Magnetic Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Single-Drop Microextraction for the Determination of Triazine Herbicides in Environmental Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
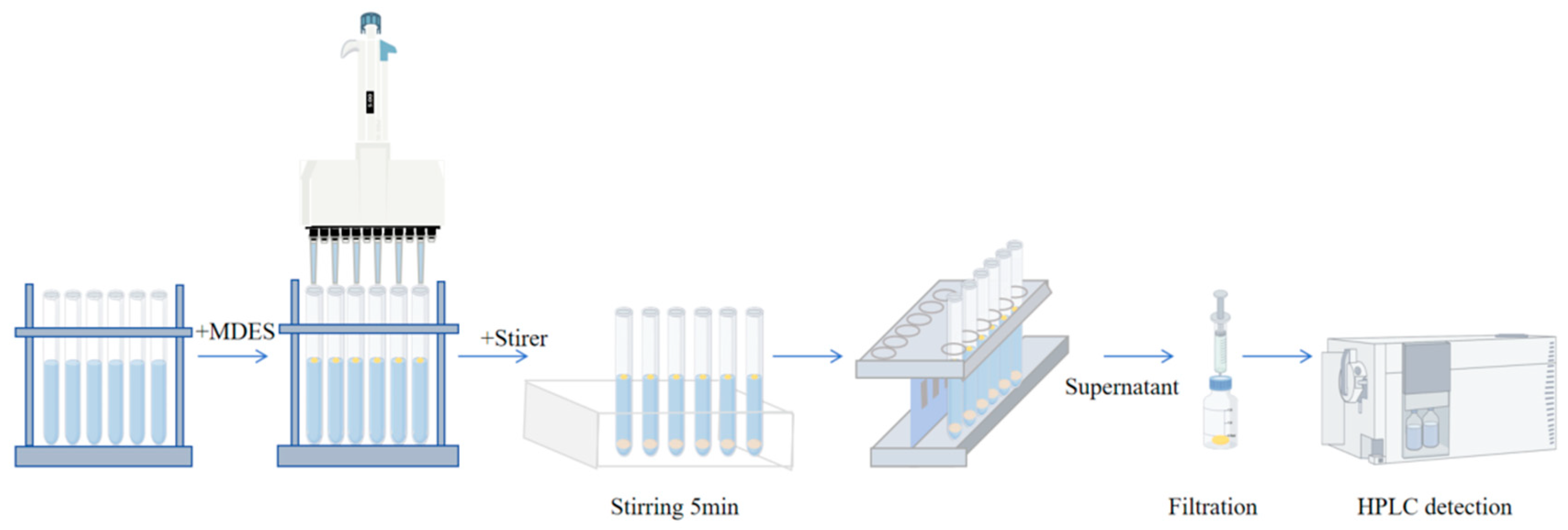
2.3. Preparation of the MDES
2.4. Microextraction
2.5. Determination of Extraction Recovery
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimizing the MDES-SDME-HPLC Method Conditions
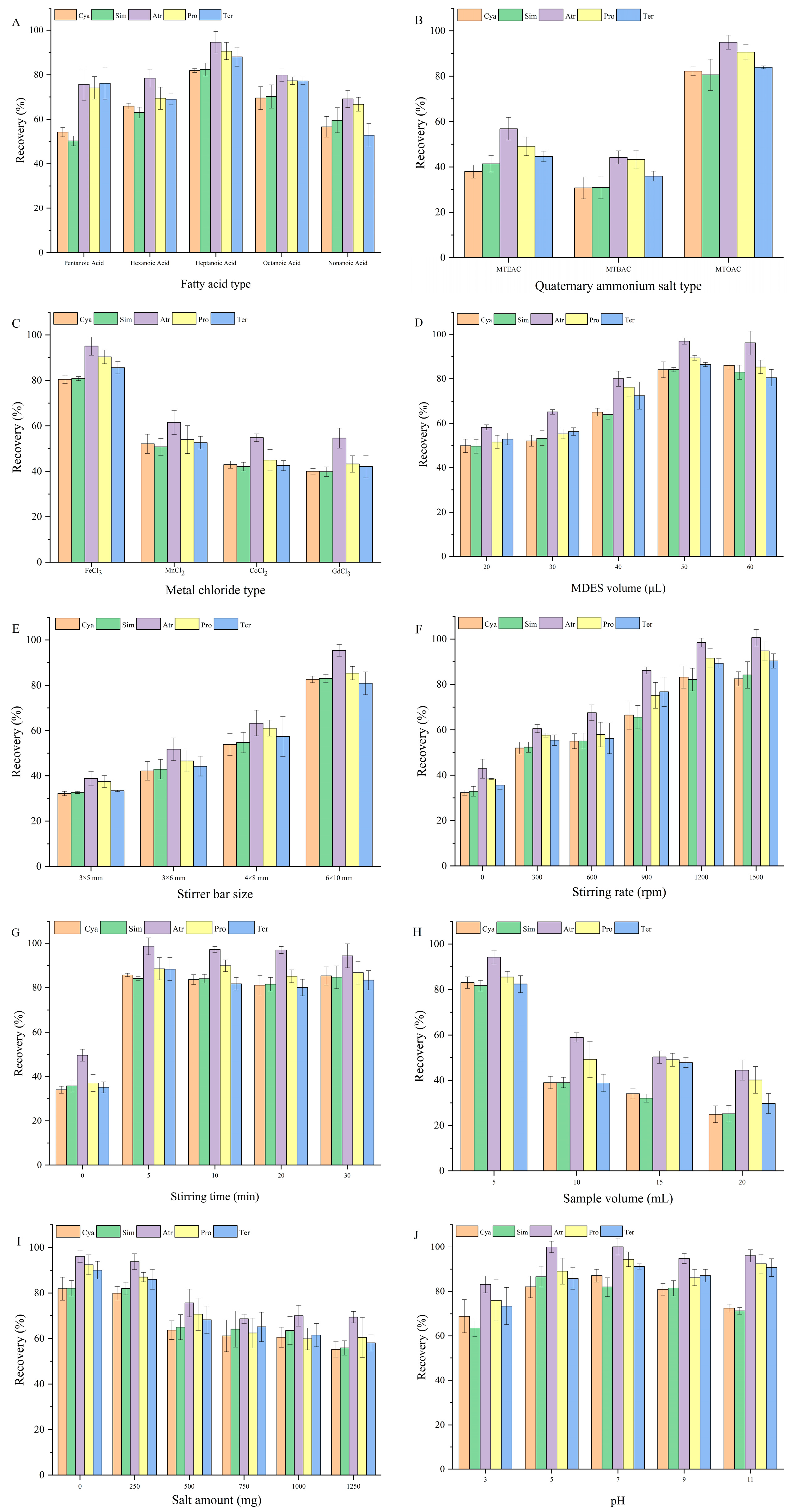
3.1.1. Effect of Fatty Acid Type
3.1.2. Effect of Quaternary Ammonium Salt Type
3.1.3. Effect of Metal Chloride Type
3.1.4. Effect of MDES Volume
3.1.5. Effect of Stirrer Bar Size
3.1.6. Effect of Stirring Rate
3.1.7. Effect of Stirring Time
3.1.8. Effect of Sample Volume
3.1.9. Effect of Salt Amount
3.1.10. Effect of pH
3.2. Method Validation
3.3. Real Samples Application
3.4. Comparison with Other Methods
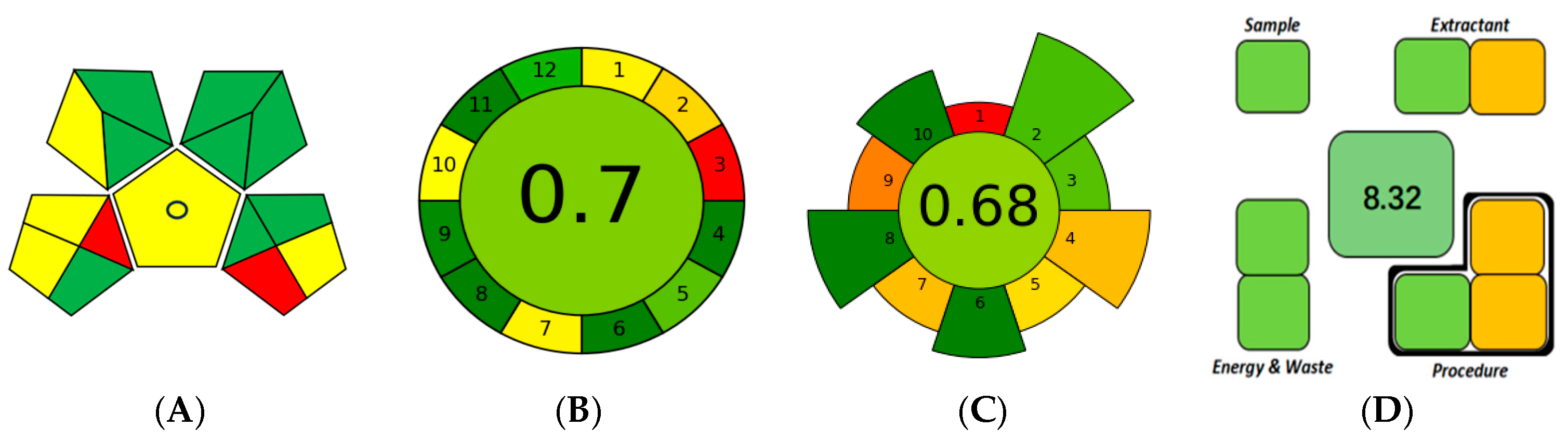
3.5. Green Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.-W.; Chen, H.; Zhao, H.-L.; Li, D.-W.; Ou, L.-J. Triazine Herbicide Reduced the Toxicity of the Harmful Dinoflagellate Karenia Mikimotoi by Impairing Its Photosynthetic Systems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 269, 115740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Jing, X.; Wu, J. Determination of Triazine Herbicides from Water, Tea, and Juice Samples Using Magnetic Dispersive Micro-Solid Phase Extraction and Magnetic Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction with HPLC. Food Chem. 2025, 468, 142430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, M.; Yu, X.; Liu, L.; Gao, C.; Li, H.; Fu, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. Presence and Distribution of Triazine Herbicides and Their Effects on Microbial Communities in the Laizhou Bay, Northern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Wang, N.; Hu, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Reshuffling the Risk Values of Pesticides in Surface-Groundwater Systems: Evidence from Mining Intensity and Hydrogeological Vulnerabilities. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 967, 178755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madesh, S.; Gopi, S.; Sau, A.; Rajagopal, R.; Namasivayam, S.K.R.; Arockiaraj, J. Chemical Contaminants and Environmental Stressors Induced Teratogenic Effect in Aquatic Ecosystem—A Comprehensive Review. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 13, 101819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Cai, M.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, K.; Wang, F. Screening Triazine Herbicides in Drinking Water in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Occurrence and Health Risk. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Han, W.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Insights into Interaction of Triazine Herbicides with Three Kinds of Different Alkyl Groups (Simetryne, Ametryn and Terbutryn) with Human Serum Albumin via Multi-Spectral Analysis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 201, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xing, H.; Yang, L.; Fei, P.; Liu, H. Development Trend and Prospect of Solid Phase Extraction Technology. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 42, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhary, A.; Leitch, M.; Liao, B.Q. Liquid–Liquid Extraction Technology for Resource Recovery: Applications, Potential, and Perspectives. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javar, K.; Foroozandeh, A.; Souri, M.; Amoli, H.S.; Hasanzadeh, M. Critical Role of Single Drop Microextraction for Drug Isolation from Complex Matrix towards Efficient Pharmaceutical Analysis: Advances and Challenges. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 185, 118163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannot, M.A.; Przyjazny, A.; Kokosa, J.M. Single Drop Microextraction—Development, Applications and Future Trends. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2326–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Row, K.H. Development of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Sustainable Chemistry. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 362, 119654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, S.; Tailor, Y.K.; Kumar, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) as Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Solvent/Catalyst Systems in Organic Transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 345–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhune, A.; Dey, R. Green and Sustainable Solvents of the Future: Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 379, 121676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, S.; Belousov, A.S.; Rashid, R.; Shafiq, I.; Aziz, K.H.H.; Riaz, N.; Khan, M.S.; Shaheen, A.; Ishaq, M.; Akhter, P.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES): Structure, Properties, and Cutting-Edge Applications in Green Catalysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 419, 126769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Row, K.H. Design and Evaluation of Polarity Controlled and Recyclable Deep Eutectic Solvent Based Biphasic System for the Polarity Driven Extraction and Separation of Compounds. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Basheer, C.; Lee, H.K. Developments in Single-Drop Microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1152, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, F.R.; Danielson, N.D. Solvent-Terminated Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction: A Tutorial. Anal. Chim. ACTA 2018, 1016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezeli, T.; Daneshfar, A. Synthesis and Application of Magnetic Deep Eutectic Solvents: Novel Solvents for Ultrasound Assisted Liquid-Liquid Microextraction of Thiophene. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortizo, R.G.G.; Sharma, V.; Tsai, M.-L.; Nargotra, P.; Wang, J.-X.; Sun, P.-P.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. Exploring the Potential of Magnetic Deep Eutectic Solvents and DES-Functionalized Nanomaterials for Food Analysis: Advancements and Current Trends. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani Pour, S.; Jahanbin Sardroodi, J.; Rastkar Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Pazuki, G.; Hadigheh Rezvan, V. A Comparative Study of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Fatty Acids and the Effect of Water on Their Intermolecular Interactions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bureš, F. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds: Simple in Structure, Complex in Application. Top. Curr. Chem. 2019, 377, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Magnetic Effervescence Tablet-Assisted Switchable Hydrophilicity Solvent-Based Liquid Phase Microextraction of Triazine Herbicides in Water Samples. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 306, 112934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, R.; Xing, R.; Chen, X.; Hu, S. Cyclodextrin Sensitized Homogeneous Liquid-Liquid Microextraction for Six Hepatotoxic Ingredients in “Psoraleae Fructus” Based on a Switchable Deep Eutectic Supramolecular Polymer. Microchem. J. 2025, 212, 113313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, S.; Hatami, M.; Farhadi, K.; Bahram, M. Hollow-Fiber-Based LPME as a Reliable Sampling Method for Gas-Chromatographic Determination of Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Valproic Acid in Rat Plasma. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojavan, S.; Tahmasebi, Z.; Davarani, S.S.H. Effect of Type of Stirring on Hollow Fiber Liquid Phase Microextraction and Electromembrane Extraction of Basic Drugs: Speed up Extraction Time and Enhancement of Extraction Efficiency. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 110221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, R. Extraction and Stirring Integrated Techniques: Examples and Recent Advances. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrucci, M.; Ricci, E.M.; Locatelli, M.; Ali, I.; Mansour, F.R.; Kabir, A.; Ulusoy, H.I. Recent Trends in Microsampling and Reduced-Volume Sample Preparation Procedures. Adv. Sample Prep. 2025, 14, 100182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, N.; El-Sayed, M.M.; Sanghvi, T.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Estimation of the Effect of NaCl on the Solubility of Organic Compounds in Aqueous Solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Braune, M.; Gröngröft, A. Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Caproic and Caprylic Acid: Solvent Properties and pH. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2023, 95, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Han, J.; Jing, X.; Yang, J. Detection of Triazine Herbicides in Water, Juice, and Tea Using Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Emulsive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Combined with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Methods 2025, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Application of Supramolecular Solvent Based on the Surface-Active Ionic Liquid in Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction of Triazine Herbicides in Tea Samples. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legesse, A.; Megersa, N.; Chandravanshi, B.S. Effervescence-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction for the Extraction and Preconcentration of Pesticide Residues in Fruit Juice Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1333, 343400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Yang, S.; Meng, Y. Investigation of pH-Switchability of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction and Preconcentration of Triazine Herbicides in Water Samples. Microchem. J. 2023, 194, 109198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Álvarez, M.; Turiel, E.; Martín-Esteban, A. Hydrophobic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on L-Menthol as Supported Liquid Membrane for Hollow Fiber Liquid-Phase Microextraction of Triazines from Water and Urine Samples. Microchem. J. 2023, 194, 109347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J. Analytical Eco-Scale for Assessing the Greenness of Analytical Procedures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J. A New Tool for the Evaluation of the Analytical Procedure: Green Analytical Procedure Index. Talanta 2018, 181, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M.; Pena-Pereira, F.; Psillakis, E. AGREEprep—Analytical Greenness Metric for Sample Preparation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 149, 116553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, R.; Gutiérrez-Serpa, A.; Pino, V.; Sajid, M. A Tool to Assess Analytical Sample Preparation Procedures: Sample Preparation Metric of Sustainability. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1707, 464291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Triazine Herbicide | Calibration Curve (μg L−1) | R2 | LOD (μg L−1) | LOQ (μg L−1) | Intra-Day RSD (%) (n = 5) | Inter-Day RSD (%) (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanazine | y = 48,733x + 1636.6 | 0.998 | 0.06 | 0.2 | 4.3 | 12.1 |
| Simazine | y = 24,876x + 852.34 | 0.999 | 0.06 | 0.2 | 4.4 | 9.8 |
| Atrazine | y = 65,638x + 625.01 | 0.998 | 0.06 | 0.2 | 5.9 | 11.6 |
| Propazine | y = 63,894x + 486.17 | 0.998 | 0.06 | 0.2 | 7.2 | 13.7 |
| Terbuthylazine | y = 64,901x + 980.21 | 0.998 | 0.06 | 0.2 | 6.1 | 9.7 |
| Triazine Herbicide | Concentration (μg L−1) | Tap Water | River Water | Lake Water | Sea Water | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER (%) | RSD (%) | ER (%) | RSD (%) | ER (%) | RSD (%) | ER (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Cyanazine | 0.2 | 95.3 | 7.1 | 79.7 | 6.5 | 81.4 | 1.7 | 89.8 | 1.2 |
| 2 | 86.5 | 2.2 | 78.1 | 5.6 | 77.2 | 7.8 | 79.1 | 5.4 | |
| 20 | 82.1 | 1.8 | 85.1 | 2.0 | 86.5 | 4.0 | 87.5 | 4.7 | |
| Simazine | 0.2 | 87.4 | 6.8 | 75.5 | 8.7 | 77.7 | 1.3 | 87.4 | 7.9 |
| 2 | 85.4 | 1.8 | 83.3 | 7.8 | 85.7 | 8.6 | 88.6 | 3.3 | |
| 20 | 82.6 | 1.2 | 86.2 | 2.0 | 94.2 | 7.8 | 85.7 | 4.9 | |
| Atrazine | 0.2 | 98.4 | 5.3 | 93.5 | 1.8 | 94.9 | 1.7 | 100.1 | 5.3 |
| 2 | 101.1 | 8.6 | 91.1 | 8.9 | 95.6 | 2.9 | 97.1 | 4.8 | |
| 20 | 102.4 | 3.8 | 97.9 | 2.4 | 96.8 | 5.6 | 95.4 | 3.2 | |
| Propazine | 0.2 | 97.6 | 0.9 | 83.5 | 1.9 | 75.9 | 4.6 | 87.3 | 5.2 |
| 2 | 102.3 | 5.2 | 84.1 | 6.1 | 87.6 | 7.4 | 81.5 | 5.1 | |
| 20 | 88.6 | 4.5 | 97.8 | 2.3 | 89.8 | 5.2 | 87.1 | 6.4 | |
| Terbuthylazine | 0.2 | 93.8 | 5.7 | 91.2 | 8.3 | 75.7 | 4.5 | 85.4 | 5.4 |
| 2 | 93.1 | 7.3 | 87.3 | 7.0 | 76.9 | 7.2 | 77.5 | 7.5 | |
| 20 | 81.6 | 2.3 | 91.1 | 1.1 | 80.3 | 2.2 | 90.7 | 5.8 | |
| Triazine Herbicide | Pretreatment Method | Extractant Type | Extractant Volume | Additional Reagent | Reagent Amount | Auxiliary Device | Detection Instrument | LOQ (μg L−1) | ER (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanazine Atrazine Propazine Terbuthylazine | DSPME- DLLME | MDES | 200 μL | Biochar Methanol | 20 mg 800 μL | Vortex (0.3 min) | HPLC-DAD | 1 | 80.1–90.6 | [2] |
| Simazine Atrazine Terbuthylazine | ELLME | DES | 200 μL | Water | 600 μL | Pipette Centrifugation (5 min) | HPLC-DAD | 25 | 84.8–102.0 | [31] |
| Propazine Prometryn Terbumeton Dipropetryn | DLLME | SUPRAS | 100 μL | Na2SO4 HCl (aq) Methanol | 200 mg Not given 200 μL | Vortex (1 min) Centrifugation (5 min) | HPLC-DAD | 5.6–7.1 | 80.0–119.9 | [32] |
| Cyanazine Atrazine | DLLME | Undecanol | 75 μL | Citric acid Na2CO3 HCl (aq) | 520 mg 210 mg Not given | Centrifugation (2 min) Ice bath | HPLC-DAD | 0.2 | 76.5–101.3 | [33] |
| Cyanazine Atrazine Simazine Propazine | LLME | DES | 60 μL | KOH (aq) HCl (aq) | 100 µL 100 μL | Ice bath | HPLC-UV | 0.5–1.5 | 91.0–107.8 | [34] |
| Desisopropylatrazine Desethylatrazine Simazine Atrazine Propazine Terbutylazine | HF-LPME | DES | NG | Hollow fiber HCl (aq) Buffer (aq) Acetonitrile | 8 cm 25 μL 60 μL 15 μL | Agitator (90 min) | HPLC-UV | 2.5–10.3 | 68.0–128.0 | [35] |
| Cyanazine Simazine Atrazine Propazine Terbuthylazine | SDME | MDES | 50 μL | - | - | Stirrer (5 min) | HPLC-UV/Vis | 0.2 | 75.5–102.4 | Current study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Bi, X.; Wu, W.; Xue, X.; Jing, X.; Zhang, Q. Magnetic Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Single-Drop Microextraction for the Determination of Triazine Herbicides in Environmental Waters. Agronomy 2026, 16, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy16010107
Bi X, Wu W, Xue X, Jing X, Zhang Q. Magnetic Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Single-Drop Microextraction for the Determination of Triazine Herbicides in Environmental Waters. Agronomy. 2026; 16(1):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy16010107
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Xinyuan, Wenying Wu, Xiaorong Xue, Xu Jing, and Qiang Zhang. 2026. "Magnetic Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Single-Drop Microextraction for the Determination of Triazine Herbicides in Environmental Waters" Agronomy 16, no. 1: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy16010107
APA StyleBi, X., Wu, W., Xue, X., Jing, X., & Zhang, Q. (2026). Magnetic Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Single-Drop Microextraction for the Determination of Triazine Herbicides in Environmental Waters. Agronomy, 16(1), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy16010107






