MicroRNAs Regulate Grain Development in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Importance of Rice Grain Development
1.2. Discovery of miRNAs and Their Important Roles in Plants
2. Biosynthesis and Action Mechanism of miRNA in Plants
2.1. Biosynthetic Pathways of miRNAs in Plants
2.2. Action Modes of miRNAs in Plants
3. Composition and Development Processes in Rice Grains
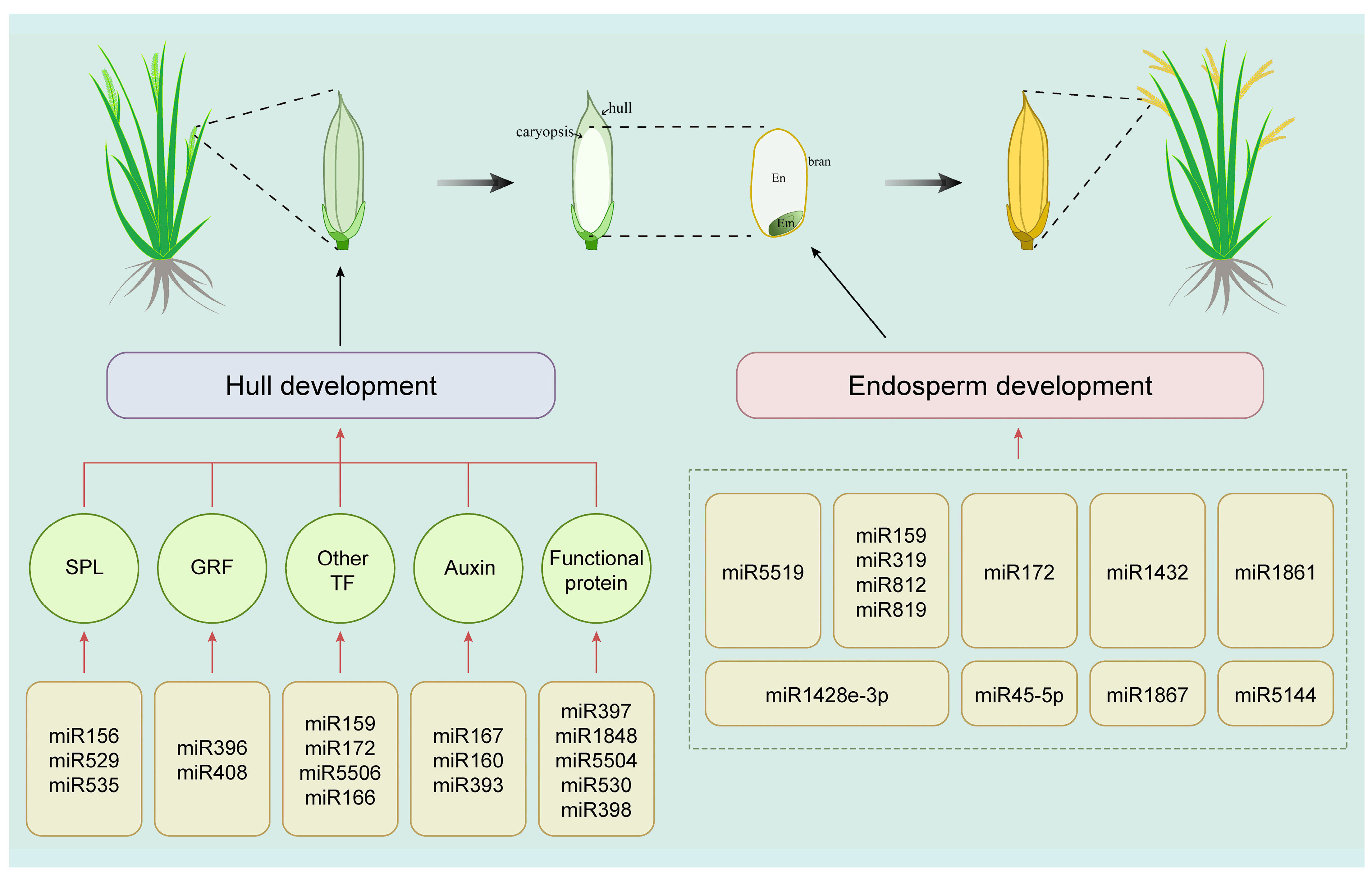
4. miRNA-Mediated Regulation of Agronomically Important Grain Traits
4.1. miRNAs Regulate Hull Development to Affect Grain Size
4.1.1. SPL-Related miRNAs
4.1.2. GRF-Related miRNAs
4.1.3. Other TFs Related to miRNAs
4.1.4. Auxin-Related miRNAs
4.1.5. Functional Protein-Related miRNAs
4.2. miRNAs Regulate Storage Substance Accumulation in the Endosperm
| miRNA Family | Target Gene | Coregulatory Genes | Grain traits Affected by miRNA | Effect of miRNA on Grain Size, Weight or Quality | Regulatory Module | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPL-related miRNAs | ||||||
| miR156 | OsSPL13/GLW7 | Grain length and yield | miR156-OsSPL13 | [84] | ||
| miR156 | OsSPL16/GW8 | GW7 | Grain length and width | miR156-OsSPL16-GW7 | [85] | |
| miR156k | OsSPL18 | DEP1 | Grain width and thickness | miR156k-OsSPL18-DEP1 | [86] | |
| miR156 | OsSPL4 | Grain size | Positive | miR156-OsSPL4 | [87,88] | |
| miR529a | OsSPL14 | Grain size | Positive | miR529a-OsSPL14 | [88,89] | |
| miR529a | OsSPLs | Grain length and width | Positive | miR529a-OsSPLs | [90] | |
| miR535 | OsSPL7/12/16, SPL14 | Grain length | Positive | miR535-OsSPL7/12/16/14 | [91,92] | |
| GRF-related miRNAs | ||||||
| miR396 | OsGRF4 | GIF1, brassinosteroid-related genes | Grain size and weight | Negative | miR396-OsGRF4-GIF1 | [95,96,97,98] |
| miR396 | OsGRF8 | GIFs | Grain size and panicle branch | Negative | miR396-OsGRF4/6/8-GIF1/2/3 | [93,99] |
| miR396 | OsGRF8 | miR408 | Grain size | Negative | miR396-OsGRF8-miR408 | [99] |
| miR408 | Copper proteins, OsUCL8 | Photosynthesis and seed size | Positive | miR408-OsUCL8 | [100,101] | |
| miR396d | OsGRF6/10 | OsGIF1 | Floral organ development | miR396d-OsGRF6/10-OsGIF1 | [102] | |
| Other TFs-related miRNAs | ||||||
| miR159 | GAMYB, GAMYBL2 | GS3, BR and GA response genes | Organ size including grain size | Positive | miR159-GAMYB-GS3 | [103,104,105,106] |
| miR172 | AP2 | OsMADS1 | Panicle phenotype including hull size | Positive | OsMADS1-miR172s-AP2s | [89,107] |
| miR5506 | LOC_Os03g11370 | Hull morphology | miR5506-LOC_Os03g11370 | [108] | ||
| miR166 | OsHB4 | Multiple phenotypes including grain size and weight | Positive | miR166-OsHB4 | [15] | |
| Auxin-related miRNAs | ||||||
| miR167a | ARF6 | OsAUX3 | Grain size and quality | Positive | miR167-ARF6-AUX3 | [109,110] |
| miR167 | ARF12 | OsGAMYBL2, OsCDKF;2 | Grain size and grain filling | Negative | OsGAMYBL2-miR167-ARF12-OsCDKF;2 | [111] |
| miR160 | ARF18 | LncRNA | Seed size and seed setting | LncRNA-miR160-ARF18 | [112,113] | |
| miR393 | OsTIR1, OsAFB2 | OsIAA1 | Hull failed to close | miR393-OsTIR1/OsAFB2-OsIAA1 | [114] | |
| Functional protein-related miRNAs | ||||||
| miR397 | OsLAC | brassinosteroid, OsTTL | Grain size and panicle branch | Positive | miR397-OsLAC-brassinosteroid | [115,116,117,118] |
| miR397b | OsAGO17 | Grain size and weight | Positive | miR397b-OsAGO17 | [56] | |
| miR1848 | OsCYP51G3 | brassinosteroid | BR deficiency phenotype including grain size | Negative | miR1848-OsCYP51G3-brassinosteroid | [119] |
| miR5504 | LOC_Os08g16914 | Grain size | Positive | miR5504-LOC_Os08g16914 | [120] | |
| miR530 | OsPL3 | OsPIL15 | Grain size and weight | Negative | OsPIL15-miRNA530-OsPL3 | [121] |
| miR398 | OsCSD2 | Grain length, width, and weight | Positive | miR398-OsCSD2 | [122] | |
| miRNAs regulate storage substances accumulation in endosperm | ||||||
| mi5519 | RSUS2 | Grain filling | Negative | mi5519-RSUS2 | [133] | |
| miR159, miR319, miR812, miR819 | Plant hormone homeostasis | Grain filling | [126] | |||
| miR1861 | OsBAM2, SBDCP1 | Grain filling | miR1861-OsBAM2, miR1861-SBDCP1 | [126,134,135] | ||
| miR45-5p | SPS | Sucrose synthesis | miR45-5p-SPS | [126] | ||
| miR1867 | GBSSII | Grain filling | miR1867-GBSSII | [134,135] | ||
| miR1428e-3p | SnRK1 | Starch accumulation | miR1428e-3p-SnRK1 | [136] | ||
| miR1432 | RAmy3D | Grain filling | miR1432-RAmy3D | [137] | ||
| miR172 | RSR1 | Starch synthesis | miR172-RSR1 | [123] | ||
| miR5144 | OsPDIL1;1 | Starch and protein content | Negative | miR5144-OsPDIL1;1 | [138] | |
| miR1432 | OsACOT | Grain filling, fatty acid elongation | Negative | miR1432-OsACOT | [139] | |
5. Conclusions and Prospects
5.1. miRNAs in Rice Agronomic Trait Improvement
5.2. Research on miRNA Mining and Regulatory Networks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupte, A.P.; Basaglia, M.; Casella, S.; Favaro, L. Rice waste streams as a promising source of biofuels: Feedstocks, biotechnologies and future perspectives. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthayya, S.; Sugimoto, J.D.; Montgomery, S.; Maberly, G.F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1324, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, N.; Sopory, S.K.; Sanan-Mishra, N. miRNAs and genes as molecular regulators of rice grain morphology and yield. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 207, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llave, C.; Kasschau, K.D.; Rector, M.A.; Carrington, J.C. Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1605–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, B. MicroRNAs in control of plant development. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’ario, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Kim, M. Small RNAs: Big impact on plant development. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.Y.; Chu, C.C. MicroRNAs in crop improvement: Fine-tuners for complex traits. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Hu, B.; Zhang, C. microRNAs and their roles in plant development. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 824240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.H. MicroRNA: A new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.W.; Li, Y.; Cao, X.F.; Qi, Y.J. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plant–environment interactions. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 489–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, L.; Rossi, R.; Paesano, L.; Marmiroli, N.; Marmiroli, M. miRNA regulation and stress adaptation in plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 184, 104369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, D.; Mao, D.; Liu, X.; Ji, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhu, L. Overexpression of microRNA319 impacts leaf morphogenesis and leads to enhanced cold tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Zhang, H.; Srivastava, A.K.; Pan, Y.J.; Bai, J.J.; Fang, J.J.; Shi, H.Z.; Zhu, J.K. Knockdown of rice microRNA166 confers drought resistance by causing leaf rolling and altering stem xylem development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 2082–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Tagiri, A. MicroRNA-targeted transcription factor gene RDD1 promotes nutrient ion uptake and accumulation in rice. Plant J. 2016, 85, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhu, C.; Li, F.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, A.; Liu, L.; Che, R.; Chu, C. LEAF TIP NECROSIS1 plays a pivotal role in the regulation of multiple phosphate starvation responses in rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.I.; Santi, C.; Jobet, E.; Lacut, E.; El Kholti, N.; Karlowski, W.M.; Verdeil, J.L.; Breitler, J.C.; Périn, C.; Ko, S.S.; et al. Complex regulation of two target genes encoding SPX-MFS proteins by rice miR827 in response to phosphate starvation. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 2119–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, N.; Yuan, S.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Hu, Q.; Luo, H. Heterologous expression of a rice miR395 gene in Nicotiana tabacum impairs sulfate homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Ding, Y.; Liu, H. MiR398 and plant stress responses. Physiol. Plant. 2011, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, S.; Gharat, S.A.; Tagirasa, R.; Chandra, T.; Behera, L.; Dash, S.K.; Shaw, B.P. Identification and expression analysis of miRNAs and elucidation of their role in salt tolerance in rice varieties susceptible and tolerant to salinity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Y.G.; Shi, Y.; Wu, L.; Xu, Y.J.; Huang, F.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhao, J.Q.; et al. Multiple rice microRNAs are involved in immunity against the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, S.; Peris-Peris, C.; Siré, C.; Moreno, A.B.; Donaire, L.; Zytnicki, M.; Notredame, C.; Llave, C.; Segundo, B.S. Identification of a novel microRNA (miRNA) from rice that targets an alternatively spliced transcript of the Nramp6 (Natural resistance associated macrophage protein 6) gene involved in pathogen resistance. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, B.; Song, X.; Ding, S.; Zheng, L.; Feng, R.; Chen, S.; et al. Osa-miR164a targets OsNAC60 and negatively regulates rice immunity against the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant J. 2018, 95, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, H.; Gao, G.; Wei, L.; Li, Y. Viral infection induces expression of novel phased microRNAs from conserved cellular microRNA precursors. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jiao, X.; Kong, X.; Hamera, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Fang, R.; Yan, Y. A signaling cascade from miR444 to RDR1 in rice antiviral RNA silencing pathway. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 2365–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Plant MicroRNAs and development. J. Genet. Genom. 2013, 40, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajczyk, M.; Jarmolowski, A.; Jozwiak, M.; Pacak, A.; Pietrykowska, H.; Sierocka, I.; Swida-Barteczka, A.; Szewc, L.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z. Recent insights into plant miRNA biogenesis: Multiple layers of miRNA level regulation. Plants 2023, 12, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Zheng, B.; Yu, Y.; Won, S.Y.; Mo, B.; Chen, X. The role of Mediator in small and long noncoding RNA production in Arabidopsis thaliana. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Allen, E.; Fahlgren, N.; Calamar, A.; Givan, S.A.; Carrington, J.C. Expression of Arabidopsis MIRNA genes. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Arabidopsis micro-RNA biogenesis through Dicer-like 1 protein functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12753–12758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, A.C.; Vaucheret, H. Functions of microRNAs and related small RNAs in plants. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, S31–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bologna, N.G.; Voinnet, O. The diversity, biogenesis, and activities of endogenous silencing small RNAs in Arabidopsis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 473–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, M.A.; Pillay, M.; Jeong, D.H.; Hetawal, A.; Luo, S.; Janardhanan, P.; Kannan, V.; Rymarquis, L.A.; Nobuta, K.; German, R.; et al. Global identification of microRNA–target RNA pairs by parallel analysis of RNA ends. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sintaha, M. Molecular mechanisms of plant stress memory: Roles of non-coding RNAs and alternative splicing. Plants 2025, 14, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Cao, S.; Chu, C.; Cao, X. Loss of function of OsDCL1 affects MicroRNA accumulation and causes developmental defects in rice. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urayama, S.; Moriyama, H.; Aoki, N.; Nakazawa, Y.; Okada, R.; Kiyota, E.; Miki, D.; Shimamoto, K.; Fukuhara, T. Knock-down of OsDCL2 in rice negatively affects maintenance of the endogenous dsRNA virus, Oryza sativa endornavirus. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.Y.; Gu, L.F.; Song, X.W.; Cui, X.K.; Lu, Z.K.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.L.; Hu, F.Y.; Zhai, J.X.; Meyers, B.C.; et al. Dicer-like 3 produces transposable element-associated 24-nt siRNAs that control agricultural traits in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3877–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S. OsDCL3b affects grain yield and quality in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 99, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaki, H.; Itoh, J.; Hayashi, K.; Hibara, K.; Satoh-Nagasawa, N.; Nosaka, M.; Mukouhata, M.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M.; et al. The small interfering RNA production pathway is required for shoot meristem initiation in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14867–14871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Nosaka, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Sato, Y.; Nagato, Y.; Itoh, J. WAVY LEAF1, an ortholog of Arabidopsis HEN1, regulates shoot development by maintaining microRNA and trans-acting small interfering RNA accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhou, H.Y.; Ni, F.R.; Wu, X.Y.; Qi, Y.J. Rice microRNA effector complexes and targets. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3421–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.G.; Yang, Z.R.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.J.; Ye, R.Q.; Ji, Y.H.; Zhao, S.S.; Ji, S.Y.; Liu, R.F.; Xu, L.; et al. Viral-inducible argonaute18 confers broad-spectrum virus resistance in rice by sequestering a host microRNA. eLife 2015, 4, e05733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.G.; Yang, R.X.; Yang, Z.R.; Yao, S.Z.; Zhao, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.C.; Song, X.W.; Jin, L.; Zhou, T.; et al. ROS accumulation and antiviral defense control by microRNA528 in rice. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.Q.; Ruan, S.; Peng, Y.L.; Wang, Z.W.; Jahan, N.S.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.T.; Hu, H.T.; Jiang, H.Z.; Ding, S.L.; et al. A recessive mutant of argonaute1b/gsnl4 leads to narrow leaf, small grain size and low seed setting in rice. Rice Sci. 2021, 28, 521–524. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.J.; Jouni, R.; Yu, C.X.; Meyers, B.C.; Liang, W.Q.; Fei, Q.L. Temperature-sensitive male sterility in rice determined by the roles of AGO1d in reproductive phasiRNA biogenesis and function. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 1529–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.Y.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.L.; Zhou, H.; Ni, E.D.; Jiang, D.G.; Liu, Z.L.; Zhuang, C.X. OsAGO2 controls ROS production and the initiation of tapetal PCD by epigenetically regulating OsHXK1 expression in rice anthers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7549–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, D.Y.; Sun, F.; Guo, W.; Wang, W.; Li, X.J.; Lan, Y.; Du, L.L.; Li, S.; Fan, Y.J.; et al. ARGONAUTE 2 increases rice susceptibility to rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection by epigenetically regulating HEXOKINASE 1 expression. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, C.; Li, X.; Xia, S.G.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yu, Z.; Tang, C.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, T.; et al. An OsPRMT5-OsAGO2/miR1875-OsHXK1 module regulates rice immunity to blast disease. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 1077–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.C.; Xiao, Y.H.; Niu, M.; Meng, W.J.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, X.X.; Liu, D.P.; Zhang, G.X.; Qian, Y.W.; Sun, Z.T.; et al. ARGONAUTE2 enhances grain length and salt tolerance by activating BIG GRAIN3 to modulate cytokinin distribution in rice. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 2292–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonomura, K.I.; Morohoshi, A.; Nakano, M.; Eiguchi, M.; Miyao, A.; Hirochika, H.; Kurata, N. A germ cell specific gene of the ARGONAUTE family is essential for the progression of premeiotic mitosis and meiosis during sporogenesis in rice. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2583–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Ito, M.; Kamiya, N.; Sato, Y.; Matsuoka, M. OsPNH1 regulates leaf development and maintenance of the shoot apical meristem in rice. Plant J. 2002, 30, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Wan, X.S.; Shen, G.Z.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, J.L. Over-expression of rice OsAGO7 gene induces upward curling of the leaf blade that enhanced erect-leaf habit. Planta 2007, 226, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, J.I.; Sato, Y.; Nagato, Y. The SHOOT ORGANIZATION2 gene coordinates leaf domain development along the central–marginal axis in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 49, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Li, T.Y.; Gao, Y.Z.; Li, X.H.; Huang, Z.H.; Zhuang, H.; He, G.H.; Luo, H.F.; Li, Y.F. DH2-dependent trans-acting siRNAs regulate leaf and lemma development in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1534038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; He, W.J.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Yao, J.L. A putative AGO protein, OsAGO17, positively regulates grain size and grain weight through OsmiR397b in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, N.; Sharma, R. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of agronomically important seed traits: A treasure trove with shades of grey! Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamthan, A.; Chaudhuri, A.; Kamthan, M.; Datta, A. Small RNAs in plants: Recent development and application for crop improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.Y.; Ding, C.Q.; Qian, Q. Molecular bases of rice grain size and quality for optimized productivity. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 314–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Tao, Y.; Chen, H.; He, M.J.; Xiao, F.; Li, G.H.; Ding, Y.F.; Liu, Z.H. Embryo-endosperm interaction and its agronomic relevance to rice quality. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 587641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Niu, B.X.; E, Z.G.; Chen, C. Towards Understanding the Genetic Regulations of Endosperm Development in Rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2021, 35, 326–341. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wu, M.; Liu, C. Cereal endosperms: Development and storage product accumulation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 255–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoni, S.; Parween, S.; Henry, R.J.; Sreenivasulu, N. Systems seed biology to understand and manipulate rice grain quality and nutrition. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2023, 43, 716–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, C. The aleurone layer of cereal grains: Development, genetic regulation, and breeding applications. Plant Comm. 2025, 6, 101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, O.A. Nuclear endosperm development in cereals and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2004, 16, S214–S227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, J.; Nonomura, K.; Ikeda, K.; Yamaki, K.; Inukai, Y.; Yamagish, H.; Kitano, H.; Nagato, Y. Rice plant development: From zygote to spikelet. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.B.; Liu, J.X.; Li, D.Q.; Liu, C.M. Rice caryopsis development I: Dynamic changes in different cell layers. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, T.J.; Rost, T.L. Histochemistry and ultrastructure of rice (Oryza sativa) zygotic embryogenesis. Am. J. Bot. 1989, 76, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.B.; Liu, J.X.; Li, D.Q.; Liu, C.M. Rice caryopsis development II: Dynamic changes in the endosperm. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becraft, P.W.; Gutierrez-Marcos, J. Endosperm development: Dynamic processes and cellular innovations underlying sibling altruism. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 1, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhu, Q.S. Proliferation of endosperm cell and its relation to the growth of grain in rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 1998, 24, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.R.; Yin, L.L.; Xue, H.W. Functional genomics based understanding of rice endosperm development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Chen, C. Mechanisms behind aleurone development in cereals and Its application in breeding. Chin. J. Rice. Sci. 2023, 37, 459–469. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Nagato, Y. Flower development in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4719–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoczynska, A.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of flower development in grasses. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.S.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, Q.F.; Liu, Q.Q. Genetic control of grain appearance quality in rice. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 60, 108014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.S.; Liu, Q.Q. Elite grain size gene enables fully mechanized hybrid rice seed production. Seed Biol. 2024, 3, e011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, F.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Deng, H.; Tang, W. Grain shape genes: Shaping the future of rice breeding. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 379–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.W.; Liu, Q.Q.; Zhao, D.S. Genetic improvement of rice grain size using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Rice 2025, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.B.; Qu, C.Q.; Xiong, L.Z. Genomic organization, differential expression, and interaction of SQUAMOSA promoter-binding-like transcription factors and microRNA156 in rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.F. Boosting rice yield by fine-tuning SPL gene expression. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Yang, F.; Chen, W.; Yuan, H. Research progress in biological functions of SPL family transcription factors in rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2024, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Hua, K.; Liu, X.; Shi, H.; Zhu, J. The grain yield modulator miR156 regulates seed dormancy through the gibberellin pathway in rice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, L.; Chen, J.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Gong, H.; Luo, J.H.; Hou, Q.Q.; Zhou, T.Y.; Lu, T.T.; Zhu, J.J.; Shangguan, Y.Y.; et al. OsSPL13 control grain size in cultivated rice. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.K.; Wu, K.; Yuan, Q.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, Z.B.; Lin, X.Y.; Zeng, R.Z.; Zhu, H.T.; Dong, G.J.; Qian, Q.; et al. Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Qin, P.; Hu, L.; Zhan, S.J.; Wang, S.F.; Gao, P.; Li, J.; Jin, M.Y.; Xu, Z.Y.; Gao, Q.; et al. OsSPL18 controls grain weight and grain number in rice. J. Genet. Genom. 2019, 46, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Hu, Q.; Hu, F.; et al. The elite alleles of OsSPL4 regulate grain size and increase grain yield in rice. Rice 2021, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, Y.Z.; Qin, T.; Guo, X.L.; Xu, K.; Xu, C.X.; Yuan, W.Y. Functional conservation and divergence of miR156 and miR529 during rice development. Crop J. 2023, 11, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, S.Y.; Jin, J.Y.; Fu, D.B.; Yang, X.F.; Weng, X.Y.; Xu, G.G.; Li, X.H.; Xiao, J.H.; Zhang, Q.F. Coordinated regulation of vegetative and reproductive branching in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15505–15509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wei, M.X.; Li, Y.; Tao, H.; Wu, H.Y.; Chen, Z.F.; Li, C.; Xu, J.H. MiR529a controls plant height, tiller number, panicle architecture and grain size by regulating SPL target genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci. 2021, 302, 110728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.Z.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, J.K.; Cai, X.X.; Zheng, G.P.; Zhu, Y.M.; Jia, B.W.; Sun, X.L. The multiple roles of OsmiR535 in modulating plant height, panicle branching and grain shape. Plant Sci. 2019, 283, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Chern, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Lu, J.H.; Li, X.P.; Dang, W.Q.; Ma, X.C.; Yang, Z.R.; et al. Suppression of rice miR168 improves yield, flowering time and immunity. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Bai, J.J.; Tao, X.P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.K. Disruption of MIR396e and MIR396f improves rice yield under nitrogen-deficient conditions. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Wang, D.; He, R.; Liu, S.; Zhu, J. Mutations in MIR396e and MIR396f increase grain size and modulate shoot architecture in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Gao, F.Y.; Xie, K.L.; Zeng, X.H.; Cao, Y.; Zeng, J.; He, Z.S.; Ren, Y.; Li, W.B.; Deng, Q.M.; et al. The OsmiR396c-OsGRF4-OsGIF1 regulatory module determines grain size and yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 2134–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.H.; Tong, H.N.; Shi, B.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Fang, S.R.; Liu, D.P.; Xiao, Y.H.; Hu, B.; Liu, L.C.; Wang, H.R.; et al. Control of grain size and rice yield by GL2-mediated brassinosteroid responses. Nat. Plants 2015, 2, 15195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.G.; Ni, S.; Wang, J.M.; Zhang, B.L.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, H.Q.; Zhu, X.D.; Li, Y.H. Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Plants 2015, 2, 15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.X.; Fang, Y.X.; Zeng, L.J.; Xu, J.; Yu, H.P.; Shi, Z.Y.; Pan, J.J.; Zhang, D.; Kang, S.J.; et al. A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Zhao, X.L.; Dai, Z.Y.; Ma, F.L.; Miao, X.X.; Shi, Z.Y. OsmiR396/growth regulating factor modulate rice grain size through direct regulation of embryo-specific miR408. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.P.; Yu, Y.; Feng, Y.Z.; Zhou, Y.F.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.W.; Lei, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, Y.Q. MiR408 regulates grain yield and photosynthesis via a phytocyanin protein. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.W.; Huang, D.H.; Guo, Z.L.; Kuang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xie, X.Y.; Ma, Z.F.; Gao, S.P.; Lerdau, M.T.; Chu, C.C.; et al. Overexpression of microRNA408 enhances photosynthesis, growth, and seed yield in diverse plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Guo, S.Y.; Xu, Y.Y.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.J.; Xu, S.J.; Zhang, C.; Chong, K. OsmiR396d-Regulated OsGRFs function in floral organogenesis in rice through binding to their targets OsJMJ706 and OsCR4. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, A.A.; Lohe, A.; Wong, G. Biology and function of miR159 in plants. Plants 2019, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Wen, H.L.; Teotia, S.; Du, Y.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.Z.; Sun, H.Z.; Tang, G.L.; Peng, T.; Zhao, Q.Z. Suppression of microRNA159 impacts multiple agronomic traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.F.; He, Y.; Tian, Z.H.; Li, J.X. A brassinosteroid responsive miRNA-target module regulates gibberellin biosynthesis and plant development. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.J.; Yang, G.Q.; Miao, X.X.; Shi, Z.Y. OsmiR159 modulate BPH resistance through regulating G-Protein γ subunit GS3 gene in rice. Rice 2023, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Miao, X.; Shi, Z. OsMADS1 represses microRNA172 in elongation of palea/lemma development in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.X.; Li, Y.J.; Li, P.G.; Huang, X.J.; Chen, M.X.; Wu, J.W.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.D.; Li, Y.J. MircroRNA profiles of early rice Inflorescence revealed a specific miRNA5506 regulating development of floral organs and female megagametophyte in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Jia, S.; Shen, D.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Han, S.; Wang, Y. Four AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR genes downregulated by microRNA167 are associated with growth and development in Oryza sativa. Funct. Plant Biol. 2012, 39, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.Y.; Jiang, H.Z.; Lin, Y.Q.; Shang, L.G.; Wang, M.; Li, D.M.; Fu, X.D.; Geisler, M.; Qi, Y.H.; Gao, Z.Y.; et al. A novel miR167a-OsARF6-OsAUX3 module regulates grain length and weight in rice. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1683–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Zhang, X.F.; Cheng, Y.; Du, X.X.; Teotia, S.; Miao, C.B.; Sun, H.W.; Fan, G.Q.; Tang, G.L.; Xue, H.W.; et al. The miR167-OsARF12 module regulates rice grain filling and grain size downstream of miR159. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, D. Deregulation of the OsmiR160 target gene OsARF18 causes growth and developmental defects with an alteration of auxin signaling in rice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, H.J.; Fang, J.; Chu, C.C.; Wang, X.J. A long noncoding RNA involved in rice reproductive development by negatively regulating osa-miR160. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Xie, Y.; Guo, F.; Han, N.; Ma, S.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, M. Distinctive expression patterns and roles of the miRNA393⁄TIR1 homolog module in regulating flag leaf inclination and primary and crown root growth in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol. 2012, 196, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Liao, J.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Qu, L.H.; Chen, F.; et al. Overexpression of microRNA OsmiR397 improves rice yield by increasing grain size and promoting panicle branching. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhou, J.; Gao, L.; Tang, Y. Plant miR397 and its functions. Funct. Plant Biol. 2021, 48, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.N.; Chen, Y.K.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Peng, Y.Q.; Yi, Y.K.; Yu, H.H.; Yi, Z.X.; Yang, J.C.; Peng, Y.; Duan, M.J.; et al. Identification of microRNAs regulating grain filling of rice inferior spikelets in response to moderate soil drying post-anthesis. Crop J. 2022, 10, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; He, R.R.; Yang, L.; Feng, Y.Z.; Xue, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.F.; Lei, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.C.; Lian, J.P.; et al. A transthyretin-like protein acts downstream of miR397 and LACCASE to regulate grain yield in rice. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 2893–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.F.; Ou, X.J.; Tang, H.D.; Wang, R.; Wu, P.; Jia, Y.X.; Wei, X.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, S.K.; et al. Rice microRNA osamiR1848 targets the obtusifoliol 14a-demethylase gene OsCYP51G3 and mediates the biosynthesis of phytosterols and brassinosteroids during development and in response to stress. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.Y.; Cui, Y.; Yan, X.; Gao, J.D.; Ouyang, J.X.; Li, S.B. Pleiotropic effects of miR5504 underlying plant height, grain yield and quality in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2024, 65, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, X.H.; Li, Y.P.; Xie, L.X.; He, Y.N.; Li, W.; Lu, X.B.; Sun, H.W.; Xie, X.H. OsmiR530 acts downstream of OsPIL15 to regulate grain yield in rice. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.S.; Yan, J.; Gou, F.; Mao, Y.F.; Tang, G.L.; Botella, J.R.; Zhu, J.K. Short tandem target mimic rice lines uncover functions of miRNAs in regulating important agronomic traits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5277–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Xue, H.W. Characterization and expression profiles of miRNAs in rice seeds. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Su, N.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, R.Z.; Wu, F.Q.; Cheng, Z.J.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.P.; Lei, C.L.; et al. Identification of novel MiRNAs and MiRNA expression profiling during grain development in indica rice. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shen, D.; Jia, S.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Han, S.; Wang, Y. Microarray-based screening of the microRNAs associated with caryopsis development in Oryza sativa. Biol. Plant. 2013, 57, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Sun, H.Z.; Du, Y.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.Z.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhao, Q.Z. Characterization and expression pattern of microRNAs involved in rice grain filling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Zhu, Z.X.; Hu, J.H.; Qian, Q.; Dai, J.C.; Ding, Y. Identification and expression analysis of microRNAs at the grain filling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) via deep sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, L.Y.; Yu, M.L.; Wang, J.B. Identification and expression analysis of microRNAs during ovule development in rice (Oryza sativa) by deep sequencing. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 1815–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, T.; Mishra, S.; Panda, B.B.; Sahu, G.; Dash, S.K.; Shaw, B.P. Study of expressions of miRNAs in the spikelets based on their spatial location on panicle in rice cultivars provided insight into their influence on grain development. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sanan-Mishra, N. Mapping the expression profiles of grain yield QTL associated miRNAs in rice varieties with different grain size. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1261–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahto, A.; Yadav, A.; Aswathi, P.V.; Parida, S.K.; Tyagi, A.K.; Agarwal, P. Cytological, transcriptome and miRNome temporal landscapes decode enhancement of rice grain size. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Zheng, Y.; Addo-Quaye, C.; Zhang, L.; Saini, A.; Jagadeeswaran, G.; Axtell, M.J.; Zhang, W.X.; Sunkar, R. Transcriptome-wide identification of microRNA targets in rice. Plant J. 2010, 62, 742–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.W.; Li, Y.T.; Wu, P.; Wu, J.W.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.D.; Chen, Z.X. OsmiR5519 regulates grain size and weight and down-regulates sucrose synthase gene RSUS2 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 2024, 259, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Sun, H.Z.; Qiao, M.M.; Zhao, Y.F.; Du, Y.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.Z.; Tang, G.L.; Zhao, Q.Z. Differentially expressed microRNA cohorts in seed development may contribute to poor grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Sunkar, R.; Zhang, W.X. SeqTar: An effective method for identifying microRNA guided cleavage sites from degradome of polyadenylated transcripts in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.H.; Spriggs, A.; Matthew, L.; Fan, L.J.; Kennedy, G.; Gubler, F.; Helliwell, C. A diverse set of microRNAs and microRNA-like small RNAs in developing rice grains. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zeng, T.; Xia, Q.; Qian, Q.; Yang, C.; Ding, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, W. Unravelling miRNA regulation in yield of rice (Oryza sativa) based on differential network model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, K.F.; Zeng, X.; Jiao, Z.L.; Li, M.L.; Xu, W.J.; Nong, Q.D.; Mo, H.; Cheng, T.H.; Zhang, M.Y. Formation of protein disulfide bonds catalyzed by OsPDIL1;1 is mediated by microRNA5144-3p in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Peng, T.; Sun, H.Z.; Teotia, S.; Wen, H.L.; Du, Y.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.Z.; Tang, G.L.; Xue, H.W.; et al. miR1432-OsACOT (Acyl-CoA thioesterase) module determines grain yield via enhancing grain filling rate in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Qiao, M.M.; Liu, H.P.; Teotia, S.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.F.; Wang, B.B.; Zhao, D.J.; Shi, L.N.; Zhang, C.; et al. A resource for inactivation of MicroRNAs using short tandem target mimic technology in model and crop plants. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1400–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyakumar, J.M.J.; Ali, A.; Wang, W.M.; Thiruvengadam, M. Characterizing the role of the miR156-SPL network in plant development and stress response. Plants 2020, 9, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; You, C.J.; Chen, X.M. The evolution of microRNAs in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 35, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Q. MicroRNAs Regulate Grain Development in Rice. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092027
Ye Y, Yuan X, Zhao D, Yang Q. MicroRNAs Regulate Grain Development in Rice. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092027
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Ying, Xiaoya Yuan, Dongsheng Zhao, and Qingqing Yang. 2025. "MicroRNAs Regulate Grain Development in Rice" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092027
APA StyleYe, Y., Yuan, X., Zhao, D., & Yang, Q. (2025). MicroRNAs Regulate Grain Development in Rice. Agronomy, 15(9), 2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092027





