Phytolith Concentration and Morphological Variation in Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz. Leaves in Response to Sodium Silicate Foliar Application Across Vegetative Phenological Stages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Determination of Phytolith Concentration
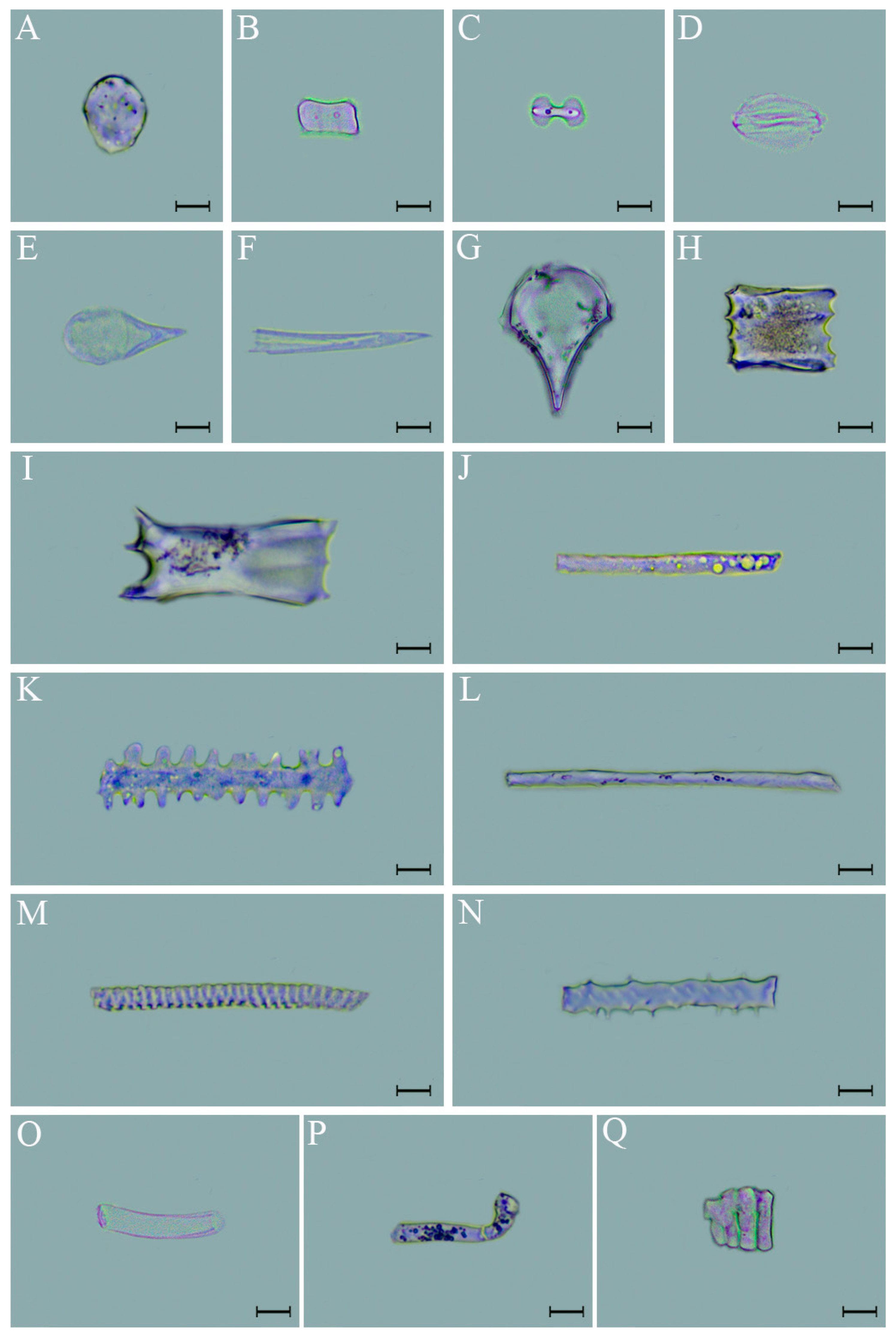
2.2.2. Phytolith Classification
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phytolith Concentration in D. brandisii Leaves at Different Phenological Stages
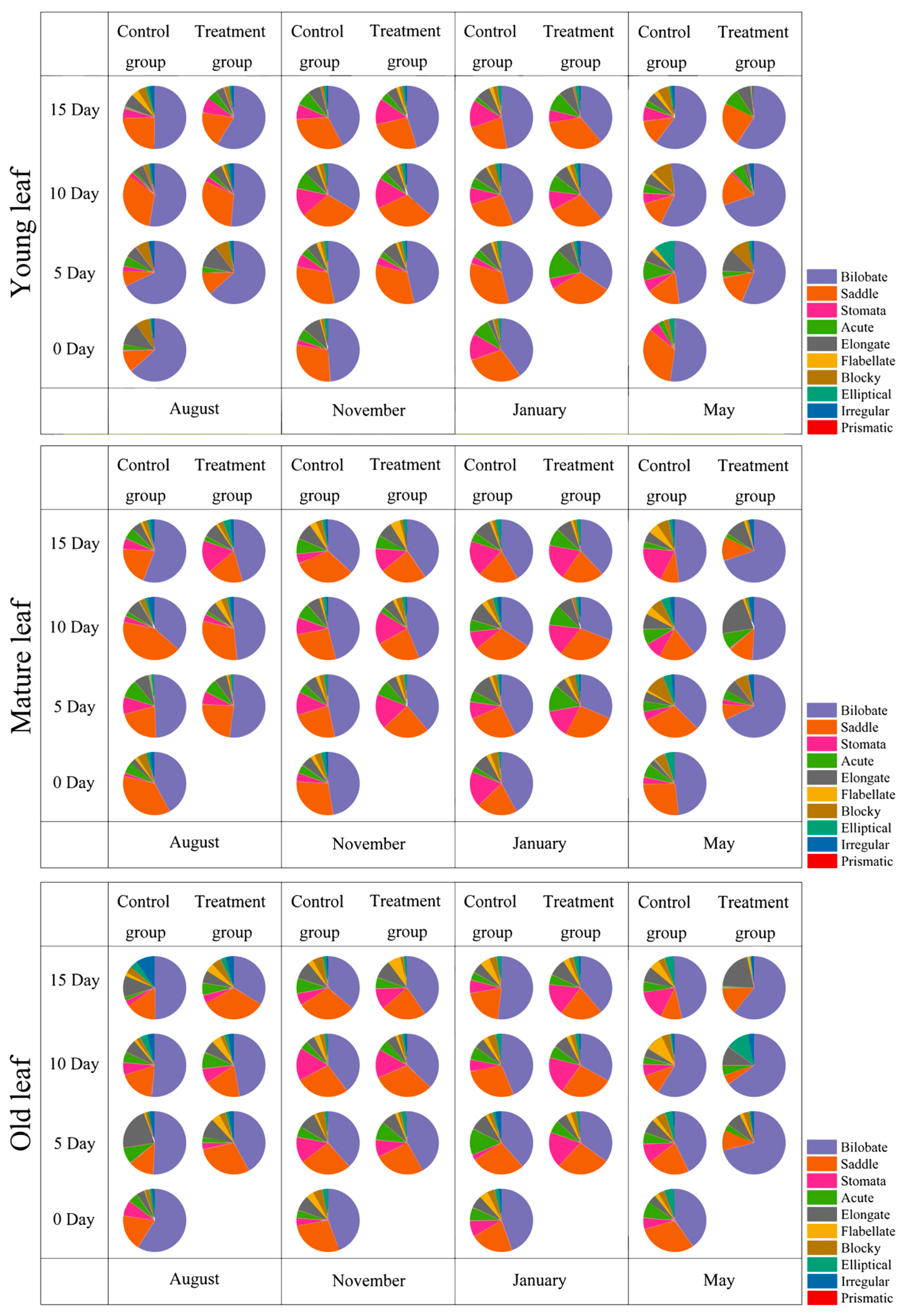
3.2. Phytolith Morphotypes and Variation in D. brandisii Leaves Under Treatment at Different Phenological Stages
3.3. Phytolith Size in D. brandisii Leaves Under Treatment at Different Phenological Stages
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of SS on Phytolith Concentration in D. brandisii Leaves at Different Phenological Stages
4.2. Effect of SS on Phytolith Morphology in D. brandisii Leaves at Different Phenological Stages
4.3. The Physiological and Ecological Significance of the Effects of SS on the Differences in Phytoliths in D. brandisii Leaves at Different Phenological Stages
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, X.; Xie, B. Phytoliths from woody plants: A review. Diversity 2022, 14, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, H. Phytolith Study and Its Application; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N. Functions and transport of silicon in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3049–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Takahashi, E. Effect of silicon on the growth of solution cultured cucumber plant. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1983, 29, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, F.P.; Hartley, S.E. Physical defences wear you down: Progressive and irreversible impacts of silica on insect herbivores. J. Anim. Ecol. 2009, 78, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Yamauchi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Ishigure, T.; Oaki, Y.; Imai, H. Optical properties of biosilicas in rice plants. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 109168–109173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandlik, R.; Thakral, V.; Raturi, G.; Shinde, S.; Nikolić, M.; Tripathi, D.K.; Sonah, H.; Deshmukh, R. Significance of silicon uptake, transport, and deposition in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 6703–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, H. The Study of Phytolith and Its Application; Haiyang Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, M.; Liu, K.; Yan, D. Effects of foliar fertilization: A review of current status and future perspectives. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laane, H.M. The effects of foliar sprays with different silicon compounds. Plants 2018, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayade, R.; Ghimire, A.; Khan, W.; Lay, L.; Attipoe, J.Q.; Kim, Y. Silicon as a smart fertilizer for sustainability and crop improvement. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, S.M.M.; de Mello Prado, R.; de Souza Júnior, J.P.; Teixeira, G.C.M.; dos Santos Duarte, J.C.; de Medeiros, R.L.S. Silicon supplied via foliar application and root to attenuate potassium deficiency in common bean plants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, Q.U.; Rashid, M.; Nawaz, R.; Hussain, A.; Ashraf, K.; Latif, M.; Heile, A.O.; Mehmood, F.; Salahuddin, S.; Chen, Y. Silicon fertilization: A step towards cadmium-free fragrant rice. Plants 2021, 10, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.H.; Milne, A.A.; Sanders, J.V. Tabashir: An opal of plant origin. Science 1966, 151, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Li, J.; Niu, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, S. Silicon variation and phytolith morphology in different organs of Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz (Bambusoideae). Braz. J. Bot. 2019, 42, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yan, H.; Zheng, M.; Liu, H.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, Y. Phytolith records from 15 continuously growing Bambusa emeiensis leaves and its climatic significance. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2022, 300, 104620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, O. Silica phytoliths in angiosperms: Phylogeny and early evolutionary history. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, S.P.; Monteiro, F.A.; De Bona, F.D. Silicon distribution and accumulation in shoot tissue of the tropical forage grass Brachiaria brizantha. Plant Soil. 2010, 336, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Honaine, M.; Osterrieth, M.L. Silicification of the adaxial epidermis of leaves of a panicoid grass in relation to leaf position and section and environmental conditions. Plant Biol. 2012, 14, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motomura, H.; Fujii, T.; Suzuki, M. Silica deposition in relation to ageing of leaf tissues in Sasa veitchii (Carriere) Rehder (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). Ann. Bot. 2004, 93, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Fan, J.; Carter, J.; Jiang, N.; Gu, Y. Monthly variations of phytoliths in the leaves of the bamboo Dendrocalamus ronganensis (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2017, 246, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Niu, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhan, H. Variation of the phytolith content and morphology of Dendrocalamus giganteus at different phenological periods. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2022, 42, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Xia, N.; Jia, L.; Guo, Z.; Yang, G.; Stapleton, C. Bambuseae. In Flora of China; Wu, Z., Raven, P., Hong, D., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Chang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Zhan, H. Foliar application of sodium gluconate enhances photosynthetic efficiency and photoassimilate accumulation in Dendrocalamus brandisii across vegetative phenological stages. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 230, 121030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Tang, N.; Deng, J.; Liu, C.; Kan, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z.; Liu, Y. Sequential extraction, structural characterization, and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Dendrocalamus brandisii bamboo shoot shell. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ding, Y.; Ranaei, F.; Ahmad, Z. Application of bamboo plants in nine aspects. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 7284203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, M.; Takenaka, C. Biological cycle of silicon in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) forests in central Japan. Ecol. Res. 2014, 29, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, D.C. Vegetative phenology and growth of a facultatively deciduous bamboo in a monsoonal climate. Biotropica 2005, 37, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhan, H.; Niu, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, S. Effects of exogenous silicon on silicon, chlorophyll, and soluble sugar contents in seedling leaf blades of Dendrocalamus brandisii. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. 2016, 45, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, J.F.; Dolic, V.; Lancaster, G.; Boyd, W.E. A microwave digestion method for the extraction of phytoliths from herbarium specimens. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2001, 116, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearsall, D.M. Paleoethnobotany: A Handbook of Procedures, 3rd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Madella, M.; Alexandre, A.; Ball, T. International code for phytolith nomenclature 1.0. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, K.; Stromberg, C.; Ball, T.; Albert, R.; Vrydaghs, L.; Cummings, L.S. International code for phytolith nomenclature (ICPN) 2.0. Ann. Bot. 2019, 124, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.; Li, K.T.; Tsang, C.H. Silicified bulliform cells of Poaceae: Morphological characteristics that distinguish subfamilies. Bot. Stud. 2020, 61, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, M.J.; White, P.J.; Mead, A.; Broadley, M.R. Phylogenetic variation in the silicon composition of plants. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chang, S.; Huang, C.; Yu, X.; Zhi, Y.; Jiang, P. Controls for phytolith accumulation in Moso bamboo leaves across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ni, Y.; Li, Z.; Yue, K.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Song, Z. Silicon in paddy fields: Benefits for rice production and the potential of rice phytoliths for biogeochemical carbon sequestration. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotmuenwai, N.; Aryuyo, K.; Kruethaworn, N.; Wattananit, W.; Yookongkaew, N. Exploring silica accumulation in bamboo leaves: A study on phytolith morphology and epidermal patterning in the tropical giant bamboo Dendrocalamus copelandii. Ann. Bot. 2025, 135, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Xu, R.; Yu, L.; Zhu, F.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhan, H. Silicon uptake and phytolith morphology in Dendrocalamus brandisii seedling leaf from different rearing methods. Forests 2023, 14, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, X.; Wen, M.; Vachula, R.; Tan, S.; Dong, H.; Zhou, L.; Gu, Z.; Xu, M. Phytolith-occluded carbon in leaves of Dendrocalamus ronganensis influenced by drought during growing season. Physiol. Plant. 2022, 174, e13748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matichenkov, V.; Bocharnikova, E. The relationship between silicon and soil physical and chemical properties. Stud. Plant Sci. 2001, 8, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg, C.A.; Di Stilio, V.S.; Song, Z. Functions of phytoliths in vascular plants: An evolutionary perspective. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Li, R.; Yu, J. Phytoliths as a method of identification for three genera of woody bamboos (Bambusoideae) in tropical southwest China. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2016, 68, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Pearsall, D.M. Phytolith morphology research on wild and domesticated rice species in East Asia. Quat. Int. 2013, 287, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tan, S.; Qin, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, G.; Liu, P. Study on the phytolith variation in maize during its growing season. Acta Micropalaeontol. Sin. 2016, 33, 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jie, D.; Liu, L.; Guo, M.; Li, N. Change characters of Phragmites australis phytolith in Northeast China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2013, 37, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gélin, U.; Spicer, R.A.; Wu, F.; Farnsworth, A.; Chen, P.; Rio, C.D.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; et al. Rapid Eocene diversification of spiny plants in subtropical woodlands of central Tibet. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Xie, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, G.; Yuan, F.; Lü, H. Effect of artificial fertilization on morphological development of rice bulliform phytoliths and its significance. Quat. Sci. 2022, 42, 1792–1805. [Google Scholar]
- Piperno, D.R. Phytoliths: A comprehensive guide for archaeologists and paleoecologists. Rowman Altamira: Lanham, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Elbaum, R. Interplay between silica deposition and viability during the life span of sorghum silica cells. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tombeur, F.; Raven, J.A.; Toussaint, A.; Lambers, H.; Cooke, J.; Hartley, S.E.; Johnson, S.N.; Coq, S.; Katz, O.; Schaller, O.; et al. Why do plants silicify? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2023, 38, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Lu, H.; Cao, Z.; Xie, J. Morphological characteristics of homozygous wild rice phytoliths and their significance in the study of rice origins. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Matsui, A.; Udatsu, T.; Fujiwara, H. Molecular genetic basis of determining subspecies of ancient rice using the shape of phytoliths. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2023, 30, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Mao, L.; Ge, Y. Bulliform phytolith size of rice and its correlation with hydrothermal environment: A preliminary morphological study on species in Southern China. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.T.; Mori, R.; Soga, K.; Wakabayashi, K.; Kamisaka, S.; Fujii, S.; Yamamoto, R.; Hoson, T. Growth promotion and an increase in cell wall extensibility by silicon in rice and some other Poaceae seedlings. J. Plant Res. 2002, 115, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, M.; Chen, D.; Qin, S.; Jiang, S. The silicification of young tissues of rice and relationship with its resistance to blast of rice. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. 1999, 4, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, K.; Gao, D.; Luo, S.; Zeng, R.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X. Physiological and cytological mechanisms of silicon-induced resistance in rice against blast disease. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 134, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayasaka, T.; Fujii, H.; Ishiguro, K. The role of silicon in preventing appressorial penetration by the rice blast fungus. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gong, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z.; Xu, K.; Li, D.; Hua, Z.; Sha, A.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Progress in research on pat terns and systematic theories of super-high-yielding cultivation in rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2010, 24, 417–424. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Zhan, X.; Cheng, S.; Cao, L. Progress on mapping and cloning genes for leaf architecture in rice (Oryza sativa. L). J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2013, 27, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Ranganathan, S.; Suvarchala, V.; Rajesh, Y.B.R.D.; Prasad, M.S.; Padmakumari, A.P.; Voleti, S.R. Effects of silicon sources on its deposition, chlorophyll content, and disease and pest resistance in rice. Biol. Plant. 2006, 50, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, N.; Sakurai, G.; Mitani-Ueno, N.; Ma, J.F. Orchestration of three transporters and distinct vascular structures in node for intervascular transfer of silicon in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11401–11406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| August | November | January | May | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average high temperature (°C) | 25 | 18 | 14 | 24 |
| Average low temperature (°C) | 16 | 9 | 4 | 15 |
| Average temperature (°C) | 20 | 15 | 10 | 17 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 235.7 | 37.3 | 37.2 | 131.4 |
| Average humidity (%) | 78.3 | 72 | 51.7 | 69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Yu, L.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhan, H. Phytolith Concentration and Morphological Variation in Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz. Leaves in Response to Sodium Silicate Foliar Application Across Vegetative Phenological Stages. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092138
Yang Y, Huang L, Yu L, Li M, Wang S, Wang C, Zhan H. Phytolith Concentration and Morphological Variation in Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz. Leaves in Response to Sodium Silicate Foliar Application Across Vegetative Phenological Stages. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092138
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuntao, Lei Huang, Lixia Yu, Maobiao Li, Shuguang Wang, Changming Wang, and Hui Zhan. 2025. "Phytolith Concentration and Morphological Variation in Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz. Leaves in Response to Sodium Silicate Foliar Application Across Vegetative Phenological Stages" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092138
APA StyleYang, Y., Huang, L., Yu, L., Li, M., Wang, S., Wang, C., & Zhan, H. (2025). Phytolith Concentration and Morphological Variation in Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz. Leaves in Response to Sodium Silicate Foliar Application Across Vegetative Phenological Stages. Agronomy, 15(9), 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092138






