Soil Nutrient Dynamics and Nitrogen Fixation Rate Changes over Plant Growth in Temperate Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Collection and Site Characterization
2.2. Biochar Making Process
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of the Soil
2.5. Potential N2 Fixing Bacterial Activities and GC-FID Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of the Soil and Biochar Used
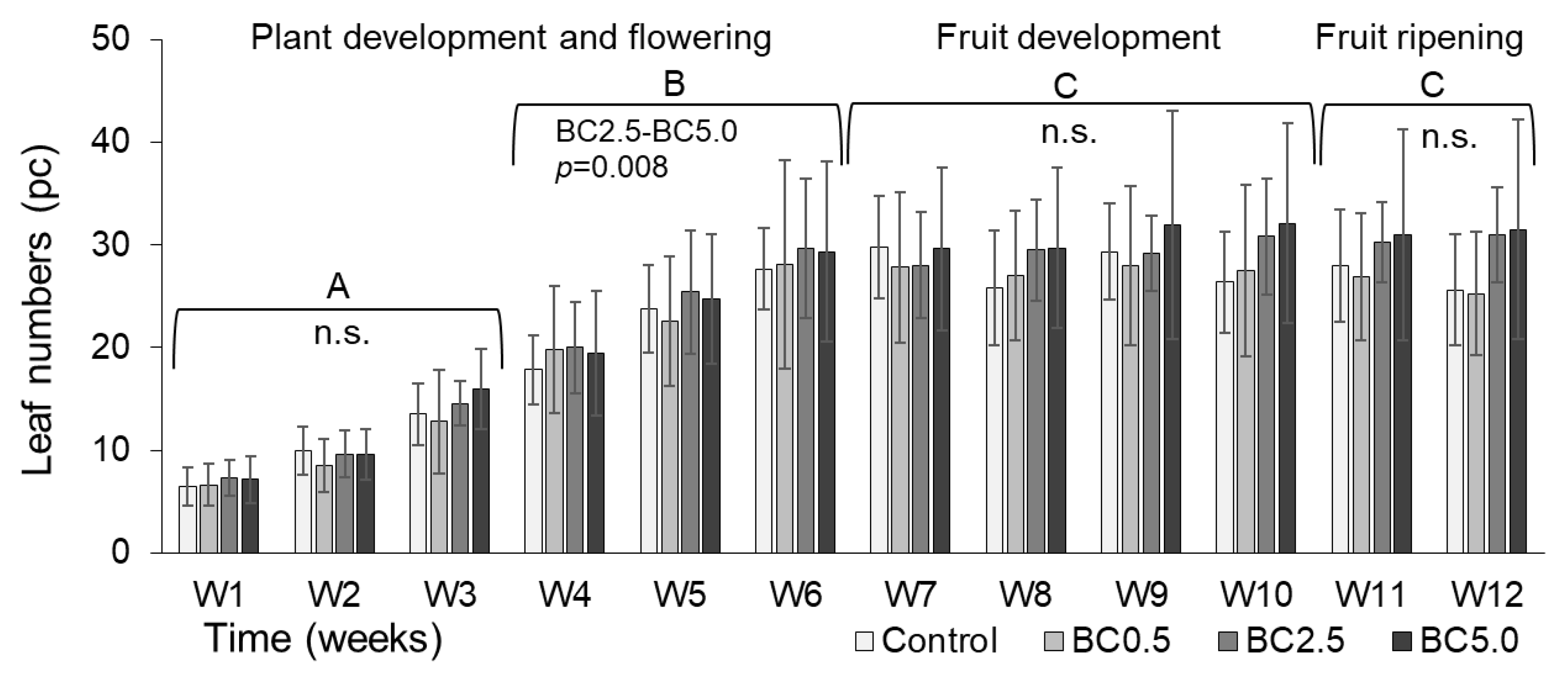
3.2. Plant Growth and Stress Response
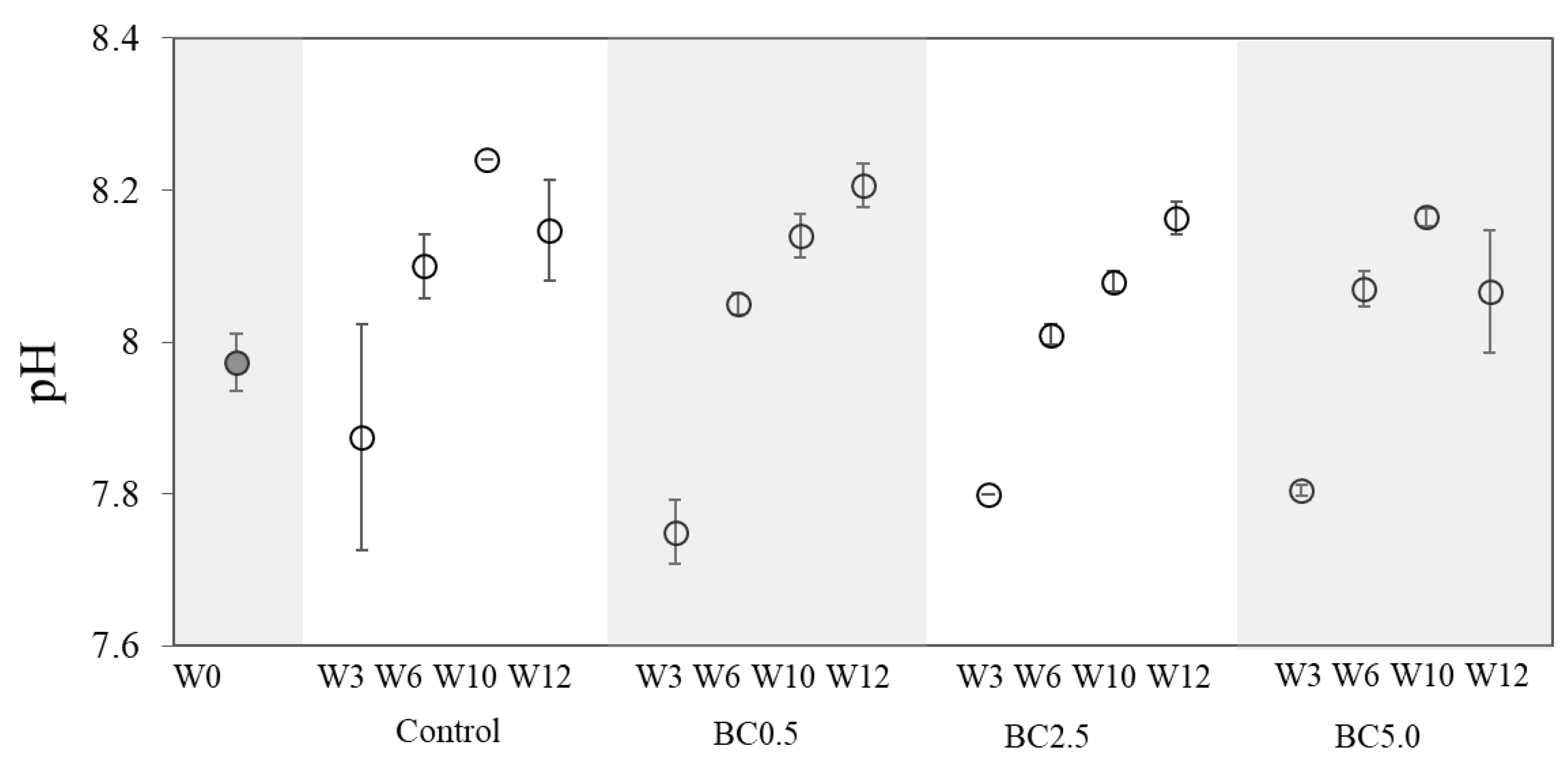
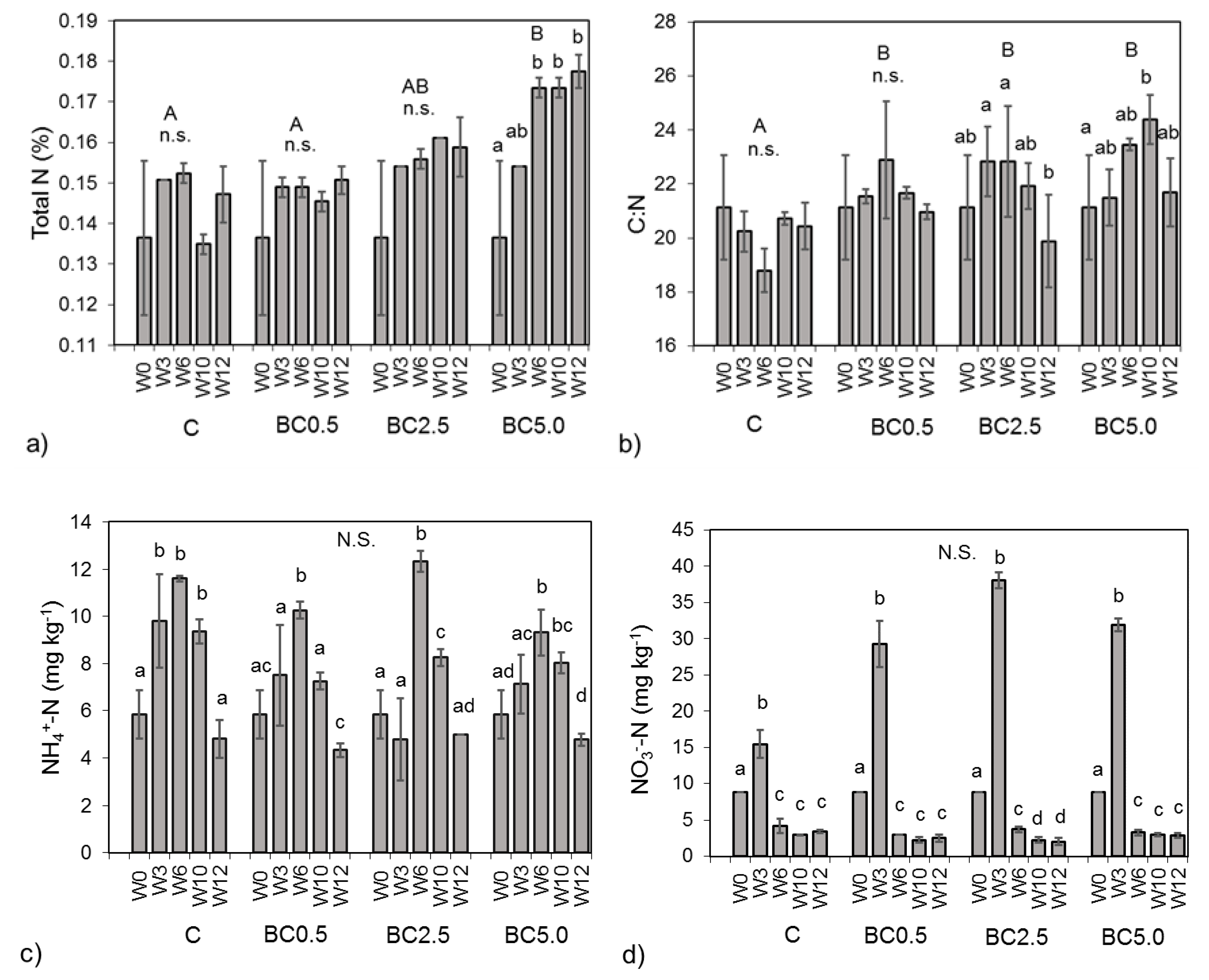
3.3. Nutrient Availability Over Time
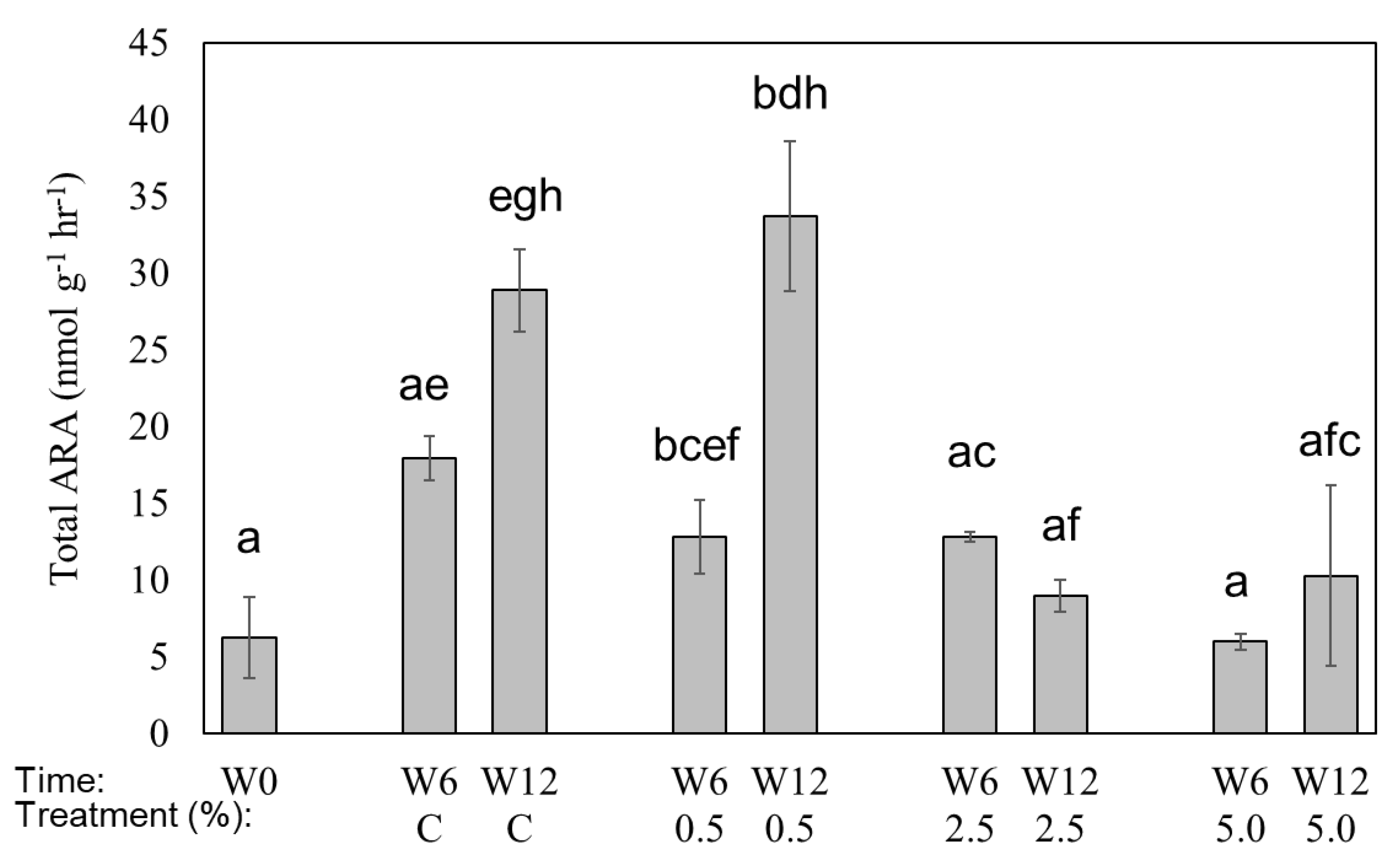
3.4. Effects of biochar on BNF Rates
4. Discussions
4.1. Effects of Biochar Addition on Plant Growth
4.2. Effects of Biochar Addition on Soil Characteristics
4.3. Effects of Biochar Addition on Potential BNF Rates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graber, E.R.; Meller Harel, Y.; Kolton, M.; Cytryn, E.; Silber, A.; Rav David, D.; Tsechansky, L.; Borenshtein, M.; Elad, Y. Biochar impact on development and productivity of pepper and tomato grown in fertigated soilless media. Plant Soil 2010, 337, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, M.A.; Lehmann, J.; Ramírez, J.; Hurtado, M. Biological nitrogen fixation by common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) increases with bio-char additions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horel, A.; Potyó, I.; Szili-Kovács, T.; Molnár, S. Potential nitrogen fixation changes under different land uses as influenced by seasons and biochar amendments. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Lu, S. Biochars improve aggregate stability, water retention, and pore-space properties of clayey soil. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2014, 177, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.M.; Lima, I.; Xing, B.; Gaskin, J.W.; Steiner, C.; Das, K.C.; Ahmedna, M.; Rehrah, D.; Watts, D.W.; Busscher, W.J.; et al. Characterization of designer biochar produced at different temperatures and their effects on a loamy sand. Ann. Environ. Sci. 2009, 3, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.R.; Condron, L.M.; Clough, T.J.; Fiers, M.; Stewart, A.; Hill, R.A.; Sherlock, R.R. Biochar induced soil microbial community change: Implications for biogeochemical cycling of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Pedobiologia 2011, 54, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horel, A.; Schiewer, S. Impact of VOC removal by activated carbon on biodegradation rates of diesel, syntroleum and biodiesel in contaminated sand. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, R.; Shen, G.; Zhang, J.; Meng, G.; Zhang, J. Effects of biochar on nutrients and the microbial community structure of tobacco-planting soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horel, A.; Bernard, R.; Mortazavi, B. Impact of crude oil exposure on nitrogen cycling in a previously impacted Juncus roemerianus salt marsh in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6982–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, B.; Chang, S.X.; Gong, J. Biochar addition affected the dynamics of ammonia oxidizers and nitrification in microcosms of a coastal alkaline soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.; Fleming, P.; Wang, B.; Horton, R.; Karlen, D. Biochar impact on nutrient leaching from a midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 2010, 158, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Zimmerman, A.R. Organic carbon and nutrient release from a range of laboratory-produced biochars and biochar—soil mixtures. Geoderma 2013, 193–194, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, S.E.; Alling, V.; Martinsen, V.; Mulder, J.; Breedveld, G.D.; Cornelissen, G. The sorption and desorption of phosphate-P, ammonium-N and nitrate-N in cacao shell and corn cob biochars. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zackrisson, O.; Nilsson, M.-C.; Wardle, D.A. Key ecological function of charcoal from wildfire in the boreal forest. Oikos 1996, 77, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, J.; Steiner, C.; Downie, A.; Lehmann, J. Biochar effects on nutrient leaching. Chapter 15. In Biochar for Environmental Management Science and Technology; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 271–287. [Google Scholar]
- Santi, C.; Bogusz, D.; Franche, C. Biological nitrogen fixation in non-legume plants. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 743–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdicek, D.F.; Kennedy, A.C. Microorganisms in Action; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1998; p. 243. [Google Scholar]
- Rillig, M.C.; Wagner, M.; Salem, M.; Antunes, P.M.; George, C.; Ramke, H.-G.; Titirici, M.-M.; Antonietti, M. Material derived from hydrothermal carbonization: Effects on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhiza. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.J.; Fitzgerald, J.D.; Hipps, N.A. Potential mechanisms for achieving agricultural benefits from biochar application to temperate soils: A review. Plant Soil 2010, 337, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, T.H.; MacKenzie, M.D.; Gundale, M.J. Biochar effects on soil nutrient transformations. In Biochar for Environmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 251–270. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Guidelines for Soil Description; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Horel, Á.; Tóth, E.; Gelybó, G.; Dencső, M.; Farkas, C. Biochar amendment affects soil water and CO2 regime during capsicum annuum plant growth. Agronomy 2019, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schon, M.K.; Compton, M.P.; Bell, E.; Burns, I. Nitrogen concentrations affect pepper yield and leachate nitrate-nitrogen from rockwool culture. HortScience 1994, 48, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuor, H.; Ben-Gal, A.; Yermiyahu, U.; Beit-Yannai, E.; Cohen, S. Nitrogen management of greenhouse pepper production: Agronomic, nutritional, and environmental implications. HortScience 2013, 50, 1688–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackley, S. The economic viability and propspects for biochar in Europe: Shifting paradigms in uncertain times. In Biochar in European Soils and Agriculture. Science and Practice; Shackley, S., Ruysschaert, G., Zwart, K., Glaser, B., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2016; pp. 205–226. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrova, L.N.; Naidenova, O.A. Laboratory Practice in Soil Science; Kolos: Leningrad, Russian, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, D.T.; Bourgués, S.; de Wit, R.; Herbert, R.A. Seasonal variations in nitrogen-fixation (acetylene reduction) and sulphate-reduction rates in the rhizosphere of Zostera noltii: Nitrogen fixation by sulphate-reducing bacteria. Mar. Biol. 1996, 125, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, D.G. Determination of nitrogenase activity in aquatic samples using the acetylene reduction procedure. In Nitrogen in the Marine Environment; Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 65–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, R.W.F.; Holsten, R.D.; Jackson, E.K.; Burns, R.C. The acetylene-ethylene assay for N2 fixation: Laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol. 1968, 43, 1185–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, W.L.; Chakrabarty, K.; Klucas, R.V.; Vidaver, A.K. Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) associated with roots of winter wheat and sorghum in Nebraska. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; He, F.; Shao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, G. Effects of biochar application on Suaeda salsa growth and saline soil properties. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Joseph, S.; Li, L.; Pan, G.; Lin, Y.; Munroe, P.; Pace, B.; Taherymoosavi, S.; van Zwieten, L.; Thomas, T.; et al. Developing more effective enhanced biochar fertilisers for improvement of pepper yield and quality. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, V.; Dorais, M.; Menard, C. Organic potted plants amended with biochar: Its effect on growth and Pythium colonization. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 93, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorland, R.E.; Went, F.W. Plant growth under controlled conditions. VIII. Growth and fruiting of the chili pepper (Capsicum annuum). Am. J. Bot. 1947, 34, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guohua, X.; Xiaorong, F.; Anthony, J.M. Plant nitrogen assimilation and use efficiency. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 153–182. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.Y.; van Zwieten, L.; Meszaros, I.; Downie, A.; Joseph, S. Agronomic values of greenwaste biochar as a soil amendment. Soil Res. 2007, 45, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, T.J.; Condron, L.M.; Kammann, C.; Muller, C. A review of biochar and soil nitrogen dynamics. Agronomy 2013, 3, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, H.; Glaser, B. Effects of biochar compared to organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil quality and plant growth in a greenhouse experiment. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rondon, M. Biochar soil management on highly weathered soils in the humid tropics. In Biological Approaches to Sustainable Soil Systems; Uphoff, N., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 517–530. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, D.N.; Gleeson, D.B.; Solaiman, Z.M.; Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V. Decreased soil microbial biomass and nitrogen mineralisation with Eucalyptus biochar addition to a coarse textured soil. Plant Soil 2012, 354, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kása, I.; Molnár, S.; Horel, Á. Net changes in nitrification in cultivated soil as a function of temperature and the type and concentration of biochar (in Hungarian). Agrokém. Talajt. 2016, 65, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilliam, R.S.; DeLuca, T.H.; Jones, D.L. Biochar application reduces nodulation but increases nitrogenase activity in clover. Plant Soil 2013, 366, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Thomas, B.W.; Sachdeva, V.; Deng, H. Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: Mechanisms and future directions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusack, D.F.; Silver, W.; McDowell, W.H. Biological nitrogen fixation in two tropical forests: Ecosystem-level patterns and effects of nitrogen fertilization. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limmer, C.; Drake, H.L. Non-symbiotic N2-fixation in acidic and pH-neutral forest soils: Aerobic and anaerobic differentials. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, M.M.; Smith, N.A. Straw decomposition and nitrogenase activity (C2H2 reduction) by free-living microorganisms from soil: Effects of pH and clay content. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1991, 23, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment Types and Times | Mean Difference | 95% Confidence Interval | p adj | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| CW0-CW6 | 11.93 | −1.27 | 25.14 | 0.095 |
| CW0-CW12 | 23.07 | 9.86 | 36.27 | <0.001 *** |
| CW0-BC0.5W6 | 15.18 | 1.97 | 28.38 | 0.017 * |
| CW0-BC0.5W12 | 28.07 | 14.87 | 41.28 | <0.001 *** |
| CW6-BC0.5W12 | 16.14 | 2.94 | 29.34 | 0.010 * |
| CW6-BC5.0W6 | −12.16 | −25.37 | 1.04 | 0.085 |
| CW12-BC5.0W12 | −18.90 | −32.11 | −5.70 | 0.002 ** |
| CW12-BC2.5W6 | −16.31 | −29.51 | −3.10 | 0.009 ** |
| CW12-BC2.5W12 | −20.22 | −33.42 | −7.01 | 0.001 ** |
| CW12-BC5.0W6 | −23.30 | −36.50 | −10.09 | <0.001 *** |
| BC0.5W6-BC0.5W12 | 12.90 | −0.31 | 26.10 | 0.059 |
| BC0.5W6-BC2.5W12 | −12.33 | −25.53 | 0.88 | 0.078 |
| BC0.5W6-BC5.0W6 | −15.41 | −28.61 | −2.20 | 0.015 * |
| BC0.5W12-BC0.5W6 | −21.31 | −34.52 | −8.11 | <0.001 *** |
| BC0.5W12-BC2.5W12 | −25.22 | −38.43 | −12.02 | <0.001 *** |
| BC0.5W12-BC5.0W6 | −28.3 | −41.51 | −15.10 | <0.001 *** |
| BC0.5W12-BC5.0W12 | 23.91 | 10.70 | 37.11 | <0.001 *** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horel, Á.; Gelybó, G.; Potyó, I.; Pokovai, K.; Bakacsi, Z. Soil Nutrient Dynamics and Nitrogen Fixation Rate Changes over Plant Growth in Temperate Soil. Agronomy 2019, 9, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9040179
Horel Á, Gelybó G, Potyó I, Pokovai K, Bakacsi Z. Soil Nutrient Dynamics and Nitrogen Fixation Rate Changes over Plant Growth in Temperate Soil. Agronomy. 2019; 9(4):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9040179
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorel, Ágota, Györgyi Gelybó, Imre Potyó, Klára Pokovai, and Zsófia Bakacsi. 2019. "Soil Nutrient Dynamics and Nitrogen Fixation Rate Changes over Plant Growth in Temperate Soil" Agronomy 9, no. 4: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9040179
APA StyleHorel, Á., Gelybó, G., Potyó, I., Pokovai, K., & Bakacsi, Z. (2019). Soil Nutrient Dynamics and Nitrogen Fixation Rate Changes over Plant Growth in Temperate Soil. Agronomy, 9(4), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9040179






