Bio-Organic Fertilizers Enhance Yield in Continuous Cotton Cropping Systems Through Rhizosphere Microbiota Modulation and Soil Nutrient Improvement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
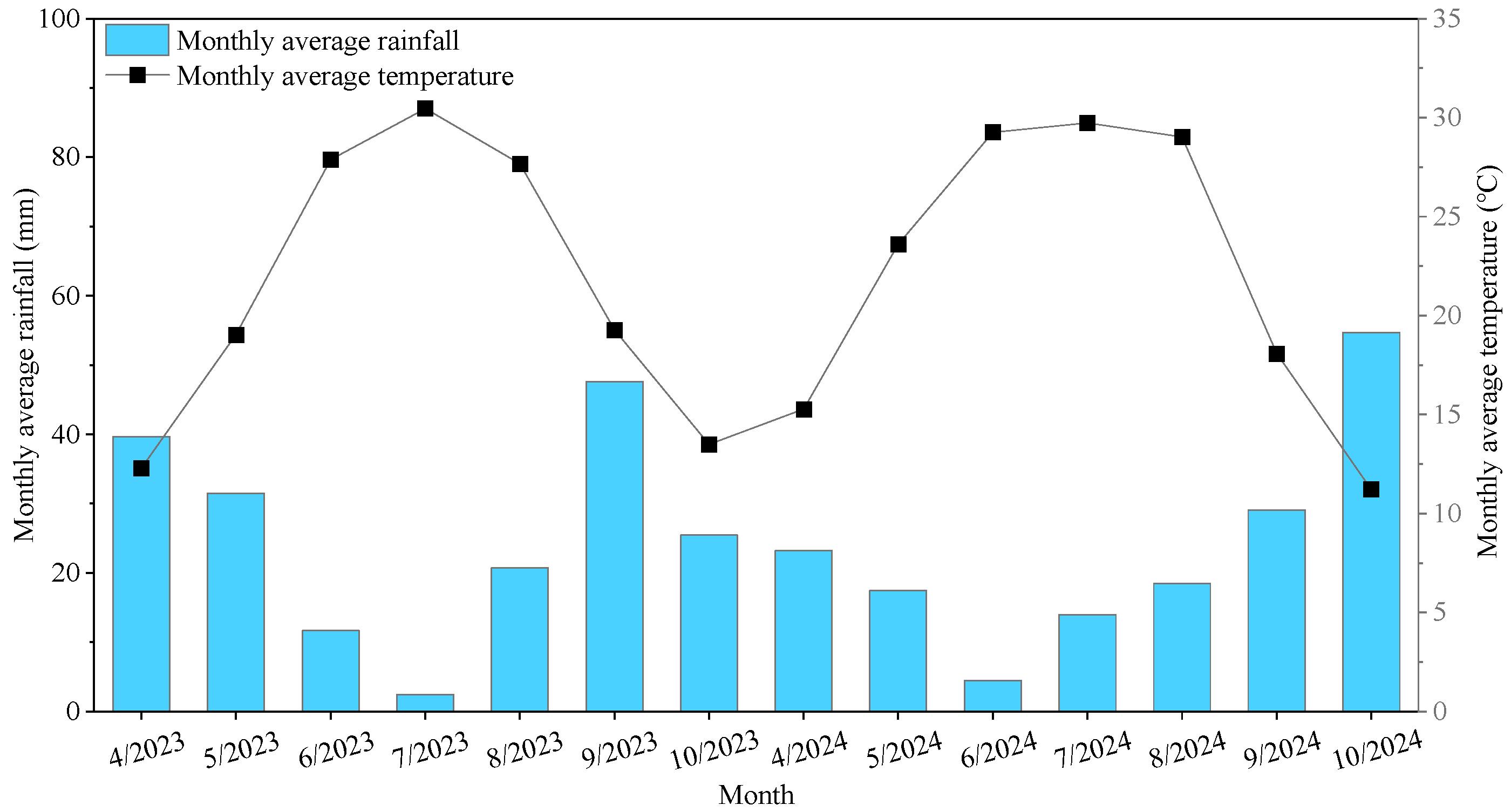
2.1. Experimental Site Description
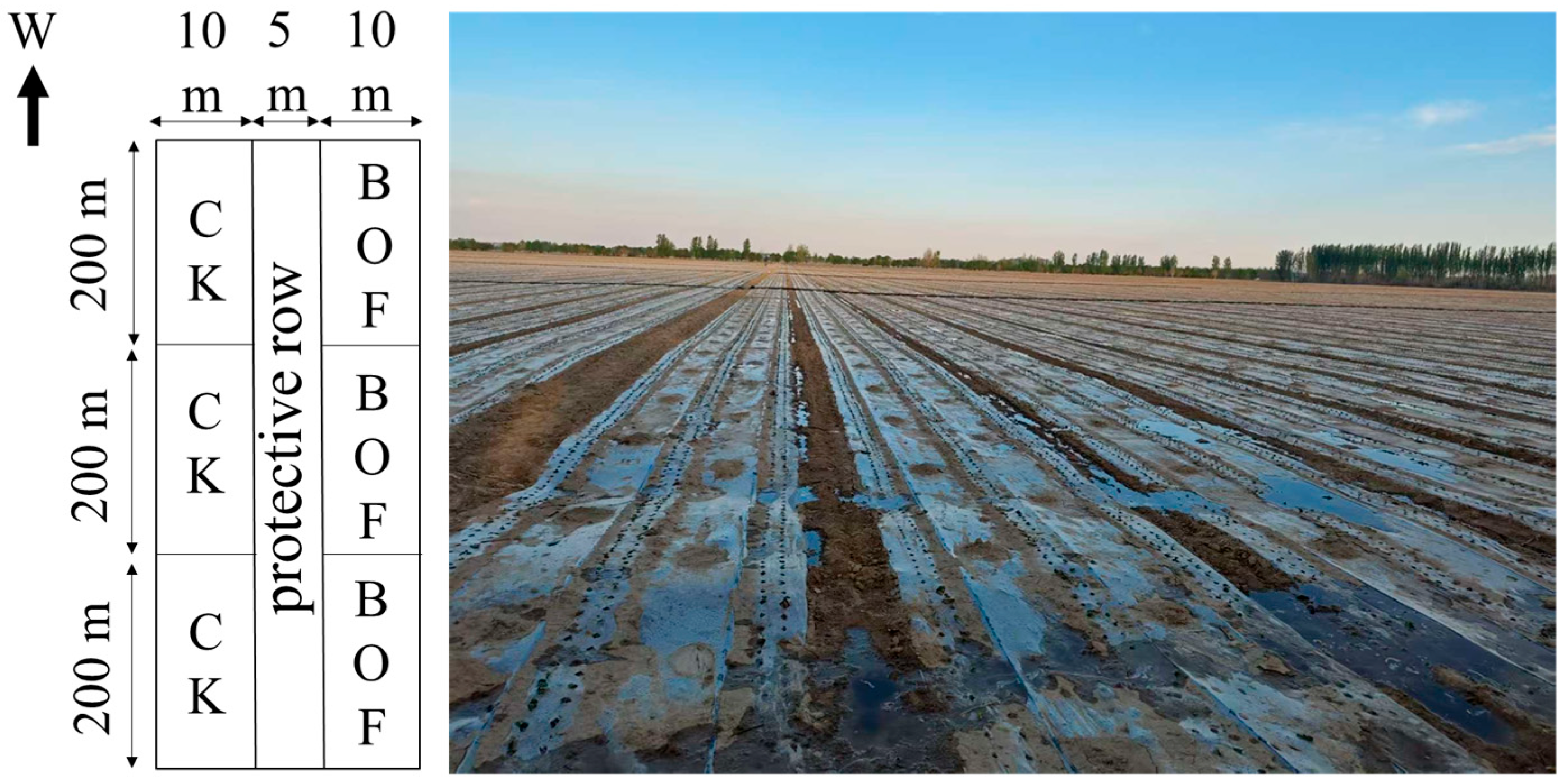
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.3.1. Plant Sample
2.3.2. Yield Measurement
2.3.3. Soil Sample
2.3.4. Rhizosphere Microbial DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
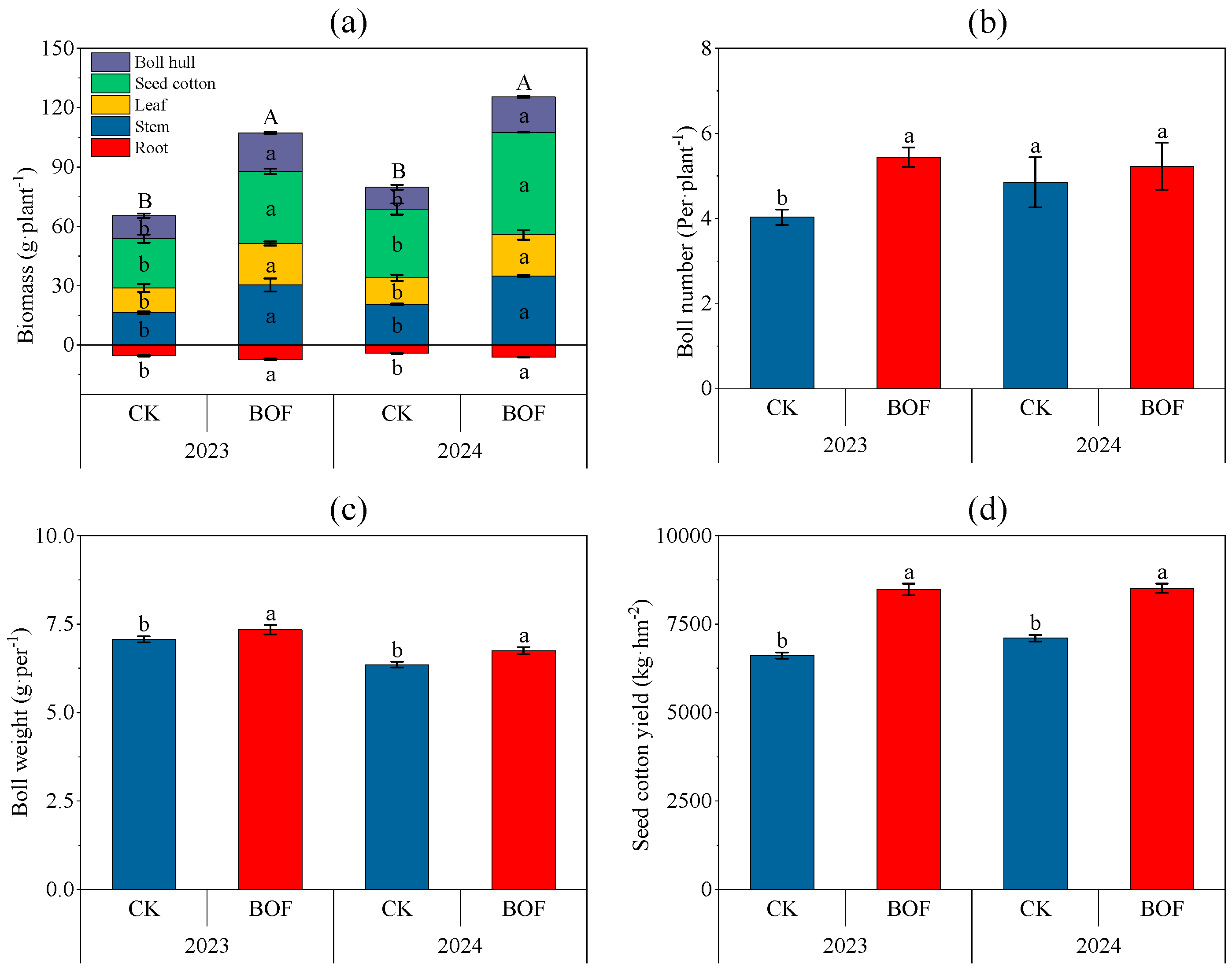
3.1. Cotton Yield and Composition Factors
3.2. Chemical Characteristics of Soil
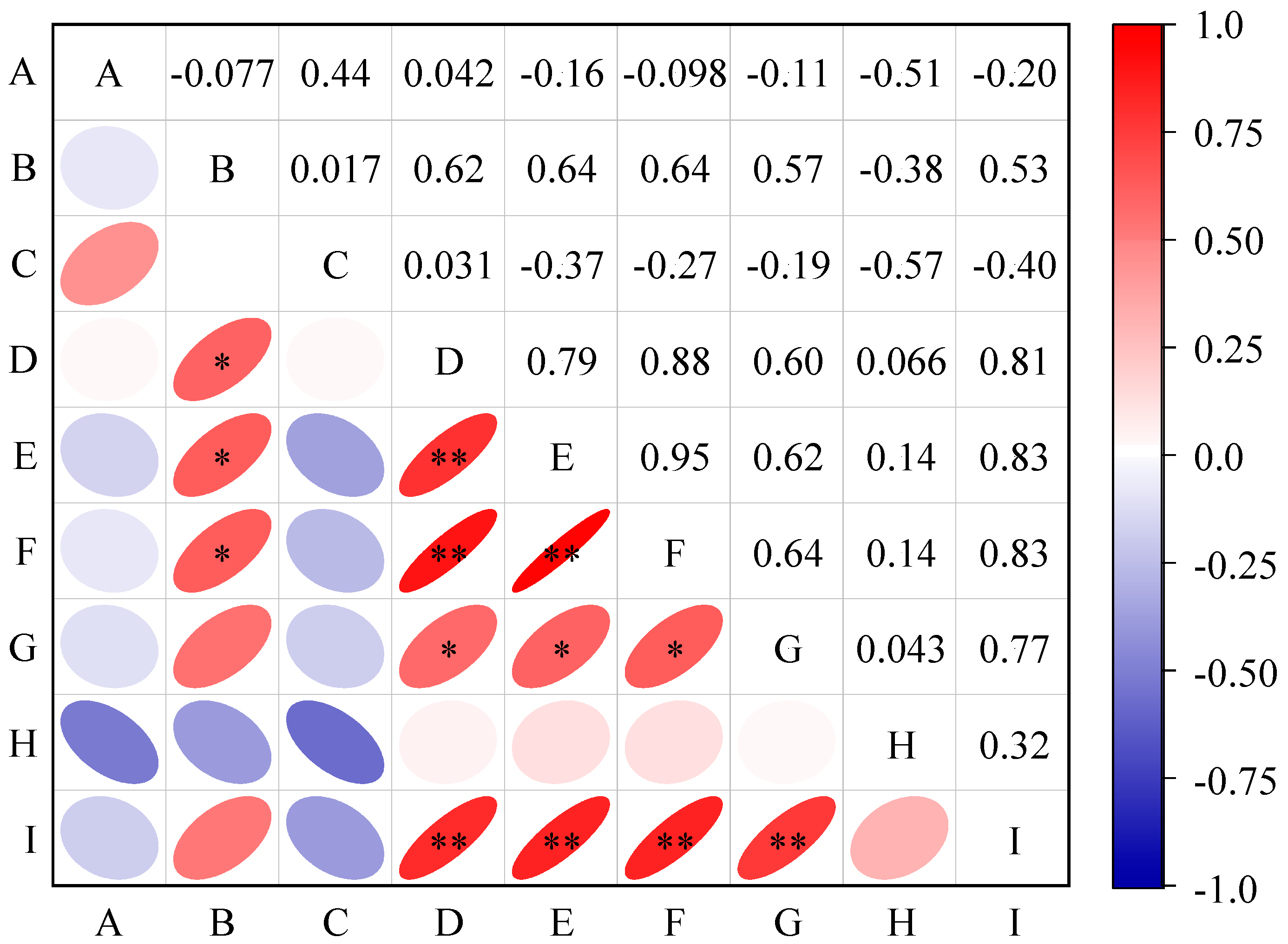
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Cotton Yield and Its Component Factors and Soil Chemical Properties
3.4. Rhizosphere Microbial Communities
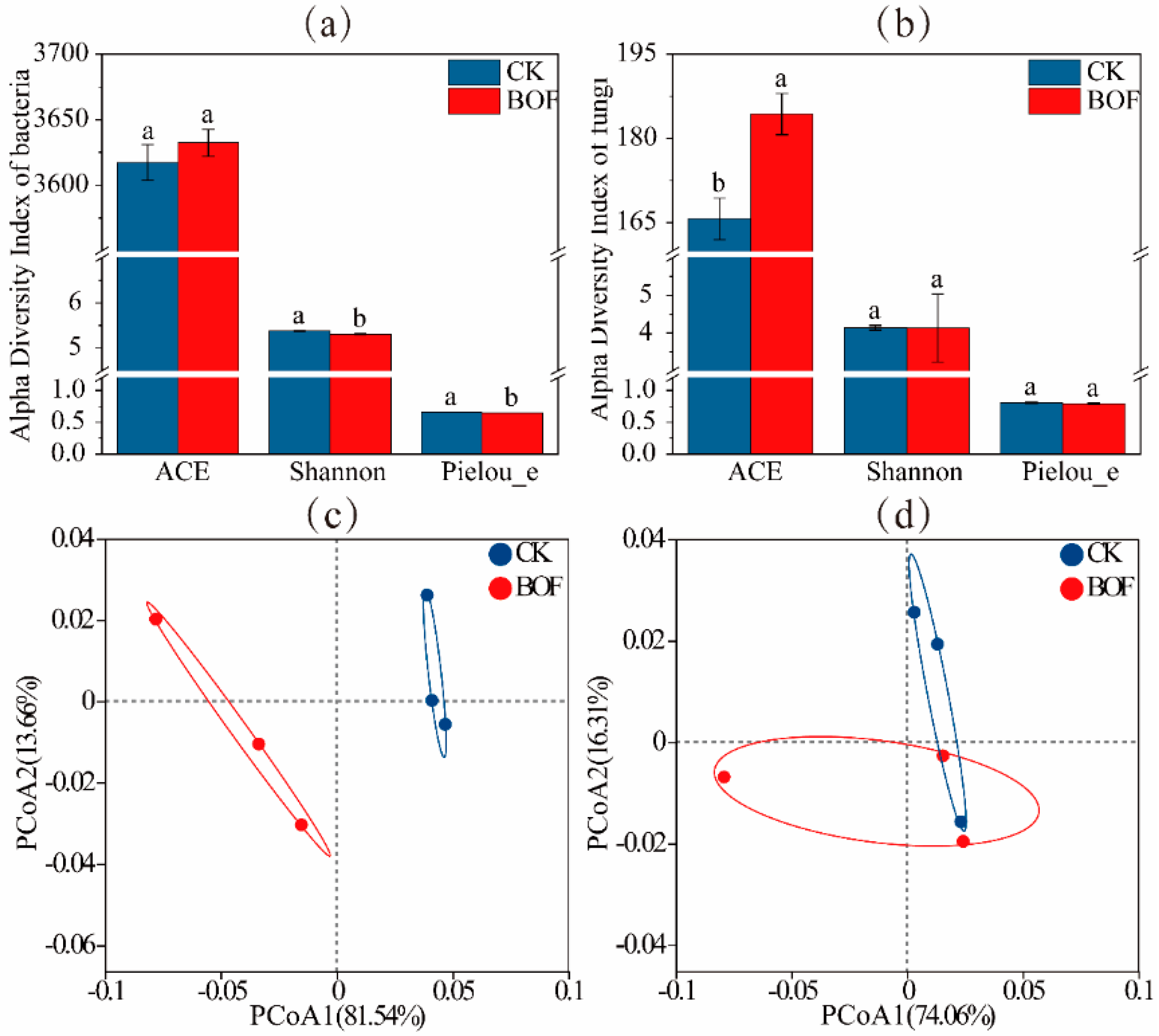
3.4.1. Microbial Diversity
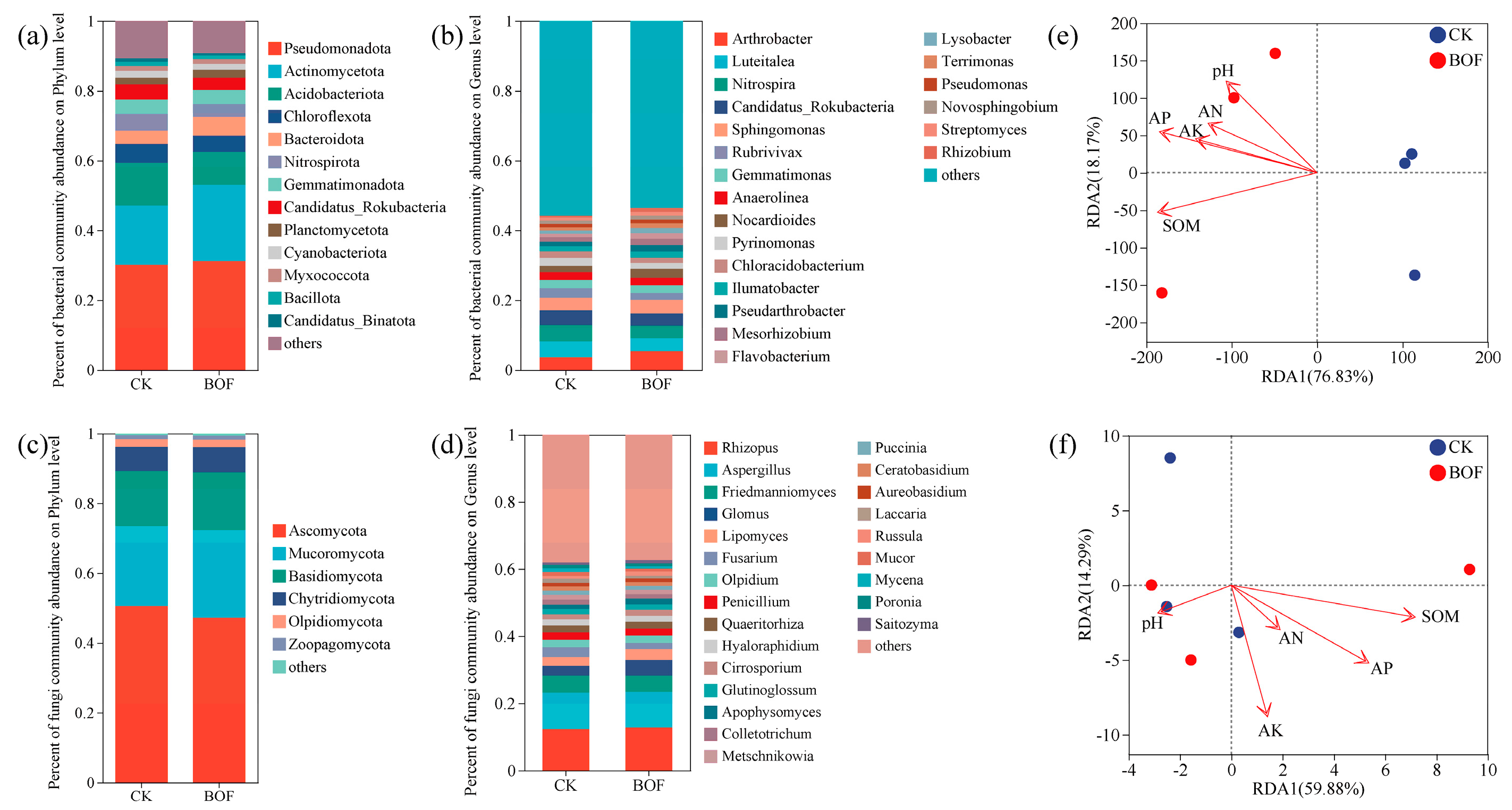
3.4.2. Microbial Community Composition
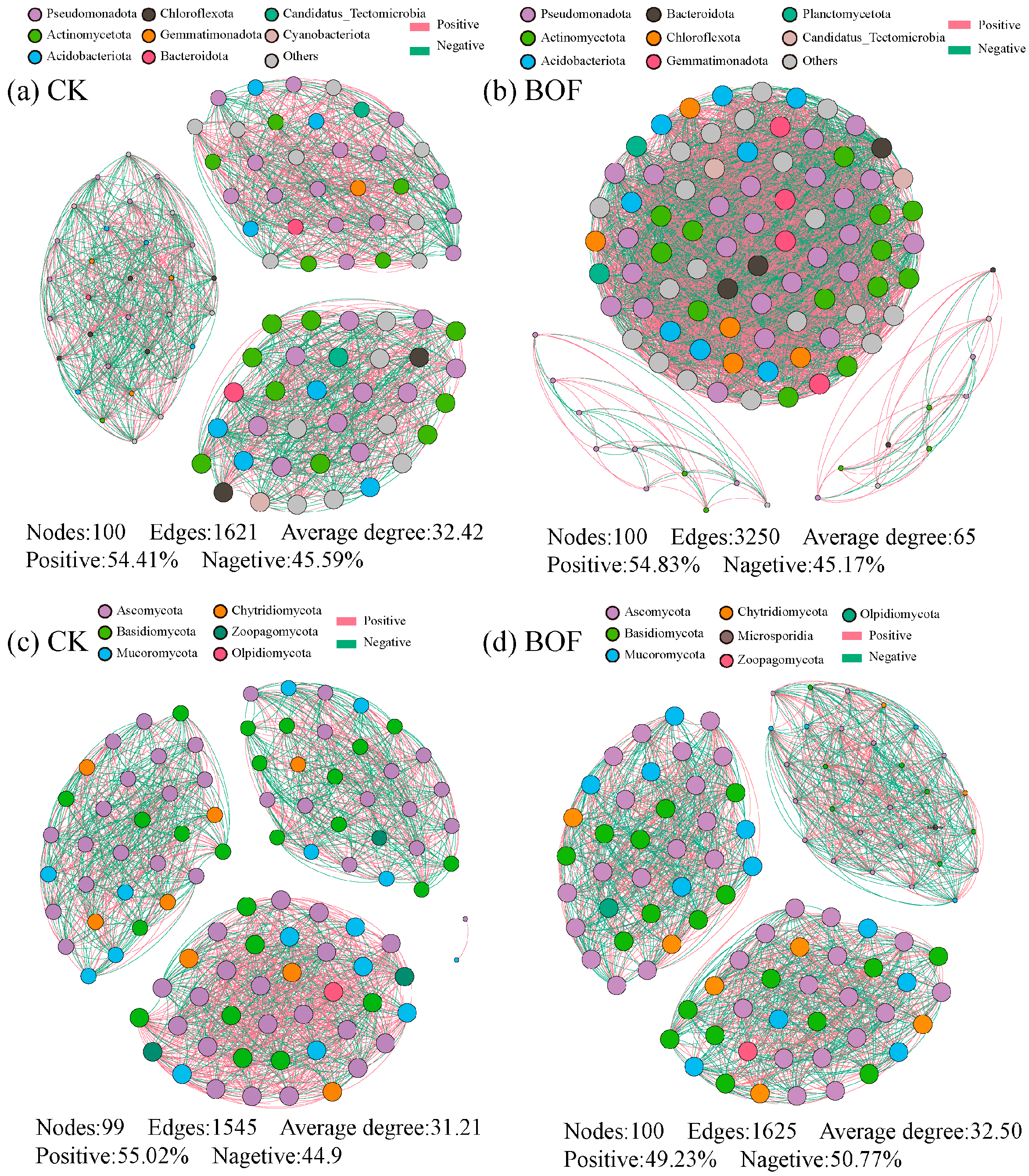
3.4.3. Microbial Ecological Networks
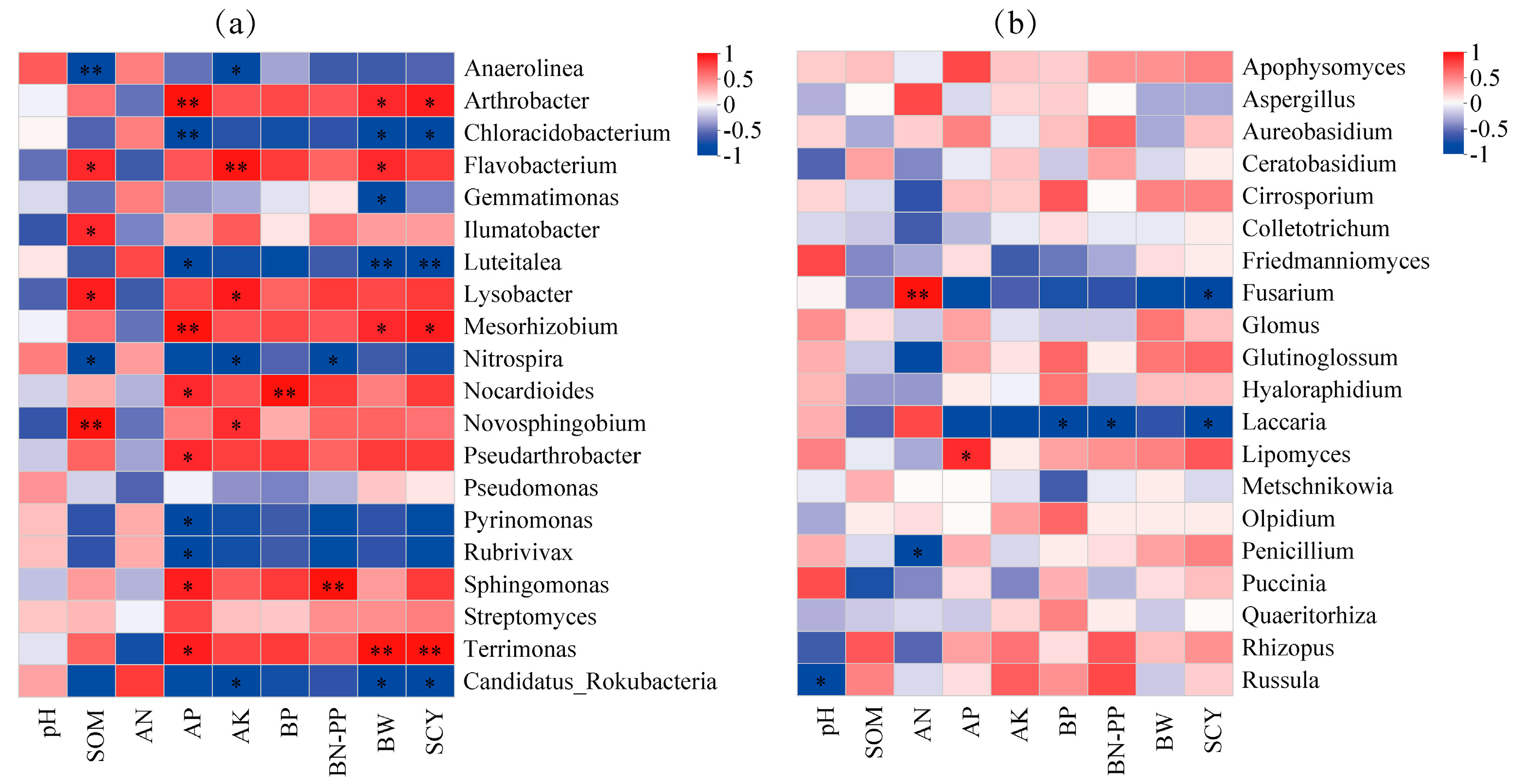
3.5. Correlations Between Soil Properties, Yield, and Microbes
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of BOFs on Cotton Yield and Soil Nutrients
4.2. Impact of BOFs on Rhizosphere Microbial Communities
4.3. The Link Between Soil-Microbe-Yield
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egbuta, M.A.; McIntosh, S.; Waters, D.L.E.; Vancov, T.; Liu, L. Biological Importance of Cotton By-Products Relative to Chemical Constituents of the Cotton Plant. Molecules 2017, 22, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheri, V.; Kumar, M.; Jaconis, S.; Zhang, B. Antioxidant Defense in Cotton under Environmental Stresses: Unraveling the Crucial Role of a Universal Defense Regulator for Enhanced Cotton Sustainability. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 204, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yu, D. Rhizosphere Fungal Community Structure Succession of Xinjiang Continuously Cropped Cotton. Fungal Biol. 2019, 123, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Xia, L.; Sun, S.; Li, H.; Rong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. A Synergistic Water-Saving Strategy Combining Stage-Specific Irrigation and Application of Exogenous Thiamine Enhances Drought Resistance of Xinjiang Cotton. In Plant Soil; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Dong, L.; Han, H.; Chen, Z. Bama Pig Manure Organic Fertilizer Regulates the Watermelon Rhizosphere Bacterial Community to Inhibit the Occurrence of Fusarium Wilt Under Continuous Cropping Conditions. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hou, C.; Zhang, C. Effects of Microbial Organic Fertilizer, Microbial Inoculant, and Quicklime on Soil Microbial Community Composition in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Continuous Cropping System. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Qu, B.; Liu, H.; Li, R.; Bai, Y.; Shen, Q.; Falcao Salles, J. Bio-Organic Soil Amendment Promotes the Suppression of Ralstonia Solanacearum by Inducing Changes in the Functionality and Composition of Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 1558–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Long, X.; Huo, X.; Chen, Y.; Lou, K. 16S rRNA-Based PCR-DGGE Analysis of Actinomycete Communities in Fields with Continuous Cotton Cropping in Xinjiang, China. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Mickan, B.S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F. Long–Term (25 Years) Continuous Cotton Cropping Combined with Residue Incorporation Affects the Fungal Communities in Reclaimed Saline Soil. Pedobiologia 2024, 102, 150928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, C.; Feng, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, H.; Wei, F. Soil Bacterial Community Response to Continuous Cropping of Cotton. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1125564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Tenga, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Ren, W.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Mechanisms by Which Organic Fertilizer and Effective Microbes Mitigate Peanut Continuous Cropping Yield Constraints in a Red Soil of South China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 128, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan Ul Haq, M.; Yu, J.; Yao, G.; Yang, H.; Iqbal, H.A.; Tahir, H.; Cui, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y. A Systematic Review on the Continuous Cropping Obstacles and Control Strategies in Medicinal Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Ding, D.; He, J. The Combined Application of Biofertilizer Alleviates the Continuous Cropping Obstacles of Replanted Zanthoxylum Bungeanum: A Preliminary Study. Plants 2025, 14, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Liu, X.; Ding, W.; Song, X.; Li, S.; Wu, X. Positive Effects of Crop Rotation on Soil Aggregation and Associated Organic Carbon Are Mainly Controlled by Climate and Initial Soil Carbon Content: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 355, 108600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zhou, D.; Wei, H.; Wu, S.; Xie, B. Alleviating Soil Degradation Caused by Watermelon Continuous Cropping Obstacle: Application of Urban Waste Compost. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, J.; Qi, G.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, H.; Feng, H.; Feng, Z. Applications of Chaetomium globosum CEF-082 Improve Soil Health and Mitigate the Continuous Cropping Obstacles for Gossypium hirsutum. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 197, 116586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Chen, Y.; Pei, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Application of Microbial Organic Fertilizers Promotes the Utilization of Nutrients and Restoration of Microbial Community Structure and Function in Rhizosphere Soils after Dazomet Fumigation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1122611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Rui, W.; Peng, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, W. Organic Carbon Fractions Affected by Long-Term Fertilization in a Subtropical Paddy Soil. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 86, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, M.; Yao, H.; Lv, L.; Shen, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; et al. Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer by Organic Fertilizer Benefits Grain Yield, Water Use Efficiency, and Economic Return of Summer Maize. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 217, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlisnikovský, L.; Kunzová, E. The Content of Topsoil Nutrients, Ph and Organic Carbon as Affected by Long-Term Application of Mineral and Organic Fertilisers. Agriculture 2014, 60, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Xu, D.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G. Advancing Sustainable Agriculture: Enhancing Crop Nutrition with next-Generation Nanotech-Based Fertilizers. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 13205–13225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Carrión, V.J.; Yin, S.; Yue, Z.; Liao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, X. Acidic Amelioration of Soil Amendments Improves Soil Health by Impacting Rhizosphere Microbial Assemblies. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 167, 108599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tao, R.; Ling, N.; Chu, G. Chemical, Organic and Bio-Fertilizer Management Practices Effect on Soil Physicochemical Property and Antagonistic Bacteria Abundance of a Cotton Field: Implications for Soil Biological Quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, H. Non-Destructive Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Distribution in Oilseed Rape Leaves by Laboratory Scale NIR Hyperspectral Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, U.-H.; Sohn, J.-Y. Cadmium-Induced Changes in Antioxidative Systems, Hydrogen Peroxide Content, and Lipid Peroxidation in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Biol. 2004, 47, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Lai, Z.; Lin, Y.; Lai, G.; Lian, C. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Superoxide Dismutase Gene Family in Musa acuminata Cv. Tianbaojiao (AAA Group). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gordo, S.; López-Jaramillo, J.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.; Taboada, J.; Palma, J.M.; Corpas, F.J. Pepper Catalase: A Broad Analysis of Its Modulation during Fruit Ripening and by Nitric Oxide. Biochem. J. 2024, 481, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riseh, R.S.; Fathi, F.; Vatankhah, M.; Kennedy, J.F. Catalase-Associated Immune Responses in Plant-Microbe Interactions: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, M.; Bhat, M.A.; Rashid, U.; Almanzalawi, E.A.; Alqahtani, T.M.; Mansoor, S.; Boo, K.-H. Enzymatic Activity Assays and Functional Component Profiling Reveals Coordinated Defense Response of Mungbean against Cercospora canescens during Leaf Spot Disease. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2024, 18, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ci, D.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xu, M.; He, K. Effect of Reducing Nitrogen Fertilization and Adding Organic Fertilizer on Net Photosynthetic Rate, Root Nodules and Yield in Peanut. Plants 2023, 12, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roni, N.G.K.; Lindawati, S.A. Productivity of Gamal (Gliricidia sepium) and Indigofera (Indigofera zollingeriana) Forage on Different Dosage of Bioorganic fertilizer. Pastura 2019, 8, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Arshad, M.; Khalid, A.; Zahir, Z.A. Effectiveness of Organic-/Bio-Fertilizer Supplemented with Chemical Fertilizers for Improving Soil Water Retention, Aggregate Stability, Growth and Nutrient Uptake of Maize (Zea mays L.). J. Sustain. Agric. 2008, 31, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-W.; Cai, H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Li, C.-L.; Wan, Y.-S.; Song, F.-P.; Chen, W.-F. Addition of Organic Fertilizer Affects Soil Nitrogen Availability in a Salinized Fluvo-Aquic Soil. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2019, 31, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; El-Sawah, A.M.; Ali, D.F.I.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y.; Shaghaleh, H.; Sheteiwy, M.S. The Integration of Bio and Organic Fertilizers Improve Plant Growth, Grain Yield, Quality and Metabolism of Hybrid Maize (Zea mays L.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Qiao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z. Impact of Bio-Organic Fertilizer Incorporation on Soil Nutrients, Enzymatic Activity, and Microbial Community in Wheat–Maize Rotation System. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; Fei, J.; Luo, G. Biochar Amendments Combined with Organic Fertilizer Improve Maize Productivity and Mitigate Nutrient Loss by Regulating the C–N–P Stoichiometry of Soil, Microbiome, and Enzymes. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, B. Effects of a Novel Bio-Organic Fertilizer on the Composition of Rhizobacterial Communities and Bacterial Wilt Outbreak in a Continuously Mono-Cropped Tomato Field. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cheng, K.; Huo, X.; Meng, P.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J. Bioorganic Fertilizer Promotes Pakchoi Growth and Shapes the Soil Microbial Structure. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1040437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Řezáčová, V. Organic Fertilization Improves Soil Aggregation through Increases in Abundance of Eubacteria and Products of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Han, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhang, Y. Soil Aggregates and Organic Carbon Affected by Bio-Fertilizer in Greenhouse Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2025, 56, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, P.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Baruah, K.K. Organic Substitution in Fertilizer Schedule: Impacts on Soil Health, Photosynthetic Efficiency, Yield and Assimilation in Wheat Grown in Alluvial Soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, S.; Fan, J.; Feng, H.; He, J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effect of Bio-Organic Fertilizer Derived from Agricultural Waste Resources on Soil Properties and Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Yield in Semi-Humid Drought-Prone Regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Li, P.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.; Meng, Q. Applying Bio-Organic Fertilizer Improved Saline Alkaline Soil Properties and Cotton Yield in Xinjiang. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zeng, Z. Dynamics of Bacterial Communities in a 30-Year Fertilized Paddy Field under Different Organic–Inorganic Fertilization Strategies. Agronomy 2019, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pei, H.; Xie, H. Synergistic Effects of Organic Fertilizer and Corn Straw on Microorganisms of Pepper Continuous Cropping Soil in China. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, C.; Li, R.; Xiong, W.; Shen, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Ruan, Y.; Geisen, S.; Shen, Q.; Kowalchuk, G.A. Bio-Organic Fertilizers Stimulate Indigenous Soil Pseudomonas Populations to Enhance Plant Disease Suppression. Microbiome 2020, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Yang, S.; Xia, F. Bioorganic Fertilizer Can Improve Potato Yield by Replacing Fertilizer with Isonitrogenous Content to Improve Microbial Community Composition. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Hu, J.; Ran, W.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q. Control of Cotton Verticillium Wilt and Fungal Diversity of Rhizosphere Soils by Bio-Organic Fertilizer. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Yin, S.; Shen, Q.; Ran, W.; Xu, Y. Efficacy of Bacillus-Fortified Organic Fertiliser in Controlling Bacterial Wilt of Tomato in the Field. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 48, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, K.; Shi, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Shen, Q.; Shen, B. Evaluation of Bacillus-Fortified Organic Fertilizer for Controlling Tobacco Bacterial Wilt in Greenhouse and Field Experiments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 75, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, F.; E, Y.; Yuan, J.; Raza, W.; Huang, Q.; Shen, Q. Long-Term Application of Bioorganic Fertilizers Improved Soil Biochemical Properties and Microbial Communities of an Apple Orchard Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Fang, Z.; Wang, L.; Yuan, S.; Guo, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q. Biological Potential of Bioorganic Fertilizer Fortified with Bacterial Antagonist for the Control of Tomato Bacterial Wilt and the Promotion of Crop Yields. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, D.; Fang, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, J. The Structure and Function of Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities: Impact of Chemical vs. Bio-Organic Fertilizers on Root Disease, Quality, and Yield of Codonopsis pilosula. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1484727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, F. Bacillus Bio-Organic Fertilizer Altered Soil Microorganisms and Improved Yield and Quality of Radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Plants 2025, 14, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H. Organic Substitution Contrasting Direct Fertilizer Reduction Increases Wheat Productivity, Soil Quality, Microbial Diversity and Network Complexity. Environ. Technol. 2024, 36, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, Z.; He, C.; Ullah, J.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, Y. Mitigating Soil Degradation in Continuous Cropping Banana Fields through Long-Term Organic Fertilization: Insights from Soil Acidification, Ammonia Oxidation, and Microbial Communities. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 213, 118385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Lee, S.-W. Bioprospecting Potential of the Soil Metagenome: Novel Enzymes and Bioactivities. Genom. Inform 2013, 11, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrold, D.D.; Zeglin, L.H.; Jansson, J.K. The Potential of Metagenomic Approaches for Understanding Soil Microbial Processes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W. Changes in Microbial Diversity, Soil Function, and Plant Biomass of Cotton Rhizosphere Soil Under the Influence of Chlorpyrifos. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, L.; Han, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, W.; Gao, H.; Huang, H.; et al. Majorbio Cloud 2024: Update Single-Cell and Multiomics Workflows. Imeta 2024, 3, e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Jin, Y.; Li, S.; Qu, J.; Zhu, Y. Organic Materials Promote Soil Phosphorus Cycling: Metagenomic Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhou, L.; Huang, X.; You, X.; Lin, J.; Han, H.; Huang, X. Effects of Salt Field Waste-Generated Bio-Organic Fertilizer Application on Bacterial Community Structure in Tea Plantations Rhizosphere Soil. Agronomy 2024, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Yu, H.-J.; Zhang, B.; Guan, Y.-Q.; Zhang, N.; Du, H.-L.; Liu, F.-M.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.-J.; Liu, J. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Replacement on the Microbial Community Structure in the Rhizosphere Soil of Soybeans in Albic Soil. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Nguyen, L.T.; Vu, H.T.T.; Phan, N.T.H.; Suralta, R.R. Inorganic-Microbial Organic Fertilizer Synergy: Improving Quinoa Yield and Seed Quality through Soil and Nutrient Modulation. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 71, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil Organic Matter Priming: The pH Effects. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, Y.; Tu, X.; Chen, Z.; Elrys, A.S.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, L. A Shift from Nitrification to Denitrification-Dominated N2O Emission in an Acidic Soil Following Organic Amendment. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Wang, P.; Guo, L.; Li, M.; Cui, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. The Remediation Effects of Microbial Organic Fertilizer on Soil Microorganisms after Chloropicrin Fumigation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Dai, K. Functional Organic Fertilizers Can Alleviate Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Continuous Cropping Obstacle via Ameliorating Soil Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community Structure. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1023693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Su, Y.-Z.; Wang, T.; Yang, Q. Effect of Chemical and Organic Fertilization on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Accumulation in a Newly Cultivated Farmland. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gu, H.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Metagenomic Strategies Uncover the Soil Bioavailable Phosphorus Improved by Organic Fertilization in Mollisols. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 349, 108462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X. Enhancing Soil Health through Balanced Fertilization: A Pathway to Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1536524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ran, W.; Hu, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q. Application of Bio-Organic Fertilizer Significantly Affected Fungal Diversity of Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Li, J.; Zhao, X. Effects of biological organic fertilizer on rhisosphere soil bacteria community and root rot diseases of continuous cropping Angelica sinensis. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2019, 30, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A.V.; Pereira e Silva, M.C.; Szturc-Koestsier, A.E.; Schmitt, H.; Falcão Salles, J.; van Elsas, J.D. Impact of Incorporated Fresh 13C Potato Tissues on the Bacterial and Fungal Community Composition of Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 49, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, A.; Campbell, C.D.; Fitter, A.H. An Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus Accelerates Decomposition and Acquires Nitrogen Directly from Organic Material. Nature 2001, 413, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimuthu, S.; Karthic, C.; Mostafa, A.A.; Mohammed Al-Enazi, N.; Abdel-Raouf, N.; Nageh Sholkamy, E. Antifungal Activity of Streptomyces sp. SLR03 against Tea Fungal Plant Pathogen Pestalotiopsis theae. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2020, 32, 3258–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Tan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, P.; Tan, J.; Ai, S.; Liang, X.; et al. A Unique Role of the Pyrimidine de Novo Synthesis Enzyme ODCase in Lysobacter enzymogenes. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 3066–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Subhan, F.; Haleem, K.; Khattak, M.; Khan, I.; Sultan, T.; Tauseef, I. Impact of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria on Yield and Disease Control of Nicotiana Tabacum. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2018, 70, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M.A.; Durán, P.; Hacquard, S. Microbial Interactions within the Plant Holobiont. Microbiome 2018, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, F.T.; Griffiths, R.I.; Bailey, M.; Craig, H.; Girlanda, M.; Gweon, H.S.; Hallin, S.; Kaisermann, A.; Keith, A.M.; Kretzschmar, M.; et al. Soil Bacterial Networks Are Less Stable under Drought than Fungal Networks. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, D.; Zhou, R.; Hao, F.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, P. Effect of Wheat Straw Addition on Organic Carbon Mineralisation and Bacterial Community in Orchard Soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4328–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; García-Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Brandón, M. Studying Microbial Communities through Co-Occurrence Network Analyses during Processes of Waste Treatment and in Organically Amended Soils: A Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial Interactions: From Networks to Models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhai, C.; Shi, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Gu, S. Dose-Dependent Effect of Compost Amendment on Soil Bacterial Community Composition and Co-Occurrence Network Patterns in Soybean Agroecosystem. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Maron, P.A.; Chemidlin-Prevost Boure, N.; Bernard, N.; Gilbert, D.; Ranjard, L. Microbial Diversity and Ecological Networks as Indicators of Environmental Quality. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.; Shen, Q.; Ling, N. DNA Stable-Isotope Probing Delineates Carbon Flows from Rice Residues into Soil Microbial Communities Depending on Fertilization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02151-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Tedersoo, L.; Crowther, T.W.; Dumbrell, A.J.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Bahram, M.; Kuang, L.; Li, T.; Wu, M.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Fossil-Fuel-Dependent Scenarios Could Lead to a Significant Decline of Global Plant-Beneficial Bacteria Abundance in Soils by 2100. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Burrill, H.M.; Podzikowski, L.Y.; Eppinga, M.B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Schultz, P.A.; Bever, J.D. Dilution of Specialist Pathogens Drives Productivity Benefits from Diversity in Plant Mixtures. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoala, T.; El-Garhy, H.A.S.; Messiha, N.A.S.; El-Abeid, S.E. The Efficacy of Nanoparticles on Soil Microbial Biodiversity and the Prevention of Fusarium Wilt Disease (Fusarium oxysporum f.Sp. lycopersici). BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trong, N.D.; Trang, T.T.T.; Quang, L.T.; Oanh, T.O.; Nguyen, P.C.; Nhan, T.C.; Xuan, L.N.T.; Xuan, D.T.; Khuong, N.Q. Effects of Rhodopseudomonas palustris and Rhodopseudomonas pentothenatexigens on Reducing Chemical NPK Fertilizer Used for Rice in Acid Sulfate Soil under Field Conditions. Paddy Water Environ. 2025, 23, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, L.; Raza, A.; Zhao, C.; Pang, X.; Zhang, J.; Müller, C.; Yin, C. Organic Fertilizer and Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens Promote Soil N Availability via Changing Different Mineralization–Immobilization Turnover Rates in Acidic Soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 366, 108950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Treatment | pH | SOM | AN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | |||||
| 2023 | CK | 8.10 ± 0.01 a | 9.99 ± 1.27 a | 49.55 ± 2.61 a | 14.33 ± 2.51 a | 267.00 ± 18.29 a |
| BOF | 8.22 ± 0.11 a | 11.76 ± 1.32 a | 49.18 ± 5.78 a | 16.55 ± 0.53 a | 300.60 ± 20.78 a | |
| 2024 | CK | 8.08 ± 0.04 a | 11.54 ± 0.27 b | 40.89 ± 0.45 b | 18.81 ± 2.16 b | 381.78 ± 2.96 b |
| BOF | 8.15 ± 0.04 a | 12.93 ± 0.38 a | 49.90 ± 0.85 a | 25.66 ± 0.51 a | 401.91 ± 9.96 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, M.; He, H.; Cheng, L.; Li, S.; Wan, T.; Qin, J.; Li, J. Bio-Organic Fertilizers Enhance Yield in Continuous Cotton Cropping Systems Through Rhizosphere Microbiota Modulation and Soil Nutrient Improvement. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092238
Yu M, He H, Cheng L, Li S, Wan T, Qin J, Li J. Bio-Organic Fertilizers Enhance Yield in Continuous Cotton Cropping Systems Through Rhizosphere Microbiota Modulation and Soil Nutrient Improvement. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092238
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Mengmeng, Hao He, Liyang Cheng, Shuai Li, Tingting Wan, Jie Qin, and Junhua Li. 2025. "Bio-Organic Fertilizers Enhance Yield in Continuous Cotton Cropping Systems Through Rhizosphere Microbiota Modulation and Soil Nutrient Improvement" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092238
APA StyleYu, M., He, H., Cheng, L., Li, S., Wan, T., Qin, J., & Li, J. (2025). Bio-Organic Fertilizers Enhance Yield in Continuous Cotton Cropping Systems Through Rhizosphere Microbiota Modulation and Soil Nutrient Improvement. Agronomy, 15(9), 2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092238





