities of Complement Factor H Are Impaired in Patients with ANCA-Positive Vasculitis. Clin. Immunol. Orlando Fla. 2017, 175, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Gou, S.-J.; Huang, J.; Hao, J.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.-H. C5a and Its Receptors in Human Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, S.-J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, M.-H.; Chen, M. Alternative Complement Pathway Activation Products in Urine and Kidneys of Patients with ANCA-Associated GN. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2013, 8, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilhorst, M.; van Paassen, P.; van Rie, H.; Bijnens, N.; Heerings-Rewinkel, P.; van Breda Vriesman, P.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W. Limburg Renal Registry Complement in ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2017, 32, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.; Walker, J.G.; Fritzler, M.; Taillefer, S.; Baron, M. Hypocomplementemia in Systemic Sclerosis--Clinical and Serological Correlations. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 2218–2223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Devresse, A.; Aydin, S.; Le Quintrec, M.; Demoulin, N.; Stordeur, P.; Lambert, C.; Gastoldi, S.; Pirson, Y.; Jadoul, M.; Morelle, J. Complement Activation and Effect of Eculizumab in Scleroderma Renal Crisis. Med. (Baltim.) 2016, 95, e4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissel, J.T.; Mendell, J.R.; Rammohan, K.W. Microvascular Deposition of Complement Membrane Attack Complex in Dermatomyositis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leddy, J.P.; Griggs, R.C.; Klemperer, M.R.; Frank, M.M. Hereditary Complement (C2) Deficiency with Dermatomyositis. Am. J. Med. 1975, 58, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascaró, J.M.; Hausmann, G.; Herrero, C.; Grau, J.M.; Cid, M.C.; Palou, J.; Mascaró, J.M. Membrane Attack Complex Deposits in Cutaneous Lesions of Dermatomyositis. Arch. Dermatol. 1995, 131, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, E.; Furuta, J.; Kawachi, Y.; Imakado, S.; Otsuka, F. Hereditary Complement (C9) Deficiency Associated with Dermatomyositis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2001, 144, 1080–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, C.M.; Licht, C.; Muus, P.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Babu, S.; Bedrosian, C.; Bingham, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Delmas, Y.; Douglas, K.; et al. Terminal Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Atypical Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J.; Hill, A.; Arnold, L.M.; Brooksbank, G.L.; Richards, S.J.; Cullen, M.; Mitchell, L.D.; Cohen, D.R.; Gregory, W.M.; Hillmen, P. Long-Term Treatment with Eculizumab in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: Sustained Efficacy and Improved Survival. Blood 2011, 117, 6786–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Young, N.S.; Schubert, J.; Brodsky, R.A.; Socié, G.; Muus, P.; Röth, A.; Szer, J.; Elebute, M.O.; Nakamura, R.; et al. The Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, M.A.; Grivcheva-Panovska, V.; Moldovan, D.; Baker, J.; Yang, W.H.; Giannetti, B.M.; Reshef, A.; Andrejevic, S.; Lockey, R.F.; Hakl, R.; et al. Recombinant Human C1 Esterase Inhibitor for Prophylaxis of Hereditary Angio-Oedema: A Phase 2, Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2017, 390, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.F.; Utsugisawa, K.; Benatar, M.; Murai, H.; Barohn, R.J.; Illa, I.; Jacob, S.; Vissing, J.; Burns, T.M.; Kissel, J.T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Eculizumab in Anti-Acetylcholine Receptor Antibody-Positive Refractory Generalised Myasthenia Gravis (REGAIN): A Phase 3, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicentre Study. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittock, S.J.; Berthele, A.; Fujihara, K.; Kim, H.J.; Levy, M.; Palace, J.; Nakashima, I.; Terzi, M.; Totolyan, N.; Viswanathan, S.; et al. Eculizumab in Aquaporin-4-Positive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, B.H.; Lee, T.J.; Snyderman, R.; Brooks, G.F. Neisseria Meningitidis and Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Bacteremia Associated with C6, C7, or C8 Deficiency. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 90, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducret, F.; Decoux, M.; Pointet, P.; Lambert, C.; Grosperrin, E.; Sédaillan, A. [Hereditary C5 deficiency and recurrent Neisseria meningitidis meningitis]. Rev. Med. Interne 1988, 9, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, C.D. The Complement Profile in Clinical Medicine. Inherited and Acquired Conditions Lowering the Serum Concentrations of Complement Component and Control Proteins. Complement Inflamm. 1989, 6, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Lambris, J.D. New Milestones Ahead in Complement-Targeted Therapy. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, R.P.; Rollins, S.A.; Mojcik, C.F.; Brodsky, R.A.; Bell, L. Discovery and Development of the Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab for the Treatment of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaffey, K.W.; Granger, C.B.; Nicolau, J.C.; Ruzyllo, W.; Weaver, W.D.; Theroux, P.; Hochman, J.S.; Filloon, T.G.; Mojcik, C.F.; Todaro, T.G.; et al. Effect of Pexelizumab, an Anti-C5 Complement Antibody, as Adjunctive Therapy to Fibrinolysis in Acute Myocardial Infarction: The COMPlement Inhibition in Myocardial Infarction Treated with ThromboLYtics (COMPLY) Trial. Circulation 2003, 108, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.B.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Weaver, W.D.; Theroux, P.; Hochman, J.S.; Filloon, T.G.; Rollins, S.; Todaro, T.G.; Nicolau, J.C.; Ruzyllo, W.; et al. Pexelizumab, an Anti-C5 Complement Antibody, as Adjunctive Therapy to Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Acute Myocardial Infarction: The COMplement Inhibition in Myocardial Infarction Treated with Angioplasty (COMMA) Trial. Circulation 2003, 108, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, R.A. Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Blood 2014, 124, 2804–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillmen, P.; Hall, C.; Marsh, J.C.W.; Elebute, M.; Bombara, M.P.; Petro, B.E.; Cullen, M.J.; Richards, S.J.; Rollins, S.A.; Mojcik, C.F.; et al. Effect of Eculizumab on Hemolysis and Transfusion Requirements in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, R.A.; Young, N.S.; Antonioli, E.; Risitano, A.M.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Schubert, J.; Gaya, A.; Coyle, L.; de Castro, C.; Fu, C.-L.; et al. Multicenter Phase 3 Study of the Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab for the Treatment of Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Blood 2008, 111, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillmen, P.; Muus, P.; Röth, A.; Elebute, M.O.; Risitano, A.M.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Szer, J.; Browne, P.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Schubert, J.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Sustained Eculizumab Treatment in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillmen, P.; Muus, P.; Dührsen, U.; Risitano, A.M.; Schubert, J.; Luzzatto, L.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Szer, J.; Brodsky, R.A.; Hill, A.; et al. Effect of the Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab on Thromboembolism in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Blood 2007, 110, 4123–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loschi, M.; Porcher, R.; Barraco, F.; Terriou, L.; Mohty, M.; de Guibert, S.; Mahe, B.; Lemal, R.; Dumas, P.-Y.; Etienne, G.; et al. Impact of Eculizumab Treatment on Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: A Treatment versus No-Treatment Study. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokiranta, T.S. HUS and Atypical HUS. Blood 2017, 129, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, C.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Muus, P.; Babu, S.; Bedrosian, C.L.; Cohen, D.J.; Delmas, Y.; Douglas, K.; Furman, R.R.; Gaber, O.A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Eculizumab in Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome from 2-Year Extensions of Phase 2 Studies. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, F.; Hourmant, M.; Campistol, J.M.; Cataland, S.R.; Espinosa, M.; Gaber, A.O.; Menne, J.; Minetti, E.E.; Provôt, F.; Rondeau, E.; et al. Terminal Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Adult Patients With Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Single-Arm, Open-Label Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2016, 68, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, L.A.; Fila, M.; Ardissino, G.; Al-Akash, S.I.; Evans, J.; Henning, P.; Lieberman, K.V.; Maringhini, S.; Pape, L.; Rees, L.; et al. Eculizumab Is a Safe and Effective Treatment in Pediatric Patients with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivarelli, M.; Emma, F. Treatment of C3 Glomerulopathy with Complement Blockers. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2014, 40, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röth, A.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Hill, A.; Bachman, E.S.; Kim, J.S.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Terriou, L.; Urbano-Ispizua, Á.; Wells, R.A.; Jang, J.H.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: Results of 2 Phase 1b/2 Studies. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Sicre de Fontbrune, F.; Wong Lee Lee, L.; Pessoa, V.; Gualandro, S.; Füreder, W.; Ptushkin, V.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Volles, L.; Shafner, L.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs. Eculizumab in Adult Patients with PNH Naive to Complement Inhibitors: The 301 Study. Blood 2019, 133, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, E.; Scully, M.; Ariceta, G.; Barbour, T.; Cataland, S.; Heyne, N.; Miyakawa, Y.; Ortiz, S.; Swenson, E.; Vallee, M.; et al. The Long-Acting C5 Inhibitor, Ravulizumab, Is Effective and Safe in Adult Patients with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Naïve to Complement Inhibitor Treatment. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinsson, K.; Erlendsson, K.; Valdimarsson, H. Successful Plasma Infusion Treatment of a Patient with C2 Deficiency and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Clinical Experience over Forty-Five Months. Arthritis Rheum. 1989, 32, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Madri, J.A.; Rollins, S.A.; Chodera, A.; Matis, L.A. Amelioration of Lupus-like Autoimmune Disease in NZB/WF1 Mice after Treatment with a Blocking Monoclonal Antibody Specific for Complement Component C5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8563–8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.H.; Caselman, N.; Ulmer, S.; Weitz, I.C. Complement-Mediated Thrombotic Microangiopathy Associated with Lupus Nephritis. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2090–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, M.C.; Ismajli, M.; Condon, M.B.; McKenna, N.; Hall, A.E.; Lightstone, L.; Terence Cook, H.; Cairns, T.D. Eculizumab as Rescue Therapy in Severe Resistant Lupus Nephritis. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2015, 54, 2286–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppo, R.; Peruzzi, L.; Amore, A.; Martino, S.; Vergano, L.; Lastauka, I.; Schieppati, A.; Noris, M.; Tovo, P.A.; Remuzzi, G. Dramatic Effects of Eculizumab in a Child with Diffuse Proliferative Lupus Nephritis Resistant to Conventional Therapy. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2015, 30, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, S.; Radin, M.; Yazdany, J.; Tektonidou, M.; Cecchi, I.; Roccatello, D.; Dall’Era, M. Expanding the Therapeutic Options for Renal Involvement in Lupus: Eculizumab, Available Evidence. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kello, N.; Khoury, L.E.; Marder, G.; Furie, R.; Zapantis, E.; Horowitz, D.L. Secondary Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Antiphospholipid Syndrome, the Role of Complement and Use of Eculizumab: Case Series and Review of Literature. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Husseini, A.; Hannan, S.; Awad, A.; Jennings, S.; Cornea, V.; Sawaya, B.P. Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Efficacy of Eculizumab. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2015, 65, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadaya, K.; Ferrari-Lacraz, S.; Fumeaux, D.; Boehlen, F.; Toso, C.; Moll, S.; Martin, P.-Y.; Villard, J. Eculizumab in Acute Recurrence of Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Renal Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2011, 11, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, I.; Andrade, D.; Allen, S.L.; Salmon, J.E. Brief Report: Induction of Sustained Remission in Recurrent Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome via Inhibition of Terminal Complement with Eculizumab. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2719–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, R.M.; Williams, A.S.; Levin, J.L.; Williams, B.D.; Morgan, B.P. Soluble Complement Receptor One (SCR1) Inhibits the Development and Progression of Rat Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 119, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, R.S.; Lee, D.; Foley, J.J.; Jurewicz, A.J.; Tornetta, M.A.; Bautsch, W.; Settmacher, B.; Klos, A.; Erhard, K.F.; Cousins, R.D.; et al. Identification of a Selective Nonpeptide Antagonist of the Anaphylatoxin C3a Receptor That Demonstrates Antiinflammatory Activity in Animal Models. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2001, 166, 6341–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, T.M.; Strachan, A.J.; Dryburgh, N.; Shiels, I.A.; Reid, R.C.; Fairlie, D.P.; Taylor, S.M. Antiarthritic Activity of an Orally Active C5a Receptor Antagonist against Antigen-Induced Monarticular Arthritis in the Rat. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2476–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.A.; Harris, C.L.; Williams, A.S.; Mizuno, M.; Gallagher, S.; Smith, R.A.G.; Morgan, B.P. Generation of a Recombinant, Membrane-Targeted Form of the Complement Regulator CD59: Activity in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48921–48927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macor, P.; Durigutto, P.; De Maso, L.; Garrovo, C.; Biffi, S.; Cortini, A.; Fischetti, F.; Sblattero, D.; Pitzalis, C.; Marzari, R.; et al. Treatment of Experimental Arthritis by Targeting Synovial Endothelium with a Neutralizing Recombinant Antibody to C5. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2559–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durigutto, P.; Macor, P.; Ziller, F.; De Maso, L.; Fischetti, F.; Marzari, R.; Sblattero, D.; Tedesco, F. Prevention of Arthritis by Locally Synthesized Recombinant Antibody Neutralizing Complement Component C5. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergunst, C.E.; Gerlag, D.M.; Dinant, H.; Schulz, L.; Vinkenoog, M.; Smeets, T.J.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Reedquist, K.A.; Tak, P.P. Blocking the Receptor for C5a in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Does Not Reduce Synovial Inflammation. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2007, 46, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barilla-Labarca, M.-L.; Toder, K.; Furie, R. Targeting the Complement System in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Other Diseases. Clin. Immunol. Orlando Fla. 2013, 148, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanoni, F.; Jorgensen, C.; Parvex, P.; Chizzolini, C.; Hofer, M. A Difficult Case of Juvenile Dermatomyositis Complicated by Thrombotic Microangiopathy and Purtscher-like Retinopathy. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2014, 12, P275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bekker, P.; Dairaghi, D.; Seitz, L.; Leleti, M.; Wang, Y.; Ertl, L.; Baumgart, T.; Shugarts, S.; Lohr, L.; Dang, T.; et al. Characterization of Pharmacologic and Pharmacokinetic Properties of CCX168, a Potent and Selective Orally Administered Complement 5a Receptor Inhibitor, Based on Preclinical Evaluation and Randomized Phase 1 Clinical Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, D.R.W.; Bruchfeld, A.N.; Harper, L.; Schaier, M.; Venning, M.C.; Hamilton, P.; Burst, V.; Grundmann, F.; Jadoul, M.; Szombati, I.; et al. Randomized Trial of C5a Receptor Inhibitor Avacopan in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2017, 28, 2756–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, P.A.; Niles, J.; Jimenez, R.; Spiera, R.F.; Rovin, B.H.; Bomback, A.; Pagnoux, C.; Potarca, A.; Schall, T.J.; Bekker, P.; et al. Adjunctive Treatment With Avacopan, an Oral C5a Receptor Inhibitor, in Patients With Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelek, W.M.; Xie, L.; Morgan, B.P.; Harris, C.L. Compendium of Current Complement Therapeutics. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballow, M. The IgG Molecule as a Biological Immune Response Modifier: Mechanisms of Action of Intravenous Immune Serum Globulin in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 315–323, quiz 324–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model Disease | Complement Deregulation | Therapeutic Management | Clinical Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antiphospholipid syndrome | C3 or C5 deficiency | C5b-9 blockade Factor B blockade C5 blockade | No fetal losses No thrombosis No fetal losses No fetal losses No fetal losses, no thrombosis |
| Rheumatoid arthritis CIA/CAIA CIA/CAIA KRN/I-Ag7 KRN/I-Ag7 KRN/I-Ag7 | Alternative pathway Alternative pathway Factor B absence | C3 or C5 blockade Factor B blockade | Arthritis development No arthritis development Arthritis development No arthritis development No arthritis development |
| AAV Anti-MPO induced vasculitis | C5 deficiency C5aR deficiency | C5aR blockade | No vasculitis development No vasculitis development No vasculitis development |
| Agent | Disease | Type of Study | Therapeutic Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eculizumab (C5a inhibitor) | SLE SLE and TMA CAPS RA DM | Clinical Trial (phase I) Case Report Case Report Clinical Trial (phase IIb) Clinical Trial (placebo-controlled double blind pilot study) Case Report | No evidence Improvement Improvement No evidence No evidence Improvement |
| PMX53 (C5aR inhibitor) | RA | Clinical trial (placebo-controlled double blind pilot study) | No evidence |
| CCX168 (C5aR inhibitor) | AAV | Clinical Trial (phase II, III) | Improvement |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galindo-Izquierdo, M.; Pablos Alvarez, J.L. Complement as a Therapeutic Target in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010148
Galindo-Izquierdo M, Pablos Alvarez JL. Complement as a Therapeutic Target in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Cells. 2021; 10(1):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010148
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalindo-Izquierdo, María, and José Luis Pablos Alvarez. 2021. "Complement as a Therapeutic Target in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases" Cells 10, no. 1: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010148
APA StyleGalindo-Izquierdo, M., & Pablos Alvarez, J. L. (2021). Complement as a Therapeutic Target in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Cells, 10(1), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010148





