Effects of Sanqi Cultivation on Soil Fertility and Heavy Metal Content in the Sanqi–Pine Agroforestry System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Location
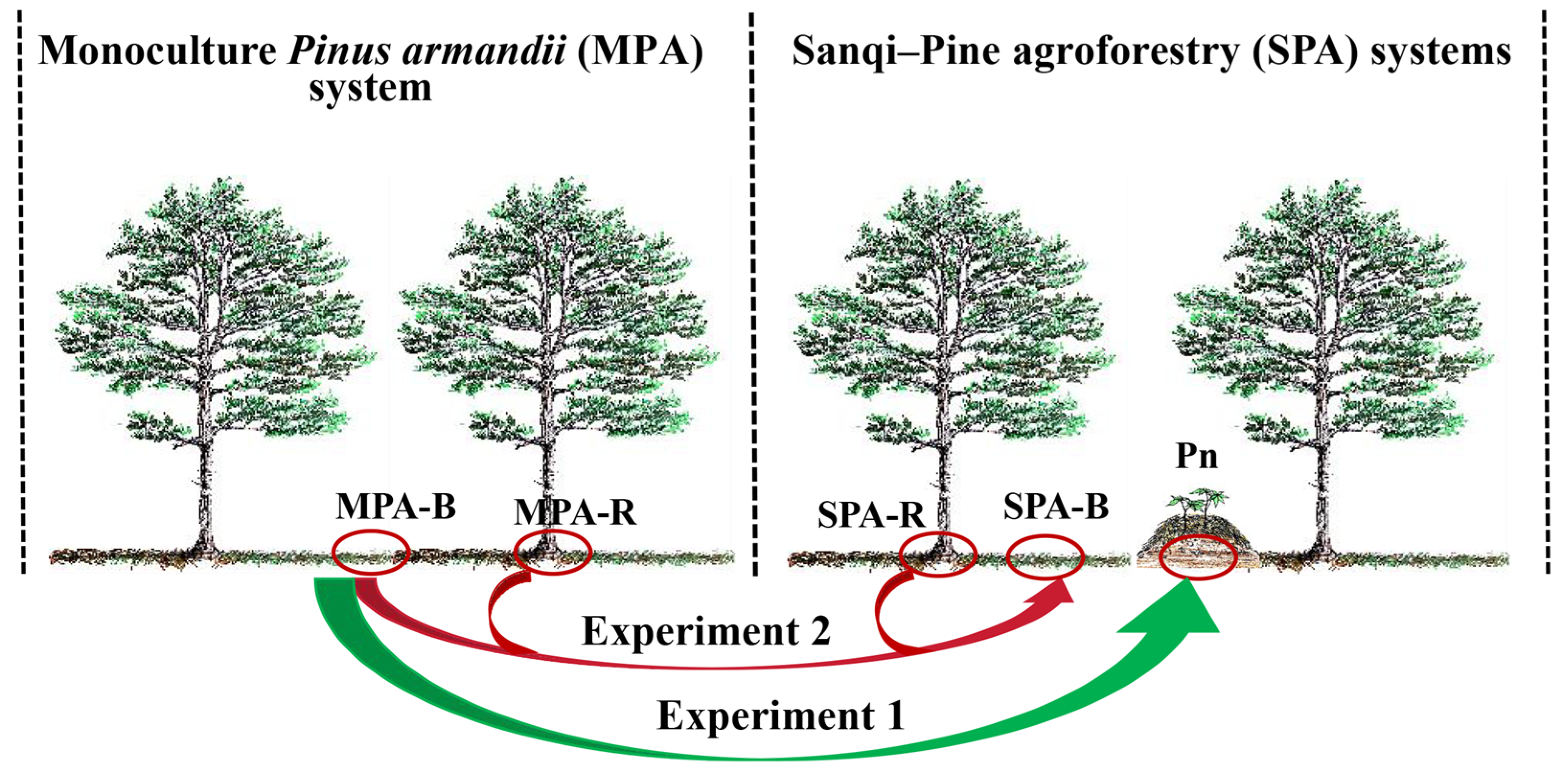
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
2.3. Determination of Soil Properties
2.4. TOPSIS Analysis of Soil Fertility and Heavy Metals
- ①
- Entropy method weighting analysis.
- (a)
- Data standardization:
- (b)
- Calculate the weight of the i sample data under the j indicator for that indicator :
- (c)
- Taking as the entropy value of the j indicator:
- (d)
- Weighting of the Indicator Wj:
- ②
- Comprehensive analysis by improved TOPSIS method.
- (a)
- Normalize the original matrix R = ()m×n to obtain a normalized decision matrix Z = {}:
- (b)
- Obtain the weighted decision evaluation matrix X = ():
- (c)
- Determine the positive and negative ideal solutions for each indicator:
- (d)
- Distances to positive and negative ideal solutions were calculated for each indicator.
- (e)
- Calculation of relative proximity:
2.5. Evaluation of the Contaminated Levels of Heavy Metals
2.6. Sensitivity Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
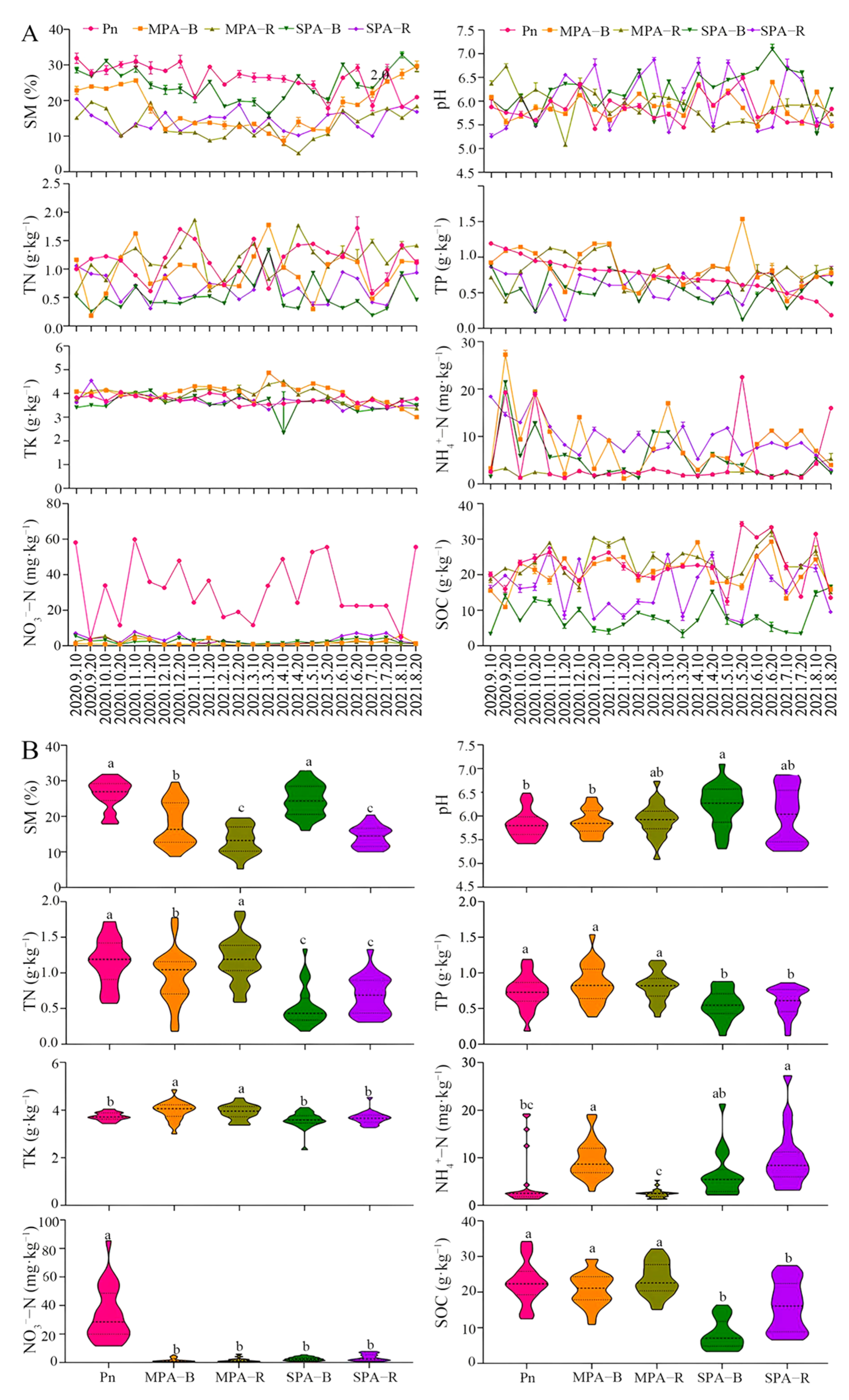
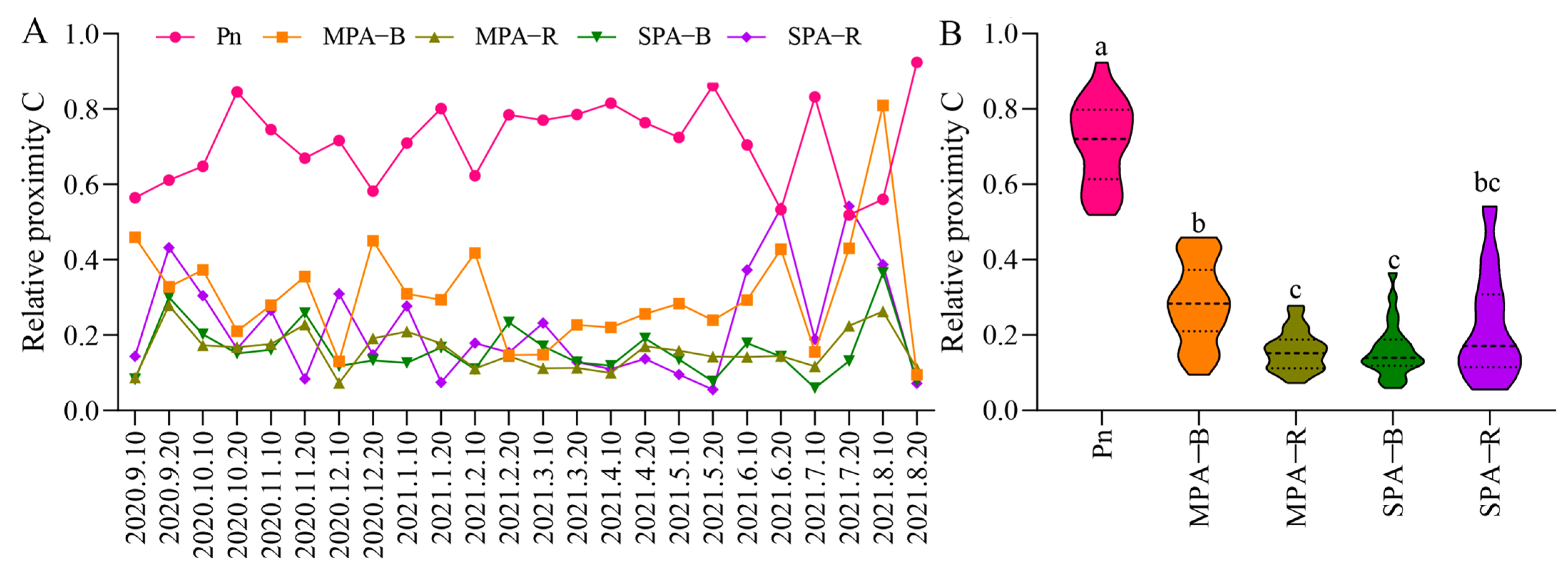
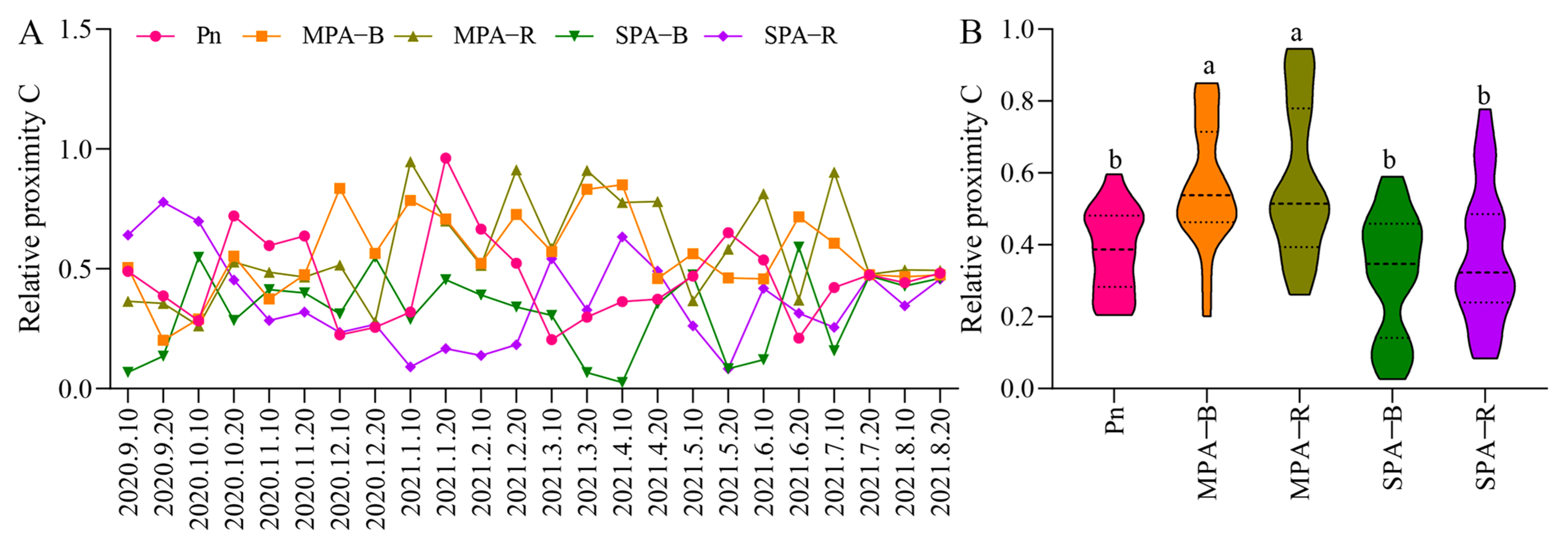
3.1. Variation Characteristics of Edaphic Factors and Evaluation of Soil Fertility in MPA and SPA Systems
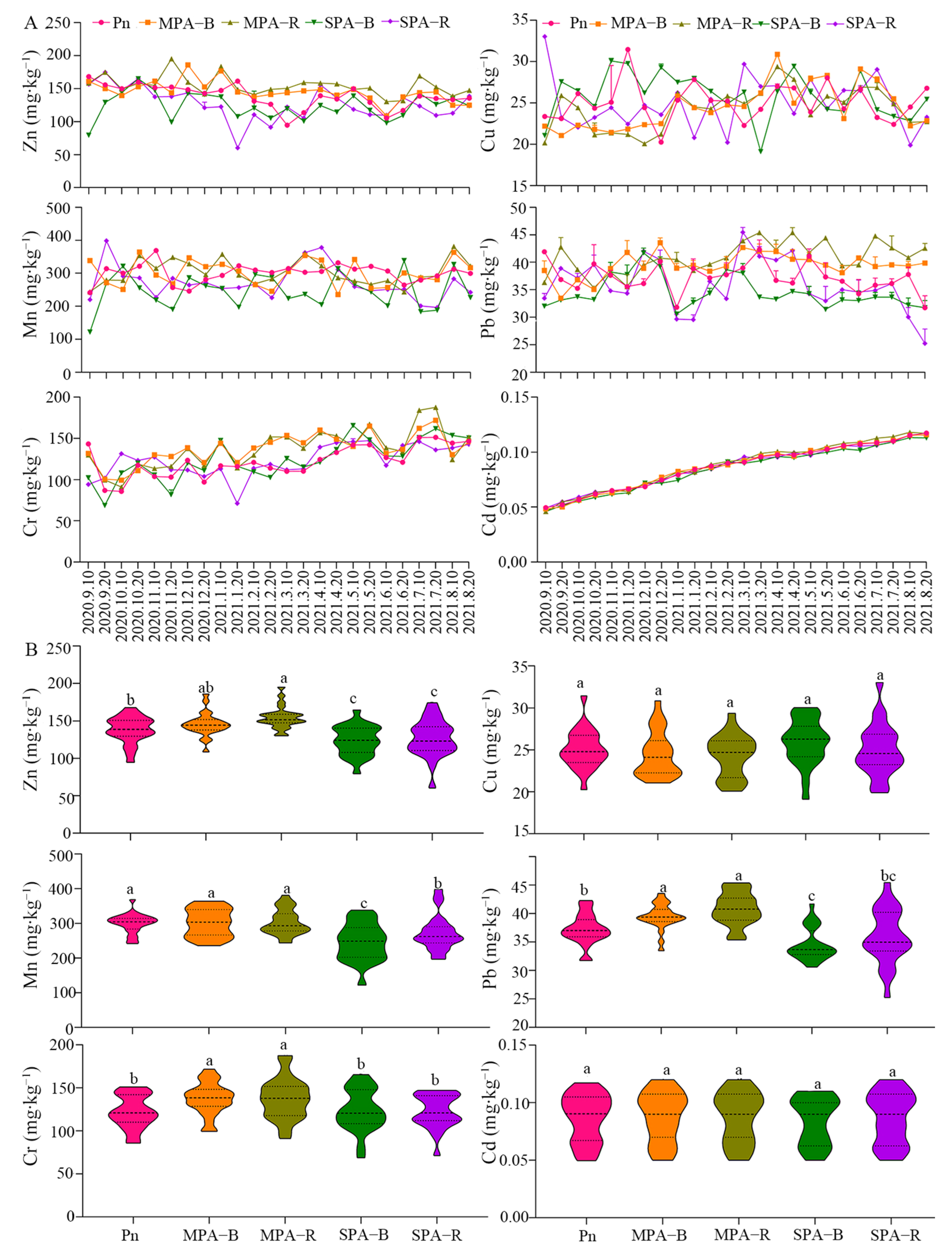
3.2. Analysis of Soils Heavy Metal Variation Characteristics and Pollution in MPA and SPA System
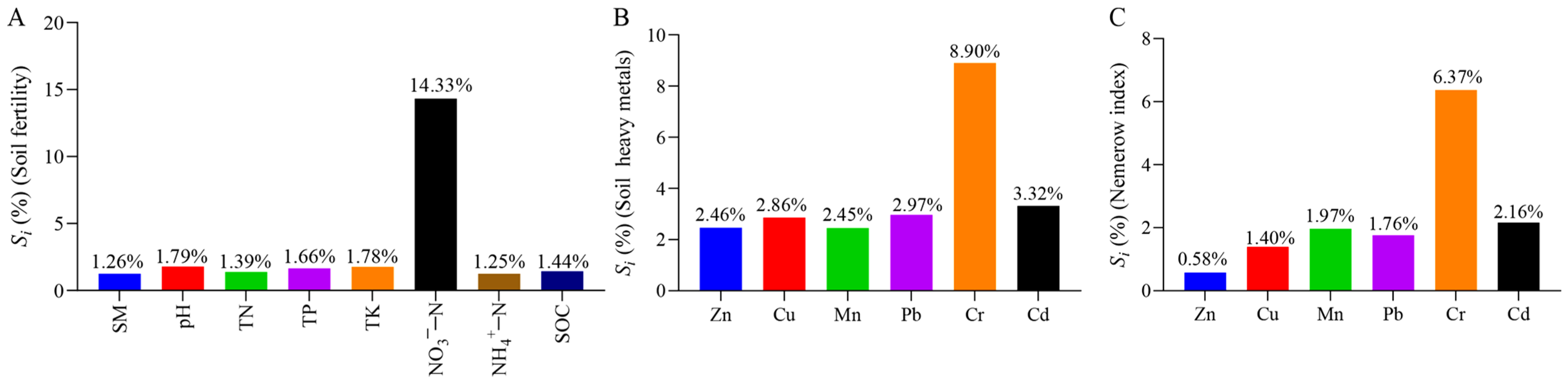
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis in the TOPSIS and Nemerow Index
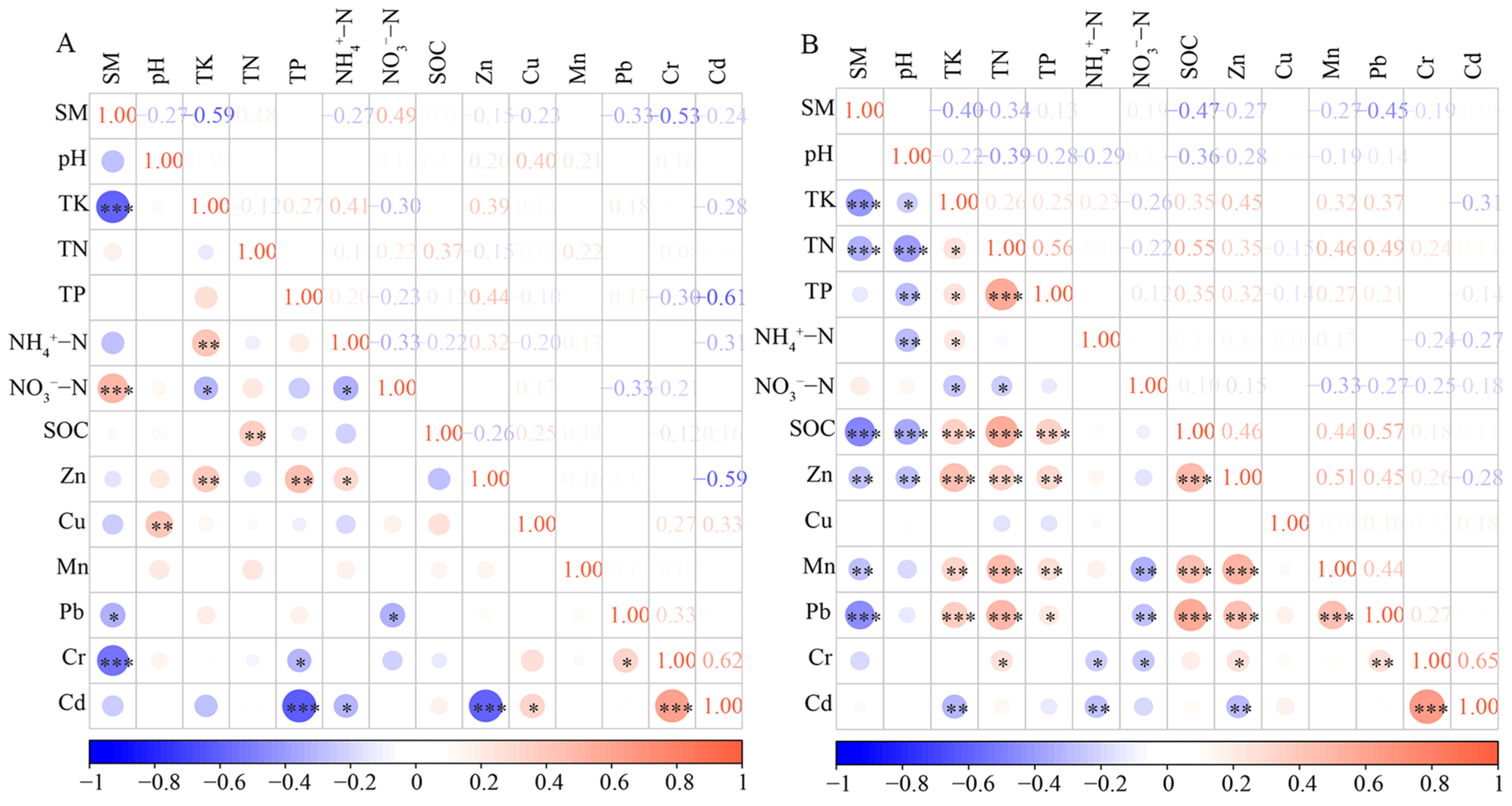
3.4. Analysis of the Correlation Between Physicochemical Properties and Heavy Metals in the Soils of Sanqi and P. armandi
4. Discussion
4.1. The Land Use from the MPA to the SPA System Enhanced the Soil Fertility for Sanqi Rather than P. armandi
4.2. Land Use Conversion of the MPA to the SPA System Reduced Heavy Metal Content in the Soil of Sanqi and P. armandi
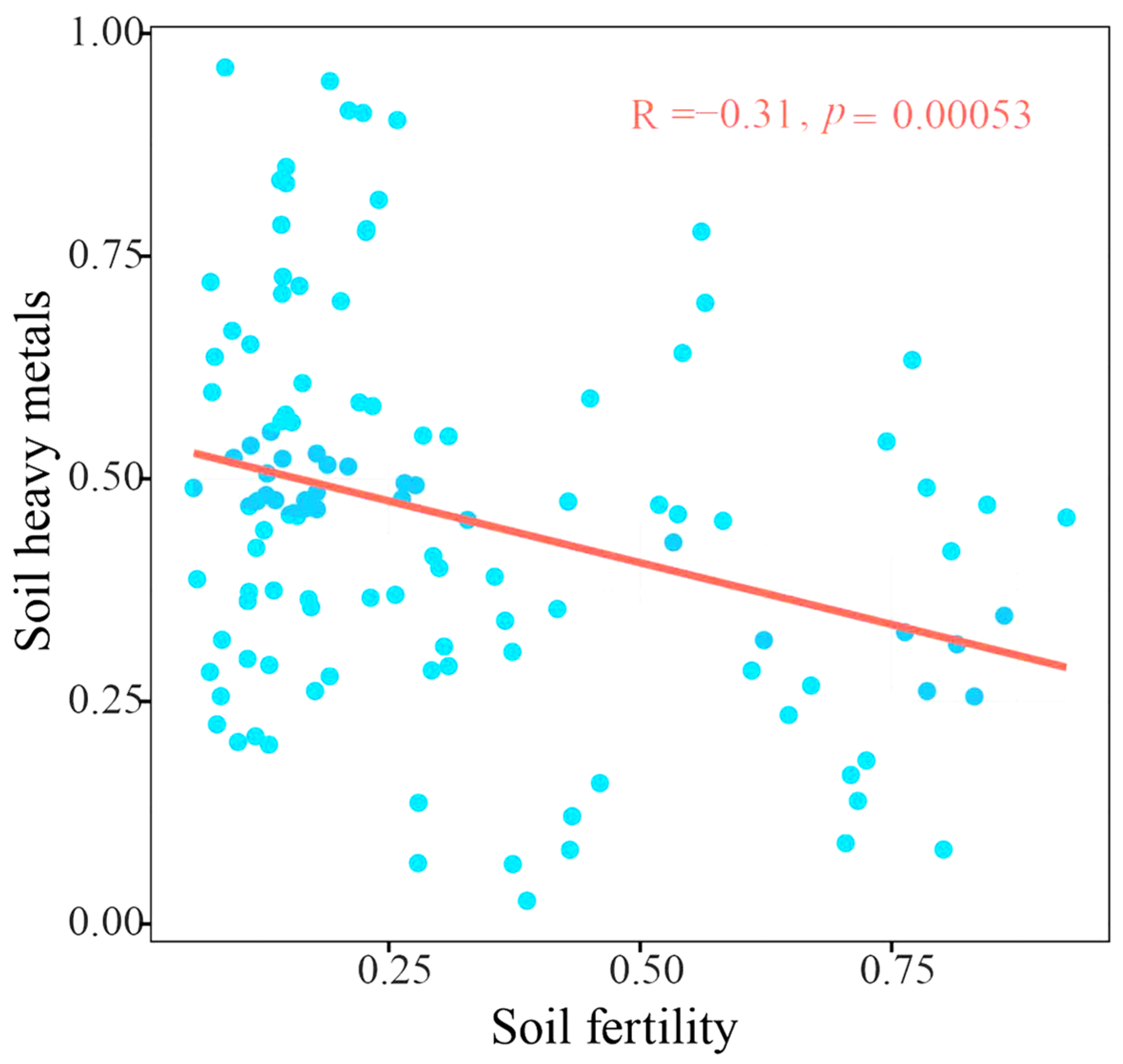
4.3. The Relationship Between Soil Fertility and Heavy Metal Content in the Soil of Sanqi and P. armandi
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.X.; Bai, Y.F.; Han, X.G. Application of N: P Stoichiometry to Ecology Studies. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2003, 45, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.B.; Luo, Z.X.; Huang, J.Y.; Liu, X.; He, H.Y.; Gong, Y.; Chen, M.; Wen, Y.B.; Ying, R.R. Geochemical behaviors of heavy metal(loid)s in soil ferromanganese nodules in Typical Karst Areas in Southwest China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.R.; Huang, L.K.; Wen, Z.Y.; Fu, Y.Y.; Liu, Q.Z.; Xu, S.N.; Li, Z.S.; Liu, C.J.; Yu, C.; Feng, Y. Effects of intercropping on safe agricultural production and phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.H.; Huang, X.J.; Su, X.M.; Bao, Y.Y. Responses of microbial communities and metabolic profiles to the rhizosphere of Tamarix ramosissima in soils contaminated by multiple heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wen, S.Z. Seasonal variation in content of heavy metal elements among forest litters and soil layers of Liquidambar formosana plantation. Hunan For. Sci. Technol. 2016, 43, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhar, M.; Lallawmkimi, M.C.; Rani, D.V.; Upadhyay, L.; Tiwari, P.; Verma, U.; Rajput, A. Agroforestry practices and their impact on soil health and fertility: A review. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2024, 46, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.H. Soil Fertility Evaluation of Wheat/Alfalfa Intercropping. Sch. J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Sivakumar, K.; Thiyageshwari, S.; Anandham, R. Assessment on the Impact of Various Agroforestry Systems on Soil Quality Parameters. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2022, 34, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Thanh, H.V.; Ebrahimzade, I.; Abbaspour-Fard, M.H.; Rohani, A. A multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) approach to determine the synthesizing routes of biomass-based carbon electrode material in supercapacitors. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Han, W. Efficiently evaluating heavy metal urban soil pollution using an improved entropy-method-based TOPSIS model. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 71, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovmand, M.F.; Kemp, K.; Kystol, J.; Johnsen, I.; Riis-Nielsen, T.; Pacyna, J.M. Atmospheric heavy metal deposition accumulated in rural forest soils of southern Scandinavia. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 155, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H.; Li, M.; He, N. Heavy metal deposition through rainfall in Chinese natural terrestrial ecosystems: Evidences from national-scale network monitoring. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, H. Heavy metals in agricultural soils: Sources, influencing factors, and remediation strategies. Toxics 2024, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehetner, F.; Rosenfellner, U.; Mentler, A.; Gerzabek, M.H. Distribution of road salt residues, heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons across a highway-forest interface. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 198, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, X.G.; Liu, J.T. Modeling Analysis of Heavy Metal Evaluation in Complex Geological Soil Based on Nemerow Index Method. Metals 2023, 13, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Lim, S.S.; Baah-Acheamfour, M.; Choi, W.J.; Fatemi, F.; Carlyle, C.N.; Bork, E.W.; Chang, S.X. Introducing trees to agricultural lands increases greenhouse gas emission during spring thaw in Canadian agroforestry systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.J.; Liang, L.N.; Xu, R.N.; Xu, H.Y.; Sun, L.L.; Liao, H. Intercropping tea plantations with soybean and rapeseed enhances nitrogen fixation through shifts in soil microbial communities. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Yuan, W.X.; Huang, W.; Wang, Q.M.; Wu, T.Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, B.J. Walnut-tea intercropping model: Variations in secondary metabolites and microbial interactions in tea under metabolomics perspective. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 227, 120774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, T.; Lei, X.G.; Cao, Y.; Liu, L.F.; Zou, Z.W.; Ma, Y.C.; Zhu, X.J.; Fang, W.P. Leguminous green manure intercropping changes the soil microbial community and increases soil nutrients and key quality components of tea leaves. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, W.Q.; He, H.L.; Wang, Z.T.; Cao, Y.H. Effects of sugarcane and soybean intercropping on the nitrogen-fixing bacterial community in the rhizosphere. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 713349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.C.; Song, F.P.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhuge, Y.P.; Niu, Y.X.; Lou, Y.L.; Pan, H.; Zhang, P.H.; Pang, L.Y. Phytoremediation potential of wheat intercropped with different densities of Sedum plumbizincicola in soil contaminated with cadmium and zinc. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.Y.; Zhong, Z.K.; Li, C.Z.; Zhang, X.P.; Gu, L.J.; Huang, Z.C.; Gai, X.; Huang, Z.Y. Intercropping improves heavy metal phytoremediation efficiency through changing properties of rhizosphere soil in bamboo plantation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.Y.; Zhong, Z.K.; Zhang, X.P.; Li, Q.L.; Huang, Z.Y. Bamboo-based agroforestry changes phytoremediation efficiency by affecting soil properties in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere in heavy metal-polluted soil (Cd/Zn/Cu). J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Zhang, X.L.; Ren, S.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhu, X.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Ma, Y.C.; Fang, W.P. Characteristics of soil nutrients, heavy metals and tea quality in different intercropping patterns. Agrofor. Syst. 2020, 94, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Ma, X.W.; Guo, R.; Ai, S.W.; Liu, B.L.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.M. A field study on heavy metals phytoattenuation potential of monocropping and intercropping of maize and/or legumes in weakly alkaline soils. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.F.; Li, H.S.; Chen, H.Y. The effects of biochar and intercropping on the Cd, Cr and Zn speciation in soils and plant uptake by Machilus pauhoi. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijałkowski, K.; Kacprzak, M.; Grobelak, A.; Placek, A. The influence of selected soil parameters on the mobility of heavy metals in soils. Inż. Ochr. Śr. 2012, 15, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Xu, H.P.; Song, F.M.; Ge, H.G.; Yue, S.Y. Effects of heavy metals on microorganisms and enzymes in soils of lead–zinc tailing ponds. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.L.; Wang, W.Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, X.K.; Shao, J.L.; Ding, Y.; Mi, Y.H. Effects of pepper–maize intercropping on the physicochemical properties, microbial communities, and metabolites of rhizosphere and bulk soils. Environ. Microbiome 2024, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; He, F.K.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Xiao, H.X.; Hoang, D.T.T.; Pu, S.Y.; Razavi, B.S. Nutrients in the rhizosphere: A meta-analysis of content, availability, and influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 153908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.X.; An, J.; Yin, Y.C.; Gao, C.C.; Wang, B.Y.; Wei, S.H. Heavy metals uptake and translocation of typical wetland plants and their ecological effects on the coastal soil of a contaminated bay in Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.W.; Peng, Y.S.; Li, X.L.; Chen, G.Z. Accumulation and partitioning of heavy metals in mangrove rhizosphere sediments. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Sahu, B.K.; Kothilmozhian Ranishree, J.; Lourduraj, A.V.; Nithyanandam, M.; Packiriswamy, N.; Panchatcharam, P. Assessment of heavy metal concentrations and associated resistant bacterial communities in bulk and rhizosphere soil of Avicennia marina of Pichavaram mangrove, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Rui, R.; Wang, S.; He, X.H. Comparative analysis of the floral fragrance compounds of Panax notoginseng flowers under the Panax notoginseng-pinus agroforestry system using SPME-GC-MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.W.; Cheung, L.W.T.; Pon, Y.L.; Wong, R.N.S.; Mak, N.K.; Fan, T.P.; Au, S.C.L.; Tombran-Tink, J.; Wong, A.S.T. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits tube-like structure formation of endothelial cells by regulating pigment epithelium-derived factor through the oestrogen β receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, Y.C.; Tan, C.S.; Ch’ng, Y.S.; Ng, C.H.; Yeap, Z.Q.; Yam, M.F. Mechanisms of action of Panax notoginseng ethanolic extract for its vasodilatory effects and partial characterization of vasoactive compounds. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.L.; Liu, Y.; Hou, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Xing, Q.J.; Liang, Q.Q. Notoginsenoside R1 (NG-R1) promoted lymphatic drainage function to ameliorating rheumatoid arthritis in TNF-Tg mice by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 730579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.Z.; Hou, E.Q.; Chen, J.Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.L.; Zang, X.W.; Wen, D.Z. Dynamics of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stocks and stoichiometry resulting from conversion of primary broadleaf forest to plantation and secondary forest in subtropical China. Catena 2020, 193, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hei, J.Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; He, X.H. Unraveling the molecular mechanisms of flavonoid biosynthesis in Panax notoginseng flowers across planting patterns and developmental stages using integrated metabolomics and transcriptomics analyses. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 335, 113362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; He, S.; Rui, R.; Hei, J.Y.; He, X.H.; Wang, S. Introduction of Panax notoginseng into pine forests significantly enhances the diversity, stochastic processes, and network complexity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1531875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.G.; Wang, M.L.; Rui, R.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xiong, B.J.; He, X.H.; Wang, S. Distribution Characteristics of Mineral Elements and Pollution Evaluation of Heavy Metals in Pinus armandii-Panax notoginseng Planting Pattern. J. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2023, 55, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.J.; Wang, S.; He, X.J.; Zhao, X.Y. Different factors drive the assembly of pine and Panax notoginseng-associated microbiomes in Panax notoginseng-pine agroforestry systems. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1018989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, R.; Hei, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Wan, X.L.; Wang, S.; He, X.H. Alleviating Microbial Carbon Limitation in Pinus armandii Forests Through Panax notoginseng Cultivation. Forests 2025, 16, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Ma, X.Y.; Song, Y.Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, M.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Gao, S.Q.; Gao, J.L.; Song, C.C. Characteristics of Microbial Abundance in Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils of Permafrost Peatland, Northeast China. Forests 2023, 14, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, J.Y.; Wang, S.; He, X.H. Effects of exogenous organic acids on the growth, edaphic factors, soil extracellular enzymes, and microbiomes predict continuous cropping obstacles of Panax notoginseng from the forest understorey. Plant Soil 2024, 503, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.J.; Hei, J.Y.; He, X.H.; Wang, S. Altitude rather than season and slope aspect has the greatest effect on the bacterial communities in subtropical forests in Yunnan, China. Plant Soil 2024, 501, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Rui, R.; Hei, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Faisal, N.; Wang, B.; He, X.H.; Wang, S. Organically managed Sanqi alters the soil C metabolism and purine metabolism pathway through metagenomic and metabolomic analyses. Plant Soil 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.F.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X.L.; Liu, X.N.; Ding, M.J.; Yang, Q.L. Effect of water and fertilizer regulation on the soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen, enzyme activity, and saponin content of Panax notoginseng. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 278, 108145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.H.; Li, C.F.; Wang, H.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, R.D.; Wen, X.F. Geochemical characteristics of heavy metals in soil and blueberries of the core Majiang blueberry production area. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.Q.; Deng, M.H.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.Q.; Yang, X.E.; He, Z.L. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.M.; Wei, D.H.; Xie, Z.; Tao, L.C.; Chen, Q.S.; Uddin, M.G.; Wang, Y.S.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Surface water and groundwater suitability assessment for drinking and irrigation in a coal-mining area of southwestern China: EWQI, IWQI, and sensitivity analysis. J. Environ. Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.K.; Yang, Q.L.; Liang, J.P.; Wang, H.D.; Yue, X.L. Water management, planting slope indicators, and economic benefit analysis for Panax notoginseng production decision under shaded and rain-shelter cultivation: A three-year sloping fields experiment. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 291, 108635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shi, Y.Z.; Luo, A.R.; Xiao, Y.N.; Liang, J.P.; He, Z.J. Effects of irrigation frequency on root growth, nutrients accumulation, yield, and water use efficiency of Panax notoginseng under micro-sprinkler irrigation. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1549506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.Q.; Yan, D.H.; Wang, D.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Dong, G.Q. Experimental analysis of the effect of forest litter cover on surface soil water dynamics under continuous rainless condition in North China. Kuwait J. Sci. 2018, 45, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.Y.; Fei, L.J.; Tuo, Y.F.; Peng, Y.L.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, R.Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, N.; Fan, Q.N. Effects of water and fertilizer regulation on soil physicochemical properties, bacterial diversity and community structure of Panax notoginseng. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 326, 112777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, J.; Lu, R.C.; Ye, C.; Huang, H.C.; Yang, M.; He, X.H.; Zhu, S.S. Modification of quicklime on acid soil under forest and their effect on the growth of Panax notoginseng. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 972–980. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.Q.; Du, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; An, J.; Zou, H.T.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yu, N. Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on greenhouse soil organic nitrogen fractions and soil-soluble nitrogen pools. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 216, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, Z.W.; Liu, C.J.; Dong, Y.B. Technologies for removing heavy metal from contaminated soils on farmland: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, Q.; Feng, Y. The endophytic bacterium relieved healthy risk of pakchoi intercropped with hyperaccumulator in the cadmium polluted greenhouse vegetable field. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114796–114803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Lu, T.T.; Qi, W.; Zhu, Y.W.; Lu, M.H.; Qi, Z.C.; Chen, W.F. Enhanced transport of heavy metal ions by low-molecular-weight organic acids in saturated porous media: Link complex stability constants to heavy metal mobility. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.J.; Li, Z.W.; Luo, N.L.; Huang, M.; Yang, R.; Zeng, G.M. Investigating organic matter properties affecting the binding behavior of heavy metals in the rhizosphere of wetlands. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.J.; Zhou, S.L.; Lv, L.G.; Su, Q.L.; Wang, J. Soil heavy metal contamination in rural land consolidation areas in the Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2018, 26, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.N.; Cheng, H.F. The leaching behavior of heavy metal from contaminated mining soil: The effect of rainfall conditions and the impact on surrounding agricultural lands. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccone, C.; Di Caterina, R.; Rotunno, T.; Quinto, M. Soil-farming system-food-health: Effect of conventional and organic fertilizers on heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) content in semolina samples. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 107, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, N.T.; Ryan, J.A.; Chaney, R.L. Trace element chemistry in residual-treated soil: Key concepts and metal bioavailability. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.H.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, X.Y.; Su, J.Q.; Zhao, C.C.; Nan, Z.R. Impact of poplar-based phytomanagement on metal bioavailability in low-phosphorus calcareous soil with multi-metal contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.Q.; Niu, L.C.; Pang, L. Characteristics of uptake and enrichment of soil heavy metals by different garden plants in Yunnan region. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Li, L.S.; Ni, X.F.; Li, C.X.; Li, J. Accumulation of Soil Heavy Metals in Five Species of Wetland Plants. Acta. Bot. Boreal. 2016, 36, 2078–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Huang, X.Y.; Yu, S.; Zheng, X.; Wei, F.; Ma, S.C. Distribution of Heavy Metals and Trace Elements in Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma with Different Colors from Yunnan Province. Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 24, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, L.; Cui, X.; Liu, D.; Yang, Y. Soil-plant metal relations in Panax notoginseng: An ecosystem health risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Heavy Metals | Risk Screening Value (mg/kg) |
|---|---|
| Zn | 200 |
| Cu | 50 |
| Mn | 626 |
| Pb | 90 |
| Cr | 150 |
| Cd | 0.3 |
| pH | 5.5 < pH ≤ 6.5 |
| Pollution Class | Pi | Pollution Degree | Pcom | Pollution Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Pi ≤ 1.0 | Safety | PCom ≤ 0.7 | Clean (safety) |
| II | 1.0 < Pi ≤ 2.0 | Slight pollution | 0.7 < PCom ≤ 1.0 | Clean (threshold) |
| III | 2.0 < Pi ≤ 3.0 | Moderate pollution | 1.0 < PCom ≤ 2.0 | Slight pollution |
| IV | 3.0 < Pi | Strong pollution | 2.0 < PCom ≤ 3.0 | Moderate pollution |
| V | PCom > 3.0 | Strong pollution |
| Pi (Zn) | Pi(Cu) | Pi (Mn) | Pi (Pb) | Pi (Cr) | Pi (Cd) | Pcom | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pn | 0.69 ± 0.004 c | 0.50 ± 0.006 b | 0.48 ± 0.002 b | 0.41 ± 0.013 c | 0.81 ± 0.007 b | 0.29 ± 0.001 b | 0.808 ± 0.008 d |
| MPA-B | 0.73 ± 0.005 b | 0.49 ± 0.003 c | 0.48 ± 0.002 a | 0.43 ± 0.011 b | 0.92 ± 0.009 a | 0.290 ± 0.001 b | 0.901 ± 0.004 b |
| MPA-R | 0.77 ± 0.006 a | 0.49 ± 0.004 c | 0.48 ± 0.002 a | 0.45 ±0.008 a | 0.92 ± 0.009 a | 0.29 ± 0.001 a | 0.971 ± 0.003 a |
| SPA-B | 0.62 ± 0.009 e | 0.52 ± 0.004 a | 0.39 ± 0.001 d | 0.38 ± 0.010 d | 0.83 ± 0.010 b | 0.28 ± 0.001 c | 0.858 ± 0.012 c |
| SPA-R | 0.64 ± 0.005 d | 0.50 ± 0.003 b | 0.44 ± 0.001 c | 0.40 ± 0.012 cd | 0.82 ± 0.008 b | 0.290 ± 0.001 b | 0.784 ± 0.010 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.; Zhao, X.; Rui, R.; Li, Y.; Hei, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; He, X. Effects of Sanqi Cultivation on Soil Fertility and Heavy Metal Content in the Sanqi–Pine Agroforestry System. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092123
Liu K, Zhao X, Rui R, Li Y, Hei J, Yu L, Wang S, He X. Effects of Sanqi Cultivation on Soil Fertility and Heavy Metal Content in the Sanqi–Pine Agroforestry System. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092123
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Keyu, Xiaoyan Zhao, Rui Rui, Yue Li, Jingying Hei, Longfeng Yu, Shu Wang, and Xiahong He. 2025. "Effects of Sanqi Cultivation on Soil Fertility and Heavy Metal Content in the Sanqi–Pine Agroforestry System" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092123
APA StyleLiu, K., Zhao, X., Rui, R., Li, Y., Hei, J., Yu, L., Wang, S., & He, X. (2025). Effects of Sanqi Cultivation on Soil Fertility and Heavy Metal Content in the Sanqi–Pine Agroforestry System. Agronomy, 15(9), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092123







