The CYP74 Gene Family in Watermelon: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Under Hormonal Stress and Root-Knot Nematode Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the CYP74 Genes in Watermelon Genome
2.2. Protein Properties, Chromosomal Locations, and Promoter Analysis
2.3. Phylogenesis, Conserved Motif, and Gene Structure Analyses
2.4. Expression Profiles of Watermelon CYP74 Genes Based on RNA-seq Data
2.5. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.6. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
3. Results
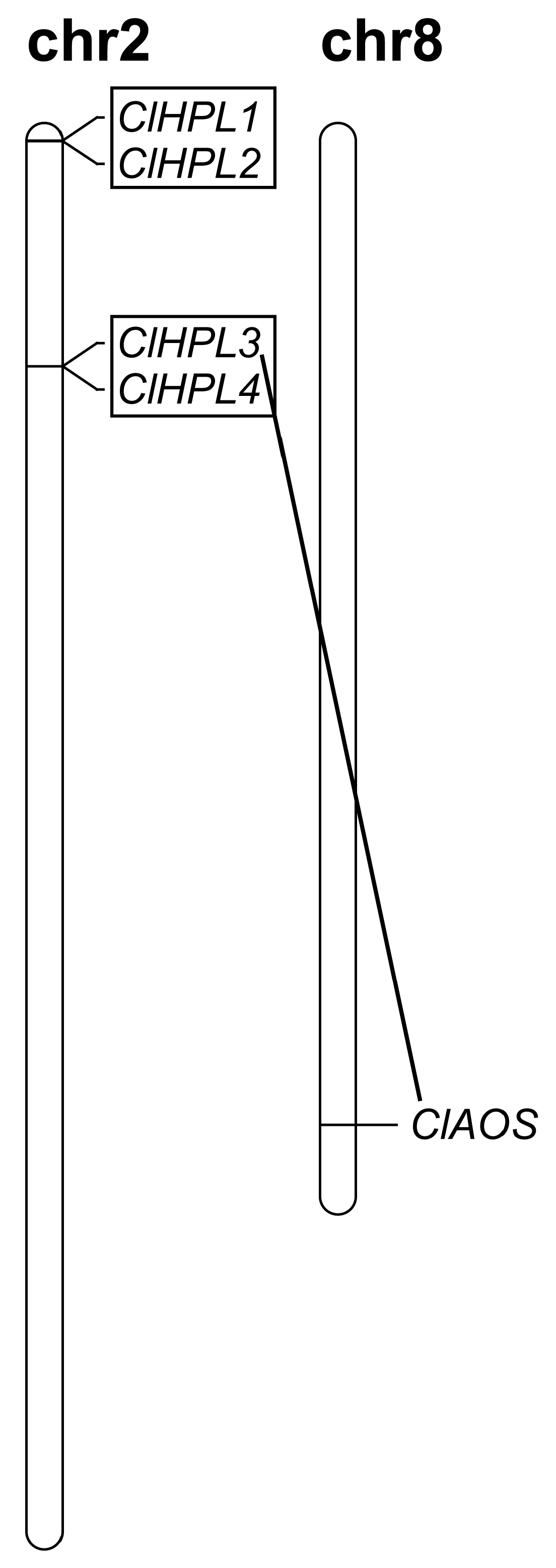
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification and Gene Duplication of the CP74 Genes in Watermelon
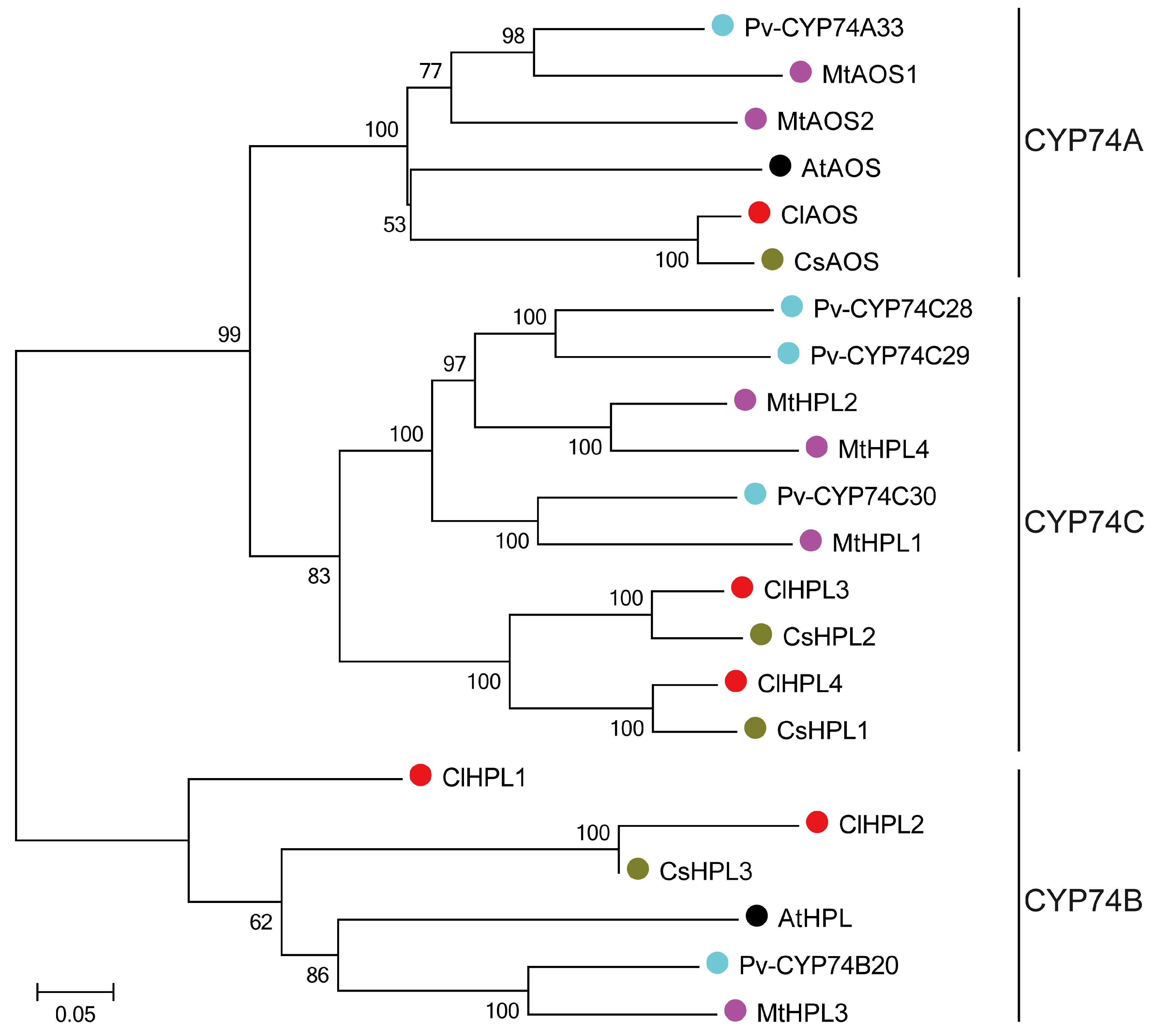
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationships of the CYP74 Proteins in Watermelon and Other Plant Species
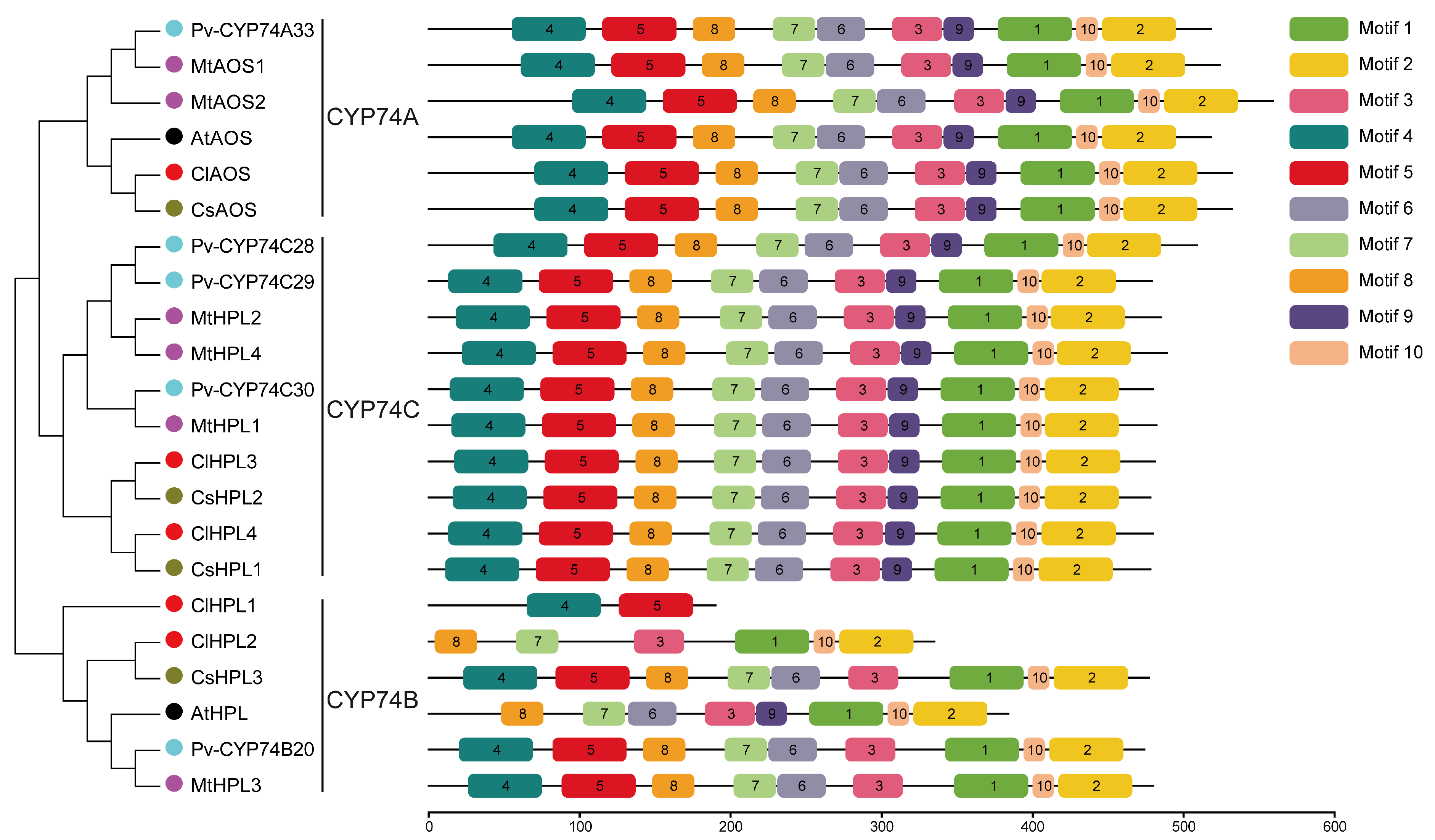
3.3. Characterization and Conserved Motif Analysis of CYP74 Proteins in Watermelon and Other Plant Species
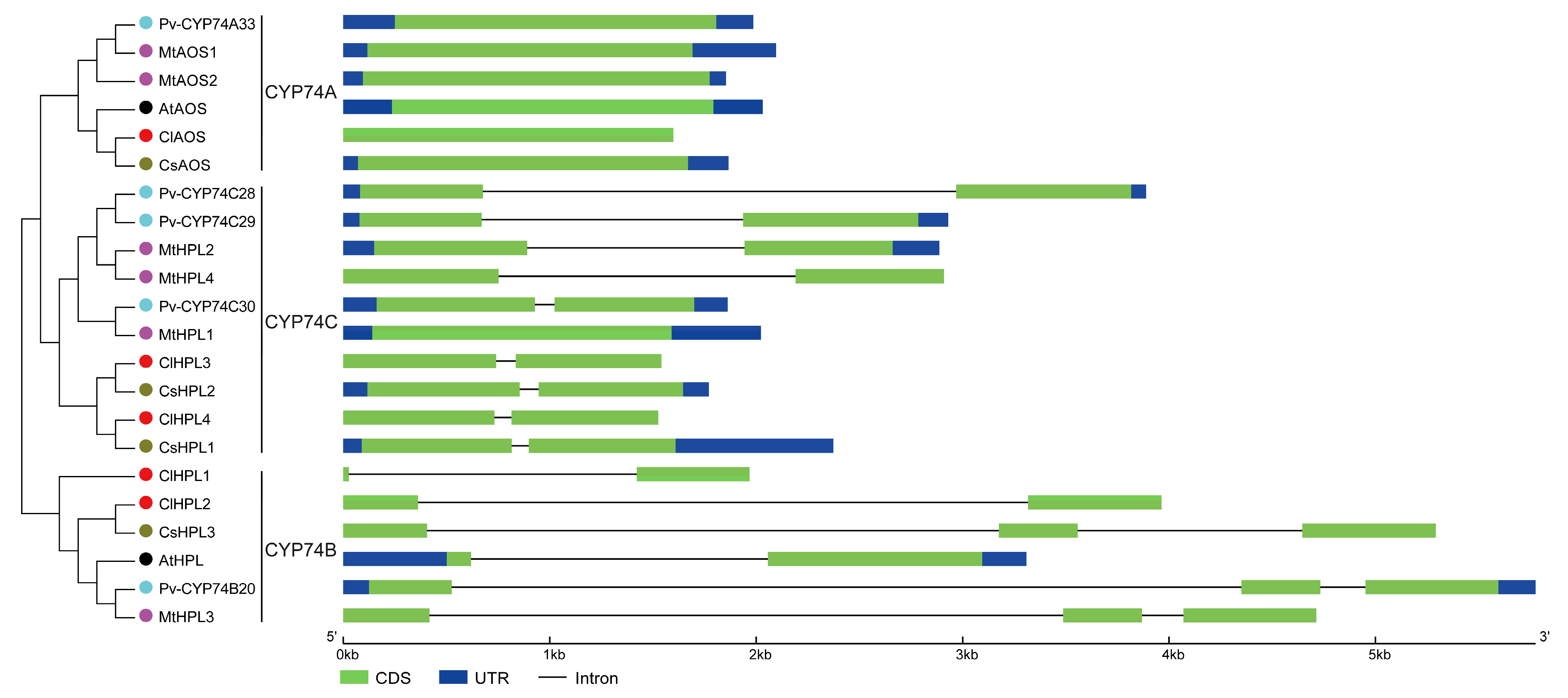
3.4. Structural Analysis of CYP74 Genes in Watermelon and Other Plant Species
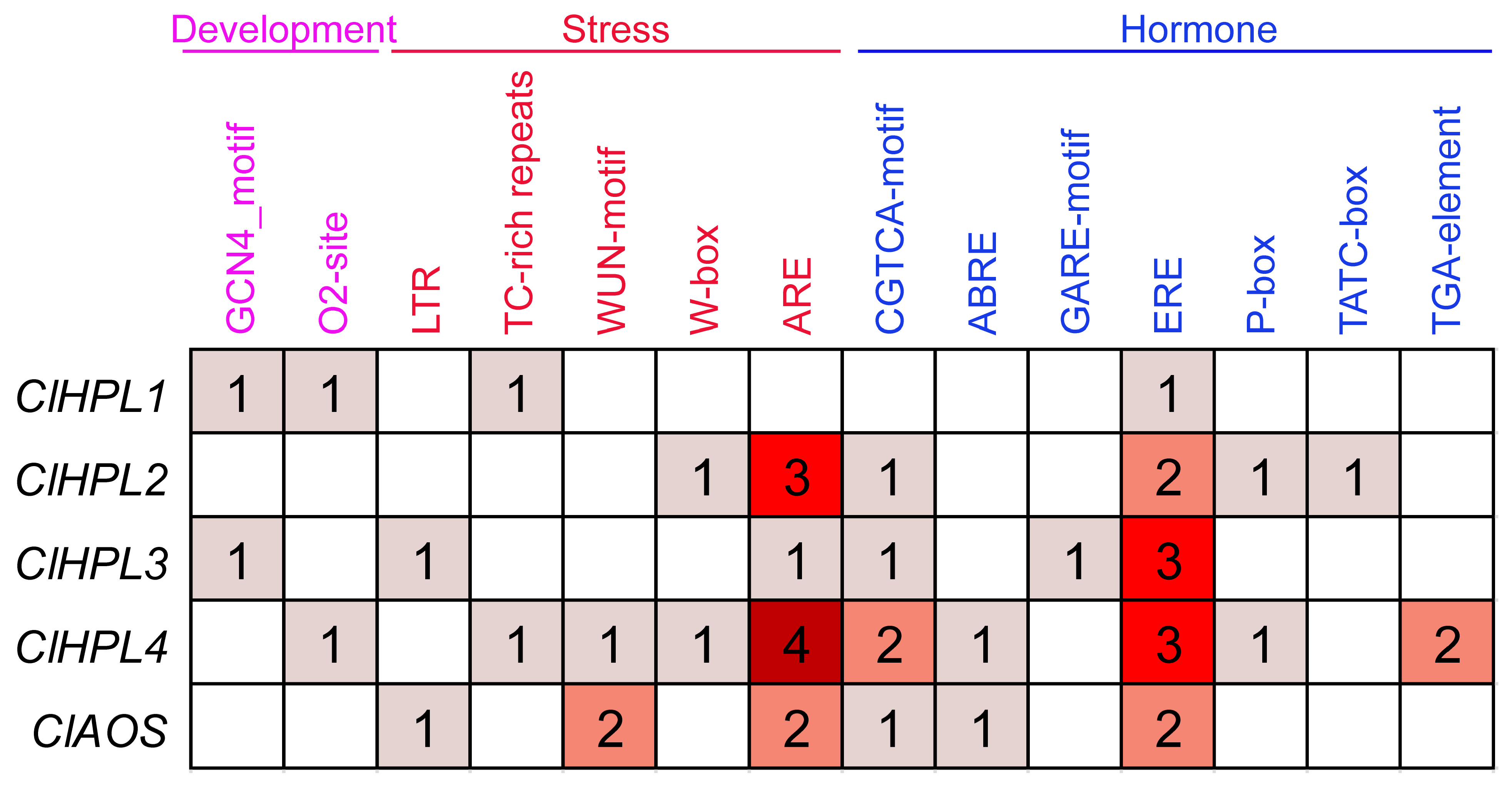
3.5. Cis-Element Analysis of Watermelon CYP74 Genes
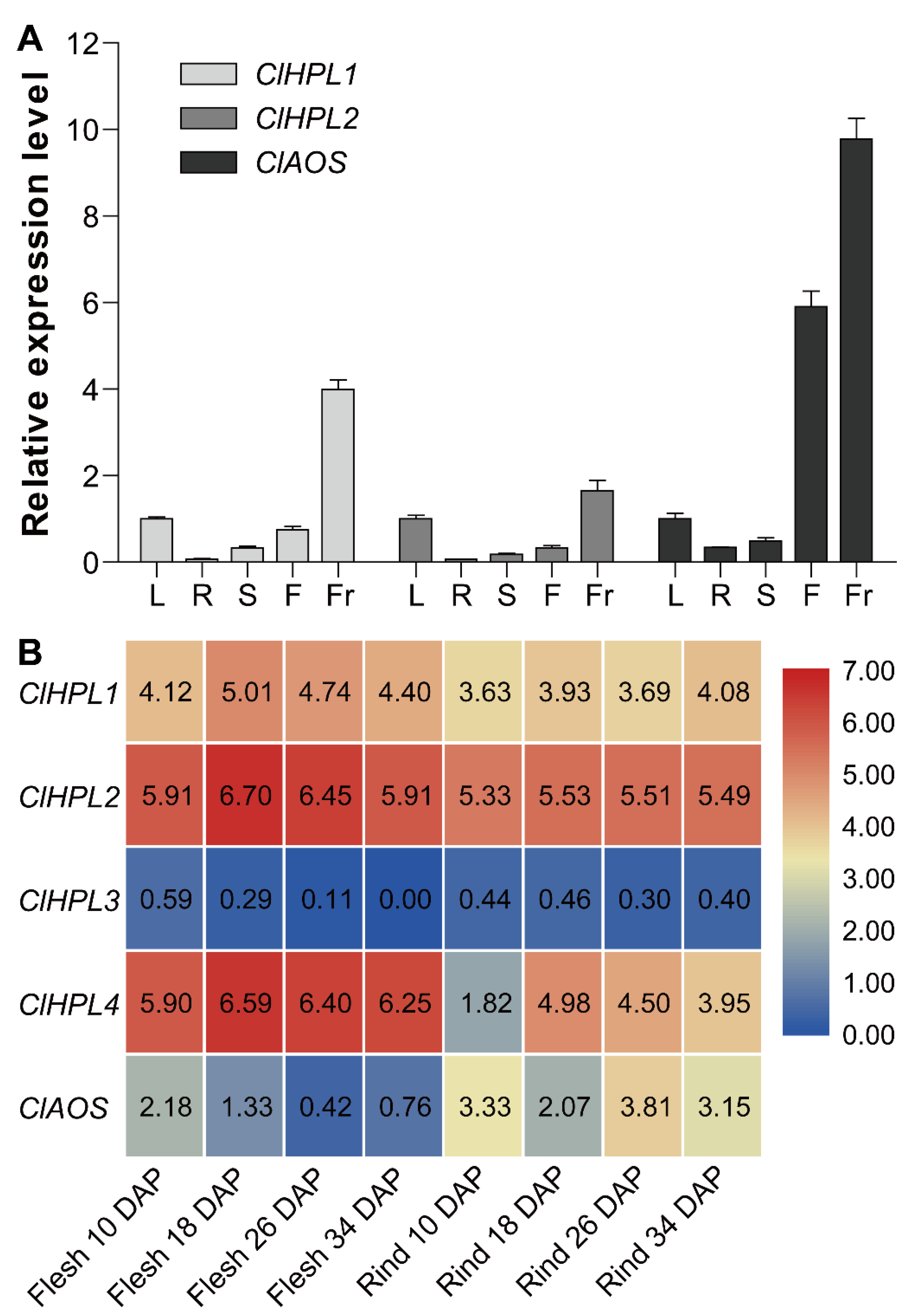
3.6. Expression Analysis of Watermelon CYP74 Genes in Different Tissues and During Fruit Development
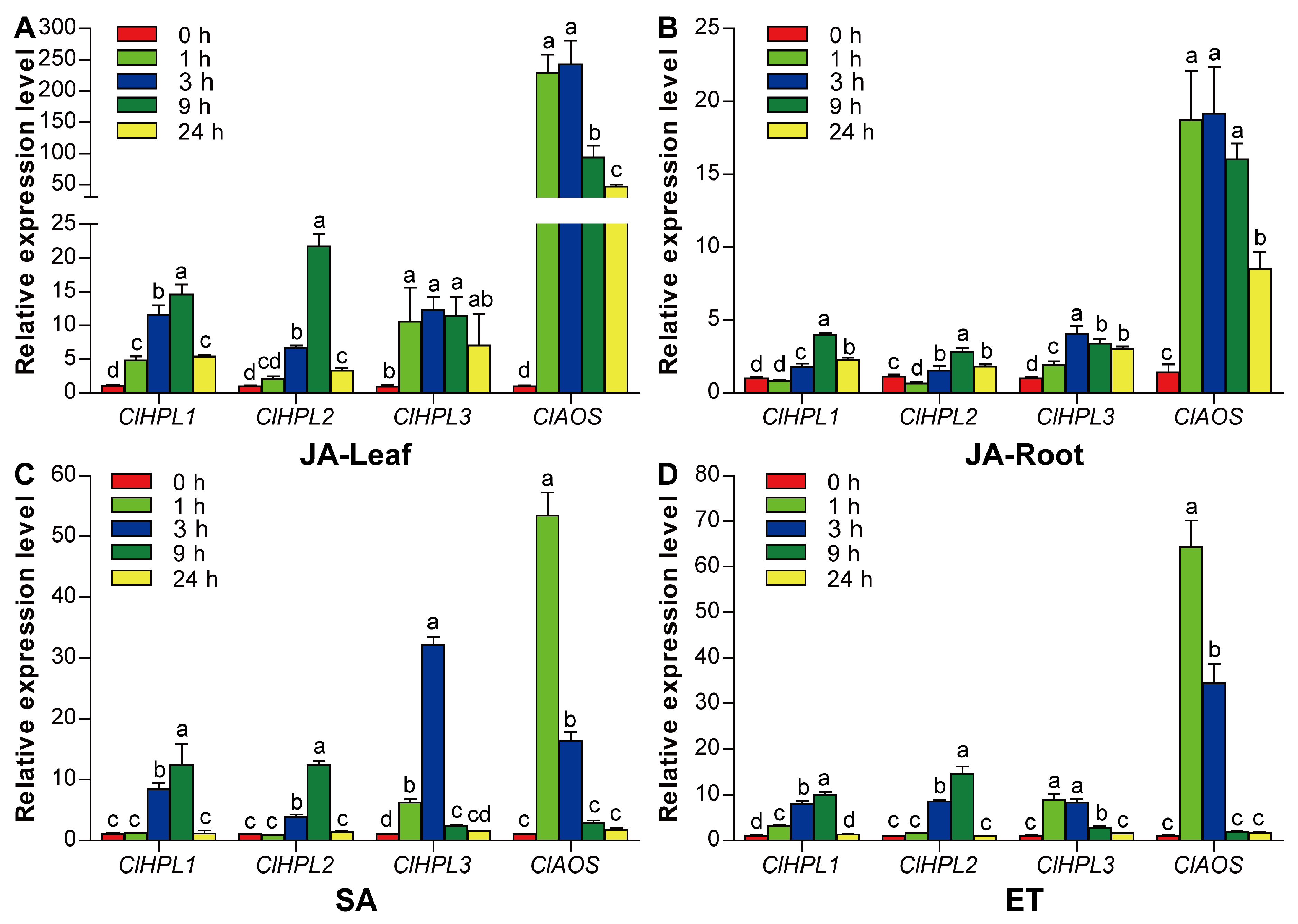
3.7. Expression Analysis of Watermelon CYP74 Genes Under Hormonal Treatments
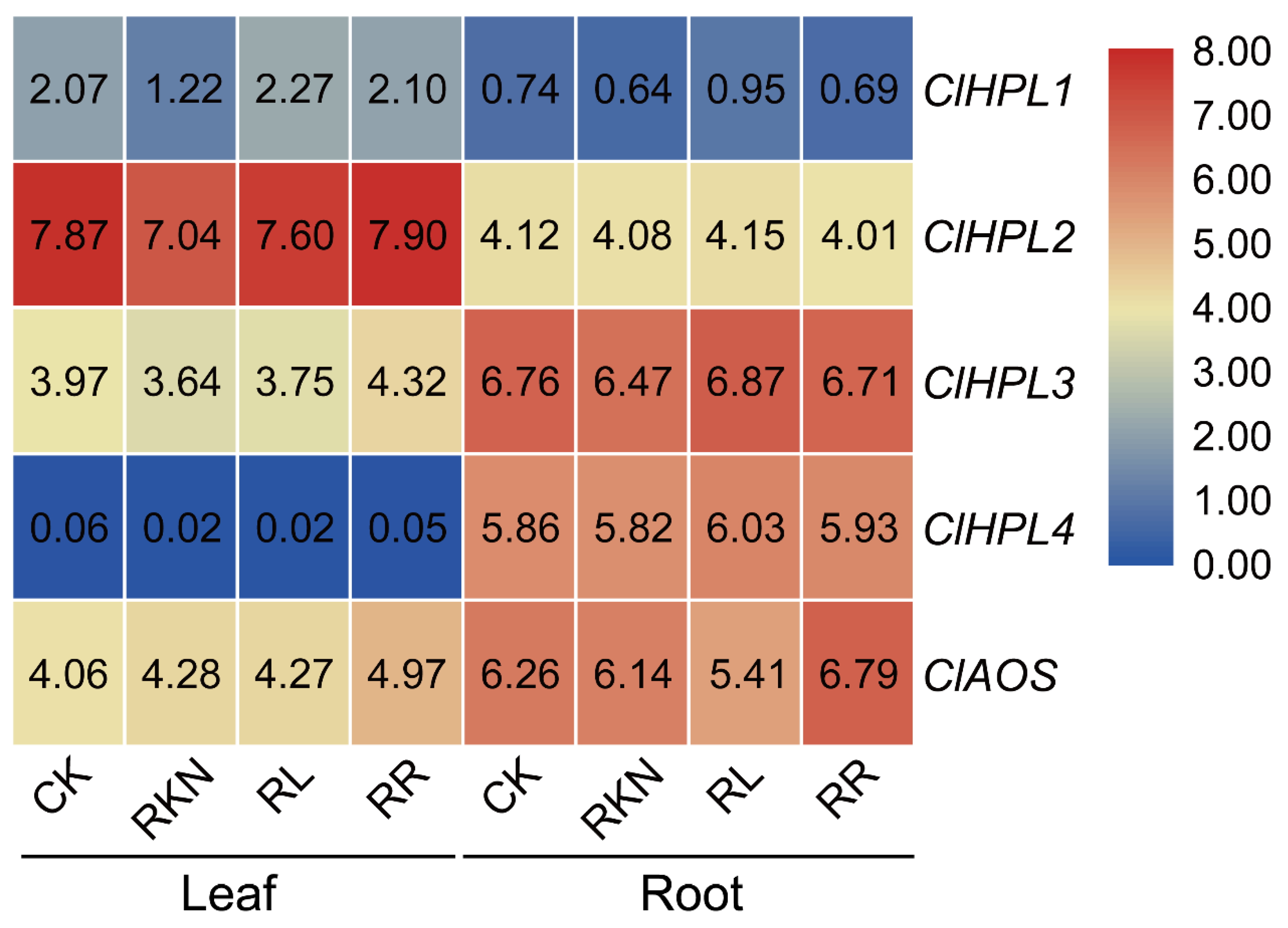
3.8. Expression Patterns of Watermelon CYP74 Genes in Response to Root-Knot Nematode Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosblech, A.; Feussner, I.; Heilmann, I. Oxylipins: Structurally diverse metabolites from fatty acid oxidation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasternack, C.; Feussner, I. The oxylipin pathways: Biochemistry and function. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreou, A.; Brodhun, F.; Feussner, I. Biosynthesis of oxylipins in non-mammals. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 148–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpe, M.; Feussner, I. Formation of oxylipins by CYP74 enzymes. Phytochem. Rev. 2006, 5, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feussner, I.; Wasternack, C. The lipoxygenase pathway. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, G.A.; Schilmiller, A.L. Oxylipin metabolism in response to stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grechkin, A.N. Hydroperoxide lyase and divinyl ether synthase. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002, 68–69, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorina, S.S.; Mukhitova, F.K.; Ilyina, T.M.; Toporkova, Y.Y.; Grechkin, A.N. Detection of unprecedented allene oxide synthase member of CYP74B subfamily: CYP74B33 of carrot (Daucus carota). Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.H.; Chen, S.X.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, R.R.; Cheng, S.Q.; Meng, H.W.; Shen, X.Q. Isolation, expression, and characterization of a hydroperoxide lyase gene from cucumber. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 22082–22101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, J.E.; Itoh, A.; Howe, G.A. Tomato allene oxide synthase and fatty acid hydroperoxide lyase, two cytochrome P450s involved in oxylipin metabolism, are targeted to different membranes of chloroplast envelope. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, G.A.; Lee, G.I.; Itoh, A.; Li, L.; DeRocher, A.E. Cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism of oxylipins in tomato. Cloning and expression of allene oxide synthase and fatty acid hydroperoxide lyase. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halitschke, R.; Ziegler, J.; Keinanen, M.; Baldwin, I.T. Silencing of hydroperoxide lyase and allene oxide synthase reveals substrate and defense signaling crosstalk in Nicotiana attenuata. Plant J. 2004, 40, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, F.; Tang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, G.; Chu, J.; Yan, C.; Wang, T.; Chu, C.; et al. Activation of the jasmonic acid pathway by depletion of the hydroperoxide lyase OsHPL3 reveals crosstalk between the HPL and AOS branches of the oxylipin pathway in rice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, H.; Oshima, T.; Kaneda, H.; Takashio, M. Identification and functional analyses of two cDNAs that encode fatty acid 9-/13-hydroperoxide lyase (CYP74C) in rice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Domenico, S.; Taurino, M.; Gallo, A.; Poltronieri, P.; Pastor, V.; Flors, V.; Santino, A. Oxylipin dynamics in Medicago truncatula in response to salt and wounding stresses. Physiol. Plan. 2019, 165, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpe, M.; Kandzia, R.; Gobel, C.; Rosahl, S.; Feussner, I. A pathogen-inducible divinyl ether synthase (CYP74D) from elicitor-treated potato suspension cells. FEBS Lett. 2001, 507, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, A.; Howe, G.A. Molecular cloning of a divinyl ether synthase. Identification as a CYP74 cytochrome P-450. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3620–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorina, S.S.; Toporkova, Y.Y.; Mukhtarova, L.S.; Chechetkin, I.R.; Khairutdinov, B.I.; Gogolev, Y.V.; Grechkin, A.N. Detection and molecular cloning of CYP74Q1 gene: Identification of Ranunculus acris leaf divinyl ether synthase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogolev, Y.V.; Gorina, S.S.; Gogoleva, N.E.; Toporkova, Y.Y.; Chechetkin, I.R.; Grechkin, A.N. Green leaf divinyl ether synthase: Gene detection, molecular cloning and identification of a unique CYP74B subfamily member. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2012, 1821, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorina, S.S.; Toporkova, Y.Y.; Mukhtarova, L.S.; Smirnova, E.O.; Chechetkin, I.R.; Khairutdinov, B.I.; Gogolev, Y.V.; Grechkin, A.N. Oxylipin biosynthesis in spikemoss Selaginella moellendorffii: Molecular cloning and identification of divinyl ether synthases CYP74M1 and CYP74M3. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Guang, Y.; Zhou, Y. The bZIP gene family in watermelon: Genome-wide identification and expression analysis under cold stress and root-knot nematode infection. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.T.; Haegeman, A.; Danchin, E.G.; Gaur, H.S.; Helder, J.; Jones, M.G.; Kikuchi, T.; Manzanilla-Lopez, R.; Palomares-Rius, J.E.; Wesemael, W.M.; et al. Top 10 plant-parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.X.; Wu, C.; Ahammed, G.J.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wan, C.; Chen, J. Red light-induced systemic resistance against root-knot nematode is mediated by a coordinated regulation of salicylic acid, jasmonic acid and redox signaling in watermelon. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Halitschke, R.; Kim, H.B.; Baldwin, I.T.; Feldmann, K.A.; Feyereisen, R. A knock-out mutation in allene oxide synthase results in male sterility and defective wound signal transduction in Arabidopsis due to a block in jasmonic acid biosynthesis. Plant J. 2002, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudert, D.; Pfannschmidt, U.; Lottspeich, F.; Hollander-Czytko, H.; Weiler, E.W. Cloning, molecular and functional characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana allene oxide synthase (CYP 74), the first enzyme of the octadecanoid pathway to jasmonates. Plant Mol. Biol. 1996, 31, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubigsteltig, I.; Laudert, D.; Weiler, E.W. Structure and regulation of the Arabidopsis thaliana allene oxide synthase gene. Planta 1999, 208, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zeng, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. In silico identification and expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Medicago truncatula. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various biological data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Salse, J.; Lucas, W.J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. The draft genome of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) and resequencing of 20 diverse accessions. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Identification and expression analysis of two allene oxide cyclase (AOC) genes in watermelon. Agriculture 2019, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Camera, S.; Gouzerh, G.; Dhondt, S.; Hoffmann, L.; Fritig, B.; Legrand, M.; Heitz, T. Metabolic reprogramming in plant innate immunity: The contributions of phenylpropanoid and oxylipin pathways. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Mo, X.; Yang, H.; Yue, L.; Song, J.; Mo, B. The U-box family genes in Medicago truncatula: Key elements in response to salt, cold, and drought stresses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Ujita, C.; Fujimoto, S.; Wilkinson, J.; Hiatt, B.; Knauf, V.; Kajiwara, T.; Feussner, I. Fatty acid 9- and 13-hydroperoxide lyases from cucumber. FEBS Lett. 2000, 481, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shailendar Kumar, M.; Srikiran Chakravarthy, S.; Babu, P.R.; Rao, K.V.; Reddy, V.D. Classification of cytochrome P450s in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Syst. Evol. 2015, 301, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumin, W.; Rostas, M.; Winefield, C. Identification and functional characterisation of an allene oxide synthase from grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. Sauvignon blanc). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.Q.; Xu, X.Q.; Wu, Y.W.; Duan, C.Q.; Pan, Q.H. Isolation and characterization of two hydroperoxide lyase genes from grape berries: HPL isogenes in Vitis vinifera grapes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 7443–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tehrim, S.; Wang, L.; Dossa, K.; Zhang, X.; Ke, T.; Liao, B. Evolutionary history and functional divergence of the cytochrome P450 gene superfamily between Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica species uncover effects of whole genome and tandem duplications. BMC Genomics 2017, 18, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Qi, J.; Zhu, X.; Mao, B.; Zeng, L.; Wang, B.; Li, Q.; Zhou, G.; Xu, X.; Lou, Y.; et al. The rice hydroperoxide lyase OsHPL3 functions in defense responses by modulating the oxylipin pathway. Plant J. 2012, 71, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehab, E.W.; Raman, G.; Walley, J.W.; Perea, J.V.; Banu, G.; Theg, S.; Dehesh, K. Rice HYDROPEROXIDE LYASES with unique expression patterns generate distinct aldehyde signatures in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Chen, H. Global identification, structural analysis and expression characterization of cytochrome P450 monooxygenase superfamily in rice. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2018, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporkova, Y.Y.; Gogolev, Y.V.; Mukhtarova, L.S.; Grechkin, A.N. Determinants governing the CYP74 catalysis: Conversion of allene oxide synthase into hydroperoxide lyase by site-directed mutagenesis. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3423–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordermeer, M.A.; Veldink, G.A.; Vliegenthart, J.F. Fatty acid hydroperoxide lyase: A plant cytochrome p450 enzyme involved in wound healing and pest resistance. Chembiochem 2001, 2, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K. Green leaf volatiles: Hydroperoxide lyase pathway of oxylipin metabolism. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauser, G.; Grata, E.; Dubugnon, L.; Rudaz, S.; Farmer, E.E.; Wolfender, J.L. Spatial and temporal dynamics of jasmonate synthesis and accumulation in Arabidopsis in response to wounding. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16400–16407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Akimitsu, K. Characterization of a hydroperoxide lyase gene and effect of C6-volatiles on expression of genes of the oxylipin metabolism in Citrus. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, R.; Manners, J.M.; Kazan, K. Jasmonate biosynthesis and signaling in monocots: A comparative overview. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Per, T.S.; Khan, M.I.R.; Anjum, N.A.; Masood, A.; Hussain, S.J.; Khan, N.A. Jasmonates in plants under abiotic stresses: Crosstalk with other phytohormones matters. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 145, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Xie, D. Jasmonate action in plant defense against insects. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 3391–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyndt, T.; Nahar, K.; Haeck, A.; Verbeek, R.; Demeestere, K.; Gheysen, G. Interplay between carotenoids, abscisic acid and jasmonate guides the compatible rice-Meloidogyne graminicola interaction. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, K.; Kyndt, T.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Hofte, M.; Gheysen, G. The jasmonate pathway is a key player in systemically induced defense against root knot nematodes in rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Medina, A.; Fernandez, I.; Lok, G.B.; Pozo, M.J.; Pieterse, C.M.; Van Wees, S.C. Shifting from priming of salicylic acid- to jasmonic acid-regulated defences by Trichoderma protects tomato against the root knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, P.; Zonno, M.C.; Molinari, S.; Altomare, C. Induction of SA-signaling pathway and ethylene biosynthesis in Trichoderma harzianum-treated tomato plants after infection of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, X.; Lei, H.; Fan, J.; Yang, R.; Li, Z.; Hu, C.; Li, M.; Zhao, F.; Wang, S. Transcriptional evidence for cross talk between JA and ET or SA during root-knot nematode invasion in tomato. Physiol. Genomics 2018, 50, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Gene ID | Genomic Position | gDNA (bp) | CDS (bp) | Protein (aa) | pI | MW (kDa) | GRAVY | Subcellular Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClHPL1 | Cla007649 | Chr2: 1075–3042 (+) | 1968 | 573 | 190 | 9.69 | 21.54 | –0.217 | Chloroplast |
| ClHPL2 | Cla007650 | Chr2: 7515–11478 (+) | 3964 | 1008 | 335 | 5.55 | 38.07 | −0.170 | Chloroplast |
| ClHPL3 | Cla015969 | Chr2: 5586383–5587923 (−) | 1541 | 1446 | 481 | 8.10 | 54.14 | −0.160 | Cytoplasmic |
| ClHPL4 | Cla015970 | Chr2: 5597014 –5598539 (−) | 1526 | 1443 | 480 | 7.62 | 54.20 | −0.132 | Chloroplast |
| ClAOS | Cla022526 | Chr8: 24373048–24374646 (+) | 1599 | 1599 | 532 | 9.02 | 60.18 | −0.285 | Chloroplast |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Guang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Ahammed, G.J.; Yang, Y. The CYP74 Gene Family in Watermelon: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Under Hormonal Stress and Root-Knot Nematode Infection. Agronomy 2019, 9, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120872
Zhou Y, Guang Y, Li J, Wang F, Ahammed GJ, Yang Y. The CYP74 Gene Family in Watermelon: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Under Hormonal Stress and Root-Knot Nematode Infection. Agronomy. 2019; 9(12):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120872
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yong, Yelan Guang, Jingwen Li, Fei Wang, Golam Jalal Ahammed, and Youxin Yang. 2019. "The CYP74 Gene Family in Watermelon: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Under Hormonal Stress and Root-Knot Nematode Infection" Agronomy 9, no. 12: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120872
APA StyleZhou, Y., Guang, Y., Li, J., Wang, F., Ahammed, G. J., & Yang, Y. (2019). The CYP74 Gene Family in Watermelon: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Under Hormonal Stress and Root-Knot Nematode Infection. Agronomy, 9(12), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120872






