Origin and Distribution of the VRN-A1 Exon 4 and Exon 7 Haplotypes in Domesticated Wheat Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Amplification
2.3. Polyacrylamide and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
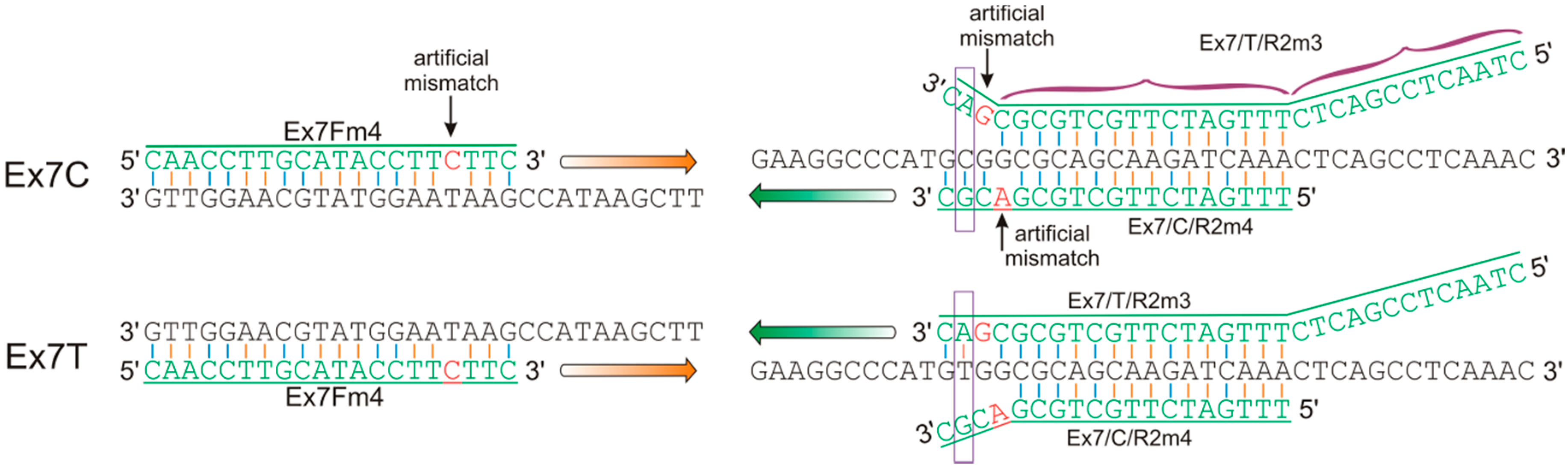
2.4. Design of Allele-Specific Primers for the VRN-A1 Exon 7 Haplotypes
2.5. Sequencing of PCR Fragments
3. Results
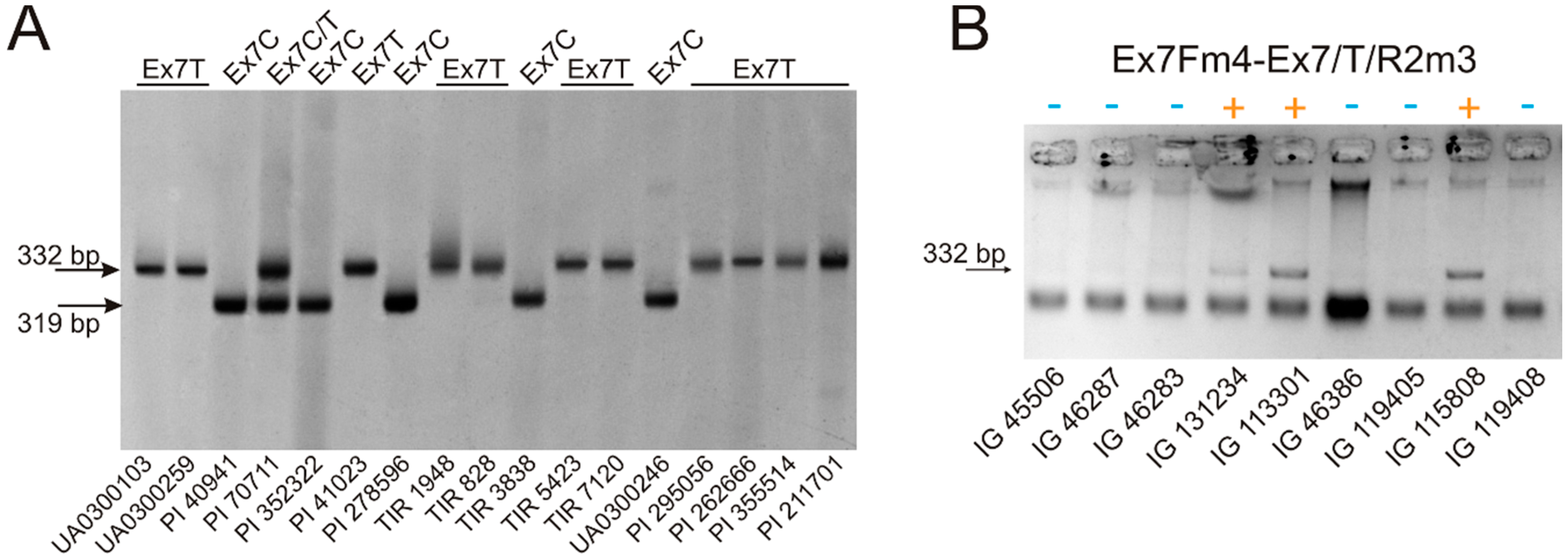
3.1. VRN-A1 exon 7 Polymorphism in Polyploid Wheat
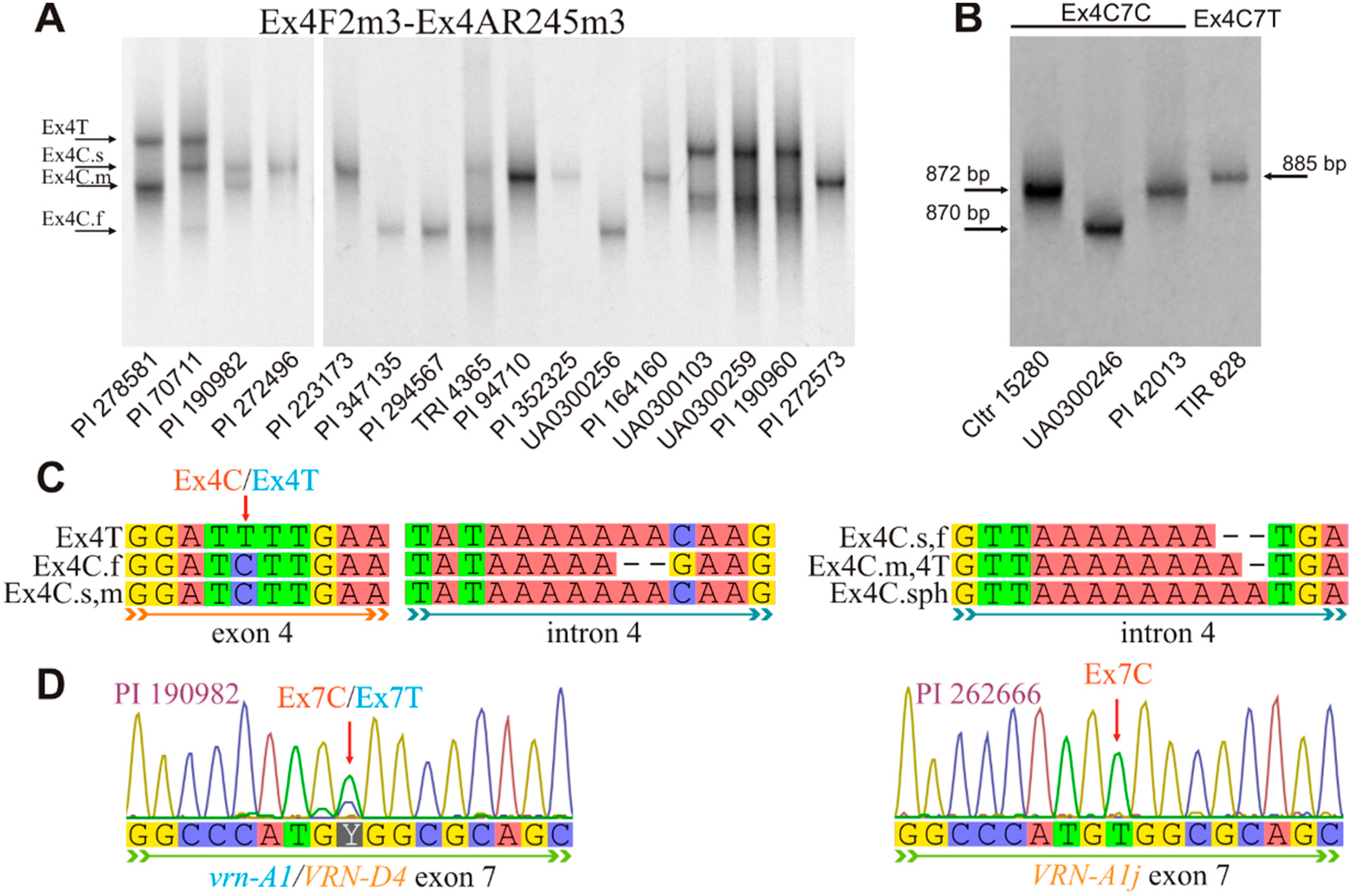
3.2. Combinations of the VRN-A1 Exon 4 and Exon 7 Haplotypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salamini, F.; Ozkan, H.; Brandolini, A.; Schäfer-Pregl, R.; Martin, W. Genetics and geography of wild cereal domestication in the near east. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, H. Discovery of the DD-analyser, one of the ancestors of Triticum vulgare (Japanese). Agric. Hortic. 1944, 19, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- FAO: FAOSTAT Database. (Crops: Wheat: Area Harvested: 2014). Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/ (accessed on 24 June 2018).
- Worland, A.J. The influence of flowering time genes on environmental adaptability in European wheats. Euphytica 1996, 89, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snape, J.W.; Butterworth, K.; Whitechurch, E.; Worland, A.J. Waiting for fine times: Genetics of flowering time in wheat. Euphytica 2001, 119, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, A.; Iqbal, M.; Spaner, D. Flowering time in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): A key factor for global adaptability. Euphytica 2014, 197, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Loukoianov, A.; Tranquilli, G.; Helguera, M.; Fahima, T.; Dubcovsky, J. Positional cloning of the wheat vernalization gene VRN1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6263–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, L.; Loukoianov, A.; Blechl, A.; Tranquilli, G.; Ramakrishna, W.; SanMiguel, P.; Bennetzen, J.; Echenique, V.; Dubcovsky, J. The wheat VRN2 gene is a flowering repressor down-regulated by vernalization. Science 2004, 303, 1640–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Fu, D.; Li, C.; Blechl, A.; Tranquilli, G.; Bonafede, M. The wheat and barley vernalization gene VRN3 is an orthologue of FT. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19581–19586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kippes, N.; Debernardi, J.M.; Vasquez-Gross, H.A.; Akpinar, B.A.; Budak, H.; Kato, K.; Chao, S.; Akhunov, E.; Dubcovsky, J. Identification of the VERNALIZATION 4 gene reveals the origin of spring growth habit in ancient wheats from South Asia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5401–E5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muterko, A.F.; Balashova, I.A.; Fayt, V.I.; Sivolap, Y.M. Molecular genetic mechanisms of regulation of growth habit in wheat. Cytol. Genet. 2015, 49, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muterko, A.; Kalendar, R.; Salina, E. Novel alleles of the VERNALIZATION1 genes in wheat are associated with modulation of DNA curvature and flexibility in the promoter region. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Carver, B.F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Yan, L. Genetic loci associated with stem elongation and winter dormancy release in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eagles, H.A.; Cane, K.; Trevaskis, B. Veery wheats carry an allele of Vrn-A1 that has implications for freezing tolerance in winter wheats. Plant Breed. 2011, 130, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yu, M.; Fang, T.; Cao, S.; Carver, B.F.; Yan, L. Vernalization requirement duration in winter wheat is controlled by TaVRN-A1 at the protein level. Plant J. 2013, 76, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Li, G.; Yu, M.; Fang, T.; Cao, S.; Carver, B.F. Genetic mechanisms of vernalization requirement duration in winter wheat cultivars. In Advances in Wheat Genetics: From Genome to Field; Ogihara, Y., Takumi, S., Handa, H., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; Volume 13, pp. 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, J.D.; Yan, L.; Talbert, L.; Dubcovsky, J. A PCR Marker for Growth Habit in Common Wheat Based on Allelic Variation at the VRN-A1 Gene. Crop Sci. 2004, 44, 1832–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.; Zikhali, M.; Turner, A.; Isaac, P.; Laurie, D. Copy number variation affecting the Photoperiod-B1 and Vernalization-A1 genes is associated with altered flowering time in wheat (Triticum aestivum). PLoS ONE 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Würschum, T.; Boeven, P.H.; Langer, S.M.; Longin, C.F.; Leiser, W.L. Multiply to conquer: Copy number variations at Ppd-B1 and Vrn-A1 facilitate global adaptation in wheat. BMC Genet. 2015, 29, 16–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muterko, A.F.; Salina, E.A. Analysis of the VERNALIZATION-A1 exon-4 polymorphism in polyploid wheat. Vavilov J. Genet. Breed. 2017, 21, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masoomi-Aladizgeh, F.; Jabbari, L.; Khayam Nekouei, R.; Aalami, A. A simple and rapid system for DNA and RNA isolation from diverse plants using handmade kit. Protoc. Exch. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Helguera, M.; Kato, K.; Fukuyama, S.; Sherman, J.; Dubcovsky, J. Allelic variation at the VRN1 promoter region in polyploid wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Szucs, P.; Yan, L.; Helguera, M.; Skinner, J.S.; von Zitzewitz, J.; Hayes, P.M.; Dubcovsky, J. Large deletions within the first intron in VRN-1 are associated with spring growth habit in barley and wheat. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2005, 273, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Sun, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Hua, W. An improved allele-specific PCR primer design method for SNP marker analysis and its application. Plant Methods 2012, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konopatskaia, I.; Vavilova, V.; Kondratenko, E.Y.; Blinov, A.; Goncharov, N.P. VRN1 genes variability in tetraploid wheat species with a spring growth habit. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shcherban, A.B.; Strygina, K.V.; Salina, E.A. VRN-1 gene- associated prerequisites of spring growth habit in wild tetraploid wheat T. dicoccoides and the diploid A genome species. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.Q.; Hu, Y.G. Detection of SNPs in the VRN-A1 gene of common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by a modified Ecotilling method using agarose gel electrophoresis. Aus. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak, J.; Deal, K.R.; Luo, M.C.; You, F.M.; von Borstel, K.; Dehghani, H. The origin of spelt and free-threshing hexaploid wheat. J. Hered. 2012, 103, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaaska, V. NADP-dependent aromatic alcohol dehydrogenase in polyploid wheats and their diploid relatives. On the origin and phylogeny of polyploid wheats. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1978, 53, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haudry, A.; Cenci, A.; Ravel, C.; Bataillon, T.; Brunel, D.; Poncet, C.; Hochu, I.; Poirier, S.; Santoni, S.; Glémin, S.; et al. Grinding up wheat: a massive loss of nucleotide diversity since domestication. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, M.; Levy, A.A. Genome evolution due to allopolyploidization in wheat. Genetics 2012, 192, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubcovsky, J.; Dvorak, J. Genome plasticity a key factor in the success of polyploid wheat under domestication. Science 2007, 316, 1862–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Sequence (5’–3’) | Primer Developer | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Region | Allele or Haplotype | PCR Fragment Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRN1AF | gaaaggaaaaattctgctcg | [22] | 58 | VRN-A1 promoter | vrn-A1 | 713 |
| VRN1-INT1R | gcaggaaatcgaaatcgaag | Vrn-A1a.1 | 944 | |||
| Vrn-A1a.2 | 924, 944 | |||||
| Vrn-A1a.3 | 765 | |||||
| Vrn-A1b | 691 | |||||
| Vrn-A1d | 685 | |||||
| Vrn-A1e | 659 | |||||
| Vrn-A1f | 658 | |||||
| Vrn-A1i | 713 | |||||
| Vrn-A1j | 659,713 | |||||
| Vrn-A1k | 755 | |||||
| vrn-Am1 | 705 | |||||
| Vrn-Am1g | 681 | |||||
| Vrn-Am1a | 671 | |||||
| vrn-Am1b | 656 | |||||
| Vrn-A1-intr_F | ccgtcgaaaggatcgctactg | [12] | 60 | VRN-A1 intact intron-1 | vrn-A1 | 541 |
| Vrn-A1-intr_R1 | cttgtccccgtgagctacttac | |||||
| Ex1/C/F | gttctccaccgagtcatggt | [23] | 56 | VRN-A1 intron-1 with large deletion | Vrn-A1c (Langdon) | 522 |
| Intr1/A/R3 | aagtaagacaacacgaatgtgaga | Vrn-A1c (IL369) | 2188 | |||
| Ex4F2m3 | ttgttccttcctgtcccaacc | [14] (modified by [20]) | 60 | VRN-A1/ VRN-D4 exon-3–4 | Ex4(C/T) | 389 |
| Ex4R | ctttgctgaacttctctgc | Ex4C.f | 387 | |||
| Ex4F2m3 | ttgttccttcctgtcccaacc | [20] | 59 | VRN-D4 exon-3–4 | VRN-D4 | 265 |
| V4/R2m3 | ccagttgctgcaactccagg | |||||
| Ex4outV4F2m3 | cctgtcccacccaaagttaсta | [20] | 57 | VRN-A1 exon-3–4 | Ex4(C/T) | 380 |
| Ex4R | ctttgctgaacttctctgc | Ex4C.f | 378 | |||
| Ex4F2m3 | ttgttccttcctgtcccaacc | [20] | 58 | VRN-A1/VRN-D4 exon-3–5 | Ex4C.sph | 592 |
| Ex4AR245m3 | gaccagttcgaataccgaagaa | Ex4C.f | 588 | |||
| Ex4C.m/ Ex4T | 591 | |||||
| Ex4C.s | 590 | |||||
| Ex4outV4F2m3 | cctgtcccacccaaagttaсta | [20] | 57 | VRN-A1 exon-3–5 | Ex4C.sph | 583 |
| Ex4AR245m3 | gaccagttcgaataccgaagaa | Ex4C.f | 579 | |||
| Ex4C.m/ Ex4T | 582 | |||||
| Ex4C.s | 581 | |||||
| Ex7Fm4 | caaccttgcataccttcttc | This study | 57–60 | VRN-A1 exon-6–7 | Ex7C | 319 |
| Ex7/C/R2m4 | tttgatcttgctgcgacgc | |||||
| Ex7Fm4 | caaccttgcataccttcttc | This study | 56–58 | VRN-A1 exon-6–7 | Ex7T | 332 |
| Ex7/T/R2m3 | ctaactccgactctttgatcttgctgcgcgac | |||||
| Ex4F2m3 | tgttccttcctgtcccaacc | This study | 57 | VRN-A1 exon-3–7 | Ex4(С/T)/7C | 872 |
| Ex7/C/R2m4 | tttgatcttgctgcgacgc | Ex4C.f/7C | 870 | |||
| Ex4/F2m3 | tgttccttcctgtcccaacc | This study | 56 | VRN-A1 exon-3–7 | Ex4(С/T)/7T | 885 |
| Ex7/T/R2m3 | ctaactccgactctttgatcttgctgcgcgac | |||||
| Ex7Fm4 | caaccttgcataccttcttc | This study | 57 | VRN-A1 exon-6–7 | Ex7(C/T) | 570 |
| Ex7R | tggatgaatgctgcacaacc |
| Allele | VRN-A1 exon 4 and exon 7 Haplotype |
|---|---|
| vrn-A1 | Ex4C.s/7C |
| Ex4C.f/7С | |
| Ex4C.s/7T | |
| Ex4C.m/7T | |
| Ex4C.sph/4T/7T | |
| Ex4C.m/4T/7T | |
| Ex4T/7T | |
| Vrn-A1a.1–2 | Ex4C.f/7С |
| Vrn-A1b.1–7 | Ex4C.s/7С |
| Vrn-A1e | Ex4C.f/7С |
| Vrn-A1i | Ex4C.f/7C |
| Vrn-A1j (GenBank: KU738894) | Ex4C.m/4T/7T |
| Vrn-A1k (GenBank: KX874608) | Ex4C.s/7С |
| Vrn-A1c (Langdon) | Ex4C.s/7С |
| Vrn-A1c (IL369) | Ex4C.m/4T/7T |
| VRN-A1 Haplotype | Tetraploid Wheat | Hexaploid Wheat |
|---|---|---|
| Ex4C.s/7C | T. dicoccoides (PI 352325, PI 428018, IG 46287) T. dicoccum (TRI 28027, TRI 16880) T. carthlicum (PI 115817, PI 190949, PI 272521, PI 283887, PI 352279, PI 532505, PI 532512) T. turgidum (PI 264991) | T. aestivum (TRI 867, TRI 4560, TRI 3838, TRI 9533, TRI 7129) T. sphaerococcum (PI 191301, PI 40941, PI 42013, PI 277141, PI 168685, CItr 17737) |
| Ex4C.f/7C | T. dicoccoides (PI 352322, UA0300256, IG 46386, IG 46527, IG 46353) T. dicoccum (K-21416) | T. aestivum (TRI 3088) T. spelta (UA0300246) |
| Ex4C.s/7T | T. dicoccoides (IG 109085, IG 115808, IG 46480) | |
| Ex4C.m/7T | T. dicoccoides (IG 131234, IG 113301, IG 131233, IG 109088, IG 131232, IG 113302) | T. aestivum (TRI 828, TRI 834, TRI 4917, TRI 1948, TRI 3111, TRI 4925) T. sphaerococcum (PI 190982, PI 278650) |
| Ex4T/7T | T. aestivum (TRI 290) | |
| Ex4C.m/4T//7T | T. aestivum (TRI 1712, TRI 3534, TRI 4078, TRI 4739, TRI 5395, TRI 950, TRI 2979, TRI 3891, TRI 5310, TRI 5394, TRI 5423, TRI 7120, TRI 8459, TRI 11031) T. compactum (PI 186391, PI 157920, PI 129523, PI 211701, PI 278541, PI 262666, PI 278581, PI 352306, PI 41023) T. spelta (UA0300103, UA0300259, PI 190960, PI 225271, PI 286048, PI 295056, PI 347850) T. macha (PI 272554, PI 352466, PI 355511, PI 355514, PI 428146, PI 428179, PI 542466, PI 572905) | |
| Ex4C.sph/4T/7T | T. sphaerococcum (PI 277142, PI 70711, PI 324492) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muterko, A.; Salina, E. Origin and Distribution of the VRN-A1 Exon 4 and Exon 7 Haplotypes in Domesticated Wheat Species. Agronomy 2018, 8, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8080156
Muterko A, Salina E. Origin and Distribution of the VRN-A1 Exon 4 and Exon 7 Haplotypes in Domesticated Wheat Species. Agronomy. 2018; 8(8):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8080156
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuterko, Alexandr, and Elena Salina. 2018. "Origin and Distribution of the VRN-A1 Exon 4 and Exon 7 Haplotypes in Domesticated Wheat Species" Agronomy 8, no. 8: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8080156
APA StyleMuterko, A., & Salina, E. (2018). Origin and Distribution of the VRN-A1 Exon 4 and Exon 7 Haplotypes in Domesticated Wheat Species. Agronomy, 8(8), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8080156





